Abstract
The Pax6 gene encodes a transcription factor with a restricted expression in the ventricular zone of the pallium and subpallium. We tested whether the function of Pax6 is necessary for the correct patterning and morphogenesis of the vertebrate telencephalon. Homozygous embryos of the Pax6/Small eye mutant lack functional PAX6 protein because of a point mutation of the gene. In the mutant Small eyeembryos we detected a ventralization of the molecular patterning of the telencephalon at two borders, the pallium/subpallium and the lateral/medial ganglionic eminence. The results indicate thatPax6 controls the lateral limit of the expression ofNkx2.1, Shh, and Lhx6 in the prechordal neural tube, the telencephalon. This finding is in agreement with previous studies and supports a model for a common genetic mechanism for modulation of the dorsoventral patterning of the prechordal and epichordal CNS. The pattern defects caused by the loss of Pax6 function result in multiple morphological abnormalities in theSmall eye brain: dysgenesis of the piriform, insular, and lateral cortices, the claustrum–endopiriform nucleus, and a failure in the differentiation of a subpopulation of the cortical precursors. Together the results demonstrate that Pax6 has an essential role for the modulation of the dorsoventral patterning of the embryonic telencephalon, influencing thereby the forebrain morphogenesis.
Keywords: Pax6, Small eye, dorsoventral patterning, telencephalon, borders, pallium/subpallium, MGE/LGE
The two main subdivisions of the embryonic telencephalon, pallium (cortex) and subpallium (basal ganglia), have a distinct molecular patterning and strikingly different developmental potentials. During development, the initial sheet of uniform pseudostratified neuroepithelium generates dorsally the six-layered cortex and ventrally the three eminences, the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE), lateral ganglionic eminence (LGE), and caudal ganglionic eminence (CGE), which later differentiate into the nuclei of the basal ganglia.
The Pax6 gene plays a crucial role in the development of the vertebrate CNS. The mouse Small eye (allele Sey)mutation is caused by a point mutation in the Pax6 gene, resulting in the production of a nonfunctional protein (Hill et al., 1991). The homozygous Small eye animals die at birth with multiple CNS defects in the eye, forebrain, cerebellum, and spinal cord (Schmahl et al., 1993; Stoykova et al., 1996; Burrill et al., 1997; Caric et al., 1997; Ericson et al., 1997; Grindley et al., 1997; Mastick et al., 1997; Osumi et al., 1997; Engelkamp et al., 1999;Warren et al., 1999). We have previously found that Pax6 mediates the establishment of distinct adhesive properties between the dorsal and ventral compartments of the embryonic telencephalon (Stoykova et al., 1997) and that Pax6 controls the differentiation of the cortical radial glia cells (Götz et al., 1998). Here we explore the role ofPax6 in the control of the dorsoventral (DV) regionalization of the telencephalon and the consequences for the brain morphogenesis in loss of Pax6 function.
In the embryonic telencephalon, the expression of Pax6 is confined to the mitotically active ventricular neuroepithelium (Ne) of the pallium (Walther and Gruss, 1991). The pallium is classically subdivided into the medial pallium (MP), dorsal pallium (DP), and lateral pallium (LP), giving rise to the archicortex (hippocampus), neocortex, and paleocortex, respectively. In addition, Pax6exhibits a particularly strong expression in a small lateralmost region of the ventricular zone of the LGE at the level of the pallial/subpallial border (Stoykova et al., 1996, 1997). This domain is intercalated between the neuroepithelium of the striatum and the lateral pallium (Fig.1A) and was recently designated as “ventral pallium” (VP) (Puelles et al., 1999, 2000) or “intermediate zone” (Smith-Fernandez et al., 1998). ThePax6 mRNA level shows a lateral-to-medial gradient, being highest in the region of the VP (Walther and Gruss, 1991; Stoykova et al., 1997; Puelles et al., 1999). Pax6 is also expressed in the ventricular zone (VZ) of LGE, although at a very low level (Hallonet et al., 1998; Puelles et al., 1999). A number of transcription factors and regulatory molecules with a restricted expression in the embryonic telencephalon are respecting the pallial/subpallial and MGE/LGE border (for review, see Rubenstein and Shimamura, 1997; Rubenstein et al., 1998). We examined therefore whether the strikingly different Pax6 expression levels at these two boundaries might have a biological function for the regionalization of the telencephalon. We show in this work that a similar constellation of genes, including Pax6, Nkx2.1/2.2,and Shh appears to modulate the DV patterning not only in the epichordal part of the neural tube (Ericson et al., 1997; Briscoe et al., 1999), but also in the prechordal part of the CNS, the telencephalon. Furthermore, we found that the disruption of the normal DV patterning in the Sey/Sey brain leads to a hypoplasia of the basolateral cortex, affecting the structures that derive from the region of the ventral pallium. Our results further suggest thatPax6 possibly controls the activity of the neural determination gene Ngn2 in a subpopulation of the cortical precursors.
Fig. 1.
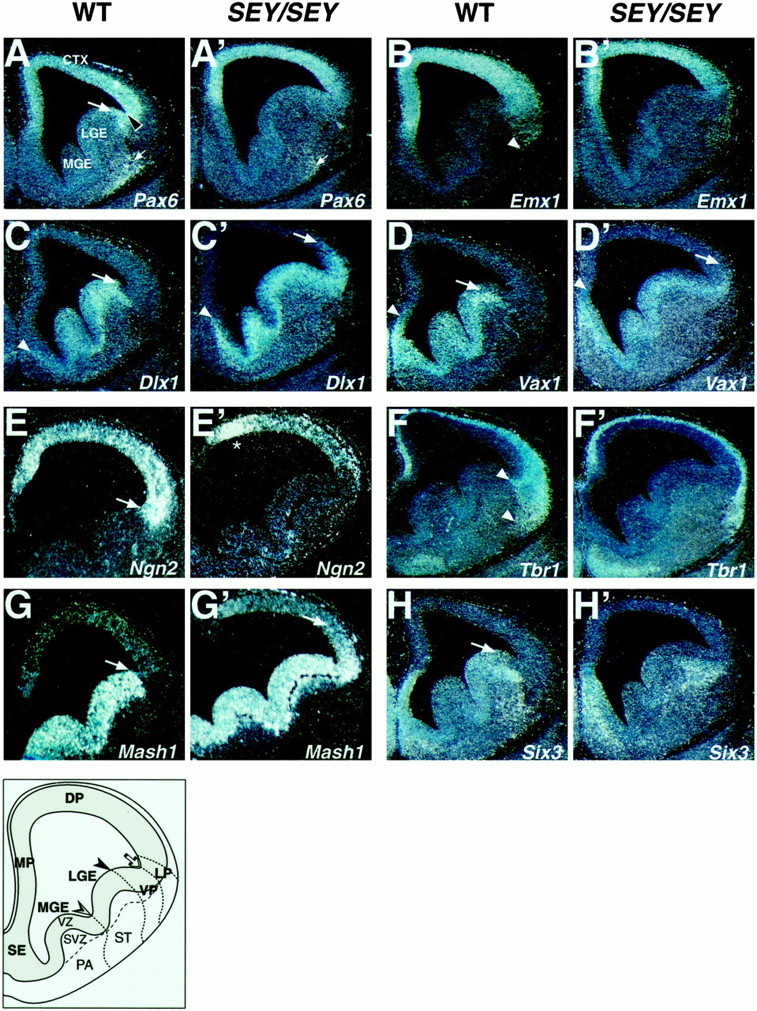
Ventralization of the neuroepithelium at the pallio/subpallial border at stage E12.5 in the Sey/Seytelencephalon. Adjacent coronal sections from the brain of wild-type (WT; A–D; F,H; E, G) and homozygous (Sey/Sey;A′–D′; F′,H′; E′, G′) littermates at E12.5 were hybridized with RNA probes for region-specific markers as indicated. The empty arrowhead inA points to the morphological corticostriatal sulcus, whereas the arrows in A,C, D, and E,H point to the pallial/subpallial border.A, The region of the ventral pallium is located between the arrowhead and the arrow (also in Figs. 5, 7). The thin arrows in A and A′) point to early-born Pax6+ cells possibly generated from the VP and migrating toward the presumptive anlage of the piriform cortex and anterior amygdala. B, B′,Emx1 is dorsally retracted from the LP in the mutant as compared with the WT brain. The subpallial markers for the VZ–SVZ are ectopically expressed in the Ne of the VP, LP, and DP of theSey/Sey as illustrated for: Dlx1(C′), Vax1 (D′), andMash1 (G′). The arrowheadsin C′ and D′ point to the extension of the Dlx1 and Vax1 expression into a more dorsal domain within the septum in the mutant brain. InH′, note that the normal expression ofSix3 in the striatal mantle extends laterally into the mantle of the VP. In E and E′, note that Ngn2 expression is abolished in the VZ of the VP, strongly suppressed in the LP and in a part of the DP, but appeared unaffected in the MP (designated by the asterisk below the MP). The two arrowheads in F point to the medial limit of Tbr1 expression along the pallial/subpallial border, thus including in its expression domain the mantle zone of the VP (the anlage of the ventromedial claustrum;Puelles et al., 1999). The expression of Tbr1 in this domain is abolished in the Sey/Sey brain (F′).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals. Embryos were derived from crosses of heterozygous Small eye mice, Sey allele (Roberts, 1967; Hogan et al., 1986) on a C57BL/6JxDBA/2J background. The point mutation in the Pax6 gene results in the generation of truncated nonfunctional protein (Hill et al., 1991), whereas the transcription is not affected, thus allowing us to study the activity of the gene in the affected brain regions. The day of the vaginal plug was considered as embryonic day 0.5 (E0.5). The brains of matched homozygous and wild-type littermates were used for the expression analysis.
In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry.Sectioning, in situ hybridization, and emulsion autoradiography were performed as previously described (Stoykova and Gruss, 1994). 35S-labeled sense and antisense RNA probes were synthesized in the presence of two radioactive nucleotides from linearized plasmid templates according to the supplier's instructions (Promega, Madison, WI). Two independentin situ analyses for each stage were performed. For the colocalization of the Ngn2 mRNA and the Pax6 antigen first a nonradioactive in situ hybridization with theNgn2 in situ probe was performed on 12 μm cryostat sections from E13.5 wild-type brain as described by Gradwohl et al. (1996). For the antibody staining the sections were further proceeded for immunohistochemistry according to Götz et al. (1998) using the anti-mouse Pax6 antibody (Development Studies Hybridoma Bank, Iowa City, IA), 1:200 and “Alexa” 568 goat anti-mouse conjugate (MoBiTec), 1:500. The terminology is in accordance with the rat brain atlases of Paxinos et al. (1994), Altman and Bayer (1995) and Foster (1998).
RESULTS
Ventralization of the molecular patterning of the pallial neuroepithelium in the Pax6/Small eye mutant telencephalon
To examine whether Pax6 plays a role in the dorsoventral regionalization at the pallial/subpallial border, we studied the molecular patterning by in situ hybridization in sections of E12.5 wild-type (WT) and homozygous Small eye(Sey/Sey) brains using the following markers:Emx1 (Simeone et al., 1992) as a dorsal telencephalic marker, which is expressed in the whole pallium except for the VP (Puelles et al., 1999, 2000); Pax6 (Walther and Gruss, 1991), Ngn2 (Gradwohl et al., 1996), and Tbr1(Bulfone et al., 1995; Puelles et al., 1999, 2000) as pallial markers that include the VP in their expression domains and Dlx1(Bulfone et al., 1993), Vax1 (Hallonet et al., 1998), Mash 1 (Guillemot and Joyner, 1993), and Six3 (Oliver et al., 1995) as ventral telencephalic markers. The comparative analysis was performed at three rostrocaudal levels of sectioning, and the detected patterns are illustrated in Figure 1.
At E12.5, Emx1 is expressed in mitotic and postmitotic cells in the anlage of the medial, dorsal, and lateral pallium (Fig.1B). In the mutant brain, Emx1expression was retracted from the depth of the basolateral wall, except for some Emx1+ cells, located very superficially (Fig.1B′). The expression of Tbr1 is restricted to early postmitotic cells in the pallium (Bulfone et al., 1995). In the basolateral telencephalon, the Tbr1 expression extends more medially than Emx1 so that the subventricular zone (SVZ), submantle, and mantle zone of the VP expresses theTbr1, but not the Emx1 gene (Fig.1F, arrowheads). Thus, the medialmost expression domain of Tbr1 in the basolateral telencephalic wall seems to consist of postmitotic cells that are generated predominantly from the neuroepithelium of the VP (Puelles et al., 2000). InSey/Sey, the expression of Tbr1 was abolished in the SVZ, submantle, and mantle zone of the VP and appeared less affected in the postmitotic neurons of the preplate in the DP and LP (Fig. 1F′).
Pax6 is expressed in the VZ of the entire pallium, showing a particularly strong signal within the region of the VP (Figs.1A,2A). InSey/Sey the mutant transcripts were much less abundant in the VP, and the pallial/subpallial border was not well delineated (Figs. 1A′, 2A′). ThePax6 and Ngn2 expression domains overlap in the pallial VZ (Fig. 1E; see Fig.5A,B). Interestingly, the expression ofNgn2 in Sey/Sey was completely abolished in the region of the VP, substantially reduced in the LP and DP, but appeared at a normal level in the MP (Fig. 1E′).
Fig. 2.
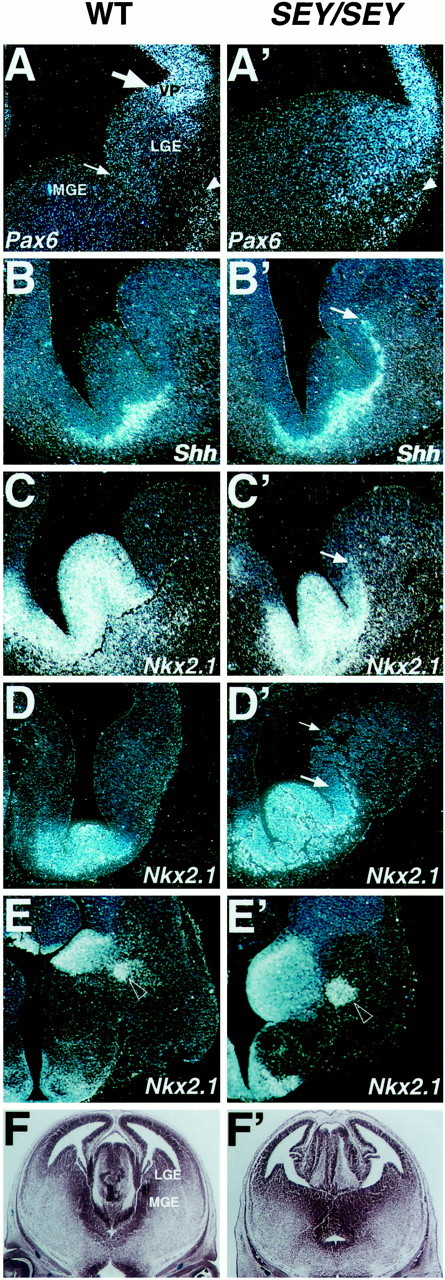
Ventralization of the neuroepithelium of the LGE in Sey/Sey. In situ hybridization on coronal (A–D′) and cross (E, E′) sections from the WT and Sey/Sey brains. Different markers for the MGE were tested at stages: E13.5 (A–C′), E12.0 (D,D′), and E14.5 (E,E′). In A, note the strikingly different level of Pax6 expression in the VZ of the VP and LGE. The arrowheads in A andA′ point to Pax6+ cells that appear to stream out from the Ne of the VP toward the basolateral telencephalon.B–C′, In the mutant telencephalon, the lateral limit of the expression of Shh(B,B′) andNkx2.1 (C,C′) extends from the MGE into the adjacent territory of the LGE. In D′, thelarge and smallarrowspoint to the lateral limit of the strong and the faint ectopic expression of Nkx2.1 within the VZ of the mutant LGE, respectively. In E and E′, note the enlarged MGE (which includes at this late stage the adjacent LGE domain with a ventralized identity) and the differentiating globus pallidus, labeled by the Nkx2.1 probe (open arrowhead). F, F′, Coronal sections from E15.5 WT (F) andSey/Sey (F′) brain at the level of the preoptic area stained with neutral red, illustrating the enlarged MGE in the Sey/Sey telencephalon.
Fig. 5.
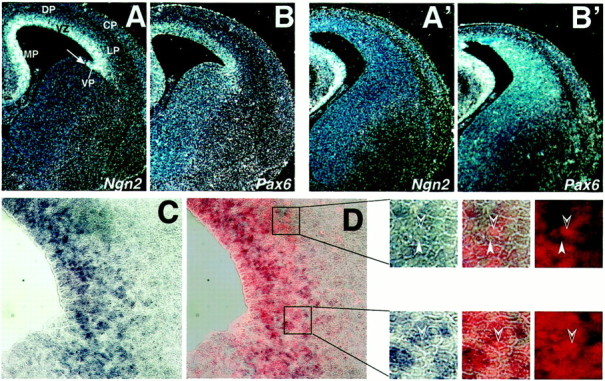
Inhibition of Ngn2 activity in a subpopulation of the cortical progenitors in Sey/Sey.Coronal sections from E16.5 wild-type (A, B) andSey/Sey (A′, B′) brain hybridized with Ngn2 (A,A′) and Pax6 (B,B′) probes. In A note that the region of the VP in the VZ of the LGE is still distinguishable at this late developmental stage. In the mutant, the expression ofNgn2 is completely abolished from the region of the VP and LP, severely repressed in the DP, but appears unaffected in the MP. In B′ note that the enlarged VZ–SVZ in theSey/Sey pallium is expressing abundantly the mutantPax6 mRNA (B′). C, D,Coronal sections from E13.5 WT brain were double-labeled by in situ histochemistry with the Ngn2 antisense RNA probe (blue cytoplasmic staining) and by immunohistochemistry with the Pax6 antibody (red nuclear stain). The enlarged inserts are higher magnifications showing that some Pax6-immunoreactive cortical progenitors expressNgn2 mRNA (open arrowheads). Thefilled arrowheads point to progenitors that are onlyNgn2+. D is a composite picture ofC and the Pax6 immunostaining; the overlay has been done in Adobe Photoshop.
In the WT brain, the transcripts of the subpallial markers Dlx1, Vax1, and Mash1 in the VZ–SVZ and Six3 in the mantle zone were clearly not detectable in the VP (Fig.1C,D,G,H). In the Pax6-deficient brain, the markers for the ventral telencephalic VZ–SVZ were ectopically expressed within the Ne of the VP and LP (Fig.1C′,D′,G′). Similarly, the expression of Six3 expanded into the mantle zone of the VP (Fig.1H′). In addition, the limit of the Dlx1and Vax1 expression extended more dorsally in the mutant septum (Fig.1C,C′,D,D′,arrowheads), which appeared enlarged as compared with the septum of the wild-type brain.
Together these data indicate that in the Sey/Seytelencephalon, the domain of the VP and LP is ventralized so that the limit of the Emx1 expression is retracted to a more dorsal position within the pallium, the expression of Ngn2 andTbr1 is abolished in the VZ and SVZ-mantle of the VP, respectively, and the subpallial markers Dlx1, Vax1, Mash,and Six3 are ectopically expressed into more dorsal pallial domains.
Ventralization of the subpallial patterning in Sey/Sey
To test whether the extremely low level of the expression ofPax6 in the VZ of the entire LGE may have a biological significance for the patterning of the basal telencephalon, we studied the expression of several markers for the MGE in sections of WT andSey/Sey brains at stages E11.5–E14.5. From E10.5 onward, the proliferative and later on the postmitotic Ne of the MGE begins to express Shh (Sussel et al., 1999) and Nkx2.1(Shimamura et al., 1997). The gene Shh encodes a powerful morphogen with ventralizing activity that can induce the expression ofNkx2.1 (Ericson et al., 1995; Shimamura et al., 1997) andDlx (Kohtz et al., 1998). Furthermore, Shhcan inhibit the activity of the dorsal pattern genes such asPax6 (Ericson et al., 1997), Emx1, andTbr1 (Kohtz et al., 1998).
As illustrated in Figure 2, B, B′, the expression of Shh at E13.5, whereas normally confined to the submantle and mantle of the MGE, was expanded into the adjacent territory of the LGE in Sey/Sey. A similar pattern was seen at stage E12.0 as well (data not shown). Likewise, the Nkx2.1 expression, while normally restricted to the germinative Ne and mantle of MGE, expanded beyond the MGE/LGE border in the mutant brain (Fig.2C′, arrow). At stage E12.0 the ectopic expression of Nkx2.1 was spread over the VZ of the adjacent LGE domain (Fig. 2D′, arrows), which normally expresses Pax6 at a very low level. Thus, it is likely that an interaction between Pax6 andNkx2.1 genes might contribute for the maintenance of the MGE/LGE border. At stage E14.5, the Nkx2.1 expression outlined an enlarged MGE in the mutant brain (Fig.2E,E′; also F,F′).
Next we examined the expression of the LIM-homeobox containing gene Lhx6, which is assumed to play a specific role in defining the MGE territory (Grigoriou et al., 1998). The expression ofLhx6 at E12.5 was restricted to a subpopulation of cells in the SVZ and submantle of the MGE with only a few Lhx6+ cells in the LGE in a proximal vicinity to the sulcus between MGE and LGE (Fig. 3A; Wanaka et al., 1997;Grigoriou et al., 1998). After E13.0, an increasing number ofLhx6+ cells were observed in the mantle of the wild-type LGE, accompanied by the appearance of a Lhx6+ layer of cells in the intermediate zone (IZ) and marginal zone (MZ) of the cortex (Fig. 3B–D; see also Lavdas et al., 1999; Parnavelas, 2000). In Sey/Sey, already at E12.5 the expression ofLhx6 in the LGE was much more widespread, strongly suggesting that the mutant LGE contains a higher number ofLhx6+ cells (Fig. 3A′). To further characterize this pattern defect, in situ hybridization analysis was performed on sections from E14.0 wild-type and Sey/Seybrains at different rostrocaudal levels. The expression ofLhx6 along the entire rostrocaudal axis was much more abundant in the mutant as compared with the wild-type LGE (Fig.3B–D′). Furthermore, while present in the MZ of theSey/Sey cortex, Lhx6+ cells were not detectable in the lower part of the mutant cortical plate (Fig.3B′–D′). In accordance with previous data showing that the Lhx6+ cells originate mainly from the Ne of the MGE (Grigoriou et al., 1998) at a very rostral level the WT septum contained only a few Lhx6+ cells (Fig. 3B). In contrast, the SVZ–submantle of the septum in Sey/Sey was abundantly populated with Lhx6+cells that seem to migrate directly into the mutant LGE (Fig. 3B′). Thus, in Pax6 loss of function the Ne of the rostral septum and MGE appears to produce a higher number of Lhx6+ cells that migrate into the territory LGE, but these cells fail to populate the lower part of the mutant cortical plate. Different possibilities may account for the observed wider expression of Lhx6 in the basolateral telencephalon inSey/Sey: (1) enhancement of the rate of the Lhx6 mRNA synthesis implicating a transcriptional regulation betweenPax6 and Lhx6; (2) increase of the number of the generated Lhx6+ cells and/or enhanced ventrodorsal cell migration between the MGE and LGE as a result of the ventralization of a part of the Ne of LGE, as noticed above; and (3) accumulation of Lhx6+ cells within the mutant LGE because of a malformation of the corticopetal axons (Kawano et al., 1999) that normally help the subpallial cells in their tangential migration toward the cortex. Further experimentation will be required to definitively distinguish between these possibilities.
Fig. 3.
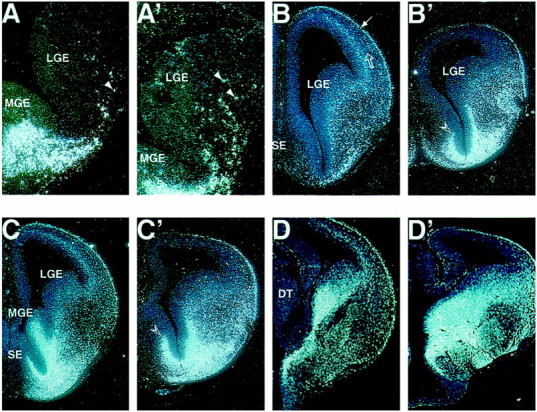
Expression of Lhx6 in the basolateral telencephalon in wild-type and Sey/Seybrain. A, A′, Coronal sections from E12.5 wild-type (A) and mutant (A′) brain. Note the enhanced number of Lhx6+ cells in the mutant LGE. B–D′, Coronal sections from E14.0 wild-type (B–D) and mutant (B′–D′) brain at different rostrocaudal levels. The open and the thin arrows in B point to a Lhx6+layer of cells in the intermediate and marginal zones of the CP, respectively. In all levels note the enhanced expression ofLhx6 in the LGE in the mutant as compared with the WT brain and the lack of Lhx6+ cells in the lower part of the Sey/Sey CP. B, B′, Note the increased expression of Lhx6 in the rostral septum inSey/Sey (open arrowhead) from where moreLhx6+ cells seem to populate directly the LGE.
Taken together, the results from the performed analysis of the patterning of the basal telencephalon indicate that in the lack of a functional Pax6 protein a more dorsal domain (LGE) of the basal telencephalon achieves characteristics of a more ventral domain (MGE).
Defects in the rostral basolateral telencephalon of theSey/Sey brain
The origin of the telencephalic basolateral structures is still under debate. Morphological studies suggested that whereas the claustrum has a neocortical origin, the endopiriform nucleus and piriform cortex originate from the Ne of the corticostriatal wedge (Bayer and Altman, 1991a) and/or from the Ne of the LGE (Valverde and Santacana, 1994; De Carlos et al., 1996).
At stage E12.5, cells expressing Pax6 or Tbr1appear to extend out from the Ne of the VP toward the basolateral telencephalon (Fig. 1A,F; see Fig. 7). To study which basolateral structures were specifically patterned by either of the two pallial markers, we examined the patterning at stage E18.5. In agreement with Bulfone et al. (1995), Tbr1 transcripts were detected in postmitotic cells of the neocortex and paleocortex, classical claustrum (Cl) (Fig.4A,C,F), and the dense layer II of the piriform cortex (Fig. 4B, open arrowhead). Recent results indicate that the classical claustrum is a derivative of the “dorsolateral claustrum” whose precursors are possibly generated from the Ne of theTbr1+/Emx1+ lateral pallium (Puelles et al., 1999, 2000). Rostrally, Pax6 was not expressed in the differentiating classical claustrum (Fig. 4D). However, Pax6 transcripts were detected in the presumptive domain of the olfactory tubercle (Tu) and in the ventral part (presumptive layer I) of the piriform cortex (Fig. 4E, filled arrowhead). In addition, Pax6 was expressed in a region, which has been designated by different authors as the endopiriform nucleus, anterior amygdalar area, ventral pallidum, and/or lateral striatal area (Fig. 4E,F, arrow). At early developmental stages this domain was referred to as the “ventromedial claustrum”, a derivative of the VP (Fig. 1F, arrowheads) (for discussion, see Puelles et al., 1999, 2000). Results from autoradiographic studies indicated that early-born cells from the Ne of the corticostriatal wedge (included in the territory of VP) are divided by the growing tip of the cortical plate at late developmental stages into a superficial part corresponding to layer I and a deep part, corresponding to cells located in the adult layer III of the piriform cortex (Valverde and Santacana, 1994). Thus, our results suggest that the early- and the late-born constituents of the piriform cortex (the primary olfactory cortex) are differentially patterned by Pax6 and Tbr1.
Fig. 7.
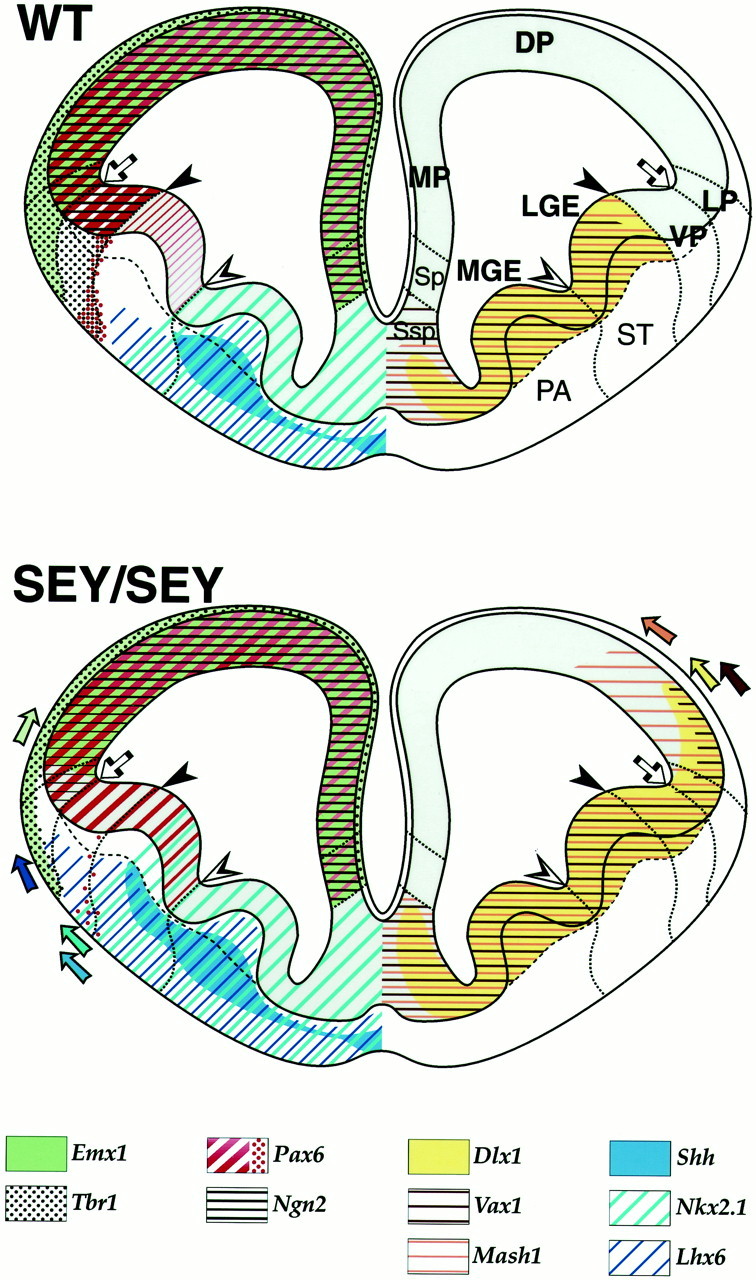
Schematic representation of the DV pattern defects in the telencephalon of the Pax6/Small eye mutant. The scheme illustrates that in the absence of functional Pax6 protein, the molecular patterning of the embryonic telencephalon is ventralized at the level of the pallial/subpallial and MGE/LGE borders. The drawing is based on the proposed subdivision of the telencephalic Ne (Puelles et al., 1999, 2000) and the results obtained from the expression analysis performed on coronal sections at a rostral level of the E12.5 wild-type (WT) and homozygous Small eye (Sey/Sey) brain. The pallial and subpallial markers have been color-coded as indicated. Thearrow points to the morphological corticostriatal sulcus. The filled arrowhead points to the pallial/subpallial border, from where a of Pax6+ stream of cells (red dots) and Tbr1+ (black dots) cells migrate toward the basolateral telencephalon as discussed in the text. Noteworthy, results from a very recent homology study in chick and mouse suggest that thePax6+ cells migrate within the striatal territory (Puelles et al., 2000). The open arrowhead points to the boundary between the MGE (pallidum) and the LGE (striatum).
Fig. 4.
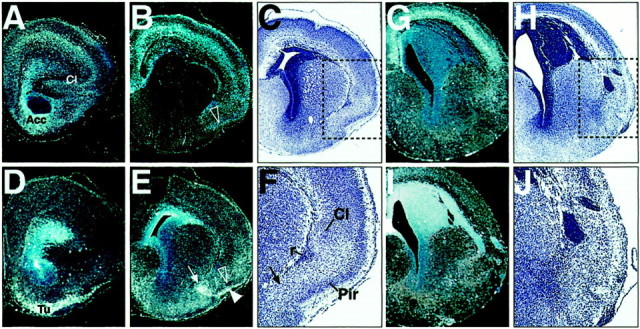
Differently patterned structures byPax6 and Tbr1 are distorted in theSey/Sey basolateral telencephalon. A, B, D, E, Adjacent coronal sections from the E18.5 WT brain were hybridized with probes for Tbr1 (A, B) and Pax6 (D, E). C is a bright-field picture of an adjacent section to the section (B) after hematoxylin–eosin (HE) staining. F is a close-up of C for the indicated field. A, B,Tbr1 expression is detected in the differentiating claustrum proper (Cl) and in the dense layer II (B, open arrowhead) of the piriform cortex. D, E,Pax6 is expressed in the olfactory tuberculum (Tu), in the ventral part (presumptive layer I) of the piriform cortex (E, arrowhead), and in the presumptive anlage of the anterior amygdala–endopiriform nucleus, a thin arrow in E and F. InE, note that the dense layer of the piriform cortex isPax6-negative (open arrowhead).G–J are adjacent coronal sections from the E18.5Sey/Sey brain, hybridized with Tbr1(G) and Pax6 (I) probes or stained with HE (H, J). In C,F, H, and Jnote that in the mutant brain, the piriform cortex, the claustrum proper, the endopiriform nucleus–anterior amygdala and the reservoir (r) are not distinguishable. The dark-stained structures in H and J are cells from the pallial germinative neuroepithelium that form clumps (or a thick band at other levels) located all along the pathway of the lateral migratory stream (Fig. 5) in the Sey/Sey pallium.
As illustrated in Figure 4, the piriform cortex, the claustrum (assumed to represent the deep layers of the insular cortex), the endopiriform nucleus, and the reservoirs cells (r) (Bayer and Altman 1991a,b) were not detectable in the rostral Sey/Sey telencephalon. Likewise, the lateral cortex including the prospective insular cortex was severely disorganized without a recognizable cortical plate at a very rostral level (Fig. 4C,H). Cells expressing defective Pax6 transcripts were detectable in the stream that extends from the Ne of the VP along the pallial/subpallial border (Fig. 1A′), implicating that Pax6 would not have a cell autonomous function for the generation of the early-born cells of the piriform cortex. We assume rather that the dysgenesis of the piriform, lateral cortex and claustrum in theSey/Sey telencephalon is a consequence of the prominent ventralization of the molecular patterning of the VP inSey/Sey as demonstrated in this work.
Defects in the differentiation of the cortical plate in Sey/Sey
The intriguing finding that at E12.5 Pax6 andNgn2 have overlapping expression domains and that the activity of Ngn2 was downregulated within theSey/Sey pallium was confirmed also later in development (Fig. 5). Recent data (Hartfuss et al., 2000) indicated that a subpopulation of acutely dissociated cortical progenitors colocalize Ngn2 and Pax6, implicating that a direct regulation between the two genes might cause the lack of the Ngn2 expression in the VP–LP. The performed double in situ and immunolabeling for Ngn2 and Pax6 revealed at E13.5 a nuclear signal for Pax6 only in a limited number of the Ngn2+pallial cells, including the region of VP and LP (Fig. 5D). These data suggest that the observed lack of Ngn2 expression might be a consequence of both, the ventralization of the neuroepithelium as described above and possibly involving also a direct gene regulation in a subset of the cortical progenitors. We assume therefore that a region-specific downregulation of the activity of the proneural gene Ngn2 in the ventrolateral pallium might contribute to the complex cortical phenotype in Sey/Sey.
A prominent feature of the Sey/Sey pallium is the thin cortical plate (CP) and the enlarged germinative neuroepithelium (VZ–SVZ) that occupies the IZ domain (Fig.6A,A′; for discussion, see also Warren et al., 1999). Highly accumulated cells appear adherent to each other all along the lateral migratory stream (Fig.6B′), a pathway that normally carries postmitotic cells populating the basolateral cortex. At stage E14.5, the early differentiation markers Tbr1 and SorLA showed only a faint expression in the superficial zone of the forming CP, but were not detected in the mutant VZ–SVZ (data not shown). We tested the differentiation of the mutant cortex further at stage E18.5 using the available layer-specific markers: Emx1 and Tbr1for all layers of the cortex (Bulfone et al., 1995), Otx1for layer V–VI (Frantz et al., 1994), mSorLA for layers V-II (Hermans-BorgMeyer et al., 1998; our unpublished observations) and reelin for the MZ (D'Arcangelo et al., 1995; Ogawa et al., 1995). In the abortive CP, the Emx1, mSorLa, and Otx1 showed a diffuse expression at a similar strength (Fig. 6C′,F′,G′), and the Tbr1 transcripts accumulated in the lower part of the CP (Fig. 6E′; Warren et al., 1999). The VZ and SVZ of the mutant pallium was labeled by the Emx1 andOtx1 probes (Fig. 6C′,G′,arrowheads). In contrast, the expression of Tbr1(Fig. 6E′) and SorLA (Fig.6F′) within the enlarged VZ–SVZ was abolished, most strongly within the region of VP and LP (Fig.6E′,F′, asterisks) as compared with the dorsomedial SVZ. This finding is consistent with the noticed above region specific inhibition of the Ngn2 activity inSey/Sey. Together, these data suggest that the inhibition of the Ngn2 activity in the Sey/Sey pallium might prevent/or causes a delay in the differentiation of a subpopulation of the cortical progenitors (mostly within the ventrolateral pallial domain) that fail to migrate and accumulate within the pathological germinative Ne.
Fig. 6.
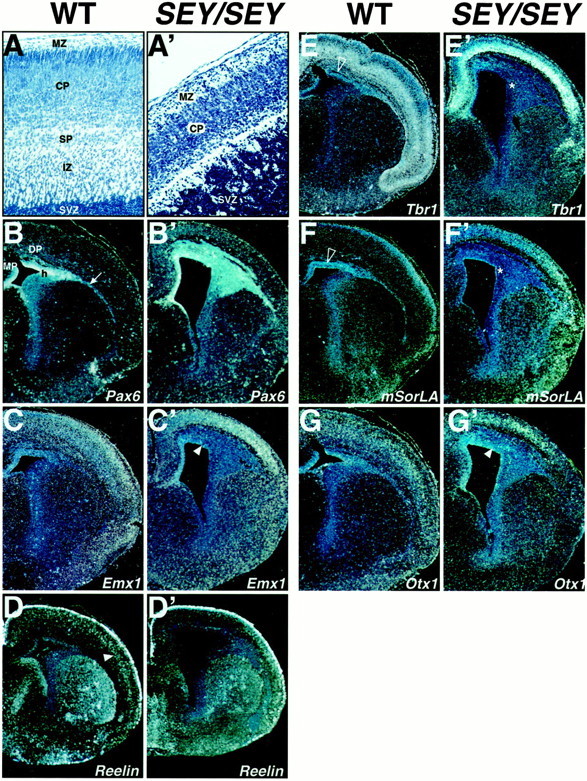
Failure in the differentiation of the cortical plate in Sey/Sey. Coronal sections at a rostral level from E18.5 WT (B–D) and Sey/Sey(B′–D′) brain were hybridized with different cortical markers, as indicated. A andA′ are Nissl-stained sections from a WT and a mutant brain illustrating the severe abnormalities of the pallium in the mutant: an enlarged germinative zone (VZ–SVZ), a lack of a delineated intermediate zone (IZ) and subplate (SP), a thin cortical plate (CP) without radial alignment of the cells, and a wide and hypercellular marginal zone (MZ). The asterisks inE′ and F′ point to the germinative Ne of the VP + LP that are compressed by the growing striatum and therefore not easily distinguishable; the thin arrow inB points to the lateral migratory stream (LMS). InB′ note the Pax6-positive VZ–SVZ in the mutant pallium, which expands within the domain of the VP, LP, DP, in the hilus (h) of the LMS, but not in the MP. InC′ and G′ note that the expression ofEmx1 and Otx1 in the pallial VZ–SVZ (arrowheads) of Sey/Sey is detectable.E, F, In the WT brain, Tbr1 andmSorLa are expressed in the SVZ (empty arrowhead) of the entire pallium and their expression outline the piriform cortex as well. E′, F′, InSey/Sey, the expression of Tbr1 andSorLA is abolished in the enlarged SVZ of the VP–LP (asterisks), except for the region of the MP. In the basolateral telencephalon note the disorganization of the lateral insular and piriform cortex. C′,F′, G′, Emx1, Otx1, andmSorLa show diffuse expression in the abortive mutant CP, whereas the Tbr1 transcripts are accumulated in the lower part of the CP (E′). InD′ note the stronger expression of reelinin the mutant MZ. The arrowhead in Dpoints to a layer of reelin+ cells in the CP that is not detectable in the Sey/Sey cortex (D′).
Given the key role of reelin in the laminar cortical development (Lambert de Rouvroit and Goffinet, 1998), it is of special interest to note that whereas the reelin expression in theSey/Sey MZ was at a higher level as compared with the wild-type brain, the reelin transcripts were lacking from the IZ of the pallium in the mutant brain (Fig.6D′,D, arrowhead).
DISCUSSION
Pax6 modulates the DV regionalization of the neuroepithelium along the entire anteroposterior axis of the developing CNS
Accumulating evidence indicates that the expression ofShh in the axial mesendoderm is essential for the ventral specification of the developing CNS, including the forebrain (Ericson et al., 1995; Chiang et al., 1996; Rubenstein and Shimamura, 1997). In the ventral neural tube the Shh signal secreted from the floor plate mediates a long-range repression of the Pax6level, forming thereby four zones of distinct progenitors, a most ventral Pax6−/Nkx2.2+ domain and progressively more dorsally located domains with low, moderate, and high levels ofPax6 expression (Ericson et al., 1995, 1997). The progenitors of these domains generate distinct neuronal populations of the motor neurons and the three columns of interneurons. Our analysis revealed a similar characteristic in three ventrodorsal domains of the telencephalic neuroepithelium for the expression of Pax6 andNkx2.1 which is another member of the Nkx gene family with a restricted expression in the anlage of the MGE (Price et al., 1992;Shimamura et al., 1995; Sussel et al., 1999). It should be noted however that the “dorsoventral” terminology used to describe our observations is preliminary because the topological relationship of the telencephalic subdivisions is still an open question (for discussion, see Rubenstein et al., 1998).
We found that the most ventrally located domain, the VZ of the MGE, that generates the cells of the pallidum is a Pax6−, butNkx2.1+/Dlx1,2+/Vax1+/Mash1+ region. In the MGE, Shh is initially expressed in the VZ (Sussel et al., 1999), and later it is expressed in the SVZ and mantle zone. The next domain is the VZ of the LGE, which produces the striatum. It expresses Pax6 at a very low level and isNkx2.1−/Dlx1,2+/Vax1+/Mash1+. The domain of the VP is the third zone, located further dorsally. It contributes to the generation of the claustrum–endopiriform nucleus, the piriform cortex, and a part of the amygdala (Bayer and Altman, 1991; for further discussion see Puelles at al., 2000). Here the expression ofPax6 (and Ngn2 as well) is very high, whereas the transcripts of Nkx2.1, Dlx1, Vax1, andMash1 are absent.
In the caudal neural tube, the loss of Pax6 function leads to a dorsal expansion of ventral markers and to a change of the cell fate (Ericson et al., 1997). Likewise we found that the Pax6 mutation leads to an expansion of the expression of the MGE marker genes Shh, Nkx2.1, and Lhx6 into the territory of the more dorsally located LGE. This pattern defect appears to result in the alteration of the regional identity of the adjacent LGE area reflected in an enlargement of the MGE territory at midgestation and underdevelopment of the striatum later on—a puzzling morphological phenotype for the Pax6 mutant brain for a long time (Glaser et al., 1994). We found further that the ventralization of the Ne of the VP, where Pax6 is expressed at a very high level, causes defects in the generation of the piriform, rostral lateral (insular) cortex, and the claustrum–endopiriform nucleus. These defects are reminiscent to observations in the Sey/Sey hindbrain and spinal cord where the columns of the dorsally and more ventrally located neurons, produced by domains with a very high and low level of Pax6expression, are either missing or show an altered identity, respectively (Burrill et al., 1997; Ericson et al., 1997). Thus, in Pax6 loss of function in appears that domains that normally have a comparable level of Pax6 expression, show similar morphological disturbances in the epichordal and prechordal part of the CNS as a result of the ventralization of the molecular identity of adjacent regions. These results indicate that the level of Pax6 expression is an essential determinant of the DV regionalization of the Ne along the entire anteroposterior axis of the developing CNS.
In the spinal cord of Nkx2.2−/− mice the fate of the most ventral column of neurons is dorsalized into the fate of the somatic motoneurons, but without a change in the Pax6expression—a fact implicating that Nkx2.2 has a decisive role for interpreting the ventralizing activity of the Shh protein produced by the notochord and floor plate (Briscoe et al., 1999). Although Shh, which is produced by the rostral mesendoderm, is an essential factor for establishing the ventral identity in the forebrain (Ericson et al., 1995; Shimamura and Rubenstein, 1997), the final specification of the DV domains in the telencephalon seems to include additional mechanisms. The expression of Nkx2.1 andShh in the MGE and Pax6 in the pallium appears almost simultaneously at ∼E10.5 (Hentges et al., 1999). In Pax6 loss of function we observed ectopic expression of both Shh andNkx2.1 into more dorsal telencephalic domains. A recent analysis of Nkx2.1−/− mice revealed opposite pattern defects as compared with the Small eye telencephalon (Sussel et al., 1999). In these mice, the lateral domain of the MGE is dorsalized showing ectopic expression of Pax6, whereas the expression of Shh in the MGE is suppressed. The alteration of the patterning leads to a lack of the globus pallidus and an enlargement of the striatum. Thus, in the Sey/Sey andNkx2.1−/− mutants, although the anlage of the MGE and LGE are specified presumably by the ventralizing activity of the mesendodermal Shh, these structures show a complementary DV pattern and morphological defects in the adjacent domains of the MGE or LGE. It is worthy to note that in the absence of the low level expression ofPax6 in the VZ of the LGE, the dorsal ectopic expression ofNkx2.1 includes the VZ of a part of the LGE. Together, these data suggest that either a direct regulation of the activity of these genes or protein–protein interactions between their products might contribute for the maintenance of the MGE/LGE border in the telencephalon.
Pax6 and the patterning of the cortex
The development of the cortex is severely affected in theSey/Sey mutant: the CP is hypocellular without radial alignment of the cells, whereas the germinative neuroepithelium (VZ–SVZ) is enlarged and consists of accumulated precursors in large clumps that occupy the area of the IZ (Schmahl et al., 1993; Warren and Price, 1999). These cells show a high level of expression of the mutantPax6 message (Stoykova et al., 1997; this study) and active incorporation of BrdU after pulse labeling at early (E10–E12.5) (Warren et al., 1999) and later (E12.5-E18.5) stages (Brunjes et al., 1998; Götz et al., 1998).
We show in this work a severe defect of the DV patterning in theSey/Sey telencephalon. As a result of the early developmental ventralization of the NE at the pallial/subpallial border, the morphogenesis of the basolateral cortex appears to be strongly affected, as shown by the malformation of the claustrum, endopiriform nucleus, piriform, and lateral cortex.
From E14.5 onward, the pallium of the Sey/Sey mutant fails to properly differentiate. The accumulated cells in the mutant VZ–SVZ express the neuron-specific marker TuJ1 (Caric et al., 1997). However, the expression of the differentiation markers Tbr1,mSorLa, and Emx1 were not detected in the SVZ of the ventrolateral and dorsal pallium, but being preserved in the MP and in the abortive cortical plate. This suggests that only a portion of the later cortical progenitors are either not generated or they are unable to properly differentiate in the Sey/Sey cortex. A similar regional inhibition of the activity of the Ngn2 gene was detected in the VZ of the mutant pallium. Ngns are vertebrate neuronal determination genes encoding for basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors, essential for the neurogenesis, including the cortex (Ma et al., 1996; 1999; Cai et al., 2000). Our previous results indicated that the expression of Pax6 is a characteristic trait of the cortical RC2+ radial glial cells with an essential role for their differentiation (Götz et al., 1998). The cortical radial glial cells might have a neurogenic potential (Alvarez-Buylla et al., 1990; Lendahl et al., 1990; Gray and Sanes, 1992). In accordance with recent results indicating that Ngn2 is detected only in those Pax6+/RC2+ radial glial cells, that contain neither the astrocyte-specific glutamate transporter (GLAST) nor the brain- lipid-binding protein (BLBP) (Götz, 2000; Hartfuss et al., 2000) we show here that at E13.5 the expression ofNgn2 and Pax6 normally colocalizes only in some cortical progenitors. Most intriguingly, the misexpression of Ngn2 in the cortical progenitor cells results in the production of neurons (Cai et al., 2000). Furthermore, isolated radial glial cells fromSey/Sey cortex generated in vitro only 44% of the neuronal clones produced by the WT radial glial cells (Malatesta and Götz, 2000). Thus, our results and the literature data support the possibility that the differentiation of not all cortical precursors in the Sey/Sey pallium is affected; indeed the mutant CP shows expression of all tested cortical markers. We favor rather the idea that only a portion, mainly the Ngn2+/Pax6+ progenitors of the ventrolateral pallium are hampered to differentiate in Pax6 loss of function.
Accumulating evidence indicates that some postmitotic cells born in the subpallium invade the pallium. Thus, a part of the cortical interneurons are produced in the subpallial Ne and populate through a tangential migration the CP as postmitotic Dlx-, GABA-, GAD67-, Lhx6-, calbindin-, calretinin-, or reelin-positive cells (for review, seeParnavelas, 2000). The absence of Dlx1/2 (Anderson et al., 1997a,b) and Mash1 (Casarosa et al., 1999) in the MGE/LGE leads to an almost complete loss of the GAD67+ cells in the CP or in the MZ, respectively, whereas the loss of Nkx2.1 in the MGE (Sussel et al., 1999) is associated with absence of calbin-din+ cells. We show in this work that early in development the proliferative Ne of the VP and LP in Sey/Sey expresses ectopicallyDlx1, Mash1, Vax1, and Six3, whereas the restricted expression of Nkx2.1 and Lhx6 to the MGE expands into the adjacent LGE territory. Therefore it is likely that the ventralized Ne in the basal telencephalon ofSey/Sey produces progenitors with altered identity, increasing thereby the portion of the subpallial cells that migrate into the cortex. This is in line with data showing that the lateral telencephalon of Sey/Sey contains twice as much postmitotic GABA+, calbindin+ and calretinin+ cells as compared with the wild-type littermates (Chapouton et al., 1999). Thus, the defects of the dorsoventral patterning of the telencephalic neuroepithelium in Pax6 loss of function are part of the complex cortical phenotype of theSmall eye mutant.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Max-Planck-Gesellschaft. We thank A. Simeone, M. Price, F. Guillemot, V. Pachnis, A. Bulfone, Chica Schaller, A. McMahon, and V. Tarabykin for providing us withEmx1, Emx2, and Otx1,Dlx1, and Nkx2.1, Mash1,Ngn1, and Ngn2, Lhx6, Tbr1,SorLa, Shh, and reelinprobes for the in situ analysis. We thank L. Puelles and M. Götz for fruitful discussions. The excellent technical assistance of S. Eckert is highly acknowledged. Thanks are due to S. Heinemann for correcting this manuscript.
Correspondence should be addressed to Anastassia Stoykova, Max-Planck Institute of Biophysical Chemistry, Department of Molecular Cell Biology, 37077 Göttingen, Germany. E-mail: astoyko@gwdg.de.
Dr. Hallonet's present address: Institut de Génétique et de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, 1 rue Laurent Fries, B.P. 163, 67404 Illkirch Cedex, France.
REFERENCES
- 1.Altman J, Bayer SA. Atlas of prenatal rat brain development. CRC; Boca Raton: 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alvarez-Buylla A, Theelen M, Nottebohm F. Proliferation “hot spots” in adult avian ventricular zone reveal radial cell division. Neuron. 1990;5:101–109. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90038-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anderson SA, Eisenstat DD, Shi L, Rubenstein JL. Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: dependence on Dlx genes. Science. 1997a;278:474–476. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5337.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anderson SA, Qiu M, Bulfone A, Eisenstat DD, Meneses J, Pedersen R, Rubenstein JL. Mutations of the homeobox genes Dlx-1 and Dlx-2 disrupt the striatal subventricular zone and differentiation of late born striatal neurons. Neuron. 1997b;19:27–37. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bayer SA, Altman J. Development of the endopiriform nucleus and the claustrum in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1991a;45:391–412. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90236-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bayer SA, Altman J. Neocortical development. Raven; New York: 1991b. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Briscoe J, Sussel L, Serup P, Hartigan-O'Connor D, Jessell TM, Rubenstein JL, Ericson J. Homeobox gene Nkx2.2 and specification of neuronal identity by graded Sonic hedgehog signalling. Nature. 1999;398:622–627. doi: 10.1038/19315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brunjes PC, Fisher M, Grainger R. The small-eye mutation results in abnormalities in the lateral cortical migratory stream. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1998;110:121–125. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(98)00089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bulfone A, Puelles L, Porteus MH, Frohman MA, Martin GR, Rubenstein JL. Spatially restricted expression of Dlx-1, Dlx-2 (Tes-1), Gbx-2, and Wnt-3 in the embryonic day 12.5 mouse forebrain defines potential transverse and longitudinal segmental boundaries. J Neurosci. 1993;13:3155–3172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-03155.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bulfone A, Smiga SM, Shimamura K, Peterson A, Puelles L, Rubenstein JL. T-brain-1: a homolog of Brachyury whose expression defines molecularly distinct domains within the cerebral cortex. Neuron. 1995;15:63–78. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Burrill J, Moran L, Goulding M, Saueressig H. PAX2 is expressed in multiple spinal cord interneurons, including a population of EN1+ interneurons that require PAX6 for their development. Development. 1997;124:4493–4503. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.22.4493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cai Li, Morrow EM, Cepko C. Misexpression of basic helix-loop-helix genes in the murine cerebral cortex affects cell fate choices and neuronal survival. Development. 2000;127:3021–3030. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.14.3021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Caric D, Gooday D, Hill RE, McConnell SK, Price DJ. Determination of the migratory capacity of embryonic cortical cells lacking the transcription factor Pax-6. Development. 1997;124:5087–5096. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.24.5087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Casarosa S, Fode C, Guillemot F. Mash1 regulates neurogenesis in the ventral telencephalon. Development. 1999;126:525–534. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.3.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chapouton P, Gartner A, Götz M. The role of Pax6 in restricting cell migration between developing cortex and basal ganglia. Development. 1999;126:5569–5579. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.24.5569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Corden JL, Westphal H, Beachy PA. Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature. 1996;383:407–413. doi: 10.1038/383407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.D'Arcangelo G, Miao GG, Chen SC, Soares HD, Morgan JI, Curran T. A protein related to extracellular matrix proteins deleted in the mouse mutant reeler. Nature. 1995;374:719–723. doi: 10.1038/374719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.De Carlos JA, Lopez-Mascaraque L, Valverde F. Dynamics of cell migration from the lateral ganglionic eminence in the rat. J Neurosci. 1996;16:6146–6156. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-19-06146.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Engelkamp D, Rashbass P, Seawright A, van Heyningen V. Role of Pax6 in development of the cerebellar system. Development. 1999;126:3585–3596. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.16.3585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ericson J, Muhr J, Placzek M, Lints T, Jessell TM, Edlund T. Sonic hedgehog induces the differentiation of ventral forebrain neurons: a common signal for ventral patterning within the neural tube. Cell 81 1995. 747 756[Erratum (1995) 82:165]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ericson J, Rashbass P, Schedl A, Brenner-Morton S, Kawakami A, van Heyningen V, Jessell TM, Briscoe J. Pax6 controls progenitor cell identity and neuronal fate in response to graded Shh signaling. Cell. 1997;90:169–180. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Foster GA. Chemical neuroanatomy of the prenatal rat brain: a developmental atlas. Oxford UP; Oxford: 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Frantz GD, Weimann JM, Levin ME, McConnell SK. Otx1 and Otx2 define layers and regions in developing cerebral cortex and cerebellum. J Neurosci. 1994;14:5725–5740. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-10-05725.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Glaser T, Jepeal L, Edwards JG, Young SR, Favor J, Maas RL. PAX6 gene dosage effect in a family with congenital cataracts, aniridia, anophthalmia and central nervous system defects. Nat Genet 7 1994. 463 471[Erratum (1994) 8:203]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Götz M. Specification of precursor subsets in the developing cortex, a new view on radial glial cells. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;[Suppl 11] 12:192. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Götz M, Stoykova A, Gruss P. Pax6 controls radial glia differentiation in the cerebral cortex. Neuron. 1998;21:1031–1044. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80621-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gradwohl G, Fode C, Guillemot F. Restricted expression of a novel murine atonal-related bHLH protein in undifferentiated neural precursors. Dev Biol. 1996;180:227–241. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gray GE, Sanes JR (1992) Lineage of radial glia in the chicken optic tectum Development 114:271–283. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 29.Grigoriou M, Tucker AS, Sharpe PT, Pachnis V. Expression and regulation of Lhx6 and Lhx7, a novel subfamily of LIM homeodomain encoding genes, suggests a role in mammalian head development. Development. 1998;125:2063–2074. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.11.2063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Grindley JC, Hargett LK, Hill RE, Ross A, Hogan BL. Disruption of PAX6 function in mice homozygous for the Pax6Sey-1Neu mutation produces abnormalities in the early development and regionalization of the diencephalon. Mech Dev. 1997;64:111–126. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(97)00055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guillemot F, Joyner AL. Dynamic expression of the murine Achaete-Scute homologue Mash-1 in the developing nervous system. Mech Dev. 1993;42:171–185. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90006-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hallonet M, Hollemann T, Wehr R, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Pieler T, Gruss P. Vax1 is a novel homeobox-containing gene expressed in the developing anterior ventral forebrain. Development. 1998;125:2599–2610. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.14.2599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hartfuss E, Guillemot F, Götz M. Immunochemical characterization of CNS precursor subtypes and radial glia. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;[Suppl 11] 12:262. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hentges K, Thompson K, Peterson A. The flat-top gene is required for the expansion and regionalization of the telencephalic primordium. Development. 1999;126:1601–1609. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.8.1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Hampe W, Schinke B, Methner A, Nykjaer A, Susens U, Fenger U, Herbarth B, Schaller HC. Unique expression pattern of a novel mosaic receptor in the developing cerebral cortex. Mech Dev. 1998;70:65–76. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(97)00177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Hill RE, Favor J, Hogan BL, Ton CC, Saunders GF, Hanson IM, Prosser J, Jordan T, Hastie ND, van Heyningen V. Mouse small eye results from mutations in a paired-like homeobox-containing gene. Nature 354 1991. 522 525[Erratum (1992) 355:750]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hogan BL, Horsburgh G, Cohen J, Hetherington CM, Fisher G, Lyon MF. Small eyes (Sey): a homozygous lethal mutation on chromosome 2 which affects the differentiation of both lens and nasal placodes in the mouse. J Embr Exp Morphol. 1986;97:95–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kawano H, Fukuda T, Kubo K, Horie M, Uyemura K, Takeuchi K, Osumi N, Eto K, Kawamura K. Pax-6 is required for thalamocortical pathway formation in fetal rats. J Comp Neurol. 1999;408:147–160. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19990531)408:2<147::aid-cne1>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kohtz JD, Baker DP, Corte G, Fishell G. Regionalization within the mammalian telencephalon is mediated by changes in responsiveness to Sonic Hedgehog. Development. 1998;125:5079–5089. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.24.5079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lampert de Rouvroit C, Goffinet AM. A new view of early cortical development. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;56:1402–1409. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(98)00209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lavdas AA, Grigoriou M, Pachnis V, Parnavelas JG. The medial ganglionic eminence gives rise to a population of early neurons in the developing cerebral cortex. J Neurosci. 1999;19:7881–7888. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-18-07881.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lendahl U, Zimmerman LB, McKay RD. CNS stem cells express a new class of intermediate filament protein. Cell. 1990;60:585–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90662-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ma Q, Kintner C, Anderson DJ. Identification of neurogenin, a vertebrate neuronal determination gene. Cell. 1996;87:43–52. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ma Q, Fode C, Guillemot F, Anderson DJ. Neurogenin1 and neurogenin2 control two distinct waves of neurogenesis in developing dorsal root ganglia. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1717–1728. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.13.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Malatesta P, Götz M. The progeny of radial glial cells of the cerebral cortex analyzed by fluorescent-activated cell sorting. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;[Suppl 11] 12:326. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mastick GS, Davis NM, Andrew GL, Easter SS., Jr Pax-6 functions in boundary formation and axon guidance in the embryonic mouse forebrain. Development. 1997;124:1985–1997. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.10.1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ogawa M, Miyata T, Nakajima K, Yagyu K, Seike M, Ikenaka K, Yamamoto H, Mikoshiba K. The reeler gene-associated antigen on Cajal-Retzius neurons is a crucial molecule for laminar organization of cortical neurons. Neuron. 1995;14:899–912. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Oliver G, Mailhos A, Wehr R, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Gruss P. Six3, a murine homologue of the sine oculis gene, demarcates the most anterior border of the developing neural plate and is expressed during eye development. Development. 1995;121:4045–4055. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.12.4045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Osumi N, Hirota A, Ohuchi H, Nakafuku M, Iimura T, Kuratani S, Fujiwara M, Noji S, Eto K. Pax-6 is involved in the specification of hindbrain motor neuron subtype. Development. 1997;124:2961–2972. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.15.2961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Parnavelas JG. The origin and migration of cortical neurones: new vistas. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:126–131. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(00)01553-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Paxinos G, Ashwell KWS, Törk I. Atlas of the developing rat nervous system. Academic; San Diego: 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Price M, Lazzaro D, Pohl T, Mattei MG, Ruther U, Olivo JC, Duboule D, Di Lauro R. Regional expression of the homeobox gene Nkx-2.2 in the developing mammalian forebrain. Neuron. 1992;8:241–255. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90291-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Puelles L, Kuwana E, Puelles E, Rubenstein JL. Comparison of the mammalian and avian telencephalon from the perspective of gene expression data. Eur J Morphol. 1999;37:139–150. doi: 10.1076/ejom.37.2.139.4756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Puelles L, Kuwana E, Puelles E, Bulfone A, Shimamura K, Keleher J, Smiga S, Rubenstein JL. Pallial and subpallial derivatives in the embryonic chick and mouse telencephalon, traced by the expression of the genes Dlx-1, Emx-1, Nkx-2.1, Pax-6 and Tbr-1. J Comp Neurol. 2000;424:409–438. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861(20000828)424:3<409::aid-cne3>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Roberts RC. Small-eyes, a new dominant mutant in the mouse. Genet Res. 1967;9:121–122. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rubenstein JLR, Shimamura K. Regulation of patterning and differentiation in the embryonic vertebrate forebrain. In: Cowan WM, Jessel TM, Zipursky SL, editors. Molecular and cellular approaches to neural development. Oxford UP; New York: 1997. pp. 359–390. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rubenstein JL, Shimamura K, Martinez S, Puelles L. Regionalization of the prosencephalic neural plate. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1998;21:445–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.21.1.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schmahl W, Knoedlseder M, Favor J, Davidson D. Defects of neuronal migration and the pathogenesis of cortical malformations are associated with Small eye (Sey) in the mouse, a point mutation at the Pax-6-locus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1993;86:126–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00334879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Shimamura K, Hartigan DJ, Martinez S, Puelles L, Rubenstein JL. Longitudinal organization of the anterior neural plate and neural tube. Development. 1995;121:3923–3933. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.12.3923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Shimamura K, Martinez S, Puelles L, Rubenstein JL. Patterns of gene expression in the neural plate and neural tube subdivide the embryonic forebrain into transverse and longitudinal domains. Dev Neurosci. 1997;19:88–96. doi: 10.1159/000111190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Simeone A, Gulisano M, Acampora D, Stornaiuolo A, Rambaldi M, Boncinelli E. Two vertebrate homeobox genes related to the Drosophila empty spiracles gene are expressed in the embryonic cerebral cortex. EMBO J. 1992;11:2541–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Smith-Fernandez A, Pieau C, Reperant J, Boncinelli E, Wassef M. Expression of the Emx-1 and Dlx-1 homeobox genes define three molecularly distinct domains in the telencephalon of mouse, chick, turtle and frog embryos: implications for the evolution of telencephalic subdivisions in amniotes. Development. 1998;125:2099–2111. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.11.2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Stoykova A, Gruss P. Roles of Pax-genes in developing and adult brain as suggested by expression patterns. J Neurosci. 1994;14:1395–1412. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-03-01395.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Stoykova A, Fritsch R, Walther C, Gruss P. Forebrain patterning defects in Small eye mutant mice. Development. 1996;122:3453–3465. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.11.3453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Stoykova A, Götz M, Gruss P, Price J. Pax6-dependent regulation of adhesive patterning, R-cadherin expression and boundary formation in developing forebrain. Development. 1997;124:3765–3777. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.19.3765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sussel L, Marin O, Kimura S, Rubenstein JL. Loss of Nkx2.1 homeobox gene function results in a ventral to dorsal molecular respecification within the basal telencephalon: evidence for a transformation of the pallidum into the striatum. Development. 1999;126:3359–3370. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.15.3359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Valverde F, Santacana M. Development and early postnatal maturation of the primary olfactory cortex. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1994;80:96–114. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(94)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Walther C, Gruss P. Pax-6, a murine paired box gene, is expressed in the developing CNS. Development. 1991;113:1435–1449. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wanaka A, Matsumoto K, Kashihara Y, Furuyama T, Tanaka T, Mori T, Tanno Y, Yokoya S, Kitanaka J, Takemura M, Tohyama M. LIM-homeodomain gene family in neural development. Dev Neurosci. 1997;19:97–100. doi: 10.1159/000111191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Warren N, Caric D, Pratt T, Clausen JA, Asavaritikrai P, Mason JO, Hill RE, Price DJ. The transcription factor, Pax6, is required for cell proliferation and differentiation in the developing cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1999;9:627–635. doi: 10.1093/cercor/9.6.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


