Abstract
Current pharmacological therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction are largely either repurposed anti‐hypertensives that blunt overactivation of the neurohormonal system or diuretics that decrease congestion. However, they do not address the symptoms of heart failure that result from reductions in cardiac output and reserve. Over the last few decades, numerous attempts have been made to develop and test positive cardiac inotropes that improve cardiac haemodynamics. However, definitive clinical trials have failed to show a survival benefit. As a result, no positive inotrope is currently approved for long‐term use in heart failure. The focus of this state‐of‐the‐art review is to revisit prior clinical trials and to understand the causes for their findings. Using the learnings from those experiences, we propose a framework for future trials of such agents that maximizes their potential for success. This includes enriching the trials with patients who are most likely to derive benefit, using biomarkers and imaging in trial design and execution, evaluating efficacy based on a wider range of intermediate phenotypes, and collecting detailed data on functional status and quality of life. With a rapidly growing population of patients with advanced heart failure, the epidemiologic insignificance of heart transplantation as a therapeutic intervention, and both the cost and morbidity associated with ventricular assist devices, there is an enormous potential for positive inotropic therapies to impact the outcomes that matter most to patients.
Keywords: Chronic heart failure, Inotropes, Clinical trials
What is an inotrope?
In the reductionist's view of the cardiovascular system, the principal function of the heart is to pump blood, and heart failure is synonymous with pump failure. Indeed, the modalities used historically — and at present — to describe and quantify heart failure have placed a large degree of emphasis on measuring contractile function of the left ventricle, the genesis of which can be traced at least as far back to the classic physiology experiments by Otto Frank and Earnest Starling.1, 2, 3 The implication has been a persistent focus on developing therapies that augment left ventricular contractility, collectively referred to as cardiac ‘inotropes’.
The word ‘inotrope’ originates from the Greek inos (fibre) and trope (turning or moving) and describes therapies that increase the force of cardiac contractions. While the strict definition of an inotrope may be both nuanced and unsettled, for the purposes of this review, we will focus on synthetic therapeutics that act directly on myocardial cells to increase cardiac contractility and thereby improve cardiac haemodynamics. We will sidestep a discussion of digoxin, which continues to be used frequently for the clinical management of heart failure and has a storied history of investigation worthy of a separate manuscript.4 We will focus only on patients with chronic heart failure with ‘reduced ejection fraction’, where the primary defect is felt to be pump dysfunction, since these are the patients for whom inotropes have been developed to date and will likely be developed in the future.
The purpose of this manuscript is to critically review prior attempts at developing synthetic positive cardiac inotropes for the chronically failing heart with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) — not acute decompensated heart failure with shock — and to explore the various reasons why they failed in their efforts to improve clinical outcomes. We will examine how these prior failures might instruct future development of effective therapies for this high‐risk, medically vulnerable, and rapidly growing patient population.
Basic mechanisms of cardiac contractility
The purpose of inotropic interventions in heart failure is to increase the muscular contractile force of the myocardium.5 Current approaches to increasing contractility are accomplished primarily through increasing the influx of calcium or maintaining higher calcium levels in the cytosol of cardiac myocytes during an action potential. Much of the mechanistic data in this realm is based on animal models. Contraction occurs in several ways (Figure 1). First, catecholamines increase contractile force largely via the β‐adrenoceptor‐adenylyl cyclase system.6 Through protein kinase A, the β‐adrenoceptor system phosphorylates L‐type calcium channels to increase calcium influx and ryanodine receptors to increase sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release, resulting in activation of actomyosin cross‐bridges. Phosphorylation of phospholamban accelerates accumulation of calcium. In addition, relaxation is supported by phosphorylation of troponin I due to reduced calcium sensitivity of troponin C (positive lusitropy). Length‐dependent activation of cross‐bridges — the so‐called ‘Frank–Starling mechanism’ — plays a role along with contraction frequency‐dependent activation of contractile force, where increasing heart rate causes more calcium to enter the cardiomyocyte for release during the next contraction. At the cross‐bridge level, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)‐mediated increase in contractility reduces the attachment time of the individual cross‐bridge. As a result, this cAMP‐mediated inotropy increases the rate of force development and rate of relaxation, potentially at the expense of ‘energetic efficiency’.
Figure 1.
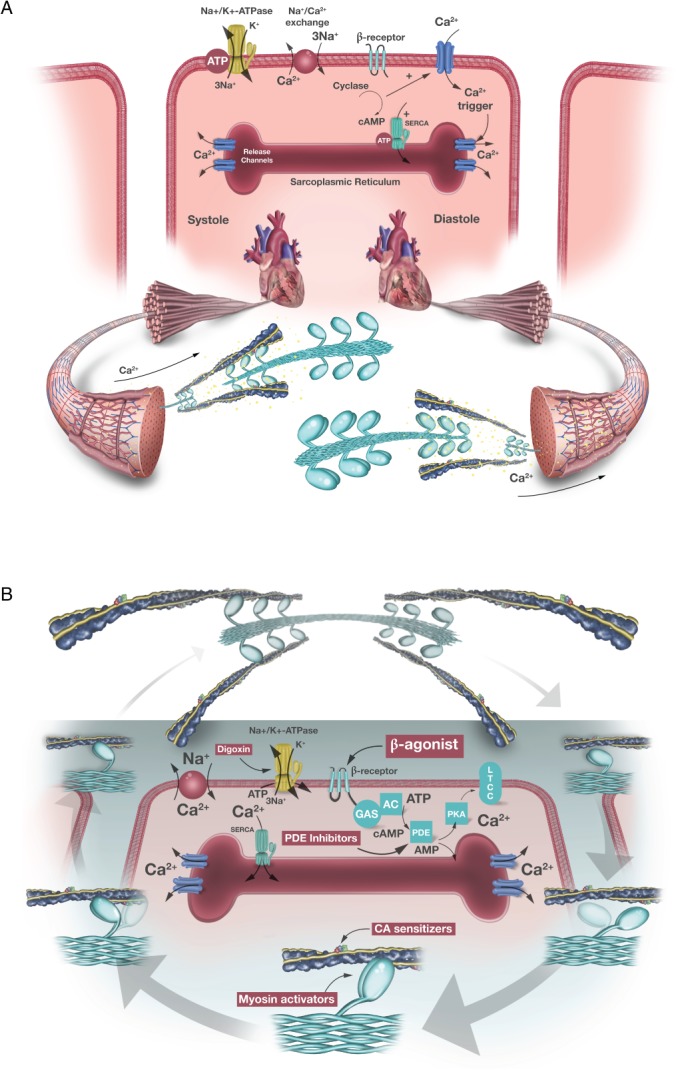
(A) Normal cardiac contraction and (B) mechanism of action of various cardiac inotropic agents. AC, adenyl cyclase; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CA, calcium; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PDE, phosphodiesterase; LTCC, L‐type Ca2+ channels; PKA, protein kinase A; SERCA, sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump.
The impact of these molecular changes occurs at the level of the smallest force‐producing unit, the actomyosin cross‐bridge. During a cross‐bridge cycle, the myosin head attaches to actin, rotates to produce force, and maintains during the ‘on‐time’. This effect is dependent upon the availability of high energy phosphates that are hydrolysed during this process. Thereafter, the cross‐bridge detaches again to enter its non‐force‐producing state for the duration of the ‘off‐time’. The contractile force depends on the number of cross‐bridges attached per unit of time. These cross‐bridges are activated by calcium binding to troponin C with the subsequent conformational changes of tropomyosin and troponin I to facilitate actomyosin interaction. The muscle relaxes when calcium is pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum by the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump (SERCA) and transported outside the cell by the sodium–calcium exchanger, a process that is also dependent on cellular metabolism. On the level of the actomyosin cross‐bridge, inotropy relies largely on: (i) the amount of calcium available to bind to troponin C, (ii) the calcium affinity of troponin C, and (iii) the duration of the force‐producing state with availability of high energy phosphates.
A brief history of inotropic agents and their impact on surrogate endpoints
Within the syndrome of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, there is a growing subgroup of patients who have worsening disease that is typified by signs and symptoms of hypotension and hypoperfusion.7 These patients, characterized as having stage D heart failure, are increasingly unable to tolerate neurohormonal blockade, and their options are limited to cardiac transplantation, ventricular assist devices, inotropic infusions, or hospice.8 The primary pathology in these patients is thought to be a decrease in cardiac contractility and the development of positive inotropes has been aimed at correcting this defect: almost every inotropic agent that survived to clinical evaluation has shared a common therapeutic goal: to increase the amplitude of cytosolic calcium transients or sensitivity of the sarcomere, thus increasing the force of contraction.
The first of these was dobutamine, created in 1975 by modifying the chemical structure of isoproterenol to reduce its chronotropic, arrhythmogenic, and vascular side effects. This increased its action on the β1 cardiac receptors whilst minimizing the impact on the α1 and β2 vascular receptors. Mechanistically, dobutamine appeared to provide the beneficial aspects of adrenergic signalling in heart failure while bypassing deleterious peripheral vasoconstriction: increasing stroke volume and decreasing systemic and pulmonary vascular resistance and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure.
A string of phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors were subsequently developed, including amrinone and followed by milrinone and enoximone, all of which worked downstream to the β1 cardiac adrenergic receptors by inhibiting the enzyme (PDE‐3), one of those role is to catalyse the breakdown of cAMP and leading to an increased intracellular calcium.9, 10, 11, 12 The most prominent of the PDE inhibitors was milrinone; both its intravenous and oral forms improved cardiac haemodynamics in heart failure patients.13 Phase 2 clinical trials of other PDE inhibitors, such as amrinone and enoximone, also improved haemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with advanced heart failure.9, 14
In the 1980s, an alternate method to increase cardiac contractility was proposed: to enhance the contractile apparatus' sensitivity to calcium.15 Levosimendan, the prototype for this mechanism of action, binds to troponin C depending on intracellular calcium concentrations. Via this mechanism, it increases calcium sensitivity only during systole without impairing diastolic relaxation.16 Levosimendan also has PDE inhibitors and ATP sensitive K+ channel activating effects that result in potent peripheral vasodilatation. In patients with heart failure, levosimendan increased cardiac output, reduced pulmonary capillary wedge pressures, and improved symptoms.17, 18 Another agent which is also a potent PDE inhibitor, pimobendan, significantly increased exercise duration, peak oxygen uptake, and quality of life in patients with heart failure (Table 1).9, 13, 14, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33
Table 1.
Mechanism of action of key inotropes and their impact on intermediate outcome measures in heart failure
| Inotrope | Mechanism of action | Impact on intermediate outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Amrinone | PDE3i | Improvement in haemodynamics and exercise capacity9, 10, 20, 21 |
| Enoximone | PDE3i | Improvement in haemodynamics11, 14 |
| Milrinone | PDE3i | Improved haemodynamics and functional status13, 22, 23 |
| Xamoterol | β1‐selective partial agonist | Improved haemodynamics and functional status24 |
| Dobutamine | β1 and β2 agonist | Improved haemodynamics25 |
| Flosequinan | Peripheral arteriolar and venous vasodilator | Improved haemodynamics, decreased natriuretic peptides, improved symptoms and exercise tolerance26 |
| Pimobendan | Calcium sensitizer and selective PDE3i | Improved functional status and reduced hospitalization19, 27 |
| Levosimendan | KATP channel activator, calcium sensitizer, PDE3i | Improved haemodynamics, decreased natriuretic peptides, improved patient symptoms15, 16, 17, 18, 28 |
| Ibopamine | DA‐1 and DA‐2 receptor activation: renal and peripheral vasodilatation | ↓Neurohormones, improved functional status29 |
| Vesnarinone | ↑Sodium–calcium exchange, mild PDE3i | Improved haemodynamics and exercise capacity12, 30 |
| Omecamtiv mecarbil | Potentiates effects of myosin on actin | ↑SET, improved ventricular function (↑SV, ↑LVEF), ventricular dimensions (↓LVEDV, ↓LVESV), decreased neurohormonal activation (↓heart rate), ↓NT‐proBNP31 |
| Istaroxime | Stimulates SERCA2a and inhibits Na‐K ATPase | ↓PCWP, ↑CO, ↓LVEDV32 |
| SERCA2a gene | Restoration of SERCA2a function to improve calcium release and reuptake from the SR | Improved functional status, ↓NT‐proBNP, ↑LVEF33 |
CO, cardiac output; LVEDV, left ventricular end‐diastolic volume; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVESV, left ventricular end‐systolic volume; NT‐proBNP, N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide; PCWP, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; PDE3i, phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor; SERCA2a, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+‐ATPase; SET, systolic ejection time; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; SV, stroke volume.
After a significant hiatus in the development of positive inotropes for heart failure, further mechanistic targets were developed in the 2000s. Pharmacological and gene therapy approaches were directed at a key enzyme responsible for myocardial calcium homeostasis that is downregulated in heart failure: sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+‐ATPase (SERCA2a). Correction of this deficiency improved the function of impaired cardiomyocytes in vitro and prolonged survival in vivo when tested on experimental models of heart failure. In human subjects, intracoronary infusion of a SERCA2a cDNA vector did not lead to a difference in heart failure exacerbations.34 This might have been due to inefficient genetic transfer; istaroxime, an intravenous inotrope, also works by stimulating SERCA2a whilst also inhibiting the sodium–potassium ATPase pump, potentially bypassing this issue.35, 36 This dual mechanism of action results in istaroxime having both inotropic action, by allowing the accumulation of cytosolic calcium during contraction, as well as having a lusitropic effect (improvement in diastolic relaxation) by sequestering calcium during relaxation. Results from animal experiments with istaroxime corroborated this favourable mechanistic profile by showing increased inotropy and accelerated relaxation without associated increased energy consumption or arrhythmias.37
Inotrope therapy expanded further with the development of agents that act directly on the actinomyosin cross‐bridge. Omecamtiv mecarbil is the first‐in‐class agent for this category with a unique mechanism of action that makes it distinct from traditional inotropes, in so much as it does not clearly fit this categorization. It works by selectively binding to the S1 domain of cardiac myosin, the main component of the thick sarcomeric filament, stabilizing the pre‐powerstroke state, leading to increased effective myosin interaction with actin causing increased and prolonged contractile force without increasing left ventricular filling pressure or intracellular calcium content38, 39 (Figure 2). Via this mechanism, omecamtiv mecarbil increases the efficiency and performance of the cardiac contractile apparatus. Early phase clinical studies have shown that omecamtiv mecarbil increases LVEF, stroke volume, systolic ejection time, and decreases left ventricular end‐diastolic and end‐systolic volumes.31
Figure 2.
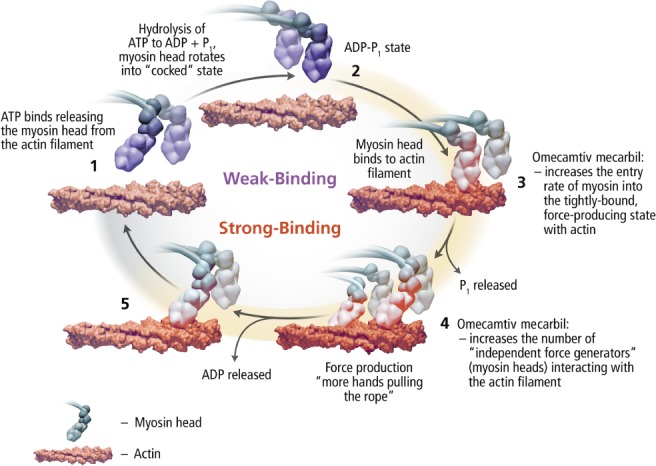
Mechanism of action of omecamtiv mecarbil. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate.
Results from clinical trials
Clinical trials of inotropes in heart failure have reinforced an important lesson: whereas short‐term surrogate endpoints such as haemodynamics might improve with these therapies, this does not necessarily translate into improvements in mortality. Inotropic therapies to date have failed to improve ‘hard’ clinical outcomes in heart failure, and the majority resulted in worse outcomes (Table 2).14, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57 Furthermore, only a subset of results from trials investigating inotropes have been published, some many years after the results were presented, and the primary data are not available for analysis making a meticulous post‐mortem of disappointing prior results challenging.58, 59
Table 2.
Results of clinical trials involving positive inotropes in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
| Clinical trial | Comparator groups | Year | No. patients | Key inclusion criteria | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amrinone Multicenter Trial40 | Amrinone vs. placebo | 1985 | 99 | NYHA class III–IV, LVEF ≤ 40% | ↑ Adverse events |
| Xamoterol in Severe Heart Failure41 | Xamoterol vs. placebo | 1990 | 516 | LVEF < 35%, NYHA class III–IV | ↑ Morbidity |
| PROMISE42 | Milrinone vs. placebo | 1991 | 1008 | LVEF ≤ 35%, NYHA class III–IV | ↑ Morbidity and mortality |
| PICO43 | Pimobendan | 1996 | 317 | NYHA class II–III, LVEF ≤ 45% |
↑ Exercise tolerance, ↑ mortality |
| PRIME II44 | Ibopamine | 1997 | 1906 | NYHA class III–IV, LVEF < 35% | ↑ Mortality |
| VEST45 | Vesnarinone | 1998 | 3833 | LVEF ≤ 30%, NYHA class III–IV |
Dose‐dependent ↑mortality (potentially arrhythmias) |
| FIRST46 | Dobutamine | 1999 | 471 | NYHA class IIIB–IV; LVEF < 30% | ↑ Mortality |
| DICE47 | Intermittent dobutamine vs. placebo | 1999 | 38 | NYHA class III–IV, cardiac index ≤2.2 L/min/m2, and LVEF ≤ 30% | No improvement in functional status |
| OPTIME‐CHF48 | Milrinone | 2002 | 951 | ADHF with LVEF < 40% | ↑ Adverse events, equivalent mortality |
| LIDO49 | Levosimendan vs. dobutamine | 2002 | 203 | ADHF with LVEF < 35%, CI < 2.5 L/min/m2, PCWP > 15 mmHg |
↑ Haemodynamics, ↓ mortality with levosimendan |
| RUSSLAN50 | Levosimendan vs. placebo | 2002 | 504 | LV failure complicating AMI | Low‐dose levosimendan reduced the risk of worsening HF |
| SURVIVE51 | Levosimendan vs. dobutamine | 2007 | 1327 | ADHF with LVEF ≤ 30% | ↓ BNP with levosimendan but no impact on clinical outcomes |
| EMOTE52 | Enoximone | 2007 | 201 | NYHA class IV, inotrope dependence, LVEF ≤ 25% | No difference is ability to wean patients off inotropes at 30 days |
| Enoximone Clinical Trials Program14, 53 | Enoximone | 2009 | 1854 |
NYHA class III–IV, LVEF ≤ 35% (two trials) |
No difference in mortality, CV hospitalizations, 6MWD, patient global assessment |
| HORIZON‐HF32 | Istaroxime | 2008 | 120 | ADHF with LVEF ≤ 35% | ↓ PCWP, ↑ SBP, and ↓ diastolic stiffness |
| CUPID 234 | SERCA2a gene | 2016 | 250 | Chronic HF, NYHA class II–III, LVEF ≤ 35%, NT‐proBNP > 1200 pg/mLa | No difference in time to recurrent events |
| REVIVE54 | Levosimendan | 2013 | 700 | ADHF with LVEF ≤ 35% | ↓ HF symptoms, ↑ risk of adverse CV events and 14‐day mortality |
| ATOMIC‐AHF55 | Omecamtiv mecarbil | 2016 | 606 | ADHF with LVEF ≤ 40%, BNP > 400 pg/mL or NT‐proBNP > 1600 pg/mLa | No difference in dyspnoea endpoint, ↑ SET, ↓ LVESD, ↑ troponin |
| COSMIC‐HF56 | Omecamtiv mecarbil | 2016 | 448 | Chronic HF, NYHA class II–III, LVEF ≤ 40%, NT‐proBNP ≥ 200 pg/mLa |
↑ SET, ↑ SV, ↓ LVESD, ↓ LVEDD, ↓ NT‐proBNP |
| PROFILE57 | Flosequinan | 2017 | 2354 | NYHA class III–IV, LVEF ≤ 35% |
↑ Exercise tolerance, ↑ mortality |
6MWD, 6‐min walk distance; ADHF, acute decompensated heart failure; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; BNP, B‐type natriuretic peptide; CI, cardiac index; CV, cardiovascular; HF, heart failure; LV, left ventricular; LVEDD, left ventricular end‐diastolic dimension; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVESD, left ventricular end‐systolic dimension; NT‐proBNP, N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide; NYHA, New York Heart Association; PCWP, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SET, systolic ejection time; SV, stroke volume.
Different cut‐points for atrial fibrillation.
Adrenergic agents
Dobutamine was the first inotrope developed, but it has never been formally compared with placebo in a clinical trial of patients with heart failure. Its safety and efficacy were extrapolated from a subgroup analysis of the Flolan International Randomized Survival Trial (FIRST) study (published in 1997) that randomized 471 patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class IIIB–IV symptoms to epoprostenol (prostacyclin) infusion vs. standard care.60 The trial was terminated early because of a strong trend toward decreased survival among patients treated with epoprostenol. Furthermore, epoprostenol therapy was not associated with improvement in distance walked or quality of life measures. A post‐hoc analysis of this study compared 80 patients who were treated with and without dobutamine at time of randomization. The investigators found that dobutamine use was associated with a higher 6‐month mortality rate. While the increased mortality persisted despite adjustment for baseline differences, the dobutamine group notably included a sicker population, which may have influenced the results. Other studies where intermittent dobutamine infusion was used showed no improvement in clinical class and increased mortality.61 This has led to the conclusion that dobutamine use might lead to harm in patients with advanced symptomatic heart failure.46
Xamoterol, a β1‐selective partial adrenergic agonist, demonstrated favourable haemodynamic and symptomatic improvement in initial studies but was found to have more than a twofold increased risk of death over placebo when evaluated in a large randomized trial published in 1990. Specifically, 516 patients with NYHA class III–IV symptoms despite treatment with diuretics and angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors were randomized in a 2:1 fashion to xamoterol 200 mg or placebo twice daily for 13 weeks. There was no difference between the treatments in exercise duration or total work done. Compared to a rate of 3.7% in the placebo arm, 9.1% of patients in the xamoterol group died within 100 days of randomization.41 Ibopamine is an oral dopaminergic agonist, which also has some α‐adrenergic and β‐adrenergic activity.62 It was shown to improve heart failure symptoms in the Prospective Randomized Study of Ibopamine on Mortality and Efficacy (PRIME).63 This led to the PRIME II trial that was stopped early because of a 26% increase in mortality among patients in the ibopamine group.44
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
Two landmark trials examined the benefit of milrinone therapy in heart failure. The Prospective Randomized Milrinone Survival Evaluation (PROMISE), published in 1991, randomized 1088 ambulatory patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and NYHA class III–IV symptoms to 40 mg of oral milrinone daily vs. placebo and followed the patients for a median of 6.1 months.42 Patients on chronic heart failure were on contemporaneous therapy of digoxin, diuretics, and angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors. As compared with placebo, milrinone therapy was associated with a 28% increase in all‐cause mortality and a 34% increase in cardiovascular mortality. Patients treated with milrinone also had more hospitalizations and more serious adverse reactions including hypotension and syncope. The investigators concluded that ‘despite its beneficial haemodynamic actions, long‐term therapy with oral milrinone increases the morbidity and mortality of patients with severe chronic heart failure’. The Outcomes of a Prospective Trial of Intravenous Milrinone for Exacerbations of Chronic Heart Failure (OPTIME‐CHF) trial was published in 2002 and randomized 951 patients with acute exacerbations of chronic heart failure to a 48 h infusion of either milrinone (0.5 μg/kg/min initially) or saline placebo.48 Results did not differ significantly in either mortality or readmission endpoints. However, those randomized to milrinone experienced more clinically relevant hypotension and atrial arrhythmias and patients with ischaemic heart disease had significantly greater in‐hospital mortality with milrinone. Comparable results regarding mortality were observed with enoximone in a smaller trial of 102 patients.64
Vesnarinone, an oral agent with PDE inhibition that also prolongs the sodium ion channel opening, was initially seen as promising because of its weak PDE inhibiting and novel ion channel properties. The large‐scale trial of vesnarinone in heart failure tested two doses of vesnarinone, 60 mg or 120 mg, vs. placebo.30 The 120 mg arm was discontinued early because of a twofold mortality increase over placebo. The trial continued with the 60 mg arm vs. placebo and showed a surprising 62% decrease in the relative risk of death in patients randomized to vesnarinone treatment. As a result of the small number of clinical endpoints in the initial trial and concern about the possibility of neutropenia from vesnarinone, the larger Vesnarinone Trial (VEST) was undertaken, comparing 30 or 60 mg of vesnarinone daily with placebo in ambulatory patients. Published in 1998, this trial demonstrated a dose‐dependent increase in mortality with vesnarinone over placebo, primarily because of arrhythmic death, and the crossover group did not respond in a similar fashion to the initially randomized group. Of note, there was a signal towards improved quality of life in the higher dose arm, and some suggested that patients with refractory end‐stage heart failure might be willing to trade‐off a slightly increased risk of mortality for improved quality of life. However, this notion has not translated to the bedside, as vesnarinone is not available for clinical use.45, 65
Oral vasodilators with positive inotropic properties
Flosequinan has both vasodilating and inotropic properties that are not entirely understood but felt to be distinct from β‐adrenergic receptor agonists and PDE inhibitors.66 This agent was initially greeted with enthusiasm based on its improvement in heart failure symptoms and quality of life scores.67 The Prospective Randomized Flosequinan Longevity Evaluation (PROFILE) study examined the clinical impact of flosequinan on 2354 patients with NYHA class III‐IV heart failure and LVEF ≤ 35%. The primary outcome of the study was all‐cause mortality. The trial was terminated early due increased mortality, and the therapy was withdrawn from the market in 1994.57, 68 Of note, results of the study were finally published 24 years after its completion.57
Calcium sensitizers
Several large randomized controlled trials in patients with heart failure have examined levosimendan, a calcium sensitizer with PDE inhibitor and KATP‐channel activating effects. Two sequential trials — Randomized Multicentre Evaluation of Intravenous Levosimendan Efficacy (REVIVE) I and II — aimed to first develop a new measure of efficacy in 100 patients, then to use this measure to evaluate levosimendan in an additional 600 patients. Patients admitted with acute exacerbations of heart failure received placebo or intravenous levosimendan for 24 h in addition to standard treatment. Levosimendan provided greater degrees of symptomatic relief but was associated with a significant increase in mortality in the first 14 days, presumably while levosimendan was pharmacologically active. This early mortality difference in events was maintained with a slightly higher risk of 90‐day all‐cause mortality in the levosimendan group (15.1%) vs. controls (11.6%).54 Levosimendan also increased atrial fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmias. The Survival of Patients with Acute Heart Failure in Need of Intravenous Inotropic Support (SURVIVE) study randomized 1327 patients hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure to levosimendan vs. dobutamine.51 There were no differences in either mortality or measures of patient symptoms. Those in the dobutamine arm had a higher incidence of cardiac failure. Of note, natriuretic peptide levels were significantly reduced in the levosimendan arm compared with the dobutamine arm. The PERSIST trial randomized 307 patients in NYHA class IIIB–IV to levosimendan 1 mg once or twice daily or placebo for at least 180 days. Levosimendan did not improve the prespecified novel outcome measure (a patient journey composite), but there was a suggestion that it improved some quality of life metrics and decreased natriuretic peptide levels.69 Levosimendan use has been approved for use in Europe for palliation on the basis of these data. Data from registries and clinical trials have demonstrated that this approach is safe and may improve clinical outcomes.70, 71
Finally, two small studies have recently assessed the use of intermittent levosimendan in advanced heart failure patients. The LION‐HEART (Intermittent Intravenous Levosimendan in Ambulatory Advanced Chronic Heart Failure Patients) pilot study randomized 69 patients to intermittent levosimendan (infusions every 2 weeks for 12 weeks) or placebo. Adverse events were similar between groups, and those randomized to levosimendan had lower N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide levels over time and fewer heart failure rehospitalizations.71 Similarly, the LAICA (Long‐Term Intermittent Administration of Levosimendan in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure) study, which has been presented but not published, showed fewer hospitalizations with intermittent levosimendan.72 Levosimendan is currently approved for use in Russia and some European and South American countries, but not in the United States.
Pimobendan, a PDE inhibitor with some calcium‐sensitization effects, was evaluated in the double‐blind randomized Pimobendan in Congestive Heart Failure (PICO) trial published in 1996.43 This multicentre European trial randomized 317 outpatients with NYHA class II–III chronic heart failure symptoms to placebo or pimobendan at 2.5 or 5 mg daily. Compared with placebo, both doses of pimobendan improved exercise duration by 6% after 24 weeks of treatment, but did not improve quality of life measures or peak oxygen uptake. More importantly, pimobendan treatment was associated with an insignificant but worrisome 1.8‐fold increased risk of all‐cause mortality, which resulted in the discontinuation of its clinical development. However, market authorization was granted in Japan where the observed mortality with its use has been noted to be lower than expected, potentially due to concomitant β‐blocker usage. Also, an oral formulation is used worldwide in veterinary medicine.43, 73, 74
Myosin activators
Omecamtiv mercarbil has been evaluated in two relatively large patient populations of acute and chronic heart failure in phase 2 studies. The Chronic Oral Study of Myosin Activation to Increase Contractility in Heart Failure (COSMIC‐HF) trial randomized 448 outpatients with well‐controlled heart failure (NYHA class II–III and LVEF ≤ 40%) to one of three groups: fixed‐dose, pharmacokinetic titration, or placebo for 20 weeks.56 The study met its primary pharmacokinetic endpoint and the investigators noted an improvement in all of the pre‐specified secondary efficacy parameters: systolic ejection time and stroke volume increased whereas left ventricular end‐systolic and end‐diastolic dimensions, heart rate and natriuretic peptide levels decreased favourably in the active treatment arm. Adverse clinical events in omecamtiv mecarbil‐treated arms were similar to placebo. The Acute Treatment with Omecamtiv Mecarbil to Increase Contractility in Acute Heart Failure (ATOMIC‐AHF) trial randomized 613 patients with acute decompensated heart failure and LVEF ≤ 40% to omecamtiv mecarbil vs. placebo for 48 h during their hospitalization.55 There were no differences in the primary efficacy endpoint of improvement in dyspnoea in the entire cohort, with a signal for benefit in the highest dose group. Of the 89 patients studied in the echocardiographic subgroup, increases in left ventricular systolic ejection time and decreases in left ventricular end‐systolic dimension were observed in a concentration‐dependent pattern. The finding that troponin levels at 48 h tended to be slightly higher in those patients that received omecamtiv mecarbil is of unresolved mechanism or clinical significance despite much deliberation.75, 76, 77, 78 The ongoing 8000 patient Global Approach to Lowering Adverse Cardiac Outcomes Through Improving Contractility in Heart Failure (GALACTIC‐HF; NCT02929329) trial is evaluating the effect of chronic oral omecamtiv mecarbil on cardiovascular mortality and heart failure events in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+‐ATPase (SERCA2a) modulation
For some time, it has been clear that myocardial SERCA2a activity is reduced in patients with heart failure, and that restoration of its activity improves myocardial function. As detailed above, istaroxime is an intravenous inotrope that stimulates SERCA2a by inhibiting the sodium–potassium ATPase pump. In the phase 2 Hemodynamic, Echocardiographic, and Neurohormonal Effects of Istaroxime, a Novel Intravenous Inotropic and Lusitropic Agent: a Randomized Controlled Trial in Patients Hospitalized with Heart Failure (HORIZON‐HF) trial, istaroxime showed that it lowered pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, increased cardiac output, and decreased left ventricular end‐diastolic volume.32 A later pilot study [Calcium Upregulation by Percutaneous Administration of Gene Therapy in Cardiac Disease (CUPID 1)] demonstrated beneficial effects of SERCA2a gene therapy in patients with advanced heart failure.33 This led to the CUPID 2 trial, which randomized 250 symptomatic heart failure patients with LVEF < 35% to receive a single intracoronary infusion of AAV1/SERCA2a or placebo.34 Results of the trial were published in 2016 and did not find any benefit of SERCA2a treatment on the primary outcome, defined as time to recurrent events (hospital admission because of heart failure or ambulatory treatment for worsening heart failure). One potential reason for failure of this approach is felt to be inefficient gene transfer, and other targets for this pathway are being evaluated.
Why have prior inotrope trials in chronic heart failure been negative?
The development of positive inotropic agents for chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction has followed a recurring theme despite testing of a variety of agents that targeted diverse molecular pathways: improvements in surrogate measures of cardiac improvement do not necessarily translate into reduction in clinical events. Some reasons for this are likely to be compound specific, but several themes have emerged from the experience. Of note, these do not apply to the use of inotropic therapies for acute cardiogenic shock, where there are compelling data in support of bridging patients to stability.
Improvements in short‐term haemodynamics may not translate into longer‐term mortality and morbidity benefits
The haemodynamic model of heart failure suggest that reversing left ventricular systolic function will make patients feel better and live longer.79 In line with this concept, haemodynamic assessments have been the entryway whereby dozens of inotropic agents have progressed to phase 3 clinical trials. Invariably, drugs that improved haemodynamics via a variety of mechanisms with documented increases of cardiac performance and improvements in blood flow to the peripheral organs failed to show clinical benefit in large clinical trials. Indeed, most were even associated with a heightened risk of death.80
The lack of a direct relationship between interventions that led to short‐term haemodynamic improvements and clinical efficacy is not restricted to inotropes. Nesiritide, a recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide, was approved for clinical use based on small studies showing reductions in filling pressures, but subsequent trials showed no evidence of therapeutic efficacy.81 Furthermore, the landmark Evaluation Study of Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Artery Catheterization Effectiveness (ESCAPE) trial demonstrated that haemodynamic‐guided therapies in heart failure did not improve clinical outcomes, among patients in whom there was equipoise about use of these data.82 Finally, the negative impact of β‐blockade on these indices prevented their clinical use for decades.83
Therefore, the aggregate data suggest that short‐range haemodynamic endpoints might be misleading as surrogate measures for long‐term morbidity and mortality benefits from inotropes, with the caveat that it is unknown as to what combination of haemodynamic parameters constitute adequate improvement, and prior studies might have erred on the side of higher doses of inotropes to achieve larger than needed changes in haemodynamics. Additionally, it is entirely plausible that temporary treatment with an effective therapy will not translate into improvement in long‐term clinical outcomes.
Benefit from inotropes might only be restricted to sub‐phenotypes of heart failure
Heart failure is not a singular disease. Rather, it is a syndrome that likely comprises several diseases with unique underlying mechanisms and trajectories.84, 85, 86 Moreover, classification systems based on a century old assessment of functional status (NYHA class), or LVEF cut‐points are fundamentally dissociated from both mechanistic and clinical actuality.87 Whereas trials of neurohormonal blockade have succeeded despite these constraints, we might now need to identify specific subgroups of the syndrome that respond favoorably to inotropes, in a manner analogous to cardiac resynchronization therapy. Thus far, all clinical trials of positive inotropes in heart failure have been anchored in broad measures of disease, leading to overly simplified and often inaccurate assumptions about how these therapies might help patients.88 The significant drawbacks of this approach were demonstrated in a post‐hoc analysis of the OPTIME‐CHF trial that showed a substantial impact of heart failure aetiology (ischaemic vs. non‐ischaemic) on clinical outcomes with milrinone, with harm seen in patients with ischaemic disease.89 In a manner analogous to how a therapy would not be tested generically for lung cancer or anaemia, we would be well served by testing future inotropes in a sub‐population of the syndrome (e.g. non‐ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy) that might benefit from the therapy. While there is a dearth of relevant data to approve therapies based on subtypes of heart failure, one population that may benefit are those with advanced, chronic heart failure and low output. Alternatively, inotropes with potentially anti‐remodelling properties, such as omecamtiv mecarbil,56 could potentially be used at an earlier stage.
The mechanism and dosage of inotropic agents can cause adverse effects
There is a possibility that the adverse effects of inotropic agents on myocardial energetics and intracellular calcium could explain the results of prior trials: by increasing energy consumption and leading to exhaustion of the energy stores, these agents could promote pump failure as well as ventricular arrhythmias via dysfunctional calcium cycling. In fact, the negative long‐term impact of catecholamines on the heart, and the beneficial impact of β‐blockade, has been demonstrated in several landmark studies.90 Additionally, data suggest that drugs acting via cAMP modulation lead to adverse effects in the long term by causing desensitization of the contractile apparatus to calcium, disturbing intracellular calcium homeostasis, causing ventricular arrhythmias, and disrupting lusitropy. Studies have shown that left ventricular function deteriorates to below pre‐treatment levels after withdrawal of inotropes, demonstrating that the therapy accelerates ventricular dysfunction.91 It is conceivable that β‐adrenergic blocking agents might have prevented this deterioration of ventricular function, but their usage was infrequent during most clinical trials.
An intriguing corollary to the notion that the inotropic effects of drugs might explain their negative impact on clinical outcomes is that many clinical trials studying these agents aimed to maximize their positive haemodynamic effects and used very high doses for this purpose. Similar to the deleterious effects of very high doses of digoxin, it is quite possible that by chasing the wrong intermediate measures of heart failure, prior studies drove up the risk of myocardial toxicity and shifted the risk–benefit equation in the wrong direction.80 This was articulated by Dr. Milton Packer in a perspective article published in a 1993 issue of JACC — in the aftermath of a large number of negative inotrope trials — where he concluded: ‘The belief that positive inotropic agents for heart failure should be developed at inotropic doses may have been the primary factor for the controversy that has surrounded these drugs for the last 200 years’.80
Medical treatment of patients in prior trials did not protect them from sudden cardiac death
As displayed in Table 3 14, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 48, 53, 54, 56, 57 most of the landmark trials that tested positive inotropes in heart failure had very low usage of key therapies — β‐blockers and implantable cardioverter‐defibrillators (ICDs) — that are known to protect heart failure patients against sudden cardiac death, the mode of death most commonly provoked by these medications. In fact, many of these trials listed β‐blocker use as an exclusion criterion as they occurred prior to when these medications were found to be of benefit in heart failure. Whereas the actual prevalence of ICD use is unclear from most of the published manuscripts, it generally occurred prior to the landmark trials showing benefit of these devices for primary and secondary prevention of sudden death in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.92 Furthermore, usage of additional neurohormonal agents was low in these trials, potentially leading to even less protection from the adverse effects of adverse remodelling. Finally, a large portion of patients in positive inotrope trials were on concomitant digoxin, often on higher doses than are currently considered therapeutic. Given the mechanistic intersections between digoxin and cardiac inotropes, it is plausible that concomitant usage might have had a negative synergistic effect.93 These have been proposed as reasons as to why contemporary outcomes from inotrope usage are better that those seen in trials.92, 93 In addition, a recent meta‐analysis has suggested that ambulatory inotrope infusions in advanced stage D heart failure may improve NYHA functional class without negatively impacting survival.94
Table 3.
Use of key contemporary heart failure therapeutics in prior clinical trials of positive inotropes
| Study | Therapy | Year | IHD | Beta‐blocker | ACEi/ARB | ICD | Digoxin | Risk of death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xamoterol in Severe Heart Failure41 | Xamoterol vs. placebo | 1990 | 60% | Excluded | > 80% | Unknown | 53% | ↑ Risk of all‐cause mortality with xamoterol |
| PROMISE42 | Milrinone vs. placebo | 1991 | 54% | Excluded | Yes, unknown | Unknown | Yes, unknown | 28% increase in all‐cause mortality, 34% increase in CV mortality |
| PICO43 | Pimobendan vs. placebo | 1996 | 70% | Excluded | Yes, 100% | Excluded | 59% | NS increase in risk of all‐cause mortality |
| PRIME II44 | Ibopamine vs. placebo | 1997 | 59% | Unknown, but low | 92% | Unknown | 64% | 26% increase in all‐cause mortality |
| VEST45 | Vesnarinone vs. placebo | 1998 | 60% | Excluded | 90% | Excluded | Unknown | 21% increase in all‐cause mortality with vesnarinone |
| FIRST46 | Epoprostenol vs. placebo | 1999 | 67% | Unknown, but low | 84% | Unknown | Yes, Unknown | ↑ Risk with epoprostenol infusion (trial stopped), ↑ risk in DBA subgroup |
| OPTIME‐CHF48 | Milrinone vs. placebo | 2002 | 51% | 22% | 82% | Unknown | 78% | ↔ No difference compared with placebo |
| REVIVE54 | Levosimendan vs. placebo | 2004 | 53% | 68% | 77% | Unknown | 52% | ↔ No difference compared with placebo |
| Enoximone Clinical Trials Program14, 53 | Enoximone vs. placebo | 2009 | 52% | 83% | 98% | 21% | 69% | ↔ No difference compared with placebo |
| COSMIC‐HF56 | Omecamtiv mecarbil vs. placebo | 2016 | 98% | 94% | 62% | 20% | Phase 2 study | |
| PROFILE57 | Flosequinan vs. placebo | 2017 | 67% | <4% | Yes, 100% | Unknown | Yes, Unknown | 39% increase in all‐cause mortality |
ACEi, angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; CV, cardiovascular; ICD, implantable cardioverter‐defibrillator; IHD, ischaemic heart disease.
Increasing contractility rather than improving efficiency
At the core of arguments about whether it is worth developing positive inotropes for heart failure is an unresolved debate about whether stimulating the failing heart is truly beneficial.80 It is possible that decreased contractility is a compensatory response aimed at preventing disease progression. If this is the case, then positive inotropes might improve cardiac performance in the short term but are likely to increase the risk of pump failure when used in a chronic manner. However, as our clinical experience with cardiac resynchronization therapy has shown, focusing on the efficiency rather than simply the contractility of the heart has the potential to both improve patient symptoms and clinical outcomes.95 Since heart failure is a state of dysfunctional cardiac energetics — the so‐called ‘engine out of fuel’ — it is possible that biomarkers including metabolic assessments could serve as surrogate measures of whether a positive inotrope is helping or hindering the heart efficiency.96 Furthermore, interventions aimed at increasing high energy phosphate production have resulted in a safe and significant effect on cardiac contractility and exercise capacity.97 In future clinical trials, patients who are likely to benefit from positive inotropy might be identified via a run‐in period with intensive biomarker and imaging assessments that track well with clinical outcomes (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
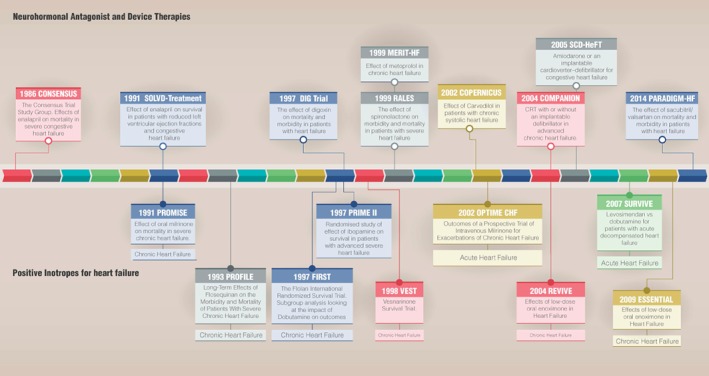
Summary of trials that evaluated neurohormonal antagonist and device therapies, and positive inotropes for heart failure. CRT, cardiac resynchronization therapy. [Correction added on 29 August 2019, after first online publication: the text under 2014 PARADIGM‐HF has been corrected.]
Why is there a disconnect between trial results and clinical use of inotropes?
Any practicing heart failure clinician would strongly argue that the two clinically available inotropes for stage D heart failure — milrinone and dobutamine — are essential tools in their therapeutic armamentarium. Their clinical use reflects this fact whereas exact numbers on a national level are unknown. Studies have approximated that more than 6% of patients admitted with heart failure are placed on intravenous inotropes and in 2014 Medicare spent $243 million for home milrinone and $3.8 million for home dobutamine infusions.98 Likely because of the rapidly increasing prevalence of end‐stage heart failure, with a large percentage of patients either medically ineligible for or opting not to undergo heart transplantation or implantation of left ventricular assist devices, the usage of inotropes is increasing rapidly. Of note, this is occurring despite the clear lack of data supporting the benefit of chronic inotropic usage in heart failure and robust evidence suggesting the potential for harm. Furthermore, it also goes against the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulatory label for both milrinone and dobutamine that has approved their use for ‘inotropic support in the short‐term treatment of patients with cardiac decompensation due to depressed contractility resulting either from organic heart disease or from cardiac surgical procedures’. In keeping with the data, the label specifically mentions that there are no data for treatment with these agents for more than 48 h — the primary way they are currently used in the clinical setting:
‘Experience with intravenous dobutamine in controlled trials does not extend beyond 48 h of repeated boluses and/or continuous infusions. Whether given orally, continuously intravenously, or intermittently intravenously, neither dobutamine nor any other cAMP‐dependent inotrope has been shown in controlled trials to be safe or effective in the long‐term treatment of congestive heart failure. In controlled trials of chronic oral therapy with various such agents, symptoms were not consistently alleviated, and the cAMP‐dependent inotropes were consistently associated with increased risks of hospitalization and death. Patients with NYHA class IV symptoms appeared to be at particular risk.’
Why is use of these agents so common? Clearly, there is a large and rapidly growing population of patients who might benefit from these medications and were not represented in prior clinical trials. At the current time, however, several questions about inotrope usage in stage D heart failure remain unanswered. We do not know: (i) how to identify the patient populations who will benefit from these therapies, (ii) whether the benefits are purely symptomatic or can extend to hard clinical outcomes, (iii) how to dose either inotropes or concomitant neurohormonal therapies, and (iv) how inotrope use can fit into the patient‐centred decision‐ making regarding complex therapies for end‐stage heart failure. The epidemiologic insignificance of heart transplantation as a therapeutic intervention and the cost and morbidity associated with ventricular assist devices create an enormous potential for positive inotropic therapies for advanced heart failure. Currently there is a large chasm between clinical practice and academic understanding of these agents. Addressing these questions are likely to bring us closer to using and developing cardiac inotropes that meet patient‐specific needs without causing disproportionate harm.
What is the future of inotropes in heart failure?
It is plausible to suggest that if prior clinical trials of positive inotropes were repeated today, more judicious study designs and a patient population on β‐blockers with ICDs would yield very different results. Indeed, if the symptomatic benefits of inotropic agents — in particular, those with oral formulations — could be extracted without undesirable clinical outcomes, it would present a much needed therapeutic option to a growing population of patients with heart failure in whom the cost and burden of alternatives such as mechanical circulatory support and cardiac transplantation is undesirable. Therefore, we propose some considerations for future trials testing positive inotropes in heart failure (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
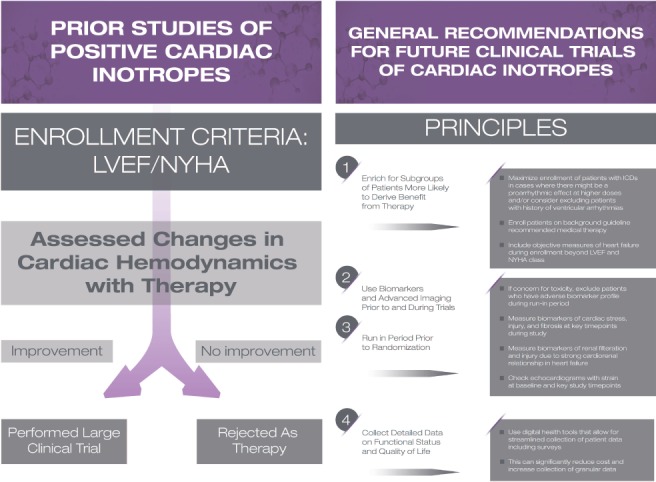
Considerations for future trials testing positive inotropes in heart failure. ICD, implantable cardioverter‐defibrillator; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; NYHA, New York Heart Association.
Enrich for subgroups of patients most likely to benefit
There is evidence to suggest that patients on neurohormonal antagonists — particularly β‐blockers — and with ICDs who are started on positive cardiac inotropes may have much better survival than seen in prior clinical trials. Therefore, enriching future clinical trials with such patients may allow for boosting the risk–reward ratio.
Use biomarkers and imaging in trial design and execution
In trials involving therapies that have potential cardiotoxicity, it might be beneficial to have a run‐in period with intensive advanced cardiac imaging measures and a comprehensive list of cardiac and cardiorenal biomarkers that track with clinical outcomes and may allow for early identification of patients who might not benefit from a positive inotrope.99 Of note, no clinical trial of inotropes has used this approach to date, but it is rather common in oncology, despite the shared goal of balancing beneficial and adverse effects of therapies. With this approach, we might exclude patients who have elevations in cardiac injury markers, for example, in a manner analogous to the Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure (PARADIGM‐HF) trial that used a run‐in period to exclude patients whose blood pressure was intolerant of the highest doses of sacubitril/valsartan.100
Evaluate efficacy based on factors beyond haemodynamics
Whereas haemodynamic measurements are the foundation on which contemporary understanding of heart failure is based, their value for either tailoring or predicting the efficacy of therapeutics has been repeatedly diminished by objective data. Indeed, showing haemodynamic improvements was the rite of passage for almost every positive cardiac inotrope that did not show clinical benefit in a phase 3 clinical trial. Since invasive haemodynamics are onerous to obtain and offer a simplistic snapshot of the cardiac impact of therapeutic interventions, their measurement should not be considered essential in the path to clinical development of a cardiac inotrope.
Collect detailed data on functional status and quality of life
A strong case could be made for the clinical approval of a positive inotrope that improved functional status and quality of life in heart failure patients but had a neutral impact on mortality. Nonetheless, despite the widespread use of inotropes for relief of symptoms, we lack even basic information on these metrics. Prior trials neglected this vital information, choosing instead to focus heavily on physiological and mortality data. Now that heart failure‐specific quality of life questionnaires have been developed and validated, future trials should be designed around outcomes that matter to heart failure patients with a focus on the ‘patient journey’ rather than an inordinate focus only on the risk of death or hospitalization.101 The use of mobile health technologies can allow for this to be done in a cheaper and more streamlined fashion while concurrently collecting granular data on individual patients.102 Importantly, the FDA has indicated that approvability of inotrope therapies could be based on improvement in symptoms even if no clear adversity in survival is found. The lack of such approvals is largely a function of deficient data rather than regulatory philosophy.
Conclusions
Current pharmacological therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction are largely either repurposed anti‐hypertensives that blunt overactivation of the neurohormonal system or diuretics that decrease congestion. They do not address the symptoms of heart failure that result from reductions in cardiac output and reserve. Over the last few decades, numerous attempts have been made to develop and test positive cardiac inotropes that improve cardiac haemodynamics but clinical trials have shown these agents to be harmful to patients. As a result, no positive inotrope is currently approved for long‐term use in heart failure. By revisiting prior clinical trials and attempting to understand why they ended in a disappointing fashion, we propose a framework for future trials of such agents that might improve chances for success. With a rapidly growing population of patients with advanced heart failure, the epidemiologic insignificance of heart transplantation as a therapeutic intervention, and both the cost and morbidity associated with ventricular assist devices, there is an enormous potential for positive inotropic therapies to impact the outcomes that matter most to patients.
Conflict of interest: T.A. has received consulting income from Amgen and Cytokinetics. N.R.D. has received consulting income from Anthem, Amgen, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Johnson and Johnson, and United Health. M.P. has received consulting fees for Roivant, Cytokinetics, and Amgen. M.B. has consulting relationships and grant funding from AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bayer, Boehringer, Medtronic, Cytokinetics, and Servier. L.A.A. has consulting relationships with ACI Clinical, Amgen, Boston Scientific, Duke Clinical Research Institute, and Janssen; grant funding from the American Heart Association, the National Institutes of Health, and the Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute. J.R.T. has received research and consulting fees from Amgen, Madeleine, Mast Therapeutics, Novartis, Relypsa, and Trevena. J.L. has received consulting fees from Abbott, Edwards Lifesciences, Boston Scientific, ResMed, Relypsa, Boehringer Ingelheim, and V‐Wave, and grant support from AstraZeneca.
The other authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1. Forrester JS, Diamond G, Chatterjee K, Swan HJ. Medical therapy of acute myocardial infarction by application of hemodynamic subsets (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 1976;295:1404–1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Forrester JS, Diamond G, Chatterjee K, Swan HJ. Medical therapy of acute myocardial infarction by application of hemodynamic subsets (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 1976;295:1356–1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Patterson SW, Starling EH. On the mechanical factors which determine the output of the ventricles. J Physiol 1914;48:357–379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Ambrosy AP, Butler J, Ahmed A, Vaduganathan M, van Veldhuisen DJ, Colucci WS, Gheorghiade M. The use of digoxin in patients with worsening chronic heart failure: reconsidering an old drug to reduce hospital admissions. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;63:1823–1832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hasenfuss G, Teerlink JR. Cardiac inotropes: current agents and future directions. Eur Heart J 2011;32:1838–1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Braunwald E, Ross J Jr, Sonnenblick EH. Mechanisms of contraction of the normal and failing heart. N Engl J Med 1967;277:910–920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Ahmad T, Patel CB, Milano CA, Rogers JG. When the heart runs out of heartbeats: treatment options for refractory end‐stage heart failure. Circulation 2012;125:2948–2955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Matlock DD, McGuire WC, Magid M, Allen L. Decision making in advanced heart failure: bench, bedside, practice, and policy. Heart Fail Rev 2017;22:559–564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Benotti JR, Grossman W, Braunwald E, Davolos DD, Alousi AA. Hemodynamic assessment of amrinone. A new inotropic agent. N Engl J Med 1978;299:1373–1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Maskin CS, Sinoway L, Chadwick B, Sonnenblick EH, Le Jemtel TH. Sustained hemodynamic and clinical effects of a new cardiotonic agent, WIN 47203, in patients with severe congestive heart failure. Circulation 1983;67:1065–1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Uretsky BF, Generalovich T, Reddy PS, Spangenberg RB, Follansbee WP. The acute hemodynamic effects of a new agent, MDL 17,043, in the treatment of congestive heart failure. Circulation 1983;67:823–828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Feldman AM, Becker LC, Llewellyn MP, Baughman KL. Evaluation of a new inotropic agent, OPC‐8212, in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Am Heart J 1988;116:771–777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Simonton CA, Chatterjee K, Cody RJ, Kubo SH, Leonard D, Daly P, Rutman H. Milrinone in congestive heart failure: acute and chronic hemodynamic and clinical evaluation. J Am Coll Cardiol 1985;6:453–459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lowes BD, Shakar SF, Metra M, Feldman AM, Eichhorn E, Freytag JW, Gerber MJ, Liard JF, Hartman C, Gorczynski R, Evans G, Linseman JV, Stewart J, Robertson AD, Roecker EB, Demets DL, Bristow MR. Rationale and design of the Enoximone Clinical Trials Program. J Card Fail 2005;11:659–669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Cleland JG, McGowan J. Levosimendan: a new era for inodilator therapy for heart failure? Curr Opin Cardiol 2002;17:257–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Edes I, Kiss E, Kitada Y, Powers FM, Papp JG, Kranias EG, Solaro RJ. Effects of levosimendan, a cardiotonic agent targeted to troponin C, on cardiac function and on phosphorylation and Ca2+ sensitivity of cardiac myofibrils and sarcoplasmic reticulum in guinea pig heart. Circ Res 1995;77:107–113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Nieminen MS, Akkila J, Hasenfuss G, Kleber FX, Lehtonen LA, Mitrovic V, Nyquist O, Remme WJ. Hemodynamic and neurohumoral effects of continuous infusion of levosimendan in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000;36:1903–1912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Slawsky MT, Colucci WS, Gottlieb SS, Greenberg BH, Haeusslein E, Hare J, Hutchins S, Leier CV, LeJemtel TH, Loh E, Nicklas J, Ogilby D, Singh BN, Smith W. Acute hemodynamic and clinical effects of levosimendan in patients with severe heart failure. Study Investigators. Circulation 2000;102:2222–2227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Kubo SH, Gollub S, Bourge R, Rahko P, Cobb F, Jessup M, Brozena S, Brodsky M, Kirlin P, Shanes J, et al Beneficial effects of pimobendan on exercise tolerance and quality of life in patients with heart failure. Results of a multicenter trial. The Pimobendan Multicenter Research Group. Circulation 1992;85:942–949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Maskin CS, Forman R, Klein NA, Sonnenblick EH, LeJemtel TH. Long‐term amrinone therapy in patients with severe heart failure: drug‐dependent hemodynamic benefits despite progression of disease. Am J Med 1982;72:113–118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Weber KT, Andrews V, Janicki JS, Wilson JR, Fishman AP. Amrinone and exercise performance in patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 1981;48:164–169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Anderson JL, Askins JC, Gilbert EM, Menlove RL, Lutz JR. Occurrence of ventricular arrhythmias in patients receiving acute and chronic infusions of milrinone. Am Heart J 1986;111:466–474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Shipley JB, Tolman D, Hastillo A, Hess ML. Milrinone: basic and clinical pharmacology and acute and chronic management. Am J Med Sci 1996;311:286–291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Pouleur H, Hanet C, Rousseau MF. The efficacy and safety of chronic oral administration of xamoterol to patients with severe heart failure treated with ACE inhibitors. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1989;28 (Suppl 1):82S–83S. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Sonnenblick EH, Frishman WH, LeJemtel TH. Dobutamine: a new synthetic cardioactive sympathetic amine. N Engl J Med 1979;300:17–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Gottlieb SS, Kukin ML, Penn J, Fisher ML, Cines M, Medina N, Yushak M, Taylor M, Packer M. Sustained hemodynamic response to flosequinan in patients with heart failure receiving angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993;22:963–967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Walter M, Liebens I, Goethals H, Renard M, Dresse A, Bernard R. Pimobendane (UD‐CG 115 BS) in the treatment of severe congestive heart failure. An acute haemodynamic cross‐over and double‐blind study with two different doses. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1988;25:323–329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Kivikko M, Lehtonen L, Colucci WS. Sustained hemodynamic effects of intravenous levosimendan. Circulation 2003;107:81–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Rajfer SI, Rossen JD, Douglas FL, Goldberg LI, Karrison T. Effects of long‐term therapy with oral ibopamine on resting hemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with heart failure: relationship to the generation of N‐methyldopamine and to plasma norepinephrine levels. Circulation 1986;73:740–748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Feldman AM, Bristow MR, Parmley WW, Carson PE, Pepine CJ, Gilbert EM, Strobeck JE, Hendrix GH, Powers ER, Bain RP, White BG. Effects of vesnarinone on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure. Vesnarinone Study Group. N Engl J Med 1993;329:149–155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Teerlink JR, Clarke CP, Saikali KG, Lee JH, Chen MM, Escandon RD, Elliott L, Bee R, Habibzadeh MR, Goldman JH, Schiller NB, Malik FI, Wolff AA. Dose‐dependent augmentation of cardiac systolic function with the selective cardiac myosin activator, omecamtiv mecarbil: a first‐in‐man study. Lancet 2011;378:667–675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gheorghiade M, Blair JE, Filippatos GS, Macarie C, Ruzyllo W, Korewicki J, Bubenek‐Turconi SI, Ceracchi M, Bianchetti M, Carminati P, Kremastinos D, Valentini G, Sabbah HN; HORIZON‐HF Investigators . Hemodynamic, echocardiographic, and neurohormonal effects of istaroxime, a novel intravenous inotropic and lusitropic agent: a randomized controlled trial in patients hospitalized with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51:2276–2285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Jessup M, Greenberg B, Mancini D, Cappola T, Pauly DF, Jaski B, Yaroshinsky A, Zsebo KM, Dittrich H, Hajjar RJ; Calcium Upregulation by Percutaneous Administration of Gene Therapy in Cardiac Disease (CUPID) Investigators . Calcium Upregulation by Percutaneous Administration of Gene Therapy in Cardiac Disease (CUPID): a phase 2 trial of intracoronary gene therapy of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+‐ATPase in patients with advanced heart failure. Circulation 2011;124:304–313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Greenberg B, Butler J, Felker GM, Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Desai AS, Barnard D, Bouchard A, Jaski B, Lyon AR, Pogoda JM, Rudy JJ, Zsebo KM. Calcium upregulation by percutaneous administration of gene therapy in patients with cardiac disease (CUPID 2): a randomised, multinational, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet 2016;387:1178–1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Alemanni M, Rocchetti M, Re D, Zaza A. Role and mechanism of subcellular Ca2+ distribution in the action of two inotropic agents with different toxicity. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2011;50:910–918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Rocchetti M, Alemanni M, Mostacciuolo G, Barassi P, Altomare C, Chisci R, Micheletti R, Ferrari P, Zaza A. Modulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum function by PST2744 [istaroxime; (E,Z)‐3‐((2‐aminoethoxy)imino) androstane‐6,17‐dione hydrochloride] in a pressure‐overload heart failure model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008;326:957–965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Lo Giudice P, Mattera GG, Gagnol JP, Borsini F. Chronic istaroxime improves cardiac function and heart rate variability in cardiomyopathic hamsters. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2011;25:133–138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Malik FI, Hartman JJ, Elias KA, Morgan BP, Rodriguez H, Brejc K, Anderson RL, Sueoka SH, Lee KH, Finer JT, Sakowicz R, Baliga R, Cox DR, Garard M, Godinez G, Kawas R, Kraynack E, Lenzi D, Lu PP, Muci A, Niu C, Qian X, Pierce DW, Pokrovskii M, Suehiro I, Sylvester S, Tochimoto T, Valdez C, Wang W, Katori T, Kass DA, Shen YT, Vatner SF, Morgans DJ. Cardiac myosin activation: a potential therapeutic approach for systolic heart failure. Science 2011;331:1439–1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Planelles‐Herrero VJ, Hartman JJ, Robert‐Paganin J, Malik FI, Houdusse A. Mechanistic and structural basis for activation of cardiac myosin force production by omecamtiv mecarbil. Nat Commun 2017;8:190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Massie B, Bourassa M, DiBianco R, Hess M, Konstam M, Likoff M, Packer M. Long‐term oral administration of amrinone for congestive heart failure: lack of efficacy in a multicenter controlled trial. Circulation 1985;71:963–971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Xamoterol in severe heart failure . The Xamoterol in Severe Heart Failure Study Group. Lancet 1990;336:1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Packer M, Carver JR, Rodeheffer RJ, Ivanhoe RJ, DiBianco R, Zeldis SM, Hendrix GH, Bommer WJ, Elkayam U, Kukin ML, Mallis GI, Sollano JA, Shannon J, Tandon PK, DeMets DL. Effect of oral milrinone on mortality in severe chronic heart failure. The PROMISE Study Research Group. N Engl J Med 1991;325:1468–1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Lubsen J, Just H, Hjalmarsson AC, La Framboise D, Remme WJ, Heinrich‐Nols J, Dumont JM, Seed P. Effect of pimobendan on exercise capacity in patients with heart failure: main results from the Pimobendan in Congestive Heart Failure (PICO) trial. Heart 1996;76:223–231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Hampton JR, van Veldhuisen DJ, Kleber FX, Cowley AJ, Ardia A, Block P, Cortina A, Cserhalmi L, Follath F, Jensen G, Kayanakis J, Lie KI, Mancia G, Skene AM. Randomised study of effect of ibopamine on survival in patients with advanced severe heart failure. Second Prospective Randomised Study of Ibopamine on Mortality and Efficacy (PRIME II) Investigators. Lancet 1997;349:971–977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Cohn JN, Goldstein SO, Greenberg BH, Lorell BH, Bourge RC, Jaski BE, Gottlieb SO, McGrew F 3rd, DeMets DL, White BG. A dose‐dependent increase in mortality with vesnarinone among patients with severe heart failure. Vesnarinone Trial Investigators. N Engl J Med 1998;339:1810–1816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. O'Connor CM, Gattis WA, Uretsky BF, Adams KF Jr, McNulty SE, Grossman SH, McKenna WJ, Zannad F, Swedberg K, Gheorghiade M, Califf RM. Continuous intravenous dobutamine is associated with an increased risk of death in patients with advanced heart failure: insights from the Flolan International Randomized Survival Trial (FIRST). Am Heart J 1999;138 (1 Pt 1):78–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Oliva F, Latini R, Politi A, Staszewsky L, Maggioni AP, Nicolis E, Mauri F. Intermittent 6‐month low‐dose dobutamine infusion in severe heart failure: DICE multicenter trial. Am Heart J 1999;138 (2 Pt 1):247–253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Cuffe MS, Califf RM, Adams KF Jr, Benza R, Bourge R, Colucci WS, Massie BM, O'Connor CM, Pina I, Quigg R, Silver MA, Gheorghiade M. Outcomes of a Prospective Trial of Intravenous Milrinone for Exacerbations of Chronic Heart Failure (OPTIME‐CHF) Ivestigators. Short‐term intravenous milrinone for acute exacerbation of chronic heart failure: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002;287:1541–1547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Follath F, Cleland JG, Just H, Papp JG, Scholz H, Peuhkurinen K, Harjola VP, Mitrovic V, Abdalla M, Sandell EP, Lehtonen L; Steering Committee and Investigators of the Levosimendan Infusion versus Dobutamine (LIDO) Study . Efficacy and safety of intravenous levosimendan compared with dobutamine in severe low‐output heart failure (the LIDO study): a randomised double‐blind trial. Lancet 2002;360:196–202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Moiseyev VS, Poder P, Andrejevs N, Ruda MY, Golikov AP, Lazebnik LB, Kobalava ZD, Lehtonen LA, Laine T, Nieminen MS, Lie KI; RUSSLAN Study Investigators . Safety and efficacy of a novel calcium sensitizer, levosimendan, in patients with left ventricular failure due to an acute myocardial infarction. A randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study (RUSSLAN). Eur Heart J 2002;23:1422–1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Mebazaa A, Nieminen MS, Packer M, Cohen‐Solal A, Kleber FX, Pocock SJ, Thakkar R, Padley RJ, Poder P, Kivikko M; SURVIVE Investigators . Levosimendan vs dobutamine for patients with acute decompensated heart failure: the SURVIVE randomized trial. JAMA 2007;297:1883–1891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Feldman AM, Oren RM, Abraham WT, Boehmer JP, Carson PE, Eichhorn E, Gilbert EM, Kao A, Leier CV, Lowes BD, Mathier MA, McGrew FA, Metra M, Zisman LS, Shakar SF, Krueger SK, Robertson AD, White BG, Gerber MJ, Wold GE, Bristow MR; EMOTE Study Group . Low‐dose oral enoximone enhances the ability to wean patients with ultra‐advanced heart failure from intravenous inotropic support: results of the Oral Enoximone in Intravenous Inotrope‐Dependent Subjects Trial. Am Heart J 2007;154:861–869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Metra M, Eichhorn E, Abraham WT, Linseman J, Bohm M, Corbalan R, De Mets D, De Marco T, Elkayam U, Gerber M, Komajda M, Liu P, Mareev V, Perrone SV, Poole‐Wilson P, Roecker E, Stewart J, Swedberg K, Tendera M, Wiens B, Bristow MR; ESSENTIAL Investigators . Effects of low‐dose oral enoximone administration on mortality, morbidity, and exercise capacity in patients with advanced heart failure: The randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel group ESSENTIAL trials. Eur Heart J 2009;30:3015–3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Packer M, Colucci W, Fisher L, Massie BM, Teerlink JR, Young J, Padley RJ, Thakkar R, Delgado‐Herrera L, Salon J, Garratt C, Huang B, Sarapohja T; REVIVE Heart Failure Study Group . Effect of levosimendan on the short‐term clinical course of patients with acutely decompensated heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 2013;1:103–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Teerlink JR, Felker GM, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Metra M, Filippatos GS, Ezekowitz JA, Dickstein K, Cleland JG, Kim JB, Lei L, Knusel B, Wolff AA, Malik FI, Wasserman SM; ATOMIC‐AHF Investigators . Acute Treatment with Omecamtiv Mecarbil to Increase Contractility in Acute Heart Failure: the ATOMIC‐AHF study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;67:1444–1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Teerlink JR, Felker GM, McMurray JJ, Solomon SD, Adams KF Jr, Cleland JG, Ezekowitz JA, Goudev A, Macdonald P, Metra M, Mitrovic V, Ponikowski P, Serpytis P, Spinar J, Tomcsanyi J, Vandekerckhove HJ, Voors AA, Monsalvo ML, Johnston J, Malik FI, Honarpour N; COSMIC‐HF Investigators . Chronic Oral Study of Myosin Activation to Increase Contractility in Heart Failure (COSMIC‐HF): a phase 2, pharmacokinetic, randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388:2895–2903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Packer M, Pitt B, Rouleau JL, Swedberg K, DeMets DL, Fisher L. Long‐term effects of flosequinan on the morbidity and mortality of patients with severe chronic heart failure: primary results of the PROFILE trial after 24 years. JACC Heart Fail 2017;5:399–407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. O'Connor C. Dead letter office. JACC Heart Fail 2013;1:181–182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. van Veldhuisen DJ, Poole‐Wilson PA. The underreporting of results and possible mechanisms of 'negative' drug trials in patients with chronic heart failure. Int J Cardiol 2001;80:19–27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Califf RM, Adams KF, McKenna WJ, Gheorghiade M, Uretsky BF, McNulty SE, Darius H, Schulman K, Zannad F, Handberg‐Thurmond E, Harrell FE Jr, Wheeler W, Soler‐Soler J, Swedberg K. A randomized controlled trial of epoprostenol therapy for severe congestive heart failure: the Flolan International Randomized Survival Trial (FIRST). Am Heart J 1997;134:44–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Stevenson LW. Clinical use of inotropic therapy for heart failure: looking backward or forward? Part I: Inotropic infusions during hospitalization. Circulation 2003;108:367–372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Nichols AJ, Ruffolo RR Jr. Evaluation of the alpha and beta adrenoceptor‐mediated activities of the novel, orally active inotropic agent, ibopamine, in the cardiovascular system of the pithed rat: comparison with epinine and dopamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1987;242:455–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Dohmen HJ, Dunselman PH, Poole‐Wilson PA. Comparison of captopril and ibopamine in mild to moderate heart failure. Heart 1997;78:285–290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Uretsky BF, Jessup M, Konstam MA, Dec GW, Leier CV, Benotti J, Murali S, Herrmann HC, Sandberg JA. Multicenter trial of oral enoximone in patients with moderate to moderately severe congestive heart failure. Lack of benefit compared with placebo. Enoximone Multicenter Trial Group. Circulation 1990;82:774–780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Cavusoglu E, Frishman WH, Klapholz M. Vesnarinone: a new inotropic agent for treating congestive heart failure. J Card Fail 1995;1:249–257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Miao L, Perreault CL, Travers KE, Morgan JP. Mechanisms of positive inotropic action of flosequinan, hydralazine, and milrinone on mammalian myocardium. Eur J Pharmacol 1997;321:201–208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Burstein S, Semigran MJ, Dec GW Jr, Boucher CA, Fifer MA. Positive inotropic and lusitropic effects of intravenous flosequinan in patients with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992;20:822–829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Massie BM, Berk MR, Brozena SC, Elkayam U, Plehn JF, Kukin ML, Packer M, Murphy BE, Neuberg GW, Steingart RM, Levine TB, DeHaan H; FACET Investigators . Can further benefit be achieved by adding flosequinan to patients with congestive heart failure who remain symptomatic on diuretic, digoxin, and an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor? Results of the Flosequinan‐ACE Inhibitor Trial (FACET). Circulation 1993;88:492–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Nieminen MS, Cleland JG, Eha J, Belenkov Y, Kivikko M, Poder P, Sarapohja T. Oral levosimendan in patients with severe chronic heart failure – the PERSIST study. Eur J Heart Fail 2008;10:1246–1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Oliva F, Perna E, Marini M, Nassiacos D, Ciro A, Malfatto G, Morandi F, Caico I, Perna G, Meloni S, Vincenzi A, Villani A, Vecchi AL, Minoia C, Verde A, De Maria R; RELEVANT‐HF Study Group . Scheduled intermittent inotropes for ambulatory advanced heart failure. The RELEVANT‐HF multicentre collaboration. Int J Cardiol 2018;272:255–259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Comin‐Colet J, Manito N, Segovia‐Cubero J, Delgado J, Garcia Pinilla JM, Almenar L, Crespo‐Leiro MG, Sionis A, Blasco T, Pascual‐Figal D, Gonzalez‐Vilchez F, Lambert‐Rodriguez JL, Grau M, Bruguera J; LION‐HEART Study Investigators . Efficacy and safety of intermittent intravenous outpatient administration of levosimendan in patients with advanced heart failure: the LION‐HEART multicentre randomised trial. Eur J Heart Fail 2018;20:1128–1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Oliva F, Comin‐Colet J, Fedele F, Fruhwald F, Gustafsson F, Kivikko M, Borbely A, Polzl G, Tschope C. Repetitive levosimendan treatment in the management of advanced heart failure. Eur Heart J Suppl 2018;20:I11–I20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Boswood A, Gordon SG, Haggstrom J, Wess G, Stepien RL, Oyama MA, Keene BW, Bonagura J, MacDonald KA, Patteson M, Smith S, Fox PR, Sanderson K, Woolley R, Szatmari V, Menaut P, Church WM, O'Sullivan ML, Jaudon JP, Kresken JG, Rush J, Barrett KA, Rosenthal SL, Saunders AB, Ljungvall I, Deinert M, Bomassi E, Estrada AH, Fernandez Del Palacio MJ, Moise NS, Abbott JA, Fujii Y, Spier A, Luethy MW, Santilli RA, Uechi M, Tidholm A, Schummer C, Watson P. Longitudinal analysis of quality of life, clinical, radiographic, echocardiographic, and laboratory variables in dogs with preclinical myxomatous mitral valve disease receiving pimobendan or placebo: the EPIC study. J Vet Intern Med 2018;32:72–85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Murai K, Seino Y, Kimata N, Inami T, Murakami D, Abe J, Yodogawa K, Maruyama M, Takano M, Ohba T, Ibuki C, Mizuno K. Efficacy and limitations of oral inotropic agents for the treatment of chronic heart failure. Int Heart J 2013;54:75–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Greenberg BH, Chou W, Saikali KG, Escandon R, Lee JH, Chen MM, Treshkur T, Megreladze I, Wasserman SM, Eisenberg P, Malik FI, Wolff AA, Shaburishvili T. Safety and tolerability of omecamtiv mecarbil during exercise in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and angina. JACC Heart Fail 2015;3:22–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Bakkehaug JP, Kildal AB, Engstad ET, Boardman N, Naesheim T, Ronning L, Aasum E, Larsen TS, Myrmel T, How OJ. Response to letter regarding article, ‘Myosin activator omecamtiv mecarbil increases myocardial oxygen consumption and impairs cardiac efficiency mediated by resting myosin ATPase activity’. Circ Heart Fail 2015;8:1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Teerlink JR, Malik FI, Kass DA. Letter by Teerlink et al regarding article, ‘Myosin activator omecamtiv mecarbil increases myocardial oxygen consumption and impairs cardiac efficiency mediated by resting myosin ATPase activity’. Circ Heart Fail 2015;8:1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Bakkehaug JP, Kildal AB, Engstad ET, Boardman N, Naesheim T, Ronning L, Aasum E, Larsen TS, Myrmel T, How OJ. Myosin activator omecamtiv mecarbil increases myocardial oxygen consumption and impairs cardiac efficiency mediated by resting myosin ATPase activity. Circ Heart Fail 2015;8:766–775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Endoh M. Amrinone, forerunner of novel cardiotonic agents, caused paradigm shift of heart failure pharmacotherapy. Circ Res 2013;113:358–361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Packer M. The development of positive inotropic agents for chronic heart failure: how have we gone astray? J Am Coll Cardiol 1993;22:119A–126A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Topol EJ. The lost decade of nesiritide. N Engl J Med 2011;365:81–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Binanay C, Califf RM, Hasselblad V, O'Connor CM, Shah MR, Sopko G, Stevenson LW, Francis GS, Leier CV, Miller LW; ESCAPE Investigators and ESCAPE Study Coordinators . Evaluation study of congestive heart failure and pulmonary artery catheterization effectiveness: the ESCAPE trial. JAMA 2005;294:1625–1633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Epstein S, Robinson BF, Kahler RL, Braunwald E. Effects of beta‐adrenergic blockade on the cardiac response to maximal and submaximal exercise in man. J Clin Invest 1965;44:1745–1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Felker GM, Thompson RE, Hare JM, Hruban RH, Clemetson DE, Howard DL, Baughman KL, Kasper EK. Underlying causes and long‐term survival in patients with initially unexplained cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1077–1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Ahmad T, Pencina MJ, Schulte PJ, O'Brien E, Whellan DJ, Pina IL, Kitzman DW, Lee KL, O'Connor CM, Felker GM. Clinical implications of chronic heart failure phenotypes defined by cluster analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;64:1765–1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Tamargo J, Rosano GM, Delpon E, Ruilope L, Lopez‐Sendon J. Pharmacological reasons that may explain why randomized clinical trials have failed in acute heart failure syndromes. Int J Cardiol 2017;233:1–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Ahmad T, Wilson FP, Desai NR. The trifecta of precision care in heart failure: biology, biomarkers, and big data. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018;72:1091–1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. de Denus S, O'Meara E, Desai AS, Claggett B, Lewis EF, Leclair G, Jutras M, Lavoie J, Solomon SD, Pitt B, Pfeffer MA, Rouleau JL. Spironolactone metabolites in TOPCAT – new insights into regional variation. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1690–1692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Felker GM, Benza RL, Chandler AB, Leimberger JD, Cuffe MS, Califf RM, Gheorghiade M, O'Connor CM; OPTIME‐CHF Investigators . Heart failure etiology and response to milrinone in decompensated heart failure: results from the OPTIME‐CHF study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:997–1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Cohn JN, Levine TB, Olivari MT, Garberg V, Lura D, Francis GS, Simon AB, Rector T. Plasma norepinephrine as a guide to prognosis in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 1984;311:819–823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Packer M, Medina N, Yushak M. Hemodynamic and clinical limitations of long‐term inotropic therapy with amrinone in patients with severe chronic heart failure. Circulation 1984;70:1038–1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Gorodeski EZ, Chu EC, Reese JR, Shishehbor MH, Hsich E, Starling RC. Prognosis on chronic dobutamine or milrinone infusions for stage D heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2009;2:320–324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Pinney SP, Stevenson LW. Chronic inotropic therapy in the current era: old wines with new pairings. Circ Heart Fail 2015;8:843–846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Nizamic T, Murad MH, Allen LA, McIlvennan CK, Wordingham SE, Matlock DD, Dunlay SM. Ambulatory inotrope infusions in advanced heart failure: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. JACC Heart Fail 2018;6:757–767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Sundell J, Engblom E, Koistinen J, Ylitalo A, Naum A, Stolen KQ, Kalliokoski R, Nekolla SG, Airaksinen KE, Bax JJ, Knuuti J. The effects of cardiac resynchronization therapy on left ventricular function, myocardial energetics, and metabolic reserve in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;43:1027–1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Ahmad T, Kelly JP, McGarrah RW, Hellkamp AS, Fiuzat M, Testani JM, Wang TS, Verma A, Samsky MD, Donahue MP, Ilkayeva OR, Bowles DE, Patel CB, Milano CA, Rogers JG, Felker GM, O'Connor CM, Shah SH, Kraus WE. Prognostic implications of long‐chain acylcarnitines in heart failure and reversibility with mechanical circulatory support. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;67:291–299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Heggermont WA, Papageorgiou AP, Heymans S, van Bilsen M. Metabolic support for the heart: complementary therapy for heart failure? Eur J Heart Fail 2016;18:1420–1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Gilstrap LG, DeFilippis EM, Stevenson LW. An unintended consequence of the 21st‐century cures act for patients with heart failure. Circulation 2017;136:123–125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Vaduganathan M, Claggett B, Packer M, McMurray JJ, Rouleau JL, Zile MR, Swedberg K, Solomon SD. Natriuretic peptides as biomarkers of treatment response in clinical trials of heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 2018;6:564–569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. JJ MM, Packer M, Desai AS, Gong J, Lefkowitz MP, Rizkala AR, Rouleau JL, Shi VC, Solomon SD, Swedberg K, Zile MR; PARADIGM‐HF Investigators and Committees . Angiotensin‐neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N Engl J Med 2014;371:993–1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Cleland JG, Charlesworth A, Lubsen J, Swedberg K, Remme WJ, Erhardt L, Di Lenarda A, Komajda M, Metra M, Torp‐Pedersen C, Poole‐Wilson PA; COMET Investigators . A comparison of the effects of carvedilol and metoprolol on well‐being, morbidity, and mortality (the "patient journey") in patients with heart failure: a report from the Carvedilol Or Metoprolol European Trial (COMET). J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:1603–1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Eapen ZJ, Turakhia MP, McConnell MV, Graham G, Dunn P, Tiner C, Rich C, Harrington RA, Peterson ED, Wayte P. Defining a mobile health roadmap for cardiovascular health and disease. J Am Heart Assoc 2016;5:e003119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


