Abstract
Production and excretion of hydrogen (H2) gas in human was reported in 1969, since then it has been regarded as non-toxic molecule. For preventive and therapeutic medical uses, a possible treatment for cancer was reported and another article was published on how H2 acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. A variety of H2 gas inhalers have been available in the market for hospital and home uses. However, H2 is odorless and flammable or explosive ignited by static electricity. We have examined the safety of a variety of H2 gas concentrations from the viewpoint of flammability and explosion. We have also measured concentrations of H2 gas inhalers in the market respectively. This paper also details how to control H2 gas concentration for preventing explosions.
Keywords: hydrogen gas, hydrogen concentration, explosion, detonation, flammability, static electricity, hydrogen gas inhaler, medical use, home use, market, safety
INTRODUCTION
Production and excretion of hydrogen (H2) gas in human was reported in 1969, since then it has been regarded as non-toxic molecule.1 H2 was recently reported by Ohsawa et al.2 as a preventive and therapeutic antioxidant. However, in 2005, 2 years ago of the Ohsawa’s report, Yanagihara et al.3 at our group reported that drinking of neutral H2-rich water produced by electrolysis could effectively reduce the oxidative stress induced by chemical oxidant in rats, indicating that this is a pioneering research in H2 medicine. H2 has also been proposed for treatment in various oxidative stress-related diseases and damages.4,5,6,7,8,9 A variety of H2 gas inhalers have been available in the market for clinical and home uses. However, H2 is odorless and flammable or explosive ignited by static electricity. In the present study, we examined the safety of a variety of H2 gas concentrations from the viewpoint of flammability and explosion. In addition, we also measured concentrations of H2 gas inhalers in the market respectively.
HOW DOES H2 GAS CONCENTRATION INFLUENCE EXPLOSION?
Taiyo Nippon Sanso Pure H2 gas G2 (Tokyo, Japan) was used in the first experiment for testing explosions based on a variety of H2 concentrations. The H2 concentration was measured by New Cosmos Electric: XP-3140 (Osaka, Japan). In order to examine the H2 gas concentrations with mixture of air, we have tested flammability and explosion under five H2 concentrations respectively: 4%, 10%, 15%, 20%, and 100%. Under the H2 concentration of 4% and 10%, no explosion/flammability was detected. Under the 15% and 100% H2 concentration, a small explosion with small sound was detected which may not cause a severe damage to user. Under the 20% H2 concentration, a large explosion (detonation) was detected which may cause a severe damage to user. From this H2 concentration experiment, we understood that the H2 concentration must be less than 10%. In addition, we did a systematic search of Google Scholar and PubMed using the search terms (“hydrogen gas” and “explosion” or “detonation” and “concentration”) before initiating this study on December 5, 2015, and we repeated this search on August 5, 2019. In these searches, many papers described the explosive concentration of H2 gas in the mixture of H2 gas and air as 4 to 75%.10,11 However, a few reports reported that H2 does not explode if it is less than 10% when mixed with air or oxygen.12,13,14 Therefore, our present experimental data are supported by the latter reports.
MEASURING H2 CONCENTRATION OF H2 GAS INHALERS
New Cosmos Electric XP-3140 was used for measuring H2 concentrations of H2 gas inhalers (15 products) in the market respectively. In the measurement of H2 concentration, we used 5 apparatus and 1 apparatus for MHG-2000α and other 14 apparatus respectively. Additionally, we confirmed that the result of H2 concentration is correct in each product catalog. Table 1 shows the result of measured H2 concentrations. Remember that H2 gas concentration over 10% is explosive and dangerous. Consumer safety regulations for H2 gas inhalers are immediately required for protecting users in order to avoid dangerous explosions.
Table 1.
Hydrogen (H2) gas inhalers (products) in the market
| Product name | Supplier | H2 concentration (%) | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| MHG-2000α | MiZ Co., Ltd., Kanagawa, Japan | 6.6±0.2* | Electrolysis |
| Hycellvator | Helix Japan Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan | 66# | |
| H2 Life | JWS International Corp., Tokyo, Japan | 66# | |
| HydroPower | Brain Hokkaido Co., Ltd., Hokkaido, Japan | 66# | |
| HydroUni | Univers Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan | 66# | |
| Hydrogen Generator | OPS Inc., Tokyo, Japan | 66# | |
| AMS-H | Asklepios Medical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan | 66# | |
| La Briller Luxe | ISMZ Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan | 98 | |
| Hydrogen Inhaler (Table top type) | Kenko Shien Center Co., Ltd., Aichi, Japan | 99 | |
| Suiso Care | Kenko Co., Ltd., Gifu, Japan | 99 | |
| PHG-150TA | Eco Higashinippon Co., Ltd., Fukushima, Japan | 99 | |
| Suisonia | Earth Engineering Co., Ltd., Fukuoka, Japan | ND | Pyrolysis |
| HydroRich | Pal Corporation, Tokyo, Japan | 99 | Chemical reaction |
| Hydrogen Generator | Kanon Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan | 99 | |
| MYC Hydro One | MYC Co., Ltd., Kumamoto, Japan | 99 |
Note: *Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 5 apparatus. #H2 and O2 gas mixed type. ND: Not detected.
H2 GAS IGNITED BY STATIC ELECTRICITY
We must examine a risk of static electricity ignition. According to Danger of H2 Gas Explosion, and Prevention Measures (Division of Gas Safety, Institute of Chemical Technology, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Sciences and Technology, Japan), the minimum ignition energy of H2 gas is 0.02 mJ.15 According to electrostatic sensitivity of H2 by Mizuki Yamakuma (National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, Japan), electrostatic charge of the human body is 0.05 mJ with 1.0 kV human charging potential.16 When assuming human is a capacitor of 90 pF, 1.0 kV (0.05 mJ) to 2.5 kV (0.28 mJ) human charging potential cannot be sensed by us at all. In other words, it is highly possible to easily ignite H2 gas by static electricity without our recognition. 0.02 mJ ignition energy can be easily satisfied in hospital and at home. In fact, we examined to observe if an explosion would occur by a lighter flame or static electricity close to the outlet of H2 gas inhaler using H2 life, La Briller Luxe, or HydRich respectively. As a result, large explosions (detonation) were detected with these three products (data not shown).
CONTROLLING H2 GAS CONCENTRATION
Although it is well known that the H2 gas concentration in detonation of the mixture of H2 gas and air is less than 4%, we recently demonstrated that the detonation limit is less than 10% by our experiment and literature search.17 Therefore, we developed the safe H2 gas supply system (MHG-2000α). As shown in Figure 1, inhalation gas was prepared by mixing H2 gas with air, where the H2 gas was produced 140 mL/min by the electrolysis of water, and the concentration was controlled about 6.0–7.0% under the detonation limit of the mixture of H2 gas and air (below 10%). Moreover, this H2 gas supply system consists of raw water in an electrolyzed chamber, the diaphragm and the electrode plate. H2 gas is directly generated from the electrode plate and cathode, based on the interaction between the fan on the water surface, the cathode gas and the diluted air. Thus, the concentration of H2 gas near the cathode during electrolysis is always maintained below 10%, the lower limit of explosion. MHG-2000α has the new remarkable function system, which is indicated H2 gas concentration, calculated from the current value and diluent gas. When it will be more than 10% of H2 gas concentration, the electrolysis of water will be stopped immediately for safe.
Figure 1.
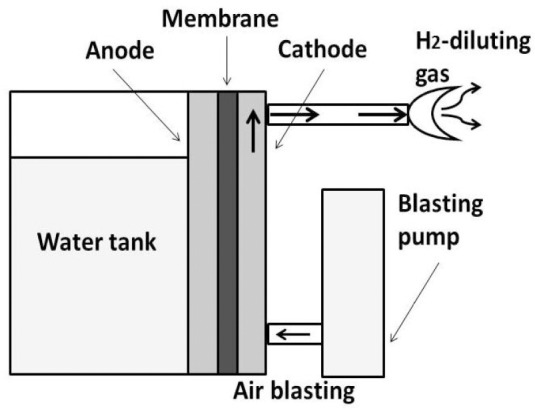
Apparatus for hydrogen (H2) gas inhalation (MHG-2000α).
Note: The inhalation gas is prepared by mixing H2 gas with air, where H2 gas was produced by the electrolysis of water, and the concentration is controlled under the detonation limit of the mixture of H2 gas and air.
In usual conditions, H2 gas does not explode at a concentration of 10% or less. Since H2 is a colorless gas with no taste or odor, we do not know the actual concentration of H2 gas produced by the H2 gas inhaler. Therefore, using a H2 gas inhaler carries a risk of explosion. In one inhaler such as Suisonia, we could not confirm H2 gas generation at all. Most of H2 gas inhalers have some risks of explosion except MHG-2000α and Suisonia. As of today, there is no legislation to regulate proper production and/or use of H2 gas inhalers. We should be fully aware of the risks of H2 gas inhalers to prevent serious accident involving human life. To our knowledge, this is the first paper demonstrating the explosion risk of H2 gas inhalers in the market. The proposed results will be useful for the information of safe H2 gas inhalers.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Mr. Fumitake Satoh, Ms. Yoko Satoh, Dr. Yi-Da Hsieh and Mr. Masatsugu Saitou (MiZ Co. Ltd., Japan) for their excellent advices in the writing of this manuscript.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Financial support
None.
Copyright license agreement
The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by all authors before publication.
Plagiarism check
Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review
Externally peer reviewed.
REFERENCES
- 1.Levitt MD. Production and excretion of hydrogen gas in man. N Engl J Med. 1969;281:122–127. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907172810303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 2007;13:688–694. doi: 10.1038/nm1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yanagihara T, Arai K, Miyamae K, et al. Electrolyzed hydrogen-saturated water for drinking use elicits an antioxidative effect: a feeding test with rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2005;69:1985–1987. doi: 10.1271/bbb.69.1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dole M, Wilson FR, Fife WP. Hyperbaric hydrogen therapy: a possible treatment for cancer. Science. 1975;190:152–154. doi: 10.1126/science.1166304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nakao A, Toyoda Y, Sharma P, Evans M, Guthrie N. Effectiveness of hydrogen rich water on antioxidant status of subjects with potential metabolic syndrome-an open label pilot study. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010;46:140–149. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.09-100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yoritaka A, Takanashi M, Hirayama M, Nakahara T, Ohta S, Hattori N. Pilot study of H(2) therapy in Parkinson’s disease: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mov Disord. 2013;28:836–839. doi: 10.1002/mds.25375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nishimaki K, Asada T, Ohsawa I, et al. Effects of molecular hydrogen assessed by an animal model and a randomized clinical study on mild cognitive impairment. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2018;15:482–492. doi: 10.2174/1567205014666171106145017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chuai Y, Gao F, Li B, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates radiation-induced male germ cell loss in mice through reducing hydroxyl radicals. Biochem J. 2012;442:49–56. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yang Y, Li B, Liu C, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects immunocytes from radiation-induced apoptosis. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18:Br144–148. doi: 10.12659/MSM.882616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.The Engineering ToolBox. Gases - Explosion and flammability concentration Limits. https://wwwengineeringtoolboxcom/explosive-concentration-limits-d_423html .
- 11.Yaws CL. Matheson Gas Data Book. McGraw-Hill Professional. (7th ed) 2001 [Google Scholar]
- 12.Thomas GO. Flame acceleration and the development of detonation in fuel-oxygen mixtures at elevated temperatures and pressures. J Hazard Mater. 2009;163:783–794. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yagyu S, Matsui H, Masuda T, Yamamoto H. Study on the explosion risk of hydrogen (1st Report) Effect of pressure on the explosive limit of hydrogen. Research Report of National Institute for Industrial Safety. 1969 RIIS-RR-18-1:3-5. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yagyu S, Masuda T, Yamamoto H. Study on the explosion danger of hydrogen (2nd Report). Explosion pressure of hydrogenair mixture. Research Report of National Institute for Industrial Safety. 1973 RIIS-RR-21-4:3-5. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Danger of Hydrogen Gas Explosion, and Prevention Measures. Division of Gas Safety, Institute of Chemical Technology, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Sciences and Technology. http://www.hess.jp/Search/data/14-02-018.pdf .
- 16.Yamakuma M. Hydrogen electrostatic sensitivity. Safety Eng. 2005;44:386–390. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kurokawa R, Komachi F, Seo T, Hirano S. 7th Meeting of the Japanese Biomedical Association of Molecular Hydrogen. Nagoya: 2017. Explosive concentration of hydrogen gas and safety of hydrogen gas inhaler. [Google Scholar]


