Key Points
Question
Is surgical hematoma evacuation compared with conservative treatment associated with improved functional outcome among patients with cerebellar intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH)?
Findings
In this individual participant data meta-analysis that included 578 patients with cerebellar ICH, the proportion of patients with a favorable functional outcome at 3 months (defined as modified Rankin scale 0-3) for patients treated with surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment was 30.9% vs 35.5%, a difference that was not statistically significant.
Meaning
Surgical hematoma evacuation in patients with cerebellar ICH was not associated with improved functional outcome.
Abstract
Importance
The association of surgical hematoma evacuation with clinical outcomes in patients with cerebellar intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) has not been established.
Objective
To determine the association of surgical hematoma evacuation with clinical outcomes in cerebellar ICH.
Design, Setting, and Participants
Individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis of 4 observational ICH studies incorporating 6580 patients treated at 64 hospitals across the United States and Germany (2006-2015).
Exposure
Surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcome was functional disability evaluated by the modified Rankin Scale ([mRS] score range: 0, no functional deficit to 6, death) at 3 months; favorable (mRS, 0-3) vs unfavorable (mRS, 4-6). Secondary outcomes included survival at 3 months and at 12 months. Analyses included propensity score matching and covariate adjustment, and predicted probabilities were used to identify treatment-related cutoff values for cerebellar ICH.
Results
Among 578 patients with cerebellar ICH, propensity score–matched groups included 152 patients with surgical hematoma evacuation vs 152 patients with conservative treatment (age, 68.9 vs 69.2 years; men, 55.9% vs 51.3%; prior anticoagulation, 60.5% vs 63.8%; and median ICH volume, 20.5 cm3 vs 18.8 cm3). After adjustment, surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment was not significantly associated with likelihood of better functional disability at 3 months (30.9% vs 35.5%; adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 0.94 [95% CI, 0.81 to 1.09], P = .43; adjusted risk difference [ARD], −3.7% [95% CI, −8.7% to 1.2%]) but was significantly associated with greater probability of survival at 3 months (78.3% vs 61.2%; AOR, 1.25 [95% CI, 1.07 to 1.45], P = .005; ARD, 18.5% [95% CI, 13.8% to 23.2%]) and at 12 months (71.7% vs 57.2%; AOR, 1.21 [95% CI, 1.03 to 1.42], P = .02; ARD, 17.0% [95% CI, 11.5% to 22.6%]). A volume range of 12 to 15 cm3 was identified; below this level, surgical hematoma evacuation was associated with lower likelihood of favorable functional outcome (volume ≤12 cm3, 30.6% vs 62.3% [P = .003]; ARD, −34.7% [−38.8% to −30.6%]; P value for interaction, .01), and above, it was associated with greater likelihood of survival (volume ≥15 cm3, 74.5% vs 45.1% [P < .001]; ARD, 28.2% [95% CI, 24.6% to 31.8%]; P value for interaction, .02).
Conclusions and Relevance
Among patients with cerebellar ICH, surgical hematoma evacuation, compared with conservative treatment, was not associated with improved functional outcome. Given the null primary outcome, investigation is necessary to establish whether there are differing associations based on hematoma volume.
This meta-analysis uses individual participant data from observational studies to compare functional disability among patients with cerebellar intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) managed with surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment.
Introduction
Based on an age-adjusted incidence-rate for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) in high-income countries for the year 2010, it was estimated that cerebellar ICH affects approximately 35 000 patients annually within the European Union and the United States.1,2,3 There have not been randomized trials of treatment interventions for patients with cerebellar ICH. Since 1984, surgical hematoma evacuation has been the preferred treatment approach, specifically in patients with larger hematomas and intraventricular involvement, given increased risk for brainstem compression and herniation.4,5,6,7,8 However, evidence on the association between surgical hematoma evacuation and clinical outcomes after cerebellar ICH has been limited to small observational studies.9,10 International guidelines including the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association guideline recommend surgical hematoma evacuation for cerebellar ICH with diameter greater than 3 cm to improve outcome; however, definite evidence to validate or refute this recommendation is currently not available.4,9,10 As a result, there is no commonly accepted management strategy for cerebellar ICH and no general agreement regarding whether, when, and how these patients should undergo surgical intervention.8,11 The purpose of this study was to assess the association of surgical hematoma evacuation with functional outcome and mortality in patients with cerebellar ICH.
Methods
This study consisted of 2 parts: (1) a systematic review and aggregate data meta-analysis of previously published studies and (2) an individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis (Figure 1). Findings are reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Individual Participant Data (PRISMA-IPD).12
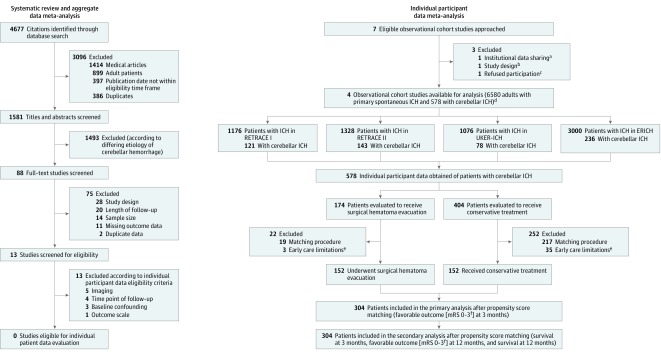
Figure 1. Flow Diagram of Study Population and Data Analysis.
Flow diagram providing the systematic database search, screening, eligibility, exclusion, and generation of the study population available for individual participant data (IPD) contribution, based on PRISMA-IPD (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of IPD) guidelines.12 This study consisted of a systematic review and aggregate data meta-analysis of previously published studies and an IPD meta-analysis.
aIndicates institutional data sharing regulations not allowing IPD contribution.
bIndicates study design not fulfilling PRISMA-IPD criteria.
cParticipation was refused due to conflicting ongoing investigations.
dOverall, IPD of 6580 adult patients with primary spontaneous ICH were provided by four observational studies (NCT01829581, NCT03093233, NCT03183167, NCT01202864) and 578 patients with cerebellar ICH according to predefined eligibility criteria were identified. The German studies (NCT01829581, NCT03093233, NCT03183167) contributed 342 cerebellar ICH patients recruited at 22 hospitals, and the American study (NCT01202864) contributed 236 cerebellar ICH patients recruited at 42 hospitals.
eEarly care limitations indicate the initiation of comfort care measures within 24 hours after hospital admission.13
fThe modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score ranges from 0 (indicating no deficit) to 6 (death).
ICH indicates intracerebral hemorrhage.
Search Strategy and Data Synthesis
Aggregate Data Meta-analysis
A systematic review of the Cochrane Library, Pubmed, and Scopus databases, and international trial registries (ClinicalTrials.gov, European Clinical Trials Database, UMIN Clinical Trials Registry, Chinese Clinical Trial Registry) was performed without language restrictions for clinical studies published from January 1, 1980, to June 6, 2019, investigating adult patients with cerebellar ICH according to treatment exposure (surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment), using search terms cerebellar OR infratentorial with hemorrhage OR hematoma. For full details of the statistical analysis plan and aggregate data meta-analysis, refer to Figure 1; eMethods, eTable 1, and eFigure 1 in the Supplement. None of the 13 identified studies of the systematic review fulfilled prespecified criteria for IPD contribution.
IPD Meta-analysis
Eligibility for IPD meta-analysis comprised the following to address baseline and treatment confounding: (1) 10 or more patients treated with surgical hematoma evacuation for primary cerebellar ICH; (2) no other competing treatment intervention; (3) data available on timing of surgery (after symptom onset and hospital admission); (4) valid ICH volume assessment (ABC/2 or volumetric measurement14); (5) recorded intraventricular hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, or both; (6) standardized scoring of neurological status (Glasgow Coma Scale; score range, 3-15 [comatose to alert]); and (7) standardized functional outcome assessed by the modified Rankin Scale (score range, 0-6 [no functional deficit to death]) recorded at 3 months and 12 months after the index event. To conduct IPD meta-analysis, authors decided to extract cerebellar ICH patients from existing large studies of general ICH patients and therefore screened appropriate registered observational studies (ClinicalTrials.gov, European Clinical Trials Database) as well as contacted established investigative teams for patients with acute primary ICH in the Western Hemisphere.
The present study (Figure 1) incorporated IPD from 4 of 7 approached studies (eTable 2 in the Supplement): 2 cohorts from the German-wide multicenter analysis of oral anticoagulation-associated intracerebral hemorrhage that integrated data from 22 tertiary care centers across Germany (RETRACE part I [German-Wide Multicenter Analysis of Oral Anticoagulation-Associated Intracerebral Hemorrhage], conducted from 2006 to 201015,16 and RETRACE part II, 2011 until 201517,18,19); UKER, a single-center observational cohort study for primary spontaneous ICH conducted at the University Hospital Erlangen, Germany from 2006 to 201520,21; and ERICH (Ethnic/Racial Variations of Intracerebral Hemorrhage), a multicenter, prospective, case-control study that included equal numbers of non-Hispanic white or black patients and Hispanic patients enrolled by 19 clinical recruitment centers encompassing 42 hospitals across the United States from 2010 to 2015.22,23 Informed consent was obtained from all participants or their legal representatives within each participating study if not waived by the respective ethical committees. Institutional review boards or ethical committees reviewed and approved all study protocols.15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23
Data Extraction and Study Population
Principal investigators were contacted, and in accordance with individual data-sharing requirements, full data sets of the entire observational cohorts were obtained. For the present analyses of cerebellar ICH patients, inclusion criteria comprised the following: (1) diagnosis of acute primary ICH; (2) ICH originating from a cerebellar location; (3) age 18 years or older at time of event; and (4) no evidence of a secondary ICH etiology. Cerebellar ICH was defined as parenchymal ICH originating from cerebellar structures, such as cerebellar hemispheres, anterior and posterior lobes, vermis, or cerebellar tonsils. Patients with ICH located in the midbrain, pons, or medulla, with or without extensions to the cerebellar peduncles or the fourth ventricle, were not scored eligible and were not enrolled into the present study.
Methodology of data acquisition and description of included studies are reported in the online supplement (eTable 3 in the Supplement). Baseline data on demographics (age, sex), prior comorbidities (hypertension, coronary artery disease, prior stroke, atrial fibrillation), prior medication exposures (oral anticoagulation, antiplatelet medication), in-hospital measures (time and date of admission to determine time from symptom-onset to admission, time from admission to surgery, admission during on or off hours, (weekdays, 7:00 am-6:00 pm),24 reversal treatment with fresh-frozen plasma or prothrombin complex concentrates), and neurological status assessed by Glasgow Coma Scale score upon hospital admission were obtained.15,16,17,19,22,23 Patients who received comfort care measures were categorized into 2 categories: early care limitations initiated within 24 hours after admission and withdrawal of care after 24 hours.13 Patients with early care limitations were excluded from outcome analyses.
For the entire study population, imaging analyses were centrally conducted at 2 imaging cores (Massachusetts General Hospital and University Hospital of Erlangen) by study investigators blinded to clinical information. Hematoma volume was determined using validated methods,14,15,16,22,23 intralaboratory measurements evaluated by Bland-Altman plots (eFigure 2 in the Supplement), and all imaging-specific analyses for the present study were corrected by using coefficients of variation. The IPD set was compiled and centrally analyzed by the coordinating center (University Hospital Erlangen, Germany).
Intervention and Outcomes
The investigated intervention was dichotomized into surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment. Surgical hematoma evacuation was defined as any surgical procedure evacuating parenchymal hematoma, such as craniectomy, open craniotomy, or minimal invasive surgery.7 The placement of an external ventricular drainage for intracranial pressure monitoring or cerebrospinal fluid diversion was not scored as surgical hematoma evacuation.
The primary outcome was predefined as the proportion of patients with favorable functional outcome at 3 months after cerebellar ICH using the modified Rankin Scale (mRS [range: 0, no functional deficit to 6, death]). Favorable outcome was defined as a score of 0 to 3 (0, no deficit to 3, being able to walk independently with a walker or a cane) on an ordinal scale for functional outcome assessment after stroke, and dichotomously compared with the proportion of patients with unfavorable outcome (mRS, 4-6).25,26 Secondary outcomes consisted of survival at 3 months (mRS 0-5), functional outcome (mRS 0-3 vs 4-6) at 12 months, and survival at 12 months. Follow-up information was obtained according to individual study protocols by personnel blinded to clinical data.15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23
Risk of Bias Assessment
The 4 observational studies were evaluated for risk of bias using the Cochrane Collaboration domains and ROBINS-I tool (Risk Of Bias In Nonrandomized Studies of Interventions)27 by consensus of the lead authors (JBK, AB, KNS, HBH) presented in eFigure 3 and eTable 4 in the Supplement.
Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis plan and further details regarding methodology of aggregate data and IPD meta-analyses are provided in the eMethods (Supplement).12 Heterogeneity was evaluated by Cochran Q testing and calculated I2 values presented with according range.28,29 For aggregate data meta-analyses and interstudy variance of treatment effects across those studies providing IPD, heterogeneity was considered significant for P values less than .1, and inconsistency of results was determined according to the GRADE Handbook.30
For the pooled IPD, study population sensitivity analyses regarding bias involved baseline confounding, treatment, error of ICH volume measurements, time-varying confounding, withdrawal of care, excluded patients, and missing outcomes. To address confounding, a doubly robust estimation technique was applied using propensity score matching and further covariate adjustments.31 Baseline confounders (age, Glasgow Coma Scale score, ICH volume, intraventricular hemorrhage, prior oral anticoagulation, reversal treatment, and on-hour admissions status) were included into the propensity score matching procedure, which was carried out by balanced parallel (1:1) using a nearest neighbor approach with a caliper of 0.2.31
IPD meta-analyses of the propensity score–matched cohort were conducted as a 1-stage approach of binary outcomes using logistic regression in a generalized estimating equations model with an exchangeable working correlation structure using a robust estimator to account for clustering. This model used a normal distribution with identity link to calculate adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and adjusted absolute risk differences (ARDs; conservative treatment as reference) derived from predicted proportions of these models.32,33,34 Baseline confounding required severity adjustments for age, neurological status (Glasgow Coma Scale), ICH volume, and intraventricular hemorrhage. The model was complemented by interaction terms to avoid ecological bias for treatment covariate interactions35 for interstudy variance (study × intervention), increased propensity of surgery during on-hour admission (on-hour admission × intervention), and for reversal treatment due to the presence of patients prescribed oral anticoagulation (reversal treatment × intervention) within the IPD study population. Potential error in ICH volume measurements was counteracted by additional integration of the coefficient of variation for ICH volume–associated analyses. Outcome information was consistent with missing completely at random (the Little MCAR test, P = .21), was not statistically different across studies and for the intervention, and was handled with multiple imputation analyses by fully conditional specifications.36 Exploratory subgroup analyses of the propensity score–matched cohort were calculated for the binary outcomes using the same regression procedure without the subgroup defining variable within categorized analyses. The interaction of surgical hematoma evacuation with outcomes was considered significant for P values of less than .05 and interactions of exploratory subgroup analyses were tested using the subgroup-defining variable (variable × intervention) and conservative treatment as reference.
Adjusted predicted probabilities (range, 0-1) of binary outcomes at 3 months (mRS, 0-3 and mRS, 0-5) were calculated, and graphical linear regression analyses of the predicted probability values were used to identify cutoff values for associations of surgical hematoma evacuation with ICH volumes. The intersections of the 95% CIs determined significant cutoff values comparing surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment. To validate predicted associations, adjusted OR estimates, based on existing data, were calculated using a binary logistic generalized estimating equations model within specific volume frames (frames = sliding windows using a variable volume range determined by the median of this window sliding upwards at 1-cm3 steps) corrected for measurement error by the coefficient of variation and for overestimation by the method of moving averages. To test the statistical significance for associations of surgical hematoma evacuation with the identified ICH volume thresholds, adjusted regression models of the propensity score–matched cohort applied interaction analyses (surgical hematoma evacuation × volume threshold). All tests were 2-sided with a significance level at α = .05, which was corrected for multiplicity using the Holm sequential Bonferroni procedure to minimize type 1 error accumulations. Analyses were conducted using SPSS version 21.0 and R software version 3.3.1.
Results
Systematic Review and Aggregate Data Meta-analysis
The systematic review of existing studies analyzing associations of surgical hematoma evacuation with functional outcome and mortality in cerebellar ICH revealed significant heterogeneity, substantial data inconsistency, and severe bias due to confounding (worse neurological status and larger cerebellar ICH volumes in surgically treated patients) across the identified 13 studies (eTable 1 and eFigure 1 in the Supplement). None of these studies fulfilled eligibility criteria for IPD pooling.
Study Population of Individual Participant Data Meta-analysis
To analyze associations of surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment with clinical outcomes the present investigation, we obtained individual participant data from 4 large observational studies (RETRACE-I [N = 1176]; RETRACE-II [N = 1328]; UKER [N = 1076]; and ERICH [N = 3000]). Of 6580 patients with ICH, 578 patients with cerebellar ICH were identified resulting in a crude prevalence of cerebellar ICH of 8.8% (578/6580; eTable 2 in the Supplement).
Risk of Bias Assessment and Adjustments
Statistical heterogeneity, with respect to interstudy variance of treatment associations with clinical outcomes, was not significant, and inconsistency of results across participating studies was determined low to moderate (I2 fluctuation span, 0%-48%; eFigure 4 in the Supplement). Risk of bias, evaluated using Cochrane Collaboration domains, was judged as low, as well as ROBINS-I evaluation, which showed overall moderate risk across all 4 studies (eFigure 3 and eTable 4 in the Supplement).
Among the study population, surgical hematoma evacuation was performed in 174 of 578 patients with cerebellar ICH (30.1%) at a median of 338 (IQR, 187-701) minutes after hospital admission (Table). As compared with patients who received conservative treatment, patients with surgical hematoma evacuation showed significant imbalances on several variables: (1) younger mean age (68.8 [SD, 11.1] years vs 71.1 [SD, 12.9] years; mean difference, −2.3 years [95% CI, −4.5 to −0.1]; standardized mean difference [SMD], −0.18 years); (2) worse neurological status on admission (Glasgow Coma Scale score, 13 [95% CI, 6 to 15] vs 15 [95% CI, 13 to 15]; mean difference, −1.9 score values [95% CI, −2.7 to −1.2]; SMD, −0.45 score values); (3) larger ICH volumes (21.8 cm3 [IQR, 14.0 to 30.6] vs 7.1 cm3 [IQR, 3.3 to 16.1]; mean difference: 11.6 cm3 [95% CI, 9.4 to 13.8]; SMD, 0.86 cm3); and (4) more frequent IVH (87/174 patients [50.0%] vs 151/404 patients [37.4%]; risk difference [RD], 12.6% [95% CI, 3.8% to 21.3%]; SMD, −0.26%) (Table).
Table. Baseline Characteristics of Patients With Cerebellar ICH Comparing Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatmenta.
| Nonmatched Cohort (n = 578) | Propensity-Matched Cohort (n = 304) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery (n = 174) |
Conservative (n = 404) |
Absolute Difference (95% CI)b |
SMDc | Surgery (n = 152) |
Conservative (n = 152) |
Absolute Difference (95% CI)b |
SMDc | |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 68.8 (11.1) | 71.1 (12.9) | −2.3 (−4.5 to −0.1) |
−0.18 | 68.9 (10.8) | 69.2 (13.6) | −0.4 (−3.1 to 2.4) |
0.03 |
| Male sex, No. (%) | 98 (56.3) | 209 (51.7) | 4.6 (−4.3 to 13.2) |
−0.09 | 85 (55.9) | 78 (51.3) | 4.6 (−6.5 to 15.6) |
−0.09 |
| Female sex, No. (%) | 76 (43.7) | 195 (48.3) | −4.6 (−13.2 to 4.3) |
0.09 | 67 (44.1) | 74 (48.7) | −4.6 (−15.6 to 6.5) |
0.09 |
| Medical history, No. (%) | ||||||||
| Hypertension | 138 (79.3) | 341 (84.4) | −5.1 (−12.5 to 1.5) |
0.14 | 121 (79.6) | 126 (82.9) | −3.3 (−12.1 to 5.5) |
0.08 |
| Prior oral anticoagulation | 106 (60.9) | 207 (51.2) | 9.7 (0.8 to 18.2) |
−0.19 | 92 (60.5) | 97 (63.8) | −3.3 (−14.0 to 7.5) |
0.07 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 84 (48.3) | 175 (43.3) | 5.0 (−3.8 to 13.7) |
−0.10 | 73 (48.0) | 80 (52.6) | −4.6 (−15.6 to 6.6) |
0.09 |
| Prior ischemic stroke | 34 (19.5) | 95 (23.5) | −4.0 (−10.8 to 3.6) |
0.10 | 32 (21.1) | 33 (21.7) | −0.7 (−9.9 to 8.6) |
0.01 |
| Antiplatelet use | 32 (18.4) | 89 (22.0) | −3.6 (−10.3 to 3.8) |
0.09 | 28 (18.4) | 20 (13.2) | 5.3 (−3.0 to 13.5) |
−0.14 |
| Coronary artery disease | 28 (16.1) | 60 (14.9) | 1.2 (−4.8 to 8.2) |
−0.03 | 27 (17.8) | 19 (12.5) | 5.3 (−2.9 to 13.4) |
−0.15 |
| On-admission status, median (IQR) | ||||||||
| Glasgow Coma Scaled | 13 (6 to 15) |
15 (13 to 15) |
−1.9 (−2.7 to −1.2) |
−0.45 | 14 (7 to 15) |
14 (5 to 15) |
0.1 (1.0 to 1.2) |
0.02 |
| ICH scoree | 2 (1 to 3) |
2 (1 to 3) |
0.4 (0.2 to 0.6) |
0.35 | 2 (1 to 3) |
2 (1 to 3) |
0.0 (−0.3 to 0.3) |
0.02 |
| Imaging | ||||||||
| ICH volume, median (IQR), cm3f | 21.8 (14.0 to 30.6) |
7.1 (3.3 to 16.1) |
11.6 (9.4 to 13.8) |
0.86 | 20.5 (13.4 to 28.4) |
18.8 (8.2 to 28.1) |
1.7 (−1.3 to 4.7) |
0.13 |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage, No. (%) | 87 (50.0) | 151 (37.4) | 12.6 (3.8 to 21.3) |
−0.26 | 74 (48.7) | 67 (44.1) | 4.6 (−6.5 to 15.6) |
−0.09 |
| IVH volume, median (IQR), cm3g | 0.2 (0.0 to 4.9) |
0.0 (0.0 to 1.0) |
0.9 (−2.5 to 0.7) |
0.10 | 0.08 (0.0 to 4.0) |
0.0 (0.0 to 3.9) |
1.3 (−0.4 to 2.4) |
0.12 |
| Graeb Score, median (IQR)h | 0 (0 to 3) |
0 (0 to 2) |
0.9 (0.3 to 1.6) |
0.39 | 0 (0 to 3) |
0 (0 to 2) |
0.6 (−0.4 to 1.2) |
0.19 |
| Time windows and other treatment | ||||||||
| Onset to admission, median (IQR), min | 215 (119 to 352) |
203 (90 to 320) |
−107 (−249 to 34) |
−0.13 | 231 (120 to 360) |
200 (90 to 321) |
−60 (−202 to 82) |
−0.10 |
| Admission to surgery, median (IQR), min | 338 (187 to 701) |
338 (193 to 710) |
||||||
| Admission during “on” hours, No. (%)i | 116 (66.7) | 239 (59.2) | 7.5 (−1.2 to 15.7) |
−0.16 | 100 (65.8) | 94 (61.8) | 3.9 (−6.8 to 14.6) |
−0.08 |
| Received reversal treatment, No. (%)j | 100 (57.5) | 152 (37.6) | 19.8 (11.0 to 28.3) |
−0.40 | 87 (57.2) | 86 (56.6) | 0.7 (−10.4 to 11.6) |
−0.01 |
| Early care limitations (<24 h), No. (%)k | 3 (1.7) | 35 (8.7) | −6.9 (−10.3 to −2.9) |
0.28 | ||||
| Withdrawal of care (>24 h), No. (%)k | 16 (9.2) | 25 (6.2) | 3.0 (−1.4 to 8.6) |
−0.06 | 11 (7.2) | 14 (9.2) | −2.0 (−8.4 to 4.4) |
0.04 |
Abbreviations: ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; IQR, interquartile range; IVH, intraventricular hemorrhage; SMD, standardized mean differences.
Surgical hematoma evacuation was performed in 144 of 174 (82.8%) patients using decompressive craniectomy, in 26 of 174 (14.9%) using craniotomy, and in 4 of 174 (2.3%) using minimal invasive techniques.
Absolute differences are provided in percent for frequency data and for scales or continuous variables as mean differences of the according measurement unit (negative values indicate a decreased frequency or unit of measurement from the reference [ie, conservatively treated patients]).
SMDs are given to compare the difference between patients with surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment as well as before and after the propensity score matching procedure.
Glasgow Coma Scale (range: 3, comatose to 15, alert).
ICH score (range: 0, highest chance of survival to 6, lowest chance of survival).
ICH volume recorded on last imaging immediately prior to surgery or in conservatively treated patients, baseline imaging or follow-up imaging, if acquired within 24 hours.
Measured in cubic centimeters for patients of the ERICH study only.
Graeb Score (extent of intraventricular involvement: 0, no blood to 12, tamponade of all ventricles) measured for patients of all other studies.
On-hour admission indicates weekdays from 7:00 am to 6:00 pm.24
Reversal treatment was scored when patients received any dose or combination of fresh frozen plasma, prothrombin complex concentrates, and activated Factor VII to restore coagulation.
Indicates a subcategory of patients who received care limitations—comfort care measures. Early care limitations were initiated within 24 hours after admission. For withdrawal of care, see Sembill et al.13
The crude distribution of functional outcome showed a significantly reduced proportion of favorable functional outcome in patients with surgical hematoma evacuation when compared at 3 months (mRS of 0-3, 48/174 patients [27.6%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (220/404 patients [54.5%]; OR, 0.32 [95% CI, 0.22 to 0.47]; P < .001; RD, −26.9% [95% CI, −34.6% to −18.3%]), and also when compared at 12 months (mRS of 0-3, 48/174 patients with surgical hematoma evacuation [27.6%] vs 217/404 patients who received conservative treatment [53.7%]; OR, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.22 to 0.48]; P < .001; RD, −26.1% [95% CI, −33.9% to −17.5%]), but it showed no significant association with survival at 3 months (136/174 patients with surgical hematoma evacuation [79.2%] vs 317/404 patients who received conservative treatment [78.5%]; OR, 1.02 [95% CI, 0.66 to 1.57]; P = .93; RD, −0.3% [95% CI, −8.0% to 6.7%]), or at 12 months (122/174 patients with surgical hematoma evacuation [70.1%] vs 302/404 patients who received conservative treatment [74.8%]; OR, 1.26 [95% CI, 0.85 to 1.87]; P = .25; RD, −4.6% [95% CI, −12.8% to 3.1%]) (eFigure 5 in the Supplement). Propensity score matching resulted in a balanced cohort (n = 304; Table; eFigure 6 in the Supplement) used for all further exploratory subgroup analyses, and sensitivity analyses of patients who were excluded (early care limitations, propensity-score-matching, and surgical time windows) showed no significant interaction between treatment and outcomes (eTables 5-7 in the Supplement).
Analyses of the Primary Outcome
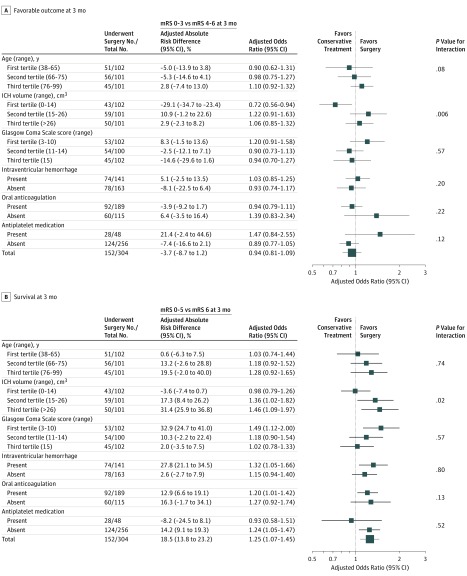
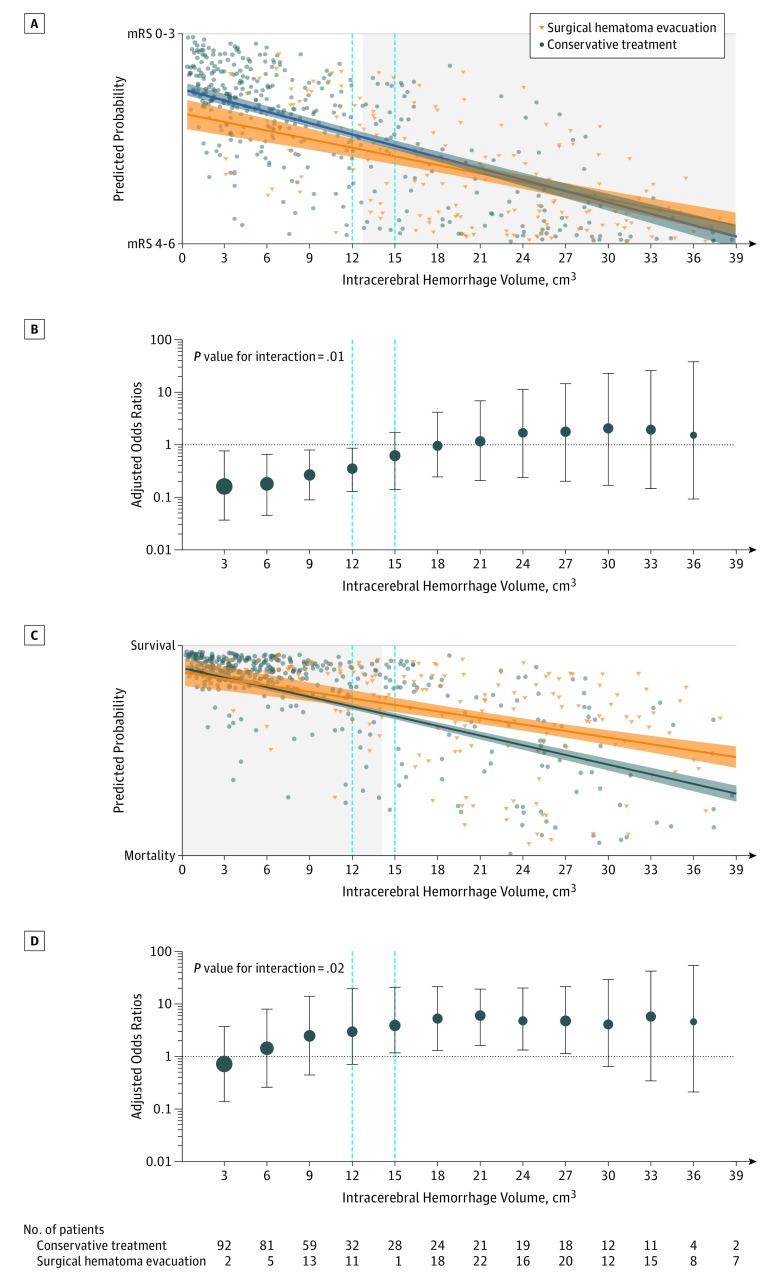
The proportion of patients who achieved a favorable functional status at 3 months was not significantly different among patients who received surgical hematoma evacuation (47/152 [30.9%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (54/152 patients [35.5%]; P = .39; adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 0.94 [95% CI, 0.81 to 1.09]; P = .43; ARD, −3.7% [95% CI, −8.7% to 1.2%]; Figure 2, Figure 3A; eTable 8 in the Supplement). Exploratory subgroup analyses showed a decreased odds to achieve favorable functional outcome at 3 months in patients with cerebellar ICH volumes of less than 14.1 cm3 who had undergone surgical hematoma evacuation (15/43 patients [34.9%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (36/59 patients [61.0%]; P = .01; AOR, 0.72 [95% CI, 0.56 to 0.94]; P = .01; ARD, −29.1% [95% CI, −34.7% to −23.4%]; P value for interaction, .006; Figure 3A; eTable 8 in the Supplement). To specify ICH volume cutoff values, adjusted predicted probabilities showed significant associations of surgical hematoma evacuation performed in ICH volumes of less than or equal to 12 cm3 with reduced favorable functional outcome (Figure 4A), which were validated using observed data estimates (11/36 patients [30.6%] vs 33/53 patients [62.3%]; P = .003; AOR, 0.78 [95% CI, 0.64 to 0.94]; P = .01; ARD, −34.7% [95% CI, −38.8% to −30.6%); P value for interaction, .01; Figure 4B).
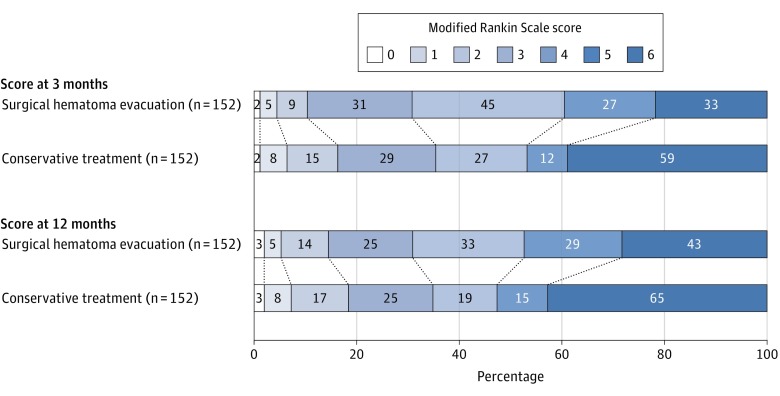
Figure 2. Distribution of Modified Rankin Scale Scores at 3 and 12 Months for the Propensity Score–Matched Cohort.
The modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores range from 0 (indicating no deficit) to 6 (death). Each cell corresponds with a score on the mRS; the width of the cell indicates the proportion of patients with equivalent scores, and the number of patients is shown within the cell. The diagonal line between the 2 study groups indicates the comparison of outcome in each severity stratum. Statistical analyses compared scores (mRS 0-3 vs 4-6 and mRS 0-5 vs 6) according to treatment exposure with corresponding significance level (χ2 model). Favorable outcome was defined as a score of 0 to 3 (3 indicates being able to walk independently with a walker or a cane).
Figure 3. Exploratory Subgroup Analyses of Primary and Secondary Outcomes According to Treatment Exposure of the Propensity Score–Matched Cohort.
Panel A shows the primary outcome (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 0-3 vs 4-6); panel B shows the secondary outcome (mRS 0-5 vs 6) using logistic regressions by a generalized estimating equations model, as described in the Statistical Analysis section. Exploratory subgroup analyses of the propensity score matched–cohort were displayed as forest plots using as dependent variables primary and secondary outcomes without the subgroup-defining variable on categorized regression models. Heterogeneity was considered significant for P values of less than .5 and interactions of exploratory subgroup analyses were tested using the subgroup-defining variable (variable × intervention) and conservative treatment as reference. Adjusted results and unadjusted frequency distributions and multiplicity correction are available online (eTables 8-11 in the Supplement). mRS score range: 0 (no deficit) to 6 (death).
Figure 4. Independent Associations of the Intervention With ICH Volumes.
Panels A and C: graphical linear regression applied on predicted probability values to achieve the primary outcome (panel A, modified Rankin Scale [mRS 0-3]) and the secondary outcome (survival) (panel C, mRS 0-5) derived from an adjusted logistic regression (generalized estimating equations) model. Values were calculated for each individual patient of the entire cohort using the same adjustments and interaction terms as described. Adjustments: age, Glasgow Coma Scale, intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) volume, intraventricular hemorrhage, interaction terms (study × intervention, on-hour admission × intervention, reversal treatment × intervention), and the coefficient of variation for ICH volume measurements. Intersections of the 95% CIs of graphical linear regression analysis (surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment) were used to identify cutoff values. Panels B and D: validation of predicted associations based on observed data points graphically depicted as adjusted odds ratio (OR) estimates for surgical hematoma evacuation vs conservative treatment with the primary outcome (panel B, mRS 0-3) and the secondary outcome (survival) panel D, mRS 0-5). Adjusted OR estimates were calculated within specific volume frames (frames = sliding windows, using a variable volume range determined by the median of this window sliding upwards at 1-cm3 steps) corrected for measurement error by the coefficient of variation and for overestimation by the method of moving averages. Mean estimates are shown with 95% CIs for volume intervals of 3 cm3. Circle size indicates the proportional number of patients included within regression models. An identical procedure was used for the secondary outcome (survival at 3 months).
Analyses of Secondary Outcomes
The proportion of patients who survived at 3 months was significantly increased among patients who received surgical hematoma evacuation (119/152 [78.3%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (93/152 [61.2%]; P = .001; AOR, 1.25 [95% CI, 1.07 to 1.45]; P = .005; ARD, 18.5% [95% CI, 13.8% to 23.2%]; Figure 2 and Figure 3B; eTable 9 in the Supplement). The proportion of patients who achieved a favorable functional status at 12 months was not significantly different among patients who received surgical hematoma evacuation (47/152 [30.9%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (53/152 [34.9%]; P = .46; AOR, 0.93 [95% CI, 0.82 to 1.07]; P = .30; ARD, −4.2% [95% CI, −9.6% to 1.3%]; Figure 2; eTable 10 in the Supplement).
The proportion of patients who survived at 12 months was significantly increased among patients who received surgical hematoma evacuation (109/152 [71.7%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (87/152 [57.2%]; P = .008; AOR, 1.21 [95% CI, 1.03 to 1.42]; P = .02; ARD, 17.0% [95% CI, 11.5% to 22.6%]; Figure 2; eTable 11 in the Supplement).
Exploratory subgroup analyses for survival at 3 months showed increased odds in patients who received surgical hematoma evacuation within and above the second tertile at ICH volumes of 14.1 cm3 or greater (50/59 [84.7%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (26/42 [61.9%]); P = .009; AOR, 1.36 [95% CI, 1.02 to 1.82]; P = .04; ARD, 17.3% [95% CI, 8.4% to 26.2%]; P value for interaction, .02; Figure 3B; eTable 9 in the Supplement). Exploratory subgroup analyses for outcomes at 12 months are provided in eTables 10 and 11 in the Supplement. To specify ICH volume cutoff values for survival at 3 months, adjusted predicted probabilities showed significant associations of surgical hematoma evacuation performed in ICH volumes of 15 cm3 or greater (Figure 4C) with increased survival, which was validated using observed data estimates (76/102 [74.5%]) vs those who received conservative treatment (41/91 [45.1%]; P < .001; AOR, 1.29 [95% CI, 1.05 to 1.58]; P = .02; ARD, 28.2% [95% CI, 24.6% to 31.8%]; P value for interaction, .02; Figure 4D).
Discussion
In the present study, surgical hematoma evacuation in patients with cerebellar ICH was not associated with improved functional outcome. Current management guidelines developed in Europe and the United States recommend surgical hematoma evacuation for patients with cerebellar ICH who present with hematoma diameter of greater than 3 cm.9,10 As confirmed by the present aggregate data meta-analysis, the observational studies originally supporting adoption of this hematoma size threshold to guide cerebellar ICH management were limited by small sample sizes and confounding due to severity and indication biases.4,5,6,7 However, clinicians have long abided by these management recommendations, reflecting empirical observations linking increased mortality rates with conservative (ie, nonsurgical) treatment in patients with larger hemorrhages.2 A cerebellar hematoma with 3-cm diameter would translate to a volume of approximately 13.5 cm3 (applying the established ABC/2 bedside technique for volume estimation),14 a threshold which closely aligns with the proposed 12 to 15 cm3 cutoff range identified here.
Study results provide additional guidance in managing treatment for patients with cerebellar ICH. Survival benefits after surgical hematoma evacuation were driven by patients with larger hematoma volumes, however not translating into concomitant improvement in postsurgical functional outcome. The latter observation contrasts with results from published meta-analyses of decompressive surgery trials for treatment of malignant middle cerebral artery infarction, which in addition to demonstrating reduced mortality risk, also reported improved functional outcomes following surgical intervention.37,38 A variety of mechanisms may account for this discrepancy. The cerebellum displays unique neuroanatomical properties, mainly reflected in the complex cerebro-, spino-, and vestibulo-cerebellar connections involved in the generation of network-induced voluntary movements, their coordination, balance, and accuracy.39 Thus, cerebellar injury may lead to neurological deficits accounted for by more complex and widespread disruption of neuroanatomical pathways, eventually compensated differently as compared with supratentorial stroke.
Accurate determination of hematoma volume mirrors a crucial step in care delivery for patients with cerebellar ICH. The identified associations of ICH volumes with clinical outcomes may facilitate clinical decision-making and communication with patients and their families in regard to expected benefits from surgical treatment. Reported data will also provide valuable effect-size estimates for future studies of cerebellar ICH.9 The potential benefits of surgical hematoma evacuation, in terms of functional outcome improvement, appear to be limited at best.4,7,8 A future pragmatic randomized clinical trial could involve those patients likely to benefit from operative interventions, as determined in this study after exploratory subgroup analyses. Specifically, while age and prior antithrombotic treatment should not necessarily represent exclusion criteria, patients who demonstrate clinical deterioration, hematoma volumes between 15 and 30 cm3, and evidence of intraventricular involvement on computed tomographic imaging should be randomized to receive either surgical or conservative treatment, ultimately to include intraventricular fibrinolysis.6,25
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, this was a retrospective study with lack of randomization, blinding, and measure of surgical success. Second, propensity score matching to account for confounding may not have completely compensated for apparent treatment bias.31 This approach was limited by lack of conservatively treated controls available for matching with (usually more severely affected) patients who underwent surgical hematoma evacuation. Mildly impaired, conservatively treated patients with smaller hematomas also proved difficult to match with similar patients who underwent surgical treatment. Thus, this study focused primarily on patients presenting with intermediate-sized hematomas, for whom optimal management remains controversial. Third, this study was limited by lack of standardization in regard to decision-making to opt for surgical hematoma evacuation or hydrocephalus treatment. While quantitative serial assessments of neurological status and standardized follow-up imaging to predict clinical decompensation (eg, basal cistern or brainstem compression) may have further enhanced analyses, they would have also required application of prospectively implemented and protocolized study procedures. Therefore, in this study, imaging measures of interest were restricted to easily quantifiable variables (ICH volume and ventricular involvement) less prone to interrater variability. Nonetheless, absent standardized volumetric assessment of hematoma volumes in all patients, approximate calculated ICH volumes may have resulted in overestimates or underestimates. Fourth, despite the relatively large number of participants in this study, sample size for subgroup analyses and for comparison of different surgical strategies may still be too small to detect relevant differences in outcomes. In addition, outcome was scored according to individual study protocols and may have been influenced by variances in time point estimation or assessment methodology.
Conclusions
Among patients with cerebellar ICH, surgical hematoma evacuation, compared with conservative treatment, was not associated with improved functional outcome. Given the null primary outcome, investigation is necessary to establish whether there are differing associations based on hematoma volume.
eMethods. Systematic Review and Statistical Analysis Plan
eTable 1. Overview of Studies Eligible for Aggregate Data Meta-analysis
eTable 2. Baseline Characteristics of the Four Participating Studies and the Three Studies Not Participating
eTable 3. Study Description of the Four Participating Studies
eTable 4. Risk of Bias Assessment for the Study Population Across Investigated Outcomes
eTable 5. Sensitivity Analyses of Excluded vs Included Patients
eTable 6. Interactions of Excluded Patients With Outcomes According to Treatment Exposure
eTable 7. Sensitivity Analyses for Associations of Surgical Time-Windows With Outcomes
eTable 8. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With mRS 0-3 at 3 Months
eTable 9. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With Survival at 3 Months
eTable 10. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With mRS 0-3 at 12 Months
eTable 11. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With Survival at 12 Months
eFigure 1. Aggregate Data Meta-Analyses and Bias Assessment of Existing Studies
eFigure 2. Agreement of Volume Measurement for the Central Imaging Cores (Bland-Altman)
eFigure 3. Risk of Bias Assessment Across Participating Studies Using Cochrane Collaboration Domains and ROBINS-I Tool
eFigure 4. Inter-Study Variance of Treatment Effects Across Participating Studies
eFigure 5. Crude Distribution of Functional Outcome at 3 and 12 Months
eFigure 6. Details Before and After Propensity Score–Matching Procedure
eReferences.
References
- 1.Krishnamurthi RV, Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, et al. ; Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, Risk Factors Study 2010 (GBD 2010); GBD Stroke Experts Group . Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob Health. 2013;1(5):e259-e281. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70089-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Datar S, Rabinstein AA. Cerebellar hemorrhage. Neurol Clin. 2014;32(4):993-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2014.07.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nichols M, Townsend N, Scarborough P, Rayner M. Cardiovascular disease in Europe: epidemiological update. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(39):3028-3034. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht356 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Da Pian R, Bazzan A, Pasqualin A. Surgical versus medical treatment of spontaneous posterior fossa haematomas: a cooperative study on 205 cases. Neurol Res. 1984;6(3):145-151. doi: 10.1080/01616412.1984.11739680 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dolderer S, Kallenberg K, Aschoff A, Schwab S, Schwarz S. Long-term outcome after spontaneous cerebellar haemorrhage. Eur Neurol. 2004;52(2):112-119. doi: 10.1159/000080268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang J, Wang L, Xiong Z, et al. . A treatment option for severe cerebellar hemorrhage with ventricular extension in elderly patients: intraventricular fibrinolysis. J Neurol. 2014;261(2):324-329. doi: 10.1007/s00415-013-7198-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hackenberg KA, Unterberg AW, Jung CS, Bösel J, Schönenberger S, Zweckberger K. Does suboccipital decompression and evacuation of intraparenchymal hematoma improve neurological outcome in patients with spontaneous cerebellar hemorrhage? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;155:22-29. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2017.01.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Donauer E, Loew F, Faubert C, Alesch F, Schaan M. Prognostic factors in the treatment of cerebellar haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1994;131(1-2):59-66. doi: 10.1007/BF01401454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hemphill JC III, Greenberg SM, Anderson CS, et al. ; American Heart Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; Council on Clinical Cardiology . Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2015;46(7):2032-2060. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Steiner T, Al-Shahi Salman R, Ntaios G.. The European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines. Int J Stroke. 2014;9(7):838-839. doi: 10.1111/ijs.12369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Loon J, Van Calenbergh F, Goffin J, Plets C. Controversies in the management of spontaneous cerebellar haemorrhage: a consecutive series of 49 cases and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1993;122(3-4):187-193. doi: 10.1007/BF01405527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Stewart LA, Clarke M, Rovers M, et al. ; PRISMA-IPD Development Group . Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analyses of individual participant data: the PRISMA-IPD Statement. JAMA. 2015;313(16):1657-1665. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.3656 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sembill JA, Gerner ST, Volbers B, et al. . Severity assessment in maximally treated ICH patients: the max-ICH score. Neurology. 2017;89(5):423-431. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kothari RU, Brott T, Broderick JP, et al. . The ABCs of measuring intracerebral hemorrhage volumes. Stroke. 1996;27(8):1304-1305. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.27.8.1304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuramatsu JB, Gerner ST, Schellinger PD, et al. . Anticoagulant reversal, blood pressure levels, and anticoagulant resumption in patients with anticoagulation-related intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA. 2015;313(8):824-836. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.0846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Medical School ClinicalTrials.gov website. German-wide multicenter analysis of oral anticoagulation-associated intracerebral hemorrhage (RETRACE). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01829581?term=NCT01829581&rank=1. Accessed June 6, 2019.
- 17.Kuramatsu JB, Sembill JA, Gerner ST, et al. . Management of therapeutic anticoagulation in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage and mechanical heart valves. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(19):1709-1723. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gerner ST, Kuramatsu JB, Sembill JA, et al. ; RETRACE II (German-Wide Multicenter Analysis of Oral Anticoagulation-Associated Intracerebral Hemorrhage II) Investigators . Association of prothrombin complex concentrate administration and hematoma enlargement in non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant-related intracerebral hemorrhage. Ann Neurol. 2018;83(1):186-196. doi: 10.1002/ana.25134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Medical School ClinicalTrials.gov website. Multicenter analysis of oral anticoagulant-associated ICH—Part Two (RETRACE-II). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03093233?term=NCT03093233&rank=1. Accessed June 6, 2019.
- 20.University of Erlangen-Nuremberg Medical School ClinicalTrials.gov website. Longitudinal cohort study on ICH Care (UKER-ICH). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03183167?term=NCT03183167&rank=1. Accessed June 6, 2019.
- 21.Sprügel MI, Kuramatsu JB, Gerner ST, et al. . Antiplatelet therapy in primary spontaneous and oral anticoagulation-associated intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2018;49(11):2621-2629. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Woo D, Rosand J, Kidwell C, et al. . The Ethnic/racial variations of intracerebral hemorrhage (ERICH) study protocol. Stroke. 2013;44(10):e120-e125. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.002332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Woo D; University of Cincinnati ClinicalTrials.gov website. Ethnic/racial variations of intracerebral hemorrhage (ERICH). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01202864?term=NCT01202864&rank=1. Accessed: June 6, 2019.
- 24.Reeves MJ, Smith E, Fonarow G, Hernandez A, Pan W, Schwamm LH; GWTG-Stroke Steering Committee & Investigators . Off-hour admission and in-hospital stroke case fatality in the get with the guidelines-stroke program. Stroke. 2009;40(2):569-576. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.519355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hanley DF, Lane K, McBee N, et al. ; CLEAR III Investigators . Thrombolytic removal of intraventricular haemorrhage in treatment of severe stroke: results of the randomised, multicentre, multiregion, placebo-controlled CLEAR III trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10069):603-611. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32410-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Qureshi AI, Palesch YY, Barsan WG, et al. ; ATACH-2 Trial Investigators and the Neurological Emergency Treatment Trials Network . Intensive blood-pressure lowering in patients with acute cerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(11):1033-1043. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, et al. . ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:i4919. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7(3):177-188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ioannidis JP. Interpretation of tests of heterogeneity and bias in meta-analysis. J Eval Clin Pract. 2008;14(5):951-957. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2008.00986.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A. GRADE handbook for grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. Updated October 2013. The GRADE Working Group. gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html. Accessed January 23, 2019.
- 31.Leisman DE. Ten pearls and pitfalls of propensity scores in critical care research: a guide for clinicians and researchers. Crit Care Med. 2019;47(2):176-185. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003567 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Saver JL, Goyal M, van der Lugt A, et al. ; HERMES Collaborators . Time to treatment with endovascular thrombectomy and outcomes from ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016;316(12):1279-1288. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.13647 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Inohara T, Xian Y, Liang L, et al. . Association of intracerebral hemorrhage among patients taking non-vitamin k antagonist vs vitamin k antagonist oral anticoagulants with in-hospital mortality. JAMA. 2018;319(5):463-473. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.21917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Askie LM, Darlow BA, Finer N, et al. ; Neonatal Oxygenation Prospective Meta-analysis (NeOProM) Collaboration . Association between oxygen saturation targeting and death or disability in extremely preterm infants in the neonatal oxygenation prospective meta-analysis collaboration. JAMA. 2018;319(21):2190-2201. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.5725 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Burke DL, Ensor J, Riley RD. Meta-analysis using individual participant data: one-stage and two-stage approaches, and why they may differ. Stat Med. 2017;36(5):855-875. doi: 10.1002/sim.7141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chevret S, Seaman S, Resche-Rigon M. Multiple imputation: a mature approach to dealing with missing data. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41(2):348-350. doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3624-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vahedi K, Hofmeijer J, Juettler E, et al. ; DECIMAL, DESTINY, and HAMLET investigators . Early decompressive surgery in malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery: a pooled analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6(3):215-222. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70036-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hofmeijer J, Kappelle LJ, Algra A, Amelink GJ, van Gijn J, van der Worp HB; HAMLET investigators . Surgical decompression for space-occupying cerebral infarction (the Hemicraniectomy After Middle Cerebral Artery infarction with Life-threatening Edema Trial [HAMLET]): a multicentre, open, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8(4):326-333. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70047-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Apps R, Garwicz M. Anatomical and physiological foundations of cerebellar information processing. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6(4):297-311. doi: 10.1038/nrn1646 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eMethods. Systematic Review and Statistical Analysis Plan
eTable 1. Overview of Studies Eligible for Aggregate Data Meta-analysis
eTable 2. Baseline Characteristics of the Four Participating Studies and the Three Studies Not Participating
eTable 3. Study Description of the Four Participating Studies
eTable 4. Risk of Bias Assessment for the Study Population Across Investigated Outcomes
eTable 5. Sensitivity Analyses of Excluded vs Included Patients
eTable 6. Interactions of Excluded Patients With Outcomes According to Treatment Exposure
eTable 7. Sensitivity Analyses for Associations of Surgical Time-Windows With Outcomes
eTable 8. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With mRS 0-3 at 3 Months
eTable 9. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With Survival at 3 Months
eTable 10. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With mRS 0-3 at 12 Months
eTable 11. Unadjusted and Adjusted Associations of Surgical Hematoma Evacuation vs Conservative Treatment With Survival at 12 Months
eFigure 1. Aggregate Data Meta-Analyses and Bias Assessment of Existing Studies
eFigure 2. Agreement of Volume Measurement for the Central Imaging Cores (Bland-Altman)
eFigure 3. Risk of Bias Assessment Across Participating Studies Using Cochrane Collaboration Domains and ROBINS-I Tool
eFigure 4. Inter-Study Variance of Treatment Effects Across Participating Studies
eFigure 5. Crude Distribution of Functional Outcome at 3 and 12 Months
eFigure 6. Details Before and After Propensity Score–Matching Procedure
eReferences.