A 14-year-old female presented with complaint of nonprogressive whitish opacity over cornea of right eye since birth. Patient's corrected distant visual acuity of right and left eye was 2/60 and 6/9, respectively. Slit lamp examination revealed nebulomacular corneal opacity of 4 mm × 7 mm size inferonasally in right eye just approaching central and paracentral region [Fig. 1]. Localized thinning of the posterior corneal layer [Fig. 2] and sclerization of the limbus was also noted. Left eye was normal apart from few peripheral anterior synechiae. In gonioscopy, prominent iris processes and multiple peripheral anterior synechiae were seen in both eyes [Fig. 3]. General and systemic examination did not reveal any other abnormality. Cycloplegic refraction found refractive error of - 12.0 D sphere and - 3.0 D cylinder @150° in right eye and +3.50 D sphere and +1.50 D cylinder @20° in left eye. We found localized defect in the posterior layers of cornea of right eye in anterior segment optical coherence tomography (OCT) [Fig. 4]. Based on these findings, we confirmed the diagnosis of peripheral type I Peters anomaly along with poor vision in right eye and goniodysgenesis in left eye.
Figure 1.
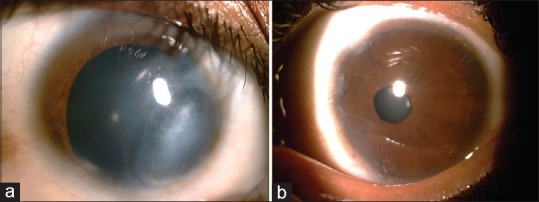
Diffuse slit lamp images of cornea. (a) Right eye corneal opacity inferonasally, image taken after dilatation. (b) Multiple peripheral anterior synechiae in left eye
Figure 2.
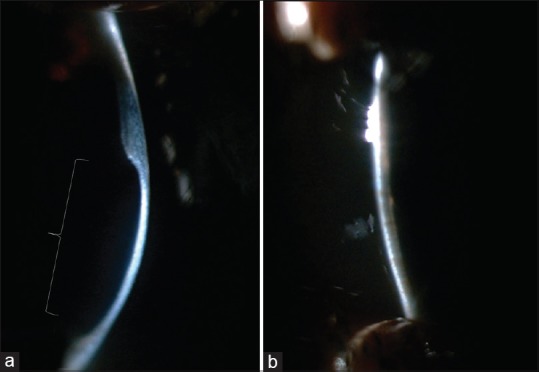
Focal illumination images of cornea. (a) Localized scarring with thinning in right eye. (b) Normal view of left ey
Figure 3.
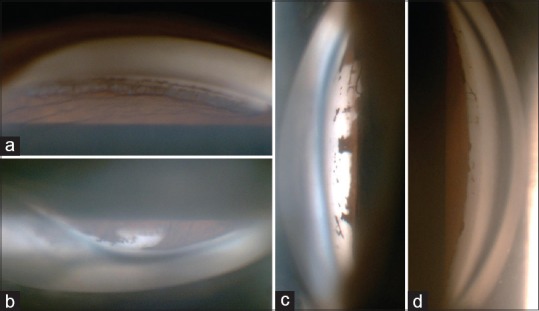
Gonioscopic images showing multiple peripheral anterior synechiae with prominent iris processes and dysgenesis in right eye (a and b) and in left eye (c and d)
Figure 4.
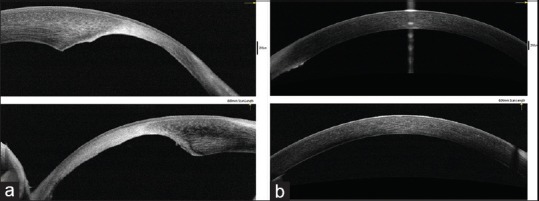
Anterior segment OCT images. (a) Localized defects in the posterior corneal layers with scarring in right eye. (b) Normal corneal image in left eye
Peters’ anomaly is a mesodermal anterior segment dysgenesis characterized by a central corneal leukoma, iridocorneal adhesions, and abnormalities of the posterior corneal stroma, Descemet's membrane, corneal endothelium, lens, and anterior chamber.[1] Peters’ anomaly is classified in two types: ‘Type I’ features corneal opacity and iridocorneal synechiae, ‘type II’ is characterized by central corneal opacity and a cataractous lens that may adhere to the cornea. ‘Peters’ plus’ is associated with systemic anomalies like short stature, developmental delay, cleft lip or palate, heart disease, ear anomalies, genitourinary defects, and spinal defects.[2] Most cases are sporadic, although autosomal dominant and recessive forms have been reported. Peters’ anomaly may be caused by mutations in the PAX6, PITX2, FOXC1, FOXE3, CYPIB1, or B3GALTL genes.[3]
Anterior segment OCT has now emerged as an important noncontact, noninvasive scanning tool to clarify diagnosis of anterior segment disorders.[4] Cauduro et al. retrospectively studied 26 eyes of 19 pediatric patients presenting with anterior segment pathology with OCT. In their study, mesodermal dysgenesis (Peters’ anomaly in two eyes) was demonstrated as increased reflectivity of the central cornea (leukoma) associated with local indentation (malformation) of the posterior surface (Descemet's membrane defect), with overall increased stromal reflectivity and thickness.[5] We confirmed the diagnosis of our case based on similar findings in OCT.
To the best of our knowledge, peripheral corneal involvement was unique in this case. If properly diagnosed and treated at an earlier age, this patient would have gained useful vision with only proper refractive error correction.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Peters A. Über angeborene defektbildung der descemetschen membran. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1906;44:27–40. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Traboulsi EI, Maumenee IH. Peters’ anomaly and associated congenital malformations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1992;110:1739–42. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1992.01080240079035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Reis LM, Semina EV. Genetics of anterior segment dysgenesis disorders. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2001;22:314–24. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0b013e328349412b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fukuda S, Kawana K, Yasuno Y, Oshika T. Anterior ocular biometry using 3-dimensional optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2009;116:882–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cauduro R, Ferraz C, Morales M, Garcia P, Lopes Y, Souza P, et al. Application of anterior segment optical coherence tomography in pediatric ophthalmology. J Ophthalmol. 2012;2012:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2012/313120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


