Abstract
Previous studies have established that strain 68–1-derived Rhesus cytomegalovirus (RhCMV) vectors expressing simian immune deficiency virus (SIV) proteins (RhCMV/SIV) are able to elicit and maintain cellular immune responses that provide protection against mucosal challenge with highly pathogenic SIV in rhesus monkeys (RM). However, these efficacious RhCMV/SIV vectors were replication- and spread-competent, and therefore have the potential to cause disease in immune-compromised subjects. To develop a safer CMV-based vaccine for clinical use, we attenuated 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors by deletion of the Rh110 gene encoding the pp71 tegument protein (ΔRh110), allowing for suppression of lytic gene expression. ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vectors are highly spread-deficient in vivo (~1000-fold compared to the parent vector) yet are still able to superinfect RhCMV+ RM and generate high frequency effector-memory-biased T cell responses. Here, we demonstrate that ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV expressing homologous or heterologous SIV antigens are highly efficacious against intravaginal (IVag) SIVmac239 challenge, providing control and progressive clearance of SIV infection in 59% of vaccinated RM. Moreover, among 12 ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV-vaccinated RM that controlled and progressively cleared an initial SIV challenge, 9 were able to stringently control a second SIV challenge ~3 years after last vaccination, demonstrating the durability of this vaccine. Thus, ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vectors have a safety and efficacy profile that warrants adaptation and clinical evaluation of corresponding HCMV vectors as a prophylactic HIV/AIDS vaccine.
Summary:
Highly attenuated pp71-deleted RhCMV/SIV vectors elicit immune responses that stringently protect 59% of vaccinated monkeys from SIV challenge.
INTRODUCTION
Although the advent of antiretroviral therapy and other preventative interventions have greatly reduced the number of new infections and AIDS-related deaths from their peak incidence, epidemiologic modelling suggests that an efficacious HIV vaccine will still be necessary to reduce the annual incidence of new HIV infections to a degree commensurate with ending the epidemic (1,2). However, despite many decades of concerted effort, vaccine platforms capable of eliciting protective immune responses against HIV or its nonhuman primate counterpart SIV are few, as these viruses are highly immune-evasive and either lack susceptibility to natural immunity, or rapidly escape immune responses that are initially effective (3). We hypothesized a number of years ago that immune control of these viruses might be possible if infection could be immediately intercepted at portals of viral entry and sites of early spread by pre-established, effector-differentiated CD8+ T cell responses, either in place in these sites (resident memory cells) or rapidly recruited from the blood (circulating effector-memory cells), without the need for the “too little, too late” process of anamnestic memory T cell expansion, effector differentiation and trafficking to sites of infection (4). Since human CMV (HCMV) and RhCMV naturally elicit and maintain effector-memory T cell responses having these properties, we investigated the possibility of exploiting CMV as a vaccine vector, using RhCMV/SIV vectors based on the 68–1 RhCMV strain in the RM-SIV model as proof-of-principle (5).
In a series of reports, we demonstrated that a 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vaccine expressing SIV Gag, Rev/Nef/Tat, Pol and Env was able to super-infect naturally RhCMV-infected RM and elicit and indefinitely maintain SIV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses that closely mimicked the characteristics of responses to RhCMV itself: high frequency, widely distributed in lymphoid and non-lymphoid sites and effector-differentiated (highly effector-memory-biased) (6–8). Insert-specific antibody (Ab) responses were absent in most vaccinated RM, and unexpectedly, the CD8+ T cell responses elicited by these vectors manifested unconventional epitope targeting characterized by extraordinary breadth and response restriction by either major histocompatibility complex II (MHC-II) or MHC-E, but not MHC-Ia, an immunologic feature that was found to be related to genetic changes in the 68–1 RhCMV strain associated with adaptation to in vitro fibroblast culture (9,10). Although the significance of this unusual CD8+ T cell antigen (Ag) recognition remains an area of active investigation, the hypothesis that pre-established circulating and tissue-based, effector-differentiated cellular immune responses might be more efficacious than conventional memory responses is supported by multiple SIV challenge studies showing that over half of 68–1 RhCMV/SIV-vaccinated RM manifested an early and complete control of SIVmac239 infection after mucosal challenge. Protected RM were found to be definitively infected after challenge, but viral spread appeared to be completely arrested prior to establishment of a permanent viral reservoir, and the infection was progressively cleared over the ensuing months, until protected RM became indistinguishable by both virologic and immunologic criteria from animals that were never challenged (8,11).
This “control and clear” vaccine effect against highly pathogenic SIV has not been reported for any other vaccine modality, and if translatable to humans, has the potential to contribute to control of the HIV epidemic, either as a stand-alone vaccine or in combination with Ab-targeted vaccines (12). However, translating CMV-based vectors as a prophylactic vaccine in humans requires careful consideration of safety. Although the vast majority of HCMV infections in people and RhCMV infections in monkeys are clinically inapparent, these viruses have the capacity to cause serious disease in settings of immune deficiency, with maternal to fetal transmission being of particular concern (13). 68–1 RhCMV, the parent strain of vectors used in the above-described efficacy studies, lacks subunits of a pentameric glycoprotein complex which facilitate viral entry into most non-fibroblast cells (14,15) and, presumably as a result of this restricted tropism, demonstrates reduced viremia, shedding and horizontal transmission compared to wildtype (WT) RhCMV (16,17). Nevertheless, 68–1 RhCMV retains the ability to disseminate in infected RM, transmit from one monkey to another, and has the potential to cause disease (18–20). “68–1-like” HCMV vectors thus still carry some potential risk for vaccine-mediated disease in otherwise healthy populations. The challenge then becomes whether CMV can be further genetically attenuated such that it retains the ability to super-infect, elicit and maintain effector-differentiated T cell responses (including the unconventionally targeted CD8+ T cell responses) and “control and clear” protective efficacy, while losing the ability to widely disseminate in the body, spread from individual to individual, and to cause disease in settings of immunodeficiency. Moreover, any genetic attenuation must be stable, minimize the likelihood for reversion by mutation or recombination, allow vector manufacture at scale, and involve a virologic mechanism that is conserved between RhCMV, where the concepts will be tested, and HCMV, which will serve as the basis of any clinical vector.
In a companion report (20), we describe a CMV attenuation strategy based on deletion of the Rh110 gene (RhCMV ortholog to HCMV UL82), which encodes pp71, a tegument phospho-protein which functions to disperse and/or degrade the host intrinsic immunity protein death-domain associated protein (DAXX). DAXX functions in nuclear ND10 bodies to repress transcription of viral immediate early (IE) genes, which are critical for early and late CMV gene expression, and thus, viral genome replication, assembly and egress (21–27). In the absence of viral pp71, DAXX represses lytic CMV replication, and the infection becomes and remains latent. Although DAXX can be overcome at high multiplicities of infection in vitro, ΔRh110 (Δpp71) RhCMV is highly spread-deficient in vivo, with infection largely restricted to the inoculating dose at the site of inoculation and draining lymph nodes (20). In contrast to parental 68–1 RhCMV, ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV was not shed in urine, nor transferred to new hosts by close contact or adoptive cell transfer, and this attenuation was stable over time with no signs of reversion in vivo. Despite this attenuation, the SIV insert-specific T cell immunogenicity of ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors was similar to its Rh110-intact counterpart in terms of magnitude, durability, effector-memory phenotype and function, and for the CD8+ T cell responses, both in breadth and unconventional epitope targeting (20). Here, we investigate whether spread-deficient ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors can provide the same “control and clear” protection against homologous SIV challenge as their spread-competent Rh110-intact counterparts, and additionally assess whether these attenuated 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors can protect against challenge with a heterologous SIV strain.
RESULTS
Experimental Design and ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV Vector Immunogenicity.
We previously reported vaccination of cycling female RM with spread-competent (Rh110-intact), strain 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors expressing SIV Gag, Rev/Tat/Nef (RTN), 5’-Pol, 3’-Pol, and Env (with inserts primarily based on SIVmac239 gene sequences). This vaccination provided stringent, aviremic (except for transient plasma viremia in early infection), long-term (>52 weeks) control of intravaginal (IVag)-introduced SIVmac239 infection in 8 of 16 vaccinees vs. 0 of 18 controls (8). Here, we sought to determine 1) whether this homologous efficacy would extend to vaccination with an attenuated (spread-deficient) ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector set expressing the same predominantly SIVmac239 sequence inserts (ΔRh110/SIVmac239), and 2) the extent to which a ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV-vectored vaccine with heterologous SIVsmE660-sequence inserts (ΔRh110/SIVsmE660) would provide protection against the same SIVmac239 challenge regimen. We elected a heterologous vaccine rather than heterologous challenge approach because available heterologous challenge strains – the SIVsmE660 swarm or SIVsmE543 clone – are sufficiently different in key immunobiologic characteristics from SIVmac239 to make direct efficacy comparisons difficult (28, 29). To this end, two ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vector sets were constructed from the parental 68–1 RhCMV bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), each with the coding region of the Rh110 (pp71) gene replaced with the SIV insert (Gag, 5’-Pol, 3’-Pol, RTN, and Env), derived from either the SIVmac239 sequence or an SIVsmE660 consensus sequence (fig. S1A). Divergence between the SIVmac239 and SIVsmE660 amino acid sequences averages 15% across all inserts (Fig. S2), differences that approximate the variation between single clade–based HIV vaccines and circulating HIV isolates within that clade (30). Two groups of 14 female RM each were vaccinated twice (week 0, 14) with the set of 5 ΔRh110/SIVmac239 (Group 1) or ΔRh110/SIVsmE660 vectors (Group 2) expressing Gag, RTN, 5’-Pol, 3’-Pol, or Env inserts by subcutaneous administration of 5 × 106 plaque-forming units (pfu) per vector (Fig. 1A). Immunogenicity was followed for 60 weeks post-initial vaccination, at which time repeated, limiting dose, IVag SIVmac239 challenge was initiated for both vaccine groups and a cohort of unvaccinated controls (Group 3; n = 20). Immunogenicity and outcome of Groups 1 and 2 were also compared to our previously reported cohort of female RM (Group 4) vaccinated with a set of WT (Rh110-intact) 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors (WT 68–1/SIVmac239) expressing the same SIVmac239 sequence inserts that were IVag SIVmac239 challenged by a similar limiting dose protocol (8).
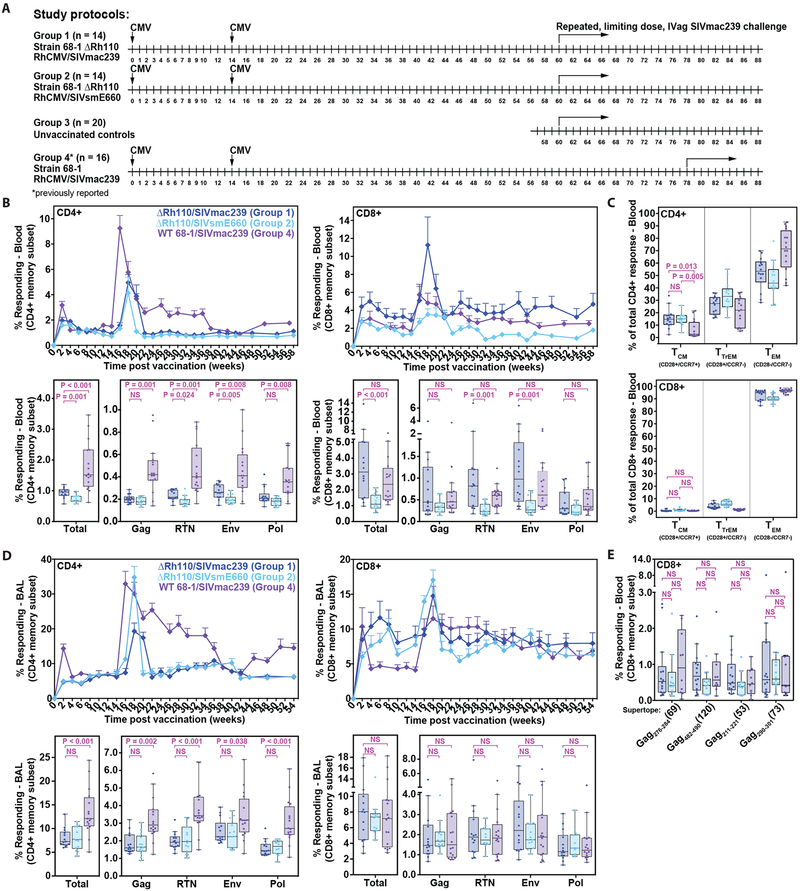
Figure 1: Immunogenicity of ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vectors.
(A) Schematic of the RM groups analyzed in this study. (B) Longitudinal and plateau-phase analysis of the vaccine-elicited, SIV Gag, Rev/Tat/Nef (RTN), Pol, and Env insert-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in peripheral blood. In the top panel, the background-subtracted frequencies of cells producing TNF and/or IFN-γ by flow cytometric ICS assay to peptide mixes comprising each of the SIV inserts (SIVmac239 sequence) within the memory CD4+ or CD8+ T cell subsets were summed for overall responses with the figure showing the mean (+ SEM) of these overall responses at each time point. In the bottom panel, boxplots compare the overall and individual SIV insert-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell response frequencies between the vaccine groups at the end of the vaccine phase (each data point is the mean of response frequencies in all samples from weeks 30–58 post-first vaccination). Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were used to compare the significance of differences in plateau-phase response frequencies between Group 1 and Group 2 (SIVmac239 vs. SIVsmE660 inserts in ΔRh110 68–1 vectors), and between Group 1 and Group 4 (SIVmac239 inserts in WT 68–1 vs. ΔRh110 68–1 vectors). (C) Boxplots compare the memory differentiation of the vaccine-elicited CD4+ and CD8+ memory T cells in peripheral blood responding to SIV Gag peptide mix (SIVmac239 sequence) with TNF and/or IFN-γ production at the end of vaccine phase (week 54 for Groups 1 and 2; week 60 for Group 4). Memory differentiation state was based on CD28 and CCR7 expression, delineating central memory (TCM), transitional effector-memory (TTrEM), and effector-memory (TEM), as designated. Two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were used to compare the significance of differences in the fraction of responding cells with a TCM phenotype (reciprocal of fraction with effector differentiation - TTrEM + TEM). (D) Same analysis as in B, but for responses in lung airspace (BAL). Each data point for the boxplots is the mean of response frequencies in all samples from weeks 30–54 post-first vaccination (E) Boxplots show plateau-phase analysis (each point is the average of all samples between weeks 24–30 post-first vaccination) of the vaccine-elicited CD8+ T cell responses to SIV Gag supertopes (SIVmac239 sequence; Fig. S1B) in peripheral blood of Group 1, Group 2, and Group 4 RM by the same ICS assay described above. Gag276–284 (69) and Gag482–490 (120) are MHC-E-restricted supertopes; Gag211–222 (53) and Gag290–301 (73) are MHC-II-restricted supertopes (9,10). Statistical testing performed as described in B. In all panels, n = 14, 14, and 16 respectively for Groups 1, 2 and 4, except Group 4 in panel E where n = 10. Analyses were adjusted for multiple comparisons across inserts (B, D), epitopes (C), and supertopes (E) using the Holm method, and P-values ≤0.05 were considered significant. Analyses of total responses (B, D) were not adjusted.
RhCMV vectors are T cell-targeted vaccines, with little to no ability to elicit insert-specific Ab responses (7, 8, 31), and in keeping with this, only 3 of 28 RM in Groups 1 and 2 (all in Group 2) showed detectable SIV Env-specific Abs after vaccination, and these 3 responses were very low titer (Fig. S3A). In contrast, using flow cytometric intracellular detection of CD69 and either or both of TNF and IFN-γ as the indicator of Ag-triggered T cells responding to pools of consecutive, overlapping, SIVmac239 sequence 15mer peptides, all RM in both ΔRh110/SIV vector-vaccinated groups developed CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in blood to all SIV inserts (Fig. 1B; top panel). In both Group 1 and Group 2, the overall response peaked 2–4 weeks following initial or boost vaccinations, prior to establishing a stable steady-state within ~12 weeks of the second vaccination that was maintained for the duration of the vaccine phase. During the plateau-phase of the vaccine response (defined here as weeks 30–58 post-initial vaccination), total SIV-specific, CD4+ and CD8+ T cell response frequencies in peripheral blood, as measured by the response to SIVmac239 sequence peptides, were significantly higher overall in Group 1 RM, given ΔRh110/SIVmac239 vectors, than in Group 2 RM, given ΔRh110/SIVsmE660 vectors (P < 0.001; Fig. 1B; bottom panel). This difference in overall response magnitude in blood was primarily driven by differences in the responses to Env and RTN (Fig. 1B; bottom panel), the SIV inserts with the most divergence between the SIVmac239 and SIVsmE660 sequences (fig. S2).
We also determined the memory differentiation phenotype of the SIV Gag-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells at plateau phase in Group 1 and Group 2 RM by intracellular cytokine staining (ICS), delineating central memory T cells (TCM), transitional effector-memory T cells (TTrEM), and effector-memory T cells (TEM) by their expression of CCR7 vs. CD28 (Fig. 1C). This analysis showed a predominance of effector-differentiated cells (TTrEM + TEM) that was similar in both vaccine groups. In keeping with this, SIV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were enriched in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples (BAL, used as an accessible effector site), and despite using SIVmac239 sequence peptides for this analysis, the magnitude of the overall and individual SIV insert-specific, CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in BAL were not different for Group 1 and Group 2 RM (Fig. 1D).
Both Rh110-intact and Rh110-deleted 68–1 RhCMV vectors elicit CD8+ T cell responses that are entirely unconventional in their MHC restriction (with epitopes presented by MHC-E or MHC-II, not MHC-Ia). Moreover, RM vaccinated with SIVmac239 Gag-expressing 68–1 RhCMV vectors invariably respond to a set of universal MHC-E- and MHC-II-restricted CD8+ T cell epitopes [so-called “supertopes” (9, 10, 20)]. All RM in Group 1 and Group 2 manifested CD8+ T cell responses to all 4 of the previously characterized SIVgag supertopes tested (2 MHC-E-restricted; 2 MHC-II-restricted), and the magnitudes of all these universal responses (3 of which were sequence identical in both the SIVmac239 and SIVsmE660 inserts and one of which was different by 3 amino acid substitutions; fig. S1B) were not different between Group 1 and Group 2 RM (Fig. 1E).
We next compared the magnitude and phenotype of responses elicited by the ΔRh110/SIVmac239 vectors (Group 1) with results from our previously reported cohort of female RM vaccinated with WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vectors (Group 4) (8). As shown in Figs. 1B–E, neither the magnitude (blood or BAL), nor the TEM + TTrEM skewing (blood) of the various SIV-specific CD8+ T cell responses, including supertope-specific responses, were different between the 2 groups. However, the magnitude of plateau-phase SIV-specific CD4+ T cell responses in blood and BAL were significantly higher (P < 0.001 for both), and in blood, the SIVgag-specific CD4+ T cell responses were significantly more TEM + TTrEM-biased (i.e., lower %TCM; P = 0.013), in the Group 4 RM compared to the Group 1 RM. These observations suggest that the restricted spread of the ΔRh110 vectors (20), and likely, diminished Ag availability, modestly reduced CD4+ T cell immunogenicity and effector differentiation, while having little to no effect on CD8+ T cell responses.
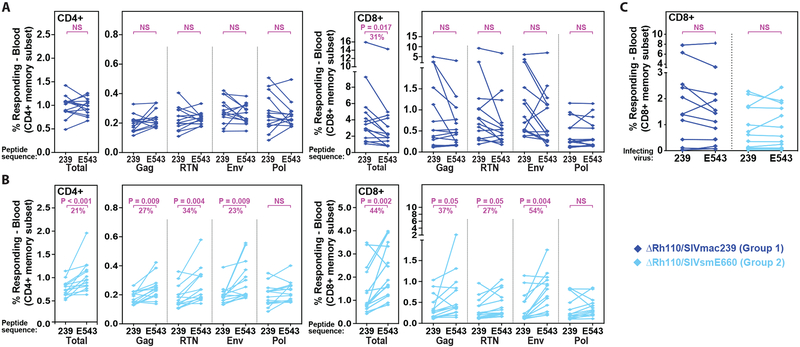
To explore heterologous T cell immunity with RhCMV vectors, we directly compared the ability of vaccine-elicited T cell responses of both Group 1 and Group 2 RM to recognize and respond to SIVmac239 vs. SIVsmE543 sequence peptides. The SIVsmE660 swarm-derived SIVsmE543 clone (29) is 96% identical to the SIVsmE660 consensus amino acid sequence and has a similar 15% overall amino acid sequence divergence from the SIVmac239, see fig. S2. For CD8+ T cells, we also examined responses to autologous CD4+ T cells infected with the cloned SIVmac239 or SIVsmE543 viruses (Fig. 2). CD4+ T cells from ΔRh110/SIVmac239-vaccinated Group 1 RM showed no difference in their plateau phase responses to matched (SIVmac239) vs. mismatched (SIVsmE543) peptide mixes, whereas CD8+ T cells from the same RM showed a significant reduction (average = 31%; P = 0.017) in the overall frequency of cells able to respond to the mismatched peptides (Fig. 2A). For ΔRh110/SIVsmE660-vaccinated Group 2 RM, both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells recognized mismatched peptides significantly less well than matched peptides, with the reduction in the magnitude of the CD4+ and CD8+ T cell response to mismatched peptides being ~21% (P < 0.001) and ~44% (P = 0.002) less, respectively, than for matched peptides (Fig. 2B). Thus, mismatch between the insert sequence and stimulating peptide sequence modestly reduced the magnitude of ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-elicited CD8+ T cell responses. Importantly, however, CD8+ T cells from both Group 1 and Group 2 RM showed equivalent ability to recognize autologous CD4+ T cells infected with SIVmac239 or SIVsmE543 virus clones (Fig. 2C), suggesting that at the level of SIV-infected cell recognition, the breadth of the CD8+ T cell responses generated by both ΔRh110/SIVmac239 and ΔRh110/SIVsmE660 vector sets was able to overcome sequence mismatch in individual epitopes.
Figure 2: Cross-recognition by ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIVmac239 and RhCMV/SIVsmE660 vector-elicited T cells.
(A,B) Flow cytometric ICS analysis of SIV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell response frequencies (using TNF and/or IFN-γ readout in memory subset) in the blood of Group 1 (n = 14; SIVmac239 inserts) and Group 2 (n= 14; SIVsmE660 inserts) RM in plateau phase (week 44 after first vaccination) comparing recognition of matched vs. mis-matched peptide mixes (SIVmac239 vs. SIVsmE543; see Fig. S2), including overall (summed) responses and responses to each SIV insert. Two-sided paired Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were used to compare the significance of differences in matched vs. mismatched peptide mix recognition. Unadjusted (total responses) or Holm-adjusted (each insert-specific response) P-values ≤0.05 were considered significant. When significant differences were observed (reduction in response frequencies with mismatched peptide mixes), the median effect size (% reduction with mismatch) is shown. (C) ICS analysis of CD8+ T cell recognition of autologous CD4+ T cells infected with the SIVmac239 vs. SIVsmE543 viruses (after background subtraction of the response to mock-infected autologous CD4+ T cells) in plateau phase (between weeks 49–57 post-first vaccination). Statistical analysis performed as described above, with n = 12 and 13, for Groups 1 and 2, respectively.
Efficacy of ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV Vectors.
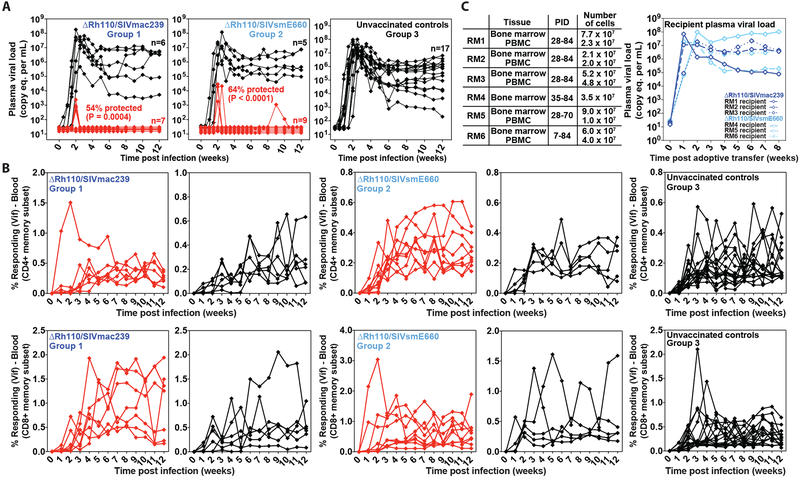
To determine if spread-deficient ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vectors retain the ability to mediate the characteristic “control and clear” protection demonstrated by spread-competent WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vectors in previous reports (7, 8, 12), we subjected the vaccinated Group 1 and Group 2 RM, and the unvaccinated Group 3 RM, to repeated (up to 12 challenges at 2–4 week intervals), limiting dose (100 focus-forming units for first 6 exposures; 300 for last 6 exposures) IVag SIVmac239 challenge. The goal was to establish infection “take” in each RM (at which time challenges were stopped), and then determine non-protection vs. protection by the presence or absence of progressive SIV infection after infection establishment (7, 8, 12). Since protected RM may or may not manifest detectable viremia after challenge, SIV infection “take” is confirmed by the onset of de novo T cell responses to SIV Vif, an SIV Ag not included in any of the RhCMV/SIV vectors (7, 8). In our challenge system, SIV Vif-specific T cells (CD4+ and CD8+) appear in blood 2–3 weeks post-productive SIV challenge, allowing attribution of successful (infection “take”-positive) challenges when successive challenges are 2 or more weeks apart. With this approach we were able to establish productive SIV infection in 13/14, 14/14, and 17/20 RM after up to 12 challenges in Groups 1–3, respectively, with no statistically significant difference in the rate of infection acquisition in the 3 challenge groups or in the overall ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-vaccinated cohort vs. unvaccinated controls (fig. S4).
In keeping with previous observations on WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector efficacy (7,8), the outcome of productive SIV challenge was strikingly different in the vaccinated Groups 1 and 2 vs. the unvaccinated Group 3. Whereas all 17 SIV-infected unvaccinated control RM manifested typical systemic SIV infection, 7 of 13 Group 1 RM (54%; P = 0.0004) and 9 of 14 Group 2 RM (64%; P < 0.0001) showed the onset of de novo SIV Vif-specific T cell responses in the absence of SIV viremia (n = 3 and n = 5 for Groups 1 and 2, respectively) or with plasma viremia positive at only a single time point (n = 4 for both Groups 1 and 2; Fig. 3A,B). To confirm the take of SIV infection in the presumptively protected (SIV Vif response-positive) RM without detectable plasma viremia, we performed adoptive transfer of bone marrow (BM) cells alone or BM cells plus PBMC obtained after the onset of SIV Vif-specific T cell responses from 6 of these RM (3 each from Group 1 and Group 2) into SIV-naïve recipients (Fig. 3C). As shown in the figure, adoptive transfer of cells from all 6 donor RM resulted in the onset of typical SIVmac239 infection in recipient RM, demonstrating the presence of fully replication-competent SIVmac239 in the donor RM and confirming stringent SIV control in these animals. Also, in keeping with previous results (7,8), there was no reduction in chronic phase plasma viremia in unprotected, vaccinated RM relative to unvaccinated controls, consistent with the “all or none” nature of RhCMV/SIV vaccine efficacy. The degree (% protected) and pattern of efficacy observed in Group 1 and Group 2 were not significantly different from the previously reported efficacy of WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector-vaccinated RM (Group 4) subjected to a similar challenge protocol [56% with initial stringent control; (8)]. Of note, across all protected vs. unprotected Group 1 plus Group 2 RM, efficacy was not predicted by the magnitude of overall or individual insert, SIVmac239 peptide-specific CD4+ or CD8+ T cell responses, or supertope-specific CD8+ T cell responses in blood at peak post-prime, peak post-boost or at vaccine response plateau phase, or by the magnitude of CD8+ T cell recognition of SIVmac239-infected CD4+ T cells at vaccine response plateau phase (fig. S5).
Figure 3: Efficacy of ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vectors.
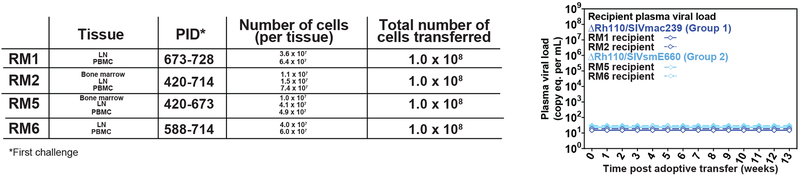
(A,B) Assessment of the outcome of effective challenge by longitudinal analysis of plasma viral load (A) and de novo development of SIV Vif-specific CD4+ (B, top panel) and CD8+ (B, bottom panel) T cell responses. RM were challenged until the onset of any above-threshold SIV Vif-specific T cell response, with the SIV dose administered 2 or 3 weeks prior to this response detection considered the infecting challenge (week 0). RM with sustained viremia were considered not protected (black); RM with no or transient viremia were considered protected (red) (8). The fraction of protected RM in the vaccinated groups (Groups 1 and 2, n = 13 and 14, respectively) were compared to that of the unvaccinated group (Group 3, n = 17) by Barnard’s exact test of binomial proportions, with the P-values shown in (A). (C) BM cells and PBMC were collected and cryopreserved from ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vaccine-protected RM without any detectable viremia (RM #1, RM #2, RM #3 from Group 1; RM #4, RM #5, RM #6 from Group 2) at the indicated time points post-effective challenge (left panel; PID – post-infection day). Cells were thawed and administered intravenously (left panel) to 6 SIV-naïve RM to assess the presence of replication-competent SIV with the plasma viral dynamics in recipient RM shown (right panel).
As previously shown for protection against SIVmac239 challenge mediated by spread-competent WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vectors, the stringent control of SIVmac239 infection mediated by the ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vectors occurred in the absence of an increased (boosted) SIV Gag- or Pol-specific T cell response in blood post-infection (fig. S6), and without development or boosting of an SIV Env-specific Ab response (fig. S3B). The lack of T cell response boosting was also observed post-infection in unprotected (viremic) vaccinated RM, indicating that the lack of increased T cell responses in protected RM was not due to limitation in SIV Ag availability. However, vaccinated, unprotected RM developed high titer SIV Env-specific Ab responses after challenge (similar to unvaccinated controls) indicating that the lack of such Ab responses in protected vaccinated RM is almost certainly a function of SIV Ag limitation due to early arrest of infection (keeping Ag levels below the threshold needed for Ab response generation). The conclusion that vaccinated, protected RM have early arrest of viral spread after initial take of infection, sharply limiting the extent of SIV infection, is also supported by the lack of the activation of circulating monocytes [as measured by increased interferon-induced expression of CD169; (11,32,33)] specifically in protected RM (fig. S7). Taken together, these results demonstrate that spread-deficient ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vaccines manifest efficacy equivalent to their spread-competent counterparts, which is not affected by a sequence mismatch between vector insert and challenge strain.
SIV Dynamics in ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV Vector-Vaccinated, Protected RM.
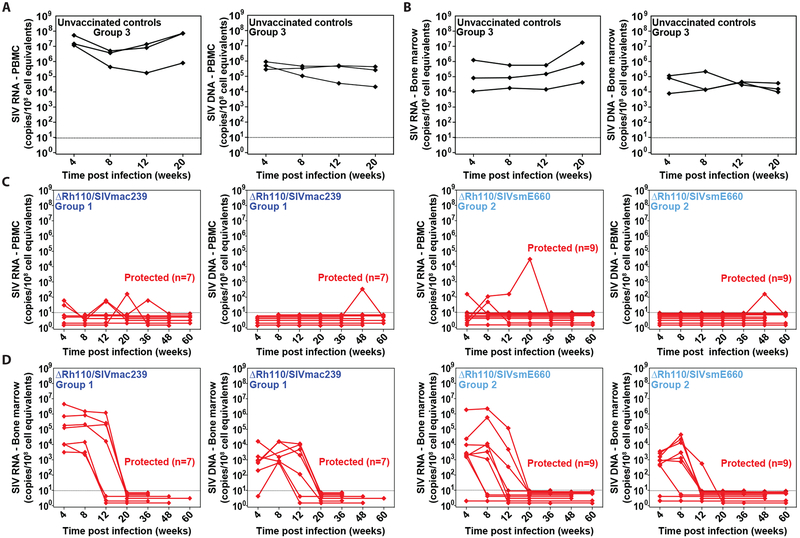
We have previously demonstrated that in RM protected by WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector vaccination, the arrest of SIV infection occurs after initial dissemination via both lymphatic and hematogenous routes, the latter including seeding of liver, spleen and BM. Over extended follow up, cells harboring SIV slowly disappear from all tissue sites until both virologic and immunologic evidence of SIV infection is lost (8). To determine if RM protected by spread-deficient ΔRh110/SIVmac239 or ΔRh110/SIVsmE660 vector vaccination have similar post-infection SIV dynamics, we quantitated cell-associated SIV DNA and RNA in blood and BM of all protected RM in Groups 1 and 2 for up to 60 weeks following SIV infection. As shown in Fig. 4A,B, as expected, overtly infected control RM showed abundant cell-associated SIV RNA and DNA in both blood and BM at all tested time points. In contrast, vaccine-protected RM in both Groups 1 and 2 manifested only sporadic detection of cell-associated virus in blood over 60 weeks of observation (Fig. 4C), consistent with the arrest of progressive SIV infection in these monkeys. Most striking, however, were the SIV dynamics in BM, previously shown to be a common site of early SIV spread in 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM (8). As shown in Fig. 4D, all but 1 of the 16 protected Group 1 and Group 2 RM manifested cell-associated SIV RNA in BM 4 weeks after infection, comparable to unvaccinated controls, and cell-associated SIV DNA was also detected in the majority of these BM samples. Similar quantities of cell-associated SIV RNA and DNA were detected in most of the BM samples from these RM at week 8 as well, but starting at week 12, there was a clear decline in cell-associated SIV in BM, and by week 20, SIV RNA and DNA were below the limit of detection in all BM samples from all RM. The difference in the number of SIV RNA- and DNA-positive samples from <20 weeks and ≥20 weeks post-infection was significant (P < 0.0001; Barnard’s exact test of binomial proportions).
Figure 4: Clearance of cell-associated SIV in the BM of ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM.
(A–D) Longitudinal analysis of PBMC-associated (A,C) and BM cell-associated (B,D) SIV RNA (left panels) and DNA (right panels) from 3 randomly selected unvaccinated RM with progressive infection (A,B), and all 16 ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-protected RM in Groups 1 and 2 (C,D).
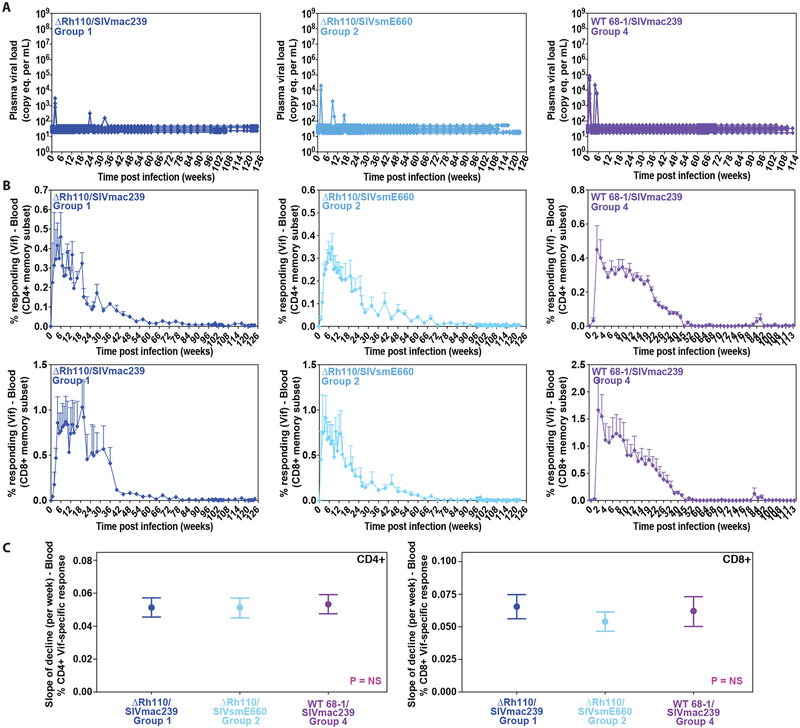
To more globally assess the “total body” SIV infection burden in vaccine-protected Group 1 and Group 2 RM, we longitudinally followed SIV Vif-specific T cell responses as an in vivo circulating immunologic “biosensor” to detect residual SIV infection-related Ag production in these animals, all of which were aviremic except for rare low-level viral blips prior to week 34 post-infection (Fig. 5A). As noted above, SIV Vif-specific T cell responses are generated and maintained by SIV infection-derived Ag; in WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector-vaccinated RM, we have previously associated decline in these responses with progressive clearance of SIV reservoirs (8). All Group 1 and 2 protected RM showed a similar overall pattern of SIV Vif-specific response dynamics characterized by increasing or stable, high frequencies of SIV Vif-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells over the first 6–12 weeks post-infection. Thereafter, there is a slow but unequivocal decline in these frequencies that starts no later than week 20 and continues to extinction (e.g., response below detection limit in blood) over the subsequent 1–2 years (Fig. 5B), a pattern that is strikingly similar to data with the WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vaccine (8). Indeed, the slope of decline of SIV Vif-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in ΔRh110/SIV vaccine-protected Group 1 and Group 2 RM was not significantly different from that of RM protected by spread-competent WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vectors (Fig. 5C; Wald test: F2,582 = 0.097 and 2.10 for CD4+ and CD8+, respectively).
Figure 5: Loss of circulating SIV infection-induced, SIV Vif-specific T cells in ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM.
(A) Long-term longitudinal analysis of plasma viral load in ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-protected (left and middle panels for Groups 1 and 2, respectively) and WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector-protected RM (Group 4, right panel, (8)). (B) Long-term longitudinal analysis of SIV Vif-specific CD4+ (top panels) and CD8+ (bottom panels) among the same groups of ΔRh110 and WT 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM with the figure showing the mean (+ SEM) of these SIV Vif-specific T cell response frequencies in the memory subset at each time point. (C) Wald tests comparing the slope (± 95% confidence intervals) of decline of log-transformed SIV Vif-specific CD4+ (left panel) and CD8+ (right panel) T cell response frequencies. Calculation of slopes is described in Materials and Methods. In all analyses, n = 7, 9, and 8 for Groups 1, 2 and 4, respectively.
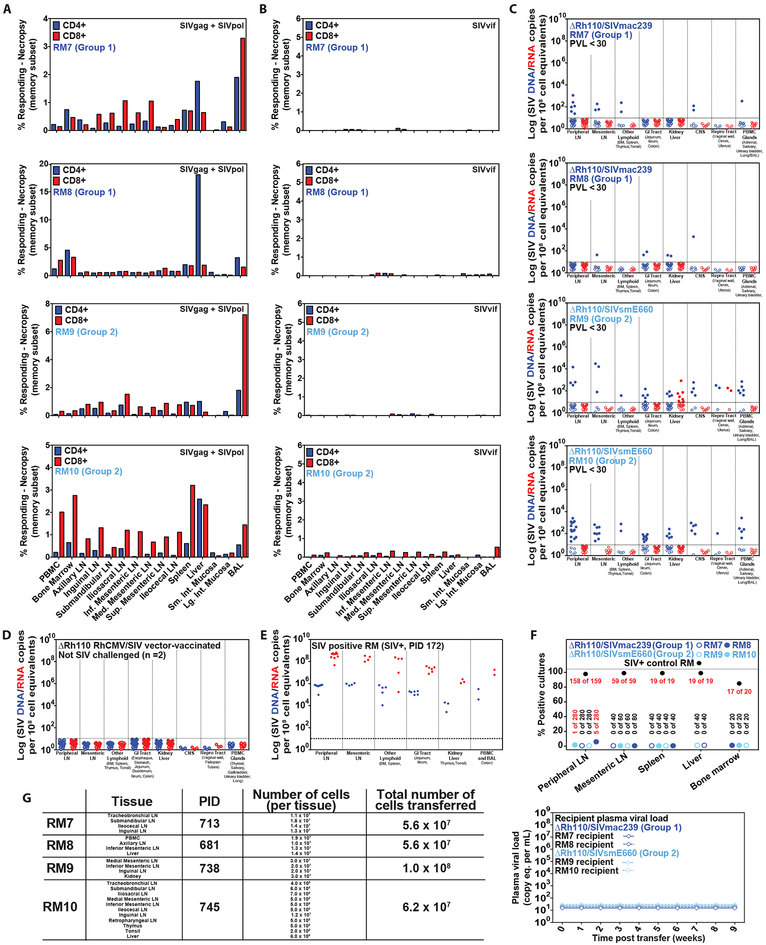
To confirm that the observed loss of SIV Vif-specific T cell responses reflected “total body” SIV clearance, we selected 4 of the ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660-vaccinated, long-term protected RM (>100 weeks post-infection; 2 RM each from Group 1 and Group 2) for detailed virologic and immunologic analysis at necropsy. Three of these 4 RM (RM #7, #9, #10) had previously manifested a single plasma viral blip early after infection and subsequently remained aviremic, whereas the 4th RM (RM #8) was aviremic throughout its course. All 4 of these RM had developed and then lost robust SIV Vif-specific T cell responses, while maintaining stable (vaccine maintained) SIV Gag- and Pol-specific T cell responses (fig. S8). At necropsy, all animals had SIV Gag- and Pol-responsive T cells in all tissues examined (Fig. 6A). In contrast, SIV Vif-specific T cell responses were predominantly negative in 3 of 4 RM (RM #7, #8, #9), with above-threshold responses in only a few tissues, and in the other RM (RM #10), were present as low frequency responses (predominantly CD8+) in multiple sites (Fig. 6B). Cell-associated SIV RNA and DNA were quantified by nested quantitative RT-PCR/PCR (8) in extensively sampled tissues from the 4 ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vaccine-protected RM (Fig. 6C) and for comparison, tissues from 2 ΔRh110/SIVgag vector-vaccinated RM never exposed to SIV (Fig. 6D) and 1 unvaccinated RM with progressive SIV infection (Fig. 6E). Both of the ΔRh110/SIVgag-vaccinated, unchallenged control RM were negative for SIV DNA and RNA in all tissues, whereas, as expected, the RM with progressive SIV infection manifested high amounts of both, with SIV RNA ~2 logs higher than DNA. All 4 ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-vaccinated RM manifested detectable, albeit low-level, cell-associated SIV DNA in 5 or more tissues with 28% (98/235) of samples positive overall (vs. 0 of 114 samples in vaccinated, unchallenged controls; P < 0.0001 using Barnard’s exact test of binomial proportions). In contrast, cell-associated SIV RNA was detectable in only 1 RM, 2.6% of overall samples (9 of 345 vs. 0 of 114 samples in controls, P = NS). To determine if this detection of SIV DNA/RNA reflected replication-competent virus, we performed co-culture analysis on a total of 1120 tissue specimens sampled from the 4 protected RM (Fig. 6F). Only 6 of these specimens (0.5%), from 2 of the 4 RM, were SIV+ upon co-culture (5 in RM #2; 1 in RM #4 vs. 270/274 SIV+ co-cultures in the unvaccinated control RM). We next combined 56–100 million cells from the necropsy tissues of each of these 4 protected RM and then adoptively transferred these cells into SIV-naïve recipient RM and found no transfer of SIV infection in any of the 4 recipient RM (Fig. 6G), observations consistent with the majority of SIV DNA signals detected in tissues at necropsy representing replication-incompetent proviruses (34).
Figure 6: Necropsy analysis of ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM.
(A–C) Analysis of SIV Gag+Pol-specific (A) and SIV Vif-specific (B) CD4+ and CD8+ T cell response frequencies by flow cytometric ICS (using SIVmac239 peptides mixes; see Fig. 1), and tissue-associated SIV DNA and RNA by nested qPCR/RT-PCR (C) in tissues of 4 ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-protected RM (RM #7 and RM #8 from Group 1; RM #9 and RM #10 from Group 2) taken to necropsy at 713 days (RM #7), 681 days (RM #8), 738 days (RM #9) and 745 days (RM #10) post-infection. (D,E) Analysis of tissue-associated SIV DNA and RNA in tissues of 2 ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIVgag (SIVmac239 sequence insert) vector-vaccinated RM that were taken to necropsy 531 and 763 days post-vaccination without SIV challenge (negative controls; D), and one SIVmac239-infected RM with progressive infection taken to necropsy 172 days post-infection (positive control; E). In C–E, each data point indicates an independent tissue sample of the indicated tissue type and the dotted lines indicate the detection threshold. (F,G) Assessment of residual replication-competent SIV in cell suspensions obtained from the indicated tissue samples by in vitro co-culture analysis (F) and by adoptive transfer of cells into 4 SIV-naïve RM (G).
Finally, we repeated the adoptive transfer experiment using cells collected at late time points from 4 different ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vaccine-protected, always aviremic RM (RM #1 and #2 from Group 1; RM #4 and #5 from Group 2) that were previously shown (early after the onset of protection) to harbor replication-competent SIV by adoptive transfer. A total of 108 pooled cells from BM, lymph node, or blood, collected at 60–102 weeks post-infection from these RM were administered to 4 SIV-naïve recipients, with no take of SIV infection detected in the recipient RM (Fig. 7). Taken together, these results provide compelling evidence that replication-competent SIV declines over time in ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV-vaccinated, long-term protected RM such that after ~2 years, lymphoid cells infected with replication-competent SIV are very rare or undetectable.
Figure 7: Loss of transferable SIV in long-term ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM.
Second assessment of replication-competent SIV by adoptive transfer of cells from 4 long-term ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-protected RM (RM #1 and RM #2 from Group 1; RM #5 and RM #6 from Group 2) that were previously shown to harbor replication SIV by the same assay.
Re-challenge of RhCMV/SIV Vector-Protected RM.
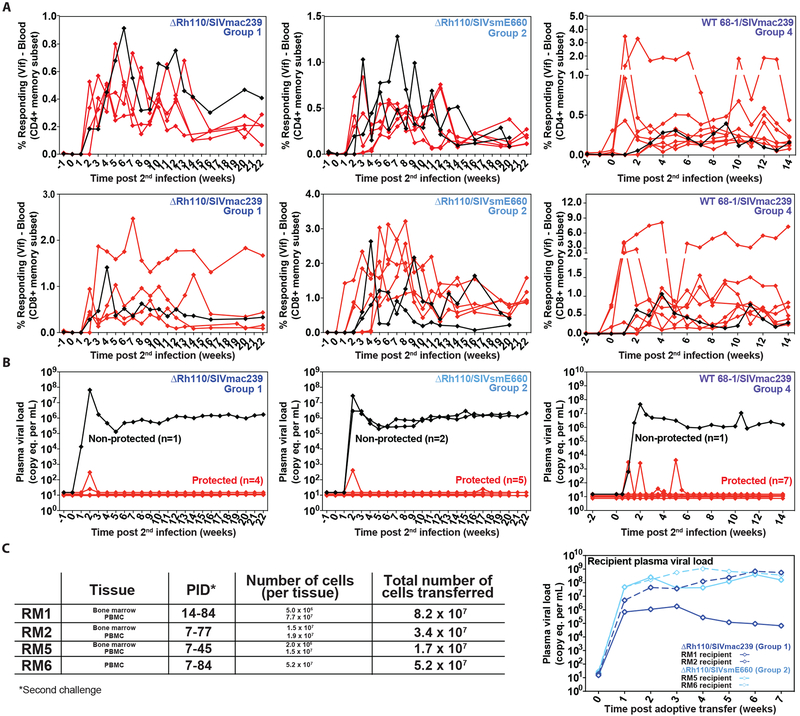
We next addressed the question of whether 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-vaccinated RM retain the capacity to clear a second SIV challenge after control and progressive clearance of an initial challenge, and if so, whether RM vaccinated with spread-competent vs. spread-deficient vectors differ in this regard. To this end, we followed 8 protected RM from our previously reported cohort of WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector-vaccinated animals (Group 4)(8) and 12 ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vaccine-protected RM from this study (5 from Group 1; 7 from Group 2) for at least 2 years after initial SIV infection. All RM developed and then lost SIV Vif-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in blood during this follow-up, while retaining stable frequencies of (vaccine-elicited) SIV Gag- and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses (fig. S9). We then initiated the same repeated limiting dose, IVag SIVmac239 challenge protocol used in the first challenge. All RM were infected by this challenge protocol, as indicated by the redevelopment of SIV Vif-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses (Fig. 8A). Strikingly, 4 of 5 Group 1 RM, 5 of 7 Group 2 RM, and 7 of 8 WT/ 68–1 SIVmac239 vector-vaccinated RM were protected after this second SIV challenge, again showing either no viremia or only transient viremia (Fig. 8B). The twice-protected Group 1 and Group 2 RM included RM #1, #2, #4, and #5, which were previously shown to lack transferable SIV prior to second challenge. BM and/or PBMC samples from these 4 RM were collected after the (second) onset of SIV Vif-specific T cell responses and were inoculated into 4 additional SIV-naïve RM. All of the 4 recipient RM became SIV-infected (Fig. 8C), indicating the presence of replication-competent SIV in these aviremic animals, and thereby confirming a second, stringently controlled SIV infection. Overall, 16 of the 20 re-challenged RhCMV/SIV vector-vaccinated RM were protected a second time. Although this degree of efficacy (80%) is higher than the overall efficacy of initial challenge (58%), this difference did not quite achieve statistical significance (P = 0.06). These data confirm that both spread-competent and spread-deficient (ΔRh110) RhCMV/SIV vectors are able to maintain efficacy for ~3 years after last vaccination and can provide protection against more than one SIV challenge.
Figure 8: Resistance of ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM to repeat SIV challenge.
(A, B) Outcome of repeat SIVmac239 challenge of long-term 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM (n = 5, 7 and 8 for Groups 1, 2 and 4, respectively) by longitudinal analysis of de novo SIV Vif-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses (A) and plasma viral load (B) with protected and non-protected RM defined as described in Fig. 3. (C) Third assessment of replication-competent SIV by adoptive transfer of cells from RM #1, RM #2, RM #5 and RM #6 after effective re-challenge (re-induction of SIV Vif-specific T cell responses) with repeated aviremic protection.
DISCUSSION
HCMV infection is ubiquitous, especially in resource poor settings, and although HCMV persists for life in infected individuals, the vast majority of these individuals will never develop CMV disease due to immune control of viral spread after primary infection and upon reactivation from latency (35–37). The vast majority of such HCMV+ individuals would not be expected to develop symptomatic infection upon administration of an HCMV-based vaccine, even one with WT replication and spread capacity. However, in the setting of prophylactic vaccination of large populations, non-HCMV-infected individuals, potentially including immunocompromised subjects, would possibly be exposed to such a WT HCMV-based vaccine, either through direct administration or potentially spread from a vaccinated subject, and a subset of such individuals would be at risk of developing overt HCMV disease (38,39). To mitigate this risk, we have sought to make a CMV-based vaccine safer by identifying an attenuation strategy that would substantially limit vector spread within and between hosts and thereby preclude disease in vaccinated individuals, spread to (and within) the fetus of pregnant subjects, and shedding in secretions (to prevent person-to-person spread). The strategy should preserve the ability of the vector to super-infect CMV+ individuals, productively infect sufficient numbers of cells to prime robust T cell responses and persist long-term to provide the antigenic stimulation needed for maintaining effector-memory differentiation. In a companion paper (20), we provide evidence that ΔRh110 RhCMV may strike such a balance in RM, showing an ~1000-fold reduction in vector spread in vivo, no vector shedding in secretions, and no animal-to-animal spread with close contact or leukocyte transfusion. This vector still retains the ability to elicit insert-specific T cell responses that are comparable in magnitude, phenotype, function, epitope-targeting, and durability as Rh110-intact RhCMV vectors. Furthermore, by insertion of the SIV antigens into the Rh110 locus we also eliminate the possibility of reversion to WT by homologous recombination with the endogenous virus present in CMV-infected hosts.
Here, we performed a large vaccination and challenge trial of ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vectors to extend the immunogenicity analysis to a larger cohort of RM vaccinated with these attenuated vectors, and to determine protection from highly pathogenic SIVmac239 challenge. We also expanded our analysis of ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vectors to include determination of the extent to which mismatch between the vector insert sequence and SIV challenge strain would affect SIV-infected cell recognition by vector-elicited T cells and vaccine efficacy, as such mismatch will be invariably present in any clinical application of this vaccine. These results confirm that ΔRh110/SIVmac239 vectors elicit insert-specific CD8+ T cell responses that are essentially indistinguishable in magnitude, phenotype, and durability from that of WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vectors. CD8+ T cell responses elicited by ΔRh110 RhCMV vectors expressing SIVmac239 vs. SIVsmE660 sequence inserts in blood were reduced in magnitude by 30–40% when tested on mismatched sequence peptides, but these responses were equivalent in their ability to recognize SIVmac239-infected and SIVsmE543-infected autologous CD4+ T cells. Thus, while epitope recognition by the unconventionally (MHC-E- and MHC-II-) restricted (9,10)CD8+ T cells elicited by ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vectors can be modestly compromised by sequence divergence, the breadth of these responses is sufficiently great to ensure equivalent recognition of cells infected by divergent SIV strains. Interestingly, ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vector-elicited CD4+ T cells were largely unaffected by insert-target sequence mismatch (0–20% reduction), but were significantly reduced, albeit modestly, in both magnitude and effector-memory bias after the boost vaccination relative to Rh110-intact RhCMV/SIV vector-elicited responses. This modest reduction is consistent with the interpretation that RhCMV vector-elicited CD4+ T cell responses may be more sensitive to reduction in overall Ag availability than the corresponding CD8+ T cell responses.
Of primary importance, we found that the extent and pattern of protection afforded by ΔRh110/SIV vector vaccination, irrespective of sequence match vs. mismatch between vector insert and challenge virus, was essentially identical to that of Rh110-intact vectors. In our previous analysis of WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector vaccination, 56% of RM were protected after initial challenge and 50% after 1 year (8). This degree of efficacy was not significantly different from 59% overall efficacy of the ΔRh110/SIV vectors observed in the present study, with all these protected RM showing both initial and long-term protection. Interestingly, the percentage of protected RM was actually higher for monkeys given the challenge-mismatched ΔRh110/SIVsmE660 vectors (64%) compared to RM given the challenge-matched ΔRh110/SIVmac239 vectors (54%). Although this difference was not statistically significant, the finding that heterologous efficacy is as good as or better than homologous efficacy is an encouraging sign for clinical translation. Moreover, the characteristics of protection after ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vaccination were very similar to that of the WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vaccine. Animals acquired SIV, but except for rare viral blips, there was complete elimination of viremia, which is consistent with replication arrest. SIV was stringently controlled prior to systemic immune activation, as demonstrated by a lack of monocyte activation, anti-Env Ab production, and in the absence of boosting of the vaccine-stimulated T cells. Taken together, these data indicate that vaccine-elicited immune protection can be achieved with substantially reduced levels of RhCMV vector spread.
We have previously demonstrated that WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector-protected RM show progressive loss of SIV infection over time, and this viral clearance process is particularly well-documented in the current analysis of ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-vaccinated RM. We demonstrate loss of detectable cell-associated SIV RNA/DNA detection in BM over the first 20 weeks post-infection and decline in SIV Vif-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in blood to below the threshold of detection over 1–2 years. Most strikingly, RM that were able to transmit infection to naïve recipients by transfer of cells obtained early after the onset of protection no longer transmitted infection 1–2 years later. Four ΔRh110/SIV vector-protected RM (2 each given vectors with matched – Group 1 – vs. mismatched – Group 2 – SIV inserts) were taken to necropsy ~2 years after infection for extensive tissue analysis. Although PCR analysis demonstrated these 4 RM had more SIV DNA than 2 ΔRh110/SIVgag-vaccinated, but never SIV-challenged controls, SIV RNA and co-culturable virus was largely undetectable, and adoptive transfer of cells from tissues from these RM did not transfer SIV infection. Taken together, these results suggest a vanishingly small amount of residual infectious SIV in these ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-protected RM. The residual SIV DNA in these 4 necropsied RM did, however, appear to be somewhat more than in our previous analysis of WT/SIVmac239 vector-protected RM. This finding and the more frequent detection of low frequency SIV Vif-specific T cells in tissues of the current RM relative to the previously studied RM (8) is consistent with the conclusion that viral clearance was not quite complete in these animals. This does not necessarily indicate a difference in the extent or kinetics of viral clearance between WT 68–1/SIVmac239 and ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-protected RM, as the WT 68–1/SIVmac239 vector-vaccinated RM studied previously at necropsy were males infected by intrarectal challenge (as opposed to females being infected via IVag challenge), and 4 of these 6 previously studied animals were taken to necropsy after >1000 days post-infection, compared to ~700 days in the current study. Indeed, given the apparent dependence of SIV Vif-specific T cell responses on SIV Vif Ag production by SIV-infected cells, the observation that the slope of decline of SIV Vif-specific T cell responses in WT 68–1/SIVmac239 and ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-protected RM were not significantly different (both CD4+ and CD8+) suggests that rate of SIV infection clearance was broadly similar with both vaccines. This is in keeping with our previous hypothesis that SIV clearance in RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM predominantly results from arrest of infection prior to seeding a long-lived SIV reservoir and the subsequent decline of the less durable reservoir that is initially seeded (11). Although this implies that vaccine-elicited T cell responses are not actively clearing the viral reservoir, these responses very likely contribute to maintaining stringent replication control while the residual viral reservoir spontaneously declines, and if this is the case, WT 68–1/SIVmac239 and ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-elicited responses appear to be equivalent in this activity.
Finally, we directly compared the outcome of a second round of SIV challenge in RM that were previously protected by WT 68–1/SIVmac239 or ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector vaccination and subsequently cleared the initial infection, as assessed by extinction of their SIV Vif-specific T cell responses over ~2 years. Remarkably, 80% of these re-challenged RM, across all vaccine groups, were able to control this second challenge, with re-infection and aviremic control demonstrated in 4 protected RM by conversion of the adoptive transfer assay of SIV infection from negative before the second challenge to positive after, in the absence of viremia. These data indicate that WT/SIVmac239 and ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vectors can maintain efficacy for up to ~3 years after last vaccination, with the striking stability of the SIV-specific T cell responses elicited by these vectors suggesting that the potential for efficacy might extend for considerably longer periods, perhaps lifelong. However, it should also be noted that SIV-specific T cell response magnitude in blood did not correlate with outcome in the first challenge for the ΔRh110/SIVmac239/smE660 vector-vaccinated RM, and that 20% of previously RhCMV/SIV vector-protected RM were not protected after the 2nd challenge, despite maintaining stable SIV-specific T cell responses. Thus, there is either an element of stochasticity to protection, or some unmeasured aspect of the innate or adaptive immune response to vaccination that is required for efficacy, and this parameter or parameters can vary over time.
The “control and clear” protection against highly pathogenic SIVmac239 challenge afforded by RhCMV/SIV vectors is unique and offers an alternative mechanism for a clinically useful prophylactic HIV/AIDS vaccine, either alone or in combination with an Ab-targeted vaccine designed to reduce HIV acquisition (12). The ability to substantially limit vector spread while preserving both the extent (%protected) and durability of efficacy is a critically important step in clinical translation of the CMV vector platform, as is the demonstration that RhCMV/SIV vector efficacy can tolerate the equivalent of an intra-clade sequence mismatch between vaccine insert and challenge virus strain without loss of efficacy. However, a major limitation of this study is that CMVs are species-specific viruses and a clinical vector for vaccination of humans against HIV will be based on HCMV, not the orthologous, but distinct, RhCMV. The pp71 protein is encoded by UL82 in HCMV, and although the RhCMV and HCMV pp71 proteins have similar function, UL82 deletion in HCMV results in a more pronounced growth defect in vitro than Rh110 deletion in RhCMV, suggesting a ΔUL82 HCMV might be more attenuated in vivo in people than ΔRh110 RhCMV in monkeys (20). While this additional attenuation increases the margin of safety for clinical testing, it might also reduce immunogenicity, or more likely, increase the dose required to achieve full immunogenicity – issues that can only be resolved through human testing. Despite this potential concern, the results presented in this study strongly support the further development of pp71-deleted, 68–1-like HCMV/HIV vectors as prophylactic vaccines for HIV/AIDS.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Design
The primary objective of this study was to determine whether attenuated (spread-deficient) ΔRh110 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors expressing homologous or heterologous SIV Ag inserts would, relative to unvaccinated controls, provide cycling female RM stringent post-acquisition control of SIVmac239 infection, administered by repeated, limiting dose IVag challenge. Based on previous experience with WT 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vectors (6–8), we randomly assigned n = 48 cycling female RM assigned to one of three vaccine groups as follows: n = 14 ΔRh110 /SIVmac239 (Group 1), n = 14 ΔRh110 /smE660 (Group 2), and n = 20 unvaccinated (Group 3). This group size was anticipated to allow us to resolve 20% protection at 90% power, pooling the vaccine groups. Although only the RM with take of infection (animals with SIVvif T cell response induction and either cell-associated SIV in tissue or plasma viremia post-challenge) were considered for evaluation of protection (n = 13 Group 1, n = 14 Group 2, n = 17 Group 3), our criteria for stringent SIV control (aviremic infection) was met in 16/27 vaccinated RM (59%), allowing us to proceed to our secondary objectives of determining the extent of viral clearance over time in these protected RM, and the ability of previously protected RM to control a second infection. At the end of an ~2 year observation period, during which time SIVvif responses in blood in all protected RM decayed to below the level of detection and all virologic assays reverted to (or remained) negative, the 16 protected RM were arbitrarily assigned to either necropsy for comprehensive tissue analysis of residual SIV (n = 4; 2 each from Group 1 and Group 2) or to repeat SIV challenge (n = 12; 5 from Group 1, 7 from Group 2). The latter analysis was also performed on long-term protected RM vaccinated with WT 68–1 RhCMV/SIV vaccine from our previous report (8). All the described RM experiments were performed once, and all results from these experiments are included in the presented data (no data were excluded as outliers). All plasma and cell-associated viral load assays were assayed by blinded analysts; however, due to logistical constraints, other staff were not blinded to treatment assignments. Primary data are reported in data file S1.
Statistical Analysis
We compared the fraction of protected RMs between treatment groups and challenges using Barnard’s exact test of binomial proportions. To compare time-to-event data, we used the Mantel-Haenszel log-rank test. To examine SIV dynamics in vaccinated and protected RMs, we fit linear models of T cell responses with time and treatment group as independent variables. Slope analyses of SIV Vif-specific T cell responses are described below. For all other comparisons, we used non-parametric Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for both paired and unpaired comparisons, and Kruskal-Wallis for comparisons of more than two groups. Neutralizing Ab titers were log10-transformed and normalized to baseline prior to computation of the area under curve (AUC) and compared using Wilcoxon rank sum tests. For log transformations when zeros were present, a small positive constant smaller than any nonzero value was added to all values prior to log transformation. For comparisons of AUC for percent responses, the data were also baseline-subtracted prior to AUC calculation. For all analyses of SIV dynamics including those described below for SIV Vif-, Gag-, and Pol-specific T cell responses, we also fit confirmatory models to account for variation among individual RMs using linear mixed, which confirmed our analysis in each case. All statistical analyses were conducted in R version 3.2.2 using the following R package versions: lmtest 0.9.34, zoo 1.8.1, survival 2.42.3, Exact 1.7, and lme 1.1.17. All P-values are based on two-sided tests and unadjusted except where noted. Adjusted P-values were computed using the Holm procedure for FWER control. Boxplots in Fig. 1 and Fig. S5 show jittered points and a box from 1st to 3rd quartiles (IQR) and a line at the median, with whiskers extending to the farthest data point within 1.5*IQR above and below the box, respectively.
For analyses of SIV-specific T cell responses, we log-transformed the responses prior to fitting to account for variance over time. For Vif-specific responses, we used Wald tests to compare models with and without specific time/group interaction terms to determine whether SIV clearance rate differed by vaccine. Models were fit using all data points in range after defining start and stop time points for each analysis according to the following predetermined procedure: we determined the start point as the time when the relevant mean response over all RMs reached its first peak before declining. The end point was the first time point after the start point at which the mean response was below the threshold for “return to baseline,” which we determined by taking the mean plus three standard deviations of all response values in the plateau phase (beyond 96 days after infection). For SIV Gag- and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses, we used Wald tests to compare individual slopes to 0.
Supplementary Material
Materials and Methods
Fig. S1. ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vector design and supertope amino acid sequences.
Fig. S2. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of SIVmac239 vs. SIVsmE660 vaccine inserts.
Fig. S3. Analysis of SIV Env-specific antibody (Ab) responses after vaccination and after acquisition of SIV infection.
Fig. S4. Acquisition of SIV infection by Group 1, 2 and 3 RM with repeated, limiting dose IVag SIVmac239 challenge.
Fig. S5. Immune correlates analysis.
Fig. S6. Analysis of SIV Gag- and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses after SIV infection.
Fig. S7. Analysis of circulating monocyte activation after SIV infection.
Fig. S8. Analysis of plasma viral load, and SIV Vif-, Gag-, and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in vaccine-protected, necropsied RM from Groups 1 and 2.
Fig. S9. Analysis of SIV Gag- and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in vaccine-protected, and subsequently re-challenged RM from Groups 1, 2, and 4.
Data File S1. Primary data
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS:
We thank A. Sylwester, A. Okoye, C. Kahl, S. Hagen, R. Lum, Y. Fukazawa, E. McDonald, L. Silipino, N. Whizin, K. Randall, A. Selseth, Z. McWatters, I. Cardle, E. Cangemi, and L. Boshears for technical or administrative assistance; B. Keele for providing SIVmac239 challenge virus, D. Montefiori for nAb assays; and A. Townsend for figure preparation.
FUNDING: This work was supported by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation-supported Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery (OPP1033121, LJP); the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) (P01 AI094417, R37 AI054292 to LJP; R01 AI059457 to KF); the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director (P51 OD011092); and the National Cancer Institute (contract HHSN261200800001E, JDL).
Footnotes
COMPETING INTERESTS: OHSU and LJP, EEM, SGH, and KF have a substantial financial interest in Vir Biotechnology, Inc., a company that may have a commercial interest in the results of this research and technology. LJP, SGH, and KF are also consultants to Vir and co-inventors of patent PCT/US2011/036657 “Recombinant RhCMV and HCMV vectors and uses thereof” licensed to Vir. JBS has received compensation for consulting for Vir. The potential individual and institutional conflicts of interest have been reviewed and managed by OHSU.
DATA AND MATERIALS AVAILABILITY: All data associated with this study are present in the paper or Supplementary Materials. The computer code used to perform statistical analysis is available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3242804. RhCMV/SIV vectors can be obtained through an MTA.
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Harmon TM, Fisher KA, McGlynn MG, Stover J, Warren MJ, Teng Y, Naveke A, Exploring the Potential Health Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of AIDS Vaccine within a Comprehensive HIV/AIDS Response in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. PLoS One 11, e0146387 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stover J, Hallett TB, Wu Z, Warren M, Gopalappa C, Pretorius C, Ghys PD, Montaner J, Schwartlander B, New G Prevention Technology Study, How can we get close to zero? The potential contribution of biomedical prevention and the investment framework towards an effective response to HIV. PLoS One 9, e111956 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Picker LJ, Hansen SG, Lifson JD, New paradigms for HIV/AIDS vaccine development. Annu Rev Med 63, 95–111 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Masopust D, Picker LJ, Hidden memories: frontline memory T cells and early pathogen interception. J Immunol 188, 5811–5817 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jarvis MA, Hansen SG, Nelson JA, Picker LJ, Früh K, in Cytomegaloviruses: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Intervention Reddehase MJ, Ed. (Caister Academic Press, 2013), vol. 2, chap. 21. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hansen SG, Vieville C, Whizin N, Coyne-Johnson L, Siess DC, Drummond DD, Legasse AW, Axthelm MK, Oswald K, Trubey CM, Piatak M Jr., Lifson JD, Nelson JA, Jarvis MA, Picker LJ, Effector memory T cell responses are associated with protection of rhesus monkeys from mucosal simian immunodeficiency virus challenge. Nat Med 15, 293–299 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hansen SG, Ford JC, Lewis MS, Ventura AB, Hughes CM, Coyne-Johnson L, Whizin N, Oswald K, Shoemaker R, Swanson T, Legasse AW, Chiuchiolo MJ, Parks CL, Axthelm MK, Nelson JA, Jarvis MA, Piatak M Jr., Lifson JD, Picker LJ, Profound early control of highly pathogenic SIV by an effector memory T-cell vaccine. Nature 473, 523–527 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hansen SG, Piatak M Jr., Ventura AB, Hughes CM, Gilbride RM, Ford JC, Oswald K, Shoemaker R, Li Y, Lewis MS, Gilliam AN, Xu G, Whizin N, Burwitz BJ, Planer SL, Turner JM, Legasse AW, Axthelm MK, Nelson JA, Fruh K, Sacha JB, Estes JD, Keele BF, Edlefsen PT, Lifson JD, Picker LJ, Immune clearance of highly pathogenic SIV infection. Nature 502, 100–104 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hansen SG, Sacha JB, Hughes CM, Ford JC, Burwitz BJ, Scholz I, Gilbride RM, Lewis MS, Gilliam AN, Ventura AB, Malouli D, Xu G, Richards R, Whizin N, Reed JS, Hammond KB, Fischer M, Turner JM, Legasse AW, Axthelm MK, Edlefsen PT, Nelson JA, Lifson JD, Fruh K, Picker LJ, Cytomegalovirus vectors violate CD8+ T cell epitope recognition paradigms. Science 340, 1237874 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hansen SG, Wu HL, Burwitz BJ, Hughes CM, Hammond KB, Ventura AB, Reed JS, Gilbride RM, Ainslie E, Morrow DW, Ford JC, Selseth AN, Pathak R, Malouli D, Legasse AW, Axthelm MK, Nelson JA, Gillespie GM, Walters LC, Brackenridge S, Sharpe HR, Lopez CA, Fruh K, Korber BT, McMichael AJ, Gnanakaran S, Sacha JB, Picker LJ, Broadly targeted CD8+ T cell responses restricted by major histocompatibility complex E. Science, 351, 714–720 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Okoye AA, Hansen SG, Vaidya M, Fukazawa Y, Park H, Duell DM, Lum R, Hughes CM, Ventura AB, Ainslie E, Ford JC, Morrow D, Gilbride RM, Legasse AW, Hesselgesser J, Geleziunas R, Li Y, Oswald K, Shoemaker R, Fast R, Bosche WJ, Borate BR, Edlefsen PT, Axthelm MK, Picker LJ, Lifson JD, Early antiretroviral therapy limits SIV reservoir establishment to delay or prevent post-treatment viral rebound. Nat Med 24, 1430–1440 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Barouch DH, Picker LJ, Novel vaccine vectors for HIV-1. Nat Rev Microbiol 12, 765–771 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boppana SB, Britt WJ, in Cytomegaloviruses, Reddehase MJ, Ed. (Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, UK, 2013), vol. 2, pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lilja AE, Shenk T, Efficient replication of rhesus cytomegalovirus variants in multiple rhesus and human cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 105, 19950–19955 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yue Y, Kaur A, Lilja A, Diamond DJ, Walter MR, Barry PA, The susceptibility of primary cultured rhesus macaque kidney epithelial cells to rhesus cytomegalovirus strains. J Gen Virol 97, 1426–1438 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oxford KL, Strelow L, Yue Y, Chang WL, Schmidt KA, Diamond DJ, Barry PA, Open reading frames carried on UL/b’ are implicated in shedding and horizontal transmission of rhesus cytomegalovirus in rhesus monkeys. J Virol 85, 5105–5114 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Assaf BT, Mansfield KG, Strelow L, Westmoreland SV, Barry PA, Kaur A, Limited dissemination and shedding of the UL128 complex-intact, UL/b’-defective rhesus cytomegalovirus strain 180.92. J Virol 88, 9310–9320 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chang WL, Tarantal AF, Zhou SS, Borowsky AD, Barry PA, A recombinant rhesus cytomegalovirus expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein retains the wild-type phenotype and pathogenicity in fetal macaques. J Virol 76, 9493–9504 (2002). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tarantal AF, Salamat MS, Britt WJ, Luciw PA, Hendrickx AG, Barry PA, Neuropathogenesis induced by rhesus cytomegalovirus in fetal rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J Infect Dis 177, 446–450 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Marshall E, Malouli D, Hansen SG, Gilbride RM, Hughes CM, Ventura AB, Ainslie E, Selseth AN, Ford JC, Burke D, Kreklywich D, Womack J, Legasse AW, Axthelm MK, Kahl C, Streblow D, Edlefsen PT, Picker LJ, Früh K, Enhancing safety of cytomegalovirus vaccine vectors by engaging host intrinsic immunity. Sci Transl Med, (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lindsay CR, Morozov VM, Ishov AM, PML NBs (ND10) and Daxx: from nuclear structure to protein function. Front Biosci 13, 7132–7142 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tang Q, Maul GG, Mouse cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein 1 binds with host cell repressors to relieve suppressive effects on viral transcription and replication during lytic infection. J Virol 77, 1357–1367 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Everett RD, Rechter S, Papior P, Tavalai N, Stamminger T, Orr A, PML contributes to a cellular mechanism of repression of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection that is inactivated by ICP0. J Virol 80, 7995–8005 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kalejta RF, Functions of human cytomegalovirus tegument proteins prior to immediate early gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 325, 101–115 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tavalai N, Papior P, Rechter S, Leis M, Stamminger T, Evidence for a role of the cellular ND10 protein PML in mediating intrinsic immunity against human cytomegalovirus infections. J Virol 80, 8006–8018 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Saffert RT, Kalejta RF, Inactivating a cellular intrinsic immune defense mediated by Daxx is the mechanism through which the human cytomegalovirus pp71 protein stimulates viral immediate-early gene expression. J Virol 80, 3863–3871 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Preston CM, Nicholl MJ, Role of the cellular protein hDaxx in human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene expression. J Gen Virol 87, 1113–1121 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kirmaier A, Wu F, Newman RM, Hall LR, Morgan JS, O’Connor S, Marx PA, Meythaler M, Goldstein S, Buckler-White A, Kaur A, Hirsch VM, Johnson WE, TRIM5 suppresses cross-species transmission of a primate immunodeficiency virus and selects for emergence of resistant variants in the new species. PLoS Biol 8, (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hirsch V, Adger-Johnson D, Campbell B, Goldstein S, Brown C, Elkins WR, Montefiori DC, A molecularly cloned, pathogenic, neutralization-resistant simian immunodeficiency virus, SIVsmE543–3. J Virol 71, 1608–1620 (1997). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Reynolds MR, Weiler AM, Weisgrau KL, Piaskowski SM, Furlott JR, Weinfurter JT, Kaizu M, Soma T, Leon EJ, MacNair C, Leaman DP, Zwick MB, Gostick E, Musani SK, Price DA, Friedrich TC, Rakasz EG, Wilson NA, McDermott AB, Boyle R, Allison DB, Burton DR, Koff WC, Watkins DI, Macaques vaccinated with live-attenuated SIV control replication of heterologous virus. J Exp Med 205, 2537–2550 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hansen SG, Zak DE, Xu G, Ford JC, Marshall EE, Malouli D, Gilbride RM, Hughes CM, Ventura AB, Ainslie E, Randall KT, Selseth AN, Rundstrom P, Herlache L, Lewis MS, Park H, Planer SL, Turner JM, Fischer M, Armstrong C, Zweig RC, Valvo J, Braun JM, Shankar S, Lu L, Sylwester AW, Legasse AW, Messerle M, Jarvis MA, Amon LM, Aderem A, Alter G, Laddy DJ, Stone M, Bonavia A, Evans TG, Axthelm MK, Fruh K, Edlefsen PT, Picker LJ, Prevention of tuberculosis in rhesus macaques by a cytomegalovirus-based vaccine. Nat Med 24, 130–143 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rempel H, Calosing C, Sun B, Pulliam L, Sialoadhesin expressed on IFN-induced monocytes binds HIV-1 and enhances infectivity. PLoS One 3, e1967 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kim WK, McGary CM, Holder GE, Filipowicz AR, Kim MM, Beydoun HA, Cai Y, Liu X, Sugimoto C, Kuroda MJ, Increased Expression of CD169 on Blood Monocytes and Its Regulation by Virus and CD8 T Cells in Macaque Models of HIV Infection and AIDS. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 31, 696–706 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bruner KM, Murray AJ, Pollack RA, Soliman MG, Laskey SB, Capoferri AA, Lai J, Strain MC, Lada SM, Hoh R, Ho YC, Richman DD, Deeks SG, Siliciano JD, Siliciano RF, Defective proviruses rapidly accumulate during acute HIV-1 infection. Nat Med 22, 1043–1049 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cannon MJ, Schmid DS, Hyde TB, Review of cytomegalovirus seroprevalence and demographic characteristics associated with infection. Rev Med Virol 20, 202–213 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pass RF, in Fields Virology, H. PM Knipe David M., Griffin Diane E., Lamb Robert A. Martin Malcolm A., Roizman Bernard and Straus Stephen E., Ed. (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2001), pp. 2675–2705. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zanghellini F, Boppana SB, Emery VC, Griffiths PD, Pass RF, Asymptomatic primary cytomegalovirus infection: virologic and immunologic features. J Inf Dis 180, 702–707 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Reinke P, Prosch S, Kern F, Volk HD, Mechanisms of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) (re)activation and its impact on organ transplant patients. Transpl Infect Dis 1, 157–164 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cannon MJ, Grosse SD, Fowler KB, in Cytomegalovirus, Reddehase MJ, Ed. (Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, UK, 2013), vol. 2, pp. 26–48. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Del Prete GQ, Park H, Fennessey CM, Reid C, Lipkey L, Newman L, Oswald K, Kahl C, Piatak M Jr., Quinones OA, Alvord WG, Smedley J, Estes JD, Lifson JD, Picker LJ, Keele BF, Molecularly tagged simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 synthetic swarm for tracking independent infection events. J Virol 88, 8077–8090 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sacha JB, Chung C, Rakasz EG, Spencer SP, Jonas AK, Bean AT, Lee W, Burwitz BJ, Stephany JJ, Loffredo JT, Allison DB, Adnan S, Hoji A, Wilson NA, Friedrich TC, Lifson JD, Yang OO, Watkins DI, Gag-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes recognize infected cells before AIDS-virus integration and viral protein expression. J Immunol 178, 2746–2754 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hansen SG, Piatak M, Ventura AB, Hughes CM, Gilbride RM, Ford JC, Oswald K, Shoemaker R, Li Y, Lewis MS, Gilliam AN, Xu G, Whizin N, Burwitz BJ, Planer SL, Turner JM, Legasse AW, Axthelm MK, Nelson JA, Fruh K, Sacha JB, Estes JD, Keele BF, Edlefsen PT, Lifson JD, Picker LJ, Addendum: Immune clearance of highly pathogenic SIV infection. Nature 547, 123–124 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Venneti S, Bonneh-Barkay D, Lopresti BJ, Bissel SJ, Wang G, Mathis CA, Piatak M Jr., Lifson JD, Nyaundi JO, Murphey-Corb M, Wiley CA, Longitudinal in vivo positron emission tomography imaging of infected and activated brain macrophages in a macaque model of human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis correlates with central and peripheral markers of encephalitis and areas of synaptic degeneration. Am J Pathol 172, 1603–1616 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hansen SG, Powers CJ, Richards R, Ventura AB, Ford JC, Siess D, Axthelm MK, Nelson JA, Jarvis MA, Picker LJ, K. Früh, Evasion of CD8+ T cells Is critical for superinfection by cytomegalovirus. Science 328, 102–106 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Walker JM, Maecker HT, Maino VC, L.J, Picker, Multicolor flow cytometric analysis in SIV-infected rhesus macaque. Methods Cell Biol 75, 535–57, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Montefiori DC, Measuring HIV neutralization in a luciferase reporter gene assay. Methods Cell Biol 485, 395–405, 2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Materials and Methods
Fig. S1. ΔRh110 RhCMV/SIV vector design and supertope amino acid sequences.
Fig. S2. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of SIVmac239 vs. SIVsmE660 vaccine inserts.
Fig. S3. Analysis of SIV Env-specific antibody (Ab) responses after vaccination and after acquisition of SIV infection.
Fig. S4. Acquisition of SIV infection by Group 1, 2 and 3 RM with repeated, limiting dose IVag SIVmac239 challenge.
Fig. S5. Immune correlates analysis.
Fig. S6. Analysis of SIV Gag- and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses after SIV infection.
Fig. S7. Analysis of circulating monocyte activation after SIV infection.
Fig. S8. Analysis of plasma viral load, and SIV Vif-, Gag-, and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in vaccine-protected, necropsied RM from Groups 1 and 2.
Fig. S9. Analysis of SIV Gag- and Pol-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses in vaccine-protected, and subsequently re-challenged RM from Groups 1, 2, and 4.
Data File S1. Primary data