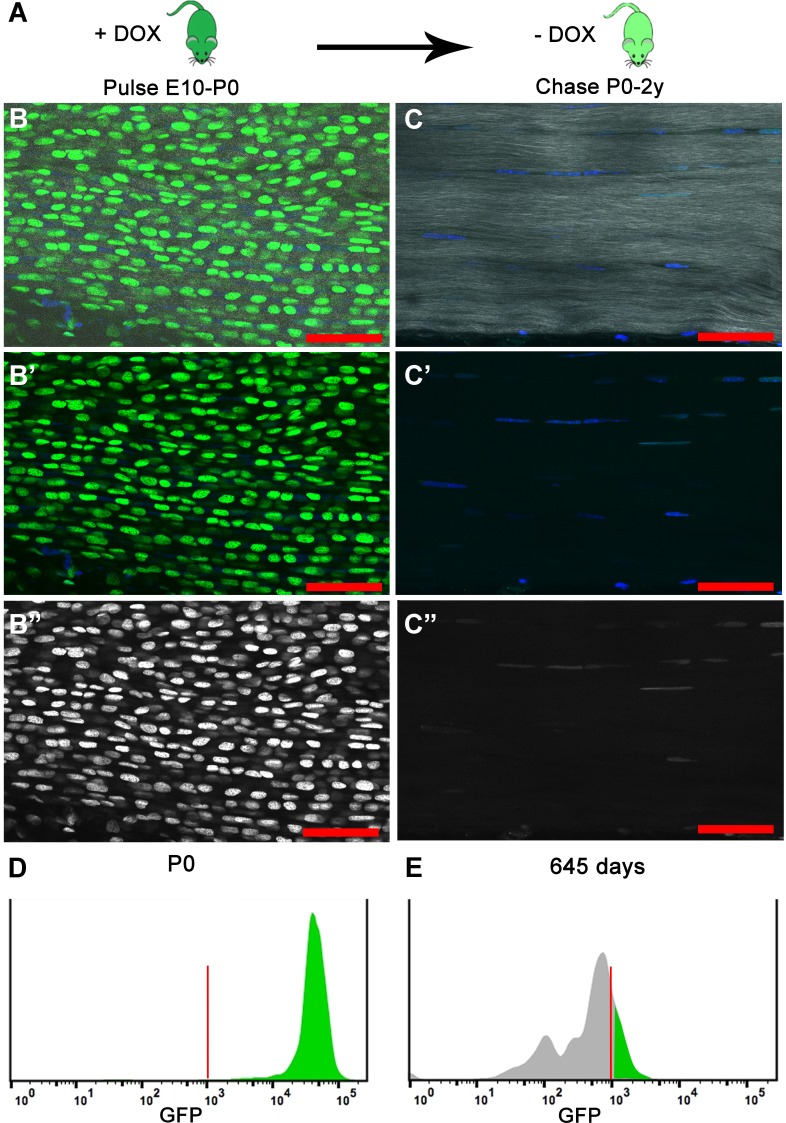
Figure 1. H2B-GFP expression is induced upon the addition of Dox to timed pregnant females from E10 to P0 (dark green); Dox is removed for the chase period of 0–2 years and H2B-GFP protein is diluted (light green) in proportion to cell division.
(A) At birth (P0), longitudinal sections of Achilles (B–B’’) tendons (n = 3 mice) show extensive H2B-GFP+ (green B, B'; white B’’) labeling of Hoechst+ nuclei (blue, B, B’). SHG is shown in white (B, C). Histogram showing that more than 95% of the cells are H2B-GFP+ at P0 (D). After 680 days, Achilles (C–C’’) tendons (n = 3 mice) have qualitatively fewer H2B-GFP+ (green C, C'; white C’’) labeled Hoechst+ nuclei (blue C, C’). Histogram showing only 20% of the cells are H2B-GFP+ and the H2B-GFP intensity has decreased at 645 days (E). For the histograms, a representative is shown; tendons from n > 3 mice were examined independently. Scale Bars, 50 µm; Vertical red lines (H, O) indicate the control GFP beads for standardizing intensity and gates.