Abstract
Evidence from randomised controlled trials supports beneficial effects of total dairy products on body weight, fat and lean mass, but evidence on associations of dairy types with distributions of body fat and lean mass is limited. We aimed to investigate associations of total and different types of dairy products with markers of adiposity, and body fat and lean mass distribution. We evaluated cross-sectional data from 12,065 adults aged 30 to 65 years recruited to the Fenland study between 2005 and 2015 in Cambridgeshire UK. Diet was assessed with a food frequency questionnaire. We estimated regression coefficients (or % differences) and their 95% CI using multiple linear regression models. The median (interquartile range) of milk, yoghurt, and cheese consumption were 293 (146 - 439), 35.3 (8.8 – 71.8), and 14.6 (4.8 – 26.9) g/d, respectively. Low-fat dairy consumption was inversely associated with visceral-to-subcutaneous fat ratio estimated with dual energy X-ray absorptiometry [-2.58% (-3.91, -1.23%) per serving/day]. Habitual consumption per serving/day (200 g) of milk was associated with 0.33 (0.19, 0.46) kg higher lean mass. Other associations were not significant after false discovery correction. Our findings suggest that the influence of milk consumption on lean mass and of low-fat dairy consumption on fat mass distribution may be potential pathways for the link between dairy consumption and metabolic risk. Our cross-sectional findings warrant further research in prospective and experimental studies in diverse populations.
Keywords: Dairy products, milk, yoghurt, cheese, butter, adiposity
Introduction
Diet is acknowledged to be a leading behavioural risk factor for cardio-metabolic diseases(1). Among dietary factors, dairy products are of particular interest due to their inverse association with cardio-metabolic health(2), thought to be related to their high nutrient density and mineral content, but also due to the controversy arising from their blood cholesterol raising saturated fat content(3). Several meta-analyses of prospective cohort studies on the associations of dairy products with cardiovascular disease(4, 5) and type 2 diabetes(6–8) have suggested that the associations vary by dairy type. There is a general concordance of observational results suggesting an inverse association between yoghurt consumption and type 2 diabetes(6–8). In contrast, evidence for associations between other dairy types and type 2 diabetes(7, 9) or cardiovascular disease(4) is inconsistent with either null or inverse associations reported for the consumption of cheese and low-fat milk(4, 7, 9).
Adiposity is one of the most well described potential pathways which might link total dairy consumption to cardio-metabolic disease pathogenesis. Evidence from randomised clinical trials shows that total dairy products decrease body weight(10) and body fat mass(10), and increase body lean mass(11) under energy restriction. However, evidence on associations between types of dairy products and markers of adiposity, especially markers of fat and lean mass distribution is sparse. Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and subcutaneous adipose tissue (SCAT) are compartments of abdominal fat. While abdominal fat is associated with cardio-metabolic diseases(12), VAT has been more strongly associated with cardio-metabolic risk than SCAT(13), which has been suggested to be potentially protective(14). Specifically the ratio of VAT to SCAT was reported to be strongly associated with cardio-metabolic risk independent of body mass index (BMI) and VAT(15). Due to the higher cost of the methods to estimate abdominal fat distribution e.g. dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), most large-scale population studies examine waist circumference as a proxy for abdominal fat, which cannot fully capture the distribution between VAT and SCAT. Only a few studies have investigated associations between dairy products (total(16) and low-fat(17)) and VAT, but evidence is lacking on associations of dairy consumption with SCAT and VAT/SCAT.
We aimed to investigate the associations of total and different types of dairy products with body fat and lean mass and their distribution in a large population-based study in the UK.
Methods
Study design and population
The Fenland study is a cohort study with baseline measurements conducted between 2005 and 2015 (n=12,434 with 27% response rate). Eligible participants were born between 1950 and 1975 and were invited via their general practice to attend the clinical sites at Ely, Wisbech, or Cambridge, UK, where the clinical and dietary assessments were conducted. Exclusion criteria, assessed by general practitioners, were known history of diabetes, psychotic or terminal illness, inability to walk unaided, pregnancy, or lactation. The study was approved by the Cambridge Local Ethics Committee. All participants gave written informed consent.
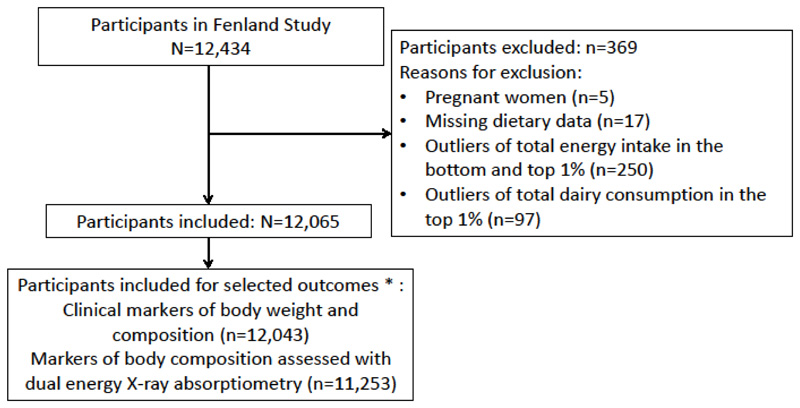
For the current analysis, we evaluated baseline data from 12,065 participants after exclusion of pregnant women (n=5), participants with missing dietary data (n=17), those in the bottom and top 1% of total energy intake (n=250), and in the top 1% of total dairy consumption (n=97). Participants with missing outcome data were also excluded (n range=1-812 depending on the outcome). A study flowchart of participant inclusion is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Participant selection for analyses of associations of dairy consumption with cardio-metabolic markers in over 12,000 adults of the Fenland Study, UK. *A minimal number of participants for each sub-group of the outcomes is presented. Numbers slightly varied depending on missing information of each outcome variable.
Dietary assessment
Participants’ diet over the previous year was assessed with a 130-item semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire(18). The dietary data were processed using FETA software(19). Dairy products were assessed in servings/d and were categorised as we previously described(20) (Table 1). Dairy servings were defined as one average glass (200 g) for milk, 125 g pot for yoghurt, a medium serving of 40 g for cheese, one tablespoon (15 g) for single cream, one tablespoon (30 g) for double cream, one teaspoon (10 g) for butter and one average scoop/tub (60 g) for ice-cream.
Table 1. Definitions of dairy groups (Fenland Study, UK).
| Dairy group | Definition |
|---|---|
| Full-fat milk | Goat's milk; Channel Islands milk; Silver top full-cream milk; Evaporated milk whole diluted; Sheep's milk |
| Low-fat milk | Semi-skimmed milk; Skimmed milk; Skimmed milk as reconstituted dried milk |
| Milk | Full-fat milk, Low-fat milk |
| Yoghurt | Full-fat yoghurt *; Low-fat yoghurt * |
| Cheese | High-fat cheese †; Low-fat cheese ‡ |
| Cream § | Single cream; Double cream |
| Low-fat fermented dairy products | Total yoghurt; Low-fat cheese |
| Fermented dairy products | Total yoghurt; Total cheese |
| High-fat dairy products | Full-fat milk; High-fat cheese; Total cream; Butter; Ice-cream |
| Low-fat dairy products | Low-fat milk; Total yoghurt; Low-fat cheese |
| Total dairy products | Total milk; Total yoghurt; Total cheese; Total cream; Butter; Ice-cream |
The variables derived directly from the FFQ questions were used
The variable derived directly from the FFQ questions on hard cheese intake was used. The assumption made here is that high-fat cheese is equivalent to hard cheese.
The variable derived directly from the FFQ questions on cottage and low-fat soft cheese intake was used. The assumption made here is that low-fat cheese is equivalent to cottage and low-fat, soft cheese.
Cream was used as a contributor to high-fat and total dairy products, but results separately for it and its types are not presented, as the very low intakes result in very unstable and imprecise estimates
Adiposity measures
These measurements were conducted at each clinical site according to standardised procedures. BMI was calculated as weight divided by height squared (kg/m2). Waist and hip circumferences were averaged from two repeated measures with a non-stretch tape. Total body fat and its distribution (peripheral fat, VAT, SCAT) and lean mass and its distribution (appendicular lean mass) were estimated with a DEXA scan (Lunar Prodigy Advanced fan beam scanner, GE Healthcare, Bedford, United Kingdom; GE encore software, version 14.10.022 to 16, GE Medical Systems(21)). Specifically, the DEXA system demarcated the boundaries of the android region based on an established protocol. VAT was estimated as part of the android region from an inbuilt algorithm of the DEXA software. SCAT was calculated after subtracting VAT from the android fat mass. These DEXA estimates of abdominal VAT and SCAT have been validated against amounts of VAT and SCAT determined by computed tomography(22) and magnetic resonance imaging(23), the reference methods for adipose tissue quantification.
Assessment of socio-demographic and lifestyle factors
A general questionnaire was administered for information on ethnicity, occupation, education, income, marital status, smoking and medication use. Physical activity was objectively measured over 7 d using a combined heart rate and movement sensor (Actiheart, CamNtech, Papworth, UK)(24) and individually calibrated with a treadmill test to derive physical activity energy expenditure (kJ/kg per d)(25). This method was previously validated with doubly-labelled water.
Statistical analyses
As primary exposures, we considered milk, yoghurt and cheese. As primary outcome, we defined the ratio of VAT to SCAT (VAT/SCAT). Other outcomes included total and peripheral body fat mass, total and appendicular body lean mass and proxies of abdominal fat i.e. waist circumference and the waist-to-hip ratio. We presented results for VAT/SCAT as %change after back-transformation (exponentiation) of the log-transformed variable, because it was positively-skewed.
Missing covariates were imputed by chained equations under the assumption of data missing at random(26). Multiple imputation involved linear, logistic and predictive mean matching models according to variable distribution and five imputation datasets were derived. Further analyses accounted for variability due to imputation. To examine cross-sectional associations between different dairy types and adiposity markers, robust multiple linear regression was used, deriving multiple maximum likelihood (MM-)estimators, which are robust against the influence of outliers(27). The initial probability of false positive findings was set to 5%. Because of the large number of tests, false discovery rate correction was applied accounting for correlations between tests(28). Associations were considered significant if they passed this correction (P<0.0005).
Associations were adjusted for potential confounders based on previous knowledge and biological plausibility. Specifically, we adjusted for socio-demographic, lifestyle and clinical factors including age, sex, test-site, ethnicity, age at completion of full-time education, education level, occupation, household income, marital status, smoking status, pack-years of smoking, physical activity energy expenditure, hormone-replacement therapy (for women only), lipid-lowering medication, anti-hypertensive medication (categorical), plasma vitamin C (as a marker of diet quality, reflecting fruit and vegetable intake), dietary supplement use, total energy intake, consumption of dietary factors (fruit, vegetables not including potatoes, potatoes, legumes, processed cereals, whole-grain cereals, poultry and eggs, red meat, processed meat, fish, sauces, margarine, nuts, sweet snacks, sugar-sweetened beverages, artificially sweetened beverages, fruit juice, regular coffee, decaffeinated coffee, tea, alcoholic beverages), and BMI. Adjustment for BMI was performed to (1) examine associations independent of BMI, (2) partly account for the possibility of dietary misreporting and (3) account for lifestyle confounding due to obesity status. Dairy types were mutually adjusted. When the outcome was lean mass, models were further adjusted for height.
Pre-specified tests for effect modification by sex and BMI for each association were investigated. As sensitivity analyses, we repeated regression analyses in the complete-case dataset, to examine stability of results based on five imputed datasets in the primary analyses. To assess whether non-linear associations were present, restricted cubic spline regressions (three knots at the 10th, 50th and 90th percentiles) were fitted in the most adjusted model above. For the same purpose, categorical exposures were used with five categories including non-consumers and quartiles among consumers for types of dairy products. Quartiles were generated from the residuals of the regression of total energy intake against dairy products(29). In addition to the analyses including BMI as a covariate, we also adjusted for the ratio of total energy intake to basal metabolic rate as an indicator of dietary misreporting(30). In post-hoc analyses, we examined whether the identified significant associations can be explained by nutrients contained in dairy products including calcium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamin A, vitamin B12, lactose, mono-unsaturated fat and saturated fat from the dairy exposure one-by-one. All analyses were conducted using Stata 14.2 (College Station, TX: StataCorp LP, 2015).
Results
Descriptive characteristics
We evaluated 12,065 adults (53.8% women) with a mean (SD) age of 48.8 (7.5) years (Table 2). Almost two-thirds of high yoghurt consumers were women. Participants of non-white ethnic background were more frequently low dairy consumers compared with participants of white ethnic background. The ethnic difference was most marked for cheese intake: the percentage of non-white participants among non-consumers of cheese was 6.3% higher than among cheese consumers. Yoghurt and cheese consumption was positively associated with higher socio-economic status and negatively associated with likelihood of being current smokers (Supplemental Table 1). Among dairy consumption levels, overall, low-fat dairy consumption was approximately seven times higher than that of high-fat dairy (Supplemental Table 1).
Table 2.
Descriptive characteristics of socio-demographic, behavioural and clinical factors* for the bottom (non-consumers) and top categories of milk, yoghurt and cheese consumption (g/d), as well as in the total sample of 12,065 adults of the Fenland study, UK
| Milk† | Yoghurt† | Cheese† | |||||
| Median (IQR) consumption (g/d) | Overall (%) | 293 (146 - 439) | 35.3 (8.8 - 71.8) | 14.6 (4.8 - 26.9) | |||
| 0 g/d | 585 - 732 g/d | 0 g/d | 99.5 - 1,134 g/d | 0 g/d | 26.8 - 284 g/d | ||
| Participants (n) | 12,065 | 921 | 1,490 | 2,787 | 3,014 | 779 | 3,028 |
| Socio-demographic factors | |||||||
| Age (years) | 48.8 (42.7-54.7) | 49.6 (42.8-55.1) | 48.0 (42.2–54.0) | 48.6 (42.4-54.6) | 50.0 (43.7-55.2) | 48.8 (42.4-55.2) | 48.1 (41.9-54.3) |
| Sex (ref. Men): Women | 53.8 | 63.7 | 38.7 | 39.5 | 65.7 | 49.0 | 60.2 |
| Ethnicity ‡ (ref. White): Non-white | 2.9 | 4.9 | 1.4 | 3.3 | 1.8 | 7.9 | 1.6 |
| Educational level ‡ (ref. Low): Medium | 46.2 | 41.8 | 48.0 | 49.0 | 46.7 | 48.1 | 41.9 |
| High | 33.9 | 40.7 | 27.5 | 25.0 | 33.5 | 23.9 | 42.1 |
| Age completing education (years) ‡ | 18.0 (16.0–21.0) | 18.0 (16.0 – 22.0) | 17.0 (16.0 – 21.0) | 17.0 (16.0 – 20.0) | 18.0 (16.0 – 21.0) | 16.5 (16.0 – 19.0) | 18.0 (16.0 – 22.0) |
| Socio-economic status (based on occupation) §(ref. Low): Medium | 19.8 | 19.7 | 14.6 | 16.4 | 23.1 | 21.2 | 19.8 |
| High | 53.3 | 58.3 | 47.6 | 46.1 | 52.5 | 42.7 | 58.4 |
| Income ‡ (ref. <£20,000): £20,000 - 40,000 | 35.4 | 32.6 | 37.5 | 37.8 | 37.3 | 38.5 | 34.4 |
| >£40,000 | 50.8 | 52.0 | 47.3 | 45.1 | 49.6 | 41.9 | 52.1 |
| Marital status ‖ (ref. Single): Married | 81.4 | 75.1 | 80.5 | 79.9 | 80.8 | 77.1 | 80.2 |
| Widowed/Separated | 9.5 | 10.3 | 9.9 | 9.3 | 10.3 | 9.6 | 9.8 |
| Lifestyle factors | |||||||
| Smoking status ‡ (ref. Never): Former | 33.3 | 35.6 | 31.8 | 32.0 | 34.0 | 27.6 | 34.3 |
| Current | 12.3 | 13.3 | 17.8 | 20.1 | 7.6 | 13.5 | 11.1 |
| Smoking (pack-years) § | 0.0 (0.0 - 2,376) | 0.0 (0.0 - 2,696) | 0.0 (0.0 - 3,701) | 0.0 (0.0 - 4,362) | 0.0 (0.0 - 1,414) | 0.0 (0.0 - 2,725) | 0.0 (0.0 - 2,192) |
| Physical activity energy expenditure (kJ/kg per d) ‡ ¶ | 50.7 (37.6 - 66.5) | 49.9 (38.1 - 63.5) | 55.4 (40.8 - 72.4) | 51.2 (37.7 - 67.8) | 50.5 (37.0 - 65.4) | 49.4 (35.7 - 65.7) | 52.0 (38.8 - 67.6) |
| Energy intake (kJ/d) | 1,851 (1,524 - 2,265) | 1,600 (1,312 - 2,030) | 2,140 (1,733 - 2,613) | 1,768 (1,433 - 2,180) | 1,932 (1,603 - 2,345) | 1,681 (1,360 - 2,081) | 2,067 (1,691 - 2,507) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.2 (23.6 - 29.4) | 25.8 (23.0 - 29.1) | 26.7 (24.2 - 29.9) | 26.6 (23.8 - 29.6) | 26.1 (23.5 - 29.3) | 26.5 (23.8 - 29.6) | 25.8 (23.2 - 29.1) |
| Medications / Supplements | |||||||
| Lipid-lowering medication ‡ (ref. No): Yes | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.7 | 4.0 | 4.4 | 3.3 |
| Anti-hypertensive medication ‡ (ref. No): Yes | 7.4 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 8.2 | 7.1 | 7.8 | 6.9 |
| Hormonal therapy ‡ (ref. No for women / Men): Yes | 2.8 | 3.4 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 2.7 | 3.2 |
| Dietary supplements ‡ (ref. No): Yes | 41.2 | 49.5 | 40.5 | 33.5 | 47.7 | 39.5 | 44.5 |
IQR, Interquartile range
Continuous variables are presented as median (IQR) and categorical variables are presented as column percentages
Five categories; Milk: Non-consumers, 146 g/d, 293 g/d, 439 g/d, 585 or 732 g/d (categories presented: non-consumers and 585-732 g/d); Yoghurt: Non-consumers and quartiles within consumers (1st quartile:8.8-8.8 g/d, 2nd quartile: 17.6 – 35.3 g/d, 3rd quartile: 54.2 – 71.8 g/d, 4th quartile: 99.5 – 1,134 g/d ;categories presented: non-consumers and 4th quartile within consumers); Cheese: Non-consumers and quartiles within consumers (1st quartile: 2.4 – 4.8 g/d, 2nd quartile: 6.6 – 13.2 g/d, 3rd quartile: 14.6 – 25.8 g/d, 4th quartile: 26.8 – 284.6 g/d; categories presented: non-consumers and 4th quartile within consumers). Dairy consumption was assessed with a food frequency questionnaire Milk consumption was assessed with two questions. In the first question, participants could choose the type of milk that they consumed most frequently (options: “Full cream, silver”, “Semi-skimmed, red/white”, “Skimmed/blue”, “Channel Islands, gold”, “Dried milk, “Soya”, “Other”, “None”). In the second question, participants could choose one of six categories for the daily amount of milk consumed [options: “None”, “Quarter of a pint” (146 g/d), “Half a pint” (293 g/d), “Three quarters of a pint” (439 g/d), “One pint” (585 g/d), “More than one pint” (732 g/d)]. Full-fat yoghurt, low-fat yoghurt, high-fat cheese, low-fat cheese, butter, cream and ice-cream were assessed with questions including nine frequencies, which ranged from “Never or less than once/month” to “6+ per day”.
Percentage of missing values < 5% with a total of 28.8% of missing values when accounting for non-overlapping missing values across all the variables
Percentage of missing values 5-15% with a total of 28.8% of missing values when accounting for non-overlapping missing values across all the variables
Percentage of missing values 15-25% with a total of 28.8% of missing values when accounting for non-overlapping missing values across all the variables
Physical activity was objectively measured with a combined heart rate and movement sensor.
Dairy products and body composition
Habitual milk consumption was significantly associated with higher BMI; each additional serving of milk/d was associated with 0.26 (95% CI: 0.16, 0.36) kg/m2 higher BMI (Supplemental Table 2). Similar associations were observed for low-fat milk and for low-fat and total dairy products. Low-fat dairy consumption was associated with 2.6% lower (-3.91, -1.23%) VAT/SCAT. A similar association was observed for VAT (Supplemental Figure 1).
Habitual milk consumption was significantly associated with 0.33 (0.19, 0.46) kg higher lean mass per serving/d (Figure 2). Low-fat milk showed similar associations (Figure 2). The association was partly attenuated when adjusted for height, but it was still significant [0.18(0.10, 0.27) kg/serving of milk/d]. Effect modification by BMI was suggested for the association between high-fat dairy and appendicular lean mass (P-interaction=0.0001). Among adults with non-overweight BMI (<25 kg/m2), appendicular lean mass was lower by 0.11 (-0.22, -0.001) kg per one serving of high-fat dairy, but associations were not observed among overweight [0.05(95% CI: -0.07 to 0.18) kg] or obese adults [0.02 (95% CI -0.16 to 0.20 kg)].
Figure 2.
Associations of types of dairy consumption (servings/d) with markers of body composition estimated with dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) among over 12,000 adults in the Fenland Study, UK. Forest plots represent regression coefficients with their 95% CIs adjusted for age (years), sex, test-site (Cambridge, Ely, Wisbech), ethnicity (white, non-white), total energy intake (kcal/d), other dairy types, educational level (low, medium, high), age when full-time education finished (years), socio-economic status based on occupation (low, medium, high), income (<£20,000, £20,000-40,000, >£40,000), marital status (single, married, widowed/separated), smoking status (never, former, current smoker), pack-years of smoking, energy expenditure due to physical activity (kJ/kg per d), lipid-lowering medication (yes/no), anti-hypertensive medication (yes/no), hormone-replacement therapy (yes/no in women), intakes (g/d) of fruit, vegetables, potatoes, legumes, processed cereals, whole-grain cereals, poultry and eggs, red meat, processed meat, fish, sauces, margarine, nuts, sweet snacks, sugar-sweetened beverages, artificially sweetened beverages, fruit juice, regular coffee, decaffeinated coffee, tea and alcoholic beverages, plasma vitamin C levels (μmol/l), dietary supplement use (Yes, No), and BMI (kg/m2). Statistically significant associations after false discovery rate corrections are marked with an asterisk. See categorisation of dairy types in Table 1. DEXA: Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry; SCAT: Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue; VAT: Visceral Adipose Tissue
Other dairy types were not significantly associated with BMI, nor any dairy products with any other anthropometric measure (Figures 2 and 3, Supplemental Figure 1).
Figure 3.
Associations of types of dairy consumption (servings/d) with waist circumference and the waist-to-hip ratio among over 12,000 adults in the Fenland Study, UK. Forest plots represent regression coefficients with their 95% CIs adjusted for age (years), sex, test-site (Cambridge, Ely, Wisbech), ethnicity (white, non-white), total energy intake (kcal/d), other dairy types, educational level (low, medium, high), age when full-time education finished (years), socio-economic status based on occupation (low, medium, high), income (<£20,000, £20,000-40,000, >£40,000), marital status (single, married, widowed/separated), smoking status (never, former, current smoker), pack-years of smoking, energy expenditure due to physical activity (kJ/kg per d), lipid-lowering medication (yes/no), anti-hypertensive medication (yes/no), hormone-replacement therapy (yes/no in women), intakes (g/d) of fruit, vegetables, potatoes, legumes, processed cereals, whole-grain cereals, poultry and eggs, red meat, processed meat, fish, sauces, margarine, nuts, sweet snacks, sugar-sweetened beverages, artificially sweetened beverages, fruit juice, regular coffee, decaffeinated coffee, tea and alcoholic beverages, plasma vitamin C levels (μmol/l), dietary supplement use (yes/no), and BMI (kg/m2). Statistically significant associations after false discovery rate corrections are marked with an asterisk. See categorisation of dairy types in Table 1.
Other analyses
Results were not altered when complete-case analyses were performed, and findings were similar when adjusting for the ratio of total energy intake to basal metabolic rate rather than adjusting for BMI or after further adjustment for dairy nutrients (Supplemental Table 3). There was no indication of a non-linear association from analyses with restricted cubic splines or categorical exposures after correction for multiple testing.
Discussion
Our study reports two main findings. The first was that habitual daily consumption of one serving of low-fat dairy products was associated with a 3% lower ratio of VAT to SCAT as a marker of fat mass distribution, a measure which is associated with diabetes risk independently of total fat mass(15). Second, habitual daily consumption of 1 serving of milk was associated with a 0.33 kg higher body lean mass.
There are no previous studies on the association between dairy consumption and VAT/SCAT. A randomized controlled trial showed a reduction in VAT among those consuming 6-7 servings of dairy products per day compared to those consuming less than 4 servings/d(16), and a cross-sectional study of twins reported an inverse association between low-fat fermented dairy products and VAT(17), but we have not identified any studies of the association between dairy consumption and SCAT. Although total dairy consumption has been consistently associated with a lower body fat mass in randomized controlled trials(31–33), the number of studies for dairy subtypes is limited. We found no significant associations between any dairy type and total or peripheral fat mass or waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as proxies for fat mass distribution. The direction of the associations we observed between low-fat dairy consumption and total body fat mass, and waist circumference was consistent with the findings of previous studies and with our findings for VAT/SCAT. The higher dairy amounts used in feeding trials compared to the consumption levels reported in observational studies could partly explain the lack of significance in certain associations. In addition, it is expected that the direction of the association of low-fat dairy products with VAT/SCAT is consistent with that of the association of low-fat dairy with waist circumference and the waist-to-hip ratio, because waist circumference is a proxy measure of abdominal fat. VAT/SCAT was estimated with higher accuracy than waist and hip circumferences. This might partly explain as to why the association with VAT/SCAT was significant after multiple test correction, but not the association with waist circumference and the waist-to-hip ratio.
No mechanism has been reported for an inverse association between low-fat dairy consumption and VAT/SCAT. Nevertheless, a plausible explanation could be that VAT is more metabolically active with a more efficient glucose uptake than SCAT(34), and therefore the effects of dairy nutrients on fat mass are more pronounced in the VAT than in SCAT. Among dairy nutrients, calcium may reduce the fat content of the adipose tissue because intracellular calcium promotes lipolysis and reduces lipogenesis(35) and calcium supplementation was previously shown to decrease VAT without changing body weight or total abdominal fat(36).
With our analyses and specifically the observed positive association between milk consumption and body lean mass, we extend the previous understanding on the positive association between total dairy consumption and total lean mass(31) to include specific dairy subtypes. Dairy products and mainly milk have been consistently associated with bone health due to their nutrients content including calcium, phosphorous, vitamin D and protein, which might partly explain the positive association with lean mass(37). Another potential mechanism is the increasing effect of milk on growth hormone(38, 39), which has been associated with a higher lean mass through a higher bone mineral density and muscle mass(40).
Strengths and limitations
Our study has several strengths including its large sample size (n=12,065), and the inclusion of several dairy subtypes, which allowed the investigation of potentially different associations with adiposity for different dairy types. By employing DEXA, we were able to use more accurate methods to assess VAT and SCAT than previous studies that used waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as proxies of central adiposity(12). Our statistical approaches were thorough including the adjustment for important potential confounders including objectively measured physical activity, the derivation of estimates robust to outliers, and the handling of missing data with multiple imputation.
Our study also has limitations. The cross-sectional design increases the risk of reverse causation and limits inference for causal association and our results can thus be used mainly for hypothesis generation. Although the food frequency questionnaire used was assessed for validity in a similar population(18) and we adjusted for BMI as an established factor of dietary misreporting(41), we cannot exclude the possibility of error due to dietary misreporting caused by the use of self-reported methods of dietary assessment. Commensurate with this, the food frequency questionnaire was limited in the detail on types of dairy products consumed, so we were not able to estimate the nutrient content accurately and thus made assumptions based on average estimates. The questionnaire also limited the assessment of various dairy definitions (e.g. sweetened yoghurt) and the influences of such variations on study results. Although we adjusted for many potential confounders, residual confounding cannot be ruled out. We were also not able to disentangle whether BMI was a confounder, a mediator or both in our cross-sectional analysis, while we could examine the associations independent of BMI. If BMI is on the causal pathway adjustment for BMI would have attenuated the findings towards the null. Future prospective analyses of change in weight (or BMI) in relation to dairy products will be better placed to investigate this further. The response rate of our study was moderate at 27%. This should be placed in the context of the internal validity of our study with our use of objective assessments i.e. DEXA on the full cohort, but we acknowledge limited external validity (generalisability) of our findings for the UK general population. Moreover, our population was largely white European, who overall consume higher amounts of dairy products compared to other populations especially in South Asia, South America and Africa (42), so generalisability of our results to other ethnic groups with different consumption patterns might be limited. Specifically, consumption of different dairy groups has a limited range in our study, with low levels of high-fat dairy products and high levels of low-fat dairy products. This might compromise the power to detect associations across a broader range of dairy consumption, which might be seen in other populations.
Conclusion
We observed an inverse association between low-fat dairy products and the ratio of visceral to subcutaneous fat, which suggests that abdominal obesity may be a potential pathway for the association of dairy consumption with cardio-metabolic disease. In addition, the observed association of higher milk consumption with a higher body lean mass could also be a potential explanation for the overall metabolic associations observed for dairy consumption. These findings are important for hypothesis-generation and should stimulate further investigation in prospective studies, clinical trials and mechanistic studies of the link between dairy products and cardiometabolic disease.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Abigail Britten, Vasileios Kaimakis, Steven Knighton, Richard Powell, Adam Dickinson, Susie Boatman, and Inge Loudon for technical assistance as members of the Fenland Study team.
Abbreviations
- DEXA
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
- IQR
Interquartile range
- SCAT
Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue
- VAT
Visceral Adipose Tissue
Footnotes
Financial support:
The Fenland study was funded by the Medical Research Council and the Wellcome Trust The current work was supported by the Medical Research Council (N.G.F., grant number MC_UU_12015/5), (N.J.W., grant number MC_UU_12015/1), (S.B., grant number MC_UU_12015/3); the National Institute of Health Research Cambridge (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre (N.G.F., S.B., and N.J.W., grant number IS-BRC-1215-20014); and the Cambridge Trust (E.T.). The funders had no role in the design, analysis or writing of this article.
Conflict of interest: None.
Authorship: N.J.W., N.G.F., S.J.G. and S.B. designed research, and N.G.F., F.I. and E.T. designed the study question; E.D.R.L. provided specialist input to anthropometric measurements; E.T. and F.I. analysed data; E.T., F.I. and N.G.F. drafted the manuscript; E.T. had primary responsibility for final content. All authors read and approved the final version.
This peer-reviewed article has been accepted for publication but not yet copyedited or typeset, and so may be subject to change during the production process. The article is considered published and may be cited using its DOI
References
- 1.Forouzanfar MH, Alexander L, Anderson HR, Bachman VF, Biryukov S, Brauer M, Burnett R, Casey D, Coates MM, Cohen A. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The Lancet. 2015;386:2287–323. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00128-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rice BH, Quann EE, Miller GD. Meeting and exceeding dairy recommendations: effects of dairy consumption on nutrient intakes and risk of chronic disease. Nutr Rev. 2013;71:209–23. doi: 10.1111/nure.12007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ramsden CE, Zamora D, Majchrzak-Hong S, Faurot KR, Broste SK, Frantz RP, Davis JM, Ringel A, Suchindran CM, Hibbeln JR. Re-evaluation of the traditional diet-heart hypothesis: analysis of recovered data from Minnesota Coronary Experiment (1968-73) bmj. 2016;353:i1246. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Guo J, Astrup A, Lovegrove JA, Gijsbers L, Givens DI, Soedamah-Muthu SS. Milk and dairy consumption and risk of cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality: dose–response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017:1, 19. doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0243-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alexander DD, Bylsma LC, Vargas AJ, Cohen SS, Doucette A, Mohamed M, Irvin SR, Miller PE, Watson H, Fryzek JP. Dairy consumption and CVD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2016;115:737–50. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515005000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Aune D, Norat T, Romundstad P, Vatten LJ. Dairy products and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98:1066–83. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.113.059030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gijsbers L, Ding EL, Malik VS, de Goede J, Geleijnse JM, Soedamah-Muthu SS. Consumption of dairy foods and diabetes incidence: a dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;103:1111–24. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.123216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gao D, Ning N, Wang C, Wang Y, Li Q, Meng Z, Liu Y, Li Q. Dairy products consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mozaffarian D. Dietary and Policy Priorities for Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Obesity A Comprehensive Review. Circulation. 2016;133:187–225. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Geng T, Qi L, Huang T. Effects of Dairy Products Consumption on Body Weight and Body Composition Among Adults: An Updated Meta-analysis of 37 Randomized Control Trials. Molecular nutrition and food research. 2018;62 doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stonehouse W, Wycherley T, Luscombe-Marsh N, Taylor P, Brinkworth G, Riley M. Dairy Intake Enhances Body Weight and Composition Changes during Energy Restriction in 18–50-Year-Old Adults—A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2016;8:394. doi: 10.3390/nu8070394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wajchenberg BL. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr Rev. 2000;21:697–738. doi: 10.1210/edrv.21.6.0415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fox CS, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Pou KM, Maurovich-Horvat P, Liu C-Y, Vasan RS, Murabito JM, Meigs JB, Cupples LA. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments. Circulation. 2007;116:39–48. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.675355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Porter SA, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Vasan RS, O'donnel CJ, Fox CS. Abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue: a protective fat depot? Diabetes care. 2009;32:1068–75. doi: 10.2337/dc08-2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kaess B, Pedley A, Massaro J, Murabito J, Hoffmann U, Fox C. The ratio of visceral to subcutaneous fat, a metric of body fat distribution, is a unique correlate of cardiometabolic risk. Diabetologia. 2012;55:2622–30. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2639-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Josse AR, Atkinson SA, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM. Increased consumption of dairy foods and protein during diet-and exercise-induced weight loss promotes fat mass loss and lean mass gain in overweight and obese premenopausal women. The Journal of nutrition. 2011;141:1626–34. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.141028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pallister T, Jackson M, Martin T, Glastonbury C, Jennings A, Beaumont M, Mohney R, Small K, MacGregor A, Steves C. Untangling the relationship between diet and visceral fat mass through blood metabolomics and gut microbiome profiling. International journal of obesity. 2017;41:1106. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2017.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bingham SA, Welch AA, McTaggart A, Mulligan AA, Runswick SA, Luben R, Oakes S, Khaw KT, Wareham N, Day NE. Nutritional methods in the European prospective investigation of cancer in Norfolk. Public health nutrition. 2001;4:847–58. doi: 10.1079/phn2000102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mulligan AA, Luben RN, Bhaniani A, Parry-Smith DJ, O'Connor L, Khawaja AP, Forouhi NG, Khaw KT. A new tool for converting food frequency questionnaire data into nutrient and food group values: FETA research methods and availability. Bmj Open. 2014;4 doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.O'Connor LM, Lentjes MA, Luben RN, Khaw KT, Wareham NJ, Forouhi NG. Dietary dairy product intake and incident type 2 diabetes: a prospective study using dietary data from a 7-day food diary. Diabetologia. 2014;57:909–17. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3176-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Clifton E, Day F, Rolfe EDL, Forouhi N, Brage S, Griffin S, Wareham N, Ong K. Associations between body mass index-related genetic variants and adult body composition: The Fenland cohort study. International Journal of Obesity. 2017;41:613–9. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2017.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kaul S, Rothney MP, Peters DM, Wacker WK, Davis CE, Shapiro MD, Ergun DL. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for quantification of visceral fat. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012;20:1313–8. doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mohammad A, De Lucia Rolfe E, Sleigh A, Kivisild T, Behbehani K, Wareham NJ, Brage S, Mohammad T. Validity of visceral adiposity estimates from DXA against MRI in Kuwaiti men and women. Nutr Diabetes. 2017;7:e238. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2016.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brage S, Brage N, Franks P, Ekelund U, Wareham N. Reliability and validity of the combined heart rate and movement sensor Actiheart. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005;59:561–70. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Brage S, Ekelund U, Brage N, Hennings MA, Froberg K, Franks PW, Wareham NJ. Hierarchy of individual calibration levels for heart rate and accelerometry to measure physical activity. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2007;103:682–92. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00092.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.White IR, Royston P, Wood AM. Multiple imputation using chained equations: issues and guidance for practice. Statistics in medicine. 2011;30:377–99. doi: 10.1002/sim.4067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Verardi V, Croux C. Robust regression in Stata. 2008 [Google Scholar]
- 28.Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Annals of statistics. 2001:1165–88. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Willett WC, Howe GR, Kushi LH. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 1997;65:1220S–8S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/65.4.1220S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Livingstone MB, Black AE. Markers of the validity of reported energy intake. J Nutr. 2003;133(Suppl 3):895S–920S. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.3.895S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Abargouei AS, Janghorbani M, Salehi-Marzijarani M, Esmaillzadeh A. Effect of dairy consumption on weight and body composition in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012;36:1485–93. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Booth AO, Huggins CE, Wattanapenpaiboon N, Nowson CA. Effect of increasing dietary calcium through supplements and dairy food on body weight and body composition: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2015;114:1013–25. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515001518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chen M, Pan A, Malik VS, Hu FB. Effects of dairy intake on body weight and fat: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96:735–47. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.037119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Christen T, Sheikine Y, Rocha VZ, Hurwitz S, Goldfine AB, Di Carli M, Libby P. Increased glucose uptake in visceral versus subcutaneous adipose tissue revealed by PET imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;3:843–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2010.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zemel MB. Role of dietary calcium and dairy products in modulating adiposity. Lipids. 2003;38:139–46. doi: 10.1007/s11745-003-1044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rosenblum JL, Castro VM, Moore CE, Kaplan LM. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation is associated with decreased abdominal visceral adipose tissue in overweight and obese adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95:101–8. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.019489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Thorning TK, Raben A, Tholstrup T, Soedamah-Muthu SS, Givens I, Astrup A. Milk and dairy products: good or bad for human health? An assessment of the totality of scientific evidence. Food and nutrition research. 2016;60:32527. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v60.32527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rich-Edwards JW, Ganmaa D, Pollak MN, Nakamoto EK, Kleinman K, Tserendolgor U, Willett WC, Frazier AL. Milk consumption and the prepubertal somatotropic axis. Nutrition journal. 2007;6:28. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-6-28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Van Vught A, Nieuwenhuizen A, Veldhorst M, Brummer R-J, Westerterp-Plantenga M. The effects of dietary protein on the somatotropic axis: a comparison of soy, gelatin,[alpha]-lactalbumin and milk. European journal of clinical nutrition. 2010;64:441. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2010.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Carroll PV, Christ the members of Growth Hormone Research Society Scientific Committee ER. Bengtsson BA, Carlsson L, Christiansen J, Clemmons D, Hintz R, Ho K, Laron Z, Sizonenko P. Growth hormone deficiency in adulthood and the effects of growth hormone replacement: a review. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1998;83:382–95. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.2.4594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Trijsburg L, Geelen A, Hollman PC, Hulshof PJ, Feskens EJ, Van't Veer P, Boshuizen HC, de Vries JH. BMI was found to be a consistent determinant related to misreporting of energy, protein and potassium intake using self-report and duplicate portion methods. Public Health Nutr. 2016:1–10. doi: 10.1017/S1368980016002743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Global Dietary Database. Global distribution of milk consumption in 2010. [cited 2018 24 June];2010 Available from: https://www.globaldietarydatabase.org/our-data/data-visualizations/dietary-data-country.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.