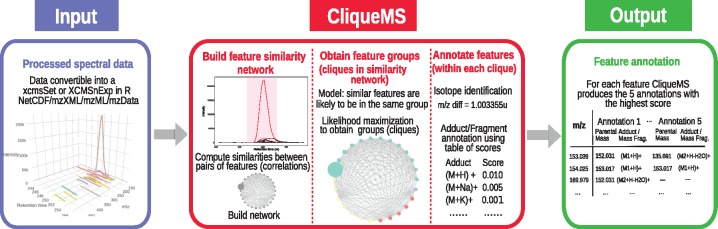
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of CliqueMS. CliqueMS identifies the features belonging to the same metabolite. CliqueMS uses as input LC-MS1 data in any format that can be converted into either an ‘xcmsSet’ or an ‘XCMSnExp’ object in R such as mzML, mzXML, mzData and NetCDF. First, CliqueMS determines peak-shape (i.e. coeluting) similarities between all pairs of features in the LC-MS1 spectrum. Then CliqueMS finds groups of features based on the network of similarities. The assumption is that the more similar a pair of features, the more likely they are to belong to the same group. Following a maximum likelihood procedure, CliqueMS finds the best division into fully connected groups of features (or cliques). Then, for each clique, CliqueMS proceeds to annotate each feature by establishing the parental ion neutral mass. Annotations are scores based on a table of empirically observed frequencies for each adduct. The final output is, for each feature, the five annotations with the highest score specifying the adducts/in-source fragment and its corresponding parental mass. See Supplementary Figure S1 for a detailed description of the installation process, input and output formats as well as the parameters and modules within CliqueMS