Abstract
The lateral eyes of the horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus undergo dramatic daily changes in structure and function that lead to enhanced retinal sensitivity and responsiveness to light at night. These changes are controlled by a circadian neural input that alters photoreceptor and pigment cell shape, pigment migration, and phototransduction. Clock input to the eyes also regulates photomechanical movements within photoreceptors, including membrane shedding. The biochemical mechanisms underlying these diverse effects of the clock on the retina are unknown, but a major biochemical consequence of activating clock input to the eyes is a rise in the concentration of cAMP in photoreceptors and the phosphorylation of a 122 kDa visual system-specific protein. We have cloned and sequenced cDNA encoding the clock-regulated 122 kDa phosphoprotein and show here that it is a new member of the myosin III family. We report thatLimulus myosin III is similar to other unconventional myosins in that it binds to calmodulin in the absence of Ca2+; it is novel in that it is phosphorylated within its myosin globular head, probably by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The protein is present throughout the photoreceptor, including the region occupied by the photosensitive rhabdom. We propose that the phosphorylation of Limulus myosin III is involved in one or more of the structural and functional changes that occur inLimulus eyes in response to clock input.
Keywords: myosin III, ninaC, Limulus polyphemus, photoreceptor cells, circadian rhythms, octopamine, unconventional myosin, cytoskeleton, Drosophila melanogaster, cAMP-dependent phosphorylation
Circadian neural input to the lateral eyes of the horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus drives structural and functional changes within the retina that lead to enhanced sensitivity and responsiveness to light at night. This input, which is activated during the late afternoon and remains active through the night (Barlow, 1983), induces changes in photoreceptor and pigment cell shape and in pigment migration (Barlow et al., 1980; Chamberlain and Barlow, 1987; Kier and Chamberlain, 1989) so that at night, the photosensitive membrane (rhabdom) of the photoreceptors is exposed to more of the available light (Chamberlain and Fiacco, 1985), enhances the depolarizing response recorded from photoreceptors for each photon absorbed (gain), and decreases the number of spontaneous depolarizations recorded from photoreceptors in the dark (noise) (Barlow et al., 1977, 1987; Kaplan and Barlow, 1980; Kaplan et al., 1990). Furthermore, this input primes processes that are driven by light such as pigment migration and membrane shedding (Chamberlain and Barlow, 1979, 1984). If the circadian neural input to the retina during the night is blocked, these light-driven processes do not occur during the day. The biochemical mechanisms underlying these diverse effects of the circadian clock on the retina are unknown.
The circadian clock that influences the eyes ofLimulus is located in the brain (Barlow et al., 1977;Barlow, 1983; Calman and Battelle, 1991; Kass and Barlow, 1992), and clock signals reach all of the eyes via well characterized octopaminergic efferent axons within each of the optic nerves (Fahrenbach 1971, 1981; Battelle et al., 1982; Evans et al., 1983;Battelle and Evans, 1984). Activation of octopamine receptors on ventral photoreceptors and in lateral eye retina stimulates a rise in intracellular cAMP (Kaupp et al., 1982; Battelle and Wishart, 1990), and many of the known effects of activating the circadian neural input to the eyes are mimicked by treatments that increase cAMP in retinal cells (Kass and Barlow, 1984; Kass and Renninger, 1988, Kass et al., 1988; Renninger et al., 1989; for review, see Battelle, 1991).
A major biochemical consequence of activating clock input to the lateral eyes in vivo and of elevating cAMP in lateral eyes or ventral photoreceptors in vitro is enhanced phosphorylation of an abundant, soluble visual system-specific protein that has an apparent molecular mass on SDS gels of 122 kDa (pp122) (Edwards and Battelle, 1987; Edwards et al., 1990). We have cloned and sequenced cDNA encoding pp122 from a lateral eye cDNA library and report here that it encodes a myosin III. The predicted protein consists of an N-terminal kinase domain and a C-terminal myosin heavy-chain head; it is similar to, but interestingly different from, the ninaC gene products of Drosophila (Montell and Rubin, 1988). Limulus myosin III is found throughout the pho-toreceptor, including the region occupied by rhabdom; it binds to calmodulin in the absence of Ca2+, and it becomes phosphorylated within its myosin globular head domain, probably by PKA.
Portions of this study have been reported in abstract form (Smith et al., 1993a)
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals. Adult intermolt L. polyphemuswere collected from the Indian River near Cape Canaveral, FL, maintained in running natural seawater at 15–18°C, and were on a 12 hr light/dark cycle.
Reagents. Unless otherwise specified, reagents were purchased from either Sigma (St. Louis, MO) or Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA).
Peptide sequencing. Lateral optic nerves were homogenized in 3-[N-morpholino]propanesulfonic acid (MOPS) homogenization buffer with protease inhibitors (Edwards and Battelle, 1987) and centrifuged for 30 min at 130,000 × g in an airfuge (Beckman Instruments, Fullerton, CA). The supernatant was mixed with 0.25 volume of fresh 4× SDS sample buffer (Laemmli, 1970) without bromophenol blue dye. The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE on 7.5% gels (Edwards and Battelle, 1987) and blotted to nitrocellulose (MSI, Westboro, MA) (Towbin et al., 1979) in buffer containing 15% methanol and 0.005% ultrapure SDS. The blot was stained with Ponceau S (Aebershold et al., 1987), and the 122 kDa band was cut out. Analysis of soluble Limulus retinal proteins on two dimensional gels showed that the 122 kDa band consisted of a single major phosphoprotein (Edwards and Battelle, 1987). Tryptic digestion and purification of peptides released from the 122 kDa band and the subsequent sequence analysis of selected peptides were performed at the Microchemistry Department of Harvard University (Cambridge, MA) according to their standard protocols.
cDNA library construction and PCR.Poly(A+) RNA isolated from the lateral eyes ofLimulus (Smith et al., 1993b) was used to construct a cDNA library (5 × 105 pfu) in λgt11 (Superscript; Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD). This library, together with degenerate oligonucleotide primers that encoded portions of the sequences of tryptic peptides released from pp122 (Figs.1, 2), were used in the PCR. The primer pair that gave our initial clone was based on a sense primer from peptide PTEEVVL [5′-CCIACIGA(A/G)GA(A/G)GTIGTI(T/C)T-3′] and an antisense primer from the peptide PLYGDQT [5′-GT(T/C)TG(A/G)TCICC(A/G)TAIA(A/G)IGG-3′]. The PCR reaction contained 5 μl of the cDNA library, 50 mmKCl, 10 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.8, 0.1% Triton X-100, 1.5 mm MgCl2, 0.2 mm dNTPs, 50 pmol of each degenerate oligonucleotide primer, and 2 U TaqDNA polymerase. Thermal cycling was 35 cycles of 2 min at 94°C, 2 min at 50°C, and 3 min at 72°C. PCR products were cloned into pCR plasmid (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), and recombinant plasmids were sequenced using standard protocols (Sequenase, version 2.0; United States Biochemicals, Cleveland, OH) (Sanger et al., 1977).
Fig. 1.
Amino acid sequences of tryptic peptides released from the 122 kDa clock-stimulated phosphoprotein. The soluble fraction of homogenates of Limulus lateral optic nerves was fractionated by SDS-PAGE and blotted to nitrocellulose. The blot was stained with Ponceau S, and the 122 kDa band was cut out and digested with trypsin. Tryptic peptides were purified by HPLC; four were sequenced at the Microchemistry Department at Harvard University (Cambridge, MA) according to their standard procedures.
Fig. 2.
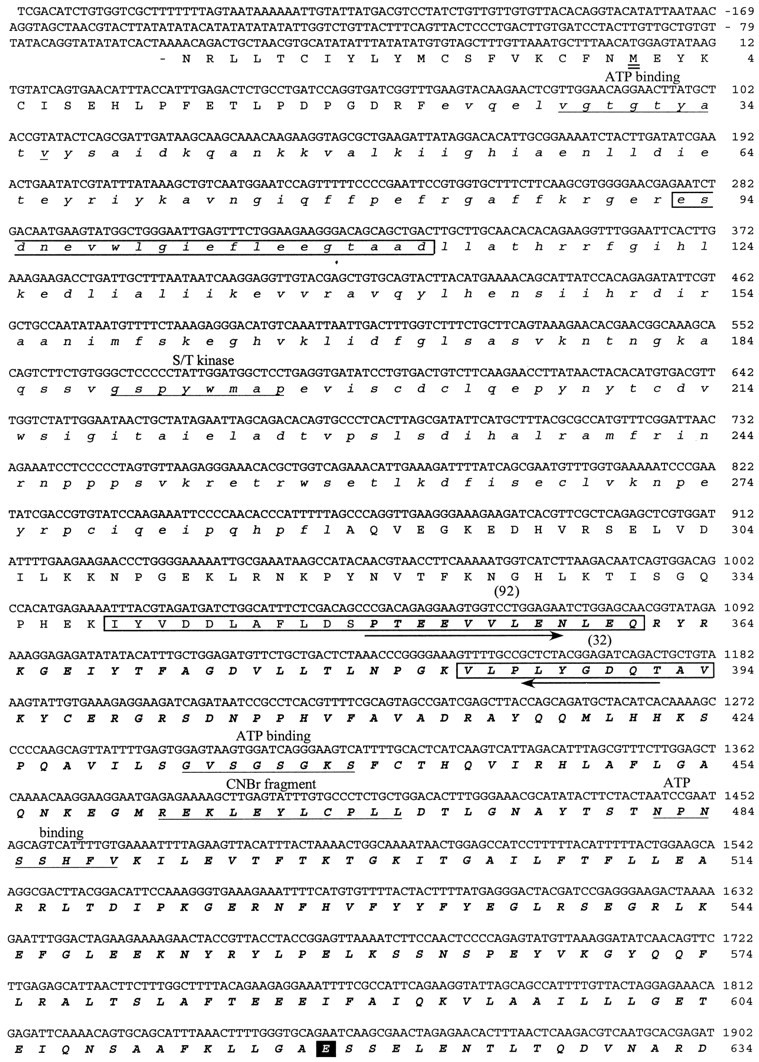

cDNA sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of the 122 kDa protein. The cDNA sequence presented was determined by sequencing three different purified cDNA clones that hybridized to an initial 125 bp PCR product. The amino acid sequences against which the initial degenerate PCR primers were designed are indicted witharrows. The kinase domain of the predicted protein is shown in lowercase italics. The myosin domain is inbold uppercase italics. The amino acid sequences obtained by directly sequencing four of the tryptic peptides released from the 122 kDa protein are boxed, and the number of the peptide is indicated above the sequence. The predicted initiation methionine is underlined twice.Underlined once are the ATP binding region of the kinase domain; the S/T kinase signature sequence; sequences involved in ATP binding to the myosin domain; the N-terminal sequence of the 50 kDa phosphorylated CNBr cleavage fragment (CNBr); the region within the myosin domain that may be involved in conformational change; and the putative IQ calmodulin binding region. The TEDS site is indicated with a black square. Three serines that are consensus PKA phosphorylation sites are circled.
Library screening. The cDNA library was screened for pp122 clones using a 125 bp fragment of pp122 cDNA spanning nucleotides 1048–1173 that had been amplified by PCR and radiolabeled with [32P]dCTP by random priming (Pharmacia, Piscataway, NJ) (Feinberg and Vogelstein, 1983). Plaque lifts of the library were hybridized to the labeled probe and washed at high-stringency (Smith et al., 1993b). Positive plaques were detected by autoradiography (X-OMAT AR film; Eastman Kodak, Rochester, NY) and purified to homogeneity by replating. cDNA inserts were amplified from the λ vector with primers specific to the vector, digested withNotI (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA) and SalI (Promega, Madison, WI) restriction enzymes, and subcloned into pSPORT plasmid (Life Technologies).
Northern blot analysis. Blots of poly(A+) RNA (10 μg) from the lateral eye were prepared as described previously (Smith et al., 1993b). The probe (a portion of the pp122 cDNA from position 1683–2403) was hybridized, and the blot was washed under the same conditions and stringency used to screen the library.
N-terminal sequencing of a phosphorylated cyanogen bromide (CNBr) cleavage product. Homogenates of lateral optic nerve were incubated with 8-bromo-cAMP and [γ-32P]ATP under standard phosphorylating conditions (Edwards and Battelle, 1987) and then centrifuged for 30 min at 100,000 × g in the airfuge. Soluble proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) (Millipore, Bedford, MA), and stained with Ponceau S. The 122 kDa band was excised and incubated overnight with 0.15 m CNBr in 70% formic acid. After the CNBr was removed, the membranes were rinsed, incubated for 30 min in elution buffer (2% SDS and 1% Triton X-100 in 50 mm Tris, pH 9.5), and then sonicated in this buffer for 5 min (bath sonicator W-225; Heat-Systems-Ultrasonics, Framingdale, NY) to release the peptides. The peptides were then separated on a Tris–Tricine gel (Schagger and von Jagow, 1987) and blotted overnight in the cold to PVDF using transfer buffer containing 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES), pH 6.0, and 20% (v/v) methanol. The blots were stained with Coomassie blue R-250 and exposed to autoradiographic film to locate the labeled peptides. A prominent 50 kDa labeled peptide was collected (∼2 pmol), and its N terminal was sequenced (automatic amino acid sequencer 473A; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) by the Protein Chemistry Core of the University of Florida’s Interdisciplinary Center for Biotechnology Research.
Calmodulin binding. Calmodulin binding to pp122 was tested on calmodulin overlays of Western blots and on calmodulin affinity columns. Conditions for the calmodulin overlay were modified from those described by Flanagan and Yost (1984, their Method I) using calmodulin iodinated according to the Iodogen system (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Briefly, proteins in total homogenates of lateral eye, lateral optic nerve, and ventral photoreceptors (Edwards and Battelle, 1987) were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted to nitrocellulose, stained with fast green, and photographed. Sample lanes were then blocked for 60 min at room temperature with solution A (50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 0.2 m NaCl, and 0.05% Tween 20) plus 1% BSA in the presence or absence of 1 mm Ca2+ and incubated for 2 hr at room temperature with 10 μCi of125I-calmodulin/lane in 10 ml of solution A plus 1% BSA with or without 1 mm Ca2+. After the incubations, the lanes were washed at least two times for 30 min each in the same solution A without calmodulin, dried, and exposed to autoradiographic film in the presence of enhancing screens.
To test for the binding of pp122 to calmodulin-Sepharose,Limulus lateral eye and lateral optic nerve tissues (50–80 mg wet weight) were homogenized together in 10 μl of ice-cold homogenizing buffer (HB-2)/mg of tissue wet weight. HB-2 contained 50 mm MOPS buffer, pH 7.2, 160 mm KCl, 1 mm EGTA, 1 mm EDTA, and protease inhibitors (6 μg/ml aprotinin, 100 μm leupeptin, 1 μmpepstatin, and 100 μm PMSF). The homogenate was centrifuged in the cold for 30 min at 100,000 × g in an airfuge. The soluble fraction was diluted to twice its original volume in HB-2 and concentrated by centrifugation through a Centricon filter (Amicon, Beverly, MA) with a 30,000 kDa cutoff to approximately half its original volume. The extract was then diluted with HB-2 to ∼1.2 ml. Appropriate volumes of 100 mm CaCl2and 100 mm EGTA were then added to separate aliquots of the extract to produce total EDTA, EGTA, and Ca2+concentrations as follows (in mm): 1 EDTA, 1 EGTA, 0 Ca2+; 1 EDTA, 1 EGTA, 1 Ca2+; 1 EDTA, 5 EGTA, 5.3 Ca2+; and 1 EDTA, 1 EGTA, 2 Ca2+. The calculated free Ca2+concentrations of these solutions are, respectively, 0, 0.1, 1.6, and 17 μm (Bers et al., 1994).
Calmodulin-Sepharose 4B (Pharmacia) and Sepharose 4B (Sigma) not conjugated with calmodulin were rinsed separately with water and then distributed into separate conical assay tubes so that each tube contained 50 μl of packed beads. The beads were rinsed separately three more times by resuspension and centrifugation (Personal centrifuge; USA Scientific, Ocala, FL) in HB-2 containing the free Ca2+ concentrations described above. Excess buffer was removed from above the beads, and 200 μl of tissue extract containing the appropriate concentration of Ca2+ was added. The extract was mixed with beads by gentle rotation for 30 min at 4°C. Then the beads were pelleted by centrifugation, and unbound material was removed. Beads were rinsed three times by resuspension and centrifugation with three volumes (150 μl) of HB-2 containing the same concentration of Ca2+ with which the beads had been equilibrated. After the third centrifugation, rinse buffer was removed from above the beads and 1 volume (50 μl) of 2× SDS sample buffer (Laemmli, 1970) was added. The samples were sonicated and centrifuged to pellet the beads, and the SDS-solubilized proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE on 7.5% gels. After electrophoresis, the proteins in the gel were stained with Coomassie blue. The 122 kDa protein was identified as a stained band that migrated near the 116 kDa molecular mass standard.
Generation of polyclonal antibodies, Western blotting, and immunostaining. A polyclonal ascites antibody was generated in Pristane-primed BALB/c mice (Harlow and Lane, 1988) against the 122 kDa protein band that had been collected from 7.5% SDS polyacrylamide gels, stained with Coomassie blue R-250 in water, mixed 1:1 (v/v), and homogenized with Freund’s complete adjuvant. A polyclonal serum antibody was generated in rats against a synthetic peptide containing the predicted sequence of the C terminus of Limulus myosin III (K1014-H1024) coupled to keyhole limpet hemacyanin (Calbiochem, La Jolla, CA) with Sulfo-MBS (Pierce). Western blotting and immunostaining of the blots were performed as described previously (Smith et al., 1995). Both primary antibodies were used at a dilution of 1:100. The immunocytochemical localization of Limulus myosin III in the lateral eye was performed on 14 μm cryosections of tissue that had been fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Calman and Battelle, 1991) and using a 1:50 dilution of the antibody generated against the C-terminal peptide ofLimulus myosin III. In control experiments, antiserum containing antibodies directed against the predicted C-terminal peptide of Limulus myosin III was incubated overnight at 4°C with 10−5m free peptide and centrifuged for 30 min at 10,000 × g in an airfuge before use.
RESULTS
Characterization of cDNA encoding the 122 kDa clock-regulated phosphoprotein
The sequences of four tryptic peptides released from pp122 are shown in Figure 1. Two degenerate oligonucleotide primers were designed based on portions of each of these sequences, one in the sense and the other in the antisense direction, because the relative positions of the peptides were not known. All combinations of sense and antisense primers were tried in a PCR using a Limulus lateral eye cDNA library as template. One combination, a sense primer based on a portion of peptide number 92 and an antisense primer based on the sequence of peptide number 32, amplified a 125 bp product. The amino acid sequence encoded by this product contained the exact sequences of the pp122 peptides adjacent to the regions used in designing the PCR primers (Fig. 2). We therefore concluded that the 125 bp product represented a portion of the cDNA encoding pp122.
Hybridization screens of the Limulus lateral eye library with the 125 bp PCR product yielded five clones ranging from 0.7 to 4 kb. Three separate clones were sequenced to obtain the full-length cDNA sequence for pp122. Clones containing inserts in the 4 kb range contained the complete open reading frame (ORF); shorter inserts contained incomplete sequences. A 3808 bp cDNA was sequenced; it encoded an ORF with 1023 residues (Fig. 2). The first “ATG” in this ORF is flanked on the 5′ end by ATAT, which is in poor agreement with Kozak’s consensus sequence for translation initiation (CANCATG; Kozak, 1984), especially with the lack of an adenosine residue at -3. On the other hand, the second ATG is flanked by the 5′ sequence TAAC, which is in good agreement with Kozak’s (1984) consensus and the consensus sequence for translation initiation in Drosophila[C/A)AA(C/A)AUG] (Cavener, 1987). Consequently, we begin the amino acid numbering from the second methionine in the ORF. The predicted protein contains 1014 residues, has a calculated molecular mass of 118 kDa, and contains all of the sequences obtained by directly sequencing tryptic peptides released from pp122 (Figs. 1, 2). The endogenous 122 kDa protein also stained specifically with an antibody directed against the C terminal of the Limulus myosin III protein predicted from the cDNA sequence (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
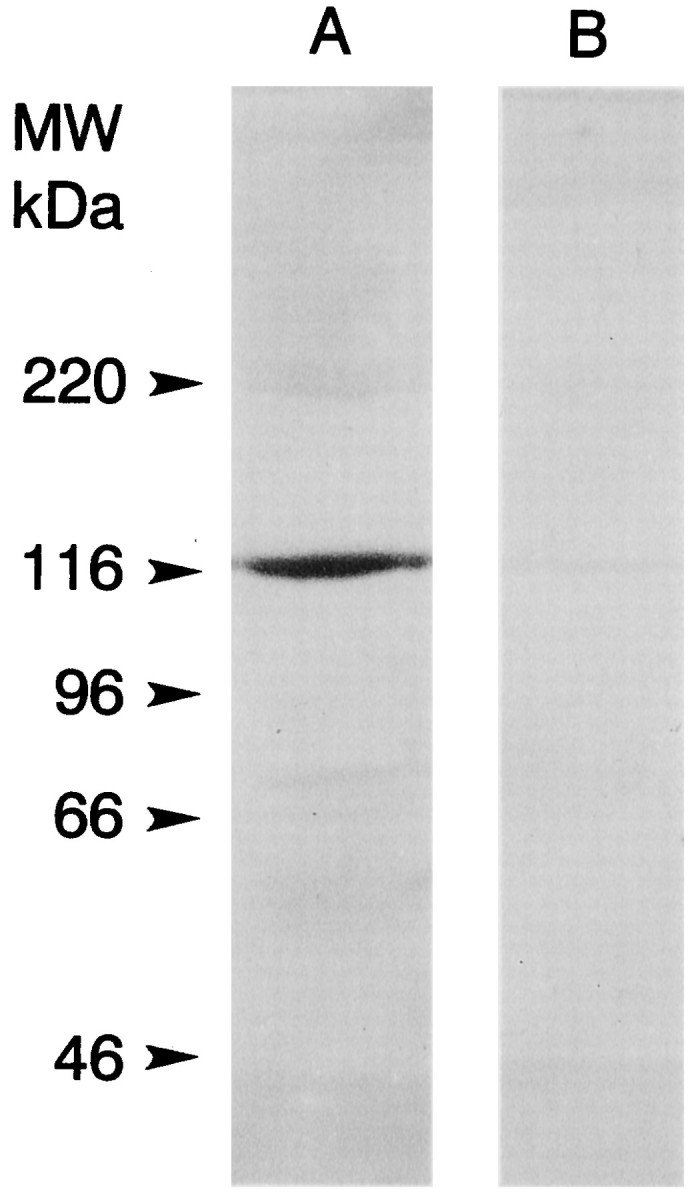
Western blots of soluble extracts of lateral eye and lateral optic nerve stained with an antibody directed against the predicted C terminus of myoIIILim. A soluble extract of lateral eye and lateral optic nerve (76 mg tissue wet weight) was prepared and concentrated as described in Materials and Methods for binding to calmodulin-Sepharose. The final volume of the concentrate was 200 μl. An aliquot was mixed 1:1 with 2× SDS sample buffer, and 5 μl/lane was fractionated by SDS-PAGE on a 7.5% gel and blotted to PVDF. Immunostaining was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The alkaline phosphatase-conjugated secondary antibody was used at a dilution of 1:2000. Lane A was incubated with a 1:100 dilution of serum from a rat injected with a peptide encoding the predicted C terminus of myoIIILim conjugated to keyhole limpet hemacyanin. A single immunostained band at ∼122 kDa was observed. Lane B was incubated with a 1:100 dilution of the same serum that had been preincubated overnight with 10−5m free C-terminal peptide. No immunostained bands were observed. The locations of the molecular mass standards are indicated.
Domain analysis of the predicted protein
The N-terminal half of the predicted protein contains many sequences and residues that are conserved among the catalytic domains of protein kinases (Hanks et al., 1988). These include a nucleotide binding domain near the N terminus (V28GTGTYA) followed by a valine (V36) two positions on the C-terminal side of this sequence; a conserved leucine (L50) positioned appropriately to be involved in the phosphotransfer reaction; the residues D152, N157, and the triplet D170FG that correspond to the same residues in other kinases thought critical for ATP binding; and the consensus sequence A195PE, a major protein kinase catalytic domain indicator.
A comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of the kinase domain of pp122 with all other sequences in the SBASE protein domain library (Pongor et al., 1994) suggests it is more similar to serine/threonine kinases than to tyrosine kinases. The sequence G189SPYWMAPE is characteristic of serine/threonine kinases; however, the sequence D152IRAAN is considered characteristic of tyrosine kinases.
The C-terminal half of pp122 contains sequences that have been implicated in the ATP binding and conformational changes of myosins (for review, see Cope et al., 1996; Rayment et al., 1996) (Fig.4). Another characteristic of most myosins that are conserved in pp122 is the so-called TEDS site (Bement and Mooseker, 1995), an acidic amino acid at the position that becomes phosphorylated in Acanthamoeba myosins I (E618 in pp122). pp122 also contains a single putative IQ calmodulin binding domain (Cheney and Mooseker, 1992) near its C terminus (V995QAIARKYFVK).
Fig. 4.
Comparisons of functionally relevant sequences in the myosin domains of Limulus pp122 andninaC with other major myosin classes. The consensus sequences for the functionally relevant regions of major myosin classes are described by Cope et al. (1996).
Comparisons of the deduced amino acid sequence of pp122 with all sequences in the GenBank database (BLAST) (Altschul et al., 1990) shows it is most similar to the ninaC proteins fromDrosophila with 38% identical and 14% similar amino acids (Fig. 5). The N terminus of theLimulus sequence shows high similarity to theDrosophila ninaC N terminus, indicating that the selection of the second ATG as the initiating methionine is probably correct. TheninaC gene products have been classified as myosins III (Hasson and Mooseker, 1995). The Limulus protein is a new member of this family; therefore, we will refer to it asLimulus myosin III (myoIIILim).
Fig. 5.
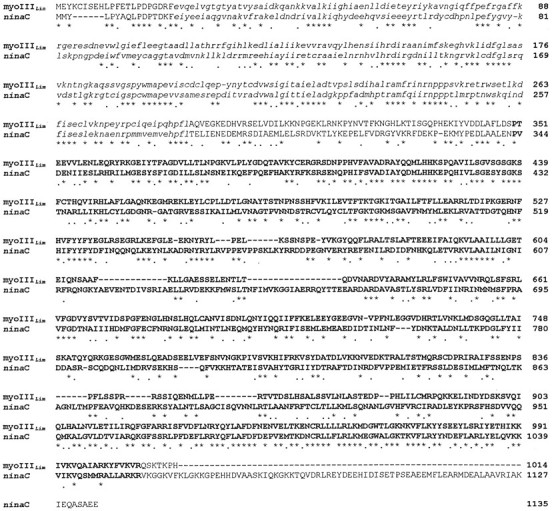
Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequence ofLimulus pp122 with that of Drosophila ninaC174 (Montell and Rubin, 1988). The alignment was performed using Clustal W (Thompson et al., 1994). Amino acids that are identical are indicated by stars. Those that are conservatively substituted are indicated bydots. Amino acids within the kinase domains are inlowercase italics. Those in the myosin domains are indicated by bold uppercase.
The ninaC gene of Drosophila is alternatively spliced and produces two mRNA and two protein products, a long form and a short form (Montell and Rubin, 1988). The cDNA for myoIIILim identified by library screening is shorter than the short form of ninaC, so we applied both molecular and immunochemical approaches to probe for longer gene products. None was found. A Northern analysis of poly(A+) RNA from lateral eye was performed using as the probe a portion of the cDNA that we predicted would be present in all myoIIILim gene products. The probe hybridized to a single band at ∼3.6 kb (Fig. 6). The 3′ end of myoIIILim cDNA was amplified with PCR using two exact oligoDNA primers (1455–1474 and 2580–2599), each paired with primers to the phage vector downstream of the poly (A+) tail. Both reactions produced a single product (data not shown). Western blots stained with an antibody directed against the 122 kDa myosin III revealed no other immunochemically similar protein in lateral eye retinal extracts (Fig.7).
Fig. 6.
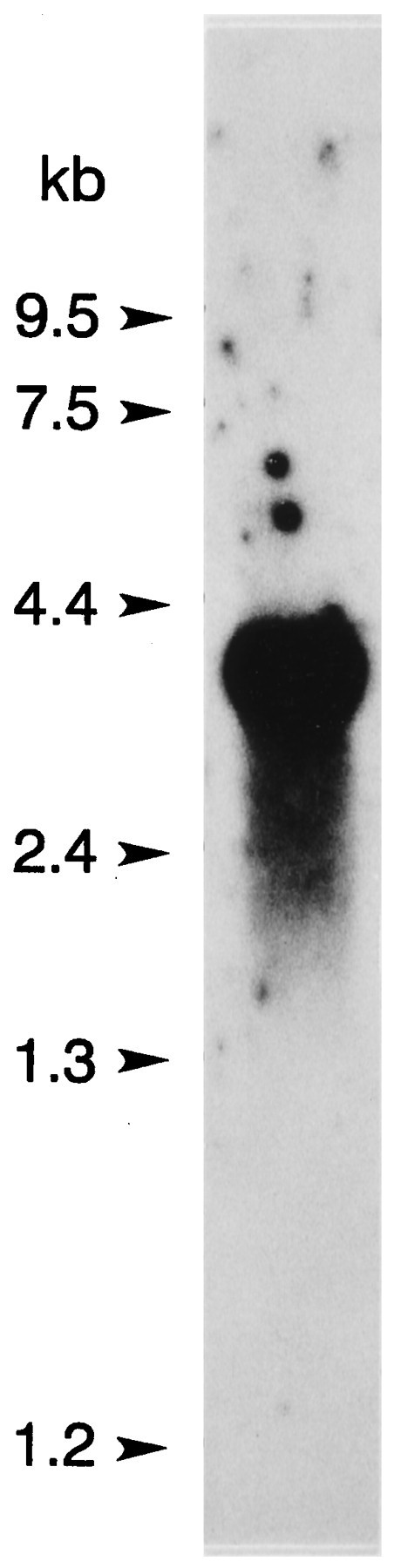
Northern blot analysis of poly (A+) RNA (10 μg) from Limuluslateral eye. The probe (pp122 cDNA from nt 1683–2403) was hybridized, and the blot was washed under the same high-stringency conditions used to screen the library (Smith et al., 1993b). The probe hybridized to a single band at ∼3.6 kb.
Fig. 7.
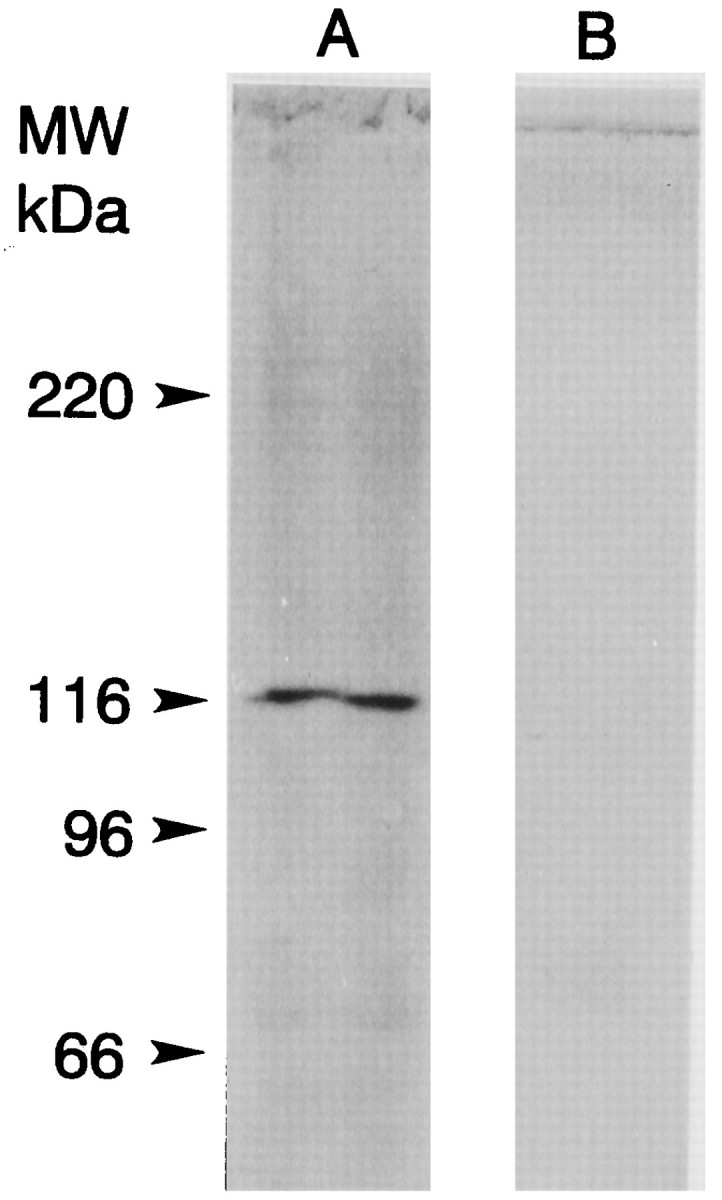
Western blot of a total protein extract of lateral eye showing myoIIILim-like immunoreactivity. Lateral eye tissue was homogenized in HB (20 μl/mg tissue wet weight) (Edwards and Battelle, 1987), and then the homogenate was diluted 1:1 with 2× SDS sample buffer and sonicated. Ten microliters of the SDS-solubilized protein were applied to the lanes. Immunostaining was performed as described in Materials and Methods and Figure 3. Lane Awas incubated with a 1:100 dilution of ascites fluid from a mouse that had been immunized with gel-purified 122 kDa myoIIILim.Lane B was incubated with a 1:100 dilution of ascites from an unimmunized mouse. The locations of the molecular mass markers are indicated. A single immunostained band at 122 kDa is seen in the lane incubated with antibody directed against the 122 kDa myoIIILim. No immunostained bands with higher molecular mass were detected.
Calmodulin binding
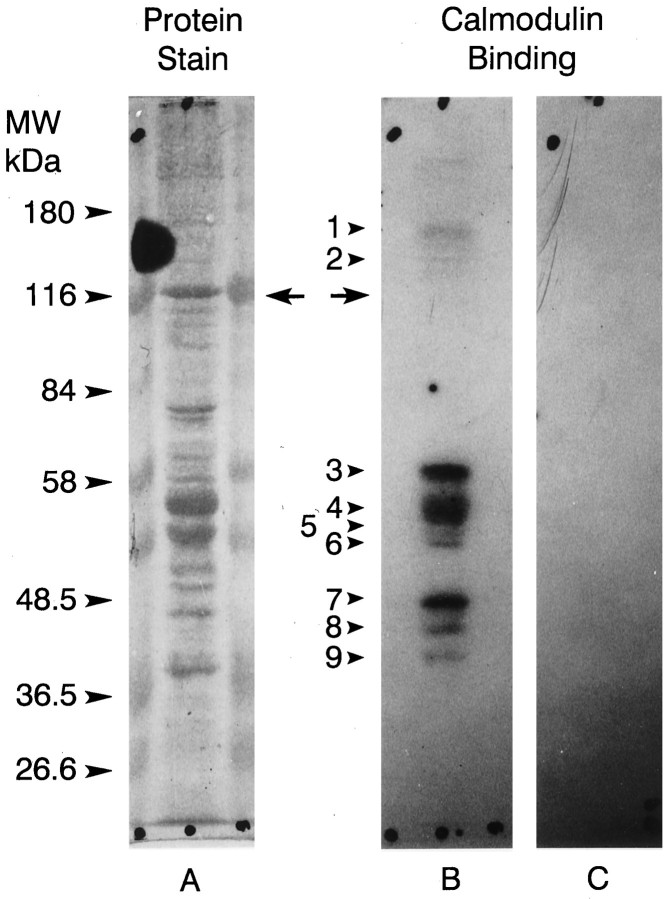
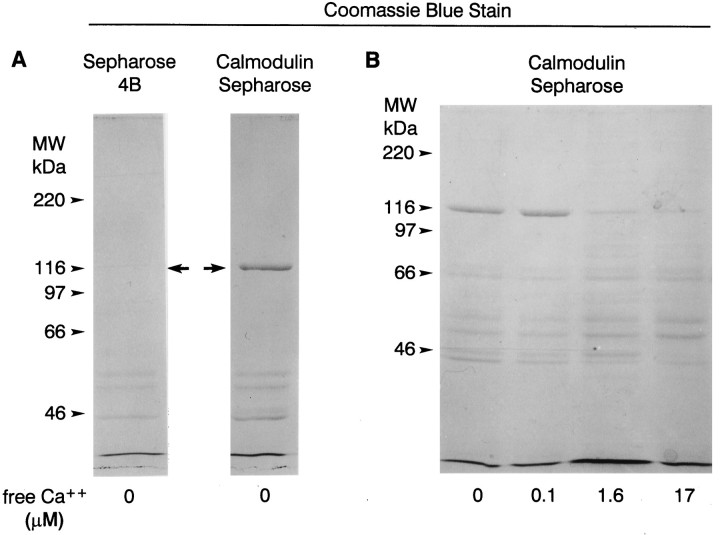
The IQ domain located near the C terminus of myoIIILimsuggests that the protein binds calmodulin. Calmodulin overlays of proteins extracted from lateral eye, lateral optic nerve, and ventral photoreceptors revealed a number of protein bands that bound calmodulin in the presence of, but not in the absence of, Ca2+(Fig. 8, Table1). Seven of these with lower molecular mass appear to correspond across tissues. The correspondence across tissues of the higher molecular mass proteins is uncertain, but calmodulin binding to the 122 kDa myoIIILim was never detected (Table 1). However, myoIIILim did bind to calmodulin-Sepharose in the absence of Ca2+ and in the presence of a low concentration (0.1 μm) of free Ca2+ (Fig. 9). Under the same conditions, little myoIIILim bound to Sepharose 4B beads that were not conjugated to calmodulin. Raising the concentration of free Ca2+ in the binding and rinse buffers to 1.6 and 17 μm reduced the binding of myoIIILim to calmodulin-Sepharose and increased the binding of other proteins, most prominently at 57 and 53 kDa. Protein bands at 57 and 53 kDa also showed consistent Ca2+-dependent calmodulin binding in calmodulin overlay experiments (Fig. 8, Table1).
Fig. 8.
125I-Calmodulin binding to Western blots of ventral photoreceptor cell body proteins. Ventral photoreceptor cell bodies dissected from two animals were pooled, homogenized (Edwards and Battelle, 1987), fractionated by SDS-PAGE on 7.5% gels, and blotted to nitrocellulose as described in Materials and Methods. A, Fast green stain of one lane of the blot.B, Autoradiograph of the same lane shown inA incubated with 125I-calmodulin plus 1 mm Ca2+. C, Autoradiograph of a duplicate lane incubated with125I-calmodulin with no added Ca2+. The locations of the molecular mass standards are indicated. Thearrows show where myoIIILim migrates. No calmodulin binding was observed in the absence of Ca2+. The protein bands that bound calmodulin in the presence of Ca2+ are indicated witharrows and numbered. Their apparent molecular masses in kilodaltons are as follows: 1, 150;2, 133; 3, 57.5; 4, 52;5, 49; 6, 47.5; 7, 42;8, 40; 9, 37.5. MyoIIILim did not bind 125I-calmodulin in the presence or absence of Ca2+.
Table 1.
Calmodulin-binding proteins in Limulus lateral eye, ventral photoreceptors, and lateral optic nerve detected in125I-calmodulin overlays of Western blots
| Lateral eye | Ventral photoreceptors | Lateral optic nerve |
|---|---|---|
| 38.3 (10) | 38.0 (6) | 37.7 (3) |
| 40.4 (5) | 40.4 (4) | 39.5 (3) |
| 42.5 (10) | 43.1 (6) | 41.8 (3) |
| 49.2 (7) | 49.4 (6) | 47.8 (2) |
| 50.9 (7) | 50.3 (3) | 49.8 (2) |
| 53.1 (7) | 53.3 (6) | 52.3 (2) |
| 57.9 (10) | 58.6 (6) | 57.3 (3) |
| 159.1 (7) | 133.8 (4) | 142.0 (1) |
| 189.7 (3) | 152.9 (6) | 161.0 (2) |
| 200.0 (1) | 210.0 (1) | 195.0 (2) |
| 207.0 (1) | 225.0 (1) | 207.0 (1) |
| 213.0 (1) | ||
| 223.0 (1) |
Values are average molecular mass in kilodaltons of each band that binds calmodulin. The number of times each band was observed is given in parentheses.
Fig. 9.
Coomassie blue-stained polyacrylamide gels showing proteins that bound to calmodulin-Sepharose and Sepharose 4B in the presence of different concentrations of Ca2+. Soluble extracts of Limulus lateral eye plus lateral optic nerves were incubated with calmodulin-Sepharose or Sepharose 4B without bound calmodulin in the absence or presence of different concentrations of Ca2+ (see Materials and Methods). Proteins that bound to the beads were extracted into SDS sample buffer, fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and stained with Coomassie blue. The positions of the molecular mass standards are indicated.A, In the absence of calcium, myoIIILim, the protein band that migrates close to the 116 kDa molecular mass standard (arrows), bound to calmodulin-Sepharose but not to Sepharose 4B. B, MyoIIILim bound to calmodulin-Sepharose in the absence of Ca2+ and in the presence of 0.1 μmfree Ca2+. Binding of myoIIILim to calmodulin-Sepharose was reduced in the presence of 1.6 and 17 μm free Ca2+, and the binding of other proteins was enhanced. Note in particular the bands that migrate at 57 and 53 kDa.
Phosphorylation
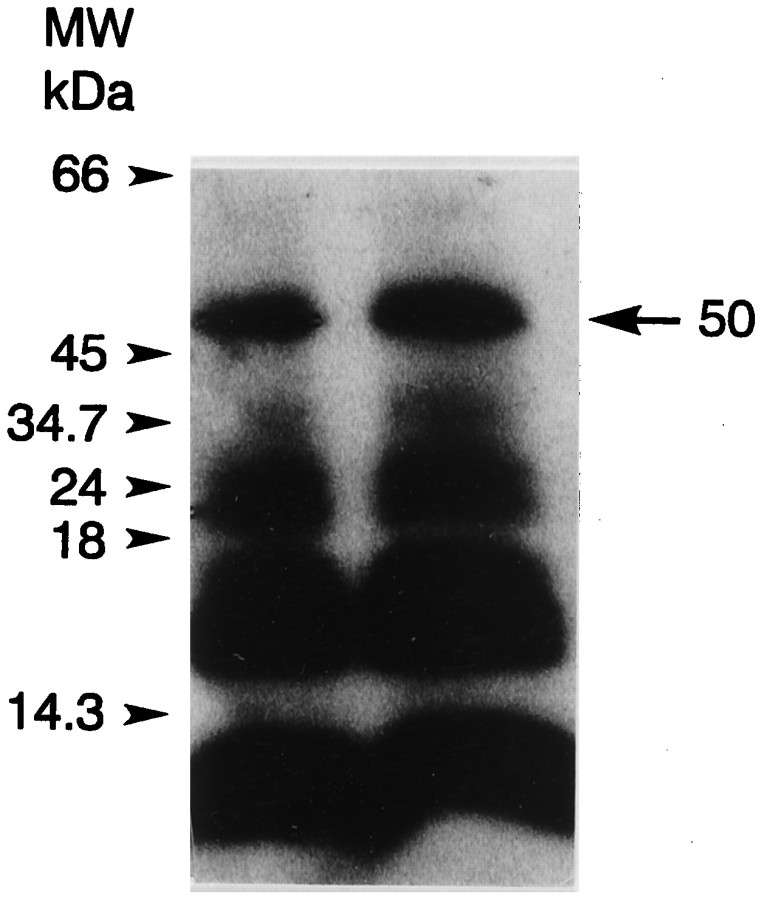
MyoIIILim was first identified as an octopamine- and cAMP-stimulated phosphoprotein in intact Limulusphotoreceptors. Further analysis showed that myoIIILimbecomes phosphorylated only on serine residues (Edwards and Battelle, 1987). The predicted amino acid sequence of myoIIILimreveals three serines that are potential sites for phosphorylation by PKA (S796, S846, and S926), and all three sites are located in the myosin domain (Fig. 2). To determine what regions of myoIIILimbecome phosphorylated, myoIIILim in soluble extracts of lateral optic nerve was phosphorylated in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP and 8-bromo-cAMP, purified by SDS-PAGE, and cleaved with CNBr. A number of phosphorylated cleavage fragments were obtained (Fig. 10). The 50 kDa phosphorylated fragment was selected for N-terminal sequencing because it was clearly separated from other bands and contained the most peptide. The analysis yielded the sequence REKFEYL-PL which, except for the F in position four, matched the predicted sequence R461EKLEYLCPL located near the N-terminal of the myosin domain of myoIIILim. These results indicate that some phosphorylation sites in myoIIILim are located within its myosin domain.
Fig. 10.
Autoradiograph showing 32P-labeled CNBr cleavage fragments of myoIIILim. Soluble proteins from lateral optic nerve homogenates that had been phosphorylated with [γ-32P]ATP in the presence of 8-bromo-cAMP were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted to PVDF, and stained with Ponceau S. The 122 kDa band was excised and cleaved with CNBr. After the CNBr cleavage fragments were released from the membrane, they were separated on a Tris–Tricine gel and blotted to PVDF. The blots were stained with Coomassie blue R-250 and exposed to autoradiographic film. The two labeled 50 kDa bands shown were cut out and pooled for N-terminal sequencing. The N-terminal sequence was determined as REKFEYL-PL, which matches closely a region in the deduced sequence of myoIIILim located near the N terminal of the myosin domain.
The reason for the single amino acid difference in this region between the predicted and the determined sequences is not clear. However, we have greater confidence in the predicted sequence because it is based on cDNA sequences obtained from three separate clones. Furthermore, the leucine in this position is similar to the valine at the same position in ninaC (Fig. 4). The amino acid sequencing reactions may have been compromised by the small amount of material (2 pmol) that was available for sequencing.
Immunocytochemical localization in the lateral eye
Myosin IIILim-like immunoreactivity was observed throughout the photoreceptor cell body, including the region occupied by rhabdom (Fig.11A,C). Staining was also seen over the eccentric cell body and dendrite. Photoreceptor staining, but not eccentric cell staining, was greatly diminished in sections incubated with antiserum that had been absorbed with peptide containing the predicted sequence of myoIIILim(Fig. 11D). This indicates that photoreceptor staining is specific and that eccentric cell staining is nonspecific.
Fig. 11.
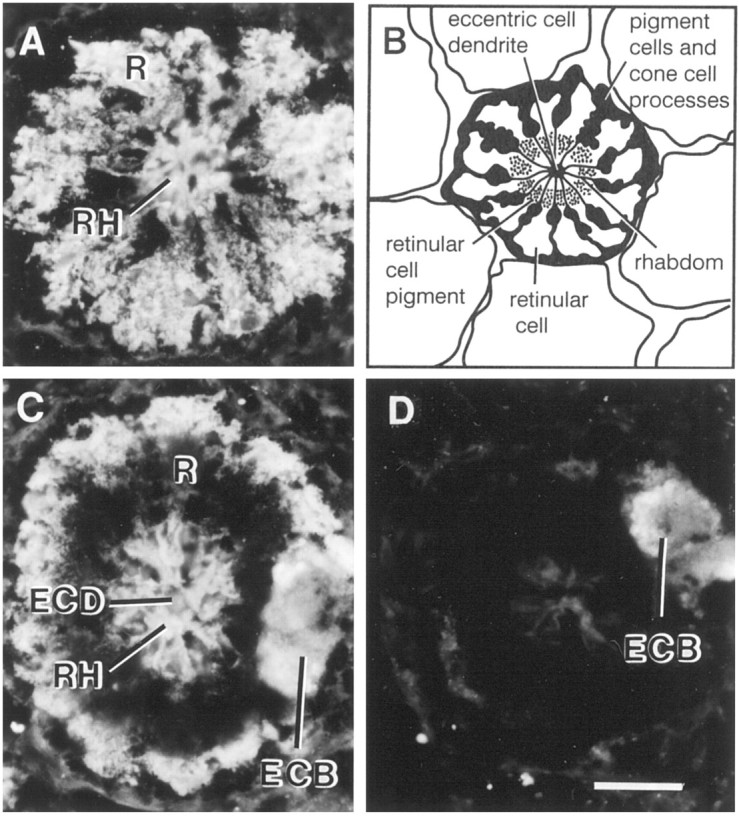
Localization of myoIIILimimmunoreactivity in fixed frozen sections of lateral eye. Lateral eyes dissected from light-adapted animals during the day were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde as described in Materials and Methods. Frozen sections (14 μm) were incubated overnight in a 1:50 dilution of rat serum containing antibodies directed against the predicted C-terminal sequence of myoIIILim. The location of the primary antibody was visualized with a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody. Specific myoIIILim is observed throughout the cytoplasm of the retinular cell and over the rhabdom. The staining observed over the eccentric cell body and dendrite is nonspecific.A, Cross-section of an ommitidium in the lateral eye at the level of the nuclei of the retinular cells. B, Diagram of a cross section of an ommitidium. The eccentric cell body is not shown. C, Cross-section of an ommatidium in the lateral eye at the level of the eccentric cell body. The dark region immediately peripheral to the rhabdom is occupied by pigment granules that absorb the fluorescent signal. D, A cross-section at a level similar to that shown in C was exposed to primary antibody that had been preincubated overnight with 10−5m free C-terminal peptide antigen.ECB, Eccentric cell body; ECD, eccentric cell dendrite; R, retinular cell; Rh, rhabdom. Scale bar, 40 μm.
DISCUSSION
Several lines of evidence indicate that the myoIIILimcDNA we have cloned encodes pp122, the abundant clock-regulated phosphoprotein described previously (Edwards and Battelle, 1987;Edwards et al., 1989, 1990). The predicted protein contains the sequences of all four tryptic peptides released from pp122 and the N-terminal sequence of a 50 kDa CNBr cleavage product of pp122. The molecular mass of the predicted protein matches closely the apparent molecular mass of pp122. An antibody raised against the C-terminal peptide sequence of the protein predicted from the cDNA sequence specifically stains pp122. pp122 binds calmodulin, a property predicted for the protein encoded by the cDNA we cloned.
MyoIIILim is a calcium-regulated calmodulin-binding protein
The idea that myoIIILim is a calcium-regulated calmodulin-binding protein is supported by the results of studies assaying myoIIILim binding to calmodulin-Sepharose. Like other calmodulin-binding myosins (Wolenski, 1995), myoIIILim bound to calmodulin in the absence of Ca2+ and when the concentration of free Ca2+ was low, but not when the free Ca2+ concentration was elevated. These assays suggest that myoIIILim binding to calmodulin is modulated between 0.1 and 1.6 μm free Ca2+, which is well within the physiological range of free Ca2+ measured in Limulusphotoreceptors during the photoresponse (Ukhanov et al., 1995). Thus, the association of calmodulin with myosin III may be modulated during the photoresponse.
The failure to detect binding of calmodulin to myoIIILimin calmodulin overlay assays leaves open the possibility that myoIIILim binding to calmodulin-Sepharose is indirect. It should be pointed out, however, that the short form of Drosophila ninaC, which is most similar to myoIIILim, binds to calmodulin in vivo and to calmodulin-Sepharose, but it does not bind calmodulin in overlay assays (Porter et al., 1993, 1995).
Calmodulin binding to other unconventional myosins modulates the ATPase and mechanochemical activities (Wolenski, 1995). Calmodulin binding to myoIIILim may have a similar function. Alternatively, or in addition, the myoIIILim may regulate the availability of calmodulin for other processes critical for photoreceptor function (Scott et al., 1997), as is suggested by the results of studies ofDrosophila mutants that lack the calmodulin-binding domains of ninaC proteins (Porter et al., 1993, 1995).
Is myoIIILim a molecular motor, and does it possess kinase activity?
Most residues involved in ATP binding in other myosins are conserved in myoIIILim, including the glycine-rich loop (Figs. 2, 3). Furthermore, another region that is conserved in most myosins and is thought to be involved in the conformation change produced by ATP hydrolysis (Cope et al., 1996; Rayment et al., 1996) is moderately conserved in myoIIILim. Thus, the myosin domain of myoIIILim probably possesses ATPase activity. On the other hand, an arginine that is conserved in all other myosins, including the ninaC proteins, and is thought to be intimately involved with binding the gamma phosphate of ATP (Cope et al., 1996; Rayment et al., 1996) is replaced in myoIIILimwith histidine (H487). The functional consequences of this change are not clear. The amino acid sequences at actin–myosin interfaces are not well conserved among the myosins (Rayment et al., 1993; for review, see Cope et al., 1996); therefore, the ATP-dependent actin-binding properties of myoIIILim cannot be predicted from its primary sequence. But ATP-dependent actin binding has been demonstrated for the homologous ninaC proteins (Hicks et al., 1996).
Experiments are in progress to test the kinase activity in myoIIILim. Kinase activity has been detected in the heterologously expressed kinase domain of ninaC (Ng et al., 1996). Although endogenous substrates have not been identified, the abnormal ERG recorded from Drosophila expressingninaC proteins that lack the kinase domain (Porter and Montell, 1993) suggests some may be involved in the photoresponse.
Is myoIIILim associated with the photosensitive rhabdom?
The distributions, and consequently the functions, ofninaC proteins of Drosophila appear to be determined by the length of their C-terminal tail domains.NinaC174, the long form, is located within the microvilli of the rhabdom where it apparently decorates and stabilizes the actin core; the short form,ninaC132, is located at the periphery of the rhabdom (Stowe and Davis, 1990; Hicks and Williams, 1992; Porter et al., 1992). NinaC174 is critical for maintaining rhabdom structure and a normal photoresponse. By itself,ninaC132 cannot maintain photoreceptor structure and function, although it contributes (Porter et al., 1992,1993; Hicks et al., 1996). NinaC132may be involved in light-dependent pigment migration (Hofstee et al., 1996) and photoreceptor membrane processing (Hicks and Williams, 1992;Hicks et al., 1996).
The tail domain of myoIIILim is extremely short; thus, the presence of myoIIILim immunoreactivity throughout the photoreceptor cytoplasm was predicted and was also consistent with results of previous biochemical results that demonstrated pp122 in all tissues containing photoreceptor cell bodies, axons, and terminals (Edwards and Battelle, 1987; Edwards et al., 1990). The presence of myoIIILim immunoreactivity in the region occupied by rhabdom was also predicted from previous biochemical studies that demonstrated light-stimulated phosphorylation of myoIIILim(Edwards et al., 1989). As in Drosophila, the microvilli ofLimulus photoreceptors contain an actin core (Johnson and Chamberlain, 1989; Calman and Chamberlain, 1992), but unlikeDrosophila, Limulus photoreceptors maintain structure and function in the absence of a long form of myosin III. If the association of a myosin with actin within the core of the microvilli is a general requirement for maintaining rhabdom structure, the myosin III we have cloned might serve this function inLimulus. Alternatively, the rhabdom may contain a different myosin isoform. We have not screened for other myosins in lateral and ventral eyes. The question of whether myoIIILim is associated with the actin core within the rhabdomeral microvilli must await results of immunocytochemical studies at the level of the electron microscope.
MyoIIILim is a novel member of the myosin superfamily
MyoIIILim is clearly a substrate for PKA (Edwards and Battelle, 1987; Edwards et al., 1989) and becomes phosphorylated within its myosin domain. Because there are three consensus sequences for PKA within the globular head region (Fig. 2), it is reasonable to predict that this region is phosphorylated by PKA. Alternatively, a different kinase, perhaps myoIIILim itself, may phosphorylate the myosin domain with PKA phosphorylating sites in the same region or elsewhere. Ng et al. (1996) have reported the phosphorylation of the myosin domain of ninaC by its kinase domain.
Phosphorylation of the myosin globular head is unusual among the myosins of metazoans but characteristic for the myosins I of protozoans (for review, see Tan et al., 1992; Moussavi et al., 1993) in which it is required for actin-activated ATPase and actin filament-based movement (Brzeska et al., 1989, 1990). In the myosins of metazoans, the requirement for phosphorylation within the globular head domain may be relieved by the replacement of an acidic residue at the site that becomes phosphorylated in the myosins I of protozoans, the so-called TEDS site (Bement and Mooseker, 1995). MyoIIILim contains an acidic amino acid at the TEDS site; therefore, its phosphorylation is probably not required for generating enzymatic or mechanochemical activity but is maybe required for the modulation of these activities. It is interesting to note that when myoIIILim is aligned with myosin II, two of the putative PKA phosphorylation sites of myoIIILim, S796 and S846, are positioned near predicted actin-myosin interfaces of myosin II (Raymont et al., 1993), and that S926 lies close to a predicted interface between the myosin II heavy chain and its light chain (Raymont et al., 1995).
Myosins I and II from metazoans typically are phosphorylated within their tail domains by Ca2+-regulated protein kinases or casein kinase II (for review, see Tan et al., 1992;Brzeska and Korn, 1996). This type of phosphorylation is unlikely in myoIIILim, because myoIIILim contains only eight amino acids in its tail domain, and the protein is not a substrate for either Ca2+/calmodulin- or Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent kinases (Edwards and Battelle, 1987; Edwards et al., 1989; Calman et al., 1996). Furthermore, the single serine in the truncated tail of myoIIILim is not a consensus site for phosphorylation by casein kinase II.
Because the phosphorylation of myoIIILim is different from that which has been observed for other myosins, the functional consequences will probably be different as well. MyoIIILimmay be phosphorylated at multiple sites, possibly by multiple kinase activities; thus, the regulation of myoIIILim by phosphorylation is probably complex.
Myosins III may be uniquely important for vision
The myosins III that have been identified so far are associated with visual systems. MyoIIILim and the homologousninaC proteins of Drosophila are visual system-specific and are found in photoreceptors (Edwards and Battelle, 1987; Montell and Rubin, 1988; Edwards et al., 1989). Recent preliminary studies describe the isolation of cDNAs encoding myosins III from the eyes of fish and humans (Hillman et al., 1996; Doséand Burnside, 1997). The myosins III of Drosophila clearly influence diverse processes within photoreceptors. InLimulus lateral eye photoreceptors, many of these same processes are modulated by the circadian clock, including the quenching of the photoresponse, rhabdom structure, membrane processing, and pigment migration (for review, see Battelle, 1991). The phosphorylation of myoIIILim may be a pivotal event for the synchronous modulation of multiple and diverse photoreceptor functions by the circadian clock.
Footnotes
This work was funded by National Science Foundation (NSF) Grants IBN-9211327 and IBN-9631565 to B-A.B., National Institutes of Health Grant EY06454 to W.S.C., NSF Grant BIR-9423959 to the Whitney Laboratory, and the Protein Core of the University of Florida Interdisciplinary Center for Biotechnology Research. J.S.K. was an NSF Research Experience for Undergraduates fellow. We thank Beth Burnside for helpful discussions, Bernd Eschweiler, Karen Kempler, and Jason S. Kingsbury for technical assistance, Lynn Milstead for artwork, and James Netherton for photography.
The GenBank accession number for Limulus myosin III is AFO 62069.
Correspondence should be addressed to B.-A. Battelle, Whitney Laboratory, 9505 Ocean Shore Boulevard, St. Augustine, FL 32086.
W. C. Smith’s Present address: Department of Ophthalmology, University of Florida, JHMHC 100284, Gainesville, FL 32610-0284
REFERENCES
- 1.Abersold RH, Leavitt J, Saavedra RA, Hood LE, Kent SB. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated on one-or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis for in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barlow RB., Jr Circadian rhythms in the Limulus visual system. J Neurosci. 1983;3:856–870. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-04-00856.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barlow RB, Jr, Bolanowski SJ, Jr, Brachman ML. Efferent optic nerve fibers mediate circadian rhythms in the Limulus eye. Science. 1977;197:86–89. doi: 10.1126/science.867057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barlow RB, Jr, Chamberlain SC, Levinson JZ. Limulus brain modulates the structure and function of the lateral eyes. Science. 1980;210:1037–1039. doi: 10.1126/science.7434015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Barlow RB, Jr, Kaplan E, Renninger GH, Saito T. Circadian rhythms in Limulus photoreceptors. I. Intracellular studies. J Gen Physiol. 1987;89:353–378. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Battelle B-A. Regulation of retinal functions byoctopaminergic efferent neurons in Limulus. Prog Retinal Res. 1991;10:335–355. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Battelle B-A, Evans JA. Octopamine release from centrifugal fibers of the Limulus peripheral visual system. J Neurochem. 1984;42:71–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Battelle B-A, Wishart AC. Cyclic AMP-linked octopamine receptors in Limulus eyes: pharmacological characteristics. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Suppl] 1990;31:331. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Battelle B-A, Evans JA, Chamberlain SC. Efferent fibers to Limulus eyes synthesize and release octopamine. Science. 1982;216:1250–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.6123151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bement WM, Mooseker MS. TEDS rule: a molecular rational for differential regulation of myosins by phosphorylation of the heavy chain head. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;31:87–92. doi: 10.1002/cm.970310202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bers D, Patton C, Nuccitelli R. A practical guide to the preparation of Ca buffers. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;40:3–29. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Brzeska H, Korn ED. Regulation of class I and class II myosins by heavy chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:16983–16986. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.29.16983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brzeska H, Lynch TJ, Martin B, Korn ED. The localization and sequence of the phosphorylation sites of Acanthamoeba myosins. I. An improved method for locating the phosphorylated amino acid. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:19340–19348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brzeska H, Lynch TJ, Martin B, Corigliano-Murphy A, Korn ED. Substrate specificity of Acanthamoeba myosin I heavy chain kinase as determined with synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:16138–16144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Calman BG, Battelle B-A. Central origin of the efferent neurons projecting to the eyes of Limulus polyphemus. Vis Neurosci. 1991;6:481–495. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800001334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Calman BG, Chamberlain SC. Localization of actin filaments and microtubules in the cells of the Limulus lateral and ventral eyes. Vis Neurosci. 1992;9:365–375. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800010774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Calman BG, Andrews AW, Rissler HM, Edwards SC, Battelle B-A. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and arrestin phosphorylation in Limulus eyes. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 1996;35:33–44. doi: 10.1016/1011-1344(96)07312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cavener DR. Combinational control of structural genes in Drosophila: solutions that work for the animal. Bioessays. 1987;7:103–107. doi: 10.1002/bies.950070303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chamberlain SC, Barlow RB., Jr Light and efferent activity control rhabdom turnover in Limulus photoreceptors. Science. 1979;206:361–363. doi: 10.1126/science.482946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chamberlain SC, Barlow RB., Jr Transient membrane shedding in Limulus photoreceptors: control mechanisms under natural lighting. J Neurosci. 1984;4:2792–2810. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chamberlain SC, Barlow RB., Jr Control of structural rhythms in the lateral eye of Limulus: interactions of natural lighting and circadian efferent activity. J Neurosci. 1987;7:2135–2144. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-07-02135.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chamberlain SC, Fiacco PA. Models of circadian changes in Limulus ommatidia: calculation of changes in acceptance angle, quantum catch and quantum gain. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Suppl] 1985;26:340. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cheney RE, Mooseker MS. Unconventional myosins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992;4:27–35. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90055-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cope MJT, Whisstock J, Rayment I, Kendrick-Jones J. Conservation within the myosin motor domain: implications for structure and function. Structure. 1996;4:969–987. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dosé AC, Burnside MB. A potential human homologue of Drosophila ninaC. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Suppl] 1997;38:1161. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Edwards SC, Battelle B-A. Octopamine- and cAMP-stimulated phosphorylation of a protein in Limulus ventral and lateral eyes. J Neurosci. 1987;7:2811–2820. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02811.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Edwards SC, Wishart AC, Wiebe EM, Battelle B-A. Light-regulated proteins in Limulus ventral photoreceptor cells. Vis Neurosci. 1989;3:95–105. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800004417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Edwards SC, Andrews AW, Renninger GH, Wiebe EM, Battelle B-A. Efferent innervation to Limulus eye in vivo phosphorylates a 122 kDa protein. Biol Bull. 1990;178:267–278. doi: 10.2307/1541828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Evans JA, Chamberlain SC, Battelle B-A. Autoradiographic localization of newly synthesized octopamine to retinal efferents in the Limulus visual system. J Comp Neurol. 1983;219:369–383. doi: 10.1002/cne.902190402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fahrenbach WH. The morphology of the Limulus visual system. IV. The lateral optic nerve. Zeitschrift fuer Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie. 1971;114:532–545. doi: 10.1007/BF00325638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fahrenbach WH. The morphology of the horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus) visual system. VII. Innervation of photoreceptor neurons by neurosecretory efferents. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;216:655–659. doi: 10.1007/BF00238660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983;132:6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Flanagan SD, Yost B. Calmodulin-binding proteins: visualization by 125I-calmodulin overlay on blots quenched with Tween 20 or bovine serum albumin and poly(ethylene oxide). Anal Biochem. 1984;140:510–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988;241:42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Harlow E, Lane D. Antibodies, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hasson T, Mooseker MS. Molecular motors, membrane movements and physiology: emerging roles for myosins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7:587–594. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hicks JL, Williams DS. Distribution of the myosin I-like ninaC proteins in the Drosophila retina and ultrastructural analysis of mutant phenotypes. J Cell Sci. 1992;101:247–254. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hicks JL, Liu X, Williams DS. The role of the ninaC proteins in photoreceptor cell structure: ultrastructure of ninaC deletion mutants and binding to actin filaments. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1996;35:367–379. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0169(1996)35:4<367::AID-CM8>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hillman D, Bost-Usinger L, Burnside B. A potential vertebrate homologue of Drosophila ninaC. Mol Biol Cell. 1996;7:39a. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hofstee CA, Henderson S, Hardie R, Stavenga DG. Differential effects of ninaC proteins (p132 and p174) on light-activated currents and pupil mechanism in Drosophila photoreceptors. Vis Neurosci. 1996;13:897–906. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800009147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Johnson JK, Chamberlain SC. Membrane-associated axial filaments in rhabdomeral microvilli of Limulus lateral eye photoreceptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Suppl] 1989;30:292. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kaplan E, Barlow RB., Jr Circadian clock in Limulus brain increases responses and decreases noise of retinal photoreceptors. Nature. 1980;286:393–395. doi: 10.1038/286393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kaplan E, Barlow RB, Jr, Renninger GH, Purpura K. Circadian rhythms in Limulus photoreceptors. II. Quantum bumps. J Gen Physiol. 1990;96:665–685. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kass L, Barlow RB., Jr Efferent neurotransmission of circadian rhythms in Limulus lateral eye. I. Octopamine-induced increases in retinal sensitivity. J Neurosci. 1984;4:908–917. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-04-00908.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kass L, Barlow RB., Jr A circadian clock in the Limulus brain transmits synchronous efferent signals to all eyes. Vis Neurosci. 1992;9:493–504. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800011299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kass L, Renninger GH. Circadian changes in function of Limulus ventral photoreceptors. Vis Neurosci. 1988;1:3–11. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800000985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kass L, Pelletier JL, Renninger GH, Barlow RB., Jr Efferent neurotransmission of circadian rhythms in Limulus lateral eye. II. Intracellular recordings in vitro. J Comp Physiol. 1988;164:95–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00612723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kaupp UB, Malbon CC, Battelle B-A, Brown JE. Octopamine stimulated rise in cAMP in Limulus ventral photoreceptors. Vision Res. 1982;22:1503–1506. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(82)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kier CK, Chamberlain SC. Dual controls of screening pigment movement in photoreceptors of the Limulus lateral eye: circadian efferent input and light. Vis Neurosci. 1989;4:237–255. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800003382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984;12:857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;277:680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Montell C, Rubin GH. The Drosophila ninaC locus encodes two photoreceptor cell specific proteins with domains homologous to protein kinases and the myosin heavy chain head. Cell. 1988;52:757–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Moussavi RS, Kelley CA, Adelstein RS. Phosphorylation of vertebrate nonmuscle and smooth muscle myosin heavy chains and light chains [review]. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993;127:219–227. doi: 10.1007/BF01076773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ng KP, Kambara T, Matsuura M, Burke M, Ikebe M. Identification of myosin III as a protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1996;35:9392–9399. doi: 10.1021/bi960181a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pongor S, Hatsagi Z, Degtyarenko K, Fabian P, Skerl V, Hegyi H, Murvia J, Bevilacqua V. The SBASE protein domain library, release 3.0: a collection of annotated protein sequence segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:3610–3615. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Porter JA, Montell C. Distinct roles of the Drosophila ninaC kinase and myosin domains revealed by systematic mutagenesis. Cell. 1993;122:601–612. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Porter JA, Hicks JL, Williams DS, Montell C. Differential localizations of and requirements for the two Drosophila ninaC kinase/myosins in photoreceptor cells. J Cell Biol. 1992;116:683–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Porter JA, Yu M, Doberstein SK, Pollard TD, Montell C. Dependence of calmodulin localization in the retina on the ninaC unconventional myosin. Science. 1993;262:1038–1042. doi: 10.1126/science.8235618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Porter JA, Minke B, Montell C. Calmodulin binding to Drosophila ninaC required for termination of phototransduction. EMBO J. 1995;14:4450–4459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rayment I, Holden HM, Whittaker M, Yohn CB, Lorenz M, Holmes KC, Milligan RA. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993;261:58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rayment I, Holden HM, Sellers JR, Fananapazir L, Epstein ND. Structural interpretation of the mutations of the B-cardiac myosin that have been implicated in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:3864–3868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rayment I, Smith C, Yount RG. The active site of myosin. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:671–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.58.030196.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Renninger GH, Schimmel R, Farrell CA. Octopamine modulates photoreceptor function in the Limulus lateral eye. Vis Neurosci. 1989;3:83–94. doi: 10.1017/s0952523800004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sanger F, Niklen S, Coulson AR. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1977;74:5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Schagger H, von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987;166:368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Scott K, Sun Y, Beckingham K, Zuker CS. Calmodulin regulation of Drosophila light-activated channels and receptor function mediates termination of the light response in vivo. Cell. 1997;91:375–383. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Smith WC, Eschweiler B, Andrews AW, Greenberg RM, Battelle B-A. Circadian efferent input to Limulus retina stimulates the phosphorylation of a protein similar to the ninaC gene products of Drosophila. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1993a;19:1199. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Smith WC, Price DA, Greenberg RM, Battelle B-A. Opsins from the lateral eye and ocelli of the horseshoe crab, Limulus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993b;90:6150–6154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Smith WC, Greenberg RM, Calman BG, Hendrix MM, Hutchinson L, Donoso LA, Battelle B-A. Isolation and expression of an arrestin cDNA from the horseshoe crab lateral eye. J Neurochem. 1995;64:1–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64010001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Stowe S, Davis DT. Anti-actin immunoreactivity is retained in rhabdoms of Drosophila ninaC photoreceptors. Cell Tissue Res. 1990;260:431–434. doi: 10.1007/BF00297222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Tan JL, Ravid S, Spudich JA. Control of nonmuscle myosins by phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:721–759. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets. Procedures and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1979;74:4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ukhanov KY, Flores TM, Hsiao HS, Mohapatra P, Pitts CH, Payne R. Measurement of cytosolic Ca++ concentration in Limulus ventral photoreceptors using fluorescent dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1995;105:95–116. doi: 10.1085/jgp.105.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Wolenski JS. Regulation of calmodulin-binding myosins. Trends Cell Biol. 1995;5:310–316. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]