Abstract
A transporter thought to mediate accumulation of GABA into synaptic vesicles has recently been cloned (McIntire et al., 1997). This vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT), the first vesicular amino acid transporter to be molecularly identified, differs in structure from previously cloned vesicular neurotransmitter transporters and defines a novel gene family. Here we use antibodies specific for N- and C-terminal epitopes of VGAT to localize the protein in the rat CNS. VGAT is highly concentrated in the nerve endings of GABAergic neurons in the brain and spinal cord but also in glycinergic nerve endings. In contrast, hippocampal mossy fiber boutons, which although glutamatergic are known to contain GABA, lack VGAT immunoreactivity. Post-embedding immunogold quantification shows that the protein specifically associates with synaptic vesicles. Triple labeling for VGAT, GABA, and glycine in the lateral oliva superior revealed a higher expression of VGAT in nerve endings rich in GABA, with or without glycine, than in others rich in glycine only. Although the great majority of nerve terminals containing GABA or glycine are immunopositive for VGAT, subpopulations of nerve endings rich in GABA or glycine appear to lack the protein. Additional vesicular transporters or alternative modes of release may therefore contribute to the inhibitory neurotransmission mediated by these two amino acids.
Keywords: neurotransmitter transport, synaptic vesicles, GABA, glycine, antibodies, immunogold, microscopy
Neurotransmitters are taken up and stored in synaptic vesicles before exocytotic release to the synaptic cleft (Liu and Edwards, 1997). Synaptic vesicle preparations express several distinct neurotransmitter transport activities, and molecular cloning has identified cDNAs encoding vesicular transporters for monoamines (VMAT1 and VMAT2) and acetylcholine (VAChT) (Erickson et al., 1992, 1994; Liu et al., 1992). However, the vesicular transport of amino acid transmitters differs in mechanism from the transport of monoamines and acetylcholine. In contrast to the VMATs and VAChT, which rely chiefly on the pH gradient (ΔpH) across the vesicle membrane to drive active transport, vesicular glutamate transport depends almost entirely on the electrical gradient (Δψ), vesicular GABA transport depends equally on Δψ and ΔpH, and vesicular glycine transport resembles vesicular GABA transport in the bioenergetic mechanism (Fykse and Fonnum, 1988, 1996; Maycox et al., 1990). However, competition studies using synaptic vesicles from different brain regions have not definitively resolved whether a single transporter packages both GABA and glycine or distinct proteins package the two transmitters (Kish et al., 1989; Christensen et al., 1990, 1991; Burger et al., 1991). Although in the forebrain most inhibitory nerve endings have high concentrations of GABA but not glycine, in the spinal cord and brainstem nerve endings colocalize GABA and glycine and at many sites are more abundant than nerve endings rich in only one of the two inhibitory amino acids (Ottersen et al., 1988, 1995; Helfert et al., 1989, 1992; Osen et al., 1990; Ottersen and Storm-Mathisen, 1990; Todd and Sullivan, 1990; Kolston et al., 1992; Wentzel et al., 1993;Örnung et al., 1994, 1996, 1998; Taal and Holstege, 1994; Juiz et al., 1996; Lahjouji et al., 1996; Yang et al., 1997).
Genetic and pharmacological studies in Caenorhabditis elegans have recently led to the identification of the first vesicular transporter for an amino acid (McIntire et al., 1997). The mutant unc-47 appears to have a presynaptic defect in GABAergic transmission and, surprisingly, accumulates large amounts of GABA. Complementation studies identified the affected gene, which encodes a polytopic membrane protein, suggesting a role in vesicular GABA transport. Supporting this possibility, expression of the gene and its mammalian homolog in heterologous cell systems conferred vesicular GABA transport with the anticipated dependence on both Δψ and ΔpH. This vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT) was competitively inhibited by glycine but with low potency (IC50 25 mm) and did not show significant transport of [3H]glycine, raising the possibility of a distinct vesicular transporter for glycine but not excluding a role for VGAT in glycine packaging. In C. elegans the protein is selectively expressed in all of the nematode’s GABAergic neurons, and in rat the distribution of VGAT mRNA also indicates expression in GABAergic neurons.
Here we use antibodies that specifically recognize VGAT to investigate the regional, cellular, and subcellular localization of the transport protein in rat brain. By electron microscopic post-embedding immunogold quantification, VGAT appears at high levels in glycinergic as well as GABAergic nerve endings and associates with synaptic vesicles. A subpopulation of boutons rich in GABA and/or glycine seems to lack VGAT.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
N-terminal fusion protein. A DNA fragment corresponding to the N-terminal 99 amino acids of VGAT was amplified by PCR from the rat cDNA using Pfu polymerase (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) and the primers 5′-CGGGATCCCATGGCCACCCTGCTCCGC-3′ and 5′-GGGAATTCGTCCTTGGAGCCCGAGGG-3′. After digestion with BamHI andEcoRI (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD), the PCR product was inserted in-frame into the glutathione S-transferase (GST) vector PGEX-3X (Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ) using T4 DNA ligase (Life Technologies). The construct was then sequenced to confirm the absence of unwanted mutations in the PCR-generated fragment.
To produce the GST-VGAT fusion protein, Escherichia colitransformed with the construct were grown overnight at 37°C in 1.6% tryptone, induced with 100 μm isopropyl β-d-thiogalactoside for an additional 3–6 hr at room temperature, pelleted, resuspended in PBS, and disrupted by vigorous sonication at 0°C. The lysate was sedimented at 14,000 ×g to remove cell debris, and the cleared extract was incubated with glutathione-Sepharose beads (1 hr at room temperature in PBS). After washing three times with PBS, the GST fusion protein was eluted from the beads with 10 mm glutathione and 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.0.
Coupling of synthetic peptide to carrier protein. A peptide corresponding to the C-terminal 17 amino acids of VGAT was synthesized with an additional N-terminal cysteine (CVHSLEGLIEAYRTNAED) and coupled to the carrier protein keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) through the N-terminal cysteine usingm-maleimidobenzoyl-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester.
Immunization. The GSH-VGAT fusion protein (300 μg) and KLH-conjugated peptide (200 μg), prepared as described above, were diluted in 500 μl of PBS, emulsified with 500 μl of Freund’s complete adjuvant (Life Technologies), and injected intradermally into 14-week-old female New Zealand White rabbits. After 1 month, the animals were boosted with a subcutaneous injection of the same amounts of fusion protein or conjugated peptide emulsified with Freund’s incomplete adjuvant (Life Technologies). Serum was collected 14 d later and stored at 4°C with 0.02% NaN3 added.
Membrane preparation of cells expressing VGAT. Wild-type PC12 cells and a previously characterized PC12 cell line stably expressing rat VGAT (McIntire et al., 1997) were grown to confluence in DME-H21 medium containing 10% equine serum and 5% Cosmic Calf Serum (HyClone, Logan, UT). To prepare membranes, the cells were collected, washed in calcium- and magnesium-free PBS, resuspended in 1 ml of SH buffer (0.3 m sucrose and 10 mm HEPES-KOH, pH 7.4) with 1.25 mm Mg-EGTA and protease inhibitors (1 mm PMSF, 2 μg/ml aprotinin, 2 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 μg/ml E64, and 1 μg/ml pepstatin)/15 cm plate, and disrupted by passage through a cell cracker at a clearance of 10 μm (McIntire et al., 1997). The homogenate was centrifuged at 27,000 ×g for 35 min, and membranes in the supernatant were pelleted at 64,000 × g for 1 hr and resuspended in SH buffer with protease inhibitors (as above).
Preparation of SDS extracts of tissues. SDS extracts from whole rat brain (four adult Sprague Dawley rats) and liver were prepared by homogenizing the tissues in PBS with SDS (10 mg/ml), 5 mm EDTA, and 1 mm PMSF with a Dounce homogenizer. The tissue samples were then diluted in SDS sample buffer containing dithiothreitol and immediately separated by SDS-PAGE or stored at −80°C.
Electrophoresis and blotting. Thirty micrograms of protein per lane were separated at 140 V for ∼2 hr or at 6 A overnight. After electrophoresis, the separated samples were electroblotted onto nitrocellulose at 1.2 mA/cm2. The transfer buffer consisted of 20 mm Tris-HCl, 150 mm glycine, and 20% methanol. Nonspecific binding to the blot was blocked by incubation of the membrane with 5% nonfat milk protein in PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 for 1 hr. The blot was then incubated with the antibodies (N2, 1:2000; C1, 1:200 or 1:400) for 2 hr or overnight at room temperature. After washing, blots were treated with peroxidase-linked anti-rabbit IgG, and the complexes were visualized on x-ray film after incubation with enhanced chemiluminescent substrate (Pierce, Rockford, IL).
Tissue for immunocytochemistry. Nine adult rats (Wistar strain; Moellegaard Hansen) of 150–200 gm were deeply anesthetized with pentobarbital (100 mg/kg), the right atrium was cut open, and the animals were perfused through the left ventricle–aorta. Animal use was according to Norwegian law and in agreement with the guidelines of the Society for Neuroscience. The liquids were delivered by a peristaltic pump at 50 ml/min. After a brief flush of 4% Dextran-T70 (molecular weight, 70,000; Pharmacia) in 0.1 m sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 (NaPi), for 10–15 sec, one of three different fixatives was introduced: (1) for fixative A, two rats were perfused with a mixture of formaldehyde/picric acid/glutaraldehyde (4/0.2/0.05%) in NaPi; (2) for fixative B, four rats were perfused with glutaraldehyde/formaldehyde/picric acid (2.5/1/0.02%) (Somogyi and Takagi, 1982) in NaPi; and (3) for fixative C, three rats were fixed by formaldehyde/picric acid (4/0.02%) in 0.1 m sodium acetate buffer, pH 6.0 (200 ml, 5 min), followed by the same fixatives in 0.1m sodium carbonate buffer, pH 10.5 (400 ml, 20 min). The latter fixative (Berod et al., 1981; Marcos et al., 1997) had the best preservation of antigenicity and acceptable ultrastructure (Dehnes et al., 1998). The brains were post-fixed in the same fixative overnight at 4°C and then kept in diluted fixative (1:10 with the buffer) at 4°C until used.
Fixatives A and C were used for light and electron microscopic immunoperoxidase; fixatives B and C were used for electron microscopic immunogold labeling. Fixative C was used for all immunogold illustrations and quantification, except for the double- and triple-labeling experiments, which require glutaraldehyde for demonstration of fixed amino acids.
Pre-embedding immunoperoxidase. Vibratome sections (40 μm thick) were cut (4–10°C) and stored (4°C overnight to 3 weeks) in NaPi containing NaN3 (0.1%). Then the sections were rinsed in NaPi, incubated (30 min) in buffer A (0.135 m NaCl and 0.01 m sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4), incubated in buffer B (0.3 m NaCl and 0.1 m Tris-HCl pH 7.4) with 10% (v/v) newborn calf serum and then incubated (overnight at room temperature) with primary antibodies diluted (1:200–1:2000) in buffer C (buffer B with 1% newborn calf serum). Triton X-100 (Triton; 0.1% in buffers B and C) was included only when stated. When not stated otherwise, the illustrations are from sections treated with N2 antibody (1:200 without Triton or 1:1000 with Triton); for illustrations, C1 antibody was used at 1:400 (with Triton). The sections were subsequently washed (three times for 1 min each and two times for 10–20 min each) in buffer C, incubated (1 hr) with biotinylated donkey anti-rabbit Ig (1:100; Amersham, Arlington Heights, IL) in buffer C, washed (three times for 1 min each and two times for 15 min each) in buffer C, incubated (1 hr) with streptavidin-biotinylated horseradish peroxidase complex (1:100; Amersham) in buffer C, and washed (three times for 1 min each and two times for 15 min each) in buffer C. Then the sections were washed (three times for 1 min each) in buffer A, preincubated for 5 min in NaPi with diaminobenzidine (0.5 mg/ml), and then incubated for 6 min in the same solution containing H2O2 (0.1 mg/ml). The reaction was stopped by rinsing with NaPi (two times for 3 min each). For light microscopy, Vibratome sections were mounted in glycerol-gelatin. Brain areas were identified referring to the atlas ofPaxinos and Watson (1986). For medium- and high-power light microscopy, sections were photographed by a Leica (Nussloch, Germany) photomicroscope with differential interference contrast (DIC) optics. For electron microscopy, the sections were treated with osmium (30–45 min, 10 mg/ml in NaPi), washed (three times for 1 min each) in NaPi, dehydrated in graded ethanols (50, 70, 80, and 96% one time for 5 min each and 100% three times for 10 min each) and propylene oxide (two times for 5 min each), and embedded in Durcupan ACM. Ultrathin sections were cut and contrasted (10 mg/ml uranyl acetate for 10–15 min and 3 mg/ml Pb-citrate for 1–2 min) before viewing in a Phillips CM10 electron microscope.
Post-embedding immunogold labeling. The freeze–substitution embedding and immunogold labeling were performed as described (Chaudhry et al., 1995). Small rectangular pieces of aldehyde-perfused brain were cut by a razor blade, rinsed in NaPi, and immersed in 10 and 20% glycerol in NaPi for 0.5 hr and subsequently in 30% glycerol in NaPi overnight at 4°C. The tissue samples were frozen by plunging into liquid propane cooled to −190°C by liquid nitrogen in a KF80 Universal Cryofixation System (Leica, Vienna, Austria). The tissue samples were then moved to a Cryo Substitution Apparatus (Leica) precooled to −90°C, where the samples were substituted with anhydrous methanol containing 0.5% uranyl acetate. After washing several times with methanol, the samples were infiltrated at −45°C with stepwise increasing concentrations of Lowicryl HM20 to methanol and subsequently with pure Lowicryl HM20 overnight. The resin was polymerized in embedding malls catalyzed by ultraviolet light of 360 nm wavelength for 2 d at −45°C. Ultrathin sections (80–90 nm) were cut on a Leica ultramicrotome with a diamond knife and put on 500 mesh nickel grids. Serial sections, for processing with three different antibodies, were put on one-hole grids with a carbon-coated Formvar film. Sections were washed with 0.1% sodium borohydride and 50 mm glycine in TBST (0.05 m Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 0.9% sodium chloride, and 0.1% Triton), blocked in TBST containing 2% human serum albumin, and then incubated with the primary antibody diluted (1:20–1:40) in the same blocking solution overnight at 4°C. They were subsequently washed with TBST and incubated with goat anti-rabbit Ig coupled to 15 nm gold particles (GAR15; Amersham, Buckinghamshire, UK; diluted 1:20 in TBST) for 1 hr. The sections were then, after washing with water, stained with uranyl acetate (10 min) and lead citrate (1 min).
Electron micrographs were taken in a Phillips CM10 electron microscope. Structures were identified referring to descriptions by Palay and Chan-Palay (1974) and Peters et al. (1991). The concentrations of gold particles were measured by means of the data program MORFOREL (Blackstad et al., 1990). The vesicular association of the gold particles was analyzed in two different ways: (1) The occurrence of synaptic vesicles and gold particles was recorded within squares of a lattice placed over the pictures (Ji et al., 1991). Particles or vesicles touching the sides of the squares were included only for the bottom and right sides. Squares containing mitochondria or partly outside an axon terminal were excluded. (2) The centers of synaptic vesicles and gold particles, as well as the circumference of the terminal and any intraterminal mitochondria and areas filled with filament bundles (in basket cell axons), were recorded on a digitizing tablet by the program Micro Trace (Leergaard and Bjaalie, 1995). Custom software was used to determine the intercenter distances from each gold particle to the nearest synaptic vesicle (Gundersen et al., 1998). This was compared with distances to vesicles from points randomly distributed over the mitochondria and filament-free parts of the VGAT-labeled nerve terminals. Statistical analyses of means and of the correlation of vesicles with immunogold particles were performed by the Statistica package, the distributions of intercenter distances were compared using the χ2 test for equality of distributions provided by the University of Amsterdam (http://fonsg3.let.uva.nl).
Antibodies. The VGAT antisera from the rabbits (N1 and N2) immunized with the N-terminal fusion protein and the rabbits (C1 and C2) immunized with the synthetic C-terminal peptide were incubated overnight in 0.1% Tween 20 containing 5% nonfat dry milk (Carnation, Los Angeles, CA), 1% goat serum, and 40 mg/ml rat liver acetone powder (Cappel, West Chester, PA). Then the solutions were transferred to centrifuge tubes with a 0.45 μm filter insert and spun in a Microfuge for 5 min at maximum speed. The N2 serum was used when not stated otherwise. For negative control, the diluted antibodies were absorbed overnight with N-terminal fusion protein or C-terminal synthetic peptide. Likewise, omission of antibody or substitution with nonimmune serum abolished labeling.
Antibody to the GABA transporter GAT-1 was obtained from a rabbit (68514) immunized with the C-terminal peptide EQPQAGSSASKEAYI (amino acid residues 584–599 of rat GAT-1) (Guastella et al., 1990) conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin by glutaraldehyde. Preparation of antigen, immunization, and purification of antibody followed procedures previously used for glutamate transporters (Lehre et al., 1995). The antibody was affinity-purified on the peptide immobilized on agarose, absorbed with immobilized carrier protein treated with glutaraldehyde, and concentrated by immobilized protein A. It was used for immunoperoxidase staining at 0.6 μg/ml with Triton.
Antiserum to aldehyde-fixed glycine (290; Kolston et al., 1992) was diluted to 1:1000 and absorbed with 200 μm GABA previously reacted with glutaraldehyde (GABA-G), 50 μml-α-alanine-G, 50 μm β-alanine-G, and 50 μm glutamine-G in TBST containing 2% human serum albumin (HSA) overnight before use. The antiserum to aldehyde-fixed GABA (990;Walberg and Ottersen, 1992) was diluted 1:1500 and absorbed with 200 μm glutamate-G, also in TBST containing 2% HSA, overnight before use. The antibodies to GABA and to glycine were generated according to the methods established for amino acid immunocytochemistry (Storm-Mathisen et al., 1983) and have been characterized for electron microscopic post-embedding immunogold labeling (Örnung et al., 1994, 1996). Ultrathin test sections of embedded amino acid conjugates (Ottersen, 1989), included with the tissue sections processed with sera 900 and 290, ascertained that significant densities of gold particles occurred only over fixed GABA or glycine, respectively, and not over conjugates of other fixed amino acids or over aldehyde-fixed brain macromolecules in the present conditions.
RESULTS
Antibodies to VGAT
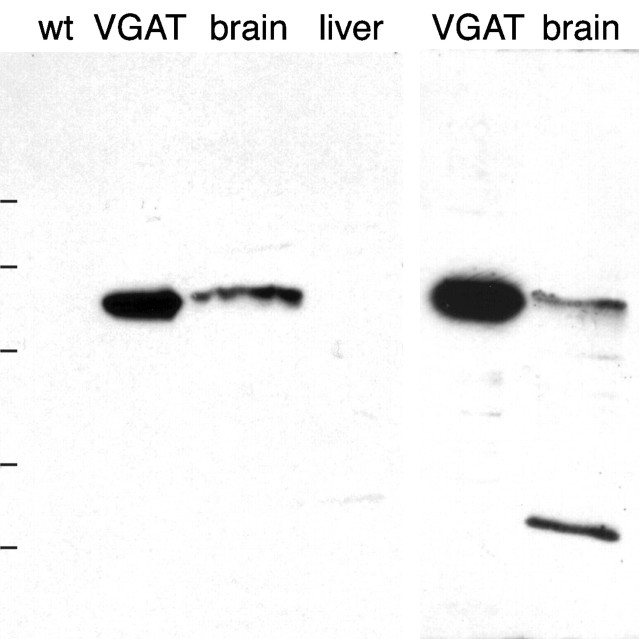
The antibodies N2 to the N-terminal fusion protein and C1 to the C-terminal peptide showed the best staining of immunoblots and were selected for further study. N2 stained one band on immunoblots of PC12 cells expressing VGAT and in extracts of whole rat brain (Fig.1, left). The apparent molecular mass of the band (55–60 kDa) is in agreement with that calculated from the amino acid composition. There was no staining of liver or control PC12 cells under the same conditions. C1 also stained a single electrophoretic band of the same molecular mass in extracts of VGAT-expressing PC12 cells, but in brain extracts there was an additional band of lower molecular mass (Fig. 1, right). The nature of this band is not resolved. The results below are therefore based on the N2 antiserum unless explicitly stated otherwise. However, except for a lower signal and higher background with the C1 antiserum, immunocytochemical results with the two antibodies were in agreement (see below).
Fig. 1.
Specificity of antibodies to VGAT as demonstrated by immunoblotting after electrophoretic (SDS-PAGE) separation of proteins. Left, N2 antibody. Right, C1 antibody. Extracts of brain and VGAT-expressing PC12 cells (VGAT) show bands with a similar molecular mass (∼57 kDa). The bands are absent in liver and wild-type PC12 cells (wt). Positions of molecular mass standards are indicated on the left (83, 62, 47.5, 32.5, and 25 kDa, consecutively from the top).
Immunoperoxidase localization
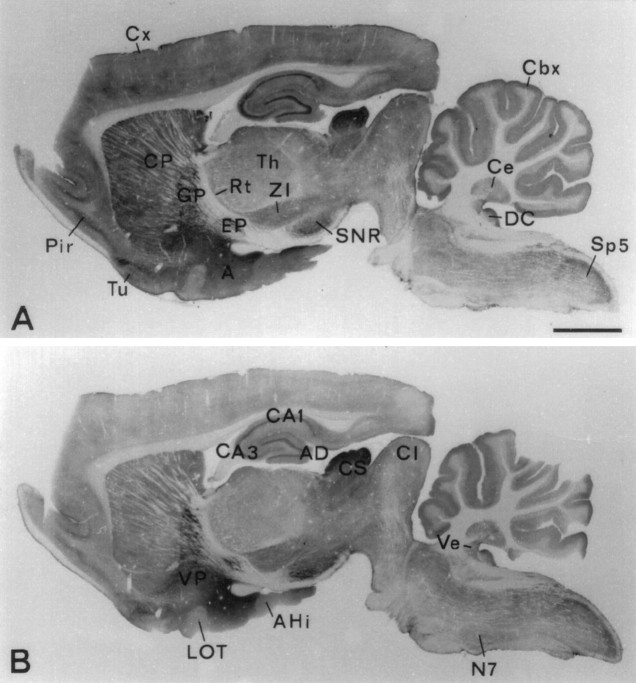
Survey of the brain with N2 antibody (Fig.2A) showed a distribution of VGAT immunoreactivity similar to those of recognized GABAergic markers glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) (Mugnaini and Oertel, 1985), GABA content and high-affinity GABA uptake (Ottersen and Storm-Mathisen, 1984), i.e., high-intensity staining in target areas of short-axon and long-axon GABAergic neurons. (In the present paper the terms “GABAergic” and “glycinergic” neurons are used to designate neurons containing high concentrations of GABA and glycine, respectively, in their nerve endings and hence being likely to use these amino acids as transmitters.) Examples of GABAergic long-axon targets are globus pallidus, ventral pallidum, nucleus entopeduncularis, substantia nigra pars reticulata, vestibular nuclei, and central cerebellar nuclei. Examples of densely innervated GABAergic short-axon targets are the pyramidal and granular layers of hippocampus and area dentata, caudatoputamen, amygdaloid area, and the Purkinje cell layer of the cerebellar cortex, as well as the superficial layers of the colliculus superior, the dorsal nucleus cochlearis, and the nucleus tractus spinalis nervi trigemini. The C1 antibody (Fig.2B) showed an almost identical distribution. (The slight differences apparent in Fig. 2A,B are explainable by a slight difference in overall staining intensity.)
Fig. 2.
Regional localization of VGAT shown by immunoperoxidase staining (with Triton) of closely spaced parasagittal Vibratome sections of rat brain. Antibodies N2 to the N-terminal fusion protein (A) and C1 to the C-terminal peptide (B) show the same distribution of immunoreactivity. Strong staining is shown in recognized targets of GABAergic nerve terminals (see Results). A, Amygdaloid nuclei; AD area dentata; AHi, amygdalohippocampal area; CA1, CA3, hippocampal subfields; Cbx, cortex cerebellaris;CI, colliculus inferior; CS colliculus superior; Cx, cortex cerebralis; Ce, central cerebellar nuclei (nucleus interpositus); CP, caudatoputamen; DC, dorsal nucleus cochlearis;EP, nucleus entopeduncularis; GP, globus pallidus; LOT, nucleus tractus olfactorius lateralis;N7, nucleus facialis; SNR, substantia nigra pars reticulata; Rt, nucleus reticularis thalami;Pir, cortex piriformis; Th, thalamic nuclei; Sp5, nucleus tractus spinalis nervi trigemini;Tu, tuberculum olfactorium; Ve, vestibular nuclei; VP, ventral pallidum;ZI, zona incerta. Scale bar, 2 mm.
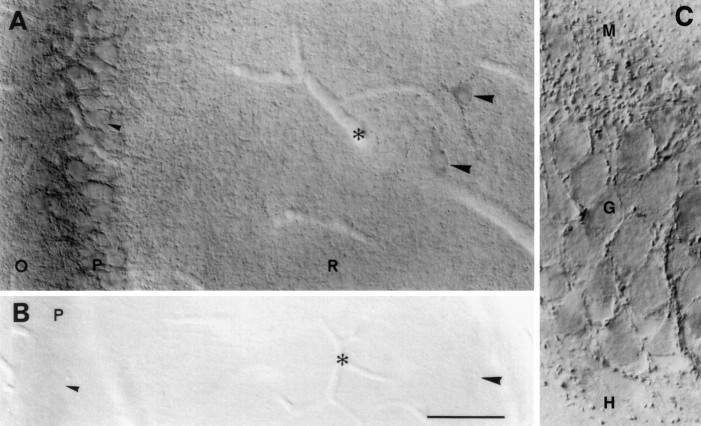
Higher magnification revealed that the VGAT staining pattern was attributable to intensely immunoreactive nerve terminal-like dots (“puncta”) present in all regions but at different densities. (Below, these are referred to as “nerve endings” or “terminals,” because subsequent electron microscopy established this identity; see below.) In hippocampus (Figs.3, 4) such dots were spread throughout the cortical layers but were concentrated on the surfaces of the perikarya of the principal neurons (pyramidal cells) and interneurons. This distribution matches that of GAD (Storm-Mathisen and Fonnum, 1971;Barber and Saito, 1976; Somogyi et al., 1983b), GABA (Storm-Mathisen et al., 1983), high-affinity GABA uptake (Hökfelt and Ljungdahl, 1971; Taxt and Storm-Mathisen, 1984), and GABA transporter GAT-1 (Radian et al., 1990; Ribak et al., 1996b). In strata oriens and pyramidale rows of VGAT-immuoreacive dots (Fig.4A) evidently represent the terminals of axoaxonic (chandellier) cells (Somogyi et al., 1983b). Hippocampal interneurons are known to be GABAergic and the source of the major part of the GABAergic nerve terminals in the region (Storm-Mathisen, 1972; Schlander et al., 1987; Soriano et al., 1990;Frotscher et al., 1992; Hálasy and Somogyi, 1993; Hálasy et al., 1996; Ceranik et al., 1997). Interneuron perikarya showed VGAT staining in the cytoplasm (Fig. 3A), probably representing the protein before insertion into the plasma membrane. Such staining was not shown by the perikarya of pyramidal or granular cells (Figs.3C, 4A). The axons of the latter, the hippocampal mossy fibers, give rise to boutons that are thought to be glutamatergic but are also enriched with GABA (Sandler and Smith, 1991). These showed no VGAT immunoreactivity (Fig.4A,B), in agreement with the low staining intensity in stratum lucidum (Fig. 2) and lack of staining of their parent cell bodies (Fig. 3C).
Fig. 3.
Cellular localization of VGAT in hippocampus CA1 and area dentata by immunoperoxidase staining. A, CA1. Nerve terminals containing VGAT are distributed throughout the layers but are concentrated around the perikarya of pyramidal cells (small arrowheads) and interneurons (large arrowheads). The cytoplasm of interneuron perikarya shows immunoreactivity but less intense than that of the nerve endings. (The diffuse staining in the pyramidal layer is attributable to the presence of many stained nerve endings below the focal plane.) N2 antibody with Triton. B, Section adjacent to that in A, processed, photographed, and printed in the same conditions but after absorption of the N2 antibody with N-terminal fusion protein.C, Area dentata. VGAT-containing nerve terminals are distributed similarly as in CA1 on the granule cell bodies and in the neuropil. N2 antibody without Triton. O, P, R, Strata oriens, pyramidale, and radiatum of hippocampus, respectively;M, G, H, strata moleculare, granulare, and hilus (CA4) of area dentata, respectively. Asterisks, Blood vessels (emptied by perfusion). DIC optics (in this and subsequent light micrographs). Scale bar: A, B 50 μm; C, 20 μm.
Fig. 4.
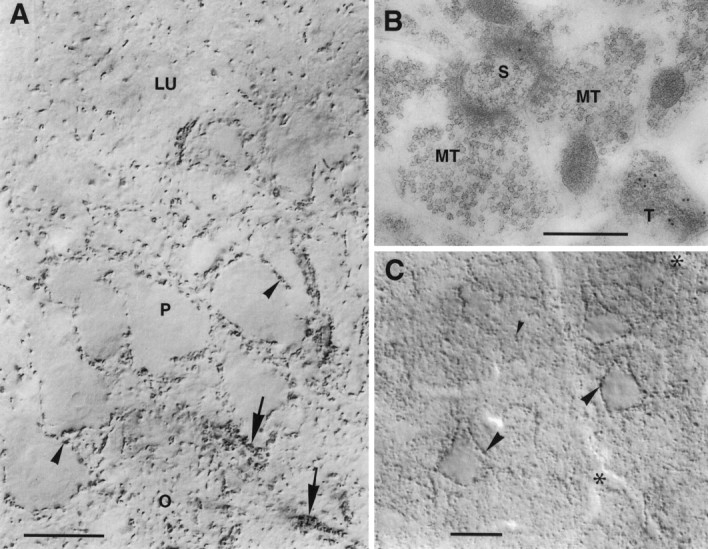
VGAT in hippocampus CA3 and neocortex.A, CA3. Nerve endings immunoperoxidase-stained for VGAT are seen to outline unstained pyramidal cell bodies (arrowheads) and the initial parts of their axons (arrows) or are spread in the neuropil. Mossy fiber terminals in the stratum lucidum (LU) are not visualized. P, O, Strata pyramidale and oriens, respectively. B, CA3, stratum lucidum. Post-embedding immunogold labeling shows VGAT in a terminal with pleomorphic vesicles (T) but not in the large mossy fiber terminals (MT) making asymmetric synapses on a spine (S). C, Limb area of parietal cortex, layer 5. Strongly immunoreactive (peroxidase with Triton) nerve terminals are concentrated along pyramidal cell perikarya (large arrowheads) and are spread in the neuropil (small arrowheads). On the apical parts of the three large pyramidal cells shown, VGAT-containing boutons on the back or front of the cells can be seen en face (in part slightly out of focus).Asterisks, Blood vessels. Scale bars: A, 20 μm; B, 0.5 μm; C, 25 μm.
In the cerebral neocortex (Fig. 4C), VGAT-immunoreactive dots were distributed similarly as in hippocampal archicortex, consistent with the distribution of nerve terminals that contain GAD and GABA, and accumulate GABA by high-affinity uptake and retrograde axonal transport (Hökfelt and Ljungdahl, 1972; Freund et al., 1983; Somogyi et al., 1981, 1983a, 1984, 1998).
In the basal ganglia (Fig. 5) VGAT-immunoreactive terminals were quite numerous in the caudatoputamen but by far more concentrated in the target nuclei of the main GABAergic projections globus pallidus (Fig. 5D) and substantia nigra (Fig. 5A–C). In the latter nuclei small immunopositive terminals could be seen to densely outline the dendrites of unstained target neurons. This is the typical pattern of GABAergic nerve terminals first revealed by GAD immunocytochemistry (Ribak et al., 1976).
Fig. 5.
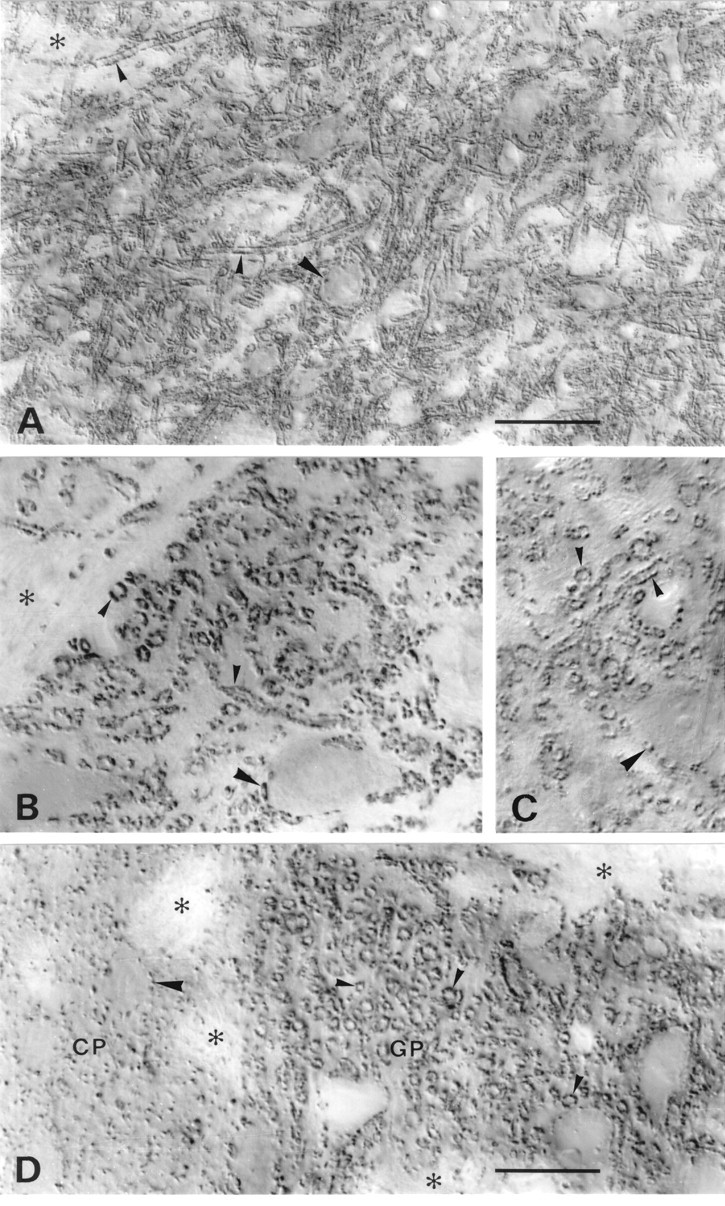
VGAT in basal ganglia and substantia nigra. A–C, Substantia nigra pars reticulata.D, Border between caudatoputamen (CP) and globus pallidus (GP). A,D, N2 antibody with Triton. B, N2 antibody without Triton. C, C1 antibody with Triton. VGAT-containing small nerve endings coat dendrites (small arrowheads) very densely and perikarya (large arrowheads) less completely. The staining pattern in substantia nigra and globus pallidus is typical of the GABAergic afferents from caudatoputamen. Antibodies to the N terminus (A, B, D) and C terminus (C) of VGAT show the same localization with (A, C, D) and without (B) Triton. Asterisks, Bundles of unstained nerve fibers. Scale bars: A, 50 μm;B–D, 20 μm. .
Motoneurons in motor nuclei of the brainstem and spinal cord were likewise decorated with VGAT-immunoreactive nerve terminals (Fig.6). The distribution would be consistent with the combined distributions of GABA-containing and glycine-containing nerve endings on the surfaces of motoneurons (Yoshida and Tanaka, 1989; Shupliakov et al., 1993; Wentzel et al., 1993; Taal and Holstege, 1994; Örnung et al., 1994, 1996, 1998;Lahjouji et al., 1996; Yang et al., 1997). Most of the terminals synapsing on the somata of spinal motoneurons are reported to be immunoreactive for glycine rather than GABA, a substantial additional proportion being immunoreactive for both glycine and GABA, whereas only very few terminals contain GABA but no glycine. Furthermore, most of the terminals contain the neuronal glycine transporter GLYT2 (Zafra et al., 1995). The results illustrated in Figure 6 therefore strongly suggest that VGAT is present in glycinergic as well as mixed GABAergic–glycinergic terminals on motoneurons.
Fig. 6.
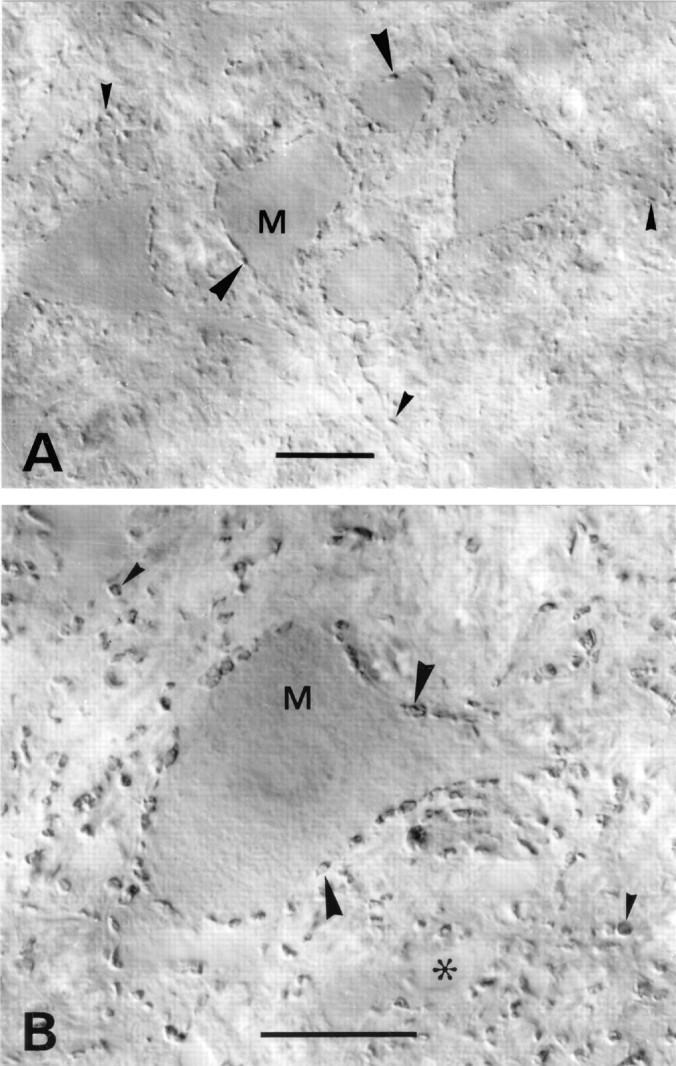
VGAT in motor nuclei. A, Medulla spinalis, ventral horn in an upper cervical segment. B, Nucleus facialis. Immunoreactive nerve terminals outline motoneuron perikarya (M, arrowheads). A high proportion of the terminals contacting these perikarya are known to contain glycine, alone or in addition to GABA. VGAT-containing terminals in the neuropil (small arrowheads) are sometimes seen to contact dendrites. Asterisk, Empty blood vessel. Scale bars: A, 25 μm; B, 20 μm.
In the cerebellar cortex (Fig. 7) there are three main types of GABAergic interneurons (stellate and basket cells of the molecular layer and Golgi cells of the granular layer) and one type of GABAergic projection neuron (Purkinje cells, the output neurons of the cerebellar cortex). Of these, Golgi cells are mixed GABAergic–glycinergic, synapsing on granule cell dendritic digits at the periphery of cerebellar glomeruli. The other types are enriched with GABA but not glycine in their terminals (Ottersen et al., 1988). We found VGAT to be enriched in the terminals of all four categories of neurons (Fig. 7). Stained stellate cell terminals outlined unstained Purkinje cell dendrites in the molecular layer (Fig. 7A). Stained basket cell terminals outlined the Purkinje cell bodies forming the dense plexus of preterminal axons (“pinceau”) surrounding the Purkinje cell axon hillock. Stained Golgi cell terminals formed the characteristic rosettes outlining cerebellar glomeruli in the granular layer. The plasma membrane GABA transporter GAT-1 was demonstrated for comparison (Fig. 7B). This protein is localized in terminals and axons of cerebellar GABAergic neurons (Radian et al., 1990; Itouji et al., 1996; Morara et al., 1996), except in those of Purkinje cells, which lack a GABA transporter in their plasma membrane (Storm-Mathisen, 1975; Ribak et al., 1996a). (They are mainly located in the subcortical nuclei.) The cortical distribution of GAT-1 was similar to that of VGAT (and GABA and GAD), but axons en route to the terminals were stained in addition to the terminals themselves. GABAergic as well as mixed GABAergic–glycinergic neurons had some VGAT immunoreactivity in their perikarya (Fig. 7A).
Fig. 7.
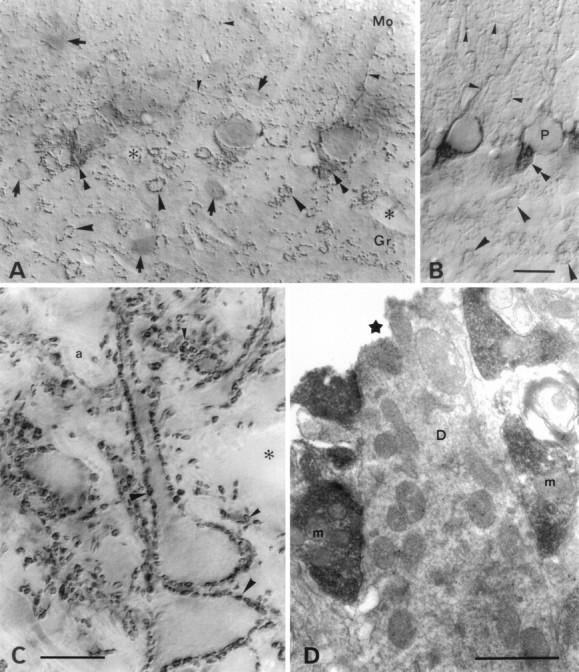
VGAT and GAT-1 in cerebellum. A, VGAT; B, GAT-1 in the cortex cerebelli. VGAT is concentrated in nerve terminals, whereas GAT-1, a plasma membrane protein, is found in terminals and axons. Both proteins are localized in the mixed GABAergic–glycinergic terminals (deriving from Golgi cells) arranged in rosettes outlining glomeruli in the granular layer (large arrowheads), as well as in the predominantly GABAergic axons and terminals of the molecular layer (small arrowheads) (deriving from stellate cells and stellate basket cells). The axons and terminals from stellate cells can be seen forming a plexus in the molecular layer. Around the initial axon segments of Purkinje cells the axons and terminals of basket cells form a dense plexus called a pinceau (double arrowheads). There is some staining for VGAT in the cytoplasm of the perikarya of stellate, basket, and Golgi cells (arrows), and Purkinje cells (P). Mo, Gr, molecular and granular layers, respectively. Asterisks, Empty blood vessels. Parasagittal sections of hemisphere, lobus anterior. C, D, VGAT in nucleus interpositus (a central cerebellar nucleus). Light microscopic (C) and electron microscopic (D) immunoperoxidase staining shows VGAT-containing nerve terminals in the neuropil (small arrowheads) densely outlining perikarya and stem dendrites of the large immunonegative neurons (large arrowheads). Boutons in this position are mainly terminals of Purkinje cell axons. The nuclei are pierced by immunonegative, refringent bundles of myelinated axons (a). Terminals are often lightly stained in their centers; electron microscopy shows this to be attributable to centrally placed mitochondria (m). A postsynaptic dendrite (D) is immunonegative despite being opened to penetration of reagents at the Vibratome cut (star).Asterisks, Blood vessels. Scale bars: A, B, 25 μm; C, 20 μm; D, 1 μm.
Purkinje cell terminals, the first GABAergic terminals to be identified in vertebrate brain (Fonnum et al., 1970), are rich in GAD (Oertel et al., 1981). They are easily identified in the lateral vestibular nuclei and in the cerebellar nuclei (Fig. 7C,D), where they form synapses densely distributed along the surface of neuronal perikarya and dendrites. These rather large terminals were shown to be immunoreactive for VGAT. A lighter center visible light microscopically in many of the boutons (Fig. 7C) could be seen electron microscopically to be attributable to clusters of mitochondria displacing synaptic vesicles from the terminal center (Fig.7D).
In the dorsal nucleus cochlearis (Fig.8A) VGAT-immunoreactive nerve terminals were densely distributed in the neuropil of the superficial layers (layers 1 and 2), partly outlining perikarya and dendrites (Fig. 8B). As in the motor nuclei, the distribution is compatible with the combined distributions of GABA-positive and glycine-positive nerve endings (Wenthold et al., 1987; Osen et al., 1990; Kolston et al., 1992; Ottersen et al., 1995;Juiz et al., 1996).
Fig. 8.
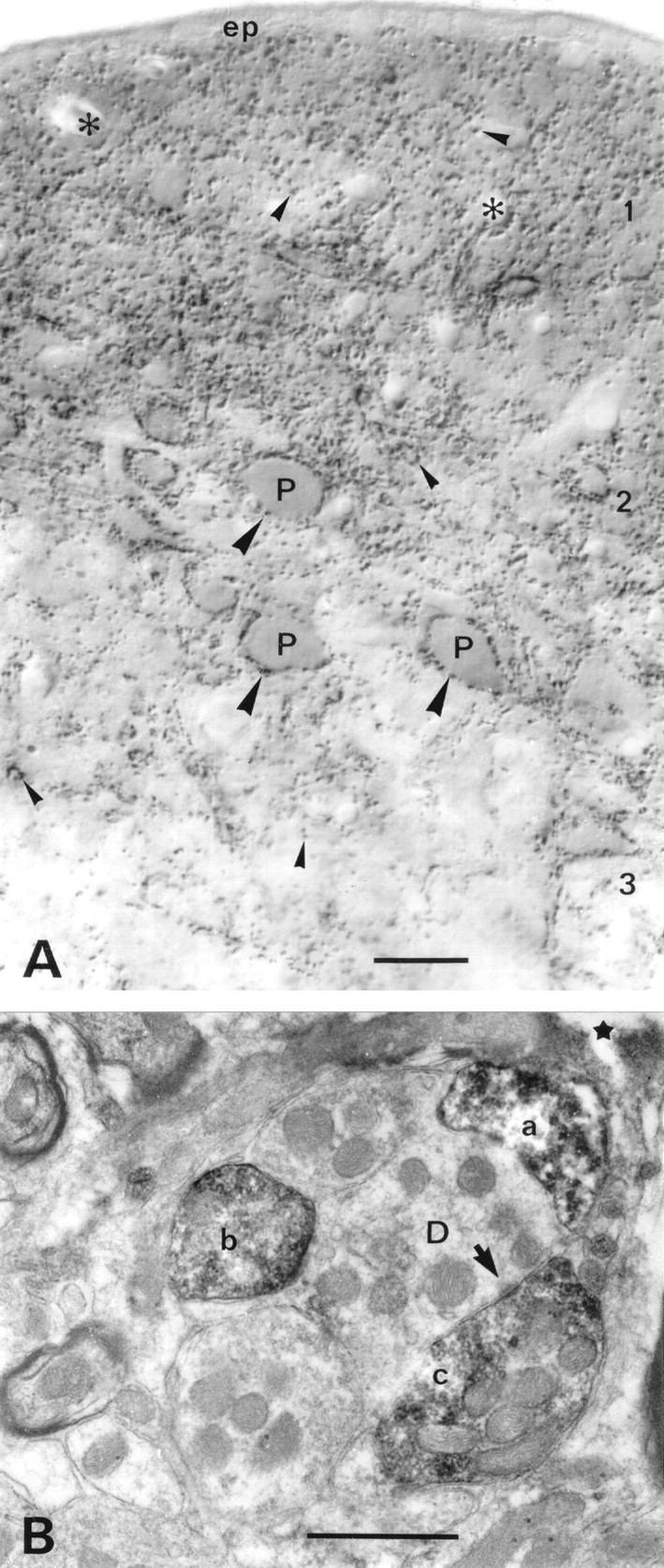
VGAT in nucleus cochlearis dorsalis.A, Light microscopic immunoperoxidase staining shows VGAT-containing nerve terminals in the neuropil (small arrowheads), where some of them can be seen to outline dendrites. Perikarya of pyramidal cells (P, fusiform cells) in layer 2 are densely surrounded with VGAT-immunoreactive terminals (large arrowheads). The highest concentration of VGAT-positive nerve endings is found in the two superficial layers. (The diffuse darkening between the immunoreactive terminals here is attributable to numerous similar terminals below the focus plane.) The distribution of immunoreactivity is compatible with the combined distributions of GABA-containing and glycine-containing nerve endings (see Results).B, Electron microscopy confirms that the immunoreactive structures are nerve endings (a–c), one of which can be seen to form a symmetric synaptic contact (arrow).D, Dendrite; 1–3, layers of the nucleus;ep, ependyma. Asterisks, Blood vessels;star, surface of Vibratome section. Parasagittal sectioning plane. Scale bars: A, 25 μm;B, 0.5 μm.
In the lateral oliva superior (LSO) (Fig.9), perikarya and dendrites were densely studded with VGAT-immunoreactive nerve terminals. Originating from glycinergic cells in the medial nucleus of the corpus trapezoideum, most of these terminals are known to be immunopositive for glycine rather than for GABA (Wenthold et al., 1987; Helfert et al., 1989,1992; Glendenning et al., 1991; Ottersen et al., 1995) and show immunoreactivity for the neuronal glycine transporter GLYT2 in their plasma membrane (Zafra et al., 1995). Again, this strongly indicates that VGAT is present in glycinergic, non-GABAergic nerve endings.
Fig. 9.
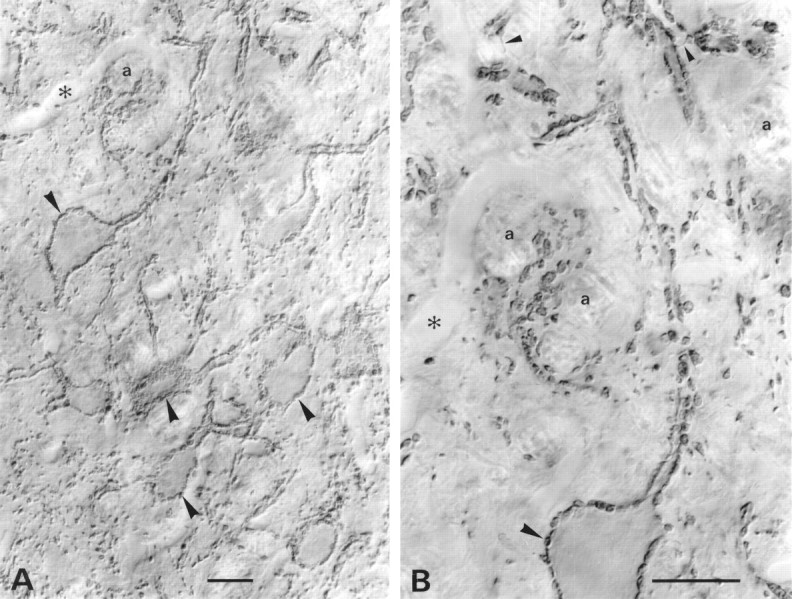
VGAT in mainly glycinergic nerve endings in the LSO. Light microscopic immunoperoxidase staining at intermediate (A) and high (B) magnification is shown. Stained nerve endings (large arrowheads), partly of large size, densely outline perikarya and stem dendrites of unstained LSO neurons. These boutons are known to be mainly glycinergic. Some of the stained boutons are shown en face on the surface of perikarya graced by the section. Others can be seen to be continuous with stained axons (small arrowheads). The nucleus is pierced by tiny bundles of unstained myelinated axons (a). Asterisks, Empty blood vessel. Parasagittal sectioning plane. Scale bars, 20 μm.
Immunogold localization
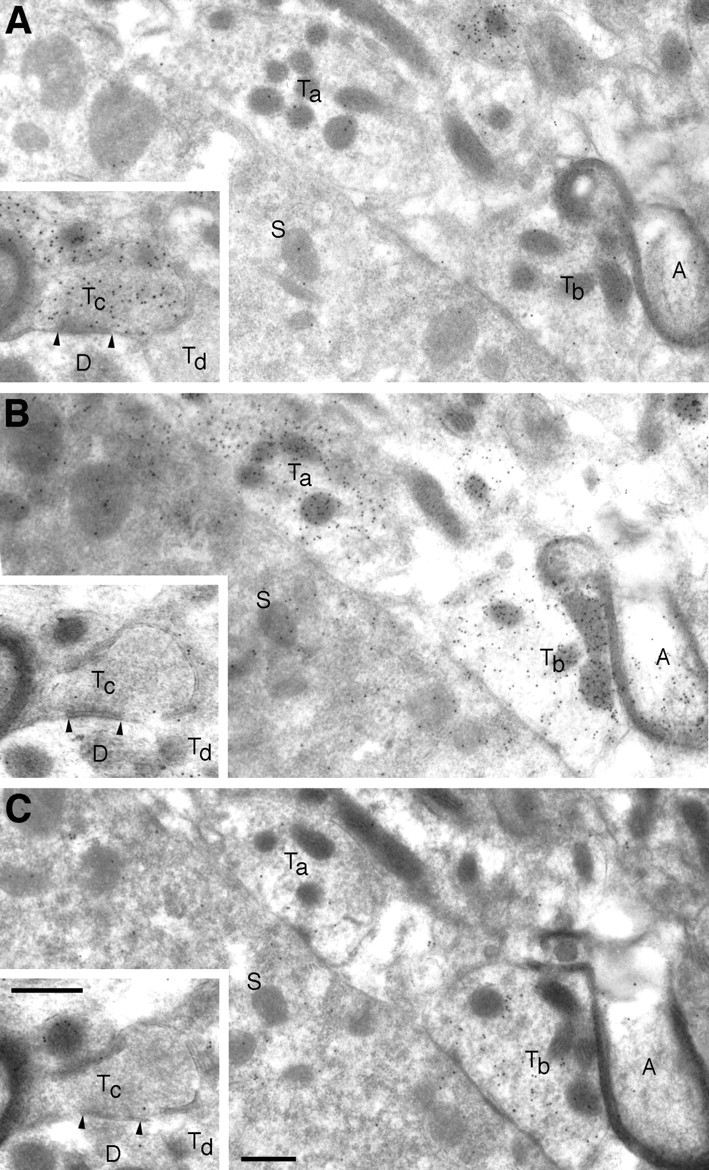
The post-embedding immunogold approach was applied for better resolution and quantification, using ultrathin sections of tissue prepared to optimize preservation of immunoreactivity and ultrastructure (Chaudhry et al., 1995; Dehnes et al., 1998). In various brain regions this method produced results (Fig.10) in agreement with those obtained by immunoperoxidase. Types of terminals immunoreactive with the latter method were also immunogold-labeled in regions including the cerebellar cortex and nuclei (Fig. 10A–D,F), hippocampus (Figs. 4B, 10E), caudatoputamen (Fig.10G), and cochlear nuclei (Fig.10H). Putative glutamatergic terminals, forming asymmetric synapses on dendritic spines, were not immunoreactive (Fig. 10C,E,G, M, T′). The C1 antibody labeled the same terminals (Fig. 10B) or the same type of terminals (Fig. 10D) as the N2 antibody in adjacent sections, although with a weaker signal and a higher background noise.
Fig. 10.
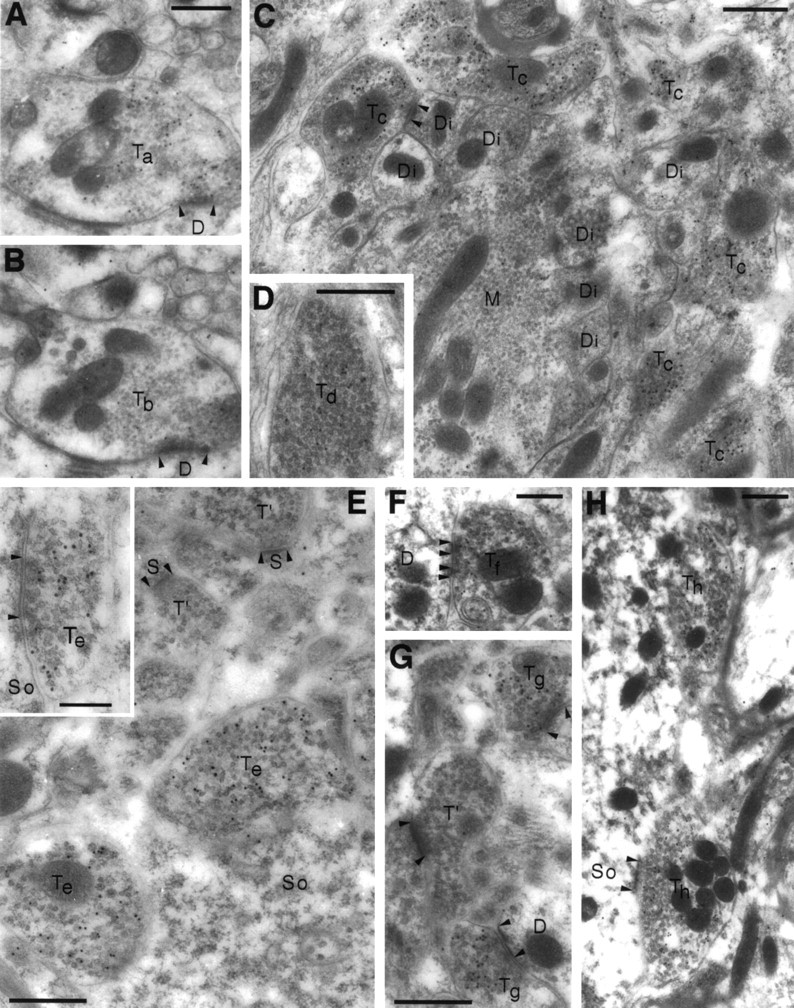
Electron microscopic post-embedding immunogold localization of VGAT illustrated in different brain regions.A–D, Cortex cerebelli. E, Hippocampus CA1. F, Nucleus interpositus (a central cerebellar nucleus). G, Caudatoputamen. H, Nucleus cochlearis dorsalis. A, C, E–H, Antiserum N2. B, D, Antiserum C1. The antiserum N2 to the N terminus of VGAT labels both basket cell boutons (Ta) contacting Purkinje cell dendrites (D) in the molecular layer and Golgi cell boutons (Tc) in the granule cell layer of cerebellum. Only few particles can be detected in mossy fiber terminals (M), granule cell dendritic digits (Di), or other structures in the neuropil. In parallel sections, the antiserum C1 to the C terminus labels the same boutons (Tb, basket) or the same type of boutons (Td, Golgi) as does the antiserum to the N terminus. Boutons with pleomorphic vesicles (Te) making symmetric contacts (E, inset) on the somata (So) of hippocampal pyramidal cells are heavily labeled for VGAT. In the cerebellar nuclei and striatum, VGAT labeling is likewise in terminals (Tf, Tg), making symmetric synapses. Terminals (T′ in E,G) making asymmetric synapses on spines (S) and other structures in the neuropil are not labeled. In the cochlear nuclei, putative glycinergic terminals (Th) are also labeled for VGAT. D, So, Dendrites (or dendritic digits) and somata contacted by VGAT-containing boutons; arrowheads, synaptic membrane specializations. Scale bars: 0.5 μm; inset, 0.25 μm.
The selectivity of the VGAT labeling is illustrated by the following immunogold particle densities (particles/μm2, excluding mitochondria; tissue fixative C) observed with the N2 antibody in the cerebellar granule cell layer [mean ± SEM (n)]: VGAT-immunoreactive Golgi terminals (i.e., mixed GABA-glycine; Ottersen et al., 1988), 66.9 ± 12.8 (83); mossy fiber terminals (i.e., glutamatergic; Ji et al., 1991), 1.7 ± 0.20 (40); and granule cell dendritic digits (i.e., postsynaptic), 1.1 ± 0.25 (87). The difference between the former and the two latter densities, indicating a low tissue background level, was statistically highly significant (p < 0.00003, ANOVA, Newman–Keuls test). Background particle density over empty resin was negligible and was not subtracted. A few terminals with appearance and size like Golgi terminals had low particle densities, similar to those over mossy fiber boutons.
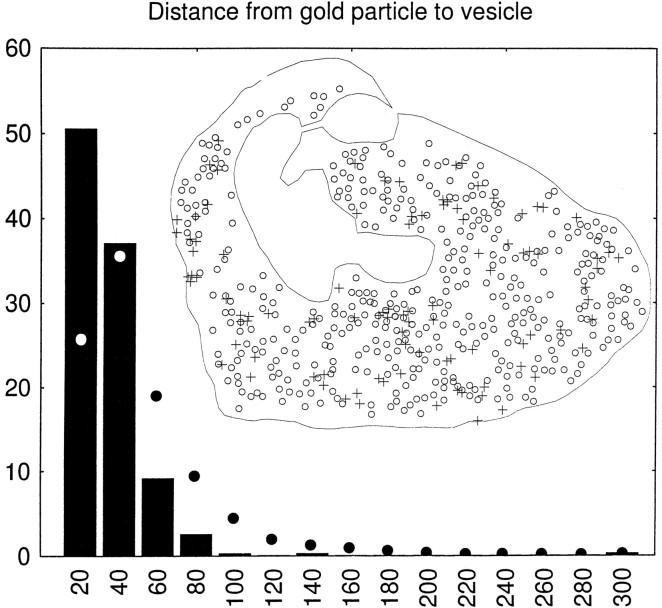
The association of VGAT with synaptic vesicles was studied in the cerebellar basket cell terminals. In these, synaptic vesicles are displaced from parts of the terminals by groups of mitochondria and bundles of filaments, and as indicated by immunoperoxidase results (Figs. 7, 8, 11A), VGAT labeling was restricted to the regions of the terminals containing synaptic vesicles (Fig.11B–D). There was no labeling of the plasma membrane (Figs. 10, 11). Within the vesicle-containing regions, the gold particles appeared more closely associated with the synaptic vesicles than with the intervening cytoplasmic matrix (Fig. 11D). This was further analyzed in two ways (see Materials and Methods): (1) the correlation of the presence of immunogold particles and synaptic vesicles within squares placed in a lattice over the terminals, excluding mitochondria, was statistically highly significant (p < 0.0001); and (2) the intercenter distance between immunogold particles and synaptic vesicles was highly significantly different from that between vesicles and points randomly distributed over the terminals, excluding mitochondria and filament bundles (Fig.12). Thus 50% of the particle centers occurred within 20 nm from the center of the nearest synaptic vesicle, compared with 25% for random points. Beyond 40 nm, random points were relatively much more frequent than gold particles.
Fig. 11.
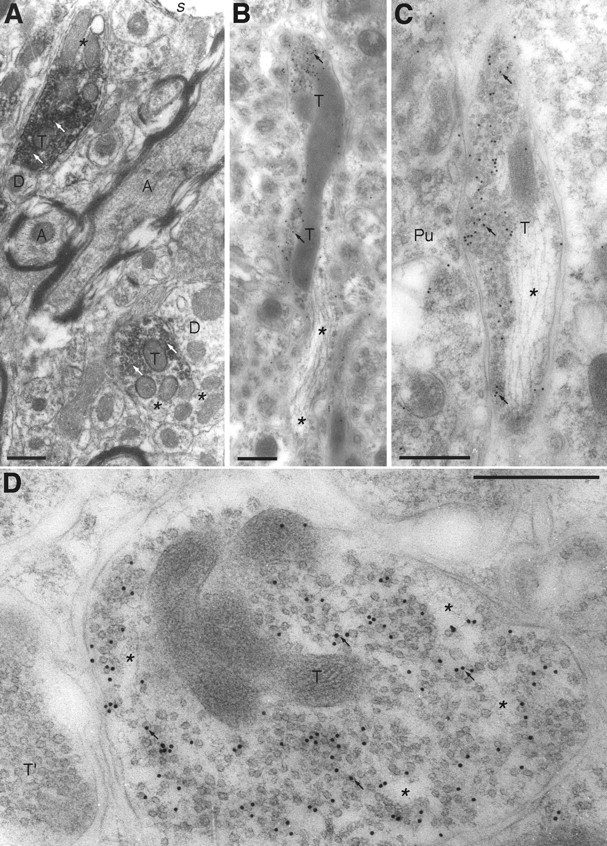
VGAT is associated with synaptic vesicles.A, Pre-embedding electron microscopic peroxidase immunocytochemistry suggests VGAT to be confined to the vesicle-rich areas (arrows) of the labeled terminals (T) and absent from the areas devoid of vesicles (stars), even when the latter are closer to the surface (s) of the Vibratome section (cerebellar nucleus with VGAT-containing terminals). B, C, The vesicular localization is confirmed by post-embedding immunogold labeling. The gold particles are restricted to vesicle-containing areas (arrows), whereas particles are rare in the rest of the terminal, containing neurofilaments (stars), mitochondria, or intervesicular cytoplasmic matrix. Note that at higher power (D), the plasma membrane appears clear of labeling, and that most of the particles are associated with the vesicles (basket cell terminals in cerebellar cortex).T, VGAT-labeled terminals; T′, VGAT-negative terminal; D, dendrites; A, myelinated axons; Pu, Purkinje cell body. Scale bars:A–C, 0.5 μm; D, 0.25 μm.
Fig. 12.
Quantification of the association of VGAT with synaptic vesicles (GABAergic basket cell terminals in the cerebellar cortex). Inset, Illustration of the recording of data, exemplified by the terminal shown as an electron micrograph in Figure11D; the center of each gold particle (+) and of each identifiable synaptic vesicle (○) is digitized, as well as the outline of the terminal, excluding mitochondria and (in other terminals) areas occupied by filaments (compare Fig.11B,C). Columns, Intercenter distances between each gold particle (394 particles in 12 terminals) and the nearest synaptic vesicle sorted into bins of 20 nm, they-axis showing percent of total in each bin (columns). Filled circles, Distances to the vesicle centers from points (1000 per terminal) randomly distributed over the parts of the terminals accessible to synaptic vesicles (see inset). The two distributions were statistically significantly different (p = 0.0005, continuity corrected χ2 test).
Nerve endings immunopositive for VGAT represent populations of predominantly GABAergic terminals (Fig. 10A,B,E–G), as well as mixed GABAergic–glycinergic (Fig. 10C,D) and predominantly glycinergic terminals (Fig. 10H). The localization of VGAT in glycinergic as well as in GABAergic nerve endings was proven by triple-labeling experiments in LSO. Three consecutive ultrathin sections were immunogold-labeled for GABA, glycine, and VGAT, respectively (Figs.13A–C,14A–C). Nerve endings rich in GABA and VGAT had varying levels of glycine (Fig. 13, Tc,Tf). On the other hand, terminals containing high levels of glycine (Fig. 13, Tb,Td) but little (Tb) or no (Td) GABA were immunopositive for VGAT. The same phenomenon is illustrated in Figure 14(terminal Tb). Some of the postsynaptic perikarya in LSO are glycine immunoreactive (cf. Ottersen et al., 1995) and showed a slight VGAT signal (Fig. 14).
Fig. 13.
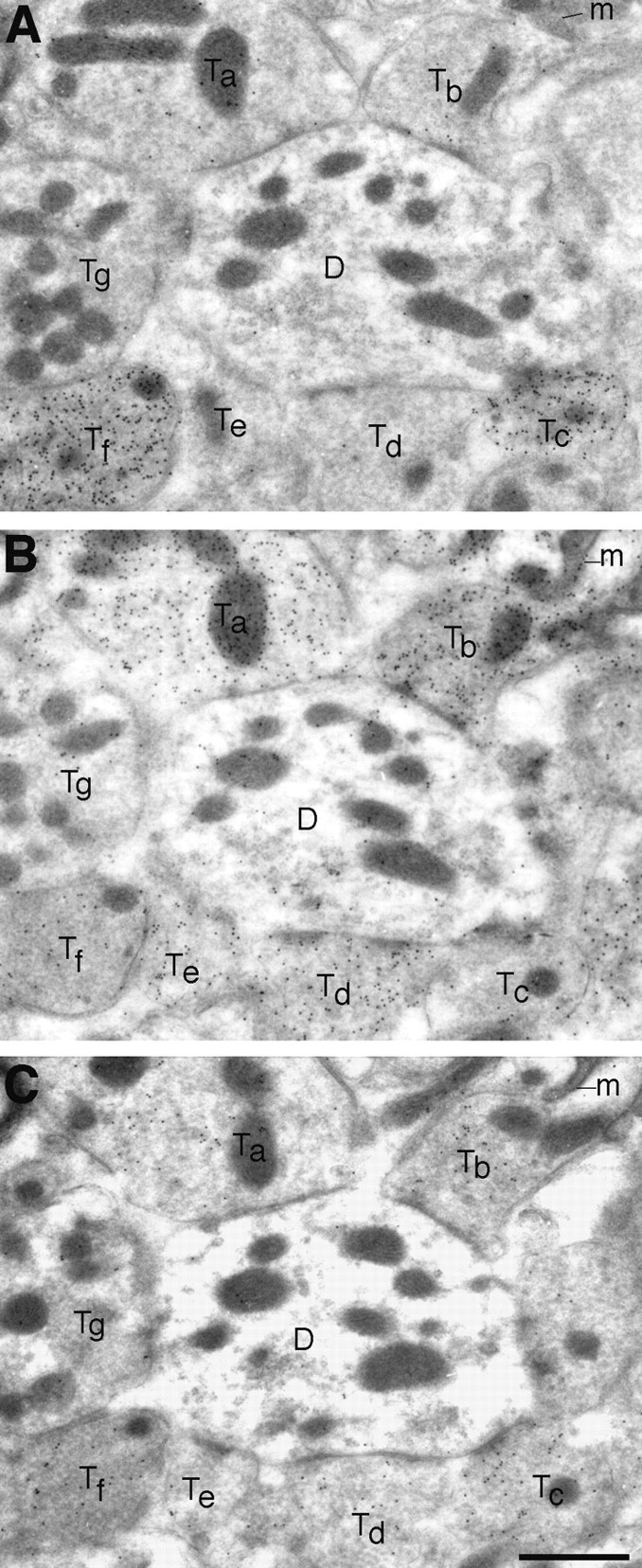
Triple labeling for GABA (A), glycine (B), and VGAT (C) in adjacent ultrathin sections of LSO. VGAT is localized in terminals selectively immunoreactive for GABA (Tc), as well as in ones showing mixed immunoreactivity for GABA and glycine (Tf) or selective immunoreactivity for glycine (Ta,Tb, Td). One small putative glycinergic terminal (Te) has only a low (perhaps insignificant) level of VGAT. A putative glutamatergic terminal (Tg) illustrates the low “background” levels of particle densities. The postsynaptic dendrite (D) has a slight glycine signal.m, Mitochondria. Scale bar, 1 μm.
Fig. 14.
Zero or low levels of VGAT in subpopulations of nerve terminals that are enriched with GABA or glycine. Adjacent ultrathin sections of LSO were incubated with antibodies to GABA (A), glycine (B), and VGAT (C). Two putatively “pure” glycinergic terminals (Taand Tb), synapsing on a neuronal soma (S), show differential VGAT labeling. AlthoughTb is enriched with VGAT,Ta is not. In A, contrast the lack of GABA immunoreactivity in vesicle-containing areas ofTa and Tb with the intense labeling of a nearby small terminal (at the top border). A myelinated axon (A) is immunoreactive for glycine. Insets, A GABA-labeled terminal (Tc), forming a symmetric synapse on a dendrite (D), is not labeled for glycine or for VGAT. Another terminal (Td) apposed to the same dendrite is unlabeled with all three antibodies. The postsynaptic neuronal soma (S) has a moderate glycine signal and a slight VGAT signal. Scale bars, 0.5 μm.
Quantitative analysis of VGAT-immunoreactive boutons in LSO showed the following immunogold particle densities [particles/μm2 of bouton area excluding mitochondria, mean ± SEM (n), tissue fixative B]: GABA-immunoreactive terminals (with or without glycine), 23.8 ± 1.2 (29); terminals immunoreactive for glycine but not for GABA, 12.7 ± 0.7 (24); and adjacent dendrites (indicating the low tissue background level), 1.35 ± 0.17 (43). All three items were statistically significantly different from each other (p = 0.0001, ANOVA, Newman–Keuls test). For these experiments, three adjacent sections were immunogold-processed for GABA, glycine, and VGAT, respectively (as in Figs. 13, 14). The same terminals were identified in all of the three sections. (These particle densities cannot be directly compared with those presented above for cerebellum, because the tissue fixative and the exposure to antibodies differed.) The results suggest that GABAergic nerve endings are equipped with a higher concentration of VGAT than are glycinergic nerve terminals.
The analysis in LSO further revealed that some nerve endings immunopositive for GABA or glycine had low or negligible labeling for VGAT. This is illustrated in Figure 14 for glycine-labeled (Ta) and GABA-labeled (Tc) terminals. In the material investigated, 10 of 39 GABA-immunoreactive terminals (with or without glycine) and 2 of 26 purely glycine-immunoreactive terminals lacked clear VGAT labeling.
DISCUSSION
Validity of the immunocytochemical labeling
The recognition by the N-terminal antibody N2 of a single protein with the expected molecular mass in brain as well as in transfected cells demonstrates the specificity of this antibody. Absorption of the antibody with VGAT fusion protein eliminated the immunoreactivity, further supporting the specificity of N2. Thus, although the existence of a cross-reacting protein with the same electrophoretic migration as VGAT cannot be strictly excluded, the observed labeling of tissue structures by N2 does represent the presence of VGAT, as far as can be judged without the availability of knock-out animals. (The use of the terms “VGAT immunoreactivity” and “VGAT labeling” imply these reservations.) If a cross-reacting protein should exist, it could be another family member very similar to VGAT. Antibody C1 to the C-terminal part of VGAT detected a band of the same molecular mass as antibody N2 but also recognized a lower molecular mass band, possibly a proteolytic cleavage product. Consistent with this possibility, although the nature of the latter species remains to be determined, immunocytochemical labeling with the antibody C1 matches labeling with the N-terminal antibody at regional, cellular (immunoperoxidase), and subcellular (post-embedding immunogold) levels.
Proof that VGAT localizes to synaptic vesicles
Our electron microscopic observations establish that VGAT is indeed restricted to synaptic vesicles in inhibitory terminals, as was inferred from light microscopic observations (McIntire et al., 1997). First, immunoperoxidase labeling was strongest in the parts of labeled nerve endings that contain large numbers of synaptic vesicles, even when vesicle-poor regions were closer to the surface from which the antibody and other immunoreactants had to diffuse. Second, post-embedding immunogold localization (in which the antibodies have direct access to the antigenic sites exposed at the surface of the ultrathin section) showed immunoreactivity to be confined to the parts of the nerve endings that contain synaptic vesicles. Third, the immunogold labeling was shown to be associated with the vesicles rather than with the intervening cytoplasmic matrix.
The latter is not a trivial task: the maximum distance between an antigenic site and an immunogold particle is of the same order of magnitude as a synaptic vesicle diameter. Thus the centers of immunogold particles occur up to >45 nm away from a membrane carrying the antigenic epitope (Chaudhry et al., 1995). On the other hand, because of the fact that the section thickness is similar to the diameter of synaptic vesicles (20–50 nm; Peters et al., 1991), extravesicular cytoplasm may be projected over a vesicle profile. For the same reason, vesicular antigenic epitopes may be inaccessible to the antibodies, when a vesicle does not reach the surface of the section onto which the antibodies are applied, because antibodies cannot penetrate the plastic to reach antigenic epitopes situated deep in the section. Because of these factors, and because vesicles tend to be closely packed, it is impossible to know whether an individual immunogold particle represents a vesicular antigenic epitope. Statistical methods were therefore applied (Gundersen et al., 1998). These showed (1) that immunogold particles and synaptic vesicles were highly correlated spatially, and (2) that the intercenter distance from an immunogold particle to the nearest synaptic vesicle was more frequently short and less frequently long, compared with points randomly distributed over the vesicle-containing areas of the immunoreactive nerve endings.
Although the membranes of synaptic vesicles must get briefly incorporated into the plasma membrane during exocytosis, VGAT evidently does not attain a high enough concentration in the plasma membrane to be demonstrated by the present method: the plasma membrane of the labeled terminals seemed clear of immunogold particles.
Presence of VGAT in both GABAergic and glycinergic nerve endings
We demonstrate VGAT immunoreactivity in the terminals of the easily identifiable GABAergic neurons in the CNS. In addition, terminals of glycinergic neurons are labeled, whereas putative glutamatergic nerve terminals show no immunoreactivity. VGAT therefore appears selectively localized in nerve endings releasing, separately or together, the inhibitory amino acids GABA and glycine. This result is consistent with most biochemical data on uptake of GABA and glycine in synaptic vesicles (Christensen et al., 1990, 1991; Burger et al., 1991). The report by Kish et al. (1989) that GABA and glycine did not inhibit the uptake of each other in synaptic vesicle preparations may have resulted from the use of a prolonged incubation time (10 min) and/or low substrate concentrations, perturbing the assay conditions (Christensen et al., 1991). Furthermore, despite the fact that inhibitory nerve endings in the forebrain are not enriched with glycine, the vesicular uptake of glycine is similar in forebrain and spinal cord (Christensen et al., 1991).
While the present study was in progress, a cDNA almost identical to that encoding VGAT was cloned in mouse (Sagné et al., 1997). This transporter was termed “vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter” (VIAAT), because glycine inhibited [3H]GABA uptake, the cDNA also appeared to induce uptake of [3H]glycine (<10% increase over background), and in situ hybridization in rat brain indicated expression of VIAAT mRNA not only in GABAergic neurons but also in regions rich in glycinergic neurons. [3H]Glycine uptake by VGAT has since been demonstrated also by E. Giovanetti, R. J. Reimer, and R. H. Edwards (unpublished data). In light of the present results, the difficulties of both groups to demonstrate a robust signal of [3H]glycine uptake probably represents a technical problem. However, the possibility still exists that glycine uptakein situ is mediated by an additional protein.
Because GABA and glycine appear to share a vesicular uptake mechanism, they must accumulate in and undergo release from the same synaptic vesicles. The latter has recently been demonstrated in the spinal cord by recording miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (Jonas et al., 1998). Other factors, such as transmitter synthesis and plasma membrane uptake, may determine whether synaptic vesicles preferentially accumulate GABA or glycine (cf. Christensen et al., 1991). These factors will differ among terminals but should be uniform for the vesicles within a single terminal. At least in the LSO, there appears to be a switch from GABAergic to mainly glycinergic during development (Kotak et al., 1998).
In the absence of GAD, most nerve endings contain virtually no GABA, whereas glycine is present in varying amounts. If the vesicles have VGAT, they will therefore contain glycine but no GABA. In the presence of GAD, the GABA formed will compete with glycine, partly or fully replacing vesicular glycine. Many nerve endings are observed to have both glycine and GABA, both of which appear to associate with synaptic vesicles (Ottersen et al., 1988, 1990). However, experiments with cerebellar slices in vitro suggest that the depolarization-induced depletion of glycine from Golgi terminals is calcium-dependent to a lesser extent than that of GABA (Ottersen et al., 1990), raising the possibility of nonvesicular release. Further experiments will be needed to determine whether this is a general phenomenon, and whether it results from reduced incorporation of glycine relative to GABA into synaptic vesicles.
The observation that GABA-rich nerve terminals in LSO contain more VGAT than do glycine-rich terminals was surprising. In synaptic vesicles isolated from rat CNS, GABA appears to have a higher affinity than glycine for vesicular uptake, and at 1 mm, GABA accumulates twice as rapidly as glycine, regardless of whether the vesicles come from the brain or spinal cord (Christensen et al., 1991). VGAT or VIAAT expressed in vitro also appear to have a higher affinity for GABA than for glycine (McIntire et al., 1997; Sagné et al., 1997). GABAergic nerve endings may therefore need less VGAT than glycinergic terminals to fill their vesicles with transmitter. Other factors, possibly including prevailing firing patterns, may therefore explain the observed opposite difference.
Glycinergic nerve endings appear to be uniquely equipped with the plasma membrane glycine transporter GLYT2 (Zafra et al., 1995). This transporter may provide a supply of glycine for the incorporation into synaptic vesicles of glycinergic nerve terminals. GLYT2 apparently does not occur in the forebrain; neither do nerve terminals enriched with glycine or functional strychnine-sensitive glycine receptors (Ottersen and Storm-Mathisen, 1990), although glycine receptor mRNAs do (Malosio et al., 1991). However, because glycine is presumably present at low concentrations in all cells, it is likely that small amounts of glycine accumulate along with GABA in VGAT-containing synaptic vesicles of forebrain GABAergic neurons and could undergo corelease with GABA. If so, this could contribute to the (low) extracellular levels of glycine that are required for activating glutamate receptors of the NMDA type (Johnson and Ascher, 1987).
Despite what has been discussed above, it should be borne in mind that the existence of other, yet unidentified, selective transporters has not been excluded. An indication that such proteins may exist is provided by our finding of nerve endings apparently devoid of VGAT but containing GABA or glycine.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the Norwegian Research Council, Fylkesakers Stiftelse, Langfeldts Fond, and Nansenfondet (F.A.C. and J.S.-M.) and by the National Institute of Mental Health and National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke (R.H.E. and R.J.R.). We are grateful to Edward Fon, Even Andersen, Carina Knutsen, Gunnar F. Lothe, and Håvard Tønnesen for technical assistance and to Jan G. Bjaalie for making available the methods for analyzing particle–vesicle distances.
Correspondence should be addressed to Jon Storm-Mathisen, Anatomical Institute, University of Oslo, P.O. Box 1105 Blindern, N-0317 Oslo, Norway. E-mail: jonsm@pons.uio.no
REFERENCES
- 1.Barber R, Saito K. Light microscopic visualization of GAD and GABA-T in immunocytochemical preparations of rodent CNS. In: Roberts E, Chase TN, Tower DB, editors. GABA in nervous system function. Raven; New York: 1976. pp. 113–132. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berod A, Hartman BK, Pujol JF. Importance of fixation in immunohistochemistry: use of formaldehyde solutions at variable pH for the localization of tyrosine hydroxylase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981;29:844–850. doi: 10.1177/29.7.6167611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Blackstad TW, Karagülle T, Ottersen OP. MORFOREL, a computer program for two dimensional analysis of micrographs of biological specimens, with emphasis on immunogold preparations. Comput Biol Med. 1990;20:15–34. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(90)90041-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burger PM, Hell J, Mehl E, Krasel C, Lottspeich F, Jahn R. GABA and glycine in synaptic vesicles: storage and transport characteristics. Neuron. 1991;7:287–293. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ceranik K, Bender R, Geiger JP, Monyer H, Jonas P, Frotscher M, Lubke J. A novel type of GABAergic interneuron connecting the input and the output regions of the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1997;17:5380–5394. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-14-05380.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chaudhry FA, Lehre KP, Van Lookeren Campagne M, Ottersen OP, Danbolt NC, Storm-Mathisen J. Glutamate transporters in glial plasma membranes: highly differentiated localizations revealed by quantitative ultrastructural immunocytochemistry. Neuron. 1995;14:711–720. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Christensen H, Fykse EM, Fonnum F. Uptake of glycin into synaptic vesicles isolated from rat spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1990;54:1142–1147. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Christensen H, Fykse EM, Fonnum F. Inhibition of gamma-aminobutyrate and glycine uptake into synaptic vesicles. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991;207:73–79. doi: 10.1016/s0922-4106(05)80040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dehnes Y, Chaudhry FA, Ullensvang K, Lehre KP, Storm-Mathisen J, Danbolt NC. The glutamate transporter EAAT4 in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells: a glutamate-gated chloride channel concentrated near the synapse in parts of the dendritic membrane facing astroglia. J Neurosci. 1998;18:3606–3619. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-10-03606.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Erickson JD, Eiden LE, Hoffman BJ. Expression cloning of a reserpine-sensitive vesicular monoamine transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:10993–10997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Erickson JD, Varoqui H, Schafer MK, Modi W, Diebler MF, Weihe E, Rand J, Eiden LE, Bonner TI, Usdin TB. Functional identification of a vesicular acetylcholine transporter and its expression from a “cholinergic” gene locus. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:21929–21932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fonnum F, Storm-Mathisen J, Walberg F. Glutamate decarboxylase in inhibitory neurons. A study of the enzyme in Purkinje cell axons and boutons in the cat. Brain Res. 1970;20:259–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Freund TF, Martin KA, Smith AD, Somogyi P. Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi-impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat’s visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1983;221:263–278. doi: 10.1002/cne.902210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Frotscher M, Soriano E, Leranth C. Cholinergic and GABAergic neurotransmission in the fascia dentata: electron microscopic immunocytochemical studies in rodents and primates. Epilepsy Res [Suppl] 1992;7:65–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fykse EM, Fonnum F. Uptake of γ-aminobutyric acid by a synaptic vesicle fraction isolated from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1988;50:1237–1242. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fykse EM, Fonnum F. Amino acid neurotransmission: dynamics of vesicular uptake. Neurochem Res. 1996;21:1053–1060. doi: 10.1007/BF02532415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Glendenning KK, Masterton RB, Baker BN, Wenthold RJ. Acoustic chiasm. III: Nature, distribution, and sources of afferents to the lateral superior olive in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1991;310:377–400. doi: 10.1002/cne.903100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guastella J, Nelson N, Nelson H, Czykzyk L, Keynan S, Miedel MC, Davidson N, Lester HA, Kanner BI. Cloning and expression of a rat brain GABA transporter. Science. 1990;249:1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.1975955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gundersen V, Chaudhry FA, Bjaalie JG, Fonnum F, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J. Synaptic vesicular localization and exocytosis of l-aspartate in excitatory nerve terminals: a quantitative immunogold analysis in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1998;18:6059–6070. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-16-06059.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hálasy K, Somogyi P. Distribution of GABAergic synapses and their targets in the dentate gyrus of rat: a quantitative immunoelectron microscopic analysis. J Hirnforsch. 1993;34:299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hálasy K, Buhl EH, Lorinczi Z, Tamas G, Somogyi P. Synaptic target selectivity and input of GABAergic basket and bistratified interneurons in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus. Hippocampus. 1996;6:306–329. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:3<306::AID-HIPO8>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Helfert RH, Bonneau JM, Wenthold RJ, Altschuler RA. GABA and glycine immunoreactivity in the guinea pig superior olivary complex. Brain Res. 1989;501:269–286. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90644-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Helfert RH, Juiz JM, Bledsoe SC, Jr, Bonneau JM, Wenthold RJ, Altschuler RA. Patterns of glutamate, glycine and GABA immunolabeling in four synaptic terminal classes in the lateral superior olive of the guinea pig. J Comp Neurol. 1992;323:305–325. doi: 10.1002/cne.903230302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl Å. Uptake of [3H]noradrenaline and γ-[3H]aminobutyric acid in isolated tissues of the rat: an autoradiographic and fluorescence microscopic study. Prog Brain Res. 1971;34:87–102. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl Å. Autoradiographic identification of cerebral and cerebellar cortical neurons accumulating labeled gamma-aminobutyric acid (3H-GABA). Exp Brain Res. 1972;14:354–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00235032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Itouji A, Sakai N, Tanaka C, Saito N. Neuronal and glial localization of two GABA transporters (GAT1 and GAT3) in the rat cerebellum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996;37:309–316. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00342-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ji Z, Aas J-E, Laake J, Walberg F, Ottersen OP. An electron microscopic, immunogold analysis of glutamate and glutamine in terminals of rat spinocerebellar fibers. J Comp Neurol. 1991;307:296–310. doi: 10.1002/cne.903070210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Johnson JW, Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987;325:529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jonas P, Bischofberger J, Sandkuhler J. Corelease of two fast neurotransmitters at a central synapse [see comments]. Science. 1998;281:419–424. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5375.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Juiz JM, Helfert RH, Bonneau JM, Wenthold RJ, Altschuler RA. Three classes of inhibitory amino acid terminals in the cochlear nucleus of the guinea pig. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373:11–26. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960909)373:1<11::AID-CNE2>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kish PE, Fischer-Bovenkerk C, Ueda T. Active transport of gamma-aminobutyric acid and glycine into synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:3877–3881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kolston J, Osen KK, Hackney CM, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J. An atlas of glycine- and GABA-like immunoreactivity and colocalization in the cochlear nuclear complex of the guinea pig. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1992;186:443–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00185459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kotak VC, Korada S, Schwartz IR, Sanes DH. A developmental shift from GABAergic to glycinergic transmission in the central auditory system. J Neurosci. 1998;18:4646–4655. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-12-04646.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lahjouji F, Barbe A, Chazal G, Bras H. Evidence for colocalization of GABA and glycine in afferents to retrogradely labelled rat abducens motoneurones. Neurosci Lett. 1996;206:161–164. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(96)12465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Leergaard TB, Bjaalie JG. Semi-automatic data acquisition for quantitative neuroanatomy. MicroTrace—computer programme for recording of the spatial distribution of neuronal populations. Neurosci Res. 1995;22:231–243. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(95)00899-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lehre KP, Levy LM, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Danbolt NC. Differential expression of two glial glutamate transporters in the rat brain: quantitative and immunocytochemical observations. J Neurosci. 1995;15:1835–1853. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-03-01835.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu Y, Edwards RH. The role of vesicular transport proteins in synaptic transmission and neural degeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1997;20:125–156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.20.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liu Y, Peter D, Roghani A, Schuldiner S, Prive GG, Eisenberg D, Brecha N, Edwards RH. A cDNA that suppresses MPP+ toxicity encodes a vesicular amine transporter. Cell. 1992;70:539–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90425-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Malosio ML, Marqueze-Pouey B, Kuhse J, Betz H. Widespread expression of glycine receptor subunit mRNAs in the adult and developing rat brain. EMBO J. 1991;10:2401–2409. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Marcos P, Corio M, Dubourg P, Covenas R, Tramu G. Double immunocytochemistry in pre-embedding electron microscopy for the detection of neurotensin and tyrosine hydroxylase in the guinea pig, using two primary antisera raised in the same species. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 1997;2:1–8. doi: 10.1016/s1385-299x(97)00018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Maycox PR, Hell JW, Jahn R. Amino acid neurotransmission: spotlight on synaptic vesicles. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13:83–87. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90178-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.McIntire SL, Reimer RJ, Schuske K, Edwards RH, Jorgensen EM. Identification and chacterization of the vesicular GABA transporter. Nature. 1997;389:870–876. doi: 10.1038/39908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Morara S, Brecha NC, Marcotti W, Provini L, Rosina A. Neuronal and glial localization of the GABA transporter GAT-1 in the cerebellar cortex. NeuroReport. 1996;7:2993–2996. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199611250-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mugnaini E, Oertel WH. An atlas of the distributionof GABAergic neurons and terminals in the rat CNS as revealed by GAD immunohistochemistry. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T, editors. Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1985. pp. 436–608. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Oertel WH, Schmechel DE, Mugnaini E, Tappaz ML, Kopin IJ. Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate decarboxylase in rat cerebellum with a new antiserum. Neuroscience. 1981;6:2715–2735. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Örnung G, Shupliakov O, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Cullheim S. Immunohistochemical evidence for coexistence of glycine and GABA in nerve terminals on cat spinal motoneurons. NeuroReport. 1994;5:889–892. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199404000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Örnung G, Shupliakov O, Lindå H, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Ulfhake B, Cullheim S. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of glycine- and GABA-immunoreactive nerve terminals on motoneuron cell bodies in the cat spinal cord: a postembedding electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol. 1996;365:413–426. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960212)365:3<413::AID-CNE6>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Örnung G, Ottersen OP, Cullheim S, Ulfhake B. Distribution of glutamate-, glycine- and GABA-immunoreactive nerve terminals on dendrites in the cat spinal motor nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1998;118:517–532. doi: 10.1007/s002210050308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Osen KK, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J. Colocalization of glycine-like and GABA-like immunoreactivities. A semiquantitative study in individual neurons in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of cat. In: Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, editors. Glycine neurotransmission. Wiley; Chichester, UK: 1990. pp. 417–451. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ottersen OP. Quantitative electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of amino acids. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1989;180:1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00321895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J. Neurons containing or accumulating transmitter amino acids. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T, Kuhar MJ, editors. Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, Vol 3. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1984. pp. 141–246. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, editors. Glycine neurotransmission. Wiley; Chichester, UK: 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Somogyi P. Colocalization of glycine-like and GABA-like immunoreactivities in Golgi cell terminals in the rat cerebellum: a postembedding light and electron microscopic study. Brain Res. 1988;450:342–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91573-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ottersen OP, Strom-Mathisen J, Laake JH. Cellular and subcellular localization of glycine studied by quantitative electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. In: Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, editors. Glycine neurotransmission. Wiley; Chichester: 1990. pp. 303–328. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ottersen OP, Hjelle OP, Osen KK, Laake JH. Amino acid transmitters. In: Paxinos G, editor. The rat nervous system. Academic; San Diego: 1995. pp. 1017–1037. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Palay SL, Chan-Palay V. Cerebellar cortex: cytology and organization. Springer; Berlin: 1974. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic; San Diego: 1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Peters A, Palay SL, Webster HF. The fine structure of the nervous system: neurons and their supporting cells. Oxford UP; New York: 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Radian R, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Castel M, Kanner BI. Immunocytochemical localization of the GABA transporter in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1990;10:1319–1330. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01319.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ribak CE, Vaughn JE, Saito K, Barber R, Roberts E. Immunocytochemical localization of glutamate decarboxylase in rat substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1976;116:287–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90906-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ribak CE, Tong WM, Brecha NC. Astrocytic processes compensate for the apparent lack of GABA transporters in the axon terminals of cerebellar Purkinje cells. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1996a;194:379–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00198540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ribak CE, Tong WM, Brecha NC. GABA plasma membrane transporters, GAT-1 and GAT-3, display different distributions in the rat hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 1996b;367:595–606. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960415)367:4<595::AID-CNE9>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sagné C, El MS, Isambert MF, Hamon M, Henry JP, Giros B, Gasnier B. Cloning of a functional vesicular GABA and glycine transporter by screening of genome databases. FEBS Lett. 1997;417:177–183. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sandler R, Smith AD. Coexistence of GABA and glutamate in mossy fiber terminals of the primate hippocampus: an ultrastructural study. J Comp Neurol. 1991;303:177–192. doi: 10.1002/cne.903030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Schlander M, Thomalske G, Frotscher M. Fine structure of GABAergic neurons and synapses in the human dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 1987;185:189–189. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shupliakov O, Örnung G, Brodin L, Ulfhake B, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Cullheim S. Immunocytochemical localization of amino acid neurotransmitter candidates in the ventral horn of the cat spinal cord: a light microscopic study. Exp Brain Res. 1993;96:404–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00234109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Somogyi P, Takagi H. A note on the use of picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative for correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience. 1982;7:1779–1783. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Somogyi P, Freund TF, Halasz N, Kisvarday ZF. Selectivity of neuronal [3H]GABA accumulation in the visual cortex as revealed by Golgi staining of the labeled neurons. Brain Res. 1981;225:431–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90849-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Somogyi P, Cowey A, Kisvarday ZF, Freund TF, Szentagothai J. Retrograde transport of γ-amino[3H]butyric acid reveals specific interlaminar connections in the striate cortex of monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1983a;80:2385–2389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Somogyi P, Smith AD, Nunzi MG, Gorio A, Takagi H, Wu JY. Glutamate decarboxylase immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of the cat: distribution of immunoreactive synaptic terminals with special reference to the axon initial segment of pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1983b;3:1450–1468. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-07-01450.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Somogyi P, Freund TF, Kisvarday ZF. Different types of 3H-GABA accumulating neurons in the visual cortex of the rat. Characterization by combined autoradiography and Golgi impregnation. Exp Brain Res. 1984;54:45–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00235817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Somogyi P, Tamas G, Lujan R, Buhl EH. Salient features of synaptic organisation in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998;26:113–135. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(97)00061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Soriano E, Nitsch R, Frotscher M. Axo-axonic chandelier cells in the rat fascia dentata: Golgi-electron microscopy and immunocytochemical studies. J Comp Neurol. 1990;293:1–25. doi: 10.1002/cne.902930102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Storm-Mathisen J. Glutamate decarboxylase in the rat hippocampal region after lesions of the afferent fibre systems. Evidence that the enzyme is localized in intrinsic neurones. Brain Res. 1972;40:215–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Storm-Mathisen J. High affinity uptake of GABA in presumed GABA-ergic nerve endings in rat brain. Brain Res. 1975;84:409–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90762-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Storm-Mathisen J, Fonnum F. Quantitative histochemistry of glutamate decarboxylase in the rat hippocampal region. J Neurochem. 1971;18:1105–1111. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Storm-Mathisen J, Leknes AK, Bore A, Vaaland JL, Edminson P, Haug FMS, Ottersen OP. First visualization of glutamate and GABA in neurones by immunocytochemistry. Nature. 1983;301:517–520. doi: 10.1038/301517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Taal W, Holstege JC. GABA and glycine frequently colocalize in terminals on cat spinal motoneurons. NeuroReport. 1994;5:2225–2228. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199411000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Taxt T, Storm-Mathisen J. Uptake of d-aspartate and l-glutamate in excitatory axon terminals in hippocampus: autoradiographic and biochemical comparison with gamma-aminobutyrate and other amino acids in normal rats and in rats with lesions. Neuroscience. 1984;11:79–100. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Todd AJ, Sullivan AC. Light microscope study of the coexistence of GABA-like immunoreactivities in the spinal cord of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990;296:496–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.902960312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Walberg F, Ottersen OP. Neuroactive amino acids in the area postrema. An immunocytochemical investigation in rat with some observations in cat and monkey (Macaca fascicularis). Anat Embryol (Berl) 1992;185:529–545. doi: 10.1007/BF00185613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wenthold RJ, Huie D, Altschuler RA, Reeks KA. Glycine immunoreactivity localized in the cochlear nucleus and superior olivary complex. Neuroscience. 1987;22:897–912. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92968-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wentzel PR, De ZC, Holstege JC, Gerrits NM. Colocalization of GABA and glycine in the rabbit oculomotor nucleus. Neurosci Lett. 1993;164:25–29. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90848-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yang HW, Min MY, Appenteng K, Batten TF. Glycine-immunoreactive terminals in the rat trigeminal motor nucleus: light- and electron-microscopic analysis of their relationships with motoneurones and with GABA-immunoreactive terminals. Brain Res. 1997;749:301–319. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(96)01326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Yoshida M, Tanaka M. Immunohistochemical evidence for convergence of GABA-containing and glycine-containing axon terminals on single spinal motoneurons of the rat. Kurume Med J. 1989;36:17–21. doi: 10.2739/kurumemedj.36.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zafra F, Aragón C, Olivares L, Danbolt NC, Giménez C, Storm-Mathisen J. Glycine transporters are differentially expressed among CNS cells. J Neurosci. 1995;15:3952–3969. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03952.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]