Abstract
Background
Heliopora coerulea, the blue coral, is the octocoral characterized by its blue skeleton. Recently, two Heliopora species were delimited by DNA markers: HC-A and HC-B. To clarify the genomic divergence of these Heliopora species (HC-A and HC-B) from sympatric and allopatric populations in Okinawa, Japan, we used a high throughput reduced representation genomic DNA sequencing approach (ezRAD).
Results
We found 6742 biallelic SNPs shared among all target populations, which successfully distinguished the HC-A and HC-B species in both the sympatric and allopatric populations, with no evidence of hybridization between the two. In addition, we detected 410 fixed SNPs linking functional gene differences, including heat resilience and reproductive timing, between HC-A and HC-B.
Conclusions
We confirmed clear genomic divergence between Heliopora species and found possible genes related to stress-responses and reproduction, which may shed light on the speciation process and ecological divergence of coral species.
Keywords: Coral, Transcriptome, Ecological divergence, Speciation
Background
Reef-building corals are morphologically and ecologically diverse and per unit area the reefs they form support more species than any other marine ecosystems [1]. Coral reefs are also among the most threatened ecosystems from direct and indirect anthropogenic pressures [2, 3]. Heliopora coerulea, the blue coral, is the only octocoral to form a massive structure like scleractinians and due to its characteristic blue skeleton it is also harvested for the aquarium, jewelry and curio trade. The blue coral is also only found in the shallow waters of the Indo-Pacific, making it particularly susceptible to long-term climate change and local anthropogenic impacts [4, 5].
Species delineation is one of the most fundamental issues when assessing conservation and biodiversity strategies, but morphological species identification of reef-building corals is often problematic due to their high plasticity and limited number of species-specific features [6], which is also applicable to octocorals [7]. Molecular techniques provide approaches to better inform these phylogenetic relationships in corals (e.g., [8–10]). However, these molecular studies often suffer from a paucity of relevant markers to elucidate detailed evolutionary processes in corals (reviewed by [11]). In particular, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), is often used to infer inter- and intra-specific differences in many animal species (reviewed in [12, 13]); however, it has slow mutation rates in corals [14, 15]. Species delineation is particularly difficult with closely related corals because of interspecific hybridization, recent speciation, shared ancestral polymorphisms, and/or extremely high intra-specific morphological variation [16–22].
Nuclear markers have sometimes been more useful and have played an important role in understanding the phylogenetic and geographic relationships of corals (e.g., [7, 18, 23–26]). However, inadequate taxonomy, discord between nuclear and mitochondrial results, hybridization or incomplete lineage sorting, cryptic species, and difficulty in distinguishing population level genetic structure from species level genetic structure all complicate efforts to resolve species boundaries in corals (e.g., [21, 27–29], reviewed by [30]). The development of high-throughput reduced representation genomic DNA sequencing provides the opportunity to easily examine hundreds to thousands of nuclear markers as short loci or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). RADseq has also been applied to octocorals [22, 31]. There are now several RADseq protocols making it easier and cost-effective to perform SNP analyses on non-model organisms including corals (e.g., [32–35]).
In this study, we applied the ezRAD [32, 36] approach to examine two closely related groups of Heliopora (Pallas 1766) corals on the southern reef of Okinawa, Japan, which reproduce at different times [37] and are often found in different habitats [38]. These two Heliopora species were recently delimited by microsatellite markers [25] and the ITS2 region [26]: HC-A and HC-B. This study aims to expand on this previous work to search for biallelic fixed SNPs in functional genes to further clarify the relationship between these octocoral Heliopora species.
Methods
Sampling, DNA extraction and library preparation
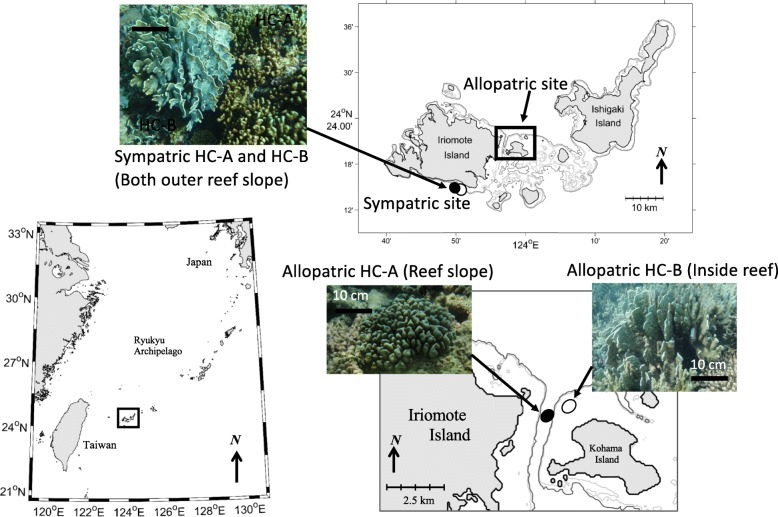
We selected four populations of two Heliopora spp. (each population was collected from two allopatric sites and one sympatric site; Fig. 1). The coral fragments (1–2 cm) were collected either by snorkeling or on SCUBA (depth: 0.8–7.8 m) as described in [25] under a permission from Okinawa Prefecture (26–10). Genomic DNA was extracted immediately after sampling of coral fragments with a Qiagen DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit. Each of the four populations had twelve individuals (Table 1), which were quantified with the Accuclear Ultra High Sensitivity dsDNA kit before pooling equimolarly. DNA samples from 12 individuals in each site were pooled and used for the following analyses. The four libraries were prepared following the ezRAD protocol [36] using Illumina TruSeq library preparation kit, and following bioanalyzer and qPCR quality control steps were run as paired-end (2 × 300 bp) reads on the Illumina Miseq sequencer.
Fig. 1.
Sampling locations of Heliopora species used in this study
Table 1.
Summary of used samples in this study
| Allopatric HC-A | Allopatric HC-B | Sympatric HC-A | Sympatric HC-B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of individuals | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| No. of reads (paired-end, forward) | 4,552,218 | 3,585,919 | 4,599,520 | 3,793,508 |
| No. of reads (paired-end, reverse) | 5,022,763 | 3,974,309 | 5,084,202 | 4,193,414 |
Bioinformatics analysis
The FASTQ files, with an average of 8.7 million 300 bp reads per paired-end population, were filtered with the FASTX-Toolkit (http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit/) to discard reads with poor quality bases (Q < 20) and less than 25 bp in length. To increase the efficiency of mapping against transcriptome data, we prepared fasta files consisting of 50 bp size sequences from filtered fastq files above. In order to call SNPs in putative protein coding regions from the coral host, we aligned the fasta files to the transcriptome data of coral host Heliopora coerulea [39] with bowtie2 by using the default setting [40]. This process excludes contaminated sequences from other micro-organisms for the following analyses. With the subsequent SAM files, we called SNPs with Stacks (programs: pstacks (default setting), cstacks (−b 1 -p 4 -n 3), sstacks (−b 1 -p 4), and genotypes (−b 1) [41];). Short read data is available from the accession No. DRA008338 (DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ)).
Based on catalog files made by Stacks, we prepared input files including only biallelic SNPs loci among 4 populations using parsing scripts by R ([42]; Additional file 1) for the following analyses. Based on the biallelic SNPs data, hierarchical clustering of the number of loci, in which two populations share the same allelic compositions and heat map visualization, were performed using heatmap.2 in the gplots ver. 3.0.1 package in R [43]. Venn diagram was drawn using VennDiagram ver. 1.6.17 package in R. We also performed a maximum likelihoood (ML) analysis with RAxML ver. 8.2.7 [44] using NEXUS file including concatenated biallelic SNPs data. For the analysis, we used the GTR-GAMMA model and 1000 bootstrap replicates to estimate the clade confidences. Using short sequences obtained by Stacks including SNPs that were alternately fixed between types (HC-A and HC-B) found by parsing scripts by R (Additional file 1), we performed BLASTN analysis (e-value cut-off: 1e− 5) against transcriptome sequences of H. coerulea published in a previous study [39] and obtained annotation information for each SNP. We performed all data processing and analyses using the supercomputer of the National Institute of Genetics (Mishima, Shizuoka, Japan).
Results and discussion
The ezRAD libraries yielded on average 8.7 million 300 bp reads per population (Table 1). After excluding contaminated sequences by using transcriptome data of H. coerulea, we succeeded in detecting 6742 variable biallelic SNPs shared among all 4 of the pooled populations. The number of loci at which pools of individuals shared the same nucleotide was higher within species (3199 and 3631 in HC-A and HC-B, respectively) than between species (2556–2750) regardless of locations (Fig. 2, Additional file 2). Based on the SNP polymorphisms, the dendrogram indicates that the HC-A and HC-B species remain clearly distinguished regardless of whether they were collected from sympatric or allopatric populations (Fig. 3). This distinction supports the previous population genetic analyses using microsatellite and ITS2 markers [26], indicating that, even in sympatric environments, there is either striking selection or no hybridization between HC-A and HC-B as suggested in previous studies [25, 26]. But considering that we used pooled RAD-seq samples, individual based analysis would be necessary in the future [45].
Fig. 2.
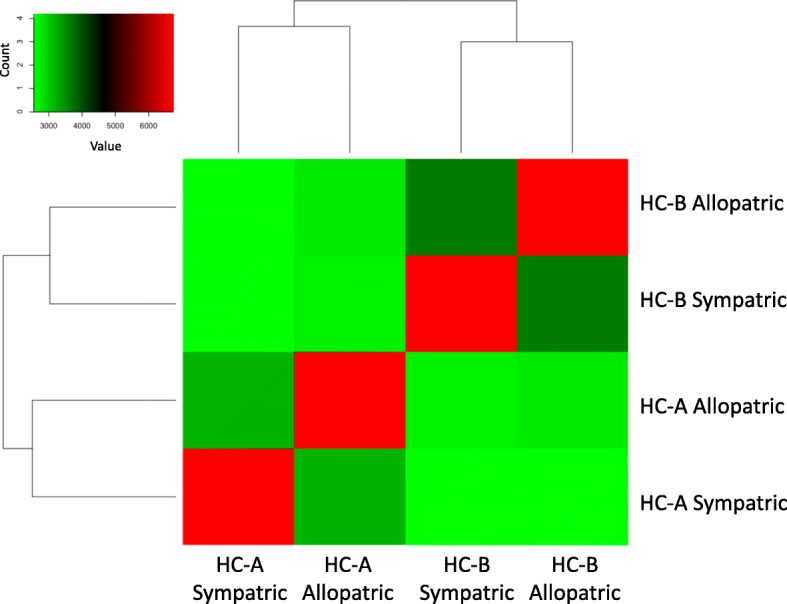
Heat map of the number of loci in which two populations share the same allele compositions
Fig. 3.
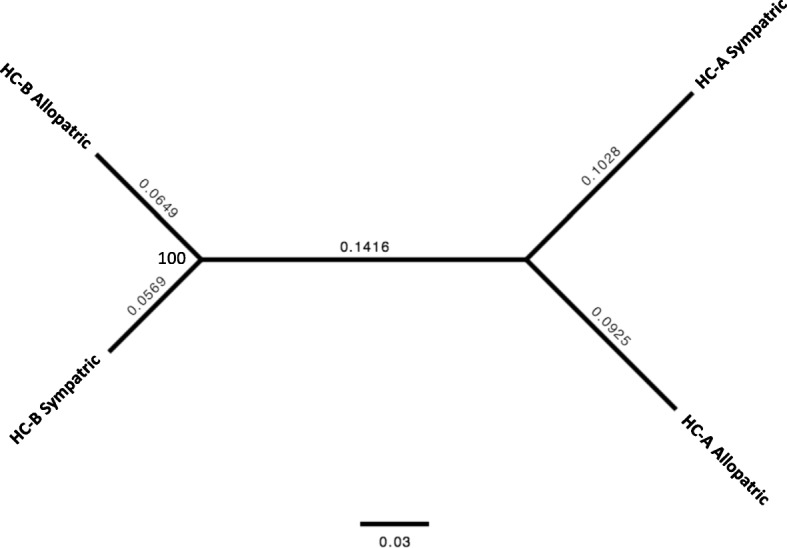
Dendrogram of the four populations of Heliopora libraries. The node values show ML-bootstrap percentage and the values above the branches are genetic distances (substitutions/site)
In addition to the population genetic distinction, we also detected 410 fixed different SNPs in sequences obtained by Stacks between the two species (HC-A and HC-B). A BLAST search revealed matches to 314 annotated genes from the coral host (almost all e-values <1e− 10; Additional file 3). The BLAST results included genes related to stress responses such as thioredoxin [46], ubiquitin-protein ligase [47, 48], and cryptochrome-1 as a candidate gene (Table 2) although these SNPs were located at synonymous positions. Bay et al. [47] reported that SNP mutation in cryptochrome-1 was potentially linked to heat resistance in populations of Acropora hyacinthus. In the well-developed fringing reef, HC-A is more commonly found on the colder outer reef slope compared to HC-B, which resides in warmer shallower waters. Indeed, distribution of HC-A is also further north than that of HC-B [49]. In addition, after a mass bleaching event in 2017, more HC-B survived than HC-A in Sekisei Lagoon (H. Kurihara and N. Yasuda unpublished data). Thus, the fixed nucleotide differences between HC-A and HC-B provide hypotheses for the underlying mechanisms of differential stress tolerances observed between these species. This stress tolerance should be further examined, because the resilience of these two Heliopora species to long-term climate change will likely differ and be an important component of future conservation and management strategies.
Table 2.
Selected candidate genes for ecological divergence of Heliopora species
| Contig ID | Accession number | Annotate description | Origine speices | Accession number | Identity (%) | E-value | Bit score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c101459_g1_i1 | IABP01020958 | PREDICTED: dopamine receptor 2-like | Acropora digitifera | XP_015754865.1 | 43.64 | 2.00E-21 | 99.4 |
| c114522_g1_i1 | IABP01022095 | PREDICTED: LOW QUALITY PROTEIN: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF103-like | Acropora digitifera | XP_015753316.1 | 41.68 | 2.00E-164 | 498 |
| c31599_g1_i1 | IABP01003528 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HECTD3 | Exaiptasia pallida | KXJ16705.1 | 56.16 | 0 | 959 |
| c41722_g1_i2 | IABP01005816 | Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 11 | Exaiptasia pallida | KXJ26582.1 | 32.17 | 2.00E-113 | 385 |
| c48657_g1_i1 | IABP01009691 | PREDICTED: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5-like isoform X8 | Parasteatoda tepidariorum | XP_015929469.1 | 42.2 | 0 | 908 |
| c52917_g1_i2 | IABP01016181 | PREDICTED: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF213 | Callorhinchus milii | XP_007886854.1 | 35.62 | 0 | 1979 |
| c61162_g1_i1 | IABP01017641 | Cryptochrome-1 | Exaiptasia pallida | KXJ26519.1 | 45.79 | 0 | 932 |
Interestingly, dopamine receptor 2-like gene was also found among the fixed SNPs gene list, which has been linked to the season an animal breeds [50]. The timing of reproduction is different between HC-A and HC-B [37, 50]. For example, in both the Philippines [51] and Japan (Taninaka et al. under review), HC-A broods their larvae about 1 month earlier than HC-B even in sympatric sites, indicating that reproductive timing of Heliopora spp. appears to be genetically controlled rather than environmentally-dictated. It is reported that dopamine is related to the spawning timing of Acropora tenuis [52]. In addition, it is suggested that cryptochrome-1 is involved in reproductive timing of acroporid coral [53]. Thus, it is possible that these fixed genetic differences in the dopamine receptor and cryptochrome-1 might contribute to the difference of reproductive patterns in Heliopora spp. and highlight the need for additional research.
Conclusions
We detected clear divergence between Heliopora species based on SNPs obtained from the ezRAD approach utilizing coral host transcriptome data. These data indicate that even among sympatric populations, HC-A and HC-B are reciprocally non-interbreeding, and therefore warrant formal recognition as valid taxonomic species. We also highlight candidate genes which may explain ecological differences between HC-A and HC-B, especially those found in the sympatric populations, which provide mechanistic hypotheses for the divergence of these groups and suggest likely differences in stress response and resilience to future climate conditions. More detailed descriptions of ecological characteristics such as reproduction and stress tolerances between HC-A and HC-B, guided by hypotheses based on fixed SNP differences discovered in this study, will contribute to a deeper understanding of the mechanistic and genetic basis of the ecological divergence of blue corals and the speciation process.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1. R script for analyzing SNPs data.
Additional file 2. Venn diagram showing the numbers of loci in which populations share the same allele compositions.
Additional file 3: Table S1. Candidate genes for ecological divergence of Heliopora species.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Seaver Institute and the 2013 Edwin W. Pauley Summer Program.
Abbreviations
- DNA
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
- ITS
Internal Transcribed Spacer
- PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- RADseq
Restriction Site Associated DNA Sequence
- SNP
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
Authors’ contributions
NY designed the experiments. NY, YH and SN collected samples and extracted DNA. ZF, RT, AI, and YY analyzed the data. AI wrote the main manuscript text. All authors contributed writing and editing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The design of the study, sample collection, data analysis, and interpretation of data were supported by the Global Environment Research Fund 4RF-1501 of the Ministry of the Environment of Japan and NSF OA#1416889.
Availability of data and materials
All data of this study are included in this article and its supplementary information.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Akira Iguchi, Phone: +81-98-55-4295, Email: iguchi.a@aist.go.jp.
Yuki Yoshioka, Email: y.yoshioka1109@gmail.com.
Zac H. Forsman, Email: zac@hawaii.edu
Ingrid S.S. Knapp, Email: ingrid.knapp16@gmail.com
Robert J. Toonen, Email: rjtoonen@gmail.com
Yuki Hongo, Email: hongoy@affrc.go.jp.
Satoshi Nagai, Email: snagai@affrc.go.jp.
Nina Yasuda, Phone: +81-985-58-7233, Email: nina27@cc.miyazaki-u.ac.jp.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12862-019-1522-0.
References
- 1.Knowlton N, Brainard RE, Fisher R, Moews M, Plaisance L, Caley MJ. Coral reef biodiversity. Life in the World’s Oceans: Diversity Distribution and Abundance. 2010. pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Halpern BS, Selkoe KA, Micheli F, Kappel CV. Evaluating and ranking the vulnerability of global marine ecosystems to anthropogenic threats. Conserv Biol. 2007;21:1301–1315. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2007.00752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Selkoe KA, Halpern BH, Ebert C, Franklin E, Selig E, Casey K, Bruno J, Toonen RJ. A map of human impacts to a “pristine” coral reef ecosystem, the Papahānaumokuākea marine national monument. Coral Reefs. 2009;28:635–650. doi: 10.1007/s00338-009-0490-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zann LP, Bolton L. The distribution, abundance and ecology of the blue coral Heliopora coerulea (Pallas) in the Pacific. Coral Reefs. 1985;4:125–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00300871. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Carpenter KE, Abrar M, Aeby G, Aronson RB, Banks S, Bruckner A, et al. One-third of reef-building corals face elevated extinction risk from climate change and local impacts. Science. 2008;321:560–563. doi: 10.1126/science.1159196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Todd PA. Morphological plasticity in scleractinian corals. Biol Rev. 2008;83:315–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2008.00045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McFadden CS, Haverkort-Yeh R, Reynolds AM, Halàsz A, Quattrini AM, Forsman ZH, Benayahu Y, Toonen RJ. Species boundaries in the absence of morphological, ecological or geographical differentiation in the Red Sea octocoral genus Ovabunda (Alcyonacea: Xeniidae) Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2017;112:174–184. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2017.04.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sanchez J, McFadden C, France S, Lasker H. Molecular phylogenetic analyses of shallow-water Caribbean octocorals. Mar Biol. 2003;142:975–987. doi: 10.1007/s00227-003-1018-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kitahara MV, Cairns SD, Stolarski J, Blair D, Miller DJ. A comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of the Scleractinia (Cnidaria, Anthozoa) based on mitochondrial CO1 sequence data. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McFadden C, Benayahu Y, Pante E, Thoma J, Nevarez P, France S. Limitations of mitochondrial gene barcoding in Octocorallia. Mol Ecol Res. 2011;11:19–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2010.02875.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McFadden CS, Sánchez JA, France SC. Molecular phylogenetic insights into the evolution of Octocorallia: a review. Integ Comp Biol. 2010;50:389–410. doi: 10.1093/icb/icq056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Avise JC. Phylogeography: the history and formation of species: Harvard University press; 2000.
- 13.Bowen BW, Shanker K, Yasuda N, Malay MCD, von der Heyden S, Paulay G, Rocha LA, Selkoe KA, Barber PH, Williams ST, Lessios HA, Crandall ED, Bernardi G, Meyer CP, Carpenter KE, Toonen RJ. Phylogeography unplugged: comparative surveys in the genomic era. Bull Mar Sci. 2014;90:13–46. doi: 10.5343/bms.2013.1007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shearer TL, van Oppen MJH, Romano SL, Wörheide G. Slow mitochondrial DNA sequence evolution in the Anthozoa (Cnidaria) Mol Ecol. 2002;11:2475–2487. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hellberg ME. No variation and low synonymous substitution rates in coral mtDNA despite high nuclear variation. BMC Evol Biol. 2006;6:24. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-6-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.van Oppen MJ, McDonald BJ, Willis B, Miller DJ. The evolutionary history of the coral genus Acropora (Scleractinia, Cnidaria) based on a mitochondrial and a nuclear marker: reticulation, incomplete lineage sorting, or morphological convergence? Mol Biol Evol. 2001;18:1315–1329. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Willis BL, van Oppen MJH, Miller DJ, Vollmer SV, Ayre DJ. The role of hybridization in the evolution of reef corals. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst. 2006;37:489–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.37.091305.110136. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Forsman ZH, Barshis DJ, Hunter CL, Toonen RJ. Shape-shifting corals: molecular markers show morphology is evolutionarily plastic in Porites. BMC Evol Biol. 2009;9:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Forsman ZH, Concepcion GT, Haverkort RD, Shaw RW, Maragos JE, Toonen RJ. Ecomorph or endangered coral? DNA and microstructure reveal Hawaiian species complexes: Montipora dilatata/flabellata/turgescens & M. patula/verrilli. PLoS One. 2010;5:e15021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Flot JF, Blanchot J, Charpy L, Cruaud C, Licuanan WY, Nakano Y, Payri C, Tillier S. Incongruence between morphotypes and genetically delimited species in the coral genus Stylophora: phenotypic plasticity, morphological convergence, morphological stasis or interspecific hybridization? BMC Ecol. 2011;11:22. doi: 10.1186/1472-6785-11-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marti-Puig P, Forsman ZH, Haverkort-Yeh RD, Knapp IS, Maragos JE, Toonen RJ. Extreme phenotypic polymorphism in the coral genus Pocillopora; micro-morphology corresponds to mitochondrial groups, while colony morphology does not. Bull Mar Sci. 2014;90:211–231. doi: 10.5343/bms.2012.1080. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Herrera S, Shank TM. RAD sequencing enables unprecedented phylogenetic resolution and objective species delimitation in recalcitrant divergent taxa. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2016;100:70–79. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Aurelle D, Pivotto ID, Malfant M, Topçu NE, Masmoudi MB, Chaoui L, et al. Fuzzy species limits in Mediterranean gorgonians (Cnidaria, Octocorallia): inferences on speciation processes. Zool Scr. 2017;46:767–778. doi: 10.1111/zsc.12245. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bongaerts P, Riginos C, Hay KB, van Oppen MJ, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Dove S. Adaptive divergence in a scleractinian coral: physiological adaptation of Seriatopora hystrix to shallow and deep reef habitats. BMC Evol Biol. 2011;11:303. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yasuda N, Taquet C, Nagai S, Fortes M, Fan T-Y, Phongsuwan N, Nadaoka K. Genetic structure and cryptic speciation in the threatened reef-building coral Heliopora coerulea along Kuroshio current. Bull Mar Sci. 2014;90:233–255. doi: 10.5343/bms.2012.1105. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yasuda N, Taquet C, Nagai S, Fortes M, Fan T, Harii S, Yoshida T, Sito Y, Nadaoka K. Genetic diversity, paraphyly and incomplete lineage sorting of mtDNA, ITS2 and microsatellite flanking region in closely related Heliopora species (Octocorallia) Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2015;93:161–171. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fukami H, Budd AF, Paulay G, Solé-Cava A, Chen CA, Iwao K, Knowlton N. Conventional taxonomy obscures deep divergence between Pacific and Atlantic corals. Nature. 2004;427:832–835. doi: 10.1038/nature02339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Huang D, Meier R, Todd PA, Chou LM. More evidence for pervasive paraphyly in scleractinian corals: systematic study of southeast Asian Faviidae (Cnidaria; Scleractinia) based on molecular and morphological data. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2009;50:102–116. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2008.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nakajima Y, Nishikawa A, Iguchi A, Nagata T, Uyeno D, Sakai K, Mitarai S. Elucidating the multiple genetic lineages and population genetic structure of the brooding coral Seriatopora (Scleractinia: Pocilloporidae) in the Ryukyu archipelago. Coral Reefs. 2017;36:415–426. doi: 10.1007/s00338-017-1557-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stat M, Baker AC, Bourne DG, Correa AMS, Forsman Z, Huggett MJ, Pochon X, Skillings D, Toonen RJ, van Oppen MJH, Gates RD. Molecular delineation of species in the coral holobiont. Adv Mar Biol. 2012;63:1–65. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394282-1.00001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pante E, Abdelkrim J, Viricel A, Gey D, France SC, Boisselier MC, Samadi S. Use of RAD sequencing for delimiting species. Heredity. 2015;114:450–459. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2014.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Toonen RJ, Puritz JB, Forsman ZH, Whitney JL, Fernandez-Silva I, Andrews KR, Bird CE. ezRAD: a simplified method for genomic genotyping in non-model organisms. PeerJ. 2013;1:e203. doi: 10.7717/peerj.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Puritz JB, Matz MV, Toonen RJ, Weber JN, Bolnick DI, Bird CE. Demystifying the RAD fad. Mol Ecol. 2014;23:5937–5942. doi: 10.1111/mec.12965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Andrews KR, Good JM, Miller MR, Luikart G, Hohenlohe PA. Harnessing the power of RADseq for ecological and evolutionary genomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:81–92. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2015.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Forsman ZH, Knapp ISS, Tisthammer K, Eaton DAR, Belcaid M, Toonen RJ. Coral hybridization or phenotypic variation? Genomic data reveal gene flow between Porites lobata and P. compressa. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2017;111:132–148. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2017.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Knapp ISS, Puritz J, Bird C, Whitney J, Sudek M, Forsman ZH, Toonen R. ezRAD- an accessible next-generation RAD sequencing protocol suitable for non-model organisms_v3.2. protocols.io. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Saito Y, Ueno M, Kitano FN, Yasuda N. Potential for different reproductive timing between sympatric Heliopora coerulea lineages southeast of Iriomote Island, Japan. Bull Mar Sci. 2015;91:397–398. doi: 10.5343/bms.2015.1024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yasuda N, Takino T, Kimura M, Lian C, Nagai S, Nadaoka K. Genetic structuring across the reef crest in the threatened blue coral Heliopora coerulea (Helioporidae, Octacorallia) in Shiraho reef, Southwest Japan. In: Urbano KV, editor. Advances in genetics research. Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York; 2010. pp. 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hongo Y, Yasuda N, Nagai S. Identification of genes for synthesis of the blue pigment, Biliverdin IXa, in the blue coral Heliopora coerulea. Biol Bull. 2017;232:71–81. doi: 10.1086/692661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9:357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Catchen JM, Amores A, Hohenlohe P, Cresko W, Postlethwait JH. Stacks : building and genotyping loci De novo from short-read sequences. Genes Genomes Genet. 2011;1:171–182. doi: 10.1534/g3.111.000240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.R Core Team . R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Warnes G, Bolker B, Bonebakker L, Gentleman R, Liaw W, Lumley T, Maechler M, Magnusson A, Moeller S, Schwartz M, Venables B. gplots: Various R programming tools for plotting data. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analyses and postanalysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Combosch DJ, Vollmer SV. Trans-Pacific RAD-Seq population genomics confirms introgressive hybridization in eastern Pacific Pocillopora corals. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2015;88:154–162. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.03.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Edge SE, Morgan MB, Gleason DF, Snell TW. Development of a coral cDNA array to examine gene expression profiles in Montastraea faveolata exposed to environmental stress. Mar Pollut Bull. 2005;51:507–523. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bay RA, Palumbi SR. Multilocus adaptation associated with heat resistance in reef-building corals. Curr Biol. 2014;24:2952–2956. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.10.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rosic N, Kaniewska P, Chan C-KK, Ling EYS, Edwards D, Dove S, Hoegh-Guldberg O. Early transcriptional changes in the reef-building coral Acropora aspera in response to thermal and nutrient stress. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:1052. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nakabayashi A, Matsumoto T, Kitano YF, Nagai S, Yasuda N. Discovery of the northernmost habitat of the blue coral Heliopora coerulea: possible range expansion due to climate change? Galaxea. 2016;18:1–2. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Eisenberg DTA, Campbell B, Mackillop J, Lum JK, Wilson DS. Season of birth and dopamine receptor gene associations with impulsivity, Sensation Seeking and Reproductive Behaviors. PLoS One. 2007;11:e1216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Villanueva RD. Cryptic speciation in the stony octocoral Heliopora coerulea: temporal reproductive isolation between two growth forms. Mar Biodivers. 2016;46:503–507. doi: 10.1007/s12526-015-0376-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Isomura N, Yamauchi C, Takeuchi Y, Takemura A. Does dopamine block the spawning of the acroporid coral Acropora tenuis? Sci Rep. 2013;3:2649. doi: 10.1038/srep02649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Oldach MJ, Workentine M, Matz MV, Fan TY, Vize PD. Transcriptome dynamics over a lunar month in a broadcast spawning acroporid coral. Mol Ecol. 2017;26:2514–2526. doi: 10.1111/mec.14043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. R script for analyzing SNPs data.
Additional file 2. Venn diagram showing the numbers of loci in which populations share the same allele compositions.
Additional file 3: Table S1. Candidate genes for ecological divergence of Heliopora species.
Data Availability Statement
All data of this study are included in this article and its supplementary information.