Abstract
Background
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is common in severe fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) and has a high mortality rate (20–50%) due to irreversible cerebral edema or sepsis. Stem cell-based treatment has emerged as a promising alternative therapeutic strategy to prolong the survival of patients suffering from FHF via the inhibition of SIRS due to their immunomodulatory effects.
Methods
3D spheroids of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (3D-ADSC) were prepared by the hanging drop method. The efficacy of the 3D-ADSC to rescue FHF was evaluated in a d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide (GalN/LPS)-induced mouse model of FHF via intraportal transplantation of the spheroids.
Results
Intraportally delivered 3D-ADSC better engrafted and localized into the damaged livers compared to 2D-cultured adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (2D-ADSC). Transplantation of 3D-ADSC rescued 50% of mice from FHF-induced lethality, whereas only 20% of mice survived when 2D-ADSC were transplanted. The improved transplantation outcomes correlated with the enhanced immunomodulatory effect of 3D-ADSC in the liver microenvironment.
Conclusion
The study shows that the transplantation of optimized 3D-ADSC can efficiently ameliorate GalN/LPS-induced FHF due to improved viability, resistance to exogenous ROS, and enhanced immunomodulatory effects of 3D-ADSC.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13287-019-1337-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cell, 2D-cultured cells, Spheroids, Intraportal delivery, Fulminant hepatic failure
Background
Toxins, drugs, viral infections, and genetic and metabolic disorders cause liver dysfunction requiring medical intervention [1]. During fulminant hepatic failure (FHF; also known as acute liver failure (ALF)), bacterial toxins or other hepatotoxins cause massive hepatocellular damage [2, 3]. In addition, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) mediated by massive stimulation of innate and/or adaptive immune system is frequently observed in severe cases of FHF. In fact, SIRS is the leading cause of fatality in FHF and 20–50% of FHF patients succumb to irreversible cerebral edema or sepsis with multiple organ dysfunction [4]. Thus, suppression of excessive immune responses during liver dysfunction may reduce the risk of hepatic failure-induced mortality.
Liver transplantation is the only life-saving treatment for permanent liver failure; however, various obstacles, such as limited donor issue, risk of fungal infection during the procedures, immune rejection response against the graft, and long-term immunosuppressant-associated complications decrease the success rate [5, 6]. To overcome the potential risks of whole organ transplantation, non-invasive cell-based therapy using primary hepatocytes is of keen interest for the treatment of liver diseases [7, 8]. However, many aspects of hepatocyte culture, including their isolation, expansion, and preservation, have proven to be difficult, and poor engraftment efficacy limits the hepatocyte transplantation [9, 10]. In this context, mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are promising candidates for cell therapy because of their multipotent differentiation ability and immunomodulatory activity [11–13]. Furthermore, MSC have been reported to rescue impaired hepatocytes by differentiating into hepatocyte-like cells and/or by improving the inflammatory, fibrotic microenvironment through paracrine effects [14] and preventing further liver damage during FHF [15]. Notably, earlier MSC-based therapies were mainly dependent on the multi-lineage differentiation ability, whereas recent studies have focused on the paracrine and autocrine functions of MSC-derived therapeutic factors [16–18]. Previous reports have revealed that the aggregation of MSC into 3D spheroids causes enhancement in the secretion of paracrine factors and proangiogenic cytokines [19, 20] and protection of the stemness [21, 22]. Furthermore, 3D culture methods have been reported to enhance stem cell survival in vitro as well as in vivo and provide better engraftment efficiency [23, 24]. Thus, 3D culture methods offer a means of improving the efficacy of stem cell therapies and eliminate the need for genetic modification and growth factor delivery.
In cell therapy, the route of cell delivery must be considered deliberately to maximize therapeutic efficacy. In most cases, MSC are administrated via intravenous injection [25–27], which results in non-specific distributions of cells. The cells are primarily accumulated in the lungs, and only a small number of cells localize into the liver despite their homing ability [28]. Although various injection routes have been considered, including delivery into targeted areas, no report has been issued on maximizing the localization of the transplanted cells in models of liver injury. In the current study, we aimed to evaluate the therapeutic potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSC) in a d-galactosamine (GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced murine model of hepatic injury, because it closely resembles FHF [2, 3]. To enhance ADSC engraftment and localization in the liver, we delivered the 3D spheroids derived from ADSC (3D-ADSC) via the portal vein. The liver-entrapped 3D-ADSC helped in the modulation of inflammatory hepatic microenvironment through the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines/growth factors and improved outcomes of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in FHF.
Material and methods
Cells
Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSC) were purchased from Zenbio (Morrisville, NC, USA). ADSC were cultured in alpha-MEM (Hyclone, South Logan, UT, USA) containing 10% v/v fetal bovine serum (Hyclone, South Logan, UT, USA) and 1% v/v antibiotics/antimycotics (GenDEPOT, Barker, TX, USA). Cells from passages 4–8 were used in this study.
Preparation and optimization of 3D-ADSC
A previously described hanging drop technique was used to prepare 3D-ADSC [29]. The differently sized spheroids, i.e., 3D-ADSC500, 3D-ADSC1000, 3D-ADSC2000, and 3D-ADSC4000 containing 500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 ADSC per spheroid, respectively, were prepared. The viability and size of 3D-ADSC were considered for the optimization of size of the 3D-ADSC for in vivo studies. The viability of differently sized 3D-ADSC was assessed using a live/dead assay kit (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA), and Western blot analysis as reported previously [30].
Induction of FHF
Balb/c nude mice (7–8 weeks old) purchased from Orient Biosciences (Seoul, Republic of Korea) were used in this study. Animals were housed in the animal facility of Yeungnam University. Animal experimental protocols were approved by the regulations of Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Yeungnam University (IACUC: YL 2018-028). For the determination of the optimal dose required to induce FHF, mixtures of GalN (Carbosynth, Old Station Business Pk, Compton RG20 6NE, UK) (1000, 1500, 2000, or 3000 mg/kg) and LPS (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) (20 μg/kg) were administered intraperitoneally (i.p.). The anti-inflammatory effect of stem cells was evaluated using an optimized GalN/LPS dose (single injection; 1500 mg/kg GalN and 20 μg/kg LPS). Mice were divided randomly into different groups after the induction of ALF.
Intraportal delivery of ADSC
The therapeutic efficacy of ADSC was determined by infusing cells via the portal vein 5 h after GalN/LPS injection. One thousand 3D-ADSC1000 or 1 × 106 2D-ADSC were suspended in 100 μL PBS and injected into the portal vein using an insulin syringe. Sham group received an intraportal injection of 100 μL PBS. Subsequently, mice were monitored 6 hourly and blood samples were obtained at 1, 3, 5, and 7 days after transplantation. Serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT) and serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) levels were measured via the colorimetric method using a chemistry analyzer (DRI-CHEM 4000i, FUJIFILM Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
DNA extraction and real-time PCR
At 10 h after MSC transplantation, the livers, lungs, and hearts were isolated to investigate the presence of the transplanted cells in these organs. Depending on the weight of the organ, lysis buffer was added and homogenized. Afterwards, DNA was extracted using a genomic DNA extraction kit (Bioneer Corp, Daejeon, South Korea) and quantified using a spectrophotometer (Nanodrop; TECAN). Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) was performed using 25 ng DNA, 5 μL SYBER green (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), 37.5 nM ALU primer, and 450 nM GAPDH primer. The primer sequences used were as follows: ALU, 5′-GTCAGGAGATCGAGACCATCCC-3′ (F) and 5′-TCCTGCCTCAGCCTCCCAAG-3′ (R), and GAPDH, 5′-ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC-3′ (F) and 5′-TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA-3′ (R). Calibration curve was prepared using crossing point (Cp) values obtained with various amounts of human DNA (16%, 8%, 4%, 2%, 1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, 0.125%, 0.0625%, 0.03125%, 0.0156%, 0.0078%, and 0.0039%).
Levels of ROS and ROS-related enzymes in 3D-ADSC1000
To understand the mechanism responsible for the effects of 3D-ADSC1000 transplantation, amounts of ROS produced by 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000 were evaluated by the fluorescence method using 20 μM of 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFDA) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and normalized with the DNA contents measured using PicoGreen Kit (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA). Similarly, levels of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), catalase (CAT), and hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1) were determined by the Western blot analysis using antibodies against SOD2 (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), CAT (Cell Signaling), and HO-1 (Cell Signaling).
Viability of 3D-ADSC1000 under oxidative stress condition
In order to examine cell viability in a highly oxidative environment that resembles the FHF liver, 3 × 104 monolayer-cultured MSCs or 30 spheroids (each spheroid containing 1000 MSCs) were cultured with different concentrations of TBHP (tert-butyl hydroperoxide) (Tokyo Chemical Industry, Nihonbashi-honcho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo, Japan) (200 and 400 μM) for 24 h in a 96-well plate. Viability was assayed by using live/dead imaging and Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) as described previously [30].
Anti-inflammatory effects of 3D-ADSC1000 and 2D-ADSC
The levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) secreted in supernatants after 3 days of culture of 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000 were measured using a PGE2 ELISA kit (R & D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). Similarly, in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of 3D-ADSC1000 and 2D-ADSC were assessed by culturing them with activated macrophages. Briefly, RAW 264.7 macrophages were cultured at a density of 4 × 104 per well in a 96-well plate for 24 h and activated by adding 1 mg/mL of LPS for 90 min. Ten 3D-ADSC1000 or 1 × 104 2D-ADSC were added to each well, and 10 h later, supernatants were collected, centrifuged, and stored at − 70 °C until analysis. Levels of IL-10 and TNF-α were measured by ELISA using a Mouse IL-10 ELISA kit (R & D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) or a Mouse TNF-α kit (Elabscience, Bethesda, MD, USA), respectively. Finally, levels of ROS in activated macrophages were measured by the fluorescence method using DCFDA.
In vivo assessment of the anti-inflammatory effect of 3D-ADSC1000 and 2D-ADSC
For the in vivo assessment of the effect of 3D-ADSC1000 and 2D-ADSC in attenuating inflammation in the FHF model, polarization of macrophage in the liver was evaluated using flow cytometry. After 7 h of cell transplantation, isolation of monocytes from the liver was conducted as described previously [31]. The isolated cells were stained with anti-mouse PE-Cy7-conjugated CD11b (Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA), PE-conjugated F4/80 (Biolegend), APC-Cy7-conjugated CD86 (Biolegend), and PE-Cy7-conjugated CD206 (Biolegend) and analyzed by BD FACS Verse flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). To check M1 and M2 phenotypes of macrophage, F4/80+ population was selected, and the expression of CD86 (M1 surface marker) and CD206 (M2 surface marker) was evaluated. Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) was calculated using FlowJo Software (FlowJo LLC, OR, USA). In addition, the concentration of IL-10 in serum was also evaluated by ELISA.
Histochemical analysis
3D-ADSC1000- and 2D-ADSC-injected mice were sacrificed 7 h after injections, and the livers were surgically removed, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde solution, and embedded in paraffin. Samples were then sectioned at 5 μm, deparaffinized in xylene, rehydrated using an alcohol series, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).
Ex vivo imaging
Cells were stained with VivoTrack680 (pernElmer, Boston, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Then, 1 × 106 monolayer cells or 1000 3D-ADSC1000 were injected into the portal vein via a surgical process. At 7 h post-transplantation, different organs were isolated to observe the fluorescence using in vivo imaging system (FOBI; NeoScience, Suwon, Korea).
Statistical analysis
Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software version 5 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). Unless otherwise stated, unpaired t test was performed to calculate the statistical significance values. Statistical significance was accepted for p < 0.05.
Results
Optimization of 3D-ADSC
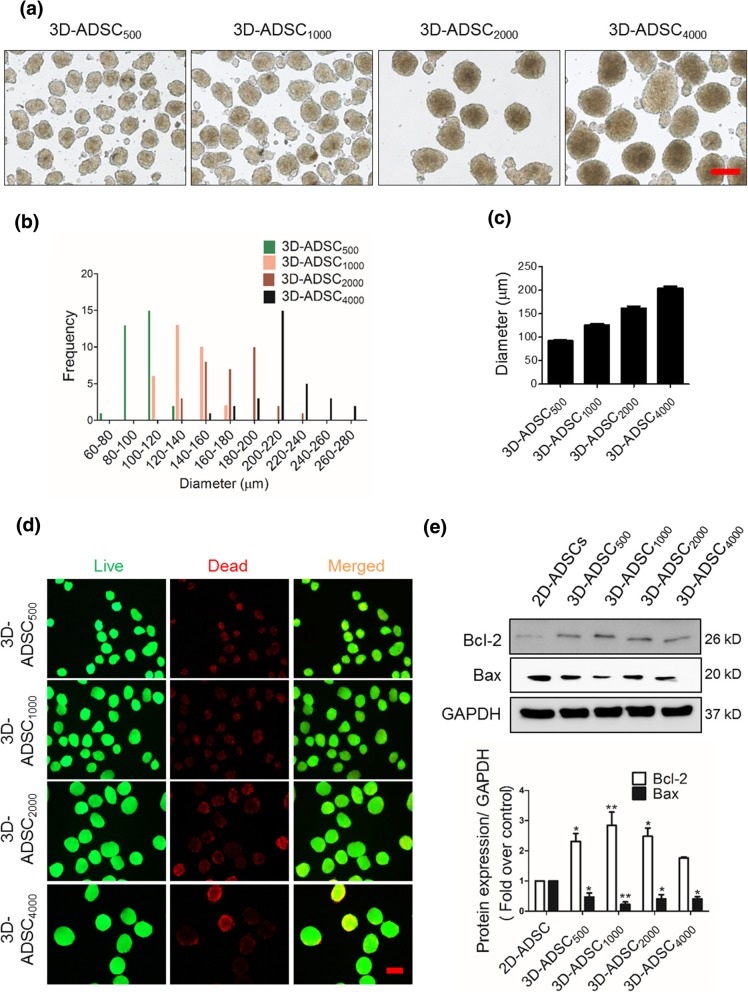
To optimize the size of spheroids, we prepared 3D-ADSC of different sizes and compared cell viability with 2D-ADSC. The average diameters of 3D-ADSC500, 3D-ADSC1000, 3D-ADSC2000, and 3D-ADSC4000 were 91.97 ± 11.80, 125.00 ± 15.93, 161.70 ± 24.39, and 203.86 ± 25.05 μm, respectively (Fig. 1a–c). Interestingly, Western blot analysis revealed two- to threefold increase in expressions of Bcl-2 (anti-apoptotic) and two- to threefold decrease in expressions of Bax (pro-apoptotic) in 3D-ADSC with different cell numbers when compared to the 2D-ADSC. Among the 3D-ADSC groups containing different numbers of cells, 3D-ADSC1000 was chosen for further experiments because this group exhibited higher cell viability and anti-apoptotic property compared to the other spheroid groups (Fig. 1d, e). In addition, given that spheroids with size exceeding 150 μm suffer from hypoxia-induced cell death after transplantation [32], 3D-ADSC1000 with size ~ 125 μm was expected to have improved efficacy, as well as minimum risk of thrombosis and embolism after transplantation.
Fig. 1.
Formation of 3D spheroids of different sizes. a Morphology of 3D-ADSC, magnification: × 100, scale bar: 200 μm. b Size distribution. c Size of 3D-ADSC (n = 31) where values represent mean ± SEM. d Live/dead images for the determination of viability of differently-sized 3D-ADSC, magnification: × 100, scale bar: 200 μm. e Representative blot showing cell viability of 2D-ADSC and differently-sized 3D-ADSC and quantitative expressions of proteins measured using GelQuantNET software. The values represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. 3D-ADSC500, 500 ADSC per spheroid; 3D-ADSC1000, 1000 ADSC per spheroid; 3D-ADSC2000, 2000 ADSC per spheroid; 3D-ADSC4000, 4000 ADSC per spheroid. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01
Intraportal delivery of 3D-ADSC1000 ameliorated FHF
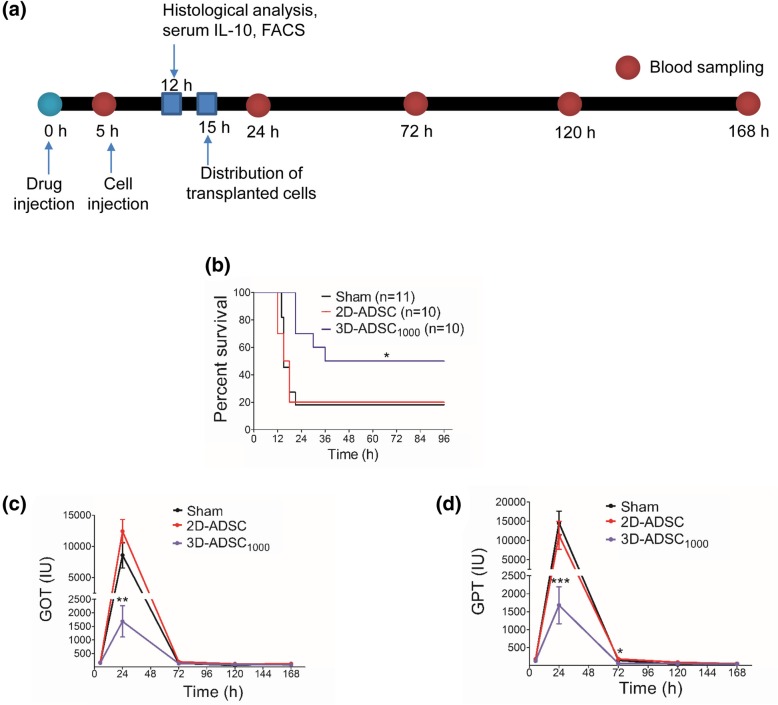
Dosage of GalN and LPS was optimized, and 1500 mg/kg GalN and 20 μg/kg LPS were chosen for the induction of FHF in BALB/c nude mice, which resulted in the deaths of 2 out of 3 mice 24 h after administration (Additional file 1: Figure S1). To assess the efficacy of ADSC in FHF, 1 × 106 2D-ADSC or 1000 3D-ADSC1000 were delivered via the portal vein. Figure 2a shows the timeline of the study. Transplantation of 3D-ADSC1000 significantly improved the survival of mice (survival rate 50%) compared with the sham-operated group (18%) and the 2D-ADSC-treated group (survival rate 20%) (Fig. 2b).
Fig. 2.
3D-ADSC1000 rescued mice from GalN/LPS-induced lethal FHF. a Timeline of the study. b Survival curve of 1500 mg/kg GalN and 20 μg/kg LPS-treated BALB/c nude mice injected with PBS, 1 × 106 2D-ADSC, or 1000 3D-ADSC1000. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to calculate the statistical significance. c Serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) levels. d Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (GPT) levels. GPT and GOT were analyzed in the surviving mice via the colorimetric method using a chemistry analyzer. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
Serum levels of GOT and GPT in the sham, 2D-ADSC, and 3D-ADSC1000 groups 5 h after GaLN/LPS injection, were significantly higher than those of untreated mice (untreated mice; GOT 110 ± 20 and GPT 32 ± 9) (Additional file 1: Figure S2). Notably, no significant difference was observed in GPT and GOT levels among all the experimental groups at the time of transplantation. However, at 19 h after cell administration, the levels of serum GPT and GOT were markedly lower in the 3D-ADSC1000-treated group compared to the 2D-ADSC-treated group (GPT: p < 0.01, GOT: p < 0.001) or the sham group (GPT: p < 0.001, GOT: p < 0.01), indicating a reduction in the severity of liver injury after spheroid transplantation. Similarly, at day 3 post-transplantation, serum GPT levels in the 3D-ADSC1000 group were significantly lower compared to those in the 2D-ADSC (p < 0.01) and sham (p < 0.05) groups (Fig. 2c, d).
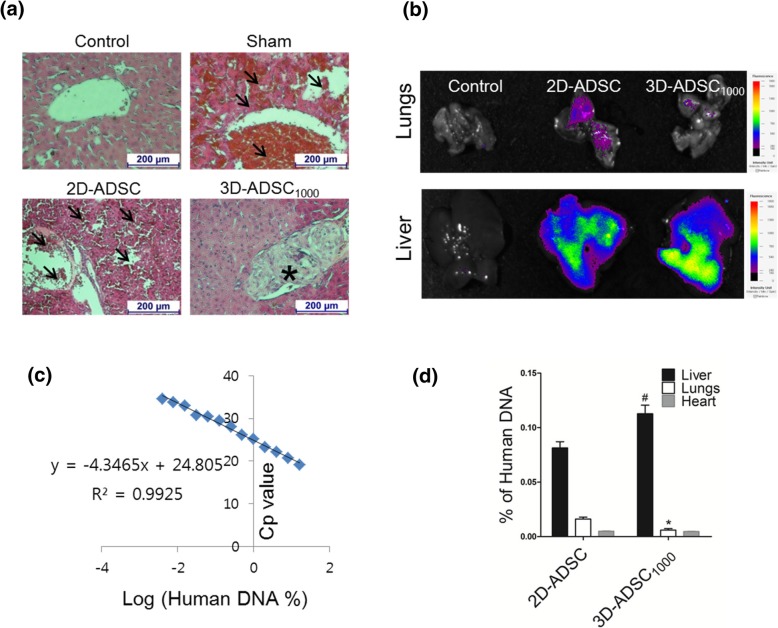
Histological analysis of liver sections from the sham and 2D-ADSC-treated groups revealed an accumulation of erythrocytes in the extra-sinusoidal region, signifying the damage of hepatic parenchymal and sinusoidal endothelial cells. In addition, the high extent of thrombosis was observed in the liver of 2D-ADSC-transplanted mice. In contrast, minimal thrombosis was observed in the recipients with 3D-ADSC1000 (Fig. 3a). Gross observation at 7 h after cell delivery demonstrated the formation of a substantial infarcted region in the liver of the 2D-ADSC group, but no significant infarction was observed in the 3D-ADSC1000 group (Additional file 1: Figure S3).
Fig. 3.
Fate of 2D- and 3D-cultured MSCs after transplantation via portal vein. a Histology of the liver 12 h after GalN/LPS administration; magnification: × 100, scale bar: 200 μm. Arrows indicate thrombosis, and the asterisk indicates localization of 3D-ADSC1000 in the liver. b Ex vivo imaging to observe the extrahepatic distribution of the transplanted cells after intraportal delivery. At 7 h of intraportal delivery of MSCs, ex vivo imaging was performed. Fluorescence was observed in the lungs of the 2D-ADSC-delivered group. However, negligible fluorescence was observed in the lungs of the 3D-ADSC1000-delivered group. In addition, significantly higher fluorescence intensity was observed in the liver of the 3D-ADSC1000-transplanted group compared to the 2D-ADSC-transplanted group. c Calibration curve for the determination of human DNA. d Percentage of human DNA observed in vital organs at 10 h of MSC transplantation (n = 3). The values represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 vs 2D-ADSC in the lungs and #p < 0.05 vs 2D-ADSC in the liver
Intraportally transplanted 3D-ADMSC1000 localized in the liver
Histological analysis revealed the localization of transplanted 3D-ADSC1000 in the portal triad. In addition, H&E staining showed an intact morphology of 3D-ADSC1000 at 7 h of transplantation (Fig. 3a). Similarly, ex vivo imaging of the liver and lungs also demonstrated the localization of ADSC in the liver and minimal migration into the lungs in the 3D-ADSC1000-transplanted group (Fig. 3b). Further, to quantify total human ADSC after transplantation, the expression of human-specific ALU sequence was evaluated in the liver, lungs, and heart. A calibration curve was generated using different percentages of human DNA mixed with mouse DNA (Fig. 3c). This equation was further used to calculate the total percent of human DNA in mouse tissue. Results revealed a higher number of cells distributed in the liver of the 3D-ADSC1000-transplanted group compared to the 2D-ADSC-transplanted group. In contrast, the percentage of human DNA in the lungs of the 3D-ADSC1000-transplanted group was significantly lower than that of the 2D-ADSC-transplanted group, suggesting a minimal migration of ADSC from the spheroids to extrahepatic tissues after transplantation. No significant migration of MSC was observed in the heart of both groups (Fig. 3b, d).
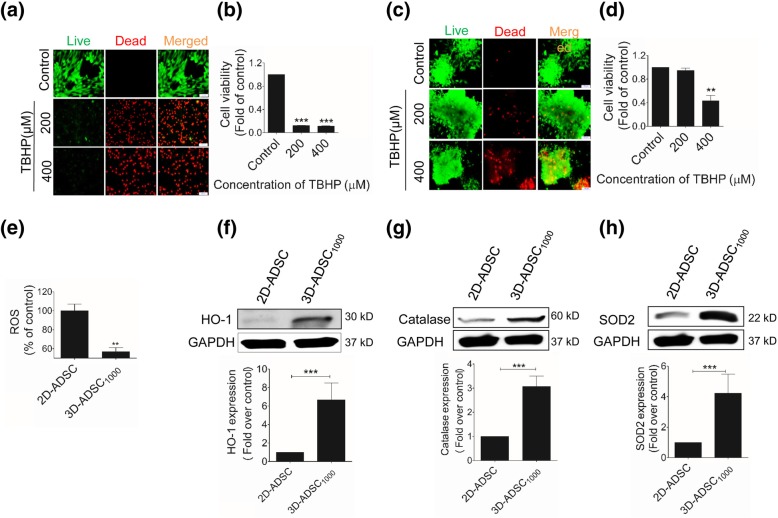
3D-ADSC1000 were resistant to oxidative stress
To evaluate the effect of oxidative stress on the viability of 2D-ADSC and the spheroids in vitro, 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000 were treated with TBHP. Results unveiled a higher number of cells stained with ethidium homodimer-1 in TBHP-treated 2D-ADSC (Fig. 4a) and < 20% of cells were viable at both concentrations (Fig. 4b). In contrast, cell viability in the 3D-ADSC1000 was not diminished by TBHP at 200 μM and approximately 40% of the cells remained viable when they were treated with TBHP at 400 μM (Fig. 4c, d). To investigate the mechanism underlying the enhanced resistance of 3D-ADSC1000 against oxidative stress, we measured levels of ROS, HO-1, SOD2, and CAT in 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000. Interestingly, we found a significantly lower (~ 50% lower) level of ROS in 3D-ADSC1000 compared to 2D-ADSC (Fig. 4e). Similarly, the expression of antioxidant proteins including HO-1, CAT, and SOD2 were remarkably higher in 3D-ADSC1000 compared to those of 2D-ADSC (Fig. 4f–h). These findings suggest that 3D-ADSC1000 possess improved resistant mechanism against oxidative stress through the upregulation of anti-oxidative enzymes.
Fig. 4.
3D-ADSC1000 resisted to oxidative stress in vitro. a Qualitative analysis of the viability of 2D-ADSC 24 h after treatment with exogenous oxidant (TBHP) using live/dead imaging; magnification × 100, scale bar 100 μm. b Quantitative analysis of viability of 2D-ADSC 24 h after treatment with exogenous oxidant (TBHP) using CCK-8 assay. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. c Representative live/dead image showing the viability of 3D-ADSC1000 24 h after treatment with TBHP; magnification × 100, scale bar 100 μm. d Quantitative assessment of viability of 3D-ADSC1000 24 h after treatment with TBHP using CCK-8 assay. The graph represents mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. e Basal levels of ROS in 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000 determined by using DCFDA reagent (mean ± SEM, three independent experiments). f Representative blot for basal level expressions of HO-1 in 3D-ADSC and 2D-ADSC and quantitative evaluation of the HO-1 expression from three independent experiments using GelQuantNET software. Representative blots and quantitative expressions of the antioxidant enzymes g SOD2 and h catalase (mean ± SEM, three independent experiments). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001
3D-ADSC1000 transplantation exerted improved immunomodulation
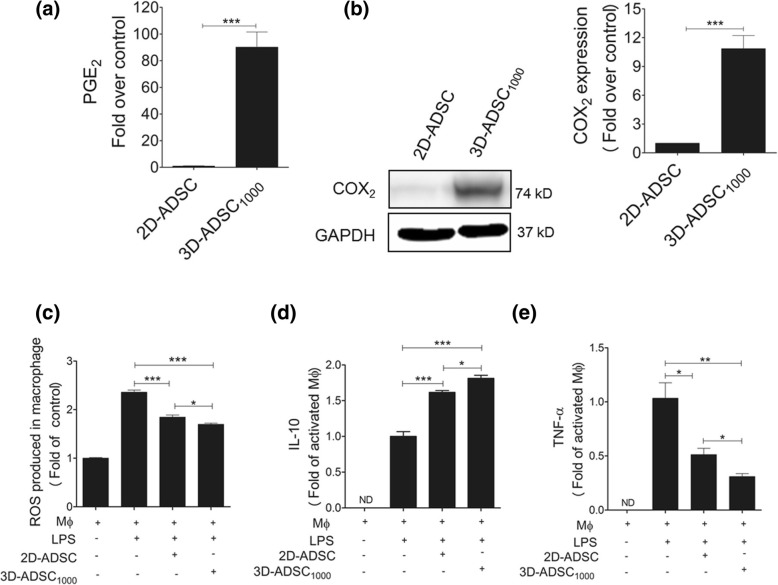
The GalN/LPS-induced FHF model is known to be accompanied by the activation of Kupffer cells and monocytes, which lead to inflammatory reactions in the liver, hepatocyte death, and systemic inflammation [33]. As PGE2 has been reported to play a vital role in the immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cells on monocytes, we quantified amounts of PGE2 secreted by 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000. Interestingly, we found a dramatically higher level of PGE2 secreted by 3D-ADSC1000 (~ 90-fold) compared to that of 2D-ADSC (Fig. 5a). Furthermore, COX2, which regulates PGE2 secretion, was markedly upregulated in 3D-ADSC1000 as compared with 2D-ADSC (Fig. 5b). Interestingly, when 2D-ADSC or 3D-ADSC1000 were separately co-cultured with the activated macrophages, ROS production in the macrophages co-cultured with 3D-ADSC1000 was remarkably attenuated as compared to that in the macrophages co-cultured with 2D-ADSC (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5c). In addition, production of IL-10 was significantly elevated when the macrophages were co-cultured with the 2D-ADSC or 3D-ADSC1000 compared to the LPS-stimulated macrophages (p < 0.0001). Notably, IL-10 secretion was greater in the macrophages co-cultured with 3D-ADSC1000 than in the macrophages co-cultured with 2D-ADSC (Fig. 5d). In contrast, TNF-α secretion was reduced when the activated macrophages were co-cultured with 2D-ADSC or 3D-ADSC1000, but this inhibitory effect was significantly higher when the macrophages were co-cultured with 3D-ADSC1000 (p < 0.01 vs 2D-ADSC) (Fig. 5e).
Fig. 5.
3D-ADSC1000 exerted enhanced immunomodulatory activity. a Basal levels of PGE2 secreted by 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. b Representative blot of COX2 expression in 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000 and quantitative estimation of COX2 expression using GelQuantNET software. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. c Evaluation of ROS production in LPS-activated macrophages after co-culture with 2D-ADSC or 3D-ADSC1000 using fluorescence method. The graph represents mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (one-way ANOVA). d IL-10 (anti-inflammatory) secretions after co-culturing activated macrophages with 2D-ADSC or 3D-ADSC1000 for 10 h using ELISA. Data indicate mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (one-way ANOVA). e TNF-α secretion after co-culture of activated macrophage with 2D-ADSC or 3D-ADSC1000 for 10 h. Data indicate mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
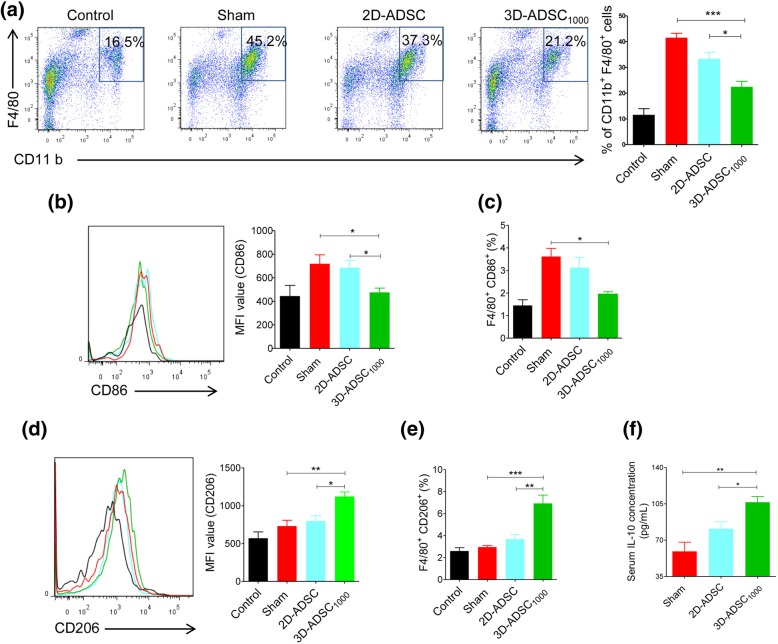
We next investigated whether 3D-ADSC1000 could exert immunoregulatory efficacy in vivo. The evaluation of macrophage infiltration and polarization in the liver showed an enhanced immunomodulatory effect of 3D-ADSC1000 to attenuate the liver inflammation. Macrophage population (CD11b+F4/80+) was significantly upregulated in sham (p < 0.001), 2D-ADSC (p < 0.001), and 3D-ADSC1000 (p < 0.05) compared to control mice. However, in the 3D-ADSC1000-transplanted group, a significant reduction in the macrophage population was observed compared to the sham (p < 0.001) or 2D-ADSC groups (p < 0.05) (Fig. 6a). Moreover, there was a significant reduction in the expression of M1 surface marker (CD86) (Fig. 6b,c), and an upregulation of M2 surface marker (CD206) (Fig. 6d,e) among the F4/80+ macrophages of the 3D-ADSC1000-transplanted group compared to the 2D-ADSC (p < 0.05) or sham group (p < 0.001), implying the polarization of macrophage into M2 phenotype after injection of 3D-ADSC1000. Furthermore, an increase in serum IL-10 level in the 3D-ADSC1000-transplanted group supported the upregulation of M2 macrophage (Fig. 6f). These results suggest that ADSC spheroids can robustly polarize the macrophages from M1 (inflammatory) to M2 (anti-inflammatory) phenotype, presumably via elevated PGE2 production (Fig. 7).
Fig. 6.
In vivo modulation of inflammatory responses by 3D-ADSC1000: a Flow cytometric analysis of surface markers (CD11b+F4/80+) for the determination of total macrophages in the liver of mice. The percentage represents CD11b+F4/80+ population, and the graph represents mean ± SEM (n = 4) (one-way ANOVA). b Expression of CD86 from F4/80+ population. The graph represents the mean ± SEM (n = 4). c Expression of CD206 from F4/80+ population. The graph represents the mean ± SEM (n = 4). d Percentage of F4/80+ CD86+ population (mean ± SEM) (n = 4) (one-way ANOVA). e Percentage of F4/80+ CD206+ population (mean ± SEM) (n = 4) (one-way ANOVA). f Serum concentration of IL-10 after 7 h of MSC transplantation (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. MFI median fluorescence intensity
Fig. 7.
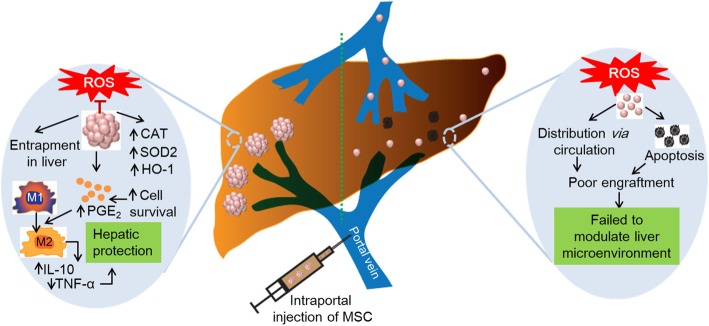
Proposed mechanism of hepatoprotection by intraportally delivered MSC spheroids. Majority of the 2D-ADSC die due to oxidative stressful environment in the inflamed liver or distribute to distant organs via circulation. This leads to a poor engraftment of MSC in the liver and failure of MSC to modulate liver microenvironment. In contrast, local delivery of 3D-ADSC via portal vein results in the engraftment of 3D-ADSC into liver sinusoids. In addition, upregulation of the antioxidant defense enzymes, such as HO-1, CAT, and SOD2, enhances survival of the 3D-ADSC against the oxidative stressful environment in the liver. This leads to a secretion of higher levels of PGE2 by 3D-ADSC which programs macrophage polarization from M1 to M2 phenotype. The M2 macrophages secrete higher level of IL-10 and lower level of TNF-α which results in hepatoprotection
Discussion
Stem cell therapy is based on cell replacement by differentiation into desired cell types or on rearrangement of the microenvironment in a manner that promotes tissue repair [34]. MSC have been reported to be useful in FHF due to their ability to differentiate into hepatocytes [35]. Furthermore, MSC have the ability to improve the liver microenvironment and promote the regeneration of hepatocytes by regulating inflammatory cells and cytokines [14, 36]. Although MSC have been demonstrated to be beneficial in various disease conditions, their effectiveness is compromised by limited survival and engraftment after transplantation [37]. 3D-ADSC have been reported to enhance cell viability possibly due to the phosphorylation of AKT or the upregulations of hypoxia-induced survival factors and nutrient deprivation-induced factors [23, 38–40]. Recently, we have developed extracellular matrix-modified scaffolds to enhance viability and therapeutic effectiveness in inflammatory diseases [41]. In the current study, transplantation of viability-strengthened MSC spheroids via the portal vein alleviated ALF by exerting a local immunomodulatory function.
Delivery of cells via the portal vein might increase risks of venous thrombosis and embolism. In a recent study, thrombosis and infarction were more prominent after intraportal delivery of 2D-ADSC compared to the 3D-ADSC-delivered group [42], which may be due to higher expressions of thrombogenic proteins, including tissue factor (TF) and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) in 2D-ADSC compared to that of the 3D-ADSC. Furthermore, 3D-ADSC containing 10,000 cells were reported to aggravate thrombosis and infarction in the livers [42], which indicates a necessity of control over spheroid size to protect the cells against hypoxia or nutrient deficiency after transplantation. The size-controlled MSC spheroids used for in vivo experiments in the current study survived well in a highly oxidative environment under in vitro conditions. This resembles the environment of an inflamed liver during FHF. Interestingly, no signs of hepatic thrombosis were observed in the 3D-ADSC-transplanted group.
GalN/LPS-induced FHF induces the activation of liver macrophage and the recruitment of neutrophils, monocytes, and natural killer cells in the liver to provoke inflammation [33]. Moreover, these activated immune cells and secreted inflammatory cytokines are responsible for the production of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) [43–45] and hepatocyte death [46, 47]. Previous studies have adopted different strategies, such as treatment with antioxidants [48, 49], overexpression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 [50], HO-1 [51, 52], or AKT [53], and hypoxic preconditioning [54], to improve MSC survival. In the present study, we used 3D-ADSC1000 which had enhanced expression of Bcl-2 and HO-1 and antioxidant proteins which led the MSCs to thrive well in the oxidative stressful environment after in vivo transplantation.
MSC may actively home to tissues via leucocyte-like cell adhesion and transmigration [55]. Alternatively, they may be passively entrapped into small-diameter blood vessels [56]. We delivered 3D-ADSC1000 via the portal vein to ensure passive entrapment by liver sinusoids and portal triads. During systemic infusion, a large fraction of MSC are typically trapped in lung capillaries [57], and this retention often results in poor homing [58]. Thus, local delivery of stem cells to injured sites probably promotes MSC entrapment in damaged organs [57, 59]. Although the mechanisms responsible for MSC engraftment and homing at sites of injury are unknown, various homing and adhesion molecules, such as intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), P-selectin, integrins, and CXCR4, have been reported to be involved [60]. Long-term culture of 2D-MSC in vitro has been reported to decrease the expressions of these adhesion and homing molecules that compromise homing and engraftment efficiencies at sites of injury [61]. In a recent study, it was reported that the upregulation of CXCR4 expression in 3D aggregates promotes the adhesion of MSC spheroids with the endothelial cells [61], which would aid the localization of transplanted 3D spheroids at the site of injury. In another study, when bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell spheroids were delivered intraportally, they were found to be entrapped in the liver, whereas spheroid-derived single cells delivered intraportally drained into the systemic circulation [42].
During inflammation, high concentrations of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IFN-γ, activate MSC to secrete soluble immunomodulatory factors, such as IDO, PGE2, and NO [62], which results in macrophage polarization to the anti-inflammatory phenotype (M2) and T cell switching to the regulatory phenotype [63]. Interestingly, 3D culture results in the upregulation of various pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-8, which creates an early inflammatory microenvironment within the 3D spheroids that activates MSC in spheroids to produce immunoregulatory factors like TNF-α-stimulated gene/protein 6 (TSG6), stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) [19], and PGE2 [20] and leads to the attenuation of inflammation or repairment of damaged tissues [64, 65]. In the present study, we observed higher COX2 and PGE2 expressions in 3D-ADSC1000 compared to 2D-ADSC, which resulted in more IL-10 secretion but less TNF-α secretion from macrophages co-cultured with 3D-ADSC1000 compared to the macrophages co-cultured with 2D-ADSC. Furthermore, an increase in M2 and a decrease in M1 macrophages in the liver suggested the better immunomodulatory role of 3D-ADSC spheroids. In our previous study, MSC were stimulated to secrete PGE2 by pretreating with muramyl dipeptide, which upregulates COX2 expression. The results reported an enhanced immunomodulatory effect in experimental colitis [66]. Similarly, IL-1β-primed MSC were reported to be more efficient at suppressing inflammation due to the upregulation of COX2 and PGE2 [67, 68]. Therefore, increased COX2 expression was correlated with increased anti-inflammatory effects. In the current study, 3D-ADSC effectively ameliorated ALF compared to 2D-ADSC, at least, in part, due to increased resistance to oxidative stress via the upregulation of various intracellular antioxidant mechanisms and enhanced polarization of macrophages to anti-inflammatory macrophage. Further studies should reveal the effectiveness of MSC spheroids in other inflammatory diseases.
Conclusion
Intraportal delivery of 3D-ADSC led to the MSC engraftment into the liver and enhanced therapeutic outcomes in a mouse model of FHF. These promising results were observed due to an upregulation of antioxidant defense mechanism during the formation of 3D spheroids from monolayer-cultured ADSC. This resulted in higher cell viability after intraportal transplantation. Furthermore, the enhanced immunomodulatory activity of 3D-ADSC led to the effective polarization of the macrophage from pro- to anti-inflammatory phenotype resulting in the attenuation of inflammation in GalN/LPS-induced hepatic toxicity. Recently, Chondrosphere® has been approved in Europe for the treatment of cartilage defects in human. Several studies including ours have revealed the superiority of 3D MSC spheroids compared to the monolayer MSC. 3D MSC spheroids have a great potential to improve the therapeutic effectiveness of MSC-based therapy. However, further studies on optimization of technique for large-scale manufacturing of clinical-grade 3D spheroids and mechanism behind the improvement of MSC effect are required for clinical translation.
Additional file
Figure S1. Determination of lethal dose of GalN for the induction of FHF. The percentage survival of Balb/c nude mice after intraperitoneal injection of different doses of GalN (1000 mg/kg, 1500 mg/kg, 2000 mg/kg, and 3000 mg/kg) with 20 μg/kg LPS. Figure S2. Serum GOT and GPT level in normal mice before induction of FHF. Figure S3. Gross observation of the liver after 7 h of intraportal delivery of 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000. Massive infarction was observed throughout the liver after 2D-ADSC delivery. In contrast, minimal infarction was observed in the 3D-ADSC1000 delivered group (the arrows indicate the areas of the infarction). (DOCX 562 kb)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- 2D-ADSC
2D-cultured adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- 3D-ADSC
3D spheroids of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- ADSC
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- ALF
Acute liver failure
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
- CAT
Catalase
- CCK-8
Cell Counting Kit-8
- CCL2
C-C motif chemokine ligand 2
- COX2
Cyclooxygenase 2
- CXCR4
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4
- DCFDA
2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescin diacetate
- ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- FHF
Fulminant hepatic failure
- GalN/LPS
d-Galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide
- GOT
Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase
- GPT
Glutamic pyruvic transaminase
- HO-1
Hemeoxygenase-1
- ICAM-1
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1
- IDO
Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase
- IL-1 α
Interleukin 1 alpha
- IL-10
Interleukin-10
- IL-1β
Interleukin 1 beta
- IL-8
Interleukin 8
- MSC
Mesenchymal stem cells
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- PGE2
Prostaglandin E2
- RNS
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- SIRS
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome
- SOD2
Superoxide dismutase 2
- STC-1
Stanniocalcin-1
- TBHP
Tert-butyl hydroperoxide
- TF
Tissue factor
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor alpha
- TSG6
Tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6
- VCAM-1
Vascular cell adhesion protein 1
Authors’ contributions
SR, SP, HSK, and JJH participated in the research design. SR and SP participated in the performance of the experiment. SR, SP, TPT, and TTN participated in the data analysis. SR participated in writing the manuscript. JHS, SY, JOK, CSY, IC, KOD, PHP, JBP, BKK, DML, IJM, and YS provided technical advice during the experiment and manuscript preparation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Korean Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (grant no. 2015R1A5A2009124 and 2018R1A5A2023879) and funded by the Ministry of Education (grant no. 2017R1D1A1B03027831); by the Korea Health Technology R & D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) and the Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare (grant no. HI18C0453); and by the Creative Economy Leading Technology Development Program through the Gyeongsangbuk-Do and Gyeongbuk Science and Technology Promotion Center of Korea (SF316001A).
Availability of data and materials
Authors.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Shobha Regmi, Email: regmishva@gmail.com.
Shiva Pathak, Email: shvptk@gmail.com.
Tung Pham Thanh, Email: pptung.hup@gmail.com.
Tiep Tien Nguyen, Email: tientiephup@gmail.com.
Jong-Hyuk Sung, Email: brain99@yonsei.ac.kr.
Simmyung Yook, Email: ysimmyung@kmu.ac.kr.
Jong Oh. Kim, Email: jongohkim@yu.ac.kr
Chul Soon Yong, Email: csyong@ynu.ac.kr.
Inho Choi, Email: inhochoi@ynu.ac.kr.
Kyoung-Oh Doh, Email: kodoh@ynu.ac.kr.
Pil-Hoon Park, Email: park.p@yu.ac.kr.
Jun-Beom Park, Email: jabassoon@yahoo.co.kr.
Yoojin Seo, Email: amaicat24@naver.com.
Bieong-Kil Kim, Email: kbk8516@gmail.com.
Dong-Mok Lee, Email: cowboyle@kitech.re.kr.
Ik-Jae Moon, Email: moonikjae@clearlab.com.
Hyung-Sik Kim, Phone: +82-51-510-8231, Email: hskimcell@pusan.ac.kr.
Jee-Heon Jeong, Phone: +82-53-810-2822, Email: jeeheon@yu.ac.kr.
References
- 1.Bernal William, Auzinger Georg, Dhawan Anil, Wendon Julia. Acute liver failure. The Lancet. 2010;376(9736):190–201. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kemelo MK, Wojnarova L, Kutinova Canova N, Farghali H. D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatotoxicity downregulates sirtuin 1 in rat liver: role of sirtuin 1 modulation in hepatoprotection. Physiol Res. 2014;63(5):615–623. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.932761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kosai K, Matsumoto K, Funakoshi H, Nakamura T. Hepatocyte growth factor prevents endotoxin-induced lethal hepatic failure in mice. Hepatology. 1999;30(1):151–159. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rolando N, Wade J, Davalos M, Wendon J, Philpott-Howard J, Williams R. The systemic inflammatory response syndrome in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 2000;32(4 Pt 1):734–739. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.17687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aberg F, Isoniemi H, Hockerstedt K. Long-term results of liver transplantation. Scand J Surg. 2011;100(1):14–21. doi: 10.1177/145749691110000104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Raghuram A, Restrepo A, Safadjou S, et al. Invasive fungal infections following liver transplantation: incidence, risk factors, survival, and impact of fluconazole-resistant Candida parapsilosis (2003-2007) Liver transplant. 2012;18(9):1100–9. doi: 10.1002/lt.23467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J, et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275–1284. doi: 10.1002/hep.20469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Joseph B, Malhi H, Bhargava KK, Palestro CJ, McCuskey RS, Gupta S. Kupffer cells participate in early clearance of syngeneic hepatocytes transplanted in the rat liver. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(5):1677–1685. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.36592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Soltys KA, Soto-Gutiérrez A, Nagaya M, et al. Barriers to the successful treatment of liver disease by hepatocyte transplantation. J Hepatol. 2010;53(4):769–774. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dhawan A. Clinical human hepatocyte transplantation: current status and challenges. Liver Transplant. 2015;21(Suppl 1):S39–S44. doi: 10.1002/lt.24226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bagno L, Hatzistergos KE, Balkan W, Hare JM. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease: progress and challenges. Mol Ther. 2018;26(7):1610–1623. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Miranda CO, Marcelo A, Silva TP, et al. Repeated mesenchymal stromal cells treatment sustainably alleviates Machado-Joseph disease. Mol Ther. 2018;26(9):2131–2151. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zheng Mei, Kim Doo-Yeong, Sung Jong-Hyuk. Ion channels and transporters in adipose-derived stem cells. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation. 2018;49(3):287–294. doi: 10.1007/s40005-018-00413-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang Z, Wang FS. Stem cell therapies for liver failure and cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2013;59(1):183–185. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuo TK, Hung SP, Chuang CH, et al. Stem cell therapy for liver disease: parameters governing the success of using bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(7):2111–2121. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Togel F, Weiss K, Yang Y, Hu Z, Zhang P, Westenfelder C. Vasculotropic, paracrine actions of infused mesenchymal stem cells are important to the recovery from acute kidney injury. A J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292(5):F1626–F1635. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00339.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Adamiak M, Sahoo S. Exosomes in myocardial repair: advances and challenges in the development of next-generation therapeutics. Mol Ther. 2018;26(7):1635–1643. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.04.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yong S-B, Chung JY, Song Y, Kim YH. Recent challenges and advances in genetically-engineered cell therapy. J Pharm Invest. 2018;48(2):199–208. doi: 10.1007/s40005-017-0381-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bartosh TJ, Ylöstalo JH, Mohammadipoor A, et al. Aggregation of human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) into 3D spheroids enhances their antiinflammatory properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107(31):13724–13729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008117107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ylöstalo JH, Bartosh TJ, Coble K, Prockop DJ. Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells cultured as spheroids are self-activated to produce prostaglandin E2 that directs stimulated macrophages into an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Stem Cells. 2012;30(10):2283–2296. doi: 10.1002/stem.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhang S, Liu P, Chen L, Wang Y, Wang Z, Zhang B. The effects of spheroid formation of adipose-derived stem cells in a microgravity bioreactor on stemness properties and therapeutic potential. Biomaterials. 2015;41:15–25. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kapur S, Wang X, Shang H, et al. Human adipose stem cells maintain proliferative, synthetic and multipotential properties when suspension cultured as self-assembling spheroids. Biofabrication. 2012;4(2):025004. doi: 10.1088/1758-5082/4/2/025004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bhang SH, Cho S-W, La W-G, et al. Angiogenesis in ischemic tissue produced by spheroid grafting of human adipose-derived stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(11):2734–2747. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.12.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xu Y, Shi T, Xu A, Zhang L. 3D spheroid culture enhances survival and therapeutic capacities of MSCs injected into ischemic kidney. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(7):1203–1213. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fischer UM, Harting MT, Jimenez F, et al. Pulmonary passage is a major obstacle for intravenous stem cell delivery: the pulmonary first-pass effect. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(5):683–692. doi: 10.1089/scd.2008.0253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Harting MT, Jimenez F, Xue H, et al. Intravenous mesenchymal stem cell therapy for traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurgery. 2009;110(6):1189–1197. doi: 10.3171/2008.9.JNS08158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(4):1005–1011. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.32.4.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Saat TC, van den Engel S, Bijman-Lachger W, et al. Fate and effect of intravenously infused mesenchymal stem cells in a mouse model of hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury and resection. Stem Cells Intl. 2016;2016:5761487. doi: 10.1155/2016/5761487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Regmi S, Cao J, Pathak S, et al. A three-dimensional assemblage of gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells and NO-releasing microspheres for improved differentiation. Int J Pharm. 2017;520(1–2):163–172. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pathak S, Regmi S, Nguyen TT, et al. Polymeric microsphere-facilitated site-specific delivery of quercetin prevents senescence of pancreatic islets in vivo and improves transplantation outcomes in mouse model of diabetes. Acta Biomater. 2018;201(10):24392–24405. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ren X, Zhang Y, Snyder J, et al. Forkhead box M1 transcription factor is required for macrophage recruitment during liver repair. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(22):5381–5393. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00876-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pathak S, Regmi S, Gupta B, et al. Engineered islet cell clusters transplanted into subcutaneous space are superior to pancreatic islets in diabetes. FASEB J. 2017;31(11):5111–5121. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700490R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yang Q, Shi Y, He J, Chen Z. The evolving story of macrophages in acute liver failure. Immuno Lett. 2012;147(1–2):1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2012.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang Y, Chen X, Cao W, Shi Y. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009–1016. doi: 10.1038/ni.3002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sato Y, Araki H, Kato J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells xenografted directly to rat liver are differentiated into human hepatocytes without fusion. Blood. 2005;106(2):756–763. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Luo X-Y, Meng X-J, Cao D-C, Wang W, Zhou K, Li L, Guo M, Wang P. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells attenuates liver fibrosis in mice by regulating macrophage subtypes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(16). 10.1186/s13287-018-1122-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Chang W, Song BW, Moon JY, et al. Anti-death strategies against oxidative stress in grafted mesenchymal stem cells. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28(12):1529–1536. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 2003;9(9):1195. doi: 10.1038/nm912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Baldari S, Di Rocco G, Piccoli M, Pozzobon M, Muraca M, Toietta G. Challenges and strategies for improving the regenerative effects of mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2087. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Petrenko Y, Syková E, Kubinová Š. The therapeutic potential of three-dimensional multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell spheroids. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8:94. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0558-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pathak S, Regmi S, Shrestha P, Choi I, Doh K-O, Jeong J-H. Mesenchymal stem cell capping on ECM-anchored caspase inhibitor–loaded PLGA microspheres for intraperitoneal injection in DSS-induced murine colitis. Small. 2019. 10.1002/smll.201901269. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Oh BJ, Jin S-M, Hwang Y, et al. Highly angiogenic, non-thrombogenic bone marrow mononuclear cells-derived spheroids in intraportal islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2018;67:473–485. doi: 10.2337/db17-0705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Asghar MN, Emani R, Alam C, et al. In vivo imaging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in murine colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20(8):1435–1447. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jaeschke H. Reactive oxygen and mechanisms of inflammatory liver injury: present concepts. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(Suppl 1):173–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jaeschke H, Ho YS, Fisher MA, Lawson JA, Farhood A. Glutathione peroxidase-deficient mice are more susceptible to neutrophil-mediated hepatic parenchymal cell injury during endotoxemia: importance of an intracellular oxidant stress. Hepatology. 1999;29(2):443–450. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wei H, Li Z, Hu S, Chen X, Cong X. Apoptosis of mesenchymal stem cells induced by hydrogen peroxide concerns both endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial death pathway through regulation of caspases, p38 and JNK. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111(4):967–978. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Li X, Shang B, Li Y-n, Shi Y, Shao C. IFNγ and TNFα synergistically induce apoptosis of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells via the induction of nitric oxide. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(18). 10.1186/s13287-018-1102-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 48.Drowley L, Okada M, Beckman S, et al. Cellular antioxidant levels influence muscle stem cell therapy. Mol Ther. 2010;18(10):1865–1873. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Valle-Prieto A, Conget PA. Human mesenchymal stem cells efficiently manage oxidative stress. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(12):1885–1893. doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Li W, Ma N, Ong LL, et al. Bcl-2 engineered MSCs inhibited apoptosis and improved heart function. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8):2118–2127. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yoon SJP, Kim SJP, Lee SMP. Overexpression of HO-1 contributes to sepsis-induced immunosuppression by modulating the Th1/Th2 balance and regulatory T-cell function. J Infect Dis. 2017;215:1608–1618. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tang YL, Tang Y, Zhang YC, Qian K, Shen L, Phillips MI. Improved graft mesenchymal stem cell survival in ischemic heart with a hypoxia-regulated heme oxygenase-1 vector. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(7):1339–1350. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gnecchi M, He H, Liang OD, et al. Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Med. 2005;11(4):367–368. doi: 10.1038/nm0405-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hu X, Yu SP, Fraser JL, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improves infarcted heart function via enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135(4):799–808. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2007.07.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Khaldoyanidi S. Directing stem cell homing. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(3):198–200. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.02.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Karp JM, Leng Teo GS. Mesenchymal stem cell homing: the devil is in the details. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(3):206–216. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Barbash IM, Chouraqui P, Baron J, et al. Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration, and body distribution. Circulation. 2003;108(7):863–868. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000084828.50310.6A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Toma C, Wagner WR, Bowry S, Schwartz A, Villanueva F. Fate of culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cells in the microvasculature. Circ Res. 2009;104(3):398–402. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.187724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Amado LC, Saliaris AP, Schuleri KH, et al. Cardiac repair with intramyocardial injection of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2005;102(32):11474–11479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504388102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Docheva D, Popov C, Mutschler W, Schieker M. Human mesenchymal stem cells in contact with their environment: surface characteristics and the integrin system. J Cell Mol Med. 2007;11(1):21–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Potapova IA, Brink PR, Cohen IS, Doronin SV. Culturing of human mesenchymal stem cells as three-dimensional aggregates induces functional expression of CXCR4 that regulates adhesion to endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(19):13100–13107. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800184200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9):726–736. doi: 10.1038/nri2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Bernardo ME, Fibbe WE. Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(4):392–402. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.González MA, Gonzalez-Rey E, Rico L, Büscher D, Delgado M. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental colitis by inhibiting inflammatory and autoimmune responses. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):978–989. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.11.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Shi Y, Su J, Roberts AI, Shou P, Rabson AB, Ren G. How mesenchymal stem cells interact with tissue immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2012;33(3):136–143. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kim HS, Shin TH, Lee BC, et al. Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells reduce colitis in mice by activating NOD2 signaling to COX2. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(6):1392–1403. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fan H, Zhao G, Liu L, et al. Pre-treatment with IL-1beta enhances the efficacy of MSC transplantation in DSS-induced colitis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2012;9(6):473–481. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2012.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Regmi S, Pathak S, Kim JO, Yong CS, Jeong J-H. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases: challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives. Eur J Cell Biol. 2019. 10.1016/j.ejcb.2019.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Determination of lethal dose of GalN for the induction of FHF. The percentage survival of Balb/c nude mice after intraperitoneal injection of different doses of GalN (1000 mg/kg, 1500 mg/kg, 2000 mg/kg, and 3000 mg/kg) with 20 μg/kg LPS. Figure S2. Serum GOT and GPT level in normal mice before induction of FHF. Figure S3. Gross observation of the liver after 7 h of intraportal delivery of 2D-ADSC and 3D-ADSC1000. Massive infarction was observed throughout the liver after 2D-ADSC delivery. In contrast, minimal infarction was observed in the 3D-ADSC1000 delivered group (the arrows indicate the areas of the infarction). (DOCX 562 kb)
Data Availability Statement
Authors.