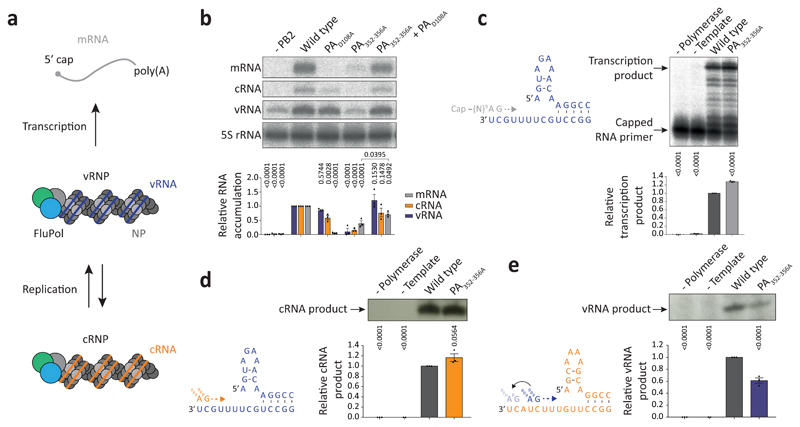
Fig. 2. Mutations at the FluPolA dimer interface inhibit cRNA to vRNA replication.
a, Scheme of transcription and replication by FluPolA in the context of viral ribonucleoproteins (vRNPs). b, vRNP reconstitution assay with the PA352-356A dimer mutant and complementation with the transcription-deficient PAD108A mutant. Data are mean ± s.e.m., n=3 independent transfections. Two-way ANOVA. P < 0.05 is considered significant. mRNA signals for PA352-356A with and without PAD108A were compared by two-tailed unpaired t-test. P < 0.05 is considered significant. c, Effect of the PA352-356A mutation on in vitro transcription by FluPolA primed with a capped RNA primer. Data are mean ± s.e.m., n=3 independent reactions. One-way ANOVA. P<0.05 is considered significant. d, e, Effect of the PA352-356A mutation on in vitro primer-independent replication by FluPolA on a vRNA (d) and cRNA (e) template. Data are mean ± s.e.m., n=3 independent reactions. One-way ANOVA. P < 0.05 is considered significant. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 2.