Mai, C.-L., Wei, X., Gui, W.-S., Xu, Y.-N., Zhang, J., Lin, Z.-J., … Liu, X.-G. (2019). Differential regulation of GSK-3β in spinal dorsal horn and in hippocampus mediated by interleukin-1beta contributes to pain hypersensitivity and memory deficits following peripheral nerve injury. Molecular Pain 2019; 15: 1–12. DOI: 10.1177/1744806919826789
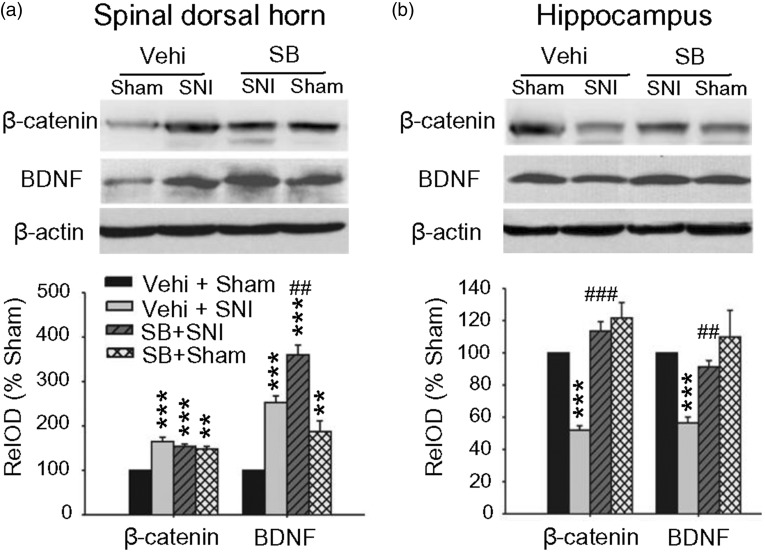
In the above referenced article, Figure 4 should be corrected as shown in the revised version below. This work reported that GSK-3β activity was enhanced in hippocampus and reduced in spinal dorsal horn following SNI, and the opposite changes may underlie memory deficits and chronic pain hypersensitivity. Therefore inhibition of GSK-3β may improve memory but enhance pain. To investigate the underlying mechanisms, the expressions of β-catenin and BDNF were measured in the spinal dorsal horn and in the hippocampus. It was found that β-catenin and BDNF were upregulated in the spinal dorsal horn but downregulated in the hippocampus (Figure 4). During preparation of this manuscript, Figure 4 was redrawn and a mistake was made in the process. In the corrected figure below, bands for BDNF remain the same, and those for β-actin and β-catenin in the hippocampus changed.
The error did not create substantive differences in the results/findings of the paper.