Abstract
Background:
Psychological stress and heightened MC activation are linked with important Immunological disorders including allergy, anaphylaxis, asthma, and functional bowel diseases, but the mechanisms remain poorly defined. We have previously demonstrated that activation of the corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) system potentiates MC degranulation responses during IgE-mediated anaphylaxis and psychological stress, via CRF receptor subtype 1 (CRF1) expressed on MCs.
Objective:
In this study, we investigated the role of CRF receptor subtype 2 (CRF2) as a modulator of stress-induced MC degranulation and associated disease pathophysiology.
Methods:
In vitro MC degranulation assays were performed with bone marrow derived MCs (BMMCs) derived from WT and CRF2-deficient (CRF2−/−) mice and RBL-2H3 MCs transfected with CRF2-overexpressing plasmid or CRF2-siRNA. In vivo MC responses and associated pathophysiology in IgE-mediated passive systemic anaphylaxis (PSA) and acute psychological restraint stress were measured in WT, CRF2−/−, and MC-deficient KitW-sh/W-sh knock-in mice.
Results:
Compared with WT mice, CRF2−/− exhibited heightened serum histamine levels and exacerbated PSA-induced anaphylactic responses and colonic permeability. In addition, CRF2−/− mice exhibited increased serum histamine and colonic permeability following acute restraint stress. Experiments with BMMCs and RBL-2H3 MCs demonstrated that CRF2 expressed on MCs suppresses store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) signaling and MC degranulation induced by diverse MC stimuli. Experiments with MC-deficient KitW-sh/W-sh mice systemically engrafted with WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs demonstrated the functional importance of MC-CRF2 in modulating stress-induced pathophysiology.
Conclusions:
MC CRF2 is a negative, global modulator of stimuli-induced MC degranulation and limits the severity of IgE-mediated anaphylaxis and stress-related disease pathogenesis.
Keywords: Mast cell, corticotropin releasing factor receptor, stress, anaphylaxis, allergy, intestinal permeability
Graphical Abstract
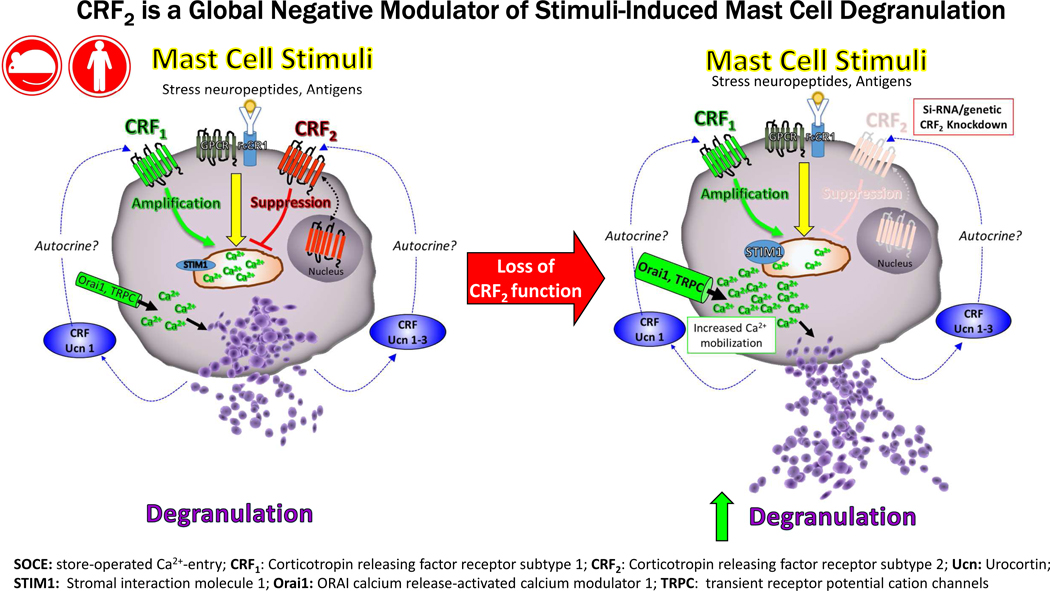
Capsule summary:
Targeting CRF2 and (or) downstream pathways has potential as a new therapeutic approach to limit excessive MC activation and intestinal permeability which initiate and perpetuate highly prevalent and burdensome diseases including allergy, anaphylaxis and functional bowel disorders.
Introduction
Psychological stress has a major influence on immune function and is a risk factor in many immune-related disorders. While numerous studies have investigated the influence of different stress paradigms on immune function and disease susceptibility, the underlying signaling pathways remain to be elucidated. Mast cells have become recognized as important early immune effectors cells in the stress response and stress-related pathophysiology. Mast cells are strategically positioned close to neurovascular units and host-environmental interfaces (e.g. mucosal epithelial barriers) and express a repertoire of receptors to sense and respond rapidly to a continuous array of stress signals from neuroendocrine, immunological and environmental origins. Upon activation, MCs release an array of preformed granule mediators including histamine proteases, and select cytokines via degranulation which trigger rapid and robust physiologic effects such as changes in blood flow, increased endothelial and epithelial permeability, hyper-secretion and immune cell activation and recruitment (1–6). While stress-induced MC degranulation and the associated tissue pathophysiology likely represents an critical host defense strategy to mobilize critical resources for the fight or flight response and enhance immune function, excessive MC activation can be detrimental and has been linked with the onset and severity of diseases including allergy, asthma and IBS (7–11).
The CRF system is well-established as a major stress regulatory system in the body (12) and is composed of a family of peptides related CRF and related family of urocortins (Ucn I-III) which mediate their actions via GPCR’s CRF1 and CRF2. The role of the CRF system has been extensively studied in the CNS with regards to HPA axis regulation and neurobehavioral paradigms (12, 13). More recently, the CRF system has been shown to be highly active in peripheral immunological and infectious challenge conditions (14–17), suggesting an important role in immune function. Comparatively, little known about the role of the CRF system in regulating the function of specific immune cells such as the MC. MCs express both CRF1 and CRF2 (18–20) and can synthesize and release ligands CRF and Ucn (21, 22). Pharmacological stimulation of CRF receptors on human and rodent MCs in vitro was shown to induce canonical GPCR signaling pathways, such as cAMP Ca2+ and pERK, and the selective release of de novo synthesized growth factors and cytokines (18, 19, 23), whereas CRF receptor ligands did not induce degranulation. The in vivo role of MC-expressed CRF receptors has remained elusive; however, we recently demonstrated that CRF1 expressed on MCs acts as a positive modulator of stress-induced MC degranulation and associated tissue pathophysiology in response to anaphylaxis and psychological stress (22). In the present study, we demonstrate that the complementary CRF receptor subtype, CRF2, is a negative modulator of MC degranulation and associated pathophysiological responses to immunological and psychological stressors, thus further supporting a critical homeostatic role for the MC-specific CRF system in mast cell activation and MC-associated diseases.
METHODS
Ethics statement
All protocols were approved by the North Carolina State University (Protocol 09-047B) and Michigan State University’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol 03/15-039-00).
Animals
Founding breeders for all mice strains were obtained from the Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME) and were housed in accordance with guidelines from the American Association for Laboratory Animal Care and Research Protocols. C57BL/6 (Stock no. 000664) and KitW-sh/W-sh mice (Stock no. 012861) used in this study were derived from homozygous breeders. Heterozygous CRF2+/− mice (B6; 129-Crhr2tm1Jsp/J; Stock no. 010842) were purchased and bred to obtain wild-type CRF2+/+ and knockout CRF2−/− mice. The knockout CRF2−/− mice have three exons, which encode for the third intracellular loop of CRF2 cytoplasmic region, replaced with a neomycin resistance cassette as described earlier (24). Standard PCR was used to genotype and confirm WT and CRF2−/− mice and BMMCs confirm both in house and via commercial services (GeneTyper, New York, New York) using PCR protocols published at www.jax.org.
Passive systemic anaphylaxis
Wildtype and CRF2−/− female mice (8 weeks of age) were sensitized by intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) with 20 µg of IgE monoclonal anti-dinitrophenyl in 100 µl PBS. The following day, mice were challenged with 1 mg of DNP in 100 µl PBS (i.p.). The mice were constantly observed and rectal body temperature recorded for 0, 15, 30, 60 and 120 minutes post DNP challenge (TH-5 Thermalert, Physitemp, Clifton, NJ). Mice were sacrificed at 0 min and 30 min post-DNP injection for serum collection via cardiac puncture and stored at −80⁰C until serum histamine level was quantified using a commercial EIA kit (Oxford Biomedical Research). Antalarmin experiments: PSA was performed as indicated above with the additional treatment group of antalarmin-treated CRF2−/− mice. Antalarmin (15 mg/kg) was injected (i.p.) in to male mice 15 minutes prior to DNP challenge. Mice were sacrificed 30 min post-DNP injection and plasma was collected via cardiac puncture for later histamine analysis.
Histamine measurements
Histamine concentrations were quantified in serum, plasma, and in cell pellets and supernatants from stimulated MC cultures with a histamine EIA kit (Oxford Biomedical Research, Rochester Hills, MI).
Quantification of tissue mast cell numbers
Small intestinal mesentery windows from wildtype and CRF2−/− mice were whole mounted on glass slides and fixed with Carnoy’s fixative and stained with Toulidine blue as described previously (25). The heart and ear from the same mice were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde embedded in paraffin, deparaffinized sections were stained with Toluidine blue. Toluidine blue stained mast cells were counted in five, non-overlapping microscopic fields at a magnification of 400x. Each filed contained tissue sections that filled the entire hpf. Mesentery mast cells were counted in at least six mesenteric widows per mouse (n=4/genotype). Prior to performing tissue counts, each slide was coded so that counts were performed in a blinded manner. The average number of mast cells per high power field (hpf) was then calculated for each tissue and within each genotype.
White Blood Cell Differential Count
Blood was collected via cardiac puncture from wildtype and CRF2−/− female mice and placed into EDTA-treated tubes (Microvette, Nümbrecht, Ger many). Blood smears were performed followed by a differential white blood cell count (# basophils/100 WBCs).
Ussing chamber studies
Distal small intestine (ileum) was harvested from each mouse immediately after euthanasia and opened along the anti-mesenteric border. The intestinal mucosa was stripped from the seromuscular layer in oxygenated (95% O2, 5% CO2) Ringer solution (in mmol/l: 154 Na+, 6.3 K+, 137 Cl−, 0.3 H2PO4, 1.2 Ca2+, 0.7 Mg2+, 24 HCO3−; pH 7.4) and mounted in 1.13 cm2 aperture Ussing chambers (World Precision Instruments, Inc., Sarasota, FL). Ileal mucosa was bathed on the serosal and mucosal sides with 10 ml Ringer’s solution. The serosal bathing solution contained 10 mM glucose, which was osmotically balanced on the mucosal side with 10 mM mannitol. Bathing solutions were oxygenated (95% O2, 5% CO2) and circulated in water-jacketed reservoirs maintained at 37°C. The spontaneous potential difference (PD) was measured using Ringer-agar bridges connected to calomel electrodes, and the PD was short-circuited through Ag-AgCl electrodes using a voltage clamp that corrected for fluid resistance. Tissues were maintained in the short-circuited state, except for brief intervals to record the open-circuit PD. Transepithelial electrical resistance (TER, measured as ×cm2) was calculated from the spontaneous PD and short-circuit current (Isc), as previously described(26). After a 30-min equilibration period on the Ussing chambers, TER was recorded at 15 min intervals over a 1-h period and then averaged to derive the basal TER values for a given animal. After a 30 min equilibration period on Ussing chambers, FD4 (Sigma, 100 mg/ml) was added to the mucosal bathing reservoir of the Ussing chambers. After a 15 min equilibration period, standards were taken from the serosal side of each chamber and a 60 min flux period was established by taking 0.5 ml samples from the mucosal compartment. The quantity of FD4 was established by measuring the fluorescence in mucosal reservoir fluid samples in a fluorescence plate reader at 540 nm. Data are presented as the rate of FD4 flux in ng FD4.min.cm2
Culture of bone marrow derived mast cells (BMMCs) and RBL-2H3 cells
Bone marrow cells derived from female WT and CRF2−/− mice of approximately 4–6 weeks of age. Isolated bone marrow progenitor cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 media (with L-glutamine) supplemented with FBS (10%), sodium pyruvate (1 mM), MEM nonessential amino acids (1X), HEPES buffer (10 mM), penicillin (100 U/ml) and streptomycin (100 µg/ml) and recombinant cytokines [stem cell factor (5 ng/ml) and interleukin-3 (5 ng/ml)]. After four weeks, cultures comprised mainly of mast cells (93%) as determined by toluidine blue (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) staining, and flow cytometry analysis (BD LSR II, East Lansing, MI) using fluorescently labeled c-Kit (Biolegend, San Diego, CA), high-affinity IgE receptor (FcƐRI) antibodies (eBioscience, San Diego, CA) and CRF2 anti-Rabbi. Media and supplements were purchased from Corning Cellgro (Manassas, VA) and recombinant cytokines from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). The rat basophilic leukemia cell MC line (RBL-2H3) were grown in MEM media with 10% fetal bovine.
Confocal immunofluorescence staining
BMMCs and peritoneal mast cells were obtained from 8 week old female c57Bl/6 mice as previously described (25). Cells were pelleted, washed once with 1x PBS, cytospun onto slides, and fixed with 4% PFA for 20 minutes at 4°C. Slides were blocked at room temperature for 1 hour with blocking buffer (10% normal donkey serum, 0.3% Triton X-100) in 1x PBS, permeabilized (0.1% triton x100), and incubated with goat anti-CRF1 (Novus Biologicals, NBP1–00175) and rabbit anti-CRF2 (Novus Biologicals, NBP100–56485) in dilution buffer at a concentration of 1:100 diluted in 1% BSA in a humidified chamber overnight at 4⁰C. Slides were washed three times for five minutes and then incubated in with anti-rabbit-Cy3 and anti-goat-FITC secondary antibodies in dilution buffer (1:300) for 1 hour at room temperature in the dark. Slides were washed three times for 5 minutes with 1x PBS and ProLong Diamond Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Thermo Fisher, P36971) was added prior to being cover-slipped. Confocal images were obtained with Olympus FV 1000 confocal laser scanning microscope, (Olympus America, Center Valley, PA).
β-Hex assay
RBL 2H3 cells or murine BMMCs (2×10 6 cells/ml) were sensitized overnight at 37°C with 1 µg/ml anti-dinitrophenyl (DNP)-IgE (Sigma-Aldrich) in complete RPMI medium with cytokines. The following day cells were washed and resuspended in Tyrode’s buffer and BMMCs were seeded in a 96 well plate (0.45×10 6 cells/well). The cells were equilibrated for an hour and stimulated with indicated concentrations of dinitrophenyl-albumin (DNP) (Sigma-Aldrich) for 1 h at 37°C. For A23187 and c48/80 stimulation, unsen sitized BMMCs were stimulated for 1 h. β-Hex activity was measured by addition of p-nitrophenol-N-acetyl-α-D-glucosaminide in 0.1 M sodium citrate (pH 4.5) for 1 hour at 37°C. The r eaction was terminated with 0.1 M carbonate buffer (pH 10.0) and the absorbance was recorded at 405 nm. The percent degranulation was calculated by dividing optical absorbance of the supernatant by the sum of optical absorbance by the supernatant and cell pellet (lysed with 0.1% Triton X-100) and multiplying by 100.
CRF2 over-expression and knockdown in RBL-2H3 MCs
Lenti ORF clone of CRF2 (CRHR2), transcript variant 1, and mGFP tagged plasmid were obtained from Origene (Rockville, MD) (Cat No: RG222881). CRF2 shRNA clone (MSH028936-LVRU6MH) were purchased from GeneCopoeia (Rockville, MD). DH5 alpha competent cells were obtained from Invitrogen (Cat no: 18265017) and the plasmids were transfected and plated on selective antibiotic resistance LB plates according to the manufacturers protocol. After overnight incubation at 37⁰C, a single colony was picked for each individual clones and inoculated on 2.5 ml LB media containing antibiotics and kept for 8 hours at 37⁰C at 200 rpm. A total of 600 µl of culture inoculum was transferred in to 300 ml of LB broth on a sterile 1 L flask with antibiotics and kept at 200 rpm at 37⁰C overnight. Plasmid was extracted and the concentration was measured according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Qiagen Cat No: 12662).
Human embryonic kidney cell 293Ta lentivirus cells were seeded at a concentration of 1.5×106 cells per well (6 well) and 2.5 µg of CRF2 over-expressed or CRF2 shRNA along with respective control eGFP or Scrambled shRNA plasmid control DNA were transfected using Lentiviral packaging kit (Origene Cat No: TR30022) according to manufacturer’s protocol. After overnight incubation at 37⁰C with 5% CO2, the transfection media was replaced with normal 5% DMEM media with polybrene (1 µl of 4 mg/ml). 48h after transfection, the supernatant was collected from the 6 well plate and filtered onto a Nalgene ultracentrifuge tube and 5 ml of 20% sucrose was added into the bottom of the tube. Centrifuged at 25,000 rpm for 2 hour at 4⁰C and the supernatant was discarded and the lentiviral over-expressing CRF2 plasmid or CRF2 shRNA, pellet was re-suspended with 150 µl of 4% lactose and kept on ice for 15 min and centrifuged at a high speed for 1 min. Lentiviral aliquots were stored at −80⁰C until transfection.
Lentivirus tittering was done and RBL-2H3 at a concentration of 2.5×105 cells were plated on a 12 well plate and grown over night. Lentivirus over expressing CRHR2 or CRF2 shRNA plasmid at MOI of 40 and polybrene at a final concentration of 8 µg/ml was added in to each well and centrifuged the plate at 300 g for 60 min at 30⁰C. The plate was incubated at 37⁰C for overnight and the media was replaced with 15% MEM. After 48 h of transfection, the cells were trypsinized and transferred onto T75 flasks. The RBL-2H3 over expressing CRF2 or CRF2 shRNA tagged with GFP (CRF2 Over expressed) or mCherry (CRF2 shRNA) were sorted on the flow cytometry (Becton Dickinson FACSAria II, UNC, Chapel Hill, NC) based on the GFP or mCherry positive cells and multiplied and the RBL-2H3 cell aliquots were stored at liquid nitrogen for further study.
CRF2 siRNA knockdown in RBL-2H3 cells
Overnight grown RBL-2H3 cells were seeded at a concentration on 5×105 in a 6 well plate were transfected with CRF2 siRNA (NM-022714, sigma) or scrambled siRNA (SIC00–1, sigma) of 150 ng using Qiagen Hi-perfect transfection reagent according to its manufacturer’s protocol. Six hours post transfection normal growth media added to each well and incubated at 37°C with 5% CO 2 for 48 hour. After the incubation, transfected cells were primed with over-night IgE or not and stimulated with 1 hour DNP or A23187 (non IgE primed) and the β hexosaminidase, histamine and calcium mobilization assay was done as described above.
Human mast cell experiments with LAD2 cells
LAD2 cells provided by A. Kirshenbaum (NIH, USA) were cultured in StemPro-34 (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) media supplemented with StemPro-34 Nutrient Supplement ((Life Technologies) l-Glutamine (2 mM) ((Life Technologies), Penicillin (100 U/ml)/Streptomycin (100 µg/ml) and rhSCF (Peprotech Inc., Rocky Hill, NJ) (100 ng/ml). Cell density was kept below 0.5 × 106/ml. and half the amount of media was replaced weekly. Cells were sensitized overnight with 100 ng/ml biotinylated human IgE (US Biologicals). On the following day, cells were washed with Tyrode’s buffer to remove excess IgE and stimulated with (vehicle, 0.1% BSA in PBS), streptavidin (100 ng/ml), and 1–100 nM of human Astressin 2B (A2B) (kind gift from Jean Rivier, The Salk Institute, La Jolla, CA). Release of β hexosaminidase was measured after 1 hour of stimulation as described above.
RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from heart tissue and BMMCs using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) followed by DNase treatment and purification using the PureLink RNA mini kit (Life Technologies). cDNA was synthesized and amplified using the SuperScript® III One-Step RT-PCR System with CRF2 specific primers (5′-TCGGGCAGGGTAGGACAG-3′ and 5′-CGGGCAGACGGTGACAGA-3′) designed to include the full mouse CRF2 coding region (Sztainberg et al., 2009). Total RNA was isolated from RBL-2H3 cells using Qiagen RNAeasy kit and transcribed to cDNA using the Maxima First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). CRF2 expression was determined using CRF2 specific primers (Forward Rat 1_Crhr2: ACTCTACTATGAGAATGAGCAG and Reverse Rat 1_Crhr2: TGACGATGTTGAACAGAAAC; Sigma-Aldrich).
Intracellular Ca2+ measurements
RBL-2H3 cells and murine BMMCs derived from WT and CRF2−/− mice were used for this study. On the day of the experiment, cells were washed and re-suspended in calcium assay buffer. Changes in intracellular calcium in response to stimulus were detected using the Fluo 4 NW Calcium assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were loaded at 37 °C for 30 min with the fluorescent Ca2+ indicator, Fluo 4 NW, in the presence of Probenecid, followed by incubation at room temperature for another 30 min. Changes in fluorescence was measured by stimulating the cells by adding different concentrations of DNP/HSA or A2187 or c48/80. Change in fluorescence was measured using the FDSS/µCELL kinetic plate reader (hamamatsu) or Fluoroskan Ascent FL microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 480 nm excitation and 540 nm emission. The ratio was calculated by average increase in fluorescence divided with the baseline was determined for each time point after the addition of stimulus.
Store operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) channel expression
BMMC lysates were prepared by re-suspending cells in RIPA buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 4°C. Lysates were sonicated and centrifuged at 21,000 x g for 10 min. The protein concentration was measured using DC Protein Assay Kit (Bio-Rad). Cellular proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. The membranes were blocked with 5% w/v BSA in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) with 0.1% Tween 20 (TBS-T) for 1 hour at room temperature, washed in TBS-T, incubated with the following Rabbit Anti-Human antibodies: STIM1 (alomone labs #ACC-063;1:500 dilution), Anti-TRPC1 (alomone labs #ACC-010;1:600 dilution), Anti-Orai1 (alomone labs #ACC-060;1:400 dilution), and β-actin (cell signaling, 4970, 1:1000) diluted in 5% w/v BSA in TBS-T for overnight at 4°C or 2 hours at room temperature, and then washed with TBS-T. Subsequently, the membranes were incubated with rabbit polyclonal secondary antibody (cell signaling 7074; 1:2000) for 1 hour at room temperature, washed with TBS-T and incubated in SuperSignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Bands were visualized with ChemiDoc MP Imager (Bio-Rad Laboratories) and the Image Lab software (version 4.1) was used for densitometric analysis.
Restraint stress model
Female mice were placed in individual transparent 50 ml plastic conical tubes, modified with air holes, for a 3 h period. Control mice remained in their original home cages for 3 h without food and water to avoid confounding effects of water or feed intake during the 3 h experimental period. Following RS, mice were immediately euthanized by CO2 inhalation, and serum and ileal mucosa were collected for measurement of serum histamine and intestinal permeability, respectively.
BMMC engraftment in KitW-sh/W-sh mice
Female KitW-sh/W-sh mice (8–10 weeks of age) were injected intraperitoneally with 1×107 BMMCs (suspended in 200 µl of sterile 1x PBS) derived from CRF2+/+ (WT) or CRF2−/− mice. At 16 weeks of age (4 weeks post-engraftment), engrafted mice were sacrificed by CO2 inhalation. Intestinal mesentery window sections were harvested fixed in Carnoy’s fixative and stained with Toluidine blue to confirm engraftment of BMMCs.
Statistical analysis
In vivo and in vitro studies are presented as means ± SE from a representative experiments with an n=6–8 animals/treatment group (unless otherwise specified). Experimental results were repeated in a minimum of 2 independent experiments while some experiments were repeated in greater than 2 independent experiments (noted in figure legends). Comparisons between multiple experimental groups was performed using a 1 or 2-Way ANOVA where appropriate with a Tukey’s post-test. Comparisons between two treatments were analyzed using an unpaired two-tailed t test. Values of p<0.05 were considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses and calculations were performed using GraphPad Prism 5 software (San Diego, CA, USA).
RESULTS
CRF2-deficiency exacerbates PSA-induced mast cell degranulation, anaphylaxis and intestinal permeability
To first define the role of CRF2 in MC-associated disease in vivo, we compared MC responses and associated pathophysiology in a MC-dependent model of PSA. Compared with WT mice, CRF2−/− mice exhibited higher (by 4.1 fold) serum histamine levels, measured at 30 min post-PSA challenge (5017 ± 919 ng/ml and 1208 ± 235 ng/ml in CRF2−/− and WT mice, respectively, P<0.001, Fig. 1A). In agreement with serum histamine levels, CRF2−/− mice exhibited a greater peak reduction in body measured at 30 minutes post-DNP challenge (∆−4.55±0.85°C and ∆−6.8±0.54°C in WT and CRF 2−/− mice, respectively, P=0.04, Fig. 1B). Measurement of cardiac blood volume reduction, an index of systemic vasodilation and fluid extravasation induced by PSA (27, 28), was also greater in CRF2−/− mice at 30 and 120 min post-DNP challenge, compared with WT mice (Fig. 1C), thus indicating a more severe hypovolemic shock response in CRF2−/− mice. Intestinal permeability, measured as increased FD4 flux rate and reduced TER across ileal mucosa mounted on Ussing chambers, was Greater in CRF2−/− mice compared with WT mice 120 min post-PSA (Fig. 1D, E). Quantification of tissue MCs by Toluidine blue staining of heart, intestinal mesentery and skin showed that WT and CRF2−/− mice had similar distributions and numbers of tissue MCs (Fig. 1F-H). Further, circulating basophil numbers were similar between WT and CRF2−/− confirming that elevated histamine levels in CRF2−/− mice, were not due to increased basophil numbers. Given that many mast cell-dependent diseases exhibit a female sex bias and our previous studies demonstrating sex differences in mast cell responses (25), we also compared the influence of CRF2 deficiency on PSA-induced serum histamine responses in female and male mice. These studies confirmed our previous research showing that females exhibit a greater release of serum histamine compared with males, CRF2−/− deficiency exacerbated serum histamine responses in both female and male mice (Supplemental Fig 1). Therefore, we conducted subsequent experiments in predominantly in female mice. Together, these experiments revealed a significant in vivo role for CRF2 in IgE-mediated MC degranulation, anaphylaxis and intestinal permeability.
FIG 1. CRF2 deficiency exacerbates passive systemic anaphylaxis and intestinal permeability.
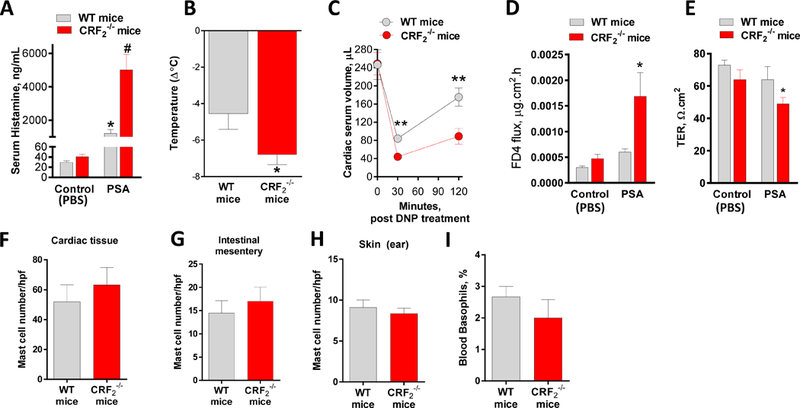
Wild type (CRF2+/+) and CRF2−/− female mice (6–8 weeks of age) were sensitized systemically overnight with IgE and challenged with either PBS vehicle (Control) or anti-IgE DNP to induce passive systemic anaphylaxis (PSA). A: Serum histamine levels were measured at 30 min post-vehicle or DNP challenge. B: rectal temperature was recorded at 0 and 30 min and the change in body temperature was calculated and presented as ∆ °C. C: Cardiac blood volume was measured at 0, 30 and 120 min post DNP challenge. D, E: 120 min post-DNP challenge, ex vivo colonic permeability was measured on Ussing chambers as FD4 flux rate (D) and TER (E). F-H: Tissues from WT and CRF2−/− mice were fixed and stained with Toluidine blue and mast cell counts were performed and presented as mast cells/hpf. G: blood basophils were counted in blood smears and expressed at the % of basophils/100 WBCs. Data are means ± SEM from a representative experiment with n=6 animals per group. Experiments were repeated in n=6 (serum histamine, body temperature) or 2 (cardiac volume, mast cell and basophil counts) independent replicates. #,* symbols differ by p<0.05 using a 1-Way ANOVA (A, D); Different asterisks indicate significance determine by unpaired two-tailed t-test (B, C, E),*p<0.05, **p<0.01.
CRF2 expressed on MCs is a negative modulator of MC degranulation
Corticotropin releasing factor receptors are widely expressed in numerous cell types, including MCs (20, 29, 30), but little is known regarding the localization or functional role of CRF2 in MC function. Using confocal microscopy, CRF2 was found to be localized to the both the surface and intracellularly in BMMCs and peritoneal (tissue) mast cells (Fig. 2). Further, a nuclear staining pattern of CRF2 was also observed predominantly in BMMCs compared PMCs. Flow cytometry confirmed the surface expression of CRF2 in BMMCs (Supplemental Fig. 2G). CRF1 showed a different pattern of expression with a predominant surface localization in PMCs and BMMCs with some intracellular staining was observed mostly in BMMCs. To explore the functional role of MC CRF2−/−, we conducted in vitro degranulation assays with BMMCs derived from WT and CRF2−/− mice. In line with in vivo PSA studies, CRF2−/− BMMCs exhibited exacerbated degranulation responses measured as enhanced β-hex release following IgE-FcƐR1 cross-linking (Fig. 3A). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed a more activated appearance of CRF2−/− BMMCs following IgE/DNP, compared with WT BMMCs, thus supporting β-hex data (Fig. 3D). To determine whether the exacerbated MC degranulation responses observed in CRF2−/− BMMCs were specific to IgE-FcƐR1-mediated pathways, WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs were also stimulated with non-IgE dependent MC stimuli including the c48/80, which acts via the G-protein coupled receptor, Mrgpb2 (31), and A23187, which acts on downstream SOCE mechanisms from intracellular (e.g. endoplasmic reticulum, ER) and extracellular stores (32). Similar to IgE stimulus, CRF2−/− BMMCs exhibited exacerbated β-hex release in response to both A23187 and c48/80 (Fig. 3 B, C). Because our previous work demonstrated that CRF1 potentiates stimuli-induced mast cell degranulation (22), we investigated whether enhanced degranulation in CRF2−/− BMMCs could be due to a reciprocal upregulation of CRF1 expression. Quantitative PCR showed that compared with WT BMMCs, CRF2 expression was down-regulated in CRF2−/− BMMCs (by ~ 40%) but CRF1 expression was not significantly altered (Supplemental Fig. 3 A,B). It should be noted that because the loss of CRF2 activity in CRF2−/− BMMCs (derived from CRF2−/− mice) is a result of a functional deletion of a c-terminal region, CRF2 is still expressed as shown in Supplemental Fig. 3A, but at a lower level than WT BMMCs. There were no significant differences between WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs with regards to the cellular content of β-hex content or phenotype determined by c-kit/FcƐR1 expression by flow cytometry analysis (Supplemental Fig. 2), confirming that enhanced degranulation in CRF2−/− BMMCs were not due to an increased intracellular granule mediator content or aberrant MC phenotype.
FIG 2. Localization of CRF1 and CRF2 in BMMCs and peritoneal mast cells.
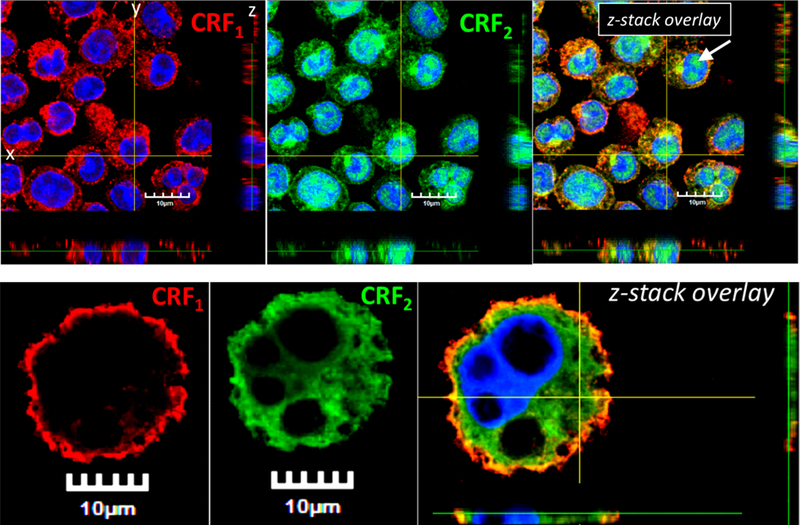
CRF1 (Cy3 Red) and CRF2 (FITC Green) nuclei (DAPI blue). z-Stack overlay images show a single plane cross section through horizontal plane (XY), sagittal plane (YZ), and coronal plane (XZ). Panels A-C) murine BMMCs. Panels D-F) PMCs. White arrow indicates the nuclear staining pattern of CRF2 (Panel C).
FIG 3. Genetic deficiency and overexpression of CRF2 induces divergent effects on stimuli induced MC degranulation. A:
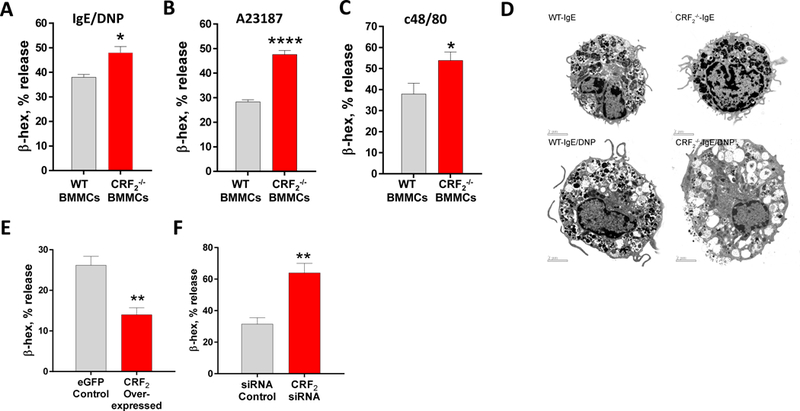
β-hex % release from IgE-sensitized WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs stimulated with DNP (32 ng/mL). B, C: β-hex release from WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs stimulated with A23187 (B) and c48/80 (C). D: Transmission electron microscopy analysis of WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs stimulated with IgE/DNP. E,F: β-hex release from RBL-2H3 MCs transfected with CRF2-overexpressing plasmid or eGFP control or CRF2-siRNA. Data are means ± SEM from a representative experiment with n=3 (bone marrow donors) per group. Experiments were repeated in n=6 (A-C) or 2 (E-F) independent replicates. *Significance between groups was determined by an unpaired two-tailed t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001
To further examine the link between CRF2 expression on MCs and degranulation responses, we transfected CRF2-plasmid into RBL-2H3 MCs to enhance CRF2 expression. We confirmed the specificity of the CRF2-over expression by qPCR which revealed and upregulation of CRF2 expression (by 6.4 Fold; Supplemental Fig. 3C) compared with the empty GFP (eGFP) plasmid, while having no significant effect on CRF1 expression (Supplemental Fig. 3D). CRF2 over-expressed RBL-2H3 MCs exhibited suppressed IgE/DNP-mediated β-hex release (by 47%), compared with empty plasmid controls (Fig. 3E). We also knocked down CRF2 expression in RBL-2H3 MCs with CRF2-directed siRNA, which resulted in a 2-fold increase in β-hex release following IgE/DNP stimulation, compared with scrambled siRNA controls (Fig. 3F). Pharmacological inhibition of CRF2 with the selective antagonist Astressin 2b (A2B) enhanced IgE-FcƐR1-induced β-hex release in both rat RBL-2H3 and human LAD2 MCs (Fig. 5), thus confirming the genetic experiments and translational significance to human MCs.
FIG 5. CRF2−/− BMMCs exhibit exacerbated Ca2+ mobilization responses to diverse mast cell stimuli.
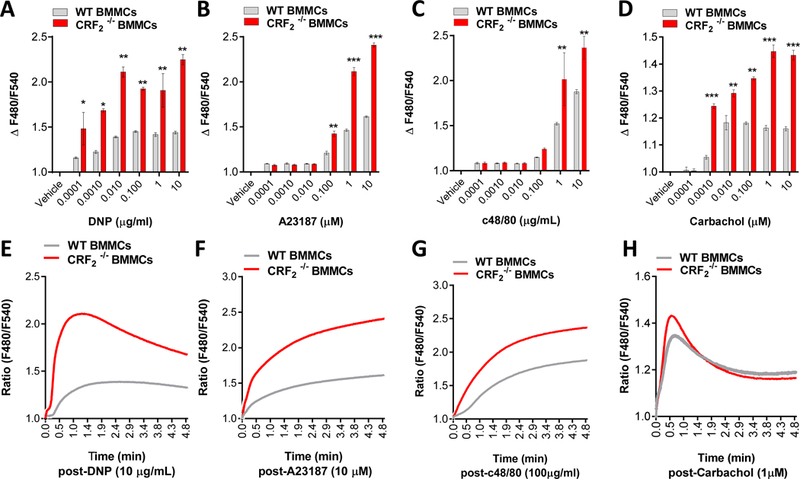
Murine BMMCs from female mice were loaded with Fluo 4 Ca2+ indicator and stimulated with indicated MC degranulation stimuli as described in the Material and Methods Section. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization (presented as ∆F480/F540 or as representative traces) in response to indicated concentrations of IgE/DNP (A,E), A23187 (B,F) and c48/80 (C,G) and Carbachol (D,H). Data shown are the means ± SE and are representative of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. Data were analyzed using a 1-way ANOVA *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001.
Given our previous work showing that MC CRF1 potentiates MC degranulation while in the present study CRF2 suppresses MC degranulation, we hypothesized that MC CRF1 and CRF2 might function in concert to regulate or balance MC degranulation responses. To test this hypothesis, we pre-treated CRF2−/− mice with the CRF1 selective antagonist Antalarmin followed by induction of IgE-mediated PSA. Antalarmin significantly attenuated the exacerbated PSA-induced histamine release in CRF2−/− mice (Supplemental Fig. 4).
CRF2 negatively regulates SOCE in MCs
We next explored the mechanism by which CRF2 caused suppression of stimuli-induced MC degranulation. Because CRF2 was shown to negatively modulate MC degranulation induced by diverse MC stimuli that utilize upstream, receptor-dependent pathways (IgE-FcεR1, and c48/80) or downstream, receptor-independent pathways (A23187) mechanisms, we hypothesized that CRF2 was targeting a common downstream signaling mechanism utilized by MC degranulation stimuli. SOCE from intracellular (endoplasmic reticulum and golgi) and extracellular stores is essential for MC granule exocytosis and degranulation (33). Therefore, we conducted Ca2+ mobilization experiments with WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs loaded with the Fluo 4 Ca2+ indicator dye. These experiments showed that CRF2−/− BMMCs exhibited heightened IgE/DNP Ca2+ mobilization following IgE/DNP stimulation (Fig. 5). Furthermore, CRF2−/− BMMCs also exhibited heightened Ca2+ signaling in response to other MC stimuli including A23187, c48/80 and the muscarinic 3 receptor agonist carbachol (Fig. 5) overall demonstrating the global inhibitory role of CRF2 in response to diverse MC stimuli.
We next conducted similar experiments in Ca2+-replete or Ca2+-free conditions (1 mM EDTA) to determine whether the heightened Ca2+ signaling in CRF2−/− BMMCs was due to enhanced release from intracellular stores such as the ER or via influx of extracellular Ca2+ via plasma membrane channels. As anticipated, removal of extracellular Ca2+ with EDTA significantly reduced Ca2+ signals induced by IgE/DNP in both WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs (Fig. 6A, B). However, EDTA did not ablate the heightened Ca2+ signaling in CRF2−/− BMMCs, compared with WT BMMCs (Fig. 6B, C) indicating heightened Ca2+ release from intracellular stores in CRF2−/− BMMCs. CRF2−/− BMMCs also exhibited increased expression of SOCE channels including the ER Ca2+ sensor stromal interacting molecule-1 (STIM1), and plasma membrane channels transient receptor potential canonical-1 (TRPC1) and Orai1 (Fig. 6D-I). Together these data indicate that CRF2 is a negative and global modulator of stimuli-induced Ca2+ signaling with actions on intracellular release and subsequent extracellular Ca2+ entry.
FIG 6. CRF2−/− BMMCs exhibit heightened intracellular Ca2+ store release and expression of SOCE channels.

BMMCs derived from WT and CRF2−/− mice were loaded with Fluo 4, and intracellular Ca2+ levels were measured following stimulation with IgE/DNP. A,B: Representative intracellular Ca2+ traces for experiments conducted under Ca2+-replete (A) or Ca2+-free (1 mM EDTA; B) conditions. C: Mean peak change in fluorescence following IgE/DNP stimulus presented as ∆ peak fluorescence. D-I: Representative Western blots and densitometry analysis for STIM1 (D, G), TRPC1 (E, H), and Orai (F, I) in WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs. *Significance between groups was determined by an unpaired two-tailed t-test (C, G-I),*p<0.05, **p<0.01.
CRF2−/− mice exhibit elevated serum MC histamine and intestinal permeability in response to acute restraint stress
In vitro MC culture experiments revealed that MC CRF2 exerted suppressive effects on MC degranulation induced by a diverse array of potent MC stimuli. Given these findings, we hypothesized that the global effects of CRF2 on MC degranulation, would extend to non-IgE-dependent in vivo models of MC degranulation. To test this hypothesis, we compared MC degranulation responses, via measurement of serum histamine levels, in WT and CRF2−/− mice following a 1-hour period of psychological restraint stress. Compared with WT mice, CRF2−/− mice exhibited higher serum histamine levels following restraint stress (97.7 ± 5.9 ng/ml and 68.2 ± 7 ng/ml in CRF2−/− and WT mice, respectively, P<0.01, Fig. 7A). We also assessed colonic permeability measured as FD4 flux rates on Ussing chambers, which showed a significantly elevated FD4 flux rate in CRF2−/− mice following restraint stress, compared with WT mice. (Fig. 7B). Together, these data indicate that CRF2 plays a global role in controlling MC degranulation and associated tissue pathophysiology induced by diverse stressors.
FIG 7. CRF2−/− mice exhibit heightened serum histamine levels and intestinal permeability following acute restraint stress.
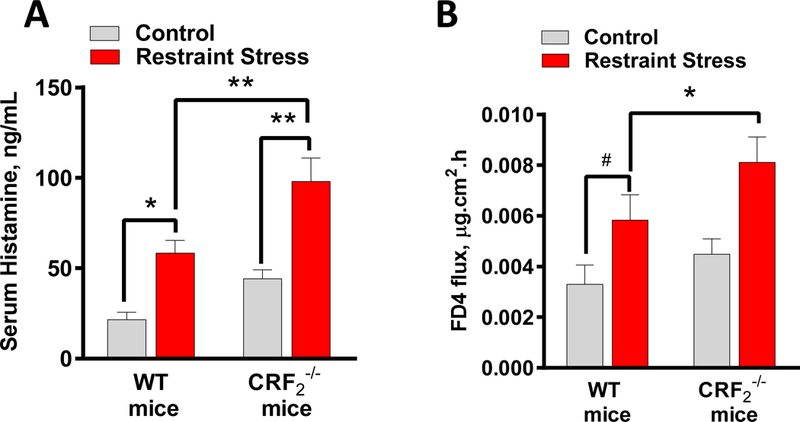
Wild type and CRF2−/− mice female mice (8–10 weeks of age) underwent 1 h of restraint stress or housed under normal cage conditions (Control) as described in Materials and Methods. Serum histamine (A) and colonic permeability (B) was measured by ELISA following 1 h of restraint stress. Data are means ± SEM (n=8 mice/group). Data were analyzed using a 2-way ANOVA, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, #P=0.07.
MC CRF2 is a negative modulator of stress-induced intestinal permeability
The above experiments demonstrated an important role for CRF2 as a negative modulator of MC-dependent intestinal permeability induced by PSA and restraint stress. Further, in vitro experiments demonstrated the role of MC-specific CRF2 in the control of stimuli-induced mast cell degranulation. We next determined the in vivo significance CRF2 expressed on MCs utilizing a MC knock-in model. MC-deficient KitW-sh/W-sh mice were systemically engrafted with BMMCs derived from either WT or CRF2−/− mice. Twelve weeks post-engraftment, mice underwent 3 h of restraint stress and colonic permeability was measured in Ussing chambers. Compared with KitW-sh/W-sh mice engrafted with WT BMMCs, CRF2−/− engrafted mice exhibited the greater colonic permeability responses, measured as FD4 flux rates (Fig. 8A). WT and CRF2−/− mice exhibited similar reductions in colonic TER following restraint stress (Fig. 8B). Toluidine blue staining and MC counts in intestinal mesenteric tissue confirmed an equal engraftment rate between WT and CRF2−/− BMMCs in MC-deficient KitW-sh/W-sh mice (Fig. 8C).
FIG 8. CRF2 expressed on mast cells is a critical modulator of stress-induced intestinal permeability.
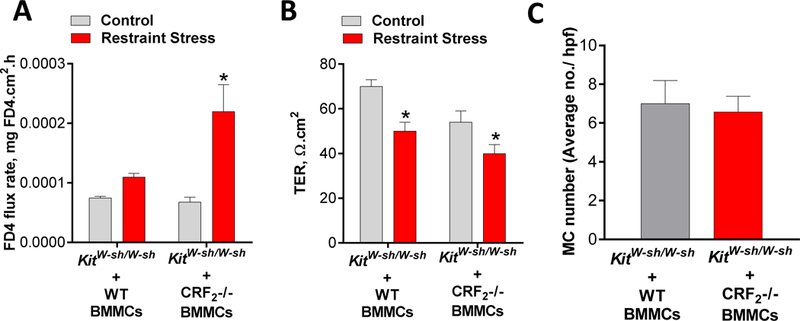
Mast cell deficient KitW-sh/W-sh mice were engrafted with BMMCs derived from WT or CRF2−/− mice. Twelve weeks post-engraftment, mice were exposed to restraint stress (RS) for 3 hours. FD4 flux rate (A) and TER (B) measured from colon mounted on Ussing chambers from WT and CRF2−/− BMMC-engrafted KitW-sh/W-sh mice. C: MC numbers, determined with Toluidine blue staining in intestinal mesenteric windows from WT and CRF2−/− engrafted KitW-sh/W-sh mice. Data are means ± SEM (n=8 mice/group). Experiments were repeated in two independent studies. Data were analyzed using a 2-way ANOVA,*p<0.05.
DISCUSSION
Stress is an important risk factor in the clinical onset and severity of important immunological disorders including allergy, asthma and functional and inflammatory GI disorders. Mast cells (MCs) play a central role in many immunological disease and have gained recognition as a critical immune effector cell in the stress response. Mast cells are rapidly activated (within minutes) of exposure to diverse stressors including psychological, chemical and physical stressors resulting in the release of preformed granule mediators (e.g. histamine, proteases, TNF, etc.) via degranulation. Released MC mediators evoke profound physiologic effects in local and systemic tissues such as increased epithelial and endothelial permeability, neuronal activation and circulatory changes. While stress-induced MC activation likely represents an early defense or alarm mechanism to mobilize resources necessary for the individual to response appropriately to the stressor, excessive or prolonged MC activation is harmful leading to immune dysregulation and tissue damage and exacerbation of disease. While the major mast cell stimuli have been identified; how environmental factors such as stress play a role in exacerbating or limiting MC activation remain poorly understood. Here we demonstrated a novel function for CRF2 expressed on MCs as a negative modulator of stimuli induced MC degranulation and MC-dependent pathophysiology associated with anaphylaxis and acute psychological stress.
Previous studies conducted in vitro with human and rodent MCs demonstrated that MC express both CRF1 and CRF2 receptors (22, 23) and that CRF receptor ligands can induce canonical GPCR pathways including cAMP and phoshoERK signaling (19, 22, 34). However, the precise role of the MC CRF system modulating MC function and MC-mediated disease pathogenesis has remained elusive. We recently demonstrated that CRF1 receptor signaling in the MC is a potentiator of stimuli-induced MC degranulation and system and intestinal pathophysiology induced by PSA and psychological restraint stress (35). In the present study, our data revealed that, in contrast to CRF1, CRF2 exerts inhibitor actions on MC degranulation as loss of CRF2 activity in in MCs, via genetic or pharmacological approaches, resulted in enhanced stimuli-induced MC degranulation and exacerbated responses to PSA and acute restraint stress. Selective inhibition of CRF1 was shown to reduce PSA-induced MC responses in CRF2−/− mice to the level of WT mice, overall indicating that MC CRF1 and CRF2 act in concert to up- and downregulate, respectively the tone of MC degranulation and resultant MC-dependent pathophysiology. Therefore, it is plausible that a disruption of MC CRF1 and CRF2 homeostasis could shift the balance between hypo- and hyper-activated MC states and ultimately disease activity.
The broad inhibitory actions of CRF2 on multiple MC degranulation stimuli and in vivo models led us to hypothesize that CRF2 was targeting a common, downstream mechanism in MC degranulation. Results from the present study demonstrated that MC CRF2 expression was negatively associated with Ca2+ mobilization induced by a diverse array of MC stimuli including IgE-antigen, c48/80 and the muscarinic receptor 3 agonist carbachol. The ability of CRF2 to inhibit Ca2+ mobilization and degranulation provides supporting evidence that CRF2 serves as a global regulation of MC activation. Experiments conducted under Ca2+-free conditions, further demonstrated that CRF2 negatively modulated cytosolic Ca2+ entry from intracellular stores, presumably the ER. The precise signaling pathways by which CRF2 inhibits intracellular store Ca2+ release remains to be fully defined. However, results from the present study revealed an increased expression of the ER Ca2+ sensing protein STIM1, and plasma membrane Ca2+ channels TRPC1 and Orai, which together represent the Ca2+ regulatory channels that play essential roles in SOCE and degranulation in MCs (33, 36). Increased expression of STIM1, Orai and TRPC1 have been associated with heightened Ca2+ mobilization and MC degranulation in food allergen-sensitized rats (37) which is in line with our findings with CRF2−/− BMMCs. The precise contribution of altered Ca2+ channel expression to CRF-mediated effects on Ca2+ mobilization and degranulation is unclear. Chronically elevated Ca2+ channel activity, due to genetic loss of CRF2 function in CRF2−/− BMMCs, could lead to increase protein expression of STIM1, TRPC1 and Orai1 resulting in heightened MC activity. However, that short-term pharmacological blockade of CRF2 and transient siRNA approaches were shown to enhance stimuli-induced MC degranulation suggests a more direct signaling event is likely involved.
Confocal microscopy revealed that CRF2 was localized on the surface of the MC and intracellularly. Further, intra-nuclear expression of CRF2 was also observed. In comparison, CRF1 was localized predominantly to the cell surface of MCs with no apparent nuclear staining patterns. Together, these finding demonstrate differential cellular localization patterns between CRF1 and CRF2 but the relationship between cellular localization and divergent functions in MC activation requires further investigation. It has become increasing clear that a number of GPCRs target to the nuclear membrane(38) and can regulate DNA synthesis(39), transcription and gene expression (40) and histone modification(41). To our knowledge, this represents the first evidence for differential localization of CRF receptor subtypes in MCs and further investigations will likely provide insight into the divergent roles that CRF1 and CRF2 in MC function and provide valuable insight into approaches for potential therapeutic modulation.
Precisely how the CRF receptor system is regulated to maintain MC homeostasis with regards to degranulation remains to be fully defined. We and others have shown that MCs release CRF1/CRF2 ligands CRF and urocortin under basal and stimulated conditions (21, 22), and that CRF1 and CRF2 receptors modulate stimuli-induced MC degranulation in vitro in the absence of exogenous ligands. Together, these findings demonstrate that MCs possess a functional CRF system and implicates an autocrine regulation mechanism. Such a system could explain the ability of the MC CRF system to modulate rapid cellular signaling events in the MC such as Ca2+ mobilization degranulation events. In view of the CRF system as a homeostatic regulator of the stress response, activation CRF1 in MCs could provide immunological protection by enhancing MC degranulation and subsequent physiological and immunological responses, especially during time of acute stressful challenges. On the other hand, CRF2 activation may provide a critical homeostatic mechanism by limiting the extent of degranulation and downstream pathophysiology. Dysfunction or imbalance of this system could lead to aberrant MC function and heightened disease states. It has been shown in cultured MCs that CRF1 and CRF2 expression levels can be influenced by psychological stress exogenous CRF receptor ligand, Substance P and LPS (18, 20). There is also substantial evidence in humans and in animal models that CRF1 and CRF2 expression is altered under pathological conditions such as urticaria (42), colitis (15) (43) and chronic and early life stress (44, 45). The contribution of altered CRF receptor expression vs function in MC-associated disease pathogenesis remains to be fully elucidated.
In summary, the present study highlights a novel role for CRF2 receptors expressed on MCs as negative modulators of MC degranulation in the acute response to immunological and psychological stress. Given the critical role of MCs as immune sentinels which rapidly respond to diverse stressful stimuli, the MC CRF2 system may represent a critical control step to limit MC degranulation and disease pathophysiology. Further understanding of the precise mechanism by which CRF2 controls MC degranulation and associated disease pathophysiology could unveil new therapeutic targets for immune diseases linked with stress and MC hyperactivity such as allergic inflammation and IBS.
Supplementary Material
FIG 4. CRF2 selective antagonism enhances mast cell degranulation in rodent and human mast cells.
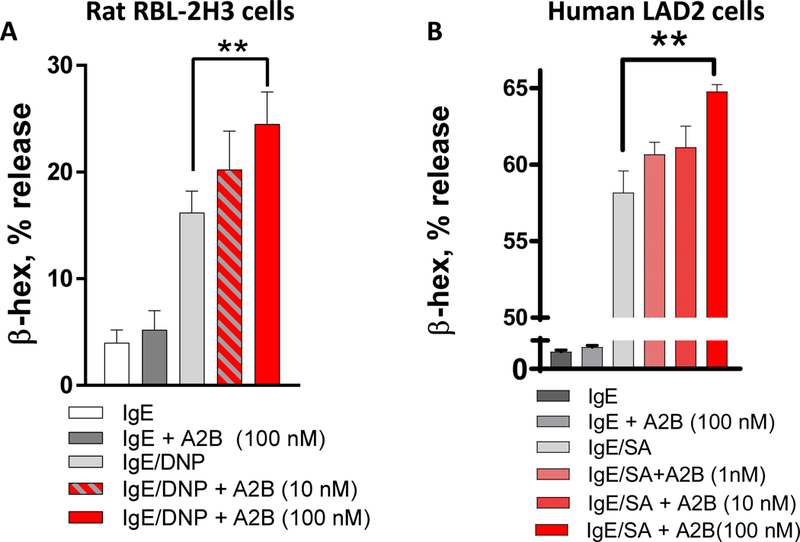
β-hex % release from RBL-2H3 mast cells (A) and human LAD2 cells (B) following pre-treatment with the CRF2 antagonist drug Astressin 2B (A2B) at indicated concentrations. **p<0.01 1-Way ANOVA (n=6 replicates/treatment). Experiments repeated in n=3 independent experiments.
Key messages.
Loss of CRF2 function induces exacerbated MC degranulation, IgE-mediated anaphylaxis and psychological stress-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction.
MC-specific CRF2 suppresses degranulation induced by diverse MC stimuli via negative regulation of SOCE.
Further characterization of the mechanisms by which CRF2 negatively modulates MC activation could lead to novel therapeutic approaches for stress-related immunological disorders associated with MC hyperactivity.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by U.S. National Institutes of Health grants R01 HD072968 (to AJM), R21 AI140413 (to AJM), K08/R03 DK097462 (to AJM), R01 DK080787 (to AB) and F30 OD025354 (to EM).
Dr. Adam Moeser is the Matilda R. Wilson Endowed Chair of Large Animal Clinical Sciences at Michigan State University, College of Veterinary Medicine.
Astressin 2B was a kind gift of Dr. Jean Rivier, Sentia Medical Sciences, Inc., Salk Institute for Biological Studies.
The authors gratefully acknowledge Tom Dexheimer PhD, Manager of the Assay Development and Drug Repurposing Core (ADDRC) at Michigan State University for his advice and technical expertise in conducting the Ca2+ fluorescence analyses. The Authors also gratefully acknowledge Darcy Honke Hulbert for the management of the mouse breeding colonies used in these experiments.
Abbreviations:
- BMMC
(Bone marrow derived mast cell)
- CRF1
(Corticotropin Releasing Factor Subtype 1)
- CRF2
(Corticotropin Releasing Factor Subtype 2)
- MC
Mast cell
- PMC
(Peritoneal mast cell)
- SOCE
(store operated Ca2+ entry)
- WT
(Wild-type)
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflict of Interest Disclosure:
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Santos J, Benjamin M, Yang PC, Prior T, Perdue MH. Chronic stress impairs rat growth and jejunal epithelial barrier function: role of mast cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000;278(6):G847–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Soderholm JD, Yang PC, Ceponis P, Vohra A, Riddell R, Sherman PM, et al. Chronic stress induces mast cell-dependent bacterial adherence and initiates mucosal inflammation in rat intestine. Gastroenterology 2002;123(4):1099–108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wallon C, Yang PC, Keita AV, Ericson AC, McKay DM, Sherman PM, et al. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) regulates macromolecular permeability via mast cells in normal human colonic biopsies in vitro. Gut 2008;57(1):50–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Santos J, Saunders PR, Hanssen NP, Yang PC, Yates D, Groot JA, et al. Corticotropin-releasing hormone mimics stress-induced colonic epithelial pathophysiology in the rat. Am J Physiol 1999;277(2 Pt 1):G391–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lennon EM, Maharshak N, Elloumi H, Borst L, Plevy SE, Moeser AJ. Early life stress triggers persistent colonic barrier dysfunction and exacerbates colitis in adult IL-10−/− mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2013;19(4):712–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moeser AJ, Ryan KA, Nighot PK, Blikslager AT. Gastrointestinal dysfunction induced by early weaning is attenuated by delayed weaning and mast cell blockade in pigs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2007;293(2):G413–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Heffner KL, Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Glaser R, Malarkey WB, Marshall GD. Stress and anxiety effects on positive skin test responses in young adults with allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2014;113(1):13–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Andrae DA PD, Drossman DA, Convington PS. Evaluation of the irritable bowel syndrome quality of life (IBS-QOL) questionnaire in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome patients. Healthy and Quality of Life Outcomes 2013;11(208). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Priftis KN, Papadimitriou A, Nicolaidou P, Chrousos GP. Dysregulation of the stress response in asthmatic children. Allergy 2009;64(1):18–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barbara G, Stanghellini V, De Giorgio R, Cremon C, Cottrell GS, Santini D, et al. Activated mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2004;126(3):693–702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Klooker TK, Braak B, Koopman KE, Welting O, Wouters MM, van der Heide S, et al. The mast cell stabiliser ketotifen decreases visceral hypersensitivity and improves intestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2010;59(9):1213–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bale TL, Vale WW. CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology 2004;44:525–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chrousos GP. Stress and disorders of the stress system. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2009;5(7):374–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.la Fleur SE, Wick EC, Idumalla PS, Grady EF, Bhargava A. Role of peripheral corticotropin-releasing factor and urocortin II in intestinal inflammation and motility in terminal ileum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102(21):7647–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu Y, Fang X, Yuan J, Sun Z, Li C, Li R, et al. The role of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 in the development of colitis-associated cancer in mouse model. Endocrine-related cancer 2014;21(4):639–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Boyer PE, D’Costa S, Edwards LL, Milloway M, Susick E, Borst LB, et al. Early-life dietary spray-dried plasma influences immunological and intestinal injury responses to later-life Salmonella typhimurium challenge. Br J Nutr 2015;113(5):783–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mahajan S, Liao M, Barkan P, Takahashi K, Bhargava A. Urocortin 3 expression at baseline and during inflammation in the colon: corticotropin releasing factor receptors cross-talk. Peptides 2014;54:58–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Asadi S, Alysandratos KD, Angelidou A, Miniati A, Sismanopoulos N, Vasiadi M, et al. Substance P (SP) induces expression of functional corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-1 (CRHR-1) in human mast cells. J Invest Dermatol 2012;132(2):324–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cao J, Cetrulo CL, Theoharides TC. Corticotropin-releasing hormone induces vascular endothelial growth factor release from human mast cells via the cAMP/protein kinase A/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Mol Pharmacol 2006;69(3):998–1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Papadopoulou NG, Oleson L, Kempuraj D, Donelan J, Cetrulo CL, Theoharides TC. Regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2 expression in human cord blood-derived cultured mast cells. Journal of molecular endocrinology 2005;35(3):R1–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kempuraj D, Papadopoulou NG, Lytinas M, Huang M, Kandere-Grzybowska K, Madhappan B, et al. Corticotropin-releasing hormone and its structurally related urocortin are synthesized and secreted by human mast cells. Endocrinology 2004;145(1):43–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ayyadurai S, Gibson AJ, D’Costa S, Overman EL, Sommerville LJ, Poopal AC, et al. Frontline Science: Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor subtype 1 is a critical modulator of mast cell degranulation and stress-induced pathophysiology. Journal of leukocyte biology 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Cao J, Papadopoulou N, Kempuraj D, Boucher WS, Sugimoto K, Cetrulo CL, et al. Human mast cells express corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) receptors and CRH leads to selective secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2005;174(12):7665–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kishimoto T, Radulovic J, Radulovic M, Lin CR, Schrick C, Hooshmand F, et al. Deletion of crhr2 reveals an anxiolytic role for corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2. Nat Genet 2000;24(4):415–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mackey E, Ayyadurai S, Pohl CS, S DC, Li Y, Moeser AJ. Sexual dimorphism in the mast cell transcriptome and the pathophysiological responses to immunological and psychological stress. Biol Sex Differ 2016;7:60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Argenzio RA, Liacos JA. Endogenous prostanoids control ion transport across neonatal porcine ileum in vitro. AmJVetRes 1990;51(5):747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bergman RK, Munoz J. CIRCULATORY COLLAPSE IN ANAPHYLAXIS AND HISTAMINE TOXICITY IN MICE. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 1965;95:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fisher MM. Clinical observations on the pathophysiology and treatment of anaphylactic cardiovascular collapse. Anaesthesia and intensive care 1986;14(1):17–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chatzaki E, Anton PA, Million M, Lambropoulou M, Constantinidis T, Kolios G, et al. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor subtype 2 in human colonic mucosa: down-regulation in ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19(9):1416–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yuan PQ, Wu SV, Pothoulakis C, Tache Y. Urocortins and CRF receptor type 2 variants in the male rat colon: gene expression and regulation by endotoxin and anti-inflammatory effect. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2016;310(6):G387–98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kashem SW, Subramanian H, Collington SJ, Magotti P, Lambris JD, Ali H. G protein coupled receptor specificity for C3a and compound 48/80-induced degranulation in human mast cells: roles of Mas-related genes MrgX1 and MrgX2. Eur J Pharmacol 2011;668(1–2):299–304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dedkova EN, Sigova AA, Zinchenko VP. Mechanism of action of calcium ionophores on intact cells: ionophore-resistant cells. Membr Cell Biol 2000;13(3):357–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Holowka D, Wilkes M, Stefan C, Baird B. Roles for Ca2+ mobilization and its regulation in mast cell functions: recent progress. Biochemical Society transactions 2016;44(2):505–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Balseiro-Gomez S, Flores JA, Acosta J, Ramirez-Ponce MP, Ales E. Identification of a New Exo-Endocytic Mechanism Triggered by Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone in Mast Cells. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 2015;195(5):2046–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Alysandratos KD, Asadi S, Angelidou A, Zhang B, Sismanopoulos N, Yang H, et al. Neurotensin and CRH interactions augment human mast cell activation. PLoS One 2012;7(11):e48934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Suzuki R, Liu X, Olivera A, Aguiniga L, Yamashita Y, Blank U, et al. Loss of TRPC1-mediated Ca2+ influx contributes to impaired degranulation in Fyn-deficient mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Journal of leukocyte biology 2010;88(5):863–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yang B, Yang C, Wang P, Li J, Huang H, Ji Q, et al. Food allergen--induced mast cell degranulation is dependent on PI3K-mediated reactive oxygen species production and upregulation of store-operated calcium channel subunits. Scandinavian journal of immunology 2013;78(1):35–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vaniotis G, Allen BG, Hébert TE. Nuclear GPCRsin cardiomyocytes: an insider’s view of β-adrenergic receptor signaling. American journal of physiology Heart and circulatory physiology 2011;301(5):H1754–H64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Watson PH, Fraher LJ, Natale BV, Kisiel M, Hendy GN, Hodsman AB. Nuclear localization of the type 1 parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptide receptor in MC3T3-E1 cells: association with serum-induced cell proliferation. Bone 2000;26(3):221–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Savard M, Barbaz D, Belanger S, Muller-Esterl W, Bkaily G, D’Orleans-Juste P, et al. Expression of endogenous nuclear bradykinin B2 receptors mediating signaling in immediate early gene activation. Journal of cellular physiology 2008;216(1):234–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Re M, Pampillo M, Savard M, Dubuc C, McArdle CA, Millar RP, et al. The human gonadotropin releasing hormone type I receptor is a functional intracellular GPCR expressed on the nuclear membrane. PLoS One 2010;5(7):e11489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Theoharides TC, Kempuraj D, Marchand J, Tzianoumis L, Vasiadi M, Katsarou-Katsari A, et al. Urticaria pigmentosa associated with acute stress and lesional skin mast-cell expression of CRF-R1. Clinical and experimental dermatology 2009;34(5):e163–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yuan PQ, Wu SV, Elliott J, Anton PA, Chatzaki E, Million M, et al. Expression of corticotropin releasing factor receptor type 1 (CRF1) in the human gastrointestinal tract and upregulation in the colonic mucosa in patients with ulcerative colitis. Peptides 2012;38(1):62–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li Y, Song Z, Kerr KA, Moeser AJ. Chronic social stress in pigs impairs intestinal barrier and nutrient transporter function, and alters neuro-immune mediator and receptor expression. PLoS One 2017;12(2):e0171617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Smith F, Clark JE, Overman BL, Tozel CC, Huang JH, Rivier JE, et al. Early weaning stress impairs development of mucosal barrier function in the porcine intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2010;298(3):G352–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


