Description
This video 1 case presents some unique technical tenets for the microsurgical clipping of a giant posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm. The patient described in this case was a 60-year-old woman with a history of coil embolisation of a left vertebral artery aneurysm. The patient presented with headaches and mild left-sided blurry vision, which remained after prior embolisation. Cerebral angiography (figure 1) demonstrated interval coil compaction with marked increase in the aneurysm base, measuring ~9.8×7.2×4.0 mm (figure 2). Alternative treatment options considered this patient included stent coiling, pipeline embolisation or left vertebral artery coil sacrifice. This case is valuable to the literature as it illustrates technical steps required for clipping of a large aneurysm using fenestrated clips and need for identification and preservation of anterior spinal artery.
Video 1.
Figure 1.
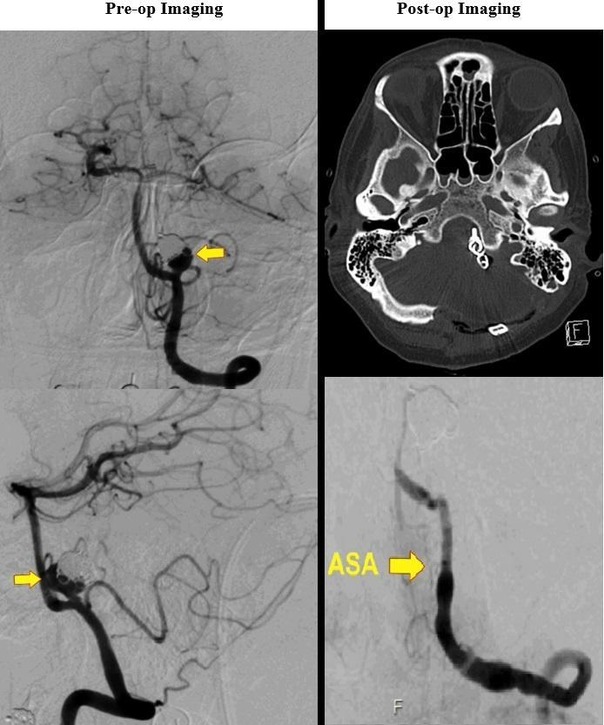
Preoperative and postoperative imaging.
Figure 2.
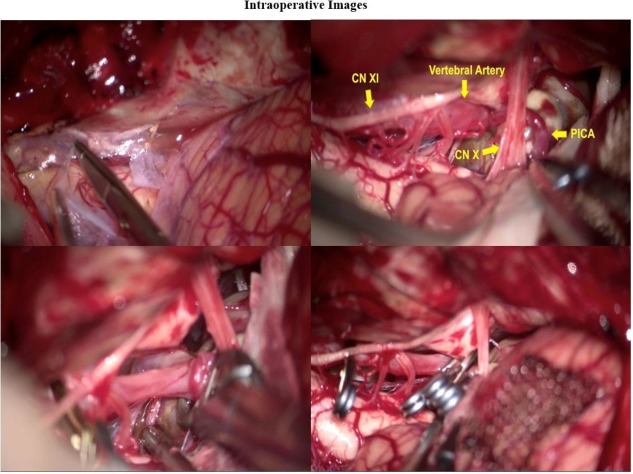
Intraoperative view of the operative field.
Learning points.
This case demonstrates the usefulness of far lateral craniotomy with transcondylar exposure for large posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms.
The video highlights the identification and preservation of the anterior spinal artery.
Footnotes
Contributors: All authors certify that they have each made a substantial contribution as to qualify for authorship as follows: OC and MP performed the procedure, OC provided video narration, GG and RD performed critical video editing and preparation for publication. All authors approved the final documents.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.