Abstract
There is a pressing need for additional clinical biomarkers to predict the aggressiveness of individual cancers. Here, we examine the potential usefulness of spatial genome organization as a prognostic tool for prostate cancer. Using fluorescence in situ hybridization on formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded human prostate tissue specimens, we compared the nuclear positions of four genes between clinically relevant subgroups of prostate tissues. We find that directional repositioning of SP100 and TGFB3 gene loci stratifies prostate cancers of differing Gleason scores. A more peripheral position of SP100 and TGFB3 in the nucleus, compared to benign tissues, is associated with low Gleason score cancers, whereas more internal positioning correlates with higher Gleason scores. Conversely, LMNA is more internally positioned in many non-metastatic prostate cancers, while its position is indistinguishable from benign tissue in metastatic cancer. The false positive rates were relatively low, whereas, the false negative rates of single or combinations of genes were high, limiting the clinical utility of this assay in its current form. Nevertheless, our findings of subtype-specific gene positioning patterns in prostate cancer provides proof-of-concept for the potential usefulness of spatial gene positioning for prognostic applications, and encourage further exploration of spatial gene positioning patterns to identify novel clinically relevant molecular biomarkers, which may aid treatment decisions for cancer patients.
Keywords: spatial genome organization, spatial gene positioning, gene positioning biomarkers, prostate cancer, cancer stratification
Introduction
The genome is highly spatially organized within the interphase nucleus (Cremer and Cremer, 2001; Bickmore, 2013). Most chromosomes, genes, and individual non-coding regions of the genome occupy preferred nuclear positions relative to the center of the nucleus or to other nuclear landmarks, such as associations with other genomic loci or nuclear bodies (Takizawa et al., 2008b; Bickmore and van Steensel, 2013; Meaburn, 2016). Some loci alter their position under different physiological conditions, for example, between cell/tissue types (Boyle et al., 2001; Parada et al., 2004; Peric-Hupkes et al., 2010; Meaburn et al., 2016) or between different proliferation states (Bridger et al., 2000; Meaburn and Misteli, 2008; Chandra et al., 2015). Spatial reorganization of the genome is also a common feature of disease, and has been documented in a wide range of pathologies, including epilepsy (Borden and Manuelidis, 1988), Down syndrome (Paz et al., 2015), laminopathies (Meaburn et al., 2007; Mewborn et al., 2010), viral and parasitic infections (Li et al., 2010; Knight et al., 2011), and cancer (Meaburn, 2016; Mai, 2018). Repositioning events are loci-specific and do not reflect global genome reorganization events (Meaburn, 2016).
Although the spatial organization of the genome has been studied for decades, how gene positioning patterns are established and maintained remains largely elusive. It is also unclear if the nuclear position of a locus is important for function or is largely a consequence of nuclear activities (Meaburn, 2016). Most often, a functional link is drawn between spatial genome organization and gene expression (Brown et al., 1997; Brickner and Walter, 2004; Williams et al., 2006; Takizawa et al., 2008a; Peric-Hupkes et al., 2010), however, there are also many instances where changes in gene expression and nuclear position of a locus are unrelated (Scheuermann et al., 2004; Williams et al., 2006; Kumaran and Spector, 2008; Meaburn and Misteli, 2008; Harewood et al., 2010; Meaburn, 2016). Most likely, there are multiple mechanisms in play to determine the spatial organization of the genome (Shachar et al., 2015; Meaburn, 2016; Randise-Hinchliff et al., 2016). In addition to gene expression, chromatin modifications, even in the absence of changes in gene expression (Towbin et al., 2012; Therizols et al., 2014; Harr et al., 2016; Cabianca et al., 2019; Falk et al., 2019), replication timing (Hiratani et al., 2008) and a variety of structural nuclear proteins (Dundr et al., 2007; Meaburn et al., 2007; Solovei et al., 2013; Zuleger et al., 2013; Shachar et al., 2015) have be implicated in the positioning of genomic loci.
While the mechanisms governing spatial positioning patterns are unclear, the fact that the genome is spatially reorganized in disease begs the question of whether spatial positioning patterns can be exploited for clinical purposes (Meaburn, 2016; Mai, 2018). We have previously demonstrated that the positioning patterns of some genes can be used to reproducibly and accurately discriminate benign breast and prostate tissues from cancerous ones (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). For instance, the positioning patterns of HES5 and FLI1 are highly indicative of cancer, with both HES5 and FLI1 repositioned in 100% of breast cancers and FLI1 repositioned in 92.9% of prostate cancers, compared to benign tissue controls (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). High repositioning rates result in low false negative detection rates. Crucially for diagnostic applications, many of the genes that reproducibly reposition in cancer show limited variability between morphologically normal tissues and do not reposition in benign disease, yielding low false positive detection rates (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). Given the sensitivity and specificity for the positioning patterns of several genes in detecting cancer, these small-scale studies suggest gene positioning biomarkers (GPBs) could be a useful addition to cancer diagnostics.
Prostate cancer is a leading cause of cancer and cancer-related deaths (Bray et al., 2018). As with most cancers, while there is value in additional diagnostic biomarkers, there is also a critical need for additional prognostic biomarkers, to predict best treatment options, including to reduce overtreatment in patients whose cancer would have remained asymptomatic during their lifetime without treatment (Welch and Black, 2010; Sandhu and Andriole, 2012). Currently, the cornerstone of predicating a patient’s outcome is the Gleason grading system, which is based on histological assessment (Epstein et al., 2005; Brimo et al., 2013). In this system the architectural structure of the prostate tissue is graded from Gleason grade 1, which represents a well differentiated tissue morphology, to the very poorly differentiated Gleason grade 5. The two most prominent Gleason grades in a given tumor/biopsy are summed to give a Gleason score (Epstein et al., 2005; Epstein, 2018). Low Gleason score cancers are more likely to be indolent, whereas higher Gleason scores correlates with poor outcomes (Albertsen et al., 1998; Pound et al., 1999; Brimo et al., 2013). However, further markers are required as there is a range in outcomes for patients with the same Gleason score.
To improve on the Gleason system, additional clinical factors, most commonly serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, T stage (size of tumor/spread to nearby tissues), percentage of cancer positive biopsy cores, and patient age are taken into account (D’Amico et al., 1998; Thompson et al., 2007; Cooperberg et al., 2009; Chang et al., 2014). ∼15% of patients are diagnosed with high-risk (likely to cause morbidity, recur, metastasize and/or be lethal) prostate cancer, based on PSA levels of >20ng/ml and/or Gleason score of 8-10 and/or T stage of either T2c-T4 or T3a-T4, depending on the classification system (Thompson et al., 2007; Cooperberg et al., 2009; Chang et al., 2014). Low-risk cancers (PSA <10ng/ml, Gleason score 2-6, and T stage T1-T2a) are generally predicted to remain asymptomatic during the patient’s lifetime and the use of active surveillance/watchful waiting is often recommended, as opposed to active treatment (Thompson et al., 2007; Cooperberg et al., 2009). Conversely, intermediate risk (Gleason score 7 or T stage T2b/c) patients generally receive treatment (Thompson et al., 2007; Cooperberg et al., 2010). Gleason scores can be subject to inter- and intra-observer variability, usually of just a single Gleason score (Montironi et al., 2005), but for patients at the border of low and intermediate risk this may make the difference of receiving treatment or not. Moreover, with the current clinical criteria to stratify risk, both over- and under-treatment remains a concern for all prostate cancer risk groups (Cooperberg et al., 2010; Punnen and Cooperberg, 2013). Improved markers are needed to better distinguish indolent from high-risk prostate cancers and to aid classification of intermediate-risk cancers, to reduce overtreatment and optimize therapeutic strategies.
There is a growing number of genomic prognostic biomarkers for prostate cancer, including several commercial assays based on the DNA methylation status of a small number of genes or on gene expression (Kornberg et al., 2018). Additionally, changes to nuclear size and shape and gross chromatin texture, which are not considered in Gleason scoring, provide additional predictive power to detect aggressive prostate cancers (Veltri and Christudass, 2014; Hveem et al., 2016). Few studies have assessed the prognostic potential of the spatial organization of the genome. The most compelling evidence for prognostic GPBs comes from telomeres, where increased telomeric aggregation correlates with progression and risk in several types of cancers (Mai, 2018). Similarly, in a single acute myeloid leukemia patient, HSA8 and 21 became more proximal to each other while the patient was in remission, prior to a disease relapse and re-emergence of t(8;21) in the patient’s bone marrow (Tian et al., 2015).
Here, we explore the utility of spatial gene positioning patterns to identify clinically distinct subgroups of prostate cancer. We find subtype-specific positioning for SP100, TGFB3 and LMNA. The direction in which SP100 and TGFB3 reposition, compared to benign tissue, distinguishes low and intermediate/high Gleason score cancers, whereas LMNA repositions in many non-metastatic cancers but not in metastatic cancers. Although the sensitivity of this assay is currently too low to be clinically useful, our findings of subtype-specific gene positioning patterns in prostate cancer provides additional evidence for the potential of spatial genome organization as a novel prognostic biomarker.
Materials and Methods
Tissue Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
4-5µm thick normal, benign disease (hyperplasia and chronic prostatitis), and cancerous formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded (FFPE) human prostate tissues were obtained from US Biomax Inc, Imgenex Corporation, BioChain Institute, or the University of Washington (Prof. Lawrence True) under the guidelines and approval of the Institutional Review Board of the University of Washington (#00-3449) ( Supplementary Table 1 ). Patient tissues were de-identified before receipt.
To generate probe DNA for FISH, bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clones were labeled with biotin- (Roche), digoxigenin- (Roche) or DY-547P1- (Dyomics GmbH) conjugated dUTPs by nick translation (Meaburn, 2010). The following BACs were used: RP11-727M18 (to position SP100, chromosome location: 2q37.1); RP11-270M14 (TGFB3, 14q24.3); RP11-1021J5 (SATB1, 3p24.3); RP11-35P22 (LMNA, 1q22) (BACPAC resource center). Single- or dual-probe FISH experiments were performed as previously described (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016), with the following modifications: for most tissues a 1 hour 60ºC bake step was performed, prior to the xylenes (Macron Fine Chemicals) deparaffinization step; 40µg yeast RNA (Life Technologies) was used in place of tRNA; DyLight 488 labeled anti-digoxigenin (Vector Laboratories) was occasionally used to detect digoxigenin-labeled probe DNA; and no probe detection steps were required for the fluorescently labeled DY-547P1-dUTP FISH probes.
Image Acquisition
Epithelial nuclei were randomly imaged throughout the tissue, unless benign and malignant glands were present in the same tissue section. In such cases, care was taken to image and analyze the different morphologies separately, whilst still acquiring epithelial cell nuclei randomly within the benign or malignant regions to capture as much diversity within the cancer (or benign tissue) as possible. Image accusation was performed as previously described, using an IX70 (Olympus) Deltavision (Applied Precision) system, with a 60x 1.42N oil objective lens (Olympus), an auxiliary magnification of 1.6, and a X-Y pixel size of 67.25nm (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016) or with a similar imaging regime using an IX71 (Olympus) Deltavision (Applied Precision) system, 100x 1.40N oil objective lens (Olympus), with an X-Y pixel size of 64.6nm. Image stacks were acquired to cover the thickness of the tissue section, with a 0.5µm or 0.25µm step interval along the Z axis, respectively. All image stacks were deconvolved and converted to maximum intensity projections using SoftWoRx (Applied Precision). The change in acquisition approach did not affect the resulting positioning data from the image datasets. We obtained similarly statistically identical distributions for the position of a gene in a given tissue using the two different acquisition methods (P = 0.79-0.86, Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test), as from repeat analysis of tissues using an identical acquisition method (P = 0.65-0.99 (Meaburn et al., 2009), unpublished data).
Image Analysis
Image analysis to determine the radial position of a gene within a tissue was performed as previously described (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). Briefly, 96-167 interphase epithelial nuclei were manually segmented in Photoshop (Adobe) for each gene in each tissue, except for TGFB3 in tissue C10 where 88 nuclei were segmented. To map the radial position of the gene loci, nuclei were run though custom image analysis software scripts, using MATLAB (The Mathsworks Inc.), with DIPImage and PRTools toolboxes [Deft University, P. Gudla and S Lockett (NCI/NIH); (Meaburn et al., 2009)]. Euclidean distance transform (EDT) was computed for each nucleus, to assign every pixel within the nucleus its distance to the nearest nuclear boundary. The software then determined the nuclear EDT position of the geometric gravity center of the automatically detected FISH signals. To normalize for variations in nuclear size and shape between specimens, the EDT of a FISH signal was normalized to the maximal nuclear EDT for that nucleus, with 0 denoting the nuclear periphery and 1 the nuclear center. The normalized FISH signal EDTs for a given gene in each specimen was then combined to produce a relative radial distribution (RRD), and a cumulative frequency distribution was generated. All detected alleles in a nucleus were included, regardless of the number present. In the case of the pooled normal distributions (PNDs), the normalized FISH EDTs from all allele in all the normal tissues analyzed, for a given gene, were combined into a single dataset ( Supplementary Figure 1 ). The number of nuclei and tissues used in each PND were as follows: the SP100 PND contained 845 nuclei from 7 normal tissues; TGFB3, 996 nuclei from 8 normal tissues; SATB1, 874 nuclei from 7 normal tissues; and LMNA, 725 nuclei from 6 normal tissues. Finally, to statistically compare a gene’s positioning patterns, RRDs between tissues, or between specimens and the PND, were cross-compared using the nonparametric two-sample 1D KS test, where P < 0.01 was considered significant.
Some previously reported RRDs were included in the current analysis [ Supplementary Table 1 ; (Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016)], which were compared to an update PND. The four PNDs used in this study included normal tissues N6 and N7, in addition to the normal tissues previously reported, which did not affect the RRDs (P = 0.83-1, 1D KS test). RRDs for TGFB3 in tissues C25, C27, B9, N3, N4, N11-14 were previously reported in (Meaburn et al., 2016), and the RRDs of SP100 in C11, C12, C13, C25, N1, N2, N6-10, SATB1 in C11, C12, C13, C25, B9, N1, N2, N6-10, and LMNA in C11, C18, C19, N5, N10 and N15-16 were reported in (Leshner et al., 2016).
Results
Mapping of Candidate Genes in Prostate Tissues
We have previously identified genes that radially reposition in breast and/or prostate cancer and have demonstrated their potential as diagnostic biomarkers (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). Here, we sought to extend these studies to determine if candidate genes occupied distinct nuclear positions between different subgroups of prostate cancer, with the goal of assessing their utility for cancer prognostics. To identify prognostic candidate genes we took advantage of our previous studies, in which we had screened the radial positions of 47 genes in a panel of prostate cancers (Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). From that gene set we chose two genes, SATB1 and LMNA, for further assessment as potential biomarkers of high-risk prostate cancer because both genes repositioned in a single high-risk T3 stage cancer, but not in two intermediate risk T2 cancers, or a low risk T2 cancer (Leshner et al., 2016). We also selected SP100 to test its potential as a marker of low risk, since we previously found it to reposition in a low risk Gleason score 6 prostate cancer, but not in three intermediate or high-risk Gleason score 7 cancers (Leshner et al., 2016). Finally, we selected TGFB3 for further analysis since it repositioned in one of two low risk Gleason score 6 prostate cancers, but not in two prostate cancers of unknown Gleason score and TNM stage (Meaburn et al., 2016), representing a potential low-risk/indolent prostate cancer biomarker.
To determine whether the positioning patterns of these genes were able to stratify prostate cancers into clinically relevant subgroups, we performed FISH on a panel of 4-5µm thick FFPE human prostate tissues, which included a diverse group of 32 prostate cancer specimens covering a range of Gleason scores and T stages, with and without known metastases, and 25 benign prostate tissues (for details see Supplementary Table 1 ). To map the spatial positioning pattern of a gene in a given tissue, we measured the radial position, normalized for nuclear size and shape, of each locus in ∼120 epithelial interphase nuclei as previously described (see Materials and Methods; (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). The normalized radial position of each gene was determined and the cumulative RRDs were statistically compared to a PND, a standardized normal distribution created by pooling all nuclei from normal tissues for a given gene, or individual tissues using the 1D KS test, with P < 0.01 considered significant (see Materials and Methods, (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016), Supplementary Figure 1 ).
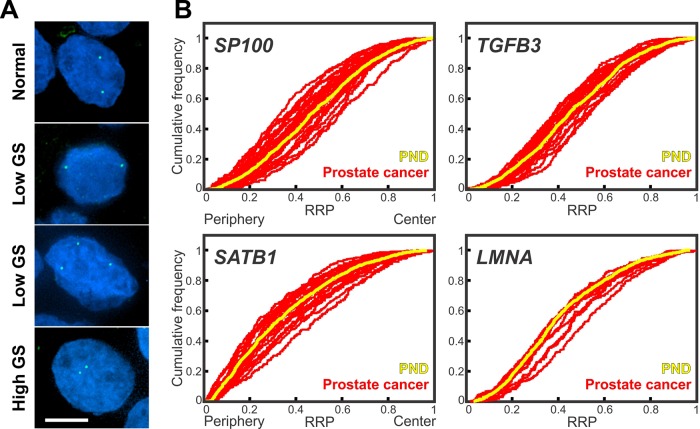
We initially assessed the repositioning rates for the candidate genes in the assorted set of prostate cancer samples. Compared to the PND, SP100 was in a statistically significantly different radial position in 44.4% (12/27) prostate cancer specimens ( Figure 1 , Table 1 , Supplementary Table 2 ). Similarly, LMNA repositioned in 36.4% (4/11), SATB1 in 34.8% (8/23), and TGFB3 in 31.8% (7/22) of prostate cancer tissues ( Figure 1 , Table 1 , Supplementary Tables 3 – 5 ). The repositioning rates are slightly higher than in the previous smaller scale studies (25-33.3%) (Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). However, in keeping with previous findings, all four genes repositioned in too few cancers to be of use as prostate cancer diagnostic GPBs since detecting cancer based on the repositioning of the gene would misclassify 55.6-68.2% of the tumors as not cancerous, depending on the gene. The likelihood of a gene repositioning in a cancer did not correlated with gene copy number ( Figure 1 , Supplementary Table 6 ).
Figure 1.
Gene positioning in prostate cancer tissues (A) Gene loci were detected by FISH in FFPE prostate tissue sections. SP100 gene loci (green) in normal and cancerous prostate tissues. GS, Gleason score. Projected image stacks shown. Nuclei were counterstain with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 5µm. (B) Cumulative RRDs for the indicated genes in prostate cancer (red) and the pooled normal distribution (PND; Yellow). RRP, relative radial position.
Table 1.
Spatial repositioning of target genes in prostate cancer.
| Tissue | SP100 | TGFB3 | SATB1 | LMNA | Gleason score | Gleason Grade | TNM | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | I | 9 (4 + 5) | 4 | T3N0M1 | High | |||
| C2 | 9 (5 + 4) | 4-5 | T2N1M1c | High | ||||
| C3 | I | 9 (5 + 4) | 5 | T3aN0M0 | High | |||
| C4 | I | 8 (4 + 4) | 4 | T3N0M0 | High | |||
| C5 | I | 9 (4 + 5) | T2N0M0 | High | ||||
| C6 | P | I | P | 9 (4 + 5) | T2N0M0 | High | ||
| C7 | I | 9 (4 + 5) | T2N0M0 | High | ||||
| C8 | P | P | 8 (4 + 4) | 4 | Unknown | High | ||
| C9 | 7 (3 + 4) | 4 | T3N0M1b | High | ||||
| C10 | 7 (3 + 4) | 3 | T4N1M1c | High | ||||
| C11 | I | I | 7 | 3 | T3N0 | High | ||
| C12 | 7 | 3 | T2N0 | Intermediate | ||||
| C13 | 7 | 3 | T2N0 | Intermediate | ||||
| C14 | I | P | 7 (3 + 4) | T2N0M0 | Intermediate | |||
| C15 | I | I | 7 (3 + 4) | 4 | T2N0M0 | Intermediate | ||
| C16 | I | 7 (3 + 4) | 4 | T2N0M0 | Intermediate | |||
| C17 | I | 7 (3 + 4) | T1N0M0 | Intermediate | ||||
| C18 | 7 | T2N0 | Intermediate | |||||
| C19 | 7 | T2N0 | Intermediate | |||||
| C20 | P | I | 4 (2 + 2) | 2 | T4N1M1 | High | ||
| C21 | P | P | 3 (1 + 2) | 2 | T3N1M1 | High | ||
| C22 | 6 (2 + 4) | 4 | T3N0M1b | High | ||||
| C23 | 6 (3 + 3) | 3 | T3N1M0 | High | ||||
| C24 | P | 6 (3 + 3) | 3 | T3N0M0 | High | |||
| C25 | P | P | 6 (3 + 3) | 3 | T2N0M0 | Low | ||
| C26 | P | P | I | 6 (3 + 3) | 3 | T2N0M0 | Low | |
| C27 | 6 | T2N0 | Low | |||||
| C28 | P | I | 5 (1 + 4) | T2N0M0 | Low | |||
| C29 | 5 (2 + 3) | 3 | T2N0M0 | Low | ||||
| C30 | 5 (2 + 3) | 3 | T2N0M0 | Low | ||||
| C31 | I | 4 (2 + 2) | 2 | T2N0M0 | Low | |||
| C32 | 3 (1 + 2) | 1 | T1N0M0 | Low |
Statistical comparisons of the RRD of a gene in individual cancer tissues to the PND, using the two-sample 1D KS test. Red, significantly different (P < 0.01); Blue, statistically similar position (P > 0.01). I, a more internal position in the cancer, compared to the PND; P, a more peripheral positioned in the cancer tissue; Red text: mark of aggressive/high risk cancer; blue text: mark of low risk cancer; purple text, intermediate Gleason score. Low risk, Gleason score 2-6 and T1/2 and N0M0; intermediate risk, Gleason score 7 and T1/2 and N0M0; high risk, Gleason score 8-10 and/or T3/4 and/or N1 and/or M1.
In addition to whether a gene was repositioned, the direction of its repositioning was also determined ( Figure 1 , Table 1 ). Of the 12 prostate cancers in which SP100 was repositioned, the gene was more internally positioned compare to the PND in five cancer tissues (5/12; 41.7%) and more peripherally positioned in seven (58.3%). Similarly, TGFB3 was more internally positioned in three (3/7; 42.9%) cancers and more peripherally positioned in four (57.1%). SATB1 was more internally positioned in five of the eight cancers where the gene was repositioned (62.5%) and more peripherally positioned in three cancers (37.5%). Conversely, LMNA repositioned to a more internal nuclear location in all four cancer specimens in which the gene was repositioned ( Figure 1 , Table 1 ). The direction of repositioning accounted for most of the differences in the positioning patterns for a given gene between the cancer tissues in which repositioning occurred. There was little variation between the RRDs of a gene between the cancers in which the gene was more internally positioned. Similarly, there was little statistical variation in RRDs among cancers in which the gene was more peripherally positioned, with the exception of SATB1 ( Table 2 , Supplementary Tables 2 – 5 ). Taken together, we find heterogeneity in the radial positioning patterns for all four candidate genes between prostate cancers.
Table 2.
Cross-comparisons between individual tissues % (number) of significantly different cross-comparison among.
| SP100 | TGFB3 | SATB1 | LMNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual cancer tissues | 46.7% (164/351) | 33.8% (78/231) | 42.3% (107/253) | 32.7% (18/55) |
| More I cancers | 0% (0/10) | 0% (0/3) | 0% (0/10) | N/A |
| More P cancers | 9.5% (2/21) | 0% (0/6) | 66.7% (2/3) | 33.3% (2/6) |
| Individual normal vs cancer tissues | 33.3% (63/189) | 28.4% (50/176) | 22.4% (36/161) | 24.2% (16/66) |
| Individual normal tissues | 0.0% (0/21) | 21.4% (6/28) | 19.0% (4/21) | 26.7% (4/15) |
| Individual benign disease tissues | 20% (2/10) | 10.0% (1/10) | 0.0% (0/10) | 0.0% (0/1) |
| Individual normal vs benign disease | 14.3% (5/35) | 10.0% (4/40) | 5.7% (2/35) | 25.0% (3/12) |
| Individual benign tissues | 10.6% (7/66) | 14.1% (11/78) | 9.1% (6/66) | 25.0% (7/28) |
Significantly different, based on a KS test, P < 0.01; More I cancers, cancers in which the gene is more internally positioned than the PND (P < 0.01); More P cancers, cancers in which the gene is more peripherally positioned than the PND (P < 0.01); N/A, not applicable.
SP100 and TGFB3 Exhibit Differential Positioning Patterns Between Low and Intermediate/High Gleason Score Cancers
Next, we sought to determine if the differences in gene repositioning patterns between prostate cancers correlated with clinicopathological features. Comparing RRDs between individual cancer tissues was not useful for subgrouping cancers. For the most part, there was a similar proportion of cross-comparisons between cancers that were significantly different to each other within clinically relevant subgroups as there was between subgroups (for P-values see Supplementary Tables 2 - 5 ). For example, SP100 was in a significantly different position in 49.1% (27/55) of cross-comparisons amongst Gleason score 2-6 prostate cancers, and 53.4% (47/88) of cross-comparisons when Gleason score 2-6 cancers were compared to Gleason score 7 cancers, and 50% (44/88) of cross-comparisons between Gleason score 2-6 and Gleason score 8-10 cancers ( Supplementary Table 2 ).
In contrast, the behavior of a gene in a cancerous tissue compared to the PND was a better indicator to detect differential positioning between subgroups ( Figure 1 , Supplementary Figure 2 , Tables 1 , 3 and 4 , Supplementary Tables 2 – 5 ). We first compared positioning patterns to Gleason score. In line with the clinical risk assessment of prostate cancers (Thompson et al., 2007), we classified Gleason scores of 2-6 as a low Gleason score, Gleason score 7 as intermediate, and scores of 8-10 as a high Gleason score. There was a modest increase in the proportion of cancer specimens with either SATB1 or LMNA repositioned, compared to the PND, with increasing Gleason score, however, in the case of LMNA this may be due to the small sample size ( Table 3 ). SATB1 was in a statistically different nuclear position in 25% (2/8) of low Gleason score cancers, 33.3% (3/9) Gleason score 7 cancers and 50% (3/6) high Gleason score cancers. Similarly, LMNA repositioned in 33.3% of low (2/6) and intermediate (1/3) Gleason score cancers, and 50% (1/2) of high Gleason score cancers. Inclusion of the direction of repositioning did little to aid stratification ( Table 3 ). Thus, we concluded that neither SATB1 nor LMNA are biomarkers of Gleason score. The proportion of cancers in which SP100 and TGFB3 repositioned also did not stratify Gleason score groups. SP100 was slightly more frequently repositioned in low Gleason score cancers specimens, repositioning in 54.5% (6/11) of low Gleason score cancers, 37.5% (3/8) of intermediate Gleason score cancers, and 37.5% (3/8) of high Gleason score cancers. TGFB3 repositioned in 30% (3/10) low Gleason score cancer tissues, 20% (1/5) of intermediate Gleason score cancers, and 42.9% (3/7) of high Gleason score cancers. On the other hand, in cancer specimens in which either gene repositioned, the direction of repositioning correlated with Gleason score ( Supplementary Figure 2A , Table 4 ). Both SP100 and TGFB3 shifted to a more peripheral position in 100% of the low Gleason score cancers in which these genes showed an altered radial position. In contrast, SP100 and TGFB3 were in a more internal position in 83.3% (5/6) and 75.0% (3/4), respectively, of the Gleason score 7 and higher cancers in which they repositioned. Intermediate/high Gleason score cancer tissue repositioning is not exclusively more internal, since for both genes a more peripheral positioning was detected in a Gleason score 9 prostate cancer ( Supplementary Figure 2A , Tables 1 and 4 ). The positioning patterns of SP100 and TGFB3 could not distinguish intermediate Gleason score cancer tissues from high Gleason score cancer tissues ( Supplementary Figure 2A , Tables 1 and 4 ).
Table 3.
Positioning patterns for SATB1 and LMNA by prostate cancer subgroups.
| Direction of repositioning: |
SATB1
% (number) of cancers SD to the PND |
LMNA
% (number) of cancers SD to the PND |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | Internal | Peripheral | Any | Internal | Peripheral | |
| All cancers | 34.8% (8/23) | 62.5% (5/8) | 37.5% (3/8) | 36.4% (4/11) | 100% (4/4) | 0% (0/4) |
| GS 2-6 | 25.0% (2/8) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) | 33.3% (2/6) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) |
| GS 7-10 | 40.0% (6/15) | 50.0% (3/6) | 50.0% (3/6) | 40.0% (2/5) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) |
| GS 7 | 33.3% (3/9) | 66.7% (2/3) | 33.3% (1/3) | 33.3% (1/3) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| GS 8-10 | 50.0% (3/6) | 33.3% (1/3) | 66.7% (2/3) | 50.0% (1/2) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| GG1/GG2 | 66.7% (2/3) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) | 0% (0/3) | ||
| GG3 | 12.5% (1/8) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (2/2) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) |
| GG4/GG5 | 44.4% (4/9) | 50.0% (2/4) | 50.0% (2/4) | 33.3% (1/3) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| Unknown GG | 33.3% (1/3) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | 33.3% (1/3) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| T1/T2 | 30.8% (4/13) | 50.0% (2/4) | 50.0% (2/4) | 42.9% (3/7) | 100% (3/3) | 0% (0/3) |
| T3/T4 | 33.3% (3/9) | 100% (3/3) | 0% (0/3) | 25.0% (1/4) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| Unknown T stage | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/0) | ||
| N0M0 | 37.5% (6/16) | 50.0% (3/6) | 50.0% (3/6) | 57.1% (4/7) | 100% (4/4) | 0% (0/4) |
| N1/M1 | 16.7% (1/6) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 0% (0/4) | ||
| Unknown N/M status | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/0) | ||
| T1/T2 N0M0 | 30.8% (4/13) | 50.0% (2/4) | 50.0% (2/4) | 50.0% (3/6) | 100% (3/3) | 0% (0/3) |
| T3N0M0 | 66.7% (2/3) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) | 100% (1/1) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| T4/N1/M1 | 16.7% (1/6) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 0% (0/4) | ||
| Unknown T/N/M | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/0) | ||
| Low risk | 25.0% (1/4) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 66.7% (2/3) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) |
| Int. risk | 33.3% (2/6) | 50.0% (1/2) | 50.0% (1/2) | 0% (0/2) | ||
| High risk | 38.5% (5/13) | 60.0% (3/5) | 40.0% (2/5) | 33.3% (2/6) | 100% (2/2) | 0% (0/2) |
SD, significantly different, based on 1D KS test (P < 0.01); GS, Gleason score; GG, Gleason grade; low risk, Gleason score 2-6 and T1/2 and N0M0; int. risk, intermediate risk (Gleason score 7 and T1/2 and N0M0); high risk, Gleason score 8-10 and/or T3/4 and/or N1 and/or M1.
Table 4.
Positioning patterns for SP100 and TGFB3 by prostate cancer subgroups.
| Direction of repositioning: |
SP100
% (number) of cancers SD to the PND |
TGFB3
% (number) of cancers SD to the PND |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | Internal | Peripheral | Any | Internal | Peripheral | |
| All cancers | 44.4% (12/27) | 41.7% (5/12) | 58.3% (7/12) | 31.8% (7/22) | 42.9% (3/7) | 57.1% (4/7) |
| GS 2-6 | 54.5% (6/11) | 0% (0/6) | 100% (6/6) | 30.0% (3/10) | 0% (0/3) | 100% (3/3) |
| GS 7-10 | 37.5% (6/16) | 83.3% (5/6) | 16.7% (1/6) | 33.3% (4/12) | 75.0% (3/4) | 25.0% (1/4) |
| GS 7 | 37.5% (3/8) | 100% (3/3) | 0% (0/3) | 20.0% (1/5) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| GS 8-10 | 37.5% (3/8) | 66.7% (2/3) | 33.3% (1/3) | 42.9% (3/7) | 66.7% (2/3) | 33.3% (1/3) |
| GG1/GG2 | 50.0% (2/4) | 0% (0/2) | 100% (2/2) | 33.3% (1/3) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) |
| GG3 | 33.3% (3/9) | 0% (0/3) | 100% (3/3) | 28.6% (2/7) | 0% (0/2) | 100% (2/2) |
| GG4/GG5 | 45.5% (5/11) | 80.0% (4/5) | 20.0% (1/5) | 30.0% (3/10) | 66.7% (2/3) | 33.3% (1/3) |
| Unknown GG | 66.7% (2/3) | 50.0% (1/2) | 50.0% (1/2) | 50.0% (1/2) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| T1/T2 | 43.8% (7/16) | 42.9% (3/7) | 57.1% (4/7) | 41.7% (5/12) | 60.0% (3/5) | 40.0% (2/5) |
| T3/T4 | 50.0% (5/10) | 40.0% (2/5) | 60.0% (3/5) | 11.1% (1/9) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) |
| Unknown T stage | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | ||
| N0M0 | 47.4% (9/19) | 44.4% (4/9) | 55.6% (5/9) | 33.3% (5/15) | 60.% (3/5) | 20.0% (2/5) |
| N1/M1 | 42.9% (3/7) | 33.3% (1/3) | 66.7% (2/3) | 16.7% (1/6) | 0% (0/0) | 100% (1/1) |
| Unknown N/M status | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | ||
| T1/T2 N0M0 | 46.7% (7/15) | 42.9% (3/7) | 57.1% (4/7) | 41.7% (5/12) | 60.0% (3/5) | 40.0% (2/5) |
| T3N0M0 | 50.0% (2/4) | 50% (1/2) | 50.0% (1/2) | 0% (0/3) | ||
| T4/N1/M1 | 42.9% (3/7) | 33.3% (1/3) | 66.7% (2/3) | 16.7% (1/6) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) |
| Unknown T/N/M status | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) | 100% (1/1) | ||
| Low risk | 50.0% (3/6) | 0% (0/3) | 100% (3/3) | 33.3% (2/6) | 0% (0/2) | 100% (2/2) |
| Int. risk | 50.0% (3/6) | 100% (3/3) | 0% (0/3) | 33.3% (1/3) | 100% (1/1) | 0% (0/1) |
| High risk | 40.0% (6/15) | 33.3% (2/6) | 66.7% (4/6) | 30.8% (4/13) | 50% (2/4) | 50% (2/4) |
SD, significantly different, based on 1D KS test (P < 0.01); GS, Gleason score; GG, Gleason grade; low risk, Gleason score 2-6 and T1/2 and N0M0; int. risk, intermediate risk (Gleason score 7 and T1/2 and N0M0); high risk, Gleason score 8-10 and/or T3/4 and/or N1 and/or M1.
We also assessed if positioning patterns correlated with Gleason grade. For all four genes, increasing Gleason grade did not correlate with the percentage of cancer specimens in which the genes repositioned ( Tables 3 and 4 ). Consistent with Gleason score, the direction that SATB1 and LMNA repositioned did not aid in stratifying cancers by Gleason grade ( Table 3 ), but the direction of repositioning did correlate with Gleason grade for SP100 and TGFB3 ( Table 4 ). As with Gleason score, in the more highly differentiated cancers (Gleason grades 1-3) SP100 and TGFB3 repositioned towards the nuclear periphery in 100% (5 and 3 cancers, respectively) of the cancers in which these genes repositioned. Yet, in the poorly differentiated cancers (Gleason grade 4 and 5) both genes preferentially repositioned towards the nuclear interior. SP100 was more internally positioned in 80% (4/5) of Gleason grade 4 and 5 cancer in which SP100 repositioned and TGFB3 was more internally positioned in 66.7% (2/3) of the Gleason grade 4 and 5 cancers in which TGFB3 was repositioned, compared to the PND ( Table 4 ). The similarity between Gleason grade and Gleason score positioning patterns are not surprising given that Gleason score is the sum of the two most prominent Gleason grades (Epstein et al., 2005; Epstein, 2018). An important caveat to be noted is that while the subgrouping of the cancers was based on the most predominant Gleason grade of the tissue, it is not necessarily the predominant Gleason grade of the nuclei analyzed from each specimen.
Collectively, these observations demonstrate that while positioning patterns performed less well than the Gleason system at stratifying cancers, we identify differential gene positioning patterns between subgroups of prostate cancers.
Multiplexing SP100 and TGFB3 Improves Detecting Intermediate and High Gleason Score Cancers
Although both SP100 and TGFB3 displayed differential positioning patterns between low and intermediate/high Gleason score cancer specimens, the sensitivity for subgrouping prostate cancers by Gleason score based on positioning patterns is low. Using a more peripheral positioning of SP100 compared to the PND as a marker of low Gleason score cancers, the false negative rate (percentage of cancers without a more peripheral positioning) is 45.4% (5/11 low Gleason score cancers; Table 1 ). For TGFB3 the false negative rate is even higher at 70% (7/10; Table 1 ). Additionally, using this criterion, false positive cancers were identified for both genes. More peripheral positioning was detected in one high Gleason score specimen for both SP100 and TGFB3, resulting in a false positive rate of 6.3% (1/16) and 8.3% (1/12), respectively, for intermediate and high Gleason score cancers ( Table 1 ). Neither gene was more internally positioned in low Gleason score cancers ( Table 1 ). Using a more internal positioning pattern as a biomarker of intermediate and high Gleason score cancers resulted in a false negative rate of 62.5% (10/16) and 66.7% (8/12) for SP100 and TGFB3, respectively ( Table 1 ).
We have previously demonstrated that the sensitivity of diagnostic GPBs can be improved by multiplexing (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016). We therefore evaluated if combining positioning data from SP100 and TGFB3 would increase the number of cancers classified as low or intermediate/high Gleason score based on gene positioning patterns. Importantly for multiplexing to improve the sensitivity, SP100 and TGFB3 would need to be frequently repositioned in different cancer specimens. Of a subset of 19 cancer tissues in which both genes were positioned, 10 (52.6%) had differential repositioning patterns for SP100 to that of TGFB3 ( Table 1 , Supplementary Table 7 ). For six of these cancers SP100 was repositioned but TGFB3 was not, whereas in three cancers only TGFB3 was repositioned. For one cancer sample, both genes were repositioned, compared to their PND, but they relocated in opposite directions, with SP100 being more peripherally positioned, while TGFB3 was more internally positioned ( Table 1 , Supplementary Table 7 ). However, multiplexing the two genes did not improve the sensitivity to detect low Gleason score cancers above using SP100 alone. SP100 was more peripherally positioned in all five cancers where at least one of the two genes repositioned ( Table 1 , Supplementary Table 7 ). Nevertheless, multiplexing increased the sensitivity of detecting intermediate/high Gleason score cancers ( Table 1 , Supplementary Table 7 ). At least one gene repositioned in eight of the 11 (72.7%) Gleason score 7 and higher cancers. Both SP100 and TGFB3 contributed to the increased proportion of cancer specimens with repositioning events. Of the seven cancers with only one of the two genes more internally repositioned, SP100 was more internally repositioned in four and TGFB3 more internally positioned in three cancers ( Table 1 , Supplementary Table 7 ).Using a more internal position of at least one of SP100 or TGFB3 the false negative rate for detecting intermediate or high Gleason score cancers was reduced to 36.4% (4/11). While most of the repositioning events in intermediate/high Gleason score cancers were to a more internal position, in one cancer the only repositioning event resulted in a more peripheral location of TGFB3 and in another cancer tissue, there was both a more peripheral and more internal repositioning events, with SP100 more peripherally position and TGFB3 more internally located ( Table 1 , Supplementary Table 7 ).
Gleason score is not a perfect measure of risk. Given the variability in positioning patterns within the same Gleason group, we asked if the positioning patterns could be useful to distinguish aggressive low Gleason core cancers from non-aggressive low Gleason score cancers. Such a marker would aid treatment decisions. However, SP100 and TGFB3 were repositioned in a similar proportion of low Gleason score cancers with or without metastasis ( Table 1 ). SP100 repositioned in 50% (2/4) of low Gleason score cancers that had metastasized and 57.1% (4/7) of low Gleason score cancers without metastases. Likewise, TGFB3 repositioned in 33.3% (1/3) of metastatic low Gleason score cancer specimens and 28.8% (2/7) of non-metastatic low Gleason score cancer specimens ( Table 1 ). Thus, in addition to the high false negative rate for Gleason score, SP100 and TGFB3 can not distinguish aggressive low Gleason score cancers from non-aggressive low Gleason score cancers, limiting their clinical potential.
Low Gleason Score Cancer Gene Positioning Patterns Are Distinct From Benign Disease
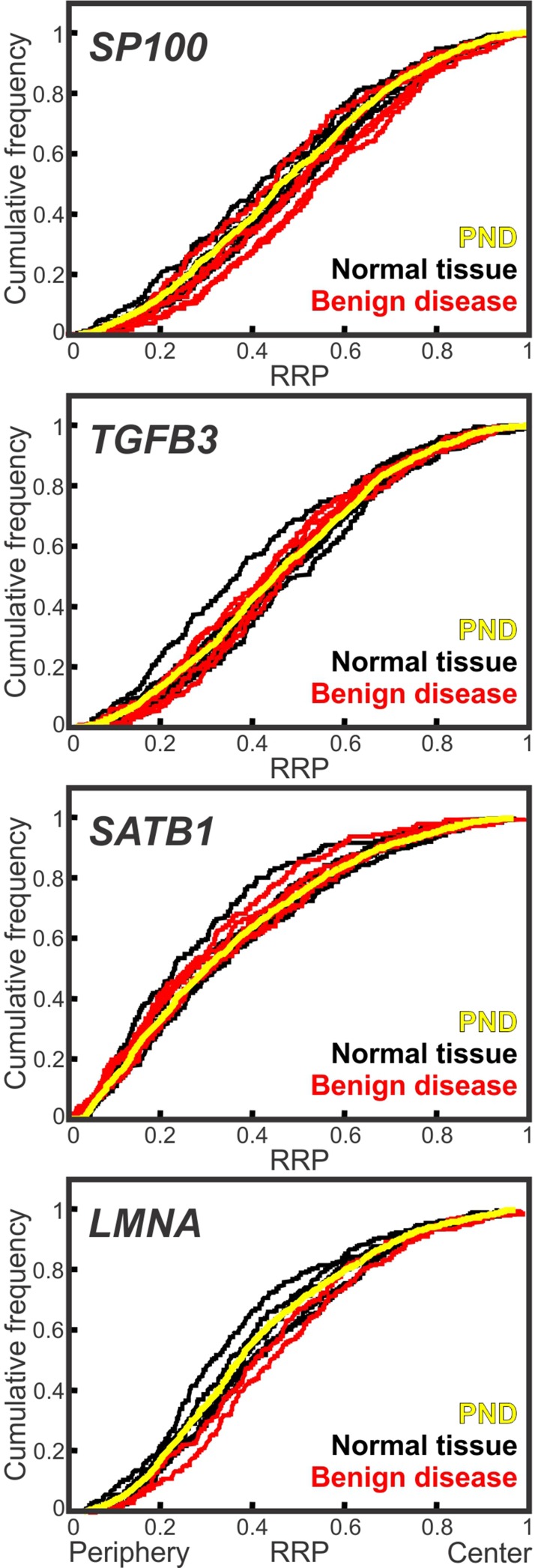
Given the fact that low Gleason score cancers are fairly well differentiated tissues, it is possible that low Gleason score cancers have a similar genome organization to benign disease. We therefore sought to determine the cancer-specificity of the repositioning events. We positioned SP100, TGFB3, SATB1 and LMNA in non-cancerous prostate tissues ( Figure 2 , Supplementary Figure 1 , Tables 5 and 6 , Supplementary Tables 2 – 5 ). For all four genes we found that the positioning patterns were highly similar between benign tissues. For SP100, TGFB3 and SATB1, only 9.1%-14.1% of comparisons between the individual non-cancerous tissues reached significance. There was a little more variability between benign tissues for LMNA, where 25% of cross-comparisons between benign tissues were significantly different ( Figure 2 , Table 2 , Supplementary Table 2 – 5 ).There was also little repositioning of the four genes in benign tissues when compared to the PND, with repositioning in 7.7%-16.7% of benign tissues, depending on the gene ( Figure 2 , Tables 5 and 6 ). SP100 was statistically similarly positioned in all seven normal tissues, compared to the PND, but was significantly repositioned in 40% (2/5) of benign disease tissue ( Figure 2 , Tables 5 and 6 ). However, the positioning patterns of SP100 were distinct in benign disease and low Gleason score cancer, since it was more internally localized in the two benign disease tissues, yet more peripherally located in low Gleason score cancers ( Tables 1 and 5 ).
Figure 2.
Conserved spatial organization of the genome in benign tissues. Cumulative RRDs for the indicated genes in normal prostate tissue (black), benign disease (red) and the pooled normal distribution (PND; yellow). RRP, relative radial position.
Table 5.
Conservation of positioning between normal prostate tissues and in benign disease.
| Tissue | SP100 | TGFB3 | SATB1 | LMNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | ||||
| N2 | P | |||
| N3 | P | |||
| N4 | ||||
| N5 | ||||
| N6 | ||||
| N7 | ||||
| N8 | ||||
| N9 | ||||
| N10 | ||||
| N11 | ||||
| N12 | ||||
| N13 | ||||
| N14 | ||||
| N15 | ||||
| N16 | ||||
| B1 | I | |||
| B2 | ||||
| B3 | I | I | ||
| B4 | ||||
| B5 | ||||
| B6 | ||||
| B7 | ||||
| B8 | ||||
| B9 |
Statistical comparisons of the RRD of a gene in individual benign tissues and to the PND, using the two-sample 1D KS test. Red, significantly different (P < 0.01); Blue, statistically similar position (P > 0.01). N1-16, normal prostate tissue; B1-9, benign disease tissues; I, a more internal position in the benign, compared to the PND; P, a more peripheral positioning in the benign tissue.
Table 6.
Comparison of individual benign tissue to the pooled normal.
| SP100 | TGFB3 | SATB1 | LMNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal tissues | 0.0% (0/7) | 12.5% (1/8) | 14.3% (1/7) | 0.0% (0/6) |
| Benign disease | 40.0 (2/5) | 0.0% (0/5) | 0.0% (0/5) | 50.0% (1/2) |
| Total benign tissues | 16.7% (2/12) | 7.7% (1/13) | 8.3% (1/12) | 12.5% (1/8) |
% (number) of benign tissues where the RRD is significantly different to the PND (P < 0.01; KS test).
Inclusion of the direction of repositioning in the analysis further confirmed the specificity of the repositioning events to the different Gleason score subgroups. When using more peripheral positioning, compared to the PND, as a marker of low Gleason score prostate cancer, the false positive rate for SP100 is very low, at 3.6%, since it is more peripherally positioned in only one of 28 normal, benign disease and higher Gleason score cancer tissues ( Tables 1 and 5 ). Similarly, TGFB3 was repositioned in a single normal tissue (12.5%; 1/8) and in none of the benign disease tissues (0/5), compared to the PND ( Figure 2 , Tables 5 and 6 ). Unlike SP100, the direction TGFB3 reposition in the normal tissue was the same as in low Gleason score cancer. However, the false positive rate for using a more peripheral positioning of TGFB3 was relatively low at 8%, because it was more peripherally positioned in two of the 25 benign tissues and higher Gleason score cancers ( Tables 1 and 5 ). The false positive rate of using a more internal position of SP100 or TGFB3 to detect intermediate/high Gleason score cancers is also low, at 8.7% and 0%, respectively, since SP100 was more internally repositioned in only two of the 23 benign tissues and low Gleason score cancer specimens and TGFB3 was not more internally repositioned in these groups of tissues (N = 23; Table 1 and 5 ). Taken together, we find the spatial organization of the genome is generally conserved between benign tissues, and benign disease tissue have a distinct genome organization to both low and intermediate/high Gleason score cancers.
LMNA Repositions in Low Risk and Non-Metastatic Cancers
Having determined the biomarker potential of the candidate genes for subgrouping prostate cancers by Gleason score, we compared their positioning patterns to other clinical markers of poor patient outcome. The TNM staging system is commonly used to aid the prediction of the aggressiveness of the cancer and the risk of poor patient outcome (Thompson et al., 2007). In stage T1 and T2 prostate cancers the tumor is contained within the prostate, whereas in stages T3 and T4 the cancer has spread from the prostate into the surrounding tissue. T1 and T2 cancers are lower risk cancers and respond better to treatment than T3 and T4 prostate cancers (Thompson et al., 2007; Chang et al., 2014). The N and M score indicates whether the cancer has spread beyond the surrounding tissue. In N0 cancers, no cancer cells are detected in the regional lymph nodes, whereas N1 denotes that the cancer has spread into the regional lymph nodes. For M0 cancers, no distant metastasis are detected, while distant metastases, to non-regional lymph nodes or organs, have occurred in M1 cancers (Thompson et al., 2007).
Positioning patterns for SP100 and SATB1 were similar in low and high T stage cancer specimens and could not be used to distinguish the different T stage group cancers from each other ( Tables 3 and 4 ). TGFB3 and LMNA were both more frequently repositioned in low T stage cancers to that of high T stage cancers, but with high false positive rates ( Tables 3 and 4 ). TGFB3 repositioned in 41.7% (5/12) of T1/2 cancers, 11.1% (1/9) of T3/4 cancers, and 7.7% (1/13) of benign tissues, compared to the PND ( Tables 1 , 4 and 6 ). This equates to a false negative rate of 58.3% (7/12) and a false positive rate of 9.1% (2/22) for using the reposition of TGFB3 to detect low T stage prostate cancer. Similarly, LMNA repositioned in 42.9% (3/7) of low T stage cancer, 25% (1/4) of high T stage cancers and 12.5% (1/8) of benign tissues ( Tables 3 and 6 ), making the false negative and positive rates of using the repositioning of LMNA to demark low T stage cancers 57.1% (4/7) and 16.7% (2/12), respectively.
Clinically, multiple factors are combined to determine risk of poor outcome. Therefore, we also compared gene positioning patterns with a multifactorial determinant of risk using standard clinical risk assessment criteria (Thompson et al., 2007; Chang et al., 2014) with the exception of PSA levels, since no information on serum PSA were available for our specimens. Moreover, we included N1 and/or M1 cancers in the high-risk group, since they are known aggressive cancers. We classified low risk cancer as Gleason score 2-6 and T1/2 and N0M0 cancers; intermediate risk cancers as Gleason score 7 and T1/2 and N0M0; high risk as Gleason score 8-10 and/or T3/4 and/or N1 and/or M1 prostate cancers. The positioning patterns of SP100, TGFB3 and SATB1 were similar in all three risk groups, and thus could not be used as markers of risk ( Tables 3 and 4 ). Conversely, LMNA was more frequently repositioned in low risk prostate cancer, since it repositioned in 66.7% (2/3) of low risk cancers, 0% (0/2) of intermediate risk and 33.3% (2/6) of high-risk groups ( Table 3 ).
Finally, as a more direct measure of the aggressiveness of a cancer we compared non-metastatic cancers (N0M0) and metastatic (N1/M1) prostate cancers ( Supplementary Figure 2B , Table 1 , 3 and 4 ). SP100 repositioned, compared to the PND, in a similar proportion of N0M0 (47.4%; 9/19) and metastatic (42.9%; 3/7) cancer specimens. Furthermore, the direction of repositioning was similarly mixed in both groups of cancer ( Table 4 ). The remaining three genes repositioned more frequently in non-metastatic cancers. For TGFB3 and SATB1 this difference is small, with the genes repositioned in ∼33.3% (5/15 and 6/16 respectively; false negative rate ∼66.7%) of non-metastatic cancers and 16.7% (1/6) of metastatic cancers ( Table 3 and 4 ). LMNA was the best marker of non-metastatic cancers. LMNA repositioned in 57.1% (4/7) of non-metastatic prostate cancer specimens and was not repositioned in metastatic (0/4) cancer tissues ( Supplementary Figure 2B , Table 3 ). As with SP100 and TGFB3 as markers of Gleason score, the false negative rate for using LMNA positioning as a marker of non-metastatic cancer was high at 42.9% (3/7), and the false positive rate is relatively low at 8.3% (1/12) ( Tables 1 , 3 and 5 ).
Taken together, our data suggest that there are distinct spatial gene positioning patterns between some subgroups of prostate cancers, although the false negative rates were generally high, limiting their potential for clinical use.
Discussion
To reduce overtreatment in cancer patients that receive no benefit from medical intervention, there is an urgent need for biomarkers that predict the aggressiveness of a cancer. Here, we assess the feasibility of utilizing the spatial positioning patterns of genes in interphase nuclei for prognostic purposes in prostate cancer. We find a differential enrichment of specific positioning patterns for multiple genes between clinically relevant subgroups of prostate cancers. While the false positive rates for prognostic evaluation are low, the false negative rates are generally high, limiting clinical usefulness. Our results of subtype-specific genome organization patterns suggest that it should be possible to find clinically valuable prognostic GPB by screening additional genes and combinations of genes.
The spatial organization of the genome is altered in diseased cells, and at least some of the changes to genomic spatial positioning patterns are disease-specific (Meaburn, 2016). For instance, HES5 repositions in breast cancer, but not in benign breast disease nor prostate cancer (Meaburn et al., 2009; Meaburn et al., 2016). Alternative spatial positioning patterns are not only found in cancers formed in different organs, but there is also heterogeneity in the spatial organization of the genome between individual cancers of the same type (Meaburn et al., 2009; Knecht et al., 2012; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016). We hypothesized that heterogeneity within a cancer type may reflect the aggressiveness of a cancer and therefore be of prognostic value. Prognosis-related repositioning of genomic regions in several types of cancer has previously been reported, with increased clustering of telomeres linked to poorer patient outcomes (Mai, 2018). For example, at the time of diagnosis telomeres were more likely to cluster in Hodgkin lymphoma patients whose disease later relapsed or progressed compared to patients who responded well to treatment (Knecht et al., 2012). Currently, Gleason score and the presence or absence of metastasis are key clinicopathological tumor features for predicting the aggressiveness of a prostate cancer. We find that SP100 and TGFB3 occupy alterative positions in low Gleason score cancers compared to higher Gleason scored cancers, and that LMNA repositions more internally in many non-metastatic and low risk prostate cancers, but infrequently reposition in high risk/aggressive cancers.
Our previous identification of diagnostic GPBs was based on the percentage of cancer specimens in which a gene had an alternative radial position, compared to its distribution in normal tissues (Meaburn, 2016). Interestingly, for SP100 and TGFB3 it was not the repositioning itself, but the direction of repositioning that was useful for stratification of prostate cancers. Repositioning of either SP100 or TGFB3 towards the nuclear periphery was associated with low Gleason score whereas repositioning towards the interior was a marker of higher Gleason score cancers. The repositioning patterns of SP100 and TGFB3 could not distinguish intermediate from high Gleason score cancers. Nevertheless, this does not necessarily rule them out as useful clinical markers since low Gleason score cancers are less likely to receive treatment than intermediate or high Gleason score cancers (Thompson et al., 2007; Cooperberg et al., 2010; Leshner et al., 2016). Given that there is inter-and intra-observer variability when scoring cancers (Montironi et al., 2005), additional markers that can clarify if a cancer is Gleason score 6 (low) or 7 (intermediate) would be useful in guiding therapeutic choices. However, because the positioning patterns of our genes could not separate aggressive, metastatic low Gleason score cancers from non-metastatic low Gleason score cancers, they are unlikely to aid the decision of whether to treat a cancer or not. In keeping with a differential spatial genome organization in cancers above and below the treatment threshold, we previously found MMP9 to reposition in 20% of low Gleason score cancers compared to 82% of intermediate/high Gleason score cancers (Leshner et al., 2016). Unlike SP100 and TGFB3, the direction MMP9 repositioned did not aid stratification (Leshner et al., 2016), unpublished data). MMP9 was positioned predominantly in Gleason score 6 and 7 prostate cancers, making it unclear how specific these positioning patterns are more generally to the different Gleason scores subgroups. SP100, TGFB3 and MMP9 each map to different chromosomes (HSA 2, 14 and 20, respectively) and therefore represent independent repositioning events within the subgroups of different Gleason score cancers.
In our analysis we find low false positive rates for distinguishing low from intermediate/high Gleason score cancers. In keeping with previous studies (Borden and Manuelidis, 1988; Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016), we find similar positioning patterns for both SP100 and TGFB3 amongst normal tissues and between normal and benign disease tissues, highlighting that the gene repositioning in cancer tissues were specific to cancer. Despite the fact that low Gleason score cancers represents fairly well differentiated tissues there were distinct positioning patterns for SP100 and TGFB3 between low Gleason score cancers and benign disease, which are considered differentiated tissues. TGFB3 did not reposition in benign disease and SP100 was repositioned in only 20% of the benign disease tissues. However, unlike low Gleason score cancers, SP100 was more internally positioned in benign disease tissues, and therefore does not contribute to the false positive rate when using more peripheral positioning of these genes to detect low Gleason score cancers. Unlike biomarkers used to diagnose cancer, the false positive rate of detecting a subtype of cancer for prognostic purposes is not only generated from non-cancerous tissues, it needs to also include cancers from the alternative subgroups. Even so, the false positive rates of detecting low Gleason score prostate cancers were low because the direction of repositioning for SP100 and TGFB3 was mostly specific to the subgroups. In contrast to the false positive rates, the false negative rates for SP100 and TGFB3 were high, at 45-70%. We have previously found that for some genes multiplexing reduces the false negative rate and thus increases the sensitivity of detecting cancer (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016). Constant with this, we find that multiplexing SP100 and TGFB3 reduces the false negative rate of detecting intermediate and higher Gleason score cancers. However, multiplexing with a more peripheral position of either SP100 or TGFB3 did not reduce the false negative rate for low Gleason score cancers from that of using SP100 alone. We conclude that the observed high false negative rates reduce marker strength and the utility of these genes for prognostic purposes.
Even though the positioning patterns of SP100 and TGFB3 are inferior to the Gleason system at stratifying cancers, our results reveal subtype-specific genome organization. Similarly, the repositioning of LMNA is also subtype-specific, but in this case the repositioning occurs only in non-metastatic cancers, although also with a high false negative rate. Interestingly, the reorganization events between the different subtypes of prostate cancer appear to be gene-specific. LMNA and SATB1 positioning patterns were not able to stratify prostate cancers by Gleason score and SP100, TGFB3 and SATB1 were not accurate markers of risk or aggressiveness of the cancer. Consistently, the radial repositioning patterns of FLI1, MMP9 and MMP2 also do not correlate with the risk/aggressiveness of prostate cancer (Leshner et al., 2016). Given that it can take many years after the initial diagnosis of prostate cancer to progress to recurrence, metastasis and/or lethality (Albertsen et al., 1998; D’Amico et al., 1998; Pound et al., 1999; Cooperberg et al., 2009), it will be necessary to analyze specimens with long-term (15+ years) follow-up to accurately assess the potential of spatial positioning for assessment of risk or aggressiveness.
It is unknown what mechanisms lead to the reorganization of the genome in disease, and many processes have been implicated in regulating spatial positioning patterns, including changes in gene expression, replication timing, chromatin modifications, altered amounts of nuclear proteins, making it likely that the mis-regulations of these cellular functions in cancer cells is related to the spatial mis-organization of the genome (Zink et al., 2004; Meaburn, 2016; Flavahan et al., 2017). The four genes we studied have all been associated with carcinogenesis and have a range of functions. SP100 is a major component of the PML nuclear body and has been implicated in transcription regulation, cellular stress, oxidative stress, telomere length and stability, senescence, apoptosis and DNA damage repair (Lallemand-Breitenbach and de The, 2010). However, most of the evidence for PML bodies role in cancer relates to the PML protein, not SP100, which has not been implicated in prostate cancer. TGFB3 is a cytokine, with important roles in development, wound healing, the immune response and acts as a tumor suppresser in early cancers but can switch to promoting cancer progression in later stages (Massague, 2008; Laverty et al., 2009). TGFB3 gene expression levels have been identified as a potential biomarker for prostate cancer, being expressed at lower levels in prostate cancer than normal tissue (Wang et al., 2017). Moreover, TGFB3 expression levels correlated weakly with both progression-free survival and Gleason score (Wang et al., 2017). SATB1, a nuclear architectural protein that facilitates DNA loop formation and chromatin remodeling (Kohwi-Shigematsu et al., 2013), promotes the progression of many cancers, including prostate cancer, and is overexpressed in high Gleason score cancers compared to low Gleason score cancers and in metastatic compared to non-metastatic prostate cancers (Mao et al., 2013; Shukla et al., 2013; Naik and Galande, 2019). LMNA encodes for A-type lamins, proteins that reside predominantly at the nuclear envelope, and have a variety of roles including in nuclear structure, transcription regulation, and spatial genome organization (Dittmer and Misteli, 2011). A-type lamins levels are altered in many types of cancer, with reduced levels often, but not always, linked to a tendency for a poorer prognostic outcome (Meaburn, 2016). It is not currently clear what effect prostate cancer has on A-type lamin protein levels. On the one hand, levels of A-type lamins in prostate cancer have been correlated with poor outcome, with reduced levels associated with an increased risk of lymph node metastasis, and poor outcome in Gleason score 7 and higher prostate cancers (Saarinen et al., 2015). On the other hand, reduced A-type lamin levels in Gleason score 6 cancer compared to high Gleason score cancer, increased A-type lamin levels in cells at the invasive leading edge of prostate cancers, and enhanced migration and invasion in the presence of high A-type lamin levels have been also been reported (Skvortsov et al., 2011; Kong et al., 2012).
Increased cell proliferation is associated with a poor outcome for prostate cancer patients (Berlin et al., 2017), and several genomic loci are differentially positioned between proliferating and non-proliferating cells (Bridger et al., 2000; Meaburn and Misteli, 2008). However, variations in proliferation rate is unlikely to be a major determinant in the gene repositioning we detect. In fact, the vast majority of cells in a prostate cancer tumor are non-proliferating, with a mean of just 6.1% proliferating cells per cancer (Berlin et al., 2017). Furthermore, in a cell culture model of breast cancer, there were distinct genome spatial rearrangements associated with proliferation status to that of carcinogenesis (Meaburn and Misteli, 2008). Similarly, although we find that changes in copy number did not correlated with propensity to reposition ( Supplementary Table 6 ; (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016), we can not fully rule out that structural genomic alterations have not influenced the spatial position of any of the genes in the tissues analyzed since, in some cases, genomic instability can lead to spatial reorganization of the genome (Croft et al., 1999; Taslerova et al., 2003; Harewood et al., 2010; Federico et al., 2019). Regardless, importantly for a clinical test, we find that even in the background of genomic instability it is still possible to use gene positioning to distinguish normal tissue from cancer (Meaburn et al., 2009; Leshner et al., 2016; Meaburn et al., 2016) and to stratify cancers into clinically distinct subgroups, as demonstrated in this study.
Taken together, this study assesses the utility of spatial gene positioning in the stratification of prostate cancers. Our results reveal correlations between gene location and the aggressiveness of a tumor, which may serve as the foundation for prognostic usage of gene positioning. While the genes analyzed here have a relatively high false negative rate of detecting cancer subgroups, our results encourage the exploration of additional candidate genes in larger sample sets for the discovery of spatial genome positioning patterns as prognostic biomarkers.
Data Availability Statement
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/ Supplementary Files .
Author Contributions
KM and TM conceived the study and wrote the manuscript. KM designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted data, and made the figures.
Funding
This work was supported by a Department of Defense Idea Award (W81XWH-15-1-0322) and the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, NCI, Center for Cancer Research.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Lawrence True for invaluable and insightful prostate pathology discussions, Prabhakar Gudla and Stephen Lockett for the FISH positioning analysis software; Delft University (Netherlands) for providing the DIPImage and PRTools toolboxes and Tatiana Karpova for microscopy support. Fluorescence imaging was performed at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Fluorescence Imaging Facility.
Abbreviations
BAC, bacterial artificial chromosome; EDT, Euclidean distance transform; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; FFPE, formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded; GPB, gene positioning biomarker; HSA, human chromosome; KS test, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test; NAT, normal adjacent to tumor; PND, pooled normal distribution; PSA, serum prostate specific antigen; RRD, relative radial distribution; TMA, tissue microarray.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2019.01029/full#supplementary-material.
References
- Albertsen P. C., Hanley J. A., Gleason D. F., Barry M. J. (1998). Competing risk analysis of men aged 55 to 74 years at diagnosis managed conservatively for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA 280, 975–980. 10.1001/jama.280.11.975 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin A., Castro-Mesta J. F., Rodriguez-Romo L., Hernandez-Barajas D., Gonzalez-Guerrero J. F., Rodriguez-Fernandez I. A., et al. (2017). Prognostic role of Ki-67 score in localized prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol. Oncol. 35, 499–506. 10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore W. A. (2013). The spatial organization of the human genome. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 14, 67–84. 10.1146/annurev-genom-091212-153515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore W. A., van Steensel B. (2013). Genome architecture: domain organization of interphase chromosomes. Cell 152, 1270–1284. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden J., Manuelidis L. (1988). Movement of the X chromosome in epilepsy. Science 242, 1687–1691. 10.1126/science.3201257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle S., Gilchrist S., Bridger J. M., Mahy N. L., Ellis J. A., Bickmore W. A. (2001). The spatial organization of human chromosomes within the nuclei of normal and emerin-mutant cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 211–219. 10.1093/hmg/10.3.211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray F., Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Siegel R. L., Torre L. A., Jemal A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickner J. H., Walter P. (2004). Gene recruitment of the activated INO1 locus to the nuclear membrane. PLoS Biol. 2, e342. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020342 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. M., Boyle S., Kill I. R., Bickmore W. A. (2000). Re-modelling of nuclear architecture in quiescent and senescent human fibroblasts. Curr. Biol. 10, 149–152. 10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00312-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimo F., Montironi R., Egevad L., Erbersdobler A., Lin D. W., Nelson J. B., et al. (2013). Contemporary grading for prostate cancer: implications for patient care. Eur. Urol. 63, 892–901. 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.10.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. E., Guest S. S., Smale S. T., Hahm K., Merkenschlager M., Fisher A. G. (1997). Association of transcriptionally silent genes with Ikaros complexes at centromeric heterochromatin. Cell 91, 845–854. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80472-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabianca D. S., Munoz-Jimenez C., Kalck V., Gaidatzis D., Padeken J., Seeber A., et al. (2019). Active chromatin marks drive spatial sequestration of heterochromatin in C. elegans nuclei. Nature 569, 734–739. 10.1038/s41586-019-1243-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra T., Ewels P. A., Schoenfelder S., Furlan-Magaril M., Wingett S. W., Kirschner K., et al. (2015). Global reorganization of the nuclear landscape in senescent cells. Cell Rep. 10, 471–483. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.12.055 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. J., Autio K. A., Roach M., 3rd, Scher H. I. (2014). High-risk prostate cancer-classification and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 11, 308–323. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.68 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperberg M. R., Broering J. M., Carroll P. R. (2009). Risk assessment for prostate cancer metastasis and mortality at the time of diagnosis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 101, 878–887. 10.1093/jnci/djp122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperberg M. R., Broering J. M., Carroll P. R. (2010). Time trends and local variation in primary treatment of localized prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 28, 1117–1123. 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.0133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer T., Cremer C. (2001). Chromosome territories, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in mammalian cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 292–301. 10.1038/35066075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft J. A., Bridger J. M., Boyle S., Perry P., Teague P., Bickmore W. A. (1999). Differences in the localization and morphology of chromosomes in the human nucleus. J. Cell Biol. 145, 1119–1131. 10.1083/jcb.145.6.1119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico A. V., Whittington R., Malkowicz S. B., Schultz D., Blank K., Broderick G. A., et al. (1998). Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA 280, 969–974. 10.1001/jama.280.11.969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmer T. A., Misteli T. (2011). The lamin protein family. Genome Biol. 12, 222. 10.1186/gb-2011-12-5-222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dundr M., Ospina J. K., Sung M. H., John S., Upender M., Ried T., et al. (2007). Actin-dependent intranuclear repositioning of an active gene locus in vivo . J. Cell Biol. 179, 1095–1103. 10.1083/jcb.200710058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J. I. (2018). Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified system. Mod. Pathol. 31, S47–S63. 10.1038/modpathol.2017.133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J. I., Allsbrook W. C., Jr., Amin M. B., Egevad L. L., Committee I. G. (2005). The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus conference on gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 29, 1228–1242. 10.1097/01.pas.0000173646.99337.b1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M., Feodorova Y., Naumova N., Imakaev M., Lajoie B. R., Leonhardt H., et al. (2019). Heterochromatin drives compartmentalization of inverted and conventional nuclei. Nature 570, 395–399. 10.1038/s41586-019-1275-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federico C., Owoka T., Ragusa D., Sturiale V., Caponnetto D., Leotta C. G., et al. (2019). Deletions of Chromosome 7q affect nuclear organization and HLXB9Gene expression in hematological disorders. Cancers (Basel) 11, 585. 10.3390/cancers11040585 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan W. A., Gaskell E., Bernstein B. E. (2017). Epigenetic plasticity and the hallmarks of cancer. Science 357. 10.1126/science.aal2380 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harewood L., Schutz F., Boyle S., Perry P., Delorenzi M., Bickmore W. A., et al. (2010). The effect of translocation-induced nuclear reorganization on gene expression. Genome Res. 20, 554–564. 10.1101/gr.103622.109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harr J. C., Gonzalez-Sandoval A., Gasser S. M. (2016). Histones and histone modifications in perinuclear chromatin anchoring: from yeast to man. EMBO Rep. 17, 139–155. 10.15252/embr.201541809 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratani I., Ryba T., Itoh M., Yokochi T., Schwaiger M., Chang C. W., et al. (2008). Global reorganization of replication domains during embryonic stem cell differentiation. PLoS Biol. 6, e245. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hveem T. S., Kleppe A., Vlatkovic L., Ersvaer E., Waehre H., Nielsen B., et al. (2016). Chromatin changes predict recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Br. J. Cancer 114, 1243–1250. 10.1038/bjc.2016.96 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht H., Kongruttanachok N., Sawan B., Brossard J., Prevost S., Turcotte E., et al. (2012). Three-dimensional telomere signatures of hodgkin- and reed-sternberg cells at diagnosis identify patients with poor response to conventional chemotherapy. Transl. Oncol. 5, 269–277. 10.1593/tlo.12142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M., Ittiprasert W., Odoemelam E. C., Adema C. M., Miller A., Raghavan N., et al. (2011). Non-random organization of the Biomphalaria glabrata genome in interphase Bge cells and the spatial repositioning of activated genes in cells co-cultured with Schistosoma mansoni. Int. J. Parasitol. 41, 61–70. 10.1016/j.ijpara.2010.07.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Poterlowicz K., Ordinario E., Han H. J., Botchkarev V. A., Kohwi Y. (2013). Genome organizing function of SATB1 in tumor progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 23, 72–79. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.06.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L., Schafer G., Bu H., Zhang Y., Zhang Y., Klocker H. (2012). Lamin A/C protein is overexpressed in tissue-invading prostate cancer and promotes prostate cancer cell growth, migration and invasion through the PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway. Carcinogenesis 33, 751–759. 10.1093/carcin/bgs022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg Z., Cooperberg M. R., Spratt D. E., Feng F. Y. (2018). Genomic biomarkers in prostate cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 7, 459–471. 10.21037/tau.2018.06.02 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaran R. I., Spector D. L. (2008). A genetic locus targeted to the nuclear periphery in living cells maintains its transcriptional competence. J. Cell Biol. 180, 51–65. 10.1083/jcb.200706060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallemand-Breitenbach V., de The H. (2010). PML nuclear bodies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a000661. 10.1101/cshperspect.a000661 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverty H. G., Wakefield L. M., Occleston N. L., O’Kane S., Ferguson M. W. (2009). TGF-beta3 and cancer: a review. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20, 305–317. 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.07.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leshner M., Devine M., Roloff G. W., True L. D., Misteli T., Meaburn K. J. (2016). Locus-specific gene repositioning in prostate cancer. Mol. Biol. Cell 27, 236–246. 10.1091/mbc.e15-05-0280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Shi Z., Zhang L., Huang Y., Liu A., Jin Y., et al. (2010). Dynamic changes of territories 17 and 18 during EBV-infection of human lymphocytes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 37, 2347–2354. 10.1007/s11033-009-9740-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mai S. (2018). The three-dimensional cancer nucleus. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 58, 462–473. 10.1002/gcc.22720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao L., Yang C., Wang J., Li W., Wen R., Chen J., et al. (2013). SATB1 is overexpressed in metastatic prostate cancer and promotes prostate cancer cell growth and invasion. J. Transl. Med. 11, 111. 10.1186/1479-5876-11-111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J. (2008). TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 134, 215–230. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meaburn K. J. (2010). Fluorescence in situ hybridization on 3D cultures of tumor cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 659, 323–336. 10.1007/978-1-60761-789-1_25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meaburn K. J. (2016). Spatial genome organization and its emerging role as a potential diagnosis tool. Front. Genet. 7, 134. 10.3389/fgene.2016.00134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meaburn K. J., Agunloye O., Devine M., Leshner M., Roloff G. W., True L. D., et al. (2016). Tissue-of-origin-specific gene repositioning in breast and prostate cancer. Histochem. Cell Biol. 145, 433–446. 10.1007/s00418-015-1401-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meaburn K. J., Cabuy E., Bonne G., Levy N., Morris G. E., Novelli G., et al. (2007). Primary laminopathy fibroblasts display altered genome organization and apoptosis. Aging Cell 6, 139–153. 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00270.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meaburn K. J., Gudla P. R., Khan S., Lockett S. J., Misteli T. (2009). Disease-specific gene repositioning in breast cancer. J. Cell Biol. 187, 801–812. 10.1083/jcb.200909127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meaburn K. J., Misteli T. (2008). Locus-specific and activity-independent gene repositioning during early tumorigenesis. J. Cell Biol. 180, 39–50. 10.1083/jcb.200708204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mewborn S. K., Puckelwartz M. J., Abuisneineh F., Fahrenbach J. P., Zhang Y., MacLeod H., et al. (2010). Altered chromosomal positioning, compaction, and gene expression with a lamin A/C gene mutation. PLoS One 5, e14342. 10.1371/journal.pone.0014342 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montironi R., Mazzuccheli R., Scarpelli M., Lopez-Beltran A., Fellegara G., Algaba F. (2005). Gleason grading of prostate cancer in needle biopsies or radical prostatectomy specimens: contemporary approach, current clinical significance and sources of pathology discrepancies. BJU Int. 95, 1146–1152. 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05540.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naik R., Galande S. (2019). SATB family chromatin organizers as master regulators of tumor progression. Oncogene 38, 1989–2004. 10.1038/s41388-018-0541-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L., McQueen P., Misteli T. (2004). Tissue-specific spatial organization of genomes. Genome Biol. 7, R44. 10.1186/gb-2004-5-7-r44 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz N., Felipe-Blanco I., Royo F., Zabala A., Guerra-Merino I., Garcia-Orad A., et al. (2015). Expression of the DYRK1A gene correlates with its 3D positioning in the interphase nucleus of Down syndrome cells. Chromosome Res. 23, 285–298. 10.1007/s10577-015-9467-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peric-Hupkes D., Meuleman W., Pagie L., Bruggeman S. W., Solovei I., Brugman W., et al. (2010). Molecular maps of the reorganization of genome-nuclear lamina interactions during differentiation. Mol. Cell 38, 603–613. 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pound C. R., Partin A. W., Eisenberger M. A., Chan D. W., Pearson J. D., Walsh P. C. (1999). Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. JAMA 281, 1591–1597. 10.1001/jama.281.17.1591 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punnen S., Cooperberg M. R. (2013). The epidemiology of high-risk prostate cancer. Curr. Opin. Urol. 23, 331–336. 10.1097/MOU.0b013e328361d48e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randise-Hinchliff C., Coukos R., Sood V., Sumner M. C., Zdraljevic S., Meldi Sholl L., et al. (2016). Strategies to regulate transcription factor-mediated gene positioning and interchromosomal clustering at the nuclear periphery. J. vCell Biol. 212, 633–646. 10.1083/jcb.201508068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saarinen I., Mirtti T., Seikkula H., Bostrom P. J., Taimen P. (2015). Differential predictive roles of A- and B-type nuclear lamins in prostate cancer progression. PLoS One 10, e0140671. 10.1371/journal.pone.0140671 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu G. S., Andriole G. L. (2012). Overdiagnosis of prostate cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2012, 146–151. 10.1093/jncimonographs/lgs031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuermann M. O., Tajbakhsh J., Kurz A., Saracoglu K., Eils R., Lichter P. (2004). Topology of genes and nontranscribed sequences in human interphase nuclei. Exp. Cell Res. 301, 266–279. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shachar S., Voss T. C., Pegoraro G., Sciascia N., Misteli T. (2015). Identification of gene positioning factors using high-throughput imaging mapping. Cell 162, 911–923. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S., Sharma H., Abbas A., MacLennan G. T., Fu P., Danielpour D., et al. (2013). Upregulation of SATB1 is associated with prostate cancer aggressiveness and disease progression. PLoS One 8, e53527. 10.1371/journal.pone.0053527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvortsov S., Schafer G., Stasyk T., Fuchsberger C., Bonn G. K., Bartsch G., et al. (2011). Proteomics profiling of microdissected low- and high-grade prostate tumors identifies Lamin A as a discriminatory biomarker. J. Proteome Res. 10, 259–268. 10.1021/pr100921j [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solovei I., Wang A. S., Thanisch K., Schmidt C. S., Krebs S., Zwerger M., et al. (2013). LBR and lamin A/C sequentially tether peripheral heterochromatin and inversely regulate differentiation. Cell 152, 584–598. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa T., Gudla P. R., Guo L., Lockett S., Misteli T. (2008. a). Allele-specific nuclear positioning of the monoallelically expressed astrocyte marker GFAP. Genes Dev. 22, 489–498. 10.1101/gad.1634608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa T., Meaburn K. J., Misteli T. (2008. b). The meaning of gene positioning. Cell 135, 9–13. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taslerova R., Kozubek S., Lukasova E., Jirsova P., Bartova E., Kozubek M. (2003). Arrangement of chromosome 11 and 22 territories, EWSR1 and FLI1 genes, and other genetic elements of these chromosomes in human lymphocytes and Ewing sarcoma cells. Hum. Genet. 112, 143–155. 10.1007/s00439-002-0847-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therizols P., Illingworth R. S., Courilleau C., Boyle S., Wood A. J., Bickmore W. A. (2014). Chromatin decondensation is sufficient to alter nuclear organization in embryonic stem cells. Science 346, 1238–1242. 10.1126/science.1259587 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson I., Thrasher J. B., Aus G., Burnett A. L., Canby-Hagino E. D., Cookson M. S., et al. (2007). Guideline for the management of clinically localized prostate cancer: 2007 update. J. Urol. 177, 2106–2131. 10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian X., Wang Y., Zhao F., Liu J., Yin J., Chen D., et al. (2015). A new classification of interphase nuclei based on spatial organizations of chromosome 8 and 21 for t(8;21) (q22;q22) acute myeloid leukemia by three-dimensional fluorescence in situ hybridization. Leuk. Res. 39, 1414–1420. 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.09.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin B. D., Gonzalez-Aguilera C., Sack R., Gaidatzis D., Kalck V., Meister P., et al. (2012). Step-wise methylation of histone H3K9 positions heterochromatin at the nuclear periphery. Cell 150, 934–947. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veltri R. W., Christudass C. S. (2014). Nuclear morphometry, epigenetic changes, and clinical relevance in prostate cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 773, 77–99. 10.1007/978-1-4899-8032-8_4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. Y., Cui J. J., Zhu T., Shao W. H., Zhao Y., Wang S., et al. (2017). Biomarkers identified for prostate cancer patients through genome-scale screening. Oncotarget 8, 92055–92063. 10.18632/oncotarget.20739 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch H. G., Black W. C. (2010). Overdiagnosis in cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 102, 605–613. 10.1093/jnci/djq099 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. R., Azuara V., Perry P., Sauer S., Dvorkina M., Jorgensen H., et al. (2006). Neural induction promotes large-scale chromatin reorganisation of the Mash1 locus. J. Cell Sci. 119, 132–140. 10.1242/jcs.02727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D., Fische A. H., Nickerson J. A. (2004). Nuclear structure in cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 677–687. 10.1038/nrc1430 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuleger N., Boyle S., Kelly D. A., de Las Heras J. I., Lazou V., Korfali N., et al. (2013). Specific nuclear envelope transmembrane proteins can promote the location of chromosomes to and from the nuclear periphery. Genome Biol. 14, R14. 10.1186/gb-2013-14-2-r14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/ Supplementary Files .