Abstract
Temperate bacteriophages are viruses that can incorporate their genomes into their bacterial hosts, existing there as prophages that refrain from killing the host cell until induced. Prophages are largely quiescent, but they can alter host phenotype through factors encoded in their genomes (often virulence factors) or by disrupting host genes as a result of integration. Here we describe another mechanism by which a prophage can modulate host phenotype. We show that a temperate phage that integrates in Escherichia coli reprograms host regulation of an anaerobic respiratory system, thereby inhibiting a bet hedging strategy. The phage exerts this effect by upregulating a host-encoded signal transduction protein through transcription initiated from a phage-encoded promoter. We further show that this phenomenon occurs not only in a laboratory strain of E. coli, but also in a natural isolate that contains a prophage at this site.
Research organism: E. coli
eLife digest
Animals and plants can all fall prey to viruses – and so can bacteria. The viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages (or phages for short), and they are found everywhere bacteria live and probably outnumber bacteria by at least ten to one.
While some phages quickly kill every bacterial cell they infect, others enter a dormant state by inserting their DNA into the DNA of their host cell. Here they lie in wait for a signal that reactivates them, triggering the production of more phages and the death of the host cell. While the phage lies dormant its DNA may harm the host by interfering with nearby bacterial genes, or it may actually provide new genes that benefit the host. In most cases the effects of dormant phages are unknown.
A bacterium known as Escherichia coli is commonly found in the intestines of humans and other mammals. It can use a nutrient called trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) to help it survive rapid decreases in oxygen levels that can occur in its environment. When a phage called HK022 infects E. coli, the phage enters a dormant state by inserting its DNA between two genes that are critical for E. coli to use TMAO. However, it is not clear what effect, if any, HK022 has on E. coli’s behavior.
To address this question, Carey et al. used genetic approaches to study E. coli cells carrying dormant HK022 phages. The experiments showed that the bacteria lost the ability to use TMAO to survive rapid decreases in oxygen because the dormant phages switched on one of the neighboring E. coli genes. Unexpectedly, the phage achieved this by neatly replacing the gene’s own promoter – the stretch of DNA that contains information about when the gene should be switched on, and how strongly – with a substitute promoter carried in the phage’s DNA. This substitute promoter is stronger than the normal version – meaning that the gene is more active than it should be.
Phages are key players in every natural population of microbes and are therefore entwined in the health of humans and the environment. The findings of Carey et al. show a new mechanism through which phages modify their hosts. In the future it may be possible to develop this mechanism into a tool to manipulate bacteria in complex environments like infection sites, for example by introducing phages that block the mechanisms that allow bacteria to tolerate antibiotics.
Introduction
Bacteria and the phages that infect them have a generally antagonistic relationship, with evolution arming each side to defeat the other. Sometimes, though, a bacterium and a temperate phage can form an uneasy truce through lysogeny, wherein the integrated prophage confers some beneficial attribute to its host cell that provides a fitness advantage; after all, unless the host cell dies on the phage’s own terms, the phage dies too. Prophage alteration of host phenotype, known as lysogenic conversion (Lederberg, 1955), can benefit the host by conferring abilities to produce toxins, resist antibiotics, increase virulence, and repel further phage infections (for recent reviews, see Argov et al., 2017; Bondy-Denomy and Davidson, 2014; Davies et al., 2016; Fortier and Sekulovic, 2013; Harrison and Brockhurst, 2017; Howard-Varona et al., 2017; Obeng et al., 2016; and Touchon et al., 2017). Oftentimes these traits are encoded within prophage genetic elements called morons, which contain genes that are regulated by their own promoters and are not involved in the phage lytic cycle (Hendrix et al., 2000; Juhala et al., 2000). Although lysogenic conversion has been under study since its first description nearly 100 years ago (Frobisher and Brown, 1927), there are likely entire classes of phage-encoded proteins that impact host fitness in as-yet-undescribed ways, as most phage genes have unknown function and no homology to any genes with known function.
Phages can alter their hosts’ behavior in more subtle or indirect ways than, say, carrying a moron that enables toxin production; indeed, in most cases the effects of lysogeny on host physiology are unknown. One study found that deleting all of the cryptic prophages in Escherichia coli BW25113 increased the strain’s susceptibility to exogenous stresses and decreased its growth rate through mechanisms yet to be understood (Wang et al., 2010). Other studies have shown that host gene expression can be regulated by phage-encoded transcription factors, as in the case of the cI repressor of phage λ that is expressed during lysogeny. This protein prevents expression of the λ lytic genes but was also discovered to act directly at the promoter of the metabolic gene pckA (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase), repressing its expression and producing a slow growth phenotype in some conditions (Chen et al., 2005). Prophages can also alter host gene expression by means of the position in the host genome where they integrate (Bondy-Denomy and Davidson, 2014; McShan and Ferretti, 2007). For instance, the Φ13 phage of Staphylococcus aureus integrates into the 5’ end of the hlb gene, disabling β-toxin expression (Coleman et al., 1991).
Disruption of host genes by prophage integration can be reversed by prophage excision, and in some bacteria prophages act as switches that regulate host gene expression through controlled excision from interrupted genes, a phenomenon called active lysogeny (Feiner et al., 2015). In Listeria monocytogenes, for example, the Φ10403S prophage integrates in and disrupts a gene that is required for efficient escape of the mammalian phagosome (Rabinovich et al., 2012). The prophage excises during infection, restoring gene function, but its bacterial lysis genes remain repressed. The excised phage later reintegrates back into the same gene without killing its host. In some cases, the prophages involved in active lysogeny have lost the genes required for production of virions but still act as key regulators of cellular processes such as differentiation (Feiner et al., 2015).
We became interested in a particular temperate phage that infects E. coli—HK022 (Dhillon and Dhillon, 1972)—because its integration site lies precisely between the genes torT and torS (Yagil et al., 1989). These genes produce a periplasmic binding protein and a sensor kinase, respectively, that together detect trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) in the periplasm and transduce this signal to the cytoplasm to phosphorylate the response regulator TorR. Phosphorylated TorR then activates transcription of the torCAD operon, which encodes TMAO reductase (see Figure 1A). This pathway enables E. coli to use TMAO as a respiratory electron acceptor. TMAO is widespread in the environment (Gibb and Hatton, 2004; Hatton and Gibb, 1999) and is particularly abundant in the tissues of many marine organisms (Eisert et al., 2005; Seibel and Walsh, 2002; Yancey et al., 1982). Animals can ingest significant amounts of this compound from seafood-rich diets (Eisert et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 1999). In addition, humans and other mammals synthesize TMAO from trimethylamine (TMA) that is liberated from dietary precursors by the gut microbiota (Fennema et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 1999). Circulating TMAO accumulates in urine and is excreted (Hai et al., 2015; Velasquez et al., 2016).
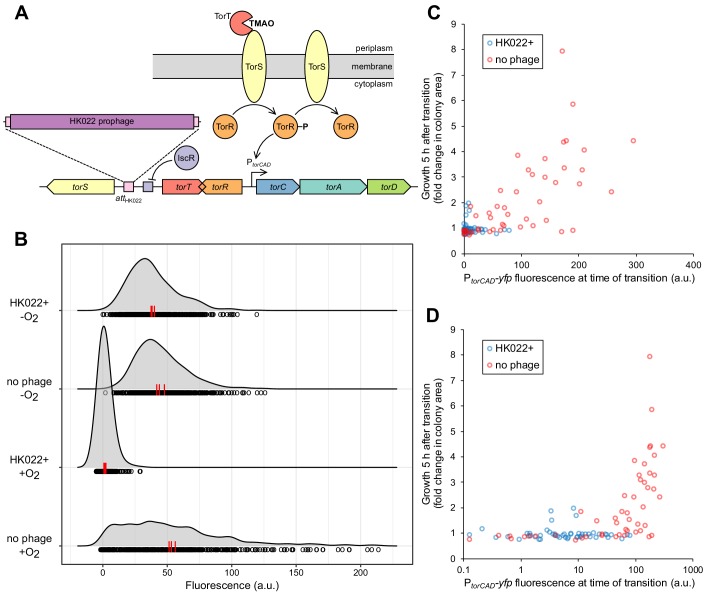
Figure 1. Bacteriophage HK022 integrates between the signaling genes torS and torT, disrupting regulation of torCAD and a metabolic bet-hedging strategy.
(A) HK022 integrates as a prophage at an integration site (attBHK022) between torS and torT, separating torS from the IscR binding site that represses its transcription. TorS regulates torCAD by phosphorylating and dephosphorylating the transcription factor TorR, which in its phosphorylated state activates transcription from the torCAD promoter. To phosphorylate TorR, TorS must interact with TMAO-bound TorT; in the absence of this interaction, TorS dephosphorylates TorR. When oxygen is present, transcription of torS and torT is repressed to an extremely low level by IscR, and stochasticity in the ratio of TorS to TorT leads to noisy torCAD transcription (Carey et al., 2018). (B) The HK022 prophage shuts off aerobic transcription of torCAD but leaves anaerobic expression intact. Distributions of single-cell fluorescence are shown for strains carrying a fluorescent reporter of torCAD transcription. Data are shown for an HK022 lysogen (DFE12) and a non-lysogen (MMR8) grown in the presence or absence of oxygen. Each circle represents a fluorescence measurement made in an individual cell. To facilitate qualitative comparisons between distributions, density curves (shown in gray) were generated from single-cell measurements (see Materials and methods). Data are pooled from three independent experiments, with the vertical red lines indicating the population mean fluorescence for each experiment. a.u., arbitrary units. (C,D) Most cells carrying the HK022 prophage fail to grow following rapid oxygen depletion. Each circle represents an individual cell monitored for growth following an aerobic-to-anaerobic transition. The same data are presented on a linear scale (C) for easier comparison with (B) and on a log scale (D) for clearer resolution of individual points. The HK022 lysogen (JNC173) constitutively expresses CFP to distinguish it from the non-lysogen (JNC174), which constitutively expresses mCherry. Both strains carry the YFP reporter of torCAD transcription and lack fhuA, the gene encoding the HK022 receptor. Growth is quantified as the ratio of microcolony area approximately 5 hr after oxygen depletion to the area of the parent cell at the time of depletion. Data are shown for a single representative experiment.
TMAO respiration allows E. coli to grow anaerobically, but it occurs even when oxygen is available (Ansaldi et al., 2007). This is surprising because of anaerobic respiration’s relatively poor energy yield compared to aerobic respiration. We recently showed that aerobic expression of torCAD occurs with high cell-to-cell variability (Roggiani and Goulian, 2015), which can benefit the population by serving as a metabolic bet-hedging strategy in the face of a rapid decrease in oxygen availability (Carey et al., 2018). Highly variable torCAD expression is regulated by oxygen and is mediated by torS and torT, the genes that flank the HK022 integration site (Carey et al., 2018; Roggiani and Goulian, 2015). The torS and torT genes are divergently transcribed but share a repressor binding site for the transcription factor IscR (Carey et al., 2018). Under aerobic conditions, IscR repression at this site leads to exceptionally low abundance of TorS and TorT protein and noisy transcription of the torCAD operon (Carey et al., 2018; Li et al., 2014; Taniguchi et al., 2010). Curiously, the HK022 integration site separates the torS coding sequence from the IscR binding site that regulates its transcription. In this work, we show that the HK022 prophage reprograms the regulation of torCAD transcription in E. coli by disrupting the native torS promoter and introducing a phage-encoded promoter that drives torS transcription. By hijacking the regulation of torS transcription, HK022 reconfigures how cells respond to the presence of oxygen—in uninfected cells, oxygen regulates cell-to-cell variability in torCAD transcription without changing the population mean expression level (Roggiani and Goulian, 2015); in infected cells, oxygen regulates the mean torCAD expression level and not cell-to-cell variability. Consequently, the HK022 prophage disables the bet-hedging strategy that aids cells during rapid oxygen depletion (Carey et al., 2018). We further show that this phenomenon is not unique to HK022 lysogeny in a laboratory strain of E. coli, since the E. coli isolate NRG 857C, which naturally has a different prophage integrated at the HK022 integration site, shows similar behavior. The mechanism uncovered here, whereby phage cis-acting factors replace those of the host at a particular locus, may be a general mechanism used by temperate phages to alter their hosts’ behavior.
Results
The HK022 prophage disables aerobic transcription of torCAD
The integration site for bacteriophage HK022 is in the short intergenic region between the divergently transcribed genes torS and torT and separates the torS open reading frame from the IscR binding site that negatively regulates torS transcription (Figure 1A). We suspected that the presence of a prophage at this integration site would disrupt the regulation of torS transcription and, ultimately, torCAD transcription, which depends on TorS and TorT (Figure 1A). To investigate the impact of HK022 lysogeny on torCAD transcription, we constructed an HK022 lysogen in an E. coli K-12 strain carrying a fluorescent protein reporter of torCAD transcription. We grew this lysogenized reporter strain aerobically in the presence of TMAO and measured torCAD transcription in single cells by fluorescence microscopy. Transcription of torCAD was undetectable in the lysogen but was observed in the non-lysogen control strain (Figure 1B).
The simplest explanation for the loss of aerobic torCAD transcription in the lysogen is that the presence of the prophage destroys the torS promoter, as cells without TorS cannot phosphorylate TorR and activate torCAD transcription (Figure 1A) (Jourlin et al., 1996). Unexpectedly, however, when we measured torCAD transcription in cells grown anaerobically in the presence of TMAO, we observed no difference between the lysogen and the non-lysogen (Figure 1B). These results indicate that torS is still transcribed in the lysogen and that the above explanation is incorrect.
We previously showed that high cell-to-cell variability in aerobic torCAD expression can function as a bet-hedging strategy that helps a population tolerate a rapid transition to anaerobiosis (Carey et al., 2018). Only cells with a recent history of high torCAD expression are able to continue growth after oxygen depletion when TMAO is present and no other respiratory electron acceptors or fermentative substrates are available. Because the HK022 lysogen does not express torCAD aerobically, we suspected that it would be unable to employ this bet-hedging strategy and would therefore be unable to grow through an aerobic-to-anaerobic transition under the conditions described above. We tested this hypothesis by growing aerobic liquid cultures of the HK022 lysogen and non-lysogen in media containing TMAO and the non-fermentable carbon source glycerol, combining the cultures, and then transferring to an anaerobic agarose pad, which we used to observe the fates of single cells by time-lapse microscopy. Both strains contained the same fluorescent protein reporter of torCAD transcription. Cellular fluorescence was used as a measure of recent torCAD transcription and was correlated with cell growth after the transition to anaerobiosis, as in Carey et al. (2018). To differentiate the lysogen from the non-lysogen, each strain was engineered to express a second fluorescent protein constitutively. Both strains carried deletion mutations of the HK022 receptor gene (fhuA) to prevent any infection of the non-lysogen by phage particles produced by spontaneous prophage induction in the lysogen. The results of this experiment, shown in Figure 1C, D, indicate that only the non-lysogen contains a subpopulation of cells that can grow substantially after oxygen depletion and that this subpopulation has high torCAD expression at the time of transition. From this we conclude that the HK022 prophage deactivates TMAO-dependent bet hedging on rapid oxygen depletion.
The HK022 prophage increases torS transcription but not torT transcription
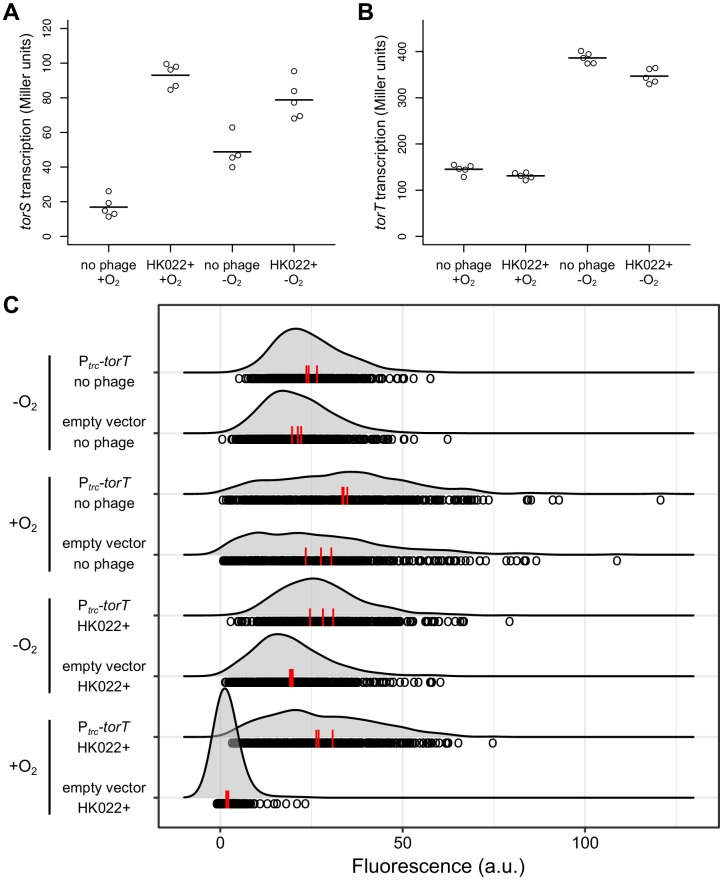
Our finding that the HK022 lysogen expresses torCAD in the absence of oxygen indicates that the prophage does not simply eradicate the torS promoter. To investigate the effect of the prophage on torS transcription, we measured β-galactosidase activity produced from an operon fusion of lacZ to torS in the HK022 lysogen and non-lysogen, both with and without oxygen. We found that torS expression was substantially elevated in the HK022 lysogen (Figure 2A). When we performed analogous experiments to measure torT transcription, we found no difference between the two strains (Figure 2B). These results suggest that the HK022 prophage shuts off aerobic torCAD transcription not by disrupting torS transcription but rather by increasing torS transcription while leaving torT transcription unchanged. TorS molecules that are not bound to TorT are unable to detect TMAO and are in a state that dephosphorylates TorR (Figure 1A). Therefore, cells with a large excess of TorS over TorT would strongly favor TorR dephosphorylation and not express torCAD (Ansaldi et al., 2001; Carey et al., 2018; Roggiani and Goulian, 2015). We note that the HK022 lysogen also shows elevated torS transcription in the absence of oxygen, and yet torCAD is still expressed in these conditions. This suggests that anaerobic TorT levels are sufficiently high for any additional TorS not to have much impact on TorR phosphorylation and torCAD expression.
Figure 2. The HK022 prophage increases torS transcription and has no effect on torT transcription.
Aerobic and anaerobic transcription of torS (A) and torT (B) was measured by β-galactosidase assays in strains carrying torS-lacZ or torT-lacZ operon fusions, with or without the HK022 prophage (strains JNC166, JNC169, JNC163, and JNC168). Each circle represents a measurement obtained from an independent experiment, and the horizontal lines indicate average values. (C) Overexpression of torT restores aerobic torCAD expression in an HK022 lysogen. The distributions of single-cell fluorescence are shown for strains carrying a fluorescent reporter of torCAD transcription. The strains are an HK022 lysogen (DFE12) and a non-lysogen (MMR8) containing a plasmid for torT overexpression (pMR26) or an empty vector control (pDSW206), grown in the presence or absence of oxygen. Expression of torT from the plasmid is driven by a weakened trc promoter without added inducer. Each circle represents a fluorescence measurement made in an individual cell. To facilitate qualitative comparisons between distributions, density curves (shown in gray) were generated from single-cell measurements (see Materials and methods). Data are pooled from three independent experiments, with the vertical red lines indicating the population mean fluorescence for each experiment. a.u., arbitrary units.
Increased expression of TorT in an HK022 lysogen restores aerobic torCAD transcription
If the model described above is correct, then it should be possible to compensate for elevated TorS levels in an HK022 lysogen and restore aerobic torCAD expression by increasing expression of TorT. To test this, we introduced a plasmid containing torT under control of a weakened trc promoter into the lysogen carrying the fluorescent torCAD transcriptional reporter and quantified torCAD expression (Figure 2C). The result of this experiment agrees with our prediction that the lysogen carrying the torT overexpression plasmid is able to express torCAD in the presence of oxygen.
Transcription of torS in a lysogen originates from within the HK022 prophage
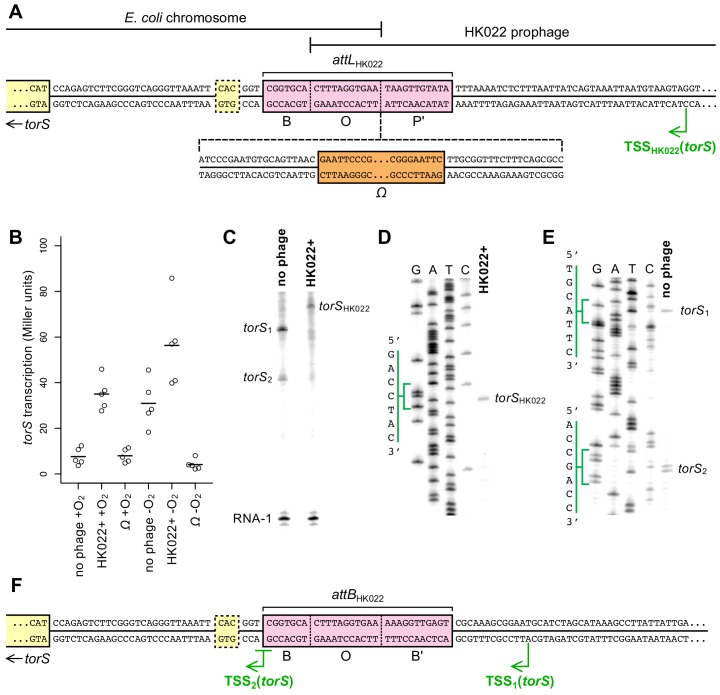
We next wanted to probe the mechanism by which the HK022 prophage increases torS transcription. We hypothesized that the phage encodes some cis-acting element(s) near its attP site that, upon integration, affect torS transcription. A simple explanation would be an outward-reading promoter that produces an mRNA transcript originating from within the prophage and reading through torS. To test this explanation, we inserted a synthetic terminator construct—an Ω element (Prentki and Krisch, 1984)—at the boundary between bacterial and prophage sequence (attLHK022) (Figure 3A). We measured torS transcription in strains containing this terminator and found that torS expression was very low during both aerobic and anaerobic growth (Figure 3B). This result strongly suggests that the mechanism by which the HK022 prophage activates torS expression is the production of torS transcripts that originate from within the prophage and are driven by a phage-encoded promoter.
Figure 3. Transcription of torS in an HK022 lysogen originates from within the prophage.
(A) Sequence of the torS-adjacent HK022 integration site (attLHK022) in an HK022 lysogen. B, O, and P’ indicate the bacterial, overlap, and phage segments of the integration site, respectively (Campbell, 1992; Yagil et al., 1989). The location of the Ω element terminator insertion in strain JNC175 is indicated. In this strain, transcription reading toward torS from within the HK022 prophage is blocked by the Ω element. The transcription start site, TSSHK022, was mapped by in vitro transcription and primer extension, shown in (C) and (D). The previously inferred torS GTG start codon is outlined, and the experimentally confirmed ATG start codon is indicated as the start of the torS coding sequence. (B) Aerobic and anaerobic transcription of torS was measured by β-galactosidase assays in strains carrying a torS-lacZ operon fusion. Strains contained the wild-type HK022 prophage (JNC169), the prophage with an Ω element (JNC175), or had no prophage at the integration site (JNC166). Each circle represents a measurement obtained from an independent experiment, and the horizontal lines indicate average values. (C) In vitro transcription from plasmids containing sequence upstream of torS from the HK022 lysogen (‘HK022+’, pPK13256) or the non-lysogen (‘no phage’, pPK12669) shows that different transcripts are produced when the prophage is present or absent. Transcription using non-lysogen sequence produces two distinct transcripts, suggesting two transcription start sites for torS. RNA-1 is a control transcript for in vitro transcription and gel loading that is generated from a σ70-regulated promoter in pPK13256 or pPK12669. (D) Primer extension was performed to map the transcription start site of the in vitro ‘HK022+’ transcript shown in (C). The position of the start site is indicated in (A). (E) Primer extension was performed to map the transcription start sites of the in vitro ‘no phage’ transcripts shown in (C). The positions of the start sites are indicated in (F). (F) Sequence upstream of torS in a non-lysogen, with the torS transcription start sites depicted. Transcripts originating from TSS2 can begin at the underlined G or A position, as indicated by the adjacent bands in (E).
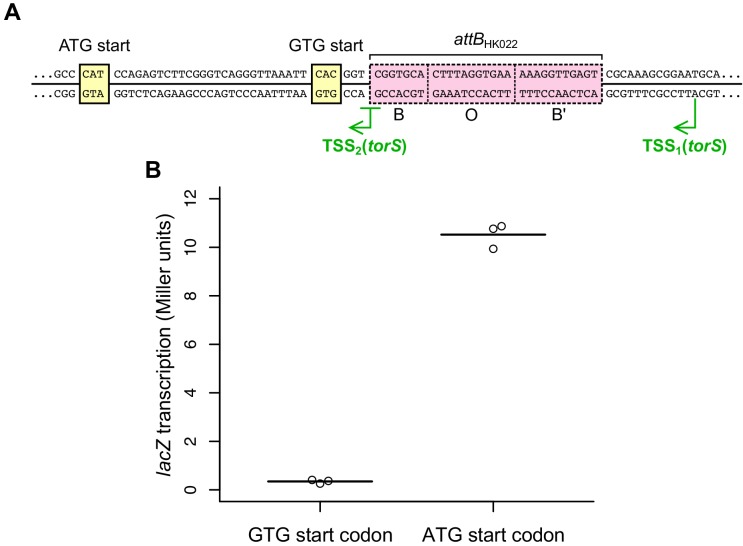
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Identification of the torS start codon.
The annotated HK022 gene nearest the torS-proximal phage/host junction encodes the viral integrase (int); there are 73 bp between the int stop codon and the junction with the E. coli chromosome. In HK022 (as in phage λ), expression of int is repressed during lysogeny (Yagil et al., 1989), but it is conceivable that transcription of torS could be coupled with leaky expression of int. To determine whether the HK022 lysogen encodes a separate torS promoter, we performed in vitro transcription using DNA sequence upstream of the torS start codon. Approximately 200 bp of upstream sequence from the lysogen was cloned into a plasmid, and an analogous plasmid was constructed using upstream sequence from the non-lysogen. In vitro transcription from both plasmids produced transcripts, and the transcripts were different lengths when produced from lysogen sequence than when produced from non-lysogen sequence (Figure 3C). Interestingly, transcripts of two distinct lengths were produced from the non-lysogen sequence, suggesting that there are two torS promoters when the prophage is absent.
To confirm that the transcripts produced by in vitro transcription were truly torS transcripts and to map the transcription start sites associated with each of them, we performed primer extension assays (Figure 3D, E). The transcript produced by the HK022 lysogen sequence mapped to a single transcription start site located within the prophage (position indicated in Figure 3A). The transcripts produced by the non-lysogen mapped to one transcription start site on the torS-proximal side of attBHK022 and one start site on the torS-distal side of attBHK022 (Figure 3F). The transcription start site for the shorter transcript (hereafter TSS2) is identical to a computationally predicted start site (Huerta and Collado-Vides, 2003), while the longer transcript (hereafter TSS1) has not previously been predicted or reported. TSS2 is so close to attBHK022 that its promoter must be at least partially ablated after prophage integration; this likely explains why no TSS2 transcripts are observed in the lysogen. TSS1 transcripts, on the other hand, are likely absent in the lysogen because TSS1 lies on the far side of the attBHK022 site from the torS coding sequence; in the lysogen, the promoter and coding sequence are separated by the entire HK022 genome. It appears, then, that the only torS transcripts made in the HK022 lysogen are produced by a phage-encoded torS promoter and that the int promoter is not required for prophage-regulated torS transcription.
After identifying the transcription start sites, we realized that TSS2 is within three base pairs of a predicted translation start site for torS and that transcripts produced from TSS2 would not have room for a ribosome binding site. This translation start site uses a GTG start codon, indicated in Figure 3A, F (UniProt Consortium, 2019). A second translation start site for torS, downstream of the GTG start codon and employing an ATG start codon, has also been inferred (Figure 3A, F) (Jourlin et al., 1996). Neither of these putative start codons is associated with a canonical Shine-Dalgarno sequence, suggesting that translation initiation is inefficient. To determine if either serves as a bona fide start codon, we constructed lacZ translational fusions to each and measured β-galactosidase activity. Only the lacZ fusion to the downstream ATG produced β-galactosidase activity (Figure 3—figure supplement 1). Accordingly, we have indicated the torS coding sequence as beginning with the ATG codon in Figure 3A, F.
E. coli strains carrying prophages at the HK022 attB site are widespread
The above results reveal that the increased torS expression caused by the HK022 prophage restricts torCAD expression to anaerobic conditions in E. coli K-12 strain MG1655, resulting in the loss of bet hedging. This prompted us to investigate the prevalence of prophages integrated at the HK022 integration site in wild E. coli strains. We searched for the torS and torT genes by BLAST (Boratyn et al., 2013) against all complete E. coli genome sequences available through NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/microbes/) at the time of this analysis and calculated the torS-torT intergenic distance for each strain. For all strains with large insertions between torS and torT (relative to E. coli MG1655), we used the PHASTER web server (Arndt et al., 2016) to identify prophages. Roughly 5% of sequenced E. coli genomes carried prophages integrated immediately upstream of torS, and prophage-containing strains were not restricted to closely related E. coli phylogenetic groups (Supplementary file 1). PHASTER indicated that the prophage integrases were all more similar to HK022 integrase than to any other phage integrase, and a multiple sequence alignment of the genomic region from torS to int revealed that, for every prophage, the attL site was in the same position relative to torS as attLHK022 (Supplementary file 2). Sequence conservation was high upstream of TSSHK022, suggesting conservation of the associated promoter (despite there being no clearly identifiable −10 or −35 sequences). In most of these strains the torS-torT intergenic distance was roughly the same size as the HK022 genome, which is 40,751 bp long (Juhala et al., 2000), although several of the strains appeared to have large genomic rearrangements relative to MG1655 in this region. Even in the strains with rearrangements, however, a prophage was integrated immediately upstream of torS at attLHK022.
Expression of torCAD in a prophage-containing wild E. coli strain is similar to expression in the HK022 prophage-carrying laboratory strain
We previously showed that torCAD expression in various wild E. coli strains lacking a prophage between torS and torT follows a similar pattern to what is seen in MG1655 (Roggiani and Goulian, 2015). As prophage integration at attBHK022 appears to be widespread in wild E. coli strains, we wondered whether torCAD expression in prophage-containing strains would resemble torCAD expression in HK022-infected MG1655. We introduced the fluorescent reporter of torCAD expression into one such strain, the Crohn’s disease-associated strain NRG 857C (Eaves-Pyles et al., 2008; Nash et al., 2010). This strain belongs to phylogenetic group B2 (Supplementary file 1) and is thus only distantly related to the laboratory strain MG1655 (which belongs to phylogenetic group A). The torCAD promoter sequences are identical between NRG 857C and MG1655, enabling us to use the same PtorCAD-yfp reporter construct that we used in MG1655-derived strains to assess torCAD transcription in NRG 857C. We integrated the transcriptional reporter into the NRG 857C chromosome by conjugation with an MG1655-derived Hfr donor strain, as NRG 857C is immune to genetic manipulation by P1 transduction. We used genetic markers in the donor and recipient strains to confirm that the tor and isc loci of NRG 857C were not replaced upon introduction of the transcriptional reporter (see Materials and methods). When we measured torCAD transcription in NRG 857C during aerobic and anaerobic growth by fluorescence microscopy (Figure 4), we found that the pattern of expression was much more similar to MG1655 HK022+ than to MG1655 without the prophage (Figure 1B). This suggests that in at least some wild E. coli strains there is prophage-mediated regulation of torCAD expression that is mechanistically similar to the HK022-mediated regulation seen in MG1655.
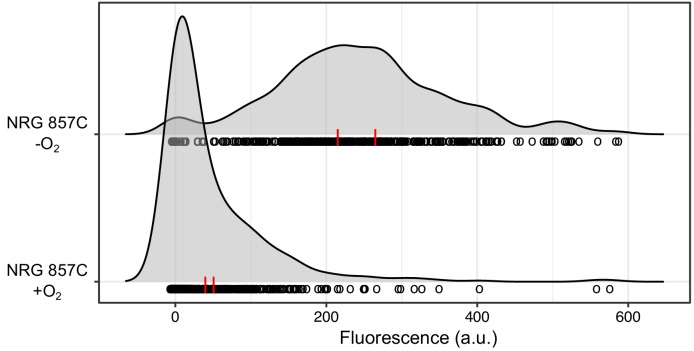
Figure 4. A wild E. coli strain carrying a prophage at attBHK022 shows an oxygen-dependent torCAD expression pattern similar to that of the HK022-infected laboratory strain.
A fluorescent reporter of torCAD transcription was introduced into the Crohn’s disease-associated E. coli strain NRG 857C and used to measure expression during aerobic and anaerobic growth. NRG 857C naturally carries a prophage at the HK022 integration site and displays a qualitatively similar pattern of torCAD expression as HK022-infected MG1655 (see Figure 1B). Distributions of single-cell fluorescence are shown for the NRG 857C PtorCAD-yfp strain (DFE34), with each circle representing a fluorescence measurement made in an individual cell. To facilitate qualitative comparisons between distributions, density curves (shown in gray) were generated from single-cell measurements (see Materials and methods). Data are pooled from two independent experiments, with the vertical red lines indicating the population mean fluorescence for each experiment. a.u., arbitrary units.
Discussion
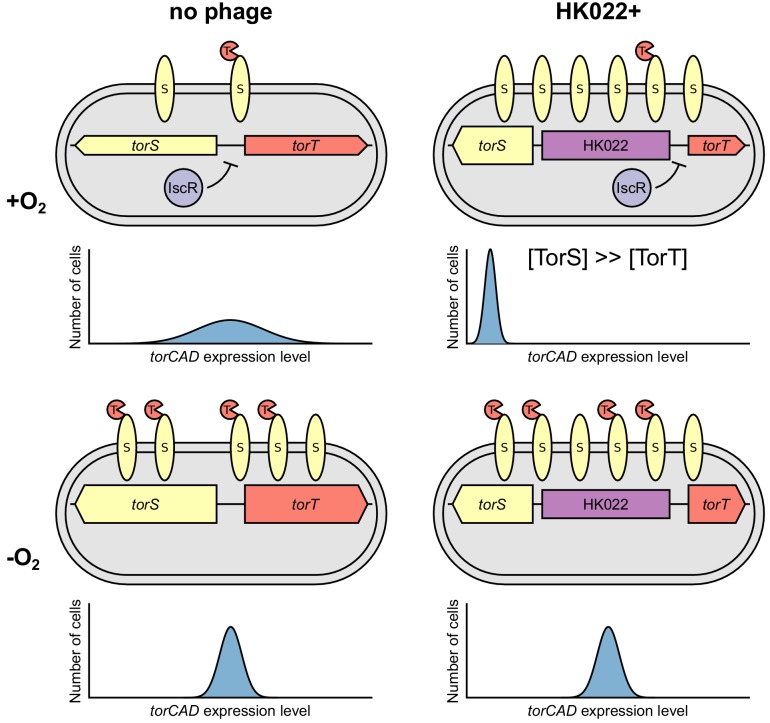
In this work, we have shown that bacteriophage HK022 reconfigures the regulation of TMAO reductase expression in E. coli. Although other cases have been described wherein a prophage alters the expression of host metabolic genes, we are unaware of other instances in which a prophage so dramatically modifies its host’s response to the presence of a metabolite. By restricting torCAD expression to anaerobic conditions, HK022 converts oxygen-dependent regulation of the variance in torCAD expression (seen in non-lysogens) into oxygen-dependent regulation of mean torCAD expression (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Model of how bacteriophage HK022 reprograms the regulation of torCAD expression during lysogeny.
In cells lacking the HK022 prophage, IscR repression of torS and torT during aerobic growth leads to very low TorS and TorT abundance. High variability in the ratio of TorS to TorT results in noisy torCAD transcription (top left). In the absence of oxygen, IscR repression of torS and torT is relieved, decreasing variability in the TorS-to-TorT ratio and noise in torCAD transcription (bottom left) (Carey et al., 2018). In HK022 lysogens, a prophage-encoded promoter drives high torS expression. IscR still represses torT during aerobic growth, and the resulting excess of TorS relative to TorT shuts down torCAD transcription (top right) (see Figure 1A). In the absence of oxygen, IscR repression of torT is relieved, and torCAD transcription is restored (bottom right).
HK022 reconfigures torCAD regulation by increasing expression of the regulatory protein TorS (Figure 5). The phage appears to achieve this by replacing the native torS promoters with a promoter located within the prophage. We mapped the transcription start site associated with this promoter to within the prophage and were able to abolish torS transcription initiated at this site by inserting a transcriptional terminator into the junction between the prophage and the E. coli chromosome (Figure 3). These results indicate that an outward-reading transcript originates from within the prophage and reads through torS.
We can only speculate on why HK022 shuts off aerobic torCAD expression and, consequently, the bet hedging associated with it. We have argued previously that there must be a fitness cost to the expression of torCAD, or else its expression would not be regulated (Carey et al., 2018). The HK022 prophage may prevent aerobic torCAD transcription to alleviate a fitness cost and thereby increase the rate of its own replication. If the primary function of aerobic torCAD expression is bet hedging on rapid oxygen depletion, shutting down aerobic expression could be a useful strategy if phages like HK022 primarily lysogenize E. coli in environments where TMAO is present but rapid oxygen loss is unlikely to occur. One can conceive of such niches existing within habitats enriched in TMAO, such as the mammalian urinary tract, animal latrines, or the marine environment (especially in association with marine animals).
The HK022 integration site is occupied by a prophage in roughly 5% of fully sequenced E. coli strains, and these prophages are found in E. coli of diverse origins and phylogenetic groups. This suggests that HK022 is not an oddity in its integration between torS and torT. All of the prophages we identified occupying this site have, like HK022, an outward-reading integrase gene as the final identifiable gene before torS, and all share the general genomic architecture of phages belonging to the lambda supercluster (Grose and Casjens, 2014). (The one partial exception is the prophage from strain STEC299, which maintains the HK022-like integrase oriented towards torS but appears to be more closely allied with the GF-2 phage supercluster (Casjens and Grose, 2016) than the lambda supercluster). We investigated oxygen-dependent torCAD expression in one of these prophage-containing strains, the Crohn’s disease-associated strain NRG 857C, and found that the torCAD expression pattern in this strain is similar to the pattern we observe in MG1655 containing the HK022 prophage. In contrast, a previous study found that two other E. coli isolates, Nissle 1917 and HS, which do not have prophages integrated at attBHK022, have torCAD expression patterns that are like that of wild-type (uninfected) MG1655 (Roggiani and Goulian, 2015). These observations suggest that it may be a general capability of the phages that integrate between torS and torT to alter host regulation of torCAD expression. However, despite the similarity of the torCAD expression pattern in NRG 857C and HK022-infected MG1655 and the high conservation of the region around TSSHK022 in prophage-carrying wild strains, we would not necessarily expect torCAD expression in all such strains to have the same behavior: there is considerable variation in overall sequence and gene content among the prophages that occupy the attBHK022 site, the host genomes they inhabit, and the habitats from which they were isolated (see Supplementary file 1).
Studying the diversity and distribution of prophage-mediated torCAD expression could provide insight into the evolutionary advantages for a phage to reconfigure the control of TMAO respiration. Prophage-mediated effects on host physiology remain largely enigmatic, and knowledge is mostly restricted to cases where the effects are readily apparent (as when prophage morons confer an observable phenotype such as toxin production; Hendrix et al., 2000). Cases where a prophage directly alters host metabolism have been described infrequently and generally with little mechanistic detail. To our knowledge, the phenomenon described in this study, where a prophage rewires the regulation of a metabolic pathway by modulating the expression of a signaling gene, has not been reported before and may exemplify a general class of mechanisms phages use to control host behavior. Phage infections certainly play a significant role in bacterial community dynamics, and much of our knowledge about the effects of phage infection is centered on lytic infection, horizontal gene transfer, and bacterial pathogenesis. A greater appreciation of the subtler effects of phage infection on host phenotype is a likely platform for developing enhanced understanding of the structure and behavior of microbial communities.
Materials and methods
Key resources table.
| Reagent type (species) or resource |
Designation | Source or reference |
Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Escherichia coli) | torS | NA | EcoCyc:G6514; UniProt:P39453 | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia virus HK022) | HK022 | PMID: 4569213 | RefSeq:NC_002166 | Dr. Max E. Gottesman (Columbia University) |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | DFE12 | this paper | MG1655 attBλ::(cat PtorCAD-yfp) ompA-cfp (HK022)n | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | DFE34 | this paper | NRG 857C ΔlacIZY::PtorCAD-yfp-FRT-kan-FRT | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | JNC151 | this paper | MG1655 (HK022)n | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | JNC163 | PMID: 29502970 | MG1655 ΔlacZYA::FRT-cat-FRT torT-lacZ-FRT-kan-FRT ΔtorR | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | JNC166 | PMID: 29502970 | MG1655 ΔlacZYA::FRT torS-lacZ-FRT-kan-FRT | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) |
JNC168 | this paper | MG1655 ΔlacZYA::FRT-cat-FRT (HK022)n torT-lacZ-FRT-kan-FRT ΔtorR | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | JNC169 | this paper | MG1655 ΔlacZYA::FRT torS-lacZ-FRT-kan-FRT (HK022)n | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | JNC173 | this paper | MG1655 ΔfhuA::FRT-kan-FRT attBλ::(cat PtorCAD-yfp) ompA-cfp (HK022)n | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | JNC174 | this paper | MG1655 ΔfhuA::FRT-kan-FRT attBλ::(cat PtorCAD-yfp) ΔxylAFG::PtetA-mcherry-FRT | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | JNC175 | this paper | MG1655 ΔlacZYA::FRT torS-lacZ-FRT-kan-FRT (HK022)n attLHK022::Ω | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | MG1655 | Coli Genetic Stock Center | CGSC:7740; RefSeq:NC_000913 | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | MMR8 | PMID: 25825431 | MG1655 attBλ::(cat PtorCAD-yfp) ompA-cfp | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | NRG 857C | PMID: 21108814 | RefSeq:NC_017634 | Dr. Alfredo G. Torres (UTMB) |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | PK13196 | this paper | MG1655 lacZ::kan-PtorS-(GTG)lacZ ΔiscR::FRT | |
| Strain, strain background (E. coli) | PK13199 | this paper | MG1655 lacZ::kan-PtorS-(ATG)lacZ ΔiscR::FRT | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pDSW206 | PMID: 9882665 | ori(pBR322) lacIq
amp Ptrc attenuated promoter. Dr. Jon Beckwith (Harvard University) |
|
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMR26 | PMID: 25825431 | pDSW206 torT | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPK7179 | PMID: 15659690 | ori(pBR322) ter(spf) amp RNA-1 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPK12669 | this paper | pPK7179 with −152 to +28 bp relative to the torS ATG start codon from MG1655 in XhoI/BamHI sites |
|
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pPK13256 | this paper | pPK7179 with −231 to +28 bp relative to the torS ATG start codon from JNC151 in XhoI/BamHI sites | |
| Sequence-based reagent | native torS | this paper | 32P-labeled DNA oligonucleotide: 5’-TTAACAGCGCCATCAG-3’ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | HK022/torS | this paper | 32P-labeled DNA oligonucleotide: 5’-GGGTCAGGGTTAAATTCACGG-3’ | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | E. coli σ70 RNA polymerase holoenzyme | New England Biolabs | NEB:M0551S | |
| Commercial assay or kit | HiSpeed Plasmid Maxi Kit | Qiagen | Qiagen:12662 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | MMLV Reverse Transcriptase 1st-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit | Lucigen | Lucigen:MM070150 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Sequenase Version 2.0 DNA Sequencing Kit | USB | USB:70770 | |
| Software, algorithm | BLAST | PMID: 23609542 | RRID:SCR_004870 | |
| Software, algorithm | ClermonTyping | PMID: 29916797 | v. 1.4.0 | |
| Software, algorithm | ggridges | Comprehensive R Archive Network | RRID:SCR_003005 | v. 0.5.0 |
| Software, algorithm | Mauve | PMID: 20593022 | RRID:SCR_012852 | v. 2015-02-25 |
| Software, algorithm | MUSCLE | PMID: 15034147 | v. 3.8.1551 | |
| Software, algorithm | R | R Foundation for Statistical Computing | RRID:SCR_001905 | v. 3.4.4 |
| Software, algorithm | SnapGene | GSL Biotech | RRID:SCR_015052 | v. 5.0b3 |
Bacterial growth media and conditions
Media and growth conditions were as described in Carey et al. (2018) except that minimal A glucose medium was supplemented with 0.1% casamino acids and 10 mM TMAO for all experiments. Antibiotics were added to media at the following concentrations unless otherwise indicated: streptomycin, 250 μg/mL; ampicillin, 50 μg/mL; kanamycin, 25 μg/mL; and spectinomycin 20 μg/mL.
Strain construction
Lists of all strains and plasmids used in this study are provided in Supplementary file 3 and Supplementary file 4, respectively. HK022 was a generous gift from M.E. Gottesman (Columbia University). P1vir transductions were performed as in Miller (1992) to create strains JNC173 (JW0146 × DFE12) and JNC174 (JW0146 × MMR65). HK022 lysogens were generated using a method adapted from protocols for making λ lysogens (Silhavy et al., 1984) and for making mycobacteriaphage lysogens (Sarkis and Hatfull, 1998). Briefly, the strain to be lysogenized was grown to saturation in LB and harvested by centrifugation. Cells were resuspended at 2× concentration in 10 mM MgSO4, and 100 μL of the suspension was added to 3 mL molten LB top agar at 45°C. The top agar was mixed, layered onto an LB agar plate prewarmed to 42°C, and allowed to solidify. HK022 lysate (50 μL) was spotted onto the top agar and allowed to dry, and the plate was incubated at 37°C overnight. On the following day, an LB plate was spread with 100 μL HK022 lysate and allowed to dry. Selection for lysogens was carried out by streaking from the turbid zone of lysis formed on the top agar plate onto the HK022-spread LB plate and incubating at 37°C overnight. HK022-resistant colonies were patched onto LB agar, and the same colonies were tested for lysogeny by patching onto a top agar lawn containing an HK022-sensitive strain (MG1655). After overnight incubation at 37°C, candidate lysogens that produced a zone of lysis around the area of the patch (from spontaneous phage release) were nonselectively purified by streaking for single colonies from the LB plate patches and incubating at 37°C overnight. The entire patch test procedure was then repeated using the purified colonies. Candidate lysogen colonies that still produced a zone of lysis around the patch after purification were tested for the presence of the HK022 prophage by PCR. Strains produced by this method were JNC151 (HK022 lysogen of MG1655), DFE12 (HK022 lysogen of MMR8), JNC168 (HK022 lysogen of JNC163), and JNC169 (HK022 lysogen of JNC166). These strains were assayed for tandem polylysogeny by PCR essentially as in Powell et al. (1994) using primers HK022-P1 (5’-GGAATCAATGCCTGAGTG-3’), HK022-P2 (5’-GCTGATACACTACAGCAATG-3’), HK022-P3 (5’-GACAGGAGCTTGTTGACTAA-3’), and HK022-P4 (5’-GGCATCAACAGCACATTC-3’). All appeared to be tandem polylysogens (denoted (HK022)n in the Key Resources Table and Supplementary file 3, following the convention of King et al., 2000), although the possible presence of contaminating virion DNA in the PCR template could not be ruled out.
The Ω element strain JNC175 was constructed by recombineering (Datsenko and Wanner, 2000). The Ω element was amplified by PCR from pJB31 using primers LRpJB31_JNC169U1 (5’-CAGAGTCTTCGGGTCAGGGTTAAATTCACGGTCGGTGCACTTTAGGTGAAATCCCGAATGTGCAGTTAAC-3’) and LRpJB31_JNC169L1 (5’-TACTTACATTAATTTACTGATAATTAAAGAGATTTTAAATATACAACTTAGGCGCTGAAAGAAACCGCAA-3’). The PCR product was digested with DpnI and purified before electroporation into JNC169 carrying helper plasmid pKD46. Cultures were spread on LB agar plates containing streptomycin (20 μg/mL), spectinomycin (20 μg/mL), and kanamycin (25 μg/mL) to select for integration of the Ω element and maintenance of the torS-lacZ fusion. The strain was cured of pKD46, and correct integration of the Ω element into attLHK022 was verified by sequencing. The attLHK022::Ω construct was transduced into a clean JNC169 background to create JNC175.
To construct strains containing chromosomally encoded PtorS-lacZ translational fusions, a DNA fragment encompassing -152 to +28 bp relative to the torS ATG start codon (as determined in this study) was PCR amplified from the MG1655 chromosome and cloned into the XhoI and BamHI sites of pPK7035 upstream of lacZ’, creating pPK12792. pPK12792 served as a template for site directed mutagenesis in which bases downstream of predicted torS start codons (GTG or ATG) through the native lacZ start codon were deleted to create plasmids harboring the translational fusion constructs kan-PtorS-(GTG)lacZ’ (pPK13169) and kan-PtorS-(ATG)lacZ’ (pPK13171). pPK13169 and pPK13171 were used as templates for PCR amplification of the translational fusion constructs using primers with homology to the native Plac region. The amplicons were electroporated into PK12556, and kanamycin resistance was used to select for integrants. The kan-PtorS-(GTG)lacZ and kan-PtorS-(ATG)lacZ constructs were then moved into PK4854 using P1vir transduction to create PK13196 and PK13199, respectively.
For in vitro transcription and primer extension assays, promoter regions were cloned into the XhoI and BamHI sites of pPK7179. For native PtorS, the aforementioned DNA fragment encompassing -152 to +28 bp relative to the torS ATG start codon was used, generating pPK12669. To identify the HK022-derived promoter driving torS expression, a DNA fragment encompassing -231 to +28 bp relative to the torS start codon was PCR amplified from the chromosome of JNC151 and cloned into pPK7179, generating pPK13256.
The PtorCAD-yfp reporter was introduced into NRG 857C by conjugation. As E. coli K-12 and E. coli NRG 857C are not closely related, synteny of their chromosomes was confirmed by genomic alignment using Mauve (Darling et al., 2004; Darling et al., 2010) before proceeding. The PtorCAD-yfp reporter was first moved from strain MMR129 into the Hfr strain SASX41B by P1vir transduction, creating DFE33. DFE33 retains the hemA41 allele of SASX41B and is therefore a δ-aminolevulinic acid auxotroph. DFE33 was mated with NRG 857C by superimposed patching of one colony of each strain onto an LB agar plate supplemented with 25 μg/mL δ-aminolevulinic acid. The plate was incubated overnight at 37°C, and on the following day bacteria growing in the patch area were streaked for single colonies onto LB agar supplemented with kanamycin and lacking δ-aminolevulinic acid. This selective media permitted growth of cells that had received the PtorCAD-yfp reporter, which is linked to a kanamycin resistance gene, but had not received the hemA41 allele: as the hemA locus is proximal to the tor locus in the direction of conjugative transfer, growth without δ-aminolevulinic acid indicated retention of the NRG 857C tor genes. Colonies were purified nonselectively on LB agar, and the resulting strain was named DFE34. The metB1 allele of DFE33, which confers methionine auxotrophy, was also verified not to have been transferred to DFE34 by confirming that DFE34 could grow on minimal glucose medium without amino acid supplementation. The metB locus is proximal to the iscR locus (and the hemA and tor loci) in the direction of conjugative transfer, so growth on minimal medium without amino acid supplementation indicated that DFE34 retained the NRG 857C iscR allele. Based on the genetic markers analyzed, the maximum amount of NRG 857C genomic sequence that could have been replaced by K-12 sequence during the construction of DFE34 is 1.1 Mbp.
Phase contrast and fluorescence microscopy
Microscopy was performed as described in Carey et al. (2018) except that cultures were grown to OD600 = 0.1–0.4 before being put on ice. Cultures were chilled on ice for 30 min at the time of streptomycin addition and then aerated on a roller drum at 37°C for 2 hr before being held at 4°C overnight. Imaging was performed the next day with no additional aeration beforehand. Figures 1 and 4 were generated using the R package ggridges (R Development Core Team, 2018; Wickham, 2009; Wilke, 2018). The density curves were generated using a Gaussian kernel function with the bandwidth selected by applying Silverman’s rule of thumb (Silverman, 1986) to the entire data set.
Aerobic-to-anaerobic transition microscopy
Aerobic-to-anaerobic transition microscopy was performed as described in Carey et al. (2018) except that no ΔtorC control strain was included.
β-Galactosidase assays
β-Galactosidase assays were performed as in Carey et al. (2018) except that cultures were grown to OD600 = 0.1–0.5 before harvesting. For the β-galactosidase assays using the PtorS-lacZ translational fusion strains PK13196 and PK13199, chloramphenicol was added to the cultures at a final concentration of 20 μg/mL before placing on ice.
In vitro transcription assays
Following purification of pPK12669 and pPK13256 with a HiSpeed Plasmid Maxi Kit (Qiagen), 2 nM supercoiled plasmid was incubated with 5 μCi of [α-32P]UTP, 50 μM unlabeled UTP, and 500 μM final concentrations each of ATP, CTP, and GTP for 5 min at 37°C in 40 mM Tris (pH 7.9), 30 mM KCl, 100 μg/mL bovine serum albumin, 1 mM dithiothreitol, and 10 mM MgCl2. E. coli σ70 RNA polymerase holoenzyme (50 nM) was added, and each reaction (20 μl total volume) was terminated after 10 min by adding 10 μL 95% (vol/vol) formamide, 20 mM EDTA, 0.05% (wt/vol) bromophenol blue, and 0.05% (wt/vol) xylene cyanol FF. After the mixture was heated to 90°C for 30 s, 5 μl was loaded onto an 8% polyacrylamide-7 M urea gel (0.5× TBE) and run at 1400 V for 3 hr. The gel was then dried and exposed to a PhosphorImager screen.
Primer extension assays
RNA was synthesized using the same protocol as for the in vitro transcription assays, with the exception that UTP was unlabeled. After phenol extraction and ethanol precipitation, 5 μg RNA was hybridized with a 32P-labeled primer (‘native torS’ or ‘HK022/torS’) by heating at 95°C for 5 min followed by slow cooling for 1 hr. Primer extension with the MMLV Reverse Transcriptase 1st-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Lucigen) was carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequencing reactions using the same primer from the primer extension assays were performed using the Sequenase Version 2.0 DNA Sequencing Kit (USB).
Sequence analysis
Phylogenetic group assignments of the prophage-carrying strains listed in Supplementary file 1 were made as described in Clermont et al. (2013) using the ClermonTyping web tool (Beghain et al., 2018) and strain sequences available from NCBI. Isolation source was identified from information in the NCBI sequence entry or linked BioSample entry (Barrett et al., 2012). The most similar phage was identified using PHASTER (Arndt et al., 2016) and is the fully sequenced phage with the highest overall protein sequence similarity to the query prophage. Prophage completeness was assessed using PHASTER. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004) as implemented in SnapGene (SnapGene, 2019).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by grants from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the NIH: R01-GM080279 to MG and R01-GM115894 to PJK.
Funding Statement
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Contributor Information
Mark Goulian, Email: goulian@sas.upenn.edu.
Michael T Laub, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, United States.
Gisela Storz, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, United States.
Funding Information
This paper was supported by the following grants:
National Institutes of Health R01-GM080279 to Mark Goulian.
National Institutes of Health R01-GM115894 to Patricia Kiley.
Additional information
Competing interests
No competing interests declared.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing.
Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—review and editing.
Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—review and editing.
Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—review and editing.
Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing—review and editing.
Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing.
Additional files
Source data for Supplementary file 2.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the manuscript and supporting files.
References
- Ansaldi M, Jourlin-Castelli C, Lepelletier M, Théraulaz L, Méjean V. Rapid dephosphorylation of the TorR response regulator by the TorS unorthodox sensor in Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology. 2001;183:2691–2695. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.8.2691-2695.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansaldi M, Théraulaz L, Baraquet C, Panis G, Méjean V. Aerobic TMAO respiration in Escherichia coli. Molecular Microbiology. 2007;66:484–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argov T, Azulay G, Pasechnek A, Stadnyuk O, Ran-Sapir S, Borovok I, Sigal N, Herskovits AA. Temperate bacteriophages as regulators of host behavior. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2017;38:81–87. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang Y, Wishart DS. PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016;44:W16–W21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T, Clark K, Gevorgyan R, Gorelenkov V, Gribov E, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Kimelman M, Pruitt KD, Resenchuk S, Tatusova T, Yaschenko E, Ostell J. BioProject and BioSample databases at NCBI: facilitating capture and organization of metadata. Nucleic Acids Research. 2012;40:D57–D63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beghain J, Bridier-Nahmias A, Le Nagard H, Denamur E, Clermont O. ClermonTyping: an easy-to-use and accurate in silico method for Escherichia genus strain phylotyping. Microbial Genomics. 2018;4:690. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy-Denomy J, Davidson AR. When a virus is not a parasite: the beneficial effects of prophages on bacterial fitness. Journal of Microbiology. 2014;52:235–242. doi: 10.1007/s12275-014-4083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boratyn GM, Camacho C, Cooper PS, Coulouris G, Fong A, Ma N, Madden TL, Matten WT, McGinnis SD, Merezhuk Y, Raytselis Y, Sayers EW, Tao T, Ye J, Zaretskaya I. BLAST: a more efficient report with usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Research. 2013;41:W29–W33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell AM. Chromosomal insertion sites for phages and plasmids. Journal of Bacteriology. 1992;174:7495–7499. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.23.7495-7499.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey JN, Mettert EL, Roggiani M, Myers KS, Kiley PJ, Goulian M. Regulated stochasticity in a bacterial signaling network permits tolerance to a rapid environmental change. Cell. 2018;175:1989–1990. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens SR, Grose JH. Contributions of P2- and P22-like prophages to understanding the enormous diversity and abundance of tailed bacteriophages. Virology. 2016;496:255–276. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.05.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Golding I, Sawai S, Guo L, Cox EC. Population fitness and the regulation of Escherichia coli genes by bacterial viruses. PLOS Biology. 2005;3:e229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clermont O, Christenson JK, Denamur E, Gordon DM. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environmental Microbiology Reports. 2013;5:58–65. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D, Knights J, Russell R, Shanley D, Birkbeck TH, Dougan G, Charles I. Insertional inactivation of the Staphylococcus aureus β-toxin by bacteriophage Φ13 occurs by site- and orientation-specific integration of the Φ13 genome. Molecular Microbiology. 1991;5:933–939. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling AC, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna NT. Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Research. 2004;14:1394–1403. doi: 10.1101/gr.2289704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling AE, Mau B, Perna NT. progressiveMauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLOS ONE. 2010;5:e11147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datsenko KA, Wanner BL. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. PNAS. 2000;97:6640–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.120163297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies EV, Winstanley C, Fothergill JL, James CE. The role of temperate bacteriophages in bacterial infection. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 2016;363:fnw015. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnw015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon TS, Dhillon EK. Studies on bacteriophage distribution. II. Isolation and host range based classification of phages active on three species of Enterobacteriaceae. Japanese Journal of Microbiology. 1972;16:297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1972.tb00662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaves-Pyles T, Allen CA, Taormina J, Swidsinski A, Tutt CB, Jezek GE, Islas-Islas M, Torres AG. Escherichia coli isolated from a Crohn's disease patient adheres, invades, and induces inflammatory responses in polarized intestinal epithelial cells. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2008;298:397–409. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2007.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research. 2004;32:1792–1797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisert R, Oftedal OT, Lever M, Ramdohr S, Breier BH, Barrell GK. Detection of food intake in a marine mammal using marine osmolytes and their analogues as dietary biomarkers. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 2005;300:213–228. doi: 10.3354/meps300213. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Feiner R, Argov T, Rabinovich L, Sigal N, Borovok I, Herskovits AA. A new perspective on lysogeny: prophages as active regulatory switches of bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2015;13:641–650. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennema D, Phillips IR, Shephard EA. Trimethylamine and trimethylamine N-oxide, a flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3)-mediated host-microbiome metabolic axis implicated in health and disease. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 2016;44:1839–1850. doi: 10.1124/dmd.116.070615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier LC, Sekulovic O. Importance of prophages to evolution and virulence of bacterial pathogens. Virulence. 2013;4:354–365. doi: 10.4161/viru.24498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frobisher M, Brown JH. Transmissible toxicogenicity of streptococci. B Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1927;41:167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Gibb SW, Hatton AD. The occurrence and distribution of trimethylamine-N-oxide in Antarctic coastal waters. Marine Chemistry. 2004;91:65–75. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2004.04.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Grose JH, Casjens SR. Understanding the enormous diversity of bacteriophages: the tailed phages that infect the bacterial family Enterobacteriaceae. Virology. 2014;468-470:421–443. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.08.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai X, Landeras V, Dobre MA, DeOreo P, Meyer TW, Hostetter TH. Mechanism of prominent trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) accumulation in hemodialysis patients. PLOS ONE. 2015;10:e0143731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison E, Brockhurst MA. Ecological and evolutionary benefits of temperate phage: what does or doesn't kill you makes you stronger. BioEssays. 2017;39:1700112. doi: 10.1002/bies.201700112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton AD, Gibb SW. A technique for the determination of trimethylamine-N-oxide in natural waters and biological media. Analytical Chemistry. 1999;71:4886–4891. doi: 10.1021/ac990366y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix RW, Lawrence JG, Hatfull GF, Casjens S. The origins and ongoing evolution of viruses. Trends in Microbiology. 2000;8:504–508. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(00)01863-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Varona C, Hargreaves KR, Abedon ST, Sullivan MB. Lysogeny in nature: mechanisms, impact and ecology of temperate phages. The ISME Journal. 2017;11:1511–1520. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2017.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerta AM, Collado-Vides J. Sigma70 promoters in Escherichia coli: specific transcription in dense regions of overlapping promoter-like signals. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2003;333:261–278. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jourlin C, Bengrine A, Chippaux M, Méjean V. An unorthodox sensor protein (TorS) mediates the induction of the tor structural genes in response to trimethylamine N-oxide in Escherichia coli. Molecular Microbiology. 1996;20:1297–1306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhala RJ, Ford ME, Duda RL, Youlton A, Hatfull GF, Hendrix RW. Genomic sequences of bacteriophages HK97 and HK022: pervasive genetic mosaicism in the lambdoid bacteriophages. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2000;299:27–51. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King RA, Madsen PL, Weisberg RA. Constitutive expression of a transcription termination factor by a repressed prophage: promoters for transcribing the phage HK022 nun gene. Journal of Bacteriology. 2000;182:456–462. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.2.456-462.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. Recombination mechanisms in bacteria. Journal of Cellular and Comparative Physiology. 1955;45:75–107. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030450506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li GW, Burkhardt D, Gross C, Weissman JS. Quantifying absolute protein synthesis rates reveals principles underlying allocation of cellular resources. Cell. 2014;157:624–635. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McShan WM, Ferretti JJ. Prophages and their contribution to host cell phenotype. In: Mc Grath S, Sinderen DV, editors. Bacteriophage. Horizon Scientific Press; 2007. pp. 229–250. [Google Scholar]
- Miller JH. A Short Course in Bacterial Genetics. Plainview: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nash JH, Villegas A, Kropinski AM, Aguilar-Valenzuela R, Konczy P, Mascarenhas M, Ziebell K, Torres AG, Karmali MA, Coombes BK. Genome sequence of adherent-invasive Escherichia coli and comparative genomic analysis with other E. coli pathotypes. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:667. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obeng N, Pratama AA, Elsas JDV. The significance of mutualistic phages for bacterial ecology and evolution. Trends in Microbiology. 2016;24:440–449. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell BS, Rivas MP, Court DL, Nakamura Y, Turnbough CL. Rapid confirmation of single copy lambda prophage integration by PCR. Nucleic Acids Research. 1994;22:5765–5766. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.25.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P, Krisch HM. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984;29:303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team . Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2018. https://www.r-project.org [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovich L, Sigal N, Borovok I, Nir-Paz R, Herskovits AA. Prophage excision activates Listeria competence genes that promote phagosomal escape and virulence. Cell. 2012;150:792–802. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggiani M, Goulian M. Oxygen-dependent cell-to-cell variability in the output of the Escherichia coli Tor phosphorelay. Journal of Bacteriology. 2015;197:1976–1987. doi: 10.1128/JB.00074-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkis GJ, Hatfull GF. Mycobacteriophages. In: Parish T, Stoker N. G, editors. Mycobacteria Protocols. Humana Press; 1998. pp. 145–173. [Google Scholar]
- Seibel BA, Walsh PJ. Trimethylamine oxide accumulation in marine animals: relationship to acylglycerol storage. The Journal of Experimental Biology. 2002;205:297–306. doi: 10.1242/jeb.205.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy TJ, Berman ML, Enquist LW. Experiments with Gene Fusions. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman BW. Density Estimation. London: Chapman and Hall; 1986. [Google Scholar]
- SnapGene . GSL Biotech; 2019. https://www.snapgene.com/ [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi Y, Choi PJ, Li GW, Chen H, Babu M, Hearn J, Emili A, Xie XS. Quantifying E. coli proteome and transcriptome with single-molecule sensitivity in single cells. Science. 2010;329:533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.1188308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchon M, Moura de Sousa JA, Rocha EP. Embracing the enemy: the diversification of microbial gene repertoires by phage-mediated horizontal gene transfer. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2017;38:66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UniProt Consortium UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Research. 2019;47:D506–D515. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasquez M, Ramezani A, Manal A, Raj D. Trimethylamine N-oxide: the good, the bad and the unknown. Toxins. 2016;8:326. doi: 10.3390/toxins8110326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Kim Y, Ma Q, Hong SH, Pokusaeva K, Sturino JM, Wood TK. Cryptic prophages help Bacteria cope with adverse environments. Nature Communications. 2010;1:147. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke CO. ggridges: ridgeline plots in “ggplot2”. 2018 https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggridges
- Yagil E, Dolev S, Oberto J, Kislev N, Ramaiah N, Weisberg RA. Determinants of site-specific recombination in the lambdoid coliphage HK022: an evolutionary change in specificity. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1989;207:695–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey PH, Clark ME, Hand SC, Bowlus RD, Somero GN. Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems. Science. 1982;217:1214–1222. doi: 10.1126/science.7112124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang AQ, Mitchell SC, Smith RL. Dietary precursors of trimethylamine in man: a pilot study. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 1999;37:515–520. doi: 10.1016/S0278-6915(99)00028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]