Abstract
Animals have evolved different foraging strategies in which some animals forage independently and others forage in groups. The evolution of social feeding does not necessarily require cooperation; social feeding can be a beneficial individual-level strategy if it provides mutualistic benefits, for example though increasing the efficiency of resource extraction or processing. We found that Trichoplax adhaerens, the simplest multicellular animal ever described, engages in social feeding behavior. T. adhaerens lacks muscle tissue, nervous and digestive systems – yet is capable of aggregating and forming groups of closely connected individuals who collectively feed. The tight physical interactions between the animals are transitory and appear to serve the goal of staying connected to neighbors during the external digestion of algae when enzymes are released on the biofilm and nutrients are absorbed through the ventral epithelium. We found that T. adhaerens are more likely to engage in social feeding when the concentrations of algae are high - both in a semi-natural conditions and in vitro. It is surprising that T. adhaerens – an organism without a nervous system – is able to engage in this social feeding behavior. Whether this behavior is cooperative is still an open question. Nevertheless, the social feeding behavior of T. adhaerens, an early multicellular animal, suggests that sociality may have played an important role in the early evolution of animals. It also suggests that T. adhaerens could be used as a simple model organism for exploring questions regarding ecology and sociobiology.
Introduction
In order to maximize their energy gain under the constraints of the environment, animals can forage on a patch of food independently or in groups (Pyke, 1984; Stephens and Krebs, 1987; Giraldeau and Caraco, 2000). Social aggregation around food sources can emerge from the fact that the rate of return is high in a particular patch and so many individuals can successfully forage there. It is also possible that organisms receive some mutualistic benefit from feeding together such as greater success at extracting or processing resources. Generally speaking, social feeding does not require cooperation among organisms (Webster and Fiorito, 2001), although cooperation in social feeding is also possible. For example, animals belonging to the same group can develop complex cooperative or altruistic foraging behaviors (Giraldeau and Caraco, 2000). Cooperation – including cooperative feeding behavior - can evolve as a result of high relatedness and/or ecological constraints. This is thought to be especially the case in the early phases of the evolution of sociality (Hamilton, 1964 a, b; 1972).
Trichoplax adhaerens (Placozoa) is the simplest multicellular animal organism ever described (Schierwater et al., 2010). Placozoa are the most basal non-bilaterian metazoan but their relationship with the other metazoans is controversial (Schierwater et al., 2009; Eitel et al., 2013). T. adhaerens is a disk-shaped free living marine organism, 2–3 mm wide and approximately 15 μm high. This organism is composed of only six somatic cell types organized in a three layer tissue anatomy. It lacks nervous and muscle tissues and a digestive system (Schierwater et al., 2009). The cells glide on the substrate by action of the cilia of the lower epithelium. T. adhaerens feeds on diatom algae by external digestion, secreting digestive enzymes in the proximity of algae from the ventral epithelium (Smith et al., 2015). In the laboratory, they only reproduce asexually through fission or budding (Schierwater et al., 2010; Eitel et al., 2011; Smith et al., 2014; Schierwater and Eitel, 2015).
Placozoa can be found worldwide in temperate and warm seas (Pearse, 2007; Eitel et al., 2013). At this time, only two species have been described (Eitel et al., 2018). The ecology and behavior of T. adhaerens in nature are mostly unknown and a large portion of the available information derives from studies in vitro. In this paper, we report new findings regarding the feeding behavior of T. adhaerens. In particular, we discovered that T. adhaerens engage in social feeding behavior where the animals join together, forming tightly connected groups of individuals that essentially form a pocket over algae, potentially allowing them to concentrate digestive enzymes and more easily process and feed on the algae as a group. T. adhaerens has not previously been observed to be social.
Methods
In order to reconstruct an environment similar to the natural habitat of T. adhaerens Grell, we set up an aquarium (Red Sea Max Nano, 75 liters) at the Biodesign Institute, Arizona State University, in which we placed rocks collected from the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea, where the strain of T. adhaerens used in our experiment was isolated (Grell and Benwitz, 1971). These rocks were covered in a variety of marine organisms including algae, bacteria, small invertebrates such as amoebae, nematodes, and vorticella. We filled the aquarium with artificial sea water (ASW) made in laboratory adding 32.5 grams of Instant Ocean® sea salt (Prod. n. SS15–10) per liter of distilled water, pH=8. We kept the water temperature at 23–24 °C. We let the algae and other organisms grow in the aquarium for 8 months, periodically checking to ensure we had not introduced wild T. adhaerens or other Placozoa specimens together with the rocks. Each inspection confirmed that no Placozoa from the wild were growing in the aquarium. We then introduced 20 specimens of T. adhaerens in the aquarium from in vitro culture plates. In order to preserve the original ecosystem we transferred the T. adhaerens specimens in a sterile glass dish and starved them for 24 hours before transferring them to the aquarium. Then, we removed any algae through successive washes and we finally transferred the open bottom glass dish containing the T. adhaerens specimens near one of the glass walls in the aquarium. After introducing the glass dish with T. adhaerens to the aquarium, we observed them move from the glass dish to the aquarium glass where they began feeding on algae in the aquarium. We recorded the movements of T. adhaerens on the aquarium wall glass surface of 1650 cm2 covered with algae in the aquarium for 7 consecutive days by marking the position and the size of the animals and aggregates on transparent plastic sheets attached to the external surface of the aquarium walls. We estimated the number of animals using ImageJ (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/). We calculated the average animal size measuring 23 single T. adhaerens observed during the first two days of observation. We define a group as an aggregate of two or more individuals that are in physical contact.
In addition to growing and observing T. adhaerens in the aquarium, we grew T. adhaerens in vitro in 100 mm diameter, 20 mm high glass Petri dishes in 30 ml ASW at a constant and controlled temperature (23°C) and humidity (60%) with a photoperiod of 14 hours/10 hours light/dark cycle in an environmental chamber (Thermo Scientific™, model 3940). The animals were fed Pyrenomonas helgolandii algae (Schierwater et al., 2010; Eitel et al., 2011; Schierwater and Eitel, 2015). These animals were used for the in vitro experiments.
Two different quantities of algae were used to test the role of algae abundance in triggering social feeding. The low density algae plates had 15 times less (high density plates=30.6×104 algae cells; low density plates=2.04×104) algae seeded on them. We grew the algae for 7 days on F2 medium (Guillard and Ryther, 1962; Guillard, 1975) then substituted the F2 medium with artificial seawater. The algae were distributed evenly on the surfaces of all plates. High algae content was tested in 7 independent experimental replicates (the average number of T. adhaerens was 170.42±7.06 s.e.m. per plate) and low algae content in 6 independent experimental replicates (the average number of T. adhaerens was 146.16±22 s.e.m. per plate). The density of the animals was in average 1/49.6 mm2. T. adhaerens were counted under a Nikon SMZ1270 dissection microscope (magnification 10X) at the same time for all plates. A grid of parallel lines were printed on transparent plastic sheets and positioned under the plate to facilitate counting. Because there are two different concentrations of algae (high and low) and the animals could potentially aggregate at different times we used the the highest number of animals counted in the aggregates for each plate for the comparisons between the two algae concentrations.
Results
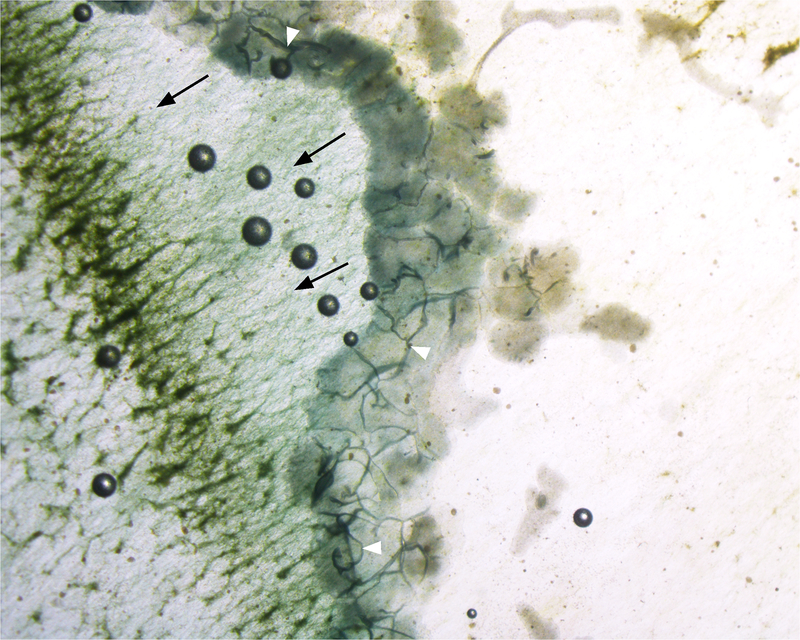
We observed that the animals congregated in groups of 2–105 individuals while feeding on the algae despite the widespread availability of algae on the surfaces of the aquarium. The aggregated animals formed a ‘moving front’ which consumed the algae as it moved along the surface of the aquarium (Fig. 1). The number of animals in the same aggregate varied dynamically as they consumed the algae. The groups of animals moved on the solid surface in the direction of the algae biofilm, digesting the algae as they passed (Supp.1). Animals of the moving front were sometimes distributed in multiple lines (Fig.1, Supp.1, 2). The animals, especially the ones in the first lines, were tightly connected to one another (Fig.2). They were observed to be in physical contact with one another other along their margin, which slightly folds over in the ventro-dorsal direction (opposite to the substrate), forming stable but dynamic junctions (Fig.1, Supp.1, 2). Occasionally, T. adhaerens would move to fill gaps in the chain of animals by binding themselves to neighbors on either side (Supp.3).
Figure 1:
T. adhaerens aggregated on the aquarium wall biofilm. Contact points between Placozoa are visible and dark (white arrowheads). Black arrows indicate the Placozoa march direction. The surface after the passage of the T. adhaerens front appears depleted of algae (asterisks, right side of picture). Magnification: 10X.
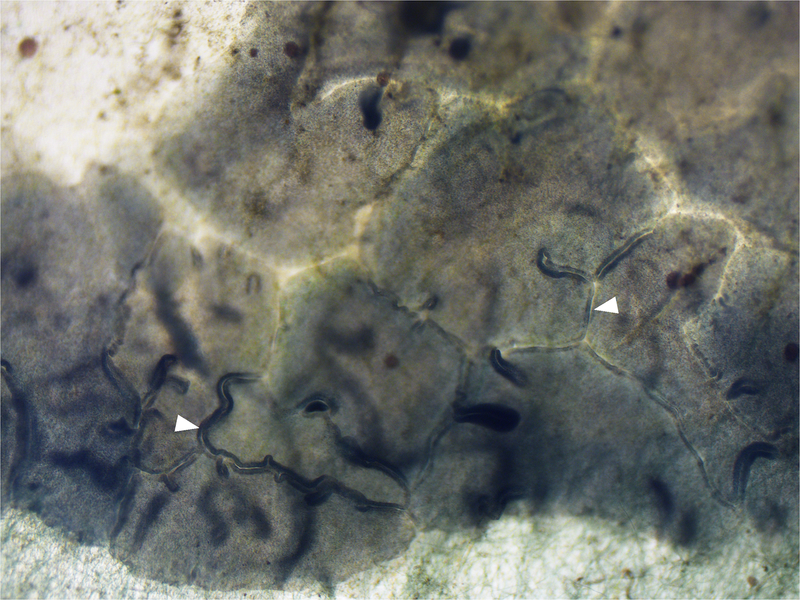
Figure 2:
Magnification of T. adhaerens aggregate on the aquarium wall biofilm. White arrowheads indicate the contact points between Placozoa. Magnification: 40X.
We documented the colonization of a glass surface covered with algae. The first day we identified 6 T. adhaerens in close vicinity (maximum distance between two animals 17 mm). After three days we estimated the presence of 347 T. adhaerens of which 81.28% aggregated in randomly distributed groups (largest aggregate = 32 animals). Gradually, the T. adhaerens formed an advancing feeding front (Supp. 4, 5) and after 7 days we estimated the presence of 847 animals, of which 56.93% was aggregated (Supp. 4–6). At this stage, the average numberof T. adhaerens aggregated per group was 3.52± 0.53 s.e.m. animals and the larger group consisted of 53 animals. The most numerous aggregate observed was composed of 105 T. adhaerens and formed after 6 days (Supp.4). Originally, the social behavior was observed in the aquarium, but we have also reproduced and observed social feeding behavior in vitro on Petri dishes (Supp. 7)
We varied the concentration of algae in to investigate whether social feeding behavior of T. adhaerens is influenced by resource density (controlling for the amount of algae per animal). Each animal had the same quantity of algae available and space on the plate surface to be a solitary feeder or engage in social feeding. We found that a larger percentage of animals engage in social feeding when the concentration of algae is higher (high algae: percentage of animals aggregate= 13.35± 2.41s.e.m; low algae: percentage of animals per aggregate= 3.34± 0.34 s.e.m., χ2= 61.232, df= 1, p<0.0001). We observed - both in the aquarium and in vitro - that social feeding behavior ceases, with T. adhaerens dispersing after all algae have been consumed.
We also observed that T. adhaerens in the aquarium can take a tubular elongated shape and they can move quickly on the substrate (Supp.1–3). This behavior has not previously been described.
Discussion
We observed feeding of T. adhaerens under semi-natural condition in the lab, finding that they engage in social feeding behavior as a sort of moving front that collectively digests algae. They establish tight junctions among themselves which seem to create a sort of pocket in which digestive enzymes are concentrated, potentially allowing them to digest the algae more quickly and effectively as an aggregation. We also tested whether resource density would influence the likelihood of social feeding and we foumnd that T. adhaerens aggregated with a significantly higher frequency when the concentration of algae was higher (controlling for the among of algae available per T. adhaerens.
Many open questions remain about the evolutionary and physiological mechanisms underlying T. adhaerens social feeding behavior. For example, it is possible that this social feeding behavior is simply a result of optimal foraging in a resource rich environment. It is also possible that higher concentrations of algae require more T. adhaerens to effectively digest them or T. adhaerens are able to cooperate by optimizing the quantity of the digestive enzymes released. It is important to underline that T. adhaerens in vitro are derived from asexual reproduction and are genetically identical. Relatedness is an important factor for social behavior and cooperation to evolve (Hamilton, 1964 a, b; 1972). This high relatedness would also occur in nature when a T. adhaerens colonizes a new source of food and rapidly reproduces asexually, creating a local density of clonal animals.
Also, cooperation, competition and cheating are not mutually exclusive possibilities - they may all play a role in different aspects of social feeding in T. adhaerens. The external digestion of food creates opportunities for both cooperation (e.g., for initial digestion through enzyme production) and competition (e.g., during the absorption of the nutrients). Moreover, the food digested by a group of T. adhaerens can then become a public goods that might create a vulnerability to cheating strategies (Strassmann and Queller, 2011; Riehl and Frederickson, 2016). Cheaters that join a group and absorb or scavenge the nutrients left behind by other animals without secreting digestive enzymes themselves could have an evolutionary advantage over producers, leading to selection for cheating. These alternative or concomitant explanations need to be tested in future work.
Another interesting aspect of our findings is our observation that T. adhaerens are able to engage in this social feeding behavior without a nervous system. Interestingly, cells capable of expressing neuronal proteins have been found in the margins of T. adhaerens (Smith et al., 2014). Therefore it is plausible that communication may be occurring among T. adhaerens as they interact during social feeding. They may also be capable of detecting the presence of algae and/or factors produced by other T. adhaerens that may be facilitating collective digestion. Future work should explore the sensing and communication capacities of T. adhaerens and how these operate during social feeding.
Considering that Placozoa are the simplest animals ever described (Schierwater et al., 2010), the discovery that they possess a social behavior is potentially the most primitive case of social behavior ever described in non-colonial animal. T. adhaerens do not have a nervous system, yet they engage in complex social feeding behavior. This is consistent with work showing that nervous systems – despite playing an important role in sociality (Blumstein et al. 2010) - are not required for it. Social behavior has been described in prokaryotic (Crespi et al., 2001) and eukaryotic unicellular organisms like dictyostelids (Fortunato et al., 2003; Queller et al., 2003). These organisms are able to achieve complex multicellular and social structures with neuronal specialization (Kessin, 2001). The social feeding behavior of T. adhaerens suggests that sociality may have played an important role in the early evolution of animals.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary 1: Video of T. adhaerens social feeding behavior. The margins of the animals in contact appear whitish because of light reflection. Tubular shaped animals are visible. 25X fast-motion video, magnification: 10X.
Supplementary 2: Video of T. adhaerens social feeding behavior at higher magnification. The T. adhaerens connected margins are detached from the substrate and slightly fold over in the ventro-dorsal direction, which causes them to sway. Fast moving tubular shaped animals are visible. 25X fast-motion video, magnification: 20X.
Supplementary 3: Video of T. adhaerens social feeding behavior. T. adhaerens aggregates occupy empty space along the placozoa feeding rim. Fast moving tubular shaped animals are visible. 25X fast-motion video, magnification: 10X.
Supplementary 4: T. adhaerens positions, size, and aggregate dimension on an aquarium wall (blue), and after 20 hours (red). Picture of the same aggregates is shown in supplementary 4.
Supplementary 5: T. adhaerens aggregates on the aquarium wall.
Supplementary 6: Number of animals and groups of individuals on the aquarium wall during 7 consecutive days of observation.
Supplementary 7: T. adhaerens aggregates in vitro. Arrowheads indicate the junctions between T. adhaerens. Magnification: 40X.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Bernd Schierwater for sending the starting culture of T. adhaerens and Emily Ayoub for assistance in the collection of samples from the Red Sea.
This work was supported in part by NIH grants U54 CA217376, U2C CA233254, R01 CA185138 and R01 CA140657 as well as CDMRP Breast Cancer Research Program Award BC132057. The findings, opinions and recommendations expressed here are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the universities where the research was performed or the National Institutes of Health.
References
- Blumstein DT, Ebensperger LA, Hayes LD, Vásquez RA, Ahern TH, Burger JR, et al. (2010). Toward an integrative understanding of social behavior: new models and new opportunities. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 4, 34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespi BJ (2001).The evolution of social behavior in microorganisms. Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 16, 178–183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eitel M, Guidi L, Hadrys H, Balsamo M, and Schierwater B (2011). New insights into placozoan sexual reproduction and development. PLoS One 6, e19639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eitel M, Osigus HJ, DeSalle R, Schierwater B (2013). Global diversity of the Placozoa. PLoS One. 8, e57131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eitel M, Francis WR, Varoqueaux F, Daraspe J, Osigus HJ, Krebs S, Vargas S, Blum H, Williams GA, Schierwater B, Wörheide G (2018). Comparative genomics and the nature of placozoan species. PLoS Biology. 31;16, e2005359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato A, Strassmann JE, Santorelli L and Queller DC (2003). Co-occurrence in nature of different clones of the social amoeba, Dictyostelium discoideum. Molecular Ecology 12, 1031–1038, pp.173–200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldeau L-A. and Caraco T (2000). Social Foraging Theory. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Grell KG, and Benwitz G (1971). Die ultrastruktur von Trichoplax adhaerens FE Schulze. Cytobiologie. 4, 216–240. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard RRL and Ryther JH. 1962. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea Cleve. Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 8, 229–239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillard RRL 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates in “Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals.” (eds: Smith WL and Chanley MH) Plenum Press, New York, USA: pp 26–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton WD (1964a). The genetical evolution of social behaviour. I. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 7, 1–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton WD (1964b). The genetical evolution of social behaviour. II. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 7, 17–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton WD (1972). Altruism and related phenomena, mainly in the social insects. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 3, 193 – 232. [Google Scholar]
- Kessin RH (2001). Dictyostelium: Evolution, Cell Biology, and the Development of Multicellularity. Cambridge University Press, New York, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Pearse VB, Voigt O (2007). Field biology of placozoans (Trichoplax): distribution, diversity, biotic interactions. Integrative and Comparative Biology. 47, 677–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke H, (1984). Optimal foraging theory: a critical review. Annual Review Ecology and Systematics.15, 523–75 [Google Scholar]
- Queller DC, Foster KF, Fortunato A, and Strassmann JE (2003). Cooperation and conflict in the social amoeba, Dictyostelium discoideum Genes, Behaviors and Evolution of Social Insects. Hokkaido University Press, Sapporo, Japan: Editors: Kikuchi T, Azuma N, Higashi S. [Google Scholar]
- Riehl C, Frederickson ME (2016). Cheating and punishment in cooperative animal societies. Philosophical Transaction of the Royal Society London B: Biological Science. 371(1687), 20150090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schierwater B, Eitel M, Jakob W, Osigus HJ, Hadrys H, Dellaporta SL, Kolokotronis SO, Desalle R (2009). Concatenated analysis sheds light on early metazoan evolution and fuels a modern “urmetazoon” hypothesis. PLoS Biology 7(1), e20, [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schierwater B, Eitel M, Osigus H, der Chevallerie K, Bergmann T, Hadrys H, et al. (2010). Trichoplax and Placozoa: one of the crucial keys to understanding metazoan evolution In: DeSalle R, Schierwater B, editors. Key transitions in animal evolution: CRC Press, 289–326. [Google Scholar]
- Schierwater B, and Eitel M (2015). Placozoa. In Evolutionary Developmental Biology of Invertebrates. 1, 107–114 [Google Scholar]
- Smith CL, Pivovarova N, and Reese TS (2015). Coordinated Feeding Behavior in Trichoplax, an Animal without Synapses. PLoS One. 2,10, e0136098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith CL, Varoqueaux F, Kittelmann M, Azzam RN, Cooper B, Winters CA, et al. (2014). Novel cell types, neurosecretory cells, and body plan of the early-diverging metazoan Trichoplax adhaerens. Current Biology 24, 1565–1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens DW and Krebs JR (1987). Foraging theory. Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Strassmann JE, Queller DC (2011). Evolution of cooperation and control of cheating in a social microbe. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA.108 Suppl 2, 10855–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster SJ. and Fiorito G (2001). Socially guided behaviour in non-insect invertebrates. Animal Cognition. 4, 69–79 [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary 1: Video of T. adhaerens social feeding behavior. The margins of the animals in contact appear whitish because of light reflection. Tubular shaped animals are visible. 25X fast-motion video, magnification: 10X.
Supplementary 2: Video of T. adhaerens social feeding behavior at higher magnification. The T. adhaerens connected margins are detached from the substrate and slightly fold over in the ventro-dorsal direction, which causes them to sway. Fast moving tubular shaped animals are visible. 25X fast-motion video, magnification: 20X.
Supplementary 3: Video of T. adhaerens social feeding behavior. T. adhaerens aggregates occupy empty space along the placozoa feeding rim. Fast moving tubular shaped animals are visible. 25X fast-motion video, magnification: 10X.
Supplementary 4: T. adhaerens positions, size, and aggregate dimension on an aquarium wall (blue), and after 20 hours (red). Picture of the same aggregates is shown in supplementary 4.
Supplementary 5: T. adhaerens aggregates on the aquarium wall.
Supplementary 6: Number of animals and groups of individuals on the aquarium wall during 7 consecutive days of observation.
Supplementary 7: T. adhaerens aggregates in vitro. Arrowheads indicate the junctions between T. adhaerens. Magnification: 40X.