Abstract
A 63-year-old woman with a prior history of chronic lower extremity lymphedema came to the hospital for evaluation of new-onset left leg pain and swelling associated with haemorrhagic blisters and foul-smelling discharge. Relevant history included a recent trip to a Hudson River Valley beach in New York 1 week prior to hospitalisation. Laboratory evaluation revealed significant leukocytosis and lactic acidosis. She was found to have sepsis and bacteremia secondary to Vibrio cholerae (serotype non-O1, non-O139). During a prolonged intensive care unit course requiring intravenous pressor support and broad-spectrum antibiotics, she underwent debridement of her left foot eschar along with skin grafting. Once clinically stable and improved, she was discharged to a subacute rehabilitation centre with close follow-up for wound care. V. cholerae infection is rare and often benign but can be transmitted from contaminated seawater to individuals with underlying chronic illness and cause severe symptoms, including sepsis.
Keywords: infections, skin, infectious diseases, adult intensive care
Background
Vibrio cholerae remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality especially in immune-compromised people with poor sanitation. It typically presents with gastrointestinal manifestations requiring supportive therapy. Though rare in the USA, V. cholerae can cause small outbreaks that spread via contaminated raw seafood and seawater exposure. Rarely, the V. cholerae non-O1/non-O139 serotype can also result in extraintestinal manifestations which can be a therapeutic challenge. In this case report, we diagnosed an elderly woman with a lower extremity soft tissue infection and bacteremia after exposure to seawater contaminated with V. cholerae. The case emphasises the need to take a detailed history to promptly diagnose V. cholerae exposure to minimise the risk of morbidity and mortality.
Case presentation
A 63-year-old morbidly obese woman with a medical history of chronic lower extremity lymphedema, hypertension, osteoarthritis, restless leg syndrome and bilateral knee arthroplasty was admitted to the hospital for 4 days of intractable left leg pain and discoloration. She denied recent consumption of seafood, history of diabetes mellitus, end-stage renal disease, hemochromatosis, hematologic malignancy, excessive alcohol intake, liver cirrhosis or iron supplementation. She reported a recent trip to a Hudson River Valley beach in New York 1 week prior to hospitalisation.
Investigations
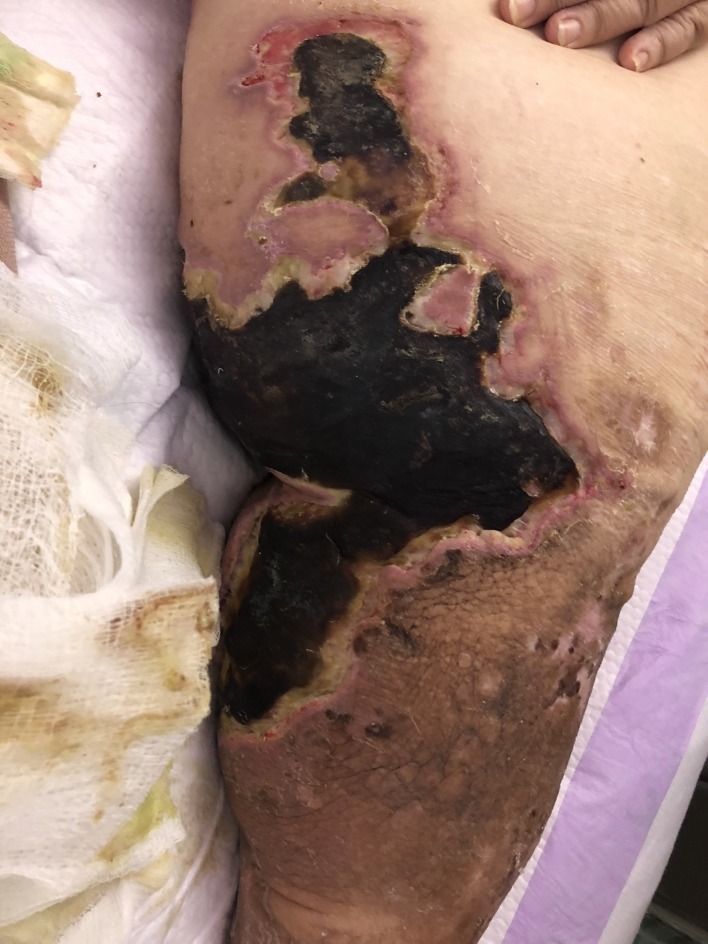
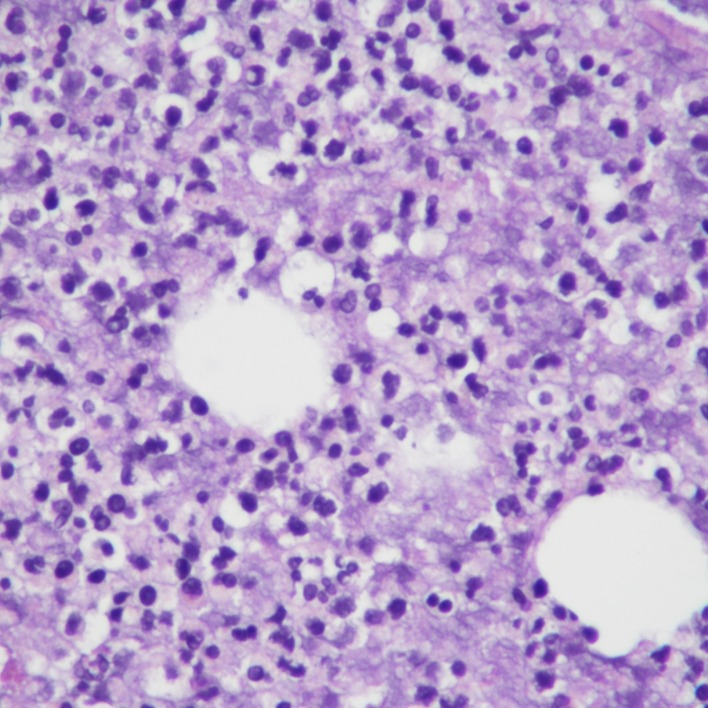
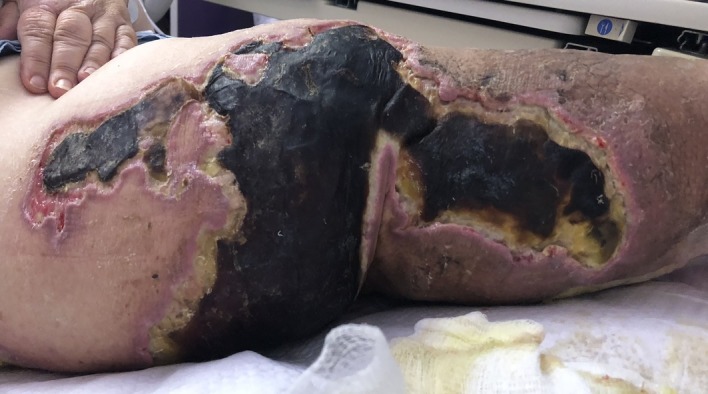
The patient presented with sepsis to the emergency department with pertinent vitals revealing a temperature of 37.3°C, pulse rate of 93 beats/min, blood pressure of 88/64 mm Hg, and respiratory rate of 26 breaths/min with 97% oxygen saturation on room air. Her body mass index was 51.9 kg/m2, and on physical exam, her bilateral lower extremities were noted to be darkened to an ash colour more prominent on the left lower extremity (figures 1 and 2). There were associated haemorrhagic blisters with foul-smelling discharge. Laboratory evaluation showed a white blood cell count of 19×109/L (reference range, 3.8–10.5×109 /L) and serum lactate level of 6.3 mmol/L (reference range, 0.7–2.0 mmoL/L). Manual differential was significant for neutrophils at 78% (reference range, 43%–77%), lymphocytes at 6% (reference range, 13%–44%) and monocytes at 16% (reference range, 2%–14%). Arterial blood gas showed a pH of 7.25 (reference range, 7.35–7.45), serum Pco2 of 31 mm Hg (reference range, 32–46 mm Hg), serum PO2 of 136 mm Hg (reference range, 74–108 mm Hg) and serum bicarbonate level of 13 mmol/L (reference range, 23–27 mmol/L). CT scan of her left lower extremity revealed marked circumferential subcutaneous soft tissue oedema with skin thickening and soft tissue calcifications. Blood cultures grew Gram-negative rods within 1 day of admission, and later, her bacteremia was found to be secondary to V. cholerae (serotype non-O1, non-O139), the sensitivities of which are given in table 1. Swab cultures from her left leg bulla also grew V. cholerae, however, her stool cultures showed no enteric pathogens. During debridement of her left leg ulcer, a surgical biopsy was performed which showed nonviable fibrofatty tissue with necro-inflammatory exudates (figure 3).
Figure 1.
Left lower extremity skin discoloration with associated haemorrhagic borders.
Figure 2.
Left lower extremity skin.
Table 1.
Blood culture sensitivities of Vibrio cholerae
| Antibiotics | Sensitive/resistance |
| Ampicillin | S |
| Gentamicin | S |
| Imipenem | S |
| Levofloxacin | S |
| Meropenem | S |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | S |
| Tetracycline/doxycycline | S |
Figure 3.
Surgical biopsy of skin showing fibrofatty tissue with necro-inflammatory exudates.
Differential diagnosis
Our patient presented with acute lower extremity cellulitis with swelling, redness, tenderness, black eschar and bullae formation superimposed on chronic lymphedema. The absence of tender, palpable cords on exam excluded the suspicion of superficial thrombophlebitis. In some cases, the presence of crepitus and free air under the skin can lead to a diagnosis of necrotising fasciitis requiring emergent surgical intervention, but this was not evident in this patient. Normal duplex studies ruled out deep vein thrombosis. History related to recent travel, tick bite and allergic exposures can help distinguish Lyme disease and contact dermatitis, which may present similarly. Use of new medication may also lead to fixed drug reactions and eosinophilic cellulitis. Calciphylaxis is an important skin pathology to consider, though this entity is mostly seen in those with end-stage renal disease. A prior history of venous insufficiency and hyperpigmentation of skin can cause stasis dermatitis. In our case, an indium scan was performed which excluded knee hardware infection and osteomyelitis in a postarthroplasty patient.
Treatment
After collecting blood and wound cultures, the patient was started on empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics (vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam). We started an aggressive intravenous hydration protocol to correct her hypotension and lactic acidosis. This was followed by consultation to the critical care providers for intravenous pressor support in the setting of refractory hypotension with transfer to the intensive care unit. Given her worsening leukocytosis and persistent shock, her antibiotic coverage was further broadened to linezolid and aztreonam. With the identification of the causative agent as V. cholera (serotype non-O1, non-O139) in her blood and swab cultures, known antibiotic sensitivities and clinical improvement, antimicrobial management was de-escalated to doxycycline. The patient’s wounds were also assessed by the general surgery service followed by two debridement procedures of the left foot eschar during the hospitalisation. Negative pressure wound therapy was applied afterward, and skin grafting was performed by the plastic surgery service before discharge from the hospital.
Outcome and follow-up
The patient recovered well after the surgery and finished her course of antibiotics in the hospital. She was discharged to a physical rehabilitation centre for gait training along with negative pressure wound therapy and close follow-up with plastic and general surgery for her wound care.
Discussion
Most commonly known infections caused by Vibrio serotypes are gastroenteritis, cholera-like diarrhoea, local wound infections, peritonitis, endophthalmitis, ear infections, meningitis, septic arthritis and bacteremia.1 2 Gastrointestinal infections, which are usually caused by V. cholera and V. parahaemolyticus, usually clear with supportive therapy; however, extra-intestinal manifestations due to V. vulnificus require early antibiotic therapy along with aggressive surgical intervention. V. cholerae is an aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria mostly inhabiting saltwater. Based on serotypes and outer membrane O-antigen composition, they are broadly classified into O1, O139, and non-O1/non-O139.1 3 V. cholera infection is rare in the USA with a generally benign course. However, V. cholerae infections may occasionally lead to severe septicemia and in such cases, carries a high risk of mortality. V. cholera non-O1/non-O139 is usually transmitted through consumption of seafood and exposure to contaminated seawater in people with underlying chronic medical diseases.4
We describe a case of V. cholera-causing contamination of a chronic wound in an elderly obese woman leading to septic shock. The patient had exposure of her chronic lower extremity lymphedema to seawater in New York before coming to the hospital. The presence of erythematous bullae, pus, leukocytosis, elevated lactate, fever and hypotension was noted on arrival. Broad-spectrum antibiotics and intravenous pressor support were started after fluid resuscitation. Blood and wound cultures showed infection from V. cholera non-O1/non-O139 strain, and her antibiotics were changed to doxycycline based on sensitivities and previously published literature.2 With the improvement in her haemodynamic state, surgical debridement was performed along with skin grafting.
Non-O1/non-O139 V. cholerae bacteremia and wound infection is a life-threatening condition.2 Education regarding the hazards of consuming raw seafood and proper food sterilisation is necessary to prevent small outbreaks.5 Suspicion of V. cholerae infections should be high if there is exposure to seawater or undercooked seafood, especially during summer.6 7 Blood and wound cultures should be collected before starting broad-spectrum antibiotics as V. cholerae has a high risk of becoming resistant via spontaneous mutation, horizontal gene transfer, and conjugated plasmids.2 Sepsis from Vibrio subtypes cannot be ruled out if cultures are sent after the administration of antibiotics. PCR has high specificity even if antibiotics are administered previously.4
Learning points.
Vibrio cholerae infection is rare and often benign in the USA, but may occasionally be transmitted from contaminated seafood or seawater to individuals with underlying chronic illness and cause severe symptoms, including sepsis
Cutaneous V. cholerae infection may need to be distinguished from such infections as necrotising fasciitis, superficial thrombophlebitis, drug reactions and deep vein thrombosis.
It is of utmost importance to assess the sensitivities of patients with V. cholerae infections as this pathogen has a high risk of mutation and antimicrobial resistance.
Footnotes
Contributors: RC supervised the project and contributed to the final version of the manuscript. TN helped in getting biopsy slides, pictures of the patient and consent form. AA wrote the manuscript with input from all authors.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1. Chowdhury G, Joshi S, Bhattacharya S, et al. Extraintestinal infections caused by Non-toxigenic Vibrio cholerae non-O1/non-O139. Front Microbiol 2016;7:144 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Laviad-Shitrit S, Sharaby Y, Izhaki I, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of environmental Non-O1/Non-O139 Vibrio cholerae isolates. Front Microbiol 1726;2018:9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Hasan NA, Rezayat T, Blatz PJ, et al. Nontoxigenic Vibrio cholerae non-O1/O139 isolate from a case of human gastroenteritis in the U.S. Gulf Coast. J Clin Microbiol 2015;53:9–14. 10.1128/JCM.02187-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Yun NR, Kim D-M. Vibrio vulnificus infection: a persistent threat to public health. Korean J Intern Med 2018;33:1070–8. 10.3904/kjim.2018.159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Crowe SJ, Newton AE, Gould LH, et al. Vibriosis, not cholera: toxigenic Vibrio cholerae non-O1, non-O139 infections in the United States, 1984-2014. Epidemiol Infect 2016;144:3335–41. 10.1017/S0950268816001783 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Johnston JM, Mcfarland LM, Bradford HB, et al. NOTES Isolation of Nontoxigenic Vibrio Cholerae 01 from a Human Wound Infection. Vol 17, 1983. Available: http://europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcrender.fcgi?accid=PMC272765&blobtype=pdf [Accessed 18 Jan 2019]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7. Oliver JD. Wound infections caused by Vibrio vulnificus and other marine bacteria. Epidemiol Infect 2005;133:383–91. 10.1017/S0950268805003894 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]