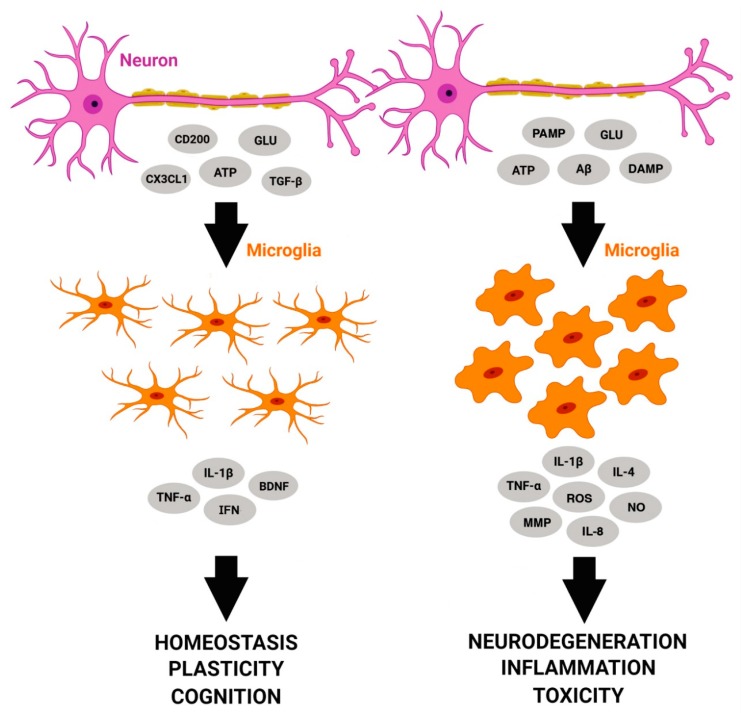
Figure 1.
Microglial responses to different molecules released by neurons. CX3CL1, CD200, glutamate, ATP, and TGF-β induce an anti-inflammatory microglial profile, with microglia performing housekeeping tasks and contributing to homeostasis, plasticity, and cognition processes through release of TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN, and BDNF. In a different scenario, ATP, glutamate, danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), and amyloid-beta proteins drive microglial behavior to a more responsive pro-inflammatory state, releasing IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-4, ROS, NO, IL-8, and MMP. When the pro-inflammatory profile is maintained for a long time, it foments pathological conditions, such as toxicity, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration.