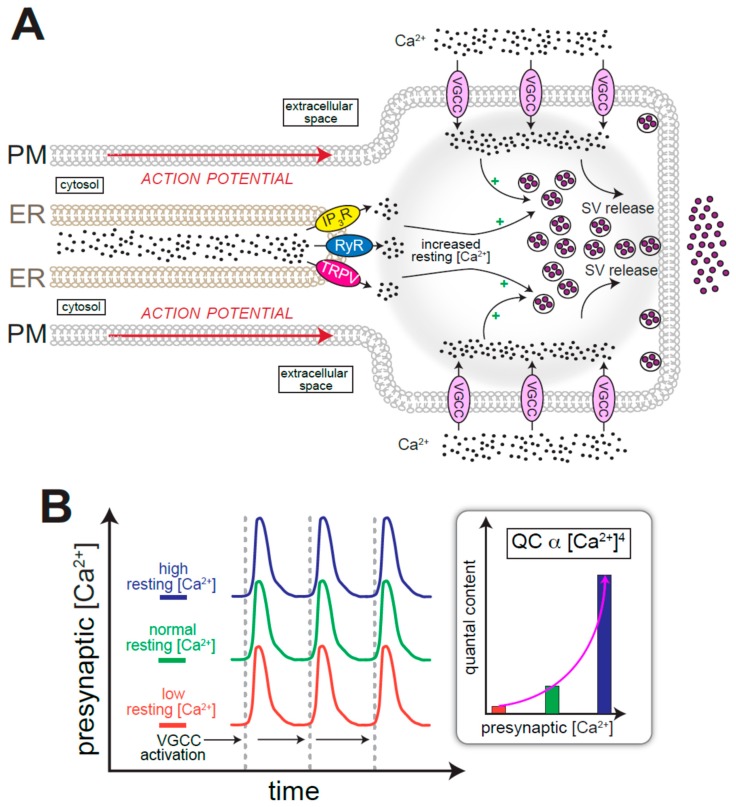
Figure 2.
Influence of ER Ca2+ release on synaptic vesicle (SV) release and neurotransmission. (A) Action potentials are propagated through axons. Depolarization of presynaptic membrane activates voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs), which causes Ca2+ to enter the synapse. ER Ca2+ release contributes to cytosolic [Ca2+], which influences release of neurotransmitter-laden SVs. (B) ER Ca2+ release, whether increased or decreased, affects the presynaptic cytosolic [Ca2+]. The presynaptic cytosolic [Ca2+] scales linearly upon activation of VGCCs. The magnitude of SV release obeys a 4th power relationship with presynaptic cytosolic [Ca2+], allowing small elevations in [Ca2+] to cause large increases in neurotransmitter release (inset).