Abstract
Fusidic acid is a steroid antibiotic known since the 1960s. It is frequently used in topical preparations, i.e., ointments, for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. There is an increasing number of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains that harbour plasmid-borne fusB/far1 or fusC that is localised on SCC elements. In this study we examined a series of related CC30-MRSA isolates from the Arabian Gulf countries that presented with SCCmec elements and fusC, including a variant that—to the best of our knowledge—has not yet formally been described. It consisted of a class B mec complex and ccrA/B-4 genes. The fusidic acid resistance gene fusC was present, but contrary to the previously sequenced element of HDE288, it was not accompanied by tirS. This element was identified in CC30 MRSA from Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates that usually also harbour the Panton-Valentin leukocidin (PVL) genes. It was also identified in CC8 and ST834 isolates. In addition, further CC30 MRSA strains with other SCCmec VI elements harbouring fusC were found to circulate in the Arabian Gulf region. It can be assumed that MRSA strains with SCCmec elements that include fusC have a selective advantage in both hospital and community settings warranting a review of the use of topical antibiotics and indicating the necessity of reducing over-the-counter sale of antibiotics, including fusidic acid, without prescription.
Introduction
Within a year after of the introduction of penicillinase-resistant semi-synthetic penicillins such as methicillin, oxacillin and the first/second generation cephalosporins, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was reported in the United Kingdom [1]. Beta-lactam resistance in MRSA is due to modified penicillin-binding proteins encoded by different mec genes, out of which mecA is by far the most common and most widespread [2, 3]. The mecA gene is located on potentially mobile, large and complex genetic elements, known as SCCmec (“staphylococcal cassette chromosome” or “staphylococcal chromosomal cassette” harbouring mecA). In addition to mecA or mecC, SCCmec elements include ccr recombinase genes, regulatory elements and, variably, additional genes encoding resistance to other antimicrobials, such as aminoglycosides or macrolides, and to heavy metal ions [4–11]. They also might contain the gene fusC encoding fusidic acid resistance [12, 13]. Fusidic acid [14, 15] is a steroid antibiotic known since the 1960s. It is frequently used in topical preparations, i.e., ointments, for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections caused by S. aureus. In some countries, intravenous preparations are licensed that are administered in combination with other antimicrobials in order to treat staphylococcal bloodstream or orthopaedic infections. Resistance in staphylococci towards fusidic acid can essentially be attributed to five different genetic causes. One is caused by random mutation under selective pressure in the ubiquitous fusA or efg gene coding for elongation factor G [16]. Similarly, point mutations in fusE, or rplF, encoding riboprotein L6 can confer resistance [17, 18]. Another mechanism is related to the presence of the plasmid-borne gene fusB, also known as far1. Its gene product binds to elongation factor G (efg) and thereby protects efg from fusidic acid. Acquired resistance due to fusB/far1 is commonly observed in the community acquired MRSA strain CC80-MRSA-IV that is common in Mediterranean and Middle Eastern countries [19–26]. A similar gene, fusC (Q6GD50) is localized on SCC elements. Such an element was first sequenced in a methicillin-susceptible strain, MSSA476 (GenBank BX571857.1) [27] where it is accompanied by ccrA/B1 genes. However, there are also various SCCmec elements that comprise both, mecA and fusC, together with various combinations of ccr genes and other markers [12, 13]. One of these markers is tirS, a putative virulence factor mimicking the human Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) resulting in attenuation of the inflammatory response [28]. Finally, there is a gene, fusD, that has been found in various coagulase-negative staphylococci (S. arlettae, S. cohnii, S. microti, S. pettenkoferi and S. saprophyticus) [17] but apparently not yet in S. aureus. A high consumption of fusidic acid at a population level has been shown to confer a clear selective advantage to strains carrying fusC and subsequently to their emergence and proliferation as it was well documented for New Zealand [29]. Much less is known on the situation in other geographic regions. However, a high prevalence of fusB/far1 nd fusC and/or a high prevalence of fusidic acid resistance suggest a similar effect in Middle Eastern/Arabian Gulf countries. Indeed, fusidic acid is—or was until recently—available for purchase over-the-counter without prescription there. In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), prescriptions for the purchase of antibiotics became mandatory in late 2017. In this work we examine a series of related MRSA isolates from Arabian Gulf countries that presented with SCCmec VI elements and fusC. This included a variant that—to the best of our knowledge—has not yet formally been described and therefore it was characterised in detail.
Material and methods
Isolates
One CC30 MRSA isolate (RUH-32) obtained in September 2014 from a patient with septic arthritis at the King Khalid University Teaching Hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, yielded a microarray hybridisation pattern that did not match hybridisation patterns of previously known SCC elements. This isolate was subjected to whole genome sequencing. The BioSample accession number for the isolate is SAMN06925305, the master accession number of the assembled contigs is SGWB00000000.1. This investigation prompted a search for additional CC30 isolates with both, SCCmec VI elements and fusC yielding one isolate from Dubai, UAE (2018), sixteen from Kuwait (2016/2017) [30]and two from Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (2014 and 2018). All were obtained from hospitalised patients. Finally, two archived non-CC30 isolates were retrospectively found by using an array for SCCmec characterisation (see below and [9]) to harbour the same variant of a SCCmec VI element as RUH-32. One was a ST834-MRSA isolated in 2011 from a cutaneous abscess of a 3 years old child from Riyadh [31]. The other one was a CC8-MRSA that was isolated in 2017 from a hospitalised patient in Dresden, Saxony, who had a history of travel to, or migration from, the Middle East.
Microarray-based molecular characterisation
All isolates were characterised using two different microarray-based assays (Alere Technologies GmbH/Abbott, Jena, Germany) designed for S. aureus typing [32, 33] and for the characterisation of SCC elements [9]. This allowed a rapid detection of species markers, virulence genes, resistance genes and SCC-related markers as well as an assignment to strains and clonal complexes. Details on DNA preparation and hybridisation procedures, as well as on probe and primer sequences and on data analysis have been described previously [9, 32, 33].
Genome sequencing
Whole-genome sequencing of the RUH-32 isolate was carried out by a commercial service provider using the Illumina HiSeq-2500 platform. Raw reads were deposited in the Short Read Archive under accession SRR5520614. Sequencing reads were assembled de-novo using SPAdes version 3.10.1 (http://bioinf.spbau.ru/spades). 51 Contigs were obtained with sizes larger than 200 nt and k-mer coverages greater than 10. Sequences from two reference strains, MRSA18 (European Nucleotide Archive accession number ERR108048) and 20121643 (ERR1595888), were downloaded from the European Nucleotide Archive and assembled with spades. In both cases, the complete SCC elements were found to be located on a single contig. The sequences of the SCC elements were excised from the respective contigs and then annotated.
Sanger sequencing for closing the gap between the contigs
Inspection of the contigs revealed that two contigs comprised typical SCC genes and that they may be linked by an IS431-like insertion element. Primers were designed for amplifying and capillary electrophoresis (CE) sequencing of the ambiguous linker region. Primer sequences are provided in Table 1. The process included PCR amplification using a thermal cycle program with an initial denaturation temperature of 96°C for 60s followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 96°C for 15s, annealing at 70°C for 60s and extension at 72°C for 90s. The PCR product was fractionated by gel electrophoresis on a 1.5% agarose, the band with the main amplicon was excised and purified with the QIAamp Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the recommendations of the manufacturer. Cycle sequencing was carried out using BigDye Terminator v1.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Darmstadt, Germany) on a ABI PRISM 3130 (Applied Biosystems). The first sequence obtained was then further extended by primer walking to a final size of 1133 nt (submitted to GenBank as “linker_RUH-32”). The final linker sequence (GenBank accession number MK991790) is overlapping with contig SGWB01000020.1 by 303 nt, and with contig SGWB01000002.1 by 490 nt. These two contigs and the linker sequence were joined to a single contiguous sequence. For detailed sequence analysis, the SCC element and its flanking genes were extracted and deposited as a separate sequence entry in GenBank (accession number is MK991791). The SCC element was annotated by comparison to a database of genes which have previously been found in related SCC elements.
Table 1. Primers for amplification and conventional sequencing.
| Primer designation | Aim | Sequence (5´-3´) |
|---|---|---|
| IS431syntheny_05 | A, S | TCT ATG GTA GTG AAA TCA AAC GGG AG |
| IS431syntheny_06 | A, S | TCG TAT TCT TCG ACT GAT AAT TGC TCT C |
| IS431-seq-01 | S | ATT GAA GAG ATT ATT TTC GG |
| IS431-seq-02 | S | CTA AGA TAT ACA TTG AGT TAT CG |
| IS431-seq-03 | S | CTT TGC TGT ATT GAT ACT TTG |
| IS431-seq-04 | S | CAA TTT TGT ATC AAA TTT GG |
A—Amplification, S—Sequencing
Results
A novel variant of a SCCmec VI element harbouring fusC
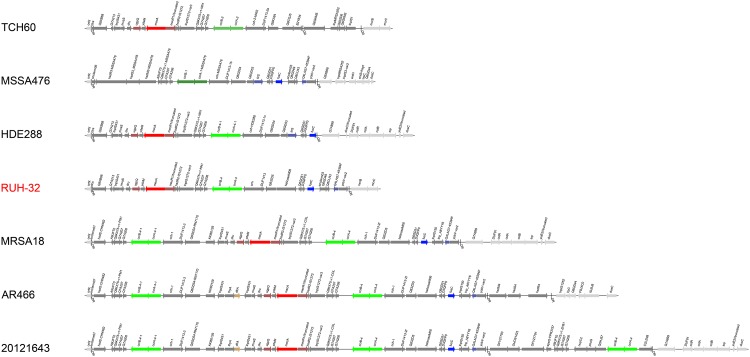
An overview on the gene content and the order of genes in the SCCmec VI (RUH-32) element is provided in Table 2 and a graphic representation is shown in Fig 1. In short, the element consists of a class B mec complex in which a mecABA000018 (a N315-like allele of mecA [2]) is combined with ugpQ and delta mecR1. The fusidic acid resistance gene fusC is present, tirS is absent. In sequences of RUH-32, ccrA/B-4 are present, but ccrA-4 does not yield signals in array experiments. The reasons are polymorphisms in the probe binding site of ccrA-4 in RUH-32. Several other SCCmec elements that include fusC can be identified among previously published sequences. One is present in the CC5 strain HDE288 (AF411935; [13]) and can also be identified in CC8 (“UK-EMRSA-12/13”) sequences ASARH101 (SAMEA1565121), MPROS978 (SAMEA2041631) and MPROS1215 (SAMEA2663833). The SCCmec VI (RUH-32) element differed from the SCCmec VI (HDE288) element in an absence of tirS. Another difference is the presence of Q4LAG7 (“putative protein”; BX571857.1, position 55452 to 55880) in the RUH-32 sequence which was also detected by microarray. Differences to SCCmec VI element harbouring fusC of the CC8 strain MRSA18 (ERR10804/SAMEA1317993; [12]) include the presence of Q9XB68-dcs and SCCterm 3 (rather than SCCterm 7). Furthermore, MRSA18 has two copies of ccrA/B-4 genes. Strain AR466 (CP029080.1), a CC45-MRSA, has a SCCmec VI element harbouring fusC that could not be differentiated from the one in MRSA18 by array (hence, it is not shown in Table 3). However, it includes an additional hsdS/M/R (type I restriction-modification) operon and dfrA (dihydrofolate reductase), which usually is plasmid borne. Finally, there is another SCCmec VI-derived element in the CC8 strain 20121643 (ERR1595888/SAMEA3924203) that harbours fusC. It differs from RUH-32 in several markers (see Fig 1) including an absence of Q9XB68-dcs, presence of speG (spermidine N-acetyltransferase) and dfrA as well as a presence of three copies of ccrA/B-4 genes.
Table 2. Genes in SCCmec VI (RUH-32).
| Gene | Description/gene product | Comments | Orientation | Start position | End position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| orfX | 23S rRNA methyltransferase with the SCC integration site being located at the 3' end of orfX | Identical (no mismatches) to GU235984.1[9:488] | FORWARD | 1 | 480 |
| DR_SCC | direct repeat of SCC | Identical to BA000033.2 [34252:34270] | FORWARD | 462 | 480 |
| Q9XB68-dcs | putative protein | Identical to AFEF01000013.1 [388744:390039:r] | FORWARD | 661 | 1,955 |
| Q7A213 | putative protein | Identical to BA000033.2 [36062:36400] | FORWARD | 2,370 | 2,609 |
| tnpIS431–06 | transposase for IS431 | Identical to BA000018.3 [36435:37109:r] | REVERSE | 2,641 | 3,315 |
| mvaS-SCC | truncated 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthase | Identical to BA000033.2 [37179:37531] | FORWARD | 3,388 | 3,740 |
| Q5HJW6 | putative protein | Identical to BA000033.2 [37629:37859] | FORWARD | 3,838 | 4,068 |
| dru | SCC direct repeat units | dru repeats 0–2d-2d-2g-2n-3a-3b-4e-4i-5a-5b-7b-7b. No match identified in dru database. | FORWARD | 3,978 | 4,415 |
| ugpQ | glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase | Identical to BA000033.2 [38288:39031] | FORWARD | 4,617 | 5,360 |
| ydeM | putative dehydratase | Identical to BA000033.2 [39128:39556] | FORWARD | 5,457 | 5,885 |
| mecA | penicillin binding protein 2a | Identical to BA000033.2 [39602:41608:r] | REVERSE | 5,949 | 7,937 |
| Delta mecR1 | truncated methicillin resistance operon repressor 1/ signal transducer protein | Identical to BA000033.2 [41708:42682] | FORWARD | 8,037 | 9,011 |
| hsdR2-IS1272 | fragment of type I restriction-modification system endonuclease | Identical to BA000033.2 [42683:42916] | FORWARD | 9,012 | 9,245 |
| tnpIS1272 | transposase for IS1272 from isolate TCH | Identical to BA000033.2 [42917:44440:r] | REVERSE | 9,246 | 10,769 |
| Q9KX75-v1-NN1 | putative protein | Identical to BA000033.2 [44576:45082:r] | REVERSE | 10,905 | 11,411 |
| Q7A207 | putative protein | Identical to BA000033.2 [45097:45408:r] | REVERSE | 11,426 | 11,737 |
| Q7A206 | putative protein | Identical to HF569097 [32048:32398:r] | REVERSE | 11,824 | 12,174 |
| UTR_ccrB | highly conserved 3'-untranslated region of ccrB | REVERSE | 12,175 | 12,649 | |
| ccrB-4 | cassette chromosome recombinase B, type 4 | REVERSE | 12,677 | 14,305 | |
| ccrA-4 | cassette chromosome recombinase A, type 4 | REVERSE | 14,302 | 15,663 | |
| cch | cassette chromosome helicase | REVERSE | 15,850 | 17,619 | |
| DUF1413 | putative protein associated with cch | REVERSE | 17,619 | 17,909 | |
| Q83ZD5 | putative protein | REVERSE | 18,080 | 19,150 | |
| helicaseM06 | DEAD/DEAH box helicase domain protein | FORWARD | 19,244 | 21,184 | |
| Q6GD51 | putative protein | Related to BX571857.1[51926:52234]; six mismatches | FORWARD | 21,441 | 21,749 |
| D3QFP0 | putative lipase/protease | Identical to BX571857.1[52281:52519] | FORWARD | 21,859 | 22,017 |
| fusC | fusidic acid resistance protein C | Related to BX571857.1[52820:53458]; one mismatch | FORWARD | 22,335 | 22,973 |
| sccterm03 | terminus of SCC towards orfX | For a discussion of the SCC terminal regions, and its variability, see [9] | FORWARD | 23,571 | 23,658 |
| Q6GD49 | putative protein within SCC | FORWARD | 23,659 | 24,288 | |
| Q8CU43 | putative protein | Identical to BX571857.1 [54788:55030] | FORWARD | 24303 | 24,545 |
| Q4LAG7–45394F | putative protein | Identical to BX571857.1 [55452:55880:r] | REVERSE | 24967 | 25,395 |
| yobV | transcriptional regulator | Related to BX571857.1[55861–56889]; two mismatches | FORWARD | 25,475 | 26,404 |
| DR_SCC | direct repeat of SCC | FORWARD | 26,501 | 26,519 | |
| UTR_mcrB | 5'- untranslated region of mcrB | Identical to BX571856.1 [92902:93144] | FORWARD | 26,520 | 26,762 |
| mcrB | type IV 5-methylcytosine-specific restriction enzyme subunit B | Identical to BX571856.1 [93145:94848] | FORWARD | 26,763 | 28,466 |
| mcrC | type IV 5-methylcytosine-specific restriction enzyme subunit C | Identical to BX571856.1 [94841:95881 | FORWARD | 28,459 | 29,499 |
Fig 1. Schematic representation of the SCCmec VI (RUH-32) element and, for comparison, of the SCCmec IVc element of another CC30 strain (TCH60, GenBank CP002110), of the SCCfus element from a CC1-MSSA (MSSA476, BX571857) and of other SCC VI elements that include fusC (HDE288, AF411935; MRSA18, ERR108048; AR466, CP029080.1 and 20121643, ERR1595888/SAMEA3924203).
Genes outside SCC are drawn in light grey, genes within dark grey. mecA is red, typical mec complex genes dark red. fusC and accompanying genes are blue. The ccr recombinase genes are indicated in different shades of green, and dfrA in brown.
Table 3. Hybridisation profiles (selected markers only) for CC30-MRSA-[VI+fus], other isolates with the SCCmec VI (RUH-32) element and predicted hybridisation patterns for reference sequences.
Column “A/S” indicates whether the isolate was characterised by array (A) or if a genome sequence was analysed (S).
| Isolate | A/S | CC | SCCmec type/subtype | ugpQ | mecA | Delta mecR1 | mvaS-SCC | Q4LAG7 (fus) | fusC (Q6GD50) | tirS | ACME and opp3 | speG | ccrA-4 | ccrB-4 | Q9XB68-dcs | SCCmec Term. 3 | SCCmec Term. 7 | mco (plasmidic) | copA2 (plasmidic) | arsB (plasmidic) | cadA (TN554) | cadC (TN554) | cadD | cadX (plasmidic) |
| Riyadh (RUH-) 32 | S | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Riyadh (RUH-) 32 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Dubai_M25 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | (+) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Kuwait_2017_17412 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Kuwait_2017_17555 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Kuwait_2017_17749 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Kuwait_4445–1 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Riyadh_52 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Dresden-10436836 | A | 8 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | + |
| Riyadh_3497247 | A | 834 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| HDE288 | S | 5 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | +* | - | - | - | - |
| Kuwait_2017_4703 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_2017_5250 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_2017_18848 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | (+) | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_2017_4924 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_2017_5145 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_2017_17841 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_2017_18255 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_4527 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_5635 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_5750–1 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Kuwait_5771 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | (+) | - | - | + | + | (+) | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| Riyadh_39 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | (+) | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - |
| MRSA18 | S | 8 | SCCmec VI (MRSA18) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Kuwait_2017_5056 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (MRSA18) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Strain 20121643** | S | 8 | SCCmec VI (Strain 20121643) | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + |
| Isolate | A/S | CC | SCCmec type/subtype | blaZ | erm(C) | msrA | linA/lnu(A) | aadD | dfrA | dfrG | tet(K) | tst1 | seb+sek+seq | sec+sel | sed+sej+ser | egc | lukF/S-PV | sea | sep (= seaN315) | sak | chp | scn | ||
| Riyadh (RUH-) 32 | S | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Riyadh (RUH-) 32 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | + | - | (+) | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Dubai_M25 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_17412 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_17555 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_17749 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_4445–1 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Riyadh_52 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Dresden-10436836 | A | 8 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | ||
| Riyadh_3497247 | A | 834 | SCCmec VI (RUH-32) | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | ||
| HDE288 | S | 5 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_4703 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_5250 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_18848 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_4924 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_5145 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_17841 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_18255 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_4527 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_5635 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_5750–1 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Kuwait_5771 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| Riyadh_39 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (HDE288) | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | ||
| MRSA18 | S | 8 | SCCmec VI (MRSA18) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | + | - | + | ||
| Kuwait_2017_5056 | A | 30 | SCCmec VI (MRSA18) | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | ||
| Strain 20121643** | S | 8 | SCCmec VI (Strain 20121643) | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | + | - | + |
* arsB in HDE288: absent in SAMN03255441, but present in SAMN03255487,
**harbours additionally genes erm(A) and ant9, which are not shown in the table.
CC30-MRSA-[VI+fus] strains in the Arabian Gulf region
The novel SCCmec VI (RUH-32) element described herein was not present in all CC30-MRSA-[VI+fus] isolates. Instead, they could be categorized into three distinct clusters (Table 3). Isolates of one cluster carried the SCCmec VI (RUH-32) element. They harboured the PVL genes although there was one exception. They also were positive for cadD, cadX, blaZ, linA/lnu(A) (again, with one exception), aadD, dfrG and tet(K). A second cluster carried another SCC [mec VI+fus] element that yielded the same hybridisation signals as expected for a previously sequenced element from the Portuguese CC5 strain HDE288 [13]. One major difference to SCCmec VI (RUH-32) was the presence of tirS. All isolates from this cluster were positive for the gene encoding the toxic shock syndrome toxin, tst1. A majority of them also were positive for pvl genes (nine out of twelve) and the enterotoxin gene sea (eleven out of twelve). Other markers included the copper resistance genes mco, copA2, arsenic and cadmium resistance genes arsB, cadA, cadC as well as blaZ and (in some isolates) erm(C). A third cluster, comprising of a single isolate harboured another SCCmec element consistent to one previously described from a CC8 isolate “MRSA18” [12]. The Kuwaiti CC30 isolate was PVL-positive. It lacked tirS and tst1. Heavy metal resistance genes were absent and tetK was the only antimicrobial resistance gene present in addition to mecA.
Other MRSA strains with the same SCCmec element
One PVL-negative CC8 isolate was identified in a patient in Saxony who had links to the Middle East. Based on array hybridisation results, it also carried the SCCmec VI (RUH-32) element (Table 3). This observation prompted an extensive database search yielding four more CC8-MRSA sequences with SCCmec VI (RUH-32) in the NCBI Short Read Archive (SAMEA2385458, SAMEA2385540, SAMEA2664046, SAMEA2664096). We also identified the same element, SCCmec VI (RUH-32), retrospectively in a ST834 isolate (Riyadh_3497247, see Table 3).
Discussion
We describe a novel variant of a SCC element that harbours determinants for both, methicillin/beta-lactam and fusidic acid resistance. It was identified when performing DNA-microarray-based typing of clinical strains from Saudi Arabia because of a previously unseen hybridisation pattern and further characterised by sequencing. This element is related, but clearly distinguishable (see Results) from other such elements observed elsewhere as well as in the studied region. Furthermore, there is evidence for its horizontal transfer as we were able to detect it in two further, unrelated lineages of S. aureus. On a practical level, the observations suggest that emerging fusidic acid resistance might hamper its use as topical treatment for staphylococcal skin and soft tissue infections. A replacement of this substance by mupirocin is not feasible as the usability of mupirocin itself is endangered by the spread of resistance [34, 35]. Other substances, such as betaisodona, polyhexanide or octenidine, should be considered. On a more theoretical level, a co-localisation of genes encoding beta-lactam (mecA) and fusidic acid (fusC) resistance on one potentially mobile genetic element is an interesting example for coalescence of two “selfish replicators” [36] for mutual advantage. A community use of easily available topical fusidic acid could thus select for mecA methicillin resistance and a hospital use of systemic beta-lactam compounds could select for fusC, conferring benefit to MRSA with such combined elements in either biotope. Thus it can be expected that such strains emerge in hospital as well as in community settings and that it will be very complicated to contain or to eradicate them once they are established in a population. Indeed, there is a remarkable variety of different types and subtypes of SCCmec elements that additionally harbour fusC, indicating ongoing emergence and evolution. Such elements have been observed in as much as twenty-two different clonal complexes of S. aureus, CC1, CC5, CC6, CC7, CC8, CC15, CC22, CC30, CC45 [agr I], CC45 [agr IV], CC50, CC59, ST72, CC88, CC97, CC121, CC152, CC361, CC779, ST834, CC913 and CC1153 from geographic regions as diverse as Germany, France, UK, Ireland, Portugal, Malta, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Kuwait, Australia and New Zealand. Regarding SCCmec VI elements that include fusC, there are at least five distinct variants (as represented by RUH-32, HDE288, MRSA18, AR466 and Strain 20121643; see above), and to the best of our knowledge, they have been identified in CC5, CC7, CC8 (“UK-EMRSA-12/13”), CC22, CC30, CC45, CC97, CC152, ST834 and CC913 from Germany, United Kingdom, Portugal, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia [9, 12, 13, 23, 29, 30, 32, 37–42]. Observations of SCCmec elements that harbour fusC geographically cluster in Western Europe, the Middle Eastern/Arabian Gulf countries, Australia and New Zealand. Whether this is caused by a sampling bias or related to formulations and usage of fusidic acid, or both, we currently cannot tell. However, given the current patterns of travel and migration, appearance and emergence of fusidic acid resistant MRSA cannot be ruled out anywhere. This phenotypic property cannot be seen any more as a surrogate marker for the presumptive identification of PVL-positive CC80-MRSA-IV (“European”/Mediterranean clone) but it should prompt further investigation. As mentioned above, co-evolution and co-selection of resistance traits that favour resistant pathogens in hospitals as well as in the community outside pose a public health hazard. This should prompt a review of the use of topical antibiotics such as fusidic acid (or mupirocin) including restrictions to uncontrolled and unlimited over-the-counter sale of such compounds.
Supporting information
(PDF)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Byrgit Hofmann (FLI Jena) for technical assistance.
Data Availability
The BioSample accession number for the isolate sequenced & described herein is SAMN06925305, the master accession number of the assembled contigs is SGWB00000000.1. The excised sequence of the SCCmec element described herein was submitted separately to GenBank and was recently released (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MK991791).
Funding Statement
The project was partially funded by internal research grant from the College of Medicine, Mohammed Bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences, UAE (Ref#: MBRU-CM-RG2018-07). The Leibniz Society supported the open access publication of the present work. Agiomix FZ-LLC provided support in the form of salary for author JM. These funders did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ section.
References
- 1.Jevons MP. "Celbenin"-resistant Staphylococci. British Medical Journal. 1961;1(5219):1924–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Monecke S, Muller E, Schwarz S, Hotzel H, Ehricht R. Rapid microarray based identification of different mecA alleles in Staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(11):5547–54. Epub 2012/08/15. 10.1128/AAC.00574-12 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Becker K, Ballhausen B, Köck R, Kriegeskorte A. Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus isolates: The “mec alphabet” with specific consideration of mecC, a mec homolog associated with zoonotic S. aureus lineages. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014;304(7):794–804. 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ito T, Katayama Y, Asada K, Mori N, Tsutsumimoto K, Tiensasitorn C, et al. Structural comparison of three types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec integrated in the chromosome in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45(5):1323–36. 10.1128/AAC.45.5.1323-1336.2001 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ito T, Katayama Y, Hiramatsu K. Cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the entire mec DNA of pre-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus N315. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43(6):1449–58. . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ito T, Ma XX, Takeuchi F, Okuma K, Yuzawa H, Hiramatsu K. Novel type V staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec driven by a novel cassette chromosome recombinase, ccrC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(7):2637–51. 10.1128/AAC.48.7.2637-2651.2004 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ito T, Okuma K, Ma XX, Yuzawa H, Hiramatsu K. Insights on antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus from its whole genome: genomic island SCC. Drug Resist Updat. 2003;6(1):41–52. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.IWG- SCC. Classification of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec): guidelines for reporting novel SCCmec elements. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(12):4961–7. 10.1128/AAC.00579-09 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Monecke S, Jatzwauk L, Muller E, Nitschke H, Pfohl K, Slickers P, et al. Diversity of SCCmec elements in Staphylococcus aureus as observed in South-Eastern Germany. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(9):e0162654 Epub 2016/09/21. 10.1371/journal.pone.0162654 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shore A, Rossney AS, Keane CT, Enright MC, Coleman DC. Seven novel variants of the staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Ireland. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49(5):2070–83. 10.1128/AAC.49.5.2070-2083.2005 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shore AC, Coleman DC. Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec: recent advances and new insights. Int J Med Microbiol. 2013;303(6–7):350–9. 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ellington MJ, Reuter S, Harris SR, Holden MT, Cartwright EJ, Greaves D, et al. Emergent and evolving antimicrobial resistance cassettes in community-associated fusidic acid and meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015;45(5):477–84. Epub 2015/03/15. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.01.009 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Oliveira DC, Milheirico C, de Lencastre H. Redefining a structural variant of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec, SCCmec type VI. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(10):3457–9. 10.1128/AAC.00629-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Williamson DA, Carter GP, Howden BP. Current and Emerging Topical Antibacterials and Antiseptics: Agents, Action, and Resistance Patterns. Clinical microbiology reviews. 2017;30(3):827–60. Epub 2017/06/07. 10.1128/CMR.00112-16 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schofer H, Simonsen L. Fusidic acid in dermatology: an updated review. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20(1):6–15. Epub 2009/12/17. 10.1684/ejd.2010.0833 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Turnidge J, Collignon P. Resistance to fusidic acid. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1999;12 Suppl 2:S35–44. Epub 1999/10/21. 10.1016/s0924-8579(98)00072-7 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Farrell DJ, Castanheira M, Chopra I. Characterization of Global Patterns and the Genetics of Fusidic Acid Resistance. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2011;52(suppl_7):S487–S92. 10.1093/cid/cir164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lannergård J, Cao S, Norström T, Delgado A, Gustafson JE, Hughes D. Genetic Complexity of Fusidic Acid-Resistant Small Colony Variants (SCV) in Staphylococcus aureus. PLOS ONE. 2011;6(11):e28366 10.1371/journal.pone.0028366 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Monecke S, Slickers P, Hotzel H, Richter-Huhn G, Pohle M, Weber S, et al. Microarray-based characterisation of a Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive community-acquired strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12(8):718–28. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01420.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Aires de Sousa M, Bartzavali C, Spiliopoulou I, Sanches IS, Crisostomo MI, de Lencastre H. Two international methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones endemic in a university hospital in Patras, Greece. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(5):2027–32. 10.1128/JCM.41.5.2027-2032.2003 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Basset P, Amhis W, Blanc DS. Changing molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an Algerian hospital. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2015;9(2):206–9. Epub 2015/02/24. 10.3855/jidc.4620 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ben Slama K, Gharsa H, Klibi N, Jouini A, Lozano C, Gomez-Sanz E, et al. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in healthy humans with different levels of contact with animals in Tunisia: genetic lineages, methicillin resistance, and virulence factors. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;30(4):499–508. Epub 2010/11/16. 10.1007/s10096-010-1109-6 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Boswihi SS, Udo EE, Al-Sweih N. Shifts in the Clonal Distribution of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Kuwait Hospitals: 1992–2010. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(9):e0162744 10.1371/journal.pone.0162744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tokajian ST, Khalil PA, Jabbour D, Rizk M, Farah MJ, Hashwa FA, et al. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in Lebanon. Epidemiol Infect. 2010;138(5):707–12. 10.1017/S0950268810000440 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Udo EE, Sarkhoo E. Genetic analysis of high-level mupirocin resistance in the ST80 clone of community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 2010;59(Pt 2):193–9. 10.1099/jmm.0.013268-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vourli S, Perimeni D, Makri A, Polemis M, Voyiatzi A, Vatopoulos A. Community acquired MRSA infections in a paediatric population in Greece. Euro Surveill. 2005;10(5):78–9. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Holden MTG, Feil EJ, Lindsay JA, Peacock SJ, Day NPJ, Enright MC, et al. Complete genomes of two clinical Staphylococcus aureus strains: Evidence for the rapid evolution of virulence and drug resistance. PNAS. 2004;101(26):9786–91. 10.1073/pnas.0402521101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Patot S, Rc Imbert P, Baude J, Martins Simões P, Campergue J-B, Louche A, et al. The TIR Homologue Lies near Resistance Genes in Staphylococcus aureus, Coupling Modulation of Virulence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility. PLOS Pathogens. 2017;13(1):e1006092 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006092 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Williamson DA, Monecke S, Heffernan H, Ritchie SR, Roberts SA, Upton A, et al. High usage of topical fusidic acid and rapid clonal expansion of fusidic acid-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a cautionary tale. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59(10):1451–4. Epub 2014/08/21. 10.1093/cid/ciu658 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Boswihi SS, Udo EE, Monecke S, Mathew B, Noronha B, Verghese T, et al. Emerging variants of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus genotypes in Kuwait hospitals. PLoS One. 2018;13(4):e0195933 Epub 2018/04/19. 10.1371/journal.pone.0195933 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Monecke S, Muller E, Buechler J, Rejman J, Stieber B, Akpaka PE, et al. Rapid detection of Panton-Valentine leukocidin in Staphylococcus aureus cultures by use of a lateral flow assay based on monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51(2):487–95. Epub 2012/11/24. 10.1128/JCM.02285-12 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Monecke S, Coombs G, Shore AC, Coleman DC, Akpaka P, Borg M, et al. A field guide to pandemic, epidemic and sporadic clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e17936 10.1371/journal.pone.0017936 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Monecke S, Slickers P, Ehricht R. Assignment of Staphylococcus aureus isolates to clonal complexes based on microarray analysis and pattern recognition. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008;53:237–51. 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00426.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Monecke S, Nitschke H, Slickers P, Ehricht R, Swanston W, Manjunath M, et al. Molecular epidemiology and characterisation of MRSA isolates from Trinidad and Tobago. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;31(7):1497–500. Epub 2011/11/10. 10.1007/s10096-011-1469-6 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Monecke S, Ruppelt-Lorz A, Muller E, Reissig A, Thurmer A, Shore AC, et al. Dissemination of high-level mupirocin-resistant CC22-MRSA-IV in Saxony. GMS Hyg Infect Control. 2017;12:Doc19. Epub 2017/12/01. 10.3205/dgkh000304 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Dawkins R. Das egoistische Gen (The selfish gene, German ed.). Heidelberg: Spektrum Verlag; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dauwalder O, Lina G, Durand G, Bes M, Meugnier H, Jarlier V, et al. Epidemiology of invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones collected in France in 2006 and 2007. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46(10):3454–8. 10.1128/JCM.01050-08 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kinnevey PM, Shore AC, Brennan GI, Sullivan DJ, Ehricht R, Monecke S, et al. Emergence of sequence type 779 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harboring a novel pseudo staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec)-SCC-SCCCRISPR composite element in Irish hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(1):524–31. Epub 2012/11/14. 10.1128/AAC.01689-12 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Monecke S, Skakni L, Hasan R, Ruppelt A, Ghazal SS, Hakawi A, et al. Characterisation of MRSA strains isolated from patients in a hospital in Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12(1):146 Epub 2012/07/25. 10.1186/1471-2180-12-146 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Scerri J, Monecke S, Borg MA. Prevalence and characteristics of community carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Malta. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2013;3(3):165–73. Epub 2013/08/13. 10.1016/j.jegh.2013.05.003 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Senok A, Ehricht R, Monecke S, Al-Saedan R, Somily A. Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in nosocomial infections in a tertiary-care facility: emergence of new clonal complexes in Saudi Arabia. New Microbes New Infect. 2016;14:13–8. Epub 2016/09/14. 10.1016/j.nmni.2016.07.009 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Senok AC, Somily AM, Slickers P, Raji MA, Garaween G, Shibl A, et al. Investigating a rare methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain: first description of genome sequencing and molecular characterization of CC15-MRSA. Infect Drug Resist. 2017;10:307–15. Epub 2017/10/19. 10.2147/IDR.S145394 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(PDF)
Data Availability Statement
The BioSample accession number for the isolate sequenced & described herein is SAMN06925305, the master accession number of the assembled contigs is SGWB00000000.1. The excised sequence of the SCCmec element described herein was submitted separately to GenBank and was recently released (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/MK991791).