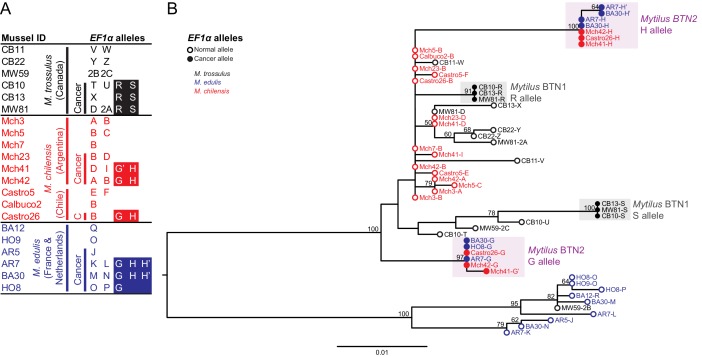
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of EF1α alleles from normal and diseased mussels.
The EF1α locus was amplified, and multiple alleles were cloned from different individual normal and diseased mussels of different species and locations: M. trossulus from BC (black), M. chilensis from Argentina and Chile (red), and M. edulis from France and the Netherlands (blue). (A) A list of cloned alleles is shown, with filled boxes marking cancer-associated alleles. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of aligned alleles shows groups of related alleles (see Figure 1—source data 1). Names of alleles on the tree specify individual ID and allele ID. Open circles mark alleles from normal individuals and host alleles from diseased individuals. Filled circles mark cancer-associated alleles on the tree (colored by host species). The tree was rooted at the midpoint, with bootstrap values below 50 removed. Model used was HKY85+G. The scale bar marks genetic distance.