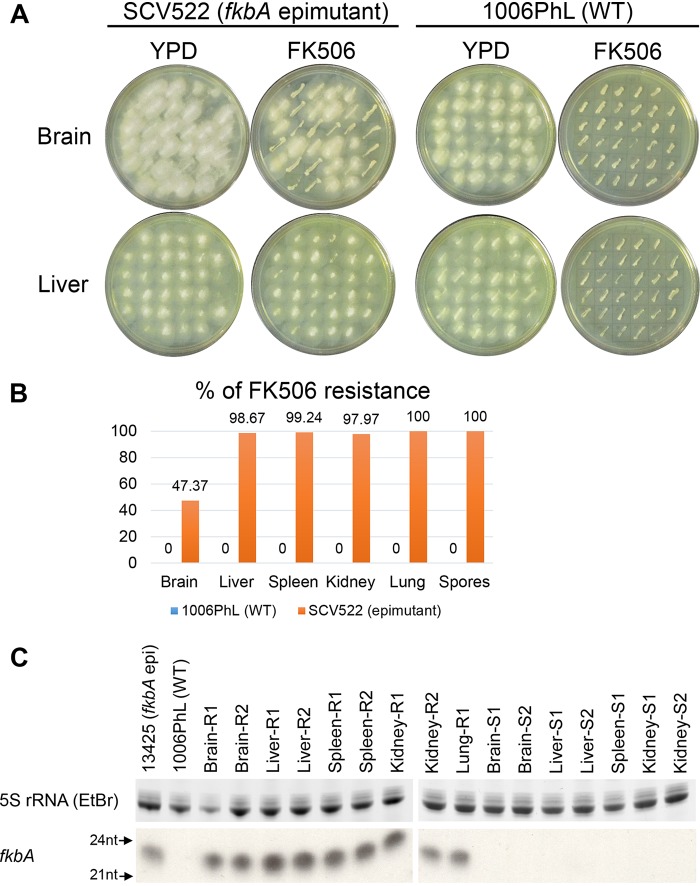
FIG 2.
FK506 epimutants revert in an organ-specific manner after in vivo passage. fkbA epimutant and wild-type M. circinelloides f. circinelloides strains were recovered from multiple organs after in vivo infection/passage in one mouse each. Strains were recovered after the mouse was moribund, 4 days postinfection. Strain SCV522 is a fkbA epimutant. Strain 1006PhL is the wild-type (WT) strain. (A) Representative images of colonies recovered from the brains and livers of mice infected with either strain SCV522 or 1006PhL and patched onto YPD with and without FK506. All colonies patched on nonselective YPD medium grew as hyphae. FK506-sensitive strains patched on YPD + FK506 medium grew as smaller yeast colonies. Loss of FK506 resistance from the epimutant strain was observed in the brain, but not in the liver. (B) Quantification of the percentage of FK506 resistance by organ, after in vivo passage. There were 150 colonies per organ; however, fewer than 150 colonies were recovered from some organs (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). The Spores column shows SCV522 and 1006PhL spores plated without in vivo passage. FK506 resistance was below the limit of detection in all strains derived from wild-type 1006PhL infection. (C) sRNA hybridization of representative sensitive (S) and resistant (R) strains randomly selected from SCV522-infected mouse after passage. All resistant isolates continued to express sRNA against fkbA, whereas reverted, FK506-sensitive isolates did not. 5S rRNA was stained with ethidium bromide (EtBr) and served as the loading control. epi, epimutant; nt, nucleotides.