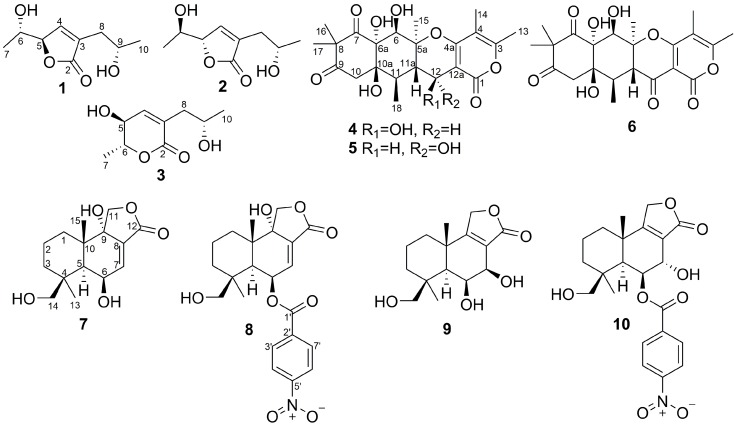
Abstract
Four new compounds were isolated from the Vietnamese marine sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus flocculosus, one aspyrone-related polyketide aspilactonol G (2), one meroterpenoid 12-epi-aspertetranone D (4), two drimane derivatives (7,9), together with five known metabolites (1,3,5,6,8,10). The structures of compounds 1–10 were established by NMR and MS techniques. The absolute stereoconfigurations of compounds 1 and 2 were determined by a modified Mosher’s method. The absolute configurations of compounds 4 and 7 were established by a combination of analysis of ROESY data and coupling constants as well as biogenetic considerations. Compounds 7 and 8 exhibited cytotoxic activity toward human prostate cancer 22Rv1, human breast cancer MCF-7, and murine neuroblastoma Neuro-2a cells.
Keywords: marine-derived fungi, secondary metabolites, polyketides, drimanes, meroterpenoids, cytotoxicity
1. Introduction
Marine fungi are rich sources of new biologically active compounds [1]. Fungi of the genus Aspergillus, section Circumdati (Aspergillus insulicola, Aspergillus flocculosus, Aspergillus ochraceus, Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis, and others) [2], are known to produce metabolites belonging to various chemical classes: aspyrone-related pentaketides [3,4], meroterpenoids [5,6], diketopiperazine alkaloids [7], drimane sesquiterpenoids and their nitrobenzoyl derivatives [8,9], steroids, and cerebrosides [10]. Many of them possess antimicrobial [4,10], antiviral [11], cytotoxic [8,11], and neuroprotective [12] activities.
Aspyrone-related pentaketides are polyketide metabolites commonly found in this fungal group [13]. Usually, they are divided into three structural types: linear (aspinonene) [3], δ-lactones (aspyrone) [3], and γ-lactones (iso-aspinonene, aspilactonols) [3,14]. Meroterpenoid metabolites of Aspergillus, section Circumdati fungi are represented mainly by triketidesesquiterpenoids with rare α-pyrone-contained linear or angular skeleton. To date, only several representatives of this chemical class belonging to the aspertetranones [5] and ochraceopones [6] series were reported. Nitrobenzoyl derivatives of drimane-sesquiterpenoids were initially found in A. insulicola species but can also be produced by other related fungi [15]. These compounds are characterized by a small structural diversity with two isomeric backbones (cinnamolide- and confertifolin-based) and various locations of acyl groups. A residue of p-nitrobenzoic acid usually can be found at positions 9-OH or 14-OH. Nitrobenzoyl derivatives are relatively unstable compounds that cannot be hydrolyzed to form the corresponding sesquiterpenoids [8]. Acetylation of these compounds with acetic anhydride results in rearrangement and formation of several products [16].
Recently, we have started a project focusing on the search for producers of novel bioactive compounds among fungi isolated from various substrates found in the Vietnamese waters of the South China Sea [17,18]. Thus, from a sediment sample collected in Nha Trang Bay, we have isolated a strain of fungus A. flocculosus. Recently, we described the new neuroprotective alkaloid mactanamide produced by this strain [12]. Herein, we report the isolation, structure elucidation and cytotoxic activity of four new (2,4,7,9) and six known (1,3,5,6,8,10) metabolites produced by the same fungus (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of the isolated compounds 1–10.
2. Results and Discussion
The molecular formula of compound 1 was determined as C9H14O4 by an HRESIMS peak at m/z 209.0785 [M + Na]+, which was supported by the 13C NMR spectrum.
A close inspection of the 1H and 13C NMR data of 1 (Table 1, Figures S1–S3) revealed the presence of two methyls (δC 23.3, 18.8; δH 1.31, 1.25), one methylene (δC 34.9; δH 2.52, 2.45), three oxygen-bearing sp3-methines (δC 84.9, 67.8, 66.2; δH 4.85, 4.08, 4.05) and one sp2-methine (δC 147.4; δH 7.27). Two remaining signals at δC 132.8 and 174.2 ppm corresponded to a quaternary sp2-carbon and a carboxyl carbon, respectively.
Table 1.
1H and 13C NMR data (δ in ppm, CDCl3) for aspilactonols G (1) and F (2).
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, mult | δH (J in Hz) | δC, mult | δH (J in Hz) | |
| 2 | 174.2, C | 174.1, C | ||
| 3 | 132.8, C | 132.9, C | ||
| 4 | 147.4, CH | 7.27, d (1.4) | 147.3, CH | 7.25, d (1.2) |
| 5 | 84.9, CH | 4.85, dd (4.4, 1.4) | 84.8, CH | 4.86, dd (4.2, 1.4) |
| 6 | 67.8, CH | 4.05, qd (6.4, 4.4) | 67.6, CH | 4.08, qd (6.6, 4.2) |
| 7 | 18.8, CH3 | 1.31, d (6.4) | 18.8, CH3 | 1.31, d (6.6) |
| 8 | 34.9, CH2 | 2.52, ddt (15.0, 3.8, 1.4) 2.45, ddt (15.0, 7.8, 1.4) |
35.2, CH2 | 2.55, ddt (14.6, 3.6, 1.4) 2.40, dd (14.6, 8.5) |
| 9 | 66.2, CH | 4.08, m | 65.8, CH | 4.04, m |
| 10 | 23.3, CH3 | 1.25, d (6.3) | 23.2, CH3 | 1.25, d (6.2) |
1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopic data were measured at 500 MHz and 125 MHz, respectively.
The HMBC correlations (Figure 2 and Figure S6) from H-4 (δH 7.27) to C-2 (δC 174.2), C-3 (δC 132.8), and C-5 (δC 84.9) and from H-5 (δH 4.85) to C-2, C-3, and C-4 (δC 147.4) suggested the presence of a dihydrofuran ring. The structure of the 1-hydroxyethyl side chain and its location at C-5 in 1 was established by COSY correlations of H-6/H-5 and H-7 and HMBC correlations from H-6 (δH 4.05) to C-4, C-5, and C-7 (δC 18.8). The data of COSY spectrum (Figure S4) and HMBC correlations from H-10 (δH 1.25) to C-8 (δC 34.9), C-9 (δC 66.2), and from both H2-8 (δH 2.52, 2.45) to C-3, C-4, C-9, and C-10 (δC 23.3) determined the structure of the 2-hydroxypropyl side chain and its location at C-3.
Figure 2.
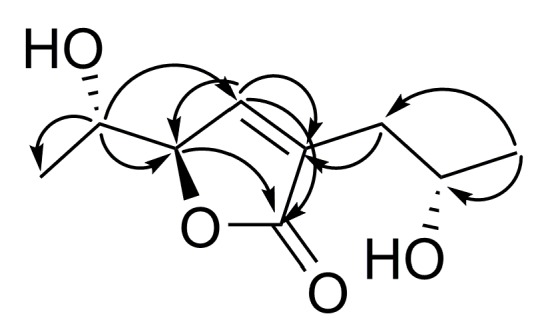
The key HMBC correlations of 1.
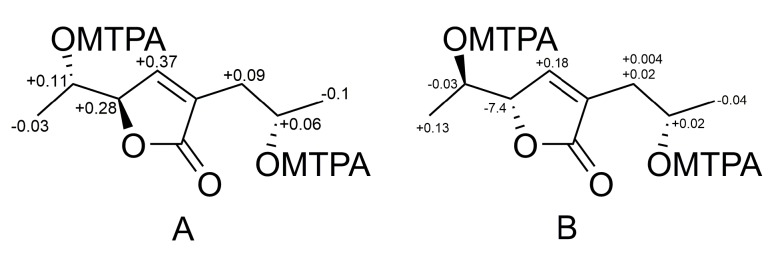
The absolute configuration of the chiral centers C-6 and C-9 of 1 was established using a modified Mosher’s method. Esterification of the C-6 and C-9 hydroxy moieties of 1 with (R)- and (S)-MTPA chloride afforded the (S)- and (R)-bis-MTPA-esters, respectively. The observed chemical shift differences Δδ (δS − δR) (Figure 3A) indicated 6S, 9S configurations. The absolute configuration of C-5 stereocenter in 1 was proven as R on the basis of a characteristic Cotton’s effect at λ217 + 11.35 in the CD spectrum (Experimental Section and Figure S8) and a coupling constant value 3JH5-H6 = 4.4 Hz [14,19]. Compound 1 was recently reported as aspilactonol F, that was a component of unseparated mixture of epimers at C-9. Our study is the first determination of the absolute configurations of all stereocenters of aspilactonol F.
Figure 3.
Δδ (δS−δR) values (in ppm) for the MTPA ester of 1 (A) and 2 (B).
The molecular formula of compound 2 was determined as C9H14O4 (the same as 1) on the basis of HRESIMS data and confirmed by 13C NMR. The NMR data of 2 were very similar to those of 1 (Table 1, Figures S9–S16). Thus, the planar structure of 2 was suggested to be the same as that of aspilactonol F (1).
Esterification of the C-6 and C-9 hydroxy moieties of 2 with (R)- and (S)-MTPA chloride afforded the (S)- and (R)-bis-MTPA-esters, respectively. The observed chemical shift differences Δδ (δS − δR) (Figure 3B) indicated 6R, 9S configurations. The absolute configuration of the C-5 stereocenter in 2 was suggested as S on the basis of a strong negative Cotton’s effect at λ216 –11.51 in the CD spectrum (Experimental Section and Figure S17) [19]. Compound 2 was named aspilactonol G.
The molecular formula of compound 4 was established as C22H28O9 on the basis of HRESIMS, containing a peak at m/z 459.1628 [M + Na]+, and was supported by the 13C NMR spectrum.
An analysis of NMR data of 4 (Table 2, Figures S20–S24) revealed the presence of six methyl groups (δC 25.1, 24.0, 18.5, 17.3, 10.8, 9.5; δH 2.24, 1.89, 1.43, 1.41, 1.39, 1.31), one sp3-methylene group (δC 45.6; δH 2.86, 2.76), two sp3-methines (δC 39.5, 39.3; δH 2.32, 2.00), two oxygen-bearing ones (δC 75.15, 63.5; δH 4.63, 4.36), one quaternary sp3-carbon (δC 55.5), three oxygen-bearing quaternary sp3-carbons (δC 83.0, 76.5, 75.07), two quaternary sp2-carbons (δC 107.3, 102.2), three oxygen-bearing quaternary sp2-carbons (δC 164.4, 162.5, 157.9), and two ketone groups (δC 211.4, 209.1).
Table 2.
1H and 13C NMR data (δ in ppm, CDCl3) for 12-epi-aspertetranone D (4).
| Position | δC, Mult | δH (J in Hz) | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 164.4, C | ||
| 3 | 157.9, C | ||
| 4 | 107.3, C | ||
| 4a | 162.5, C | ||
| 5a | 83.0, C | ||
| 6 | 75.15, CH | 4.36, s | 5a, 6a, 7, 10a, 11a, 15 |
| 6a | 76.5, C | ||
| 7 | 211.4, C | ||
| 8 | 55.5, C | ||
| 9 | 209.1, C | ||
| 10 | 45.6, CH2 | 2.86, d (17.7) 2.76, dd (17.7, 2.7) |
6a, 9, 10a 9, 10a |
| 10a | 75.07, C | ||
| 11 | 39.5, CH | 2.00, dd (12.0, 6.8) | 5a, 10a, 11a, 18 |
| 11a | 39.3, CH | 2.32, dd (12.0, 9.4) | 5a, 6, 10a, 11, 12, 18 |
| 12 | 63.5, CH | 4.63, d (9.4) | 1, 4a, 11, 11a, 12a |
| 12a | 102.2, C | ||
| 13 | 17.3, CH3 | 2.24, s | 3, 4, 4a |
| 14 | 9.5, CH3 | 1.89, s | 3, 4, 4a |
| 15 | 18.5, CH3 | 1.43, s | 5a, 6, 11a |
| 16 | 25.1, CH3 | 1.39, s | 7, 8, 9, 17 |
| 17 | 24.0, CH3 | 1.41, s | 7, 8, 9, 16 |
| 18 | 10.8, CH3 | 1.31, d (6.8) | 10a, 11, 11a |
| 6-OH | 3.57, brs | ||
| 6a-OH | 3.12, brs | ||
| 10a-OH | 4.01, d (2.7) | 10, 10a | |
| 12-OH | 4.43, brs | 11a, 12 |
1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopic data were measured at 500 MHz and 125 MHz, respectively.
The HMBC correlations of 4 (Figure 4 and Figure S25, Table 2) suggested the presence of a linear tetracyclic backbone like in the recently reported merosesquiterpenoids aspetetranones A-D [5]. The general features of the 13C NMR spectrum of 4 (Table 2, Figures S21–S22) were similar to those of aspertetranone D (5) [5], with the exception of the C-6, C-11, C-11a, C-12, C-15, and C-18 carbon signals. The main patterns of the experimental CD spectrum of 4 in methanol (Experimental section, Figure S27) matched well with those of aspertetranone D (5) [5]. The value of the vicinal coupling constant between H-11a and H-12 (9.4 Hz) in 4 instead of 3JH11a-H12 = 3.9 Hz in aspertetranone D (5) indicated a β orientation of the OH group at C-12 in 4. Thus, the absolute configurations of chiral centers in 4 were suggested as 5aS, 6R, 6aR, 10aR, 11R, 11aS, 12S. Compound 4 was named 12-epi-aspertetranone D.
Figure 4.
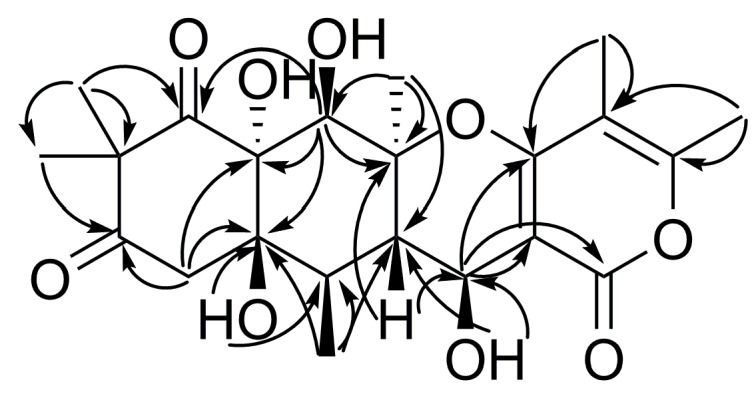
The key HMBC correlations of 4.
The molecular formula of compound 7 was established as C15H22O5 on the basis of an HRESIMS peak at m/z 305.1361 [M + Na]+, which was supported by the 13C NMR spectrum and corresponded to four double-bond equivalents.
A close inspection of the 1H and 13C NMR data of 7 (Table 3, Figures S30–S32) revealed the presence of two methyl groups (δC 26.8, 20.8; δH 1.23, 1.15), three sp3-methylene groups (δC 42.0, 32.6, 17.6; δH 2.13, 1.63, 1.50 (2H), 1.38, 1.24), two oxygen-bearing sp3-methylene groups (δC 75.0, 68.4; δH 4.44, 4.41, 4.24, 3.42), two sp3-methine groups (δC 63.5, 47.1; δH 4.62, 2.00), including one oxygen-bearing, one sp2-methine group (δC 139.1; δH 6.96), three quaternary sp3-carbons (δC 77.5, 39.0, 38.3), including one oxygen-bearing, and two quaternary sp2-carbons (δC 169.6, 130.1).
Table 3.
1H and 13C NMR data (δ in ppm) for 6β,9α,14-trihydroxycinnamolide (7) and 6β,7β,14-trihydroxyconfertifolin (9).
| Position | 7 a | 9 b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, mult | δH (J in Hz) | HMBC | δC, mult | δH (J in Hz) | HMBC | |
| 1 | 32.6, CH2 | 1.24, m 2.13, td (12.7, 5.7) |
2, 3, 5, 9, 10, 15 | 37.8, CH2 | 1.59, m 1.54, m |
2, 3, 5, 15 |
| 2 | 17.6, CH2 | 1.50, m | 1, 3, 4 | 18.0, CH2 | 1.71, m 1.45, m |
1, 3 |
| 3 | 42.0, CH2 | 1.38, td (12.9, 5.3) 1.63, m |
2, 4, 13, 14 1, 2, 4, 5, 14 |
37.8, CH2 | 1.32, td (13.0, 3.8) 1.10, td (13.6, 4.3) |
1, 2, 13, 14 |
| 4 | 38.3, C | 38.3, C | ||||
| 5 | 47.1, CH | 2.00, d (4.0) | 4, 6, 9, 13, 14, 15 | 48.6, CH | 1.57, brs | 1, 6, 9, 10, 14, 15 |
| 6 | 63.5, CH | 4.62, t (4.2) | 7, 8, 10 | 70.0, CH | 3.99, brs | 5, 7, 8, 9, 10 |
| 7 | 139.1, CH | 6.96, d (4.0) | 5, 9, 12 | 64.1, CH | 4.00, d (2.1) | 5, 6, 12 |
| 8 | 130.1, C | 122.1, C | ||||
| 9 | 77.5, C | 173.1, C | ||||
| 10 | 39.0, C | 36.3, C | ||||
| 11 | 75.0, CH2 | 4.24, d (9.8) 4.44, d (9.8) |
8, 9, 12 | 68.1, CH2 | 4.94, dd (17.6, 1.7) 4.79, brd (17.6) |
7, 8, 9 |
| 12 | 169.6, C | 173.4, C | ||||
| 13 | 26.8, CH3 | 1.15, s | 3, 4, 5, 14 | 27.9, CH3 | 0.97, s | 3, 4, 5, 14 |
| 14 | 68.4, CH2 | 3.42, d (11.4) 4.41, d (11.4) |
3, 4, 5, 13 | 65.6, CH2 | 3.94, dd (11.3, 3.8) 3.26, dd (11.3, 6.0) |
3, 4, 5, 13 |
| 15 | 20.8, CH3 | 1.23, s | 1, 5, 9, 10 | 21.6, CH3 | 1.40, s | 1, 5, 9, 10 |
1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopic data were measured a in CDCl3 at 500 MHz and 125 MHz, respectively, and b in DMSO-d6 at 700 MHz and 176 MHz, respectively.
The 13C NMR data of 7 were similar to those of the drimane moiety of insulicolide A (8) [15], also reported as 9α-14-dihydroxy-6β-p-nitrobenzoylcinnamolide [8], with the exception of the C-3, C-6, C-7, C-8, and C-14 carbon signals. The COSY spectrum data (Figure S33) and HMBC correlations (Figure S35, Table 3) from H-6 (δH 4.62) to C-7 (δC 139.1), C-8 (δC 130.1), and C-10 (δC 39.0), from H-7 (δH 6.96) to C-5 (δC 47.1), C-9, and C-12 (δC 169.6), from H3-13 (δH 1.15) to C-3 (δC 42.0), C-4 (δC 38.3), C-5 (δC 47.1), and C-14 (δC 68.4), and from H3-15 (δH 1.23) to C-1 (δC 32.6), C-5, C-9, and C-10 proved the drimane framework of 7 the same as in insulicolide A (8).
The ROESY correlations (Figure S36) of H3-13 with H-5 (δH 2.00) and H-6, long-range COSY correlation H3-15/H-5, together with the vicinal coupling constant 3JH5-H6 = 4.4 Hz established the relative configurations of the C-4, C-5, C-6, and C-10 chiral centers. The absolute configurations of the stereocenters in 7 were suggested as depicted in Figure 1 from CD spectra similarity (Figures S37 and S38) and biogenetic relationship with insulicolide A (8), whose absolute configurations were determined previously by X-ray analysis [15]. Compound 7 was named 6β,9α,14-trihydroxycinnamolide.
The molecular formula of compound 9 was established as C15H22O5 on the basis of an HRESIMS peak at m/z 305.1361 [M + Na]+, which was supported by the 13C NMR spectrum.
A close inspection of the 1H and 13C NMR data of 9 (Table 3, Figures S39–S41) revealed the presence of two methyl groups (δC 27.9, 21.6; δH 1.40, 0.97), three sp3-methylene groups (δC 37.8 (2C), 18.0; δH 1.71, 1.59, 1.54, 1.45, 1.32, 1.10), two oxygen-bearing sp3-methylene groups (δC 68.1, 65.6; δH 4.94, 4.79, 3.94, 3.26), three sp3-methine groups (δC 70.0, 64.1, 48.6; δH 4.00, 3.99, 1.57), including two oxygen-bearing, two quaternary sp3-carbons (δC 38.3, 36.3), and three quaternary sp2-carbons (δC 173.4, 173.1, 122.1).
The HMBC correlations (Table 3, Figure S42) from H-6 (δH 3.99) to C-5 (δC 48.6), C-7 (δC 64.1), C-8 (δC 122.1), C-9 (δC 173.1), and C-10 (δC 36.3), from H-7 (δH 4.00) to C-12 (δC 173.4), from H2-11 (δH 4.94, 4.79) to C-8, C-9, and C-12, from H3-13 (δH 0.97) to C-3 (δC 37.8), C-4 (δC 38.3), C-5, and C-14 (δC 65.6), from H3-15 (δH 1.40) to C-1 (δC 37.8), C-5, C-9, and C-10 indicated the drimane moiety in 9 being the same as in 7α,14-dihydroxy-6β-p-nitrobenzoylconfertifolin [8].
The ROESY correlations (Figure 5 and Figure S43) of H3-13 with H-5 (δH 1.57), H-6 (δH 3.99), and H-7 (δH 4.00), of H3-15 with H2-14 (δH 3.94, 3.26), together with the coupling constant 3JH6-H7 = 2.1 Hz indicated the related configurations of the chiral centers in 9 as depicted (Figure 1). Compound 9 was named 6β,7β,14-trihydroxyconfertifolin.
Figure 5.
Key ROESY correlations of 9.
Besides the new compounds 1,2,4,7, and 9, the known dihydroaspirone (3) [14], aspertetranones D (5) [5,6] and A (6) [5], insulicolide A (8) [15], and 7α,14-dihydroxy-6β-p-nitrobenzoylconfertifolin (10) [8] were isolated from this fungal strain.
All isolated compounds were tested for cytotoxicity toward murine neuroblastoma Neuro-2a cells (Table 4). Compound 7 demonstrated cytotoxic activity toward Neuro-2a cell, with the IC50 of 24.1 μM, while its analogue 9 was non-cytotoxic up to 100 μM. The highest activity was demonstrated for 9α,14-dihydroxy-6β-p-nitrobenzoylcinnamolide (8), with IC50 of 4.9 μM, while its analogue 10 did not affect the viability of Neuro-2a cells. Compounds 1–6 were non-cytotoxic against Neuro-2a cells at concentrations up to 100 μM.
Table 4.
Cytotoxic effects of the isolated compounds 1–10.
| Compounds | Cytotoxicity IC50, µM | Colony Formation, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuro-2a | 22Rv1 | MCF-7 | 22Rv1 | |
| 1 | >100 | >100 | nt | - |
| 2 | >100 | >100 | nt | - |
| 3 | >100 | >100 | nt | - |
| 4 | >100 | >100 | nt | 41 |
| 5 | >100 | >100 | nt | - |
| 6 | >100 | >100 | nt | - |
| 7 | 24.1 | 31.5 | >100 | - |
| 8 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 59.6 | - |
| 9 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 36 |
| 10 | >100 | >100 | >100 | - |
| Docetaxel | nt | 0.02 | nt | nt |
“nt”: compound was not tested; “-“: compound did not demonstrate any effect at the concentration of 100 µM.
Then, we investigated the effect of the compounds 1–10 on the viability and colony formation ability of human drug-resistant prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells (Table 4). MTT assay revealed the compounds 7 and 8 to be cytotoxic in 22Rv1 cells, with IC50 values of 31.5 µM and 3.0 µM, respectively. Compounds 1–6, 9, and 10 were non-cytotoxic against these cells at concentrations up to 100 µM. In this model, docetaxel (positive control) showed cytotoxicity, with IC50 of 0.02 µM. At the same time, compounds 4 and 9 were able to inhibit the colony formation of 22Rv1 prostate cancer cells (in vitro prototype of in vivo anti-metastatic activity) for 41% and 36%, respectively, at 100 µM. It is known that 22Rv1 cells are resistant to hormone therapy because they express the androgen receptor splice variant AR-V7 [20]. The compounds which demonstrated cytotoxic activity toward AR-V7-positive 22Rv1 cells therefore may be promising for the therapy of human drug-resistant prostate cancer.
Finally, the new compounds 7 and 9 were tested for cytotoxicity toward human breast cancer cells MCF-7 and did not show any effect up to 100 µM (Table 4). Additionally, the known compounds 8 and 10 were examined in this experiment as reference substances. Compound 8 showed a weak cytotoxic effect, with IC50 of 59.6 μM, whereas, previously, a higher cytotoxicity of 8 toward MCF-7 cells was reported (IC50 = 6.08 μM) [11]. This could be explained by different treatment times used by us (24 h) in comparison with those used by Fang and colleagues (72 h) [11]. Moreover, different amounts of cells per well were used. Note, compound 10 was non-cytotoxic up to 100 µM.
The analysis of structure–activity relationships of compounds 7–10, together with literature data, showed that these compounds have three relevant structural sites. First, a double bond at C7=C8 as part of an α,β-unsaturated lactone. Previously, it was shown that the cytotoxicity of such moiety can be explained by a nucleophilic Michael addition reaction with biological nucleophiles [8,21]. In the case of the non-cytotoxic compounds 9 and 10, the double bond of the α,β-unsuturated lactone may be inaccessible for a nucleophile attack because of steric obstacles. Second, a hydroxyl group at C-9 in the drimane core is also essential for cytotoxicity. In fact, a recent report of a series of similar compounds revealed the most pronounced cytotoxicity for compounds possessing a 9-OH group [9]. Finally, our results strongly suggest that the presence of a p-nitrobenzoyl moiety significantly enhances the cytotoxic activity. Previously, Tan et al. [9] demonstrated that the nitrobezoylation of 6-OH increased the cytotoxicity of related compounds towards human renal cell carcinoma cells compared with that of 14-OH-derivatives. At the same time, it should be noted that another study of 6- and 14-nitrobenzoate derivatives cytotoxicity toward other cancer cell lines did not support this observation [11].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were measured on a Perkin-Elmer 343 polarimeter (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). UV spectra were recorded on a Specord UV−vis spectrometer (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) in methanol. NMR spectra were recorded in CDCl3, acetone-d6 and DMSO-d6 with Bruker DPX-500 (Bruker BioSpin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany) and Bruker DRX-700 (Bruker BioSpin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany) spectrometers, using TMS as an internal standard. HRESIMS spectra were measured on a Maxis impact mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany).
Low-pressure liquid column chromatography was performed using silica gel (50/100 μm, Imid, Russia). Plates (4.5 cm × 6.0 cm) precoated with silica gel (5–17 μm, Imid) were used for thin-layer chromatography. Preparative HPLC was carried out with a Shimadzu LC-20 chromatograph (Shimadzu USA Manufacturing, Canby, OR, USA) using YMC ODS-AM (YMC Co., Ishikawa, Japan) (5 µm, 10 mm × 250 mm) and YMC SIL (YMC Co., Ishikawa, Japan) (5 µm, 10 mm × 250 mm) columns with a Shimadzu RID-20A refractometer (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan).
3.2. Fungal Strain
The strain of A. flocculosus was isolated from a sediment sample (Nha Trang Bay, South China Sea, Vietnam) and identified as described earlier [12]. The strain is stored at the collection of microorganisms of Nha Trang Institute of Technology and Research Application VAST (Nha Trang, Vietnam) under the code 01NT.1.12.3.
3.3. Cultivation of the Fungus
The fungus was cultured at 28 °C for three weeks in 50 × 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, each containing rice (20.0 g), yeast extract (20.0 mg), KH2PO4 (10 mg), and natural sea water from Nha Trang Bay (40 mL).
3.4. Extraction and Isolation
The fungal mycelia of A. flocculosus with the medium were extracted for 24 h with 15 L of EtOAc. Evaporation of the solvent, under reduced pressure, gave a dark brown oil (5.0 g), to which 250 mL H2O–EtOH (4:1) was added, and the mixture was thoroughly stirred to yield a suspension. It was extracted, successively, with hexane (150 mL × 2), EtOAc (150 mL × 2), and n-BuOH (150 mL × 2). After evaporation of the EtOAc layer, the residual materials (3.36 g) were passed over a silica gel column (35.0 cm × 2.5 cm), which was eluted with a hexane–EtOAc gradient (1:0–0:1). The n-hexane–EtOAc (80:20, 1.3 g) fraction was purified by a Sephadex LH-20 column (80 cm × 2 cm, 50 g) with CHCl3 to yield compound 8 (245 mg). The n-hexane–EtOAc (75:25) fraction AF-1-64 (393 mg) was purified by HPLC on a YMC-SIL column eluting with CHCl3–MeOH–NH4OAc (97:3:1) to yield compounds 3 (220 mg) and 4 (11 mg). The n-hexane–EtOAc (75:25) fraction AF-1-67 (483 mg) was purified by HPLC on a YMC-SIL column eluting with CHCl3–MeOH–NH4OAc (97:3:1) to yield compounds 5 (5.9 mg), 7 (9.0 mg), and 10 (3.1 mg). The n-hexane–EtOAc (75:25) fraction AF-1-88 (68.3 mg) was purified by HPLC on a YMC-SIL column eluting with CHCl3–MeOH–NH4OAc (97:3:1) to yield compounds 1 (2.9 mg) and 2 (3.8 mg). The n-hexane–EtOAc (70:30) fraction AF-1-93 (784 mg) was purified by HPLC first on a YMC-SIL column eluting with CHCl3–MeOH–NH4OAc (97:3:1) and then on a YMC ODS-AM column, eluting with MeOH–H2O (55:45) to yield compound 9 (5.5 mg). The n-hexane–EtOAc (60:40, 282 mg) fraction was purified by Sephadex LH-20 column (80 cm × 2 cm, 50 g) with CHCl3-EtOH (3:1) to yield compound 6 (68 mg).
Aspilactonol F (1): white powder; +98 (c 0.20, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 214 (4.03) nm; ECD (0.9 mM, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 217 (+11.35) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data see Table 1, Figures S1–S7; HR ESIMS m/z 209.0785 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C9H14O4Na, 209.0784, Δ −0.1 ppm).
Aspilactonol G (2): white powder; –49 (c 0.49, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 214 (4.05) nm; ECD (1.1 mM, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 216 (–11.51) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data see Table 1, Figures S9–S16; HRESIMS m/z 209.0782 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C9H14O4Na, 209.0784, Δ +1.1 ppm).
12-Epi-aspertetranone D (4): white powder; +78 (c 0.07, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 290 (3.93), 208 (4.53) nm; ECD (0.5 mM, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 209 (+25.54), 284 (+1.86) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data see Table 2, Figures S20–S26; HRESIMS m/z 459.1628 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C22H28O9Na, 459.1626, Δ −0.2 ppm).
6β,9α,14-trihydroxycinnamolide (7): white crystals; –7.3 (c 0.15, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 206 (3.61) nm; ECD (2.8 mM, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 224 (–2.33) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data see Table 3, Figures S30–S36; HRESIMS m/z 305.1361 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C15H22O5Na, 305.1359, Δ −0.5 ppm).
6β,7β,14-trihydroxyconfertifolin (9): white crystals; +93.5 (c 0.36, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 214 (4.00) nm; ECD (1.1 mM, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 217 (+3.68), 243 (+1.51) nm; 1H and 13C NMR data see Table 3, Figures S39–S47; HRESIMS m/z 305.1361 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C15H22O5Na, 305.1359, Δ −0.5 ppm).
3.5. Preparation of (S)-MTPA and (R)-MTPA Esters of Aspilactonol F (1)
The compounds 4-dimethylaminopyridine (a few crystals) and (R)-MTPA-Cl (4 μL) were added to a solution of 1 (1.0 mg) in pyridine at room temperature and stirred for 5 h. After evaporation of the solvent, the residue was purified by HPLC on a YMC SIL column (EtOAc–hexane, 20:80) to afford the (S)-MTPA ester (0.5 mg). The (R)-MTPA ester (0.5 mg) was prepared in a similar manner using (S)-MTPA-Cl.
(S)-MTPA ester of 1: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500.13 MHz) δ: 6.88 (1H, brs, H-4), 5.28-5.34 (2H, m, H-6, H-9), 4.84 (1H, dd, J = 3.9; 1.7 Hz, H-5), 3.48 (3H, s, OMe), 3.43 (3H, s, OMe), 2.56-2.60 (2H, m, H2-8), 1.26 (3H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, Me-7), 1.24 (3H, d, J = 6.3 Hz, Me-10), 7.39–7.48 (10H, m, 2Ph). HRESIMS m/z 641.1576 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C29H28F6Na, 641.1581, Δ = 0.8 ppm).
(R)-MTPA ester of 1: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500.13 MHz) δ: 6.52 (1H, brs, H-4), 5.25 (1H, m, H-9), 5.20 (1H, dd, J = 6.6, 4.3 Hz, H-6), 4.56 (1H, dd, J = 4.3, 1.6 Hz, Hz, H-5), 3.56 (3H, s, OMe), 3.50 (3H, s, OMe), 2.48-2.51 (2H, m, H2-8), 1.35 (3H, d, J = 6.2 Hz, Me-10), 1.29 (3H, d, J = 6.6 Hz, Me-7), 7.38–7.52 (10H, m, 2Ph). HRESIMS m/z 641.1577 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C29H28F6Na, 641.1581, Δ = 0.6 ppm).
3.6. Preparation of (S)-MTPA and (R)-MTPA Esters of Aspilactonol G (2)
(R)-MTPA-Cl (9 μL) was added to a solution of 2 (1.9 mg) in pyridine at room temperature and stirred for 2 h. After evaporation of the solvent, the residue was purified by HPLC on a YMC SIL column (acetone–hexane, 25:75) to afford the (S)-MTPA ester (1.4 mg). The (R)-MTPA ester (1.5 mg) was prepared in a similar manner using (S)-MTPA-Cl.
(S)-MTPA ester of 2: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 700 MHz) δ: 6.86 (1H, brs, H-4), 5.32 (1H, m, H-9), 5.23 (1H, m, H-6), 4.81 (1H, brd, J = 5.0 Hz, H-5), 3.52 (3H, s, OMe), 3.47 (3H, s, OMe), 2.65 (1H, dd, J = 15.8; 6.9, H-8), 2.48 (1H, ddt, J = 15.9; 5.0; 1.5, H-8), 1.39 (3H, d, J = 6.5 Hz, Me-7), 1.29 (3H, d, J = 6.2 Hz, Me-10), 7.38–7.50 (10H, m, 2Ph). HRESIMS m/z 641.1576 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C29H28F6Na, 641.1581, Δ = 0.8 ppm).
(R)-MTPA ester of 2: 1H NMR (CDCl3, 700 MHz) δ: 6.68 (1H, brs, H-4), 5.30 (1H, m, H-9), 5.26 (1H, m, H-6), 4.82 (1H, m, Hz, H-5), 3.53 (3H, s, OMe), 3.48 (3H, s, OMe), 2.61 (1H, dd, J = 15.9; 7.2, H-8), 2.46 (1H, dd, J = 15.9; 4.7, H-8), 1.33 (3H, d, J = 6.3 Hz, Me-10), 1.25 (3H, d, J = 6.7 Hz, Me-7), 7.37–7.52 (10H, m, 2Ph). HRESIMS m/z 641.1576 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C29H28F6Na, 641.1581, Δ = 0.8 ppm).
3.7. Cell Culture
All cell lines used in this investigation were purchased from ATCC.
The neuroblastoma cell line Neuro-2a and the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Biolot, St. Petersburg, Russia) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
The human prostate cancer cell line 22Rv1 was cultured according to the manufacturer’s instructions in 10% FBS/RPMI medium (Invitrogen). Cells were continuously kept in culture for a maximum of 3 months, were routinely inspected microscopically for stable phenotype, and regularly checked for contamination with mycoplasma. Cell line authentication was performed by DSMZ (Braunschweig, Germany) using highly polymorphic short tandem repeat loci [22].
All cells were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% (v/v) CO2.
3.8. Cytotoxicity Assay
The in vitro cytotoxicity of individual substances was evaluated using the MTT assay, which was performed as previously described [23]. Docetaxel was used as a control.
3.9. Colony Formation Assay
The colony formation assay was performed as described before with slight modifications [22]. 22Rv1 cells were treated with the testing compounds for 48 h and then were trypsinized. The number of alive cells was counted with the trypan blue exclusion assay as described before [24]. In total, 100 viable cells were plated into each well of six-well plates in complete fresh medium (3 mL/well) and were incubated for 14 days. Then, the medium was aspirated, and the surviving colonies were fixed with 100% MeOH, followed by washing with PBS, and air-drying at RT. Next, the cells were incubated with a Giemsa staining solution was for 25 min at RT, the staining solution was aspirated, and the wells were rinsed with dH2O and air-dried. The number of cell colonies was counted by naked eye.
4. Conclusions
A new aspyrone-related polyketide, aspilactonol G (2), a new meroterpenoid, 12-epi-aspertetranone D (4), two new drimane derivatives (7,9), together with six known metabolites were isolated from the Vietnamese marine sediment-derived fungus A. flocculosus. The structures of compounds 1–10 were established using spectroscopic methods. The absolute configurations of chiral centers were determined using either a modified Mosher’s method (for compounds 1 and 2) or a combination of ROESY data, coupling constants analysis and biogenetic considerations for compounds 4, 7 and 9. Drimane sesquiterpenoid derivatives 7 and 8 showed cytotoxicity toward human prostate cancer 22Rv1, human breast cancer MCF-7, and murine neuroblastoma Neuro-2a cells. The analysis of structure–activity relationships of compounds 7–10 together with literature data showed that these compounds have three sites in their structures related to cytotoxicity, i.e., a double bond at C7=C8, a hydroxyl group at C-9, and a p-nitrobenzoyl moiety.
Acknowledgments
The study was carried out on the equipment of the Collective Facilities Center “The Far Eastern Center for Structural Molecular Research (NMR/MS) PIBOC FEB RAS”. The authors thank Ekaterina A. Yurchenko (PIBOC FEB RAS, Vladivostok, Russia) for valuable comments in the work and writing of the article and Natalya Yu. Kim (PIBOC FEB RAS, Vladivostok, Russia) for CD spectra acquisition. The authors are grateful to Andrea Speckmann and Dipl.-Ing. Jessica Hauschild (Universitätsklinikum Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) for assistance in the performance of the biological experiments and data analysis
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/17/10/579/s1, Figures S1–S57: 1D and 2D NMR spectra and ECD spectra of compounds 1–10.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.N.Y.; Data curation, P.T.H.T. and S.A.D.; Formal analysis, E.V.G., O.F.S., A.B.R., R.S.P., S.A.D. and E.S.M.; Funding acquisition, G.v.A., T.T.T.V. and S.S.A.; Investigation, P.T.H.T., E.V.G., O.F.S., A.B.R., R.S.P., S.A.D. and E.S.M.; Methodology, A.N.Y.; Project administration, T.T.T.V. and S.S.A.; Resources, A.N.Y., G.v.A. and S.S.A.; Supervision, G.v.A., T.T.T.V. and S.S.A.; Validation, A.N.Y. and S.A.D.; Visualization, A.N.Y.; Writing—original draft, A.N.Y., P.T.H.T. and S.A.D.; Writing—review ' editing, A.N.Y., G.v.A., T.T.T.V. and S.S.A.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant No 19-74-10014 for the chemical study of compounds 7–10), by the Russian Foundation of Basic Research (grants No 18-34-00737 for the cytotoxicity study on MCF-7 and Neuro-2A, No 19-53-54002 for the chemical study of compounds 1–6 and cytotoxicity study), and by the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (grant No QTRU01.03/19-20) for microbiology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Carroll A.R., Copp B.R., Davis R.A., Keyzers R.A., Prinsep M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019;36:122–173. doi: 10.1039/C8NP00092A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Varga J., Tóth B., Rigó K., Téren J., Hoekstra R.F., Kozakiewicz Z. Phylogenetic analysis of aspergillus section circumdati based on sequences of the internal transcribed spacer regions and the 5.8 S rRNA gene. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000;30:71–80. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.2000.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fuchser J., Zeeck A. Secondary metabolites by chemical screening, 34—Aspinolides and Aspinonene/Aspyrone co-metabolites, new pentaketides produced by aspergillus ochraceus. Liebigs Ann. 1997;1997:87–95. doi: 10.1002/jlac.199719970114. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liu Y., Li X.M., Meng L.H., Wang B.G. Polyketides from the marine mangrove-derived fungus aspergillus ochraceus ma-15 and their activity against aquatic pathogenic bacteria. Phytochem. Lett. 2015;12:232–236. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2015.04.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wang Y., Qi S., Zhan Y., Zhang N., Wu A.A., Gui F., Guo K., Yang Y., Cao S., Hu Z., et al. Aspertetranones a-d, putative meroterpenoids from the marine algal-associated fungus aspergillus sp. ZL0-1b14. J. Nat. Prod. 2015;78:2405–2410. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang J., Wei X., Qin X., Tian X., Liao L., Li K., Zhou X., Yang X., Wang F., Zhang T., et al. Antiviral merosesquiterpenoids produced by the antarctic fungus aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. J. Nat. Prod. 2016;79:59–65. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shin H.J., Choi B.K., Trinh P.T.H., Lee H.S., Kang J.S., Van T.T.T., Lee H.S., Lee J.S., Lee Y.J., Lee J. Suppression of rankl-induced osteoclastogenesis by the metabolites from the marine fungus aspergillus flocculosus isolated from a sponge stylissa sp. Mar. Drugs. 2018;16:14. doi: 10.3390/md16010014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Belofsky G.N., Jensen P.R., Renner M.K., Fenical W. New cytotoxic sesquiterpenoid nitrobenzoyl esters from a marine isolate of the fungus aspergillus versicolor. Tetrahedron. 1998;54:1715–1724. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(97)10396-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tan Y., Yang B., Lin X., Luo X., Pang X., Tang L., Liu Y., Li X., Zhou X. Nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids with cytotoxic activities from a marine-derived aspergillus ochraceus fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2018;81:92–97. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zheng J., Wang Y., Wang J., Liu P., Li J., Zhu W. Antimicrobial ergosteroids and pyrrole derivatives from halotolerant aspergillus flocculosus PT05-1 cultured in a hypersaline medium. Extrem. Life Under Extrem. Cond. 2013;17:963–971. doi: 10.1007/s00792-013-0578-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fang W., Lin X., Zhou X., Wan J., Lu X., Yang B., Ai W., Lin J., Zhang T., Tu Z., et al. Cytotoxic and antiviral nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus aspergillus ochraceus Jcma1F17. MedChemComm. 2014;5:701–705. doi: 10.1039/C3MD00371J. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yurchenko E.A., Menchinskaya E.S., Pislyagin E.A., Trinh P.T.H., Ivanets E.V., Smetanina O.F., Yurchenko A.N. Neuroprotective activity of some marine fungal metabolites in the 6-hydroxydopamin- and paraquat-induced parkinson’s disease models. Mar. Drugs. 2018;16:457. doi: 10.3390/md16110457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kito K., Ookura R., Yoshida S., Namikoshi M., Ooi T., Kusumi T. Pentaketides relating to aspinonene and dihydroaspyrone from a marine-derived fungus, aspergillus ostianus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007;70:2022–2025. doi: 10.1021/np070301n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen X.W., Li C.W., Cui C.B., Hua W., Zhu T.J., Gu Q.Q. Nine new and five known polyketides derived from a deep sea-sourced aspergillus sp. 16-02-1. Mar. Drugs. 2014;12:3116–3137. doi: 10.3390/md12063116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rahbaek L., Christophersen C., Frisvad J., Bengaard H.S., Larsen S., Rassing B.R. Insulicolide a: A new nitrobenzoyloxy-substituted sesquiterpene from the marine fungus aspergillus insulicola. J. Nat. Prod. 1997;60:811–813. doi: 10.1021/np970142f. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhao H.Y., Anbuchezhian R., Sun W., Shao C.L., Zhang F.L., Yin Y., Yu Z.S., Li Z.Y., Wang C.Y. Cytotoxic nitrobenzoyloxy-substituted sesquiterpenes from spongederived endozoic fungus aspergillus insulicola md10-2. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016;17:271–274. doi: 10.2174/1389201017666151223123424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Smetanina O.F., Yurchenko A.N., Ivanets E.V., Kalinovsky A.I., Khudyakova Y.V., Dyshlovoy S.A., Von Amsberg G., Yurchenko E.A., Afiyatullov S.S. Unique prostate cancer-toxic polyketides from marine sediment-derived fungus isaria felina. J. Antibiot. 2017;70:856–858. doi: 10.1038/ja.2017.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yurchenko A., Smetanina O., Ivanets E., Kalinovsky A., Khudyakova Y., Kirichuk N., Popov R., Bokemeyer C., von Amsberg G., Chingizova E., et al. Pretrichodermamides d–f from a marine algicolous fungus penicillium sp. KMM 4672. Mar. Drugs. 2016;14:122. doi: 10.3390/md14070122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gawronski J.K., Van Oeveren A., Van Der Deen H., Leung C.W., Feringa B.L. Simple circular dichroic method for the determination of absolute configuration of 5-substituted 2(5H)-furanones. J. Org. Chem. 1996;61:1513–1515. doi: 10.1021/jo951400l. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu C., Lou W., Zhu Y., Nadiminty N., Schwartz C.T., Evans C.P., Gao A.C. Niclosamide inhibits androgen receptor variants expression and overcomes enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014;20:3198–3210. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Beekman A.C., Woerdenbag H.J., Van Uden W., Pras N., Konings A.W.T., Wikström H.V., Schmidt T.J. Structure-cytotoxicity relationships of some helenanolide-type sesquiterpene lactones. J. Nat. Prod. 1997;60:252–257. doi: 10.1021/np960517h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dyshlovoy S.A., Menchinskaya E.S., Venz S., Rast S., Amann K., Hauschild J., Otte K., Kalinin V.I., Silchenko A.S., Avilov S.A., et al. The marine triterpene glycoside frondoside a exhibits activity in vitro and in vivo in prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2016;138:2450–2465. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dyshlovoy S.A., Venz S., Shubina L.K., Fedorov S.N., Walther R., Jacobsen C., Stonik V.A., Bokemeyer C., Balabanov S., Honecker F. Activity of aaptamine and two derivatives, demethyloxyaaptamine and isoaaptamine, in cisplatin-resistant germ cell cancer. J. Proteom. 2014;96:223–239. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dyshlovoy S.A., Hauschild J., Amann K., Tabakmakher K.M., Venz S., Walther R., Guzii A.G., Makarieva T.N., Shubina L.K., Fedorov S.N., et al. Marine alkaloid monanchocidin a overcomes drug resistance by induction of autophagy and lysosomal membrane permeabilization. Oncotarget. 2015;6:17328–17341. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.