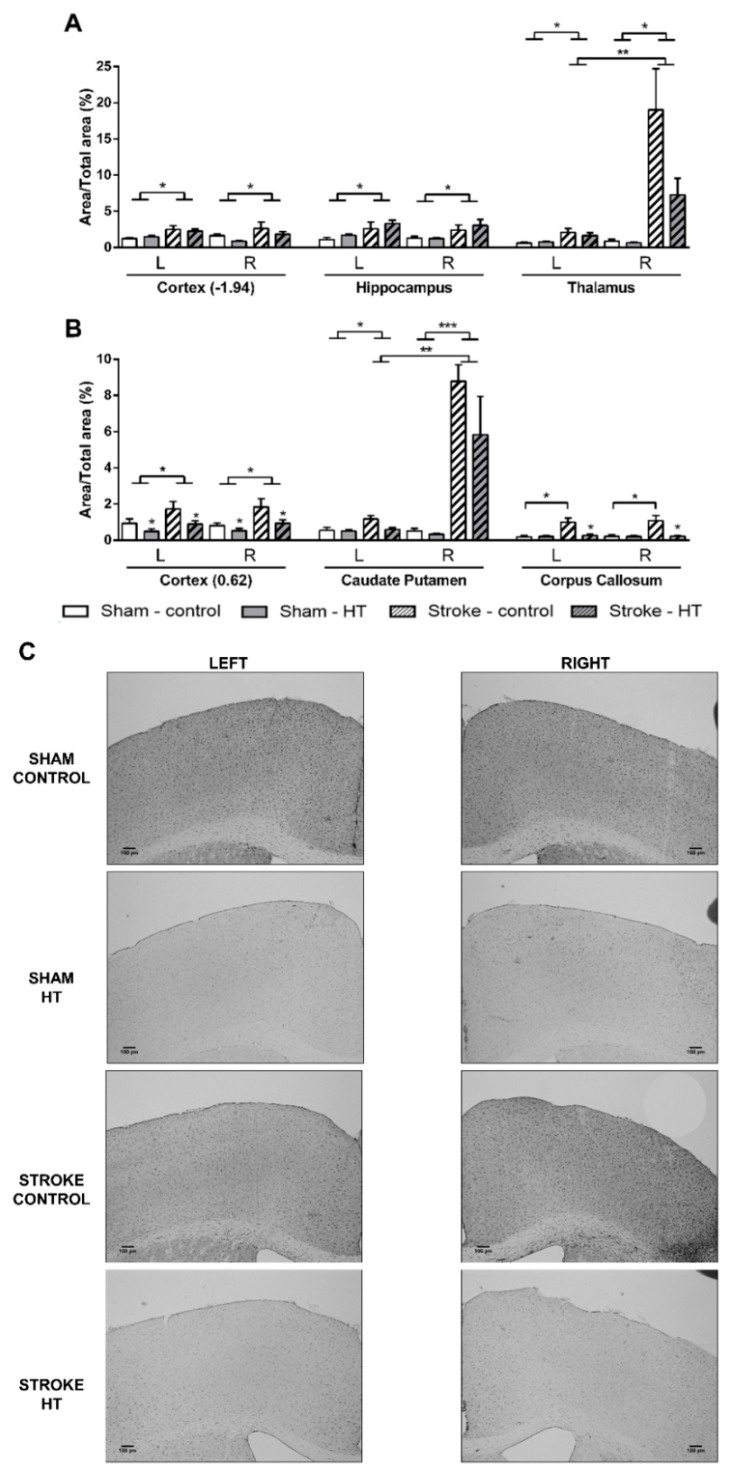
Figure 14.
Immunohistochemical stainings for ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule-1 (IBA-1) in brains of HT and control-fed mice 35 days after surgery. All stroke mice showed a higher IBA1+-area than sham mice in (A) the cortex (bregma −1.94) (p < 0.046), hippocampus (p < 0.019), in both left (p < 0.002) and right (p < 0.002) thalamus, (B) cortex (bregma 0.62) (p < 0.027), and in both left (p < 0.037) and right (p < 0.001) caudate putamen. (B) Notably, in the corpus callosum, only in stroke-control mice a heightened IBA1+-area was found compared to sham-control mice (p < 0.011). Moreover, only in stroke mice in the right thalamus (p < 0.006) and in the right caudate putamen (p < 0.001) IBA1+-area was increased compared to their corresponding left hemispheric part. In the cortex at bregma 0.62, HT diet lowered IBA1+-area compared to control diet in both sham and stroke mice (p < 0.039). In the corpus callosum, IBA1+-area was decreased by HT diet only in stroke mice (p < 0.022). (C) Representative images of IBA-1 staining in cortex (bregma 0.62). Values represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.