Abstract
Background
The sophisticated insect olfactory system plays an important role in recognizing external odors and enabling insects to adapt to environment. Foraging, host seeking, mating, ovipositing and other forms of chemical communication are based on olfaction, which requires the participation of multiple olfactory genes. The exclusive evolutionary trend of the olfactory system in Orthoptera insects is an excellent model for studying olfactory evolution, but limited olfaction research is available for these species. The olfactory-related genes of Ceracris nigricornis Walker (Orthoptera: Acrididae), a severe pest of bamboos, have not yet been reported.
Results
We sequenced and analyzed the transcriptomes from different tissues of C. nigricornis and obtained 223.76 Gb clean data that were assembled into 43,603 unigenes with an N50 length of 2235 bp. Among the transcripts, 66.79% of unigenes were annotated. Based on annotation and tBLASTn results, 112 candidate olfactory-related genes were identified for the first time, including 20 odorant-binding proteins (OBPs), 10 chemosensory-binding proteins (CSPs), 71 odorant receptors (ORs), eight ionotropic receptors (IRs) and three sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs). The fragments per kilobase per million mapped fragments (FPKM) values showed that most olfactory-related differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were enriched in the antennae, and these results were confirmed by detecting the expression of olfactory-related genes with quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Among these antennae-enriched genes, some were sex-biased, indicating their different roles in the olfactory system of C. nigricornis.
Conclusions
This study provides the first comprehensive list and expression profiles of olfactory-related genes in C. nigricornis and a foundation for functional studies of these olfactory-related genes at the molecular level.
Keywords: Ceracris nigricornis, Transcriptome, Expression profiles analysis, Odorant-binding protein, Chemosensory-binding protein, Odorant receptor, Ionotropic receptor, Sensory neuron membrane protein
Background
Ceracris nigricornis Walker (Orthoptera: Acrididae) is a severe grasshopper pest of bamboos such as Phyllostachys heterocycla, Phyllostachys viridis and Phyllostachys glauca. C. nigricornis can also harm rice, corn, sorghum and other crops and can cause serious economic losses. Typically, the application of a substantial quantity of chemical insecticides, especially wide-spectrum insecticides, is the main method for controlling this pest. However, long-term application of pesticides may lead to pesticide resistance, pesticide residues, environmental pollution, and a decrease in the natural enemies of C. nigricornis [1–4]. In recent years, the use of eco-friendly nonhost plant volatiles to control phytophagous insects has increased; for example, plant volatiles from Trifolium repens L., Castanea mollissima Blume, Citrus reticulata Blanco, Kigelia africana (Lam.) and Myrica rubra (Lour.) have been used to interfere with the orientation and selection of plant volatiles of tea leaves in the olfactory system of Empoasca vitis, which reduces the level of E. vitis [5–7]. The ability of these nonhost plant volatiles to control the level of insects depends largely on the highly sensitive insect olfactory system [8]. Therefore, the elucidation of the molecular basis of the insect olfactory system is of great importance for new bio-pesticide development and pest control.
Olfaction is the primary sensory modality in insects and plays an important role in finding mating partners, food, oviposition sites and suitable habitats [9–11]. The insect olfactory system involves several different proteins, including binding proteins (odorant-binding proteins, OBPs; and chemosensory-binding proteins, CSPs), chemosensory membrane proteins (odorant receptors, ORs; ionotropic receptors, IRs; gustatory receptors, GRs; and sensory neuron membrane proteins, SNMPs), and odorant-degrading esterases (ODEs) [12, 13]. OBPs and CSPs are highly concentrated in the lymph of chemosensilla and are regarded as carriers of pheromones and odorants in insect chemoreception [13–15]. OBPs are small globular, water-soluble proteins that generally contain six highly conversed cysteine residues paired into three interlocking disulfide bridges [16, 17]. OBPs can bind and transport external odorant molecules to the olfactory receptors in the olfactory neuronal membrane, which is often considered the first step in olfactory recognition [18, 19]. CSPs are also small soluble proteins, also known as olfactory system of Drosophila melanogaster (OS-D)-like proteins or sensory appendage proteins, which contain only four conserved cysteine residues but have more conserved nucleotide sequences than OBPs across insect species [20–22]. CSPs are expressed in various chemosensory organs and have many functions. CSPs are also present in nonchemosensory organs and play a role in the transmission of pheromones, the solubility of nutrients, and the development of insecticide resistance [23–25].
The recognition and transmission of olfaction begins with the interaction between odorant molecules and ORs on the dendrites of olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs). Insect ORs were first identified in the D. melanogaster genome; ORs contain seven transmembrane domains (TMDs) and a membrane topology with an intracellular N-terminus and an extracellular C-terminus, and the membrane topology of insect ORs are reversed compared to that of vertebrate ORs [26]. ORs are nonselective cationic channels with high selectivity and specificity for odorant molecules. ORs can convert chemical signals of odorant molecules into electrical signals and play a role as a transit station in insect olfactory reactions. IR is a newly discovered gene family that was first studied in the olfactory system of D. melanogaster [27]. IRs evolved from the ionotropic glutamate receptor superfamily (iGluRs) and contains iGluRs conserved structural regions: three TMDs, a bipartite ligand-binding domain with two lobes and one ion channel pore [28]. IRs are expressed in coeloconic olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) without ORs or coreceptors (ORcos) and mainly function in detecting acids, amines and other chemicals that cannot be recognized by ORs [29]. SNMPs are double transmembrane proteins that have a transmembrane domain at the C- and N-termini of the chain. SNMPs belong to the CD36 receptor family and are divided into two subfamilies, SNMP1 and SNMP2 [30]. The SNMP1 subfamily is coexpressed with pheromone receptors, and in situ hybridization indicated that it is associated with pheromone-sensitive neurons [31]. SNMP1 has been confirmed to participate in pheromone signal transduction. The SNMP2 subfamily was first identified from Manduca sexta and associates with pheromone-sensitive neurons, but it was expressed only in sensilla support cells [32].
Locusts and grasshoppers are major economic pests, but their genetic information is lacking, partly because their genomes are often very large. Currently, there are data for more than 100 genomes of Orthoptera species in the Genome Size Database (www.genomesize.com). The known variation in Orthoptera genome size ranges from 1.52 Gb for the cave cricket (Hadenoecus subterraneus) to 16.56 Gb for the mountain grasshopper (Podisma pedestris), with an 11-fold difference in size [33, 34]. Sequencing large genomes has higher requirements for sequencing technology and for human and material resources than sequencing small genomes, which explains why only the migratory locust Locusta migratoria (genome size is ~ 6.3 Gb) of Orthoptera has a complete genome sequence thus far [35]. Transcriptomic approaches offer an alternative to genomic approaches; transcriptomic approaches can generate almost all transcripts of a specific organ or tissue of a certain species in a comprehensive and rapid manner, and most molecular mechanisms of different biological processes are also elucidated in the transcriptome [36]. Transcriptomic sequencing results have less data and are more convenient for analysis than genomic sequencing results.
In recent years, there have been increasing reports on the transcriptome of the order Orthoptera, and such reports potentially provide resources for advancing the postgenomic research of Orthoptera insects; however, limited olfaction research is available for these species. Thus far, olfaction studies have been published regarding only L. migratoria [37–41], Oedaleus asiaticus [42], Oedaleus infernalis [43], Ceracris kiangsu [44] and Schistocerca gregaria [16, 45–47], and most investigations have focused on OBP genes. Here, we present a de novo transcriptome assembly for the bamboo grasshopper C. nigricornis and identified 112 putative olfactory-related genes comprising 20 OBPs, 10 CSPs, 71 ORs, 8 IRs and 3 SNMPs. Then, we evaluated the distribution of the expression patterns of these genes in different tissues of female and male adults by transcriptome analyses and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Our study provides the foundation for further studies of the molecular mechanism regulating the olfactory system in C. nigricornis.
Results
Sequencing and de novo assembly
The transcriptomes of the antennae (A), head (antennae were cut off; H), abdomen-thorax (T), legs (L) and wings (W) of female and male C. nigricornis were separately sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq X Ten platform. After the low-quality reads were filtered, a total of 223.76 Gb clean data were obtained from all 30 tissue samples, and the clean data of each tissue sample reached 6.30 Gb with a Q30 percentage greater than 94% (Additional file 1: Table S1). After all of the samples were assembled, 43,603 unigenes were generated with an N50 length of 2235 bp, and among them, 20,914 unigenes (47.96%) had a length of over 1 kb (Additional file 1: Table S2). To assess the transcriptome assembly completeness, the benchmarking sets of universal single-copy orthologs (BUSCO) v3.0.2 completeness assessment tool was used together with the Insecta odb9 database with 1658 reference genes [48]. The result had a completeness score of 89.1%, a fragmented score of 2.5% and a missing BUSCO score of only 8.4% (Additional file 1: Table S3).
Functional annotation
A total of 24,832 (56.95%), 15,750 (36.12%), 13,150 (30.16%), 11,503 (26.38%), 18,100 (41.51%), 26,933 (61.77%), 22,295 (51.13%) and 12,102 (27.75%) unigenes were successfully annotated to National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nonredundant protein sequences (NR), Swiss-Prot (a manually annotated and reviewed protein sequence database), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), euKaryotic Orthologous Groups of proteins (KOG), Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins (COG), EggNOG (A database of orthologous groups and functional annotation), Protein family (Pfam) and Gene Ontology (GO) databases, respectively, which covered a total of 29,122 (66.79%) unigenes (Additional file 1: Table S4).
A query of the NR database indicated that a high percentage of C. nigricornis sequences closely matched insect sequences (11,695, 74.94%). Among these sequences, the highest match sequence and percentage was identified with sequences of Cryptotermes secundus (2548, 21.79%), followed by sequences of Zootermopsis nevadensis (1765, 15.09%), Nilaparvata lugens (883, 7.55%), L. migratoria (729, 6.23%), Rhagoletis zephyria (223, 1.91%), Lasius niger (198, 1.69%), Bemisia tabaci (195, 1.67%), S. gregaria (144, 1.23%), and Tribolium castaneum (141, 1.21%) (Additional file 2: Figure S1).
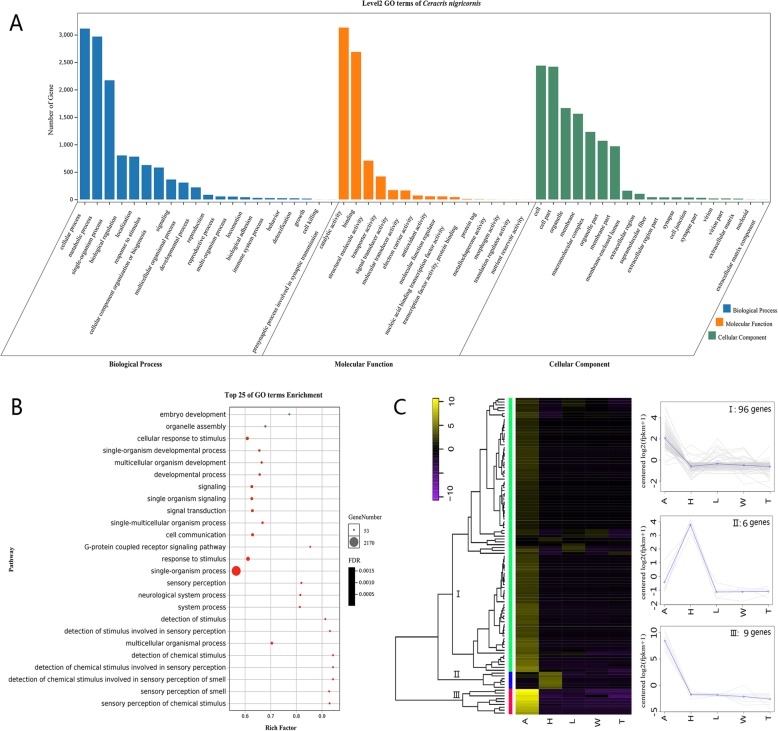
Blast2GO was applied to classify the functional groups of all unigenes of C. nigricornis. As one unigene could align to multiple GO categories, the assigned GO term was apparently larger than the annotated loci. In total, 12,102 unigenes were classified into at least one of the three main GO categories: 8661 (71.57%) were assigned to biological process, 6828 (56.42%) were assigned to cellular component and 9766 (80.70%) were assigned to molecular function. For the biological process (including 22 subcategories) category, metabolic process (5787 unigenes), cellular process (5539 unigenes) and single-organism process (3361 unigenes) were the most highly enriched GO terms, whereas cell (4705 unigenes), cell part (4674 unigenes), and organelle (3263 unigenes) were the most predominant GO terms in the cellular component (including 17 subcategories) category. For molecular function (including 16 subcategories), the most represented GO terms were catalytic activity (5846 unigenes), binding (5140 unigenes) and structural molecule activity (1190 unigenes) (Additional file 2: Figure S2).
Olfactory-related gene identification
Based on functional annotation and tBLASTn results, a total of 20 candidate OBP genes (CnigOBP1–20) were identified in the transcriptome of C. nigricornis (Table 1). All of these candidate OBP genes had six conserved cysteine residues (Additional file 2: Figure S3). Among the 20 OBP genes, 17 had intact open reading frames (ORFs) with lengths ranging from 408 bp to 816 bp. Except for CnigOBP11 and CnigOBP16, all full-length OBPs had a predicted signal peptide (a signature of secretory proteins) at the N-terminal region (Table 1). The conserved domain prediction of these candidate OBP genes showed that all of them had the domain of a pheromone/general odorant-binding protein (PhBP or PBP_GOBP) (InterPro: IPR006170) (Additional file 1: Table S5).
Table 1.
Summary of odorant binding proteins (OBPs) identified in C. nigricornis
| Gene name | Accession number | Full length | ORF (bp) | Amino acid length (AA) | Signal peptide (AA) | Homology match | Score | E-value | Identity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Species | Accession number | |||||||||
| CnigOBP1 | MK982654 | Y | 468 | 155 | 1–18 | odorant-binding protein 7 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255957.1 | 750 | 0 | 95.53 |
| CnigOBP2 | MK982655 | Y | 537 | 178 | 1–17 | odorant-binding protein 7 | Oedaleus infernalis | MG507284.1 | 590 | 2.67E-168 | 92.86 |
| CnigOBP3 | MK982656 | Y | 450 | 149 | 1–27 | odorant binding protein 11 | Schistocerca gregaria | MF716568.1 | 577 | 2.22E-164 | 89.27 |
| CnigOBP4 | MK982657 | Y | 456 | 151 | 1–19 | odorant-binding protein 5 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255955.1 | 521 | 7.04E-148 | 97.39 |
| CnigOBP5 | MK982658 | 3′ | 360 | 119 | 1–52 | odorant-binding protein 2 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255952.1 | 560 | 2.19E-159 | 95.95 |
| CnigOBP6 | MK982659 | Y | 459 | 152 | 1–21 | odorant-binding protein 1 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255951.1 | 798 | 0 | 98.04 |
| CnigOBP7 | MK982660 | Y | 465 | 154 | 1–18 | odorant-binding protein 4 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255954.1 | 704 | 0 | 93.98 |
| CnigOBP8 | MK982661 | M | 318 | 105 | NO | odorant binding protein 1 | Schistocerca gregaria | MF716558.1 | 405 | 1.11E-112 | 89.51 |
| CnigOBP9 | MK982662 | Y | 474 | 157 | 1–21 | odorant-binding protein 16 | Oedaleus infernalis | MG507293.1 | 401 | 1.43E-111 | 83.76 |
| CnigOBP10 | MK982663 | Y | 468 | 155 | 1–24 | odorant-binding protein 8 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255958.1 | 693 | 0 | 93.38 |
| CnigOBP11 | MK982664 | Y | 495 | 164 | NO | odorant-binding protein 15 | Oedaleus infernalis | MG507292.1 | 274 | 3.58E-73 | 78.18 |
| CnigOBP12 | MK982665 | Y | 471 | 156 | 1–18 | odorant-binding protein 3 | Oedaleus infernalis | MG507280.1 | 483 | 5.22E-136 | 85.2 |
| CnigOBP13 | MK982666 | Y | 456 | 151 | 1–19 | odorant-binding protein 3 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255953.1 | 684 | 0 | 93.55 |
| CnigOBP14 | MK982667 | Y | 816 | 271 | 1–22 | odorant binding protein 12 | Schistocerca gregaria | MF716569.1 | 1105 | 0 | 91.09 |
| CnigOBP15 | MK982668 | 3′ | 642 | 213 | 1–20 | odorant-binding protein 7 | Schistocerca gregaria | MF716564.1 | 372 | 1.00E-98 | 80.2 |
| CnigOBP16 | MK982669 | Y | 468 | 155 | NO | odorant-binding protein 6 | Ceracris kiangsu | KP255956.1 | 693 | 0 | 93.59 |
| CnigOBP17 | MK982670 | Y | 417 | 138 | 1–30 | odorant binding protein 17 | Locusta migratoria | MH176616.1 | 429 | 1.03E-119 | 85.57 |
| CnigOBP18 | MK982671 | Y | 480 | 159 | 1–25 | odorant-binding protein 18 | Oedaleus infernalis | MG507295.1 | 647 | 0 | 92.31 |
| CnigOBP19 | MK982672 | Y | 408 | 135 | 1–26 | odorant-binding protein 4 | Oedaleus infernalis | MG507281.1 | 549 | 4.36E-156 | 90.93 |
| CnigOBP20 | MK982673 | Y | 438 | 145 | 1–43 | odorant binding protein 5 | Schistocerca gregaria | MF716562.1 | 556 | 2.79E-158 | 89.73 |
The mark of Y, 5′, 3′, and M means that the fragment of the unigene consists of complete open reading frame, 5′-end containing start codon, 3′-end containing stop codon, and the middle part without start and stop codon, respectively
A total of 10 candidate CSP genes (CnigCSP1–10) were identified from the transcriptomes of different tissues of C. nigricornis (Table 2). All of these candidate CSP genes had four conserved cysteine residues and a conserved OS-D domain (InterPro: IPR005055); however, for CnigCSP9, two OS-D domains were identified by the conserved domain prediction (Additional file 2: Figure S4 and Additional file 1: Table S6). Among the 10 CSP genes, six CSP genes had full-length ORFs, the remaining CSP genes were incomplete due to a lack of a 5′ or 3′ terminus. The SignalP tests showed that all full-length CSP genes had a predicted signal peptide (Table 2).
Table 2.
Summary of chemosensory proteins (CSPs) identified in C. nigricornis
| Gene name | Accession number | Full length | ORF (bp) | Amino acid length (AA) | Signal peptide (AA) | Homology match | Score | E-value | Identity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Species | Accession number | |||||||||
| CnigCSP1 | MK989603 | Y | 447 | 148 | 1–17 | chemosensory protein 7 | Oedaleus infernalis | MH568703.1 | 490 | 2.57E-137 | 88.107 |
| CnigCSP2 | MK989604 | Y | 381 | 126 | 1–21 | chemosensory protein 8 | Oedaleus infernalis | MH568704.1 | 324 | 6.65E-88 | 82.105 |
| CnigCSP3 | MK989605 | Y | 462 | 153 | 1–35 | chemosensory protein 12 | Oedaleus asiaticus | KX905068.1 | 287 | 3.66E-77 | 82.769 |
| CnigCSP4 | MK989606 | Y | 453 | 150 | 1–19 | chemosensory protein 2 | Oedaleus asiaticus | KX905058.1 | 473 | 2.57E-133 | 88.718 |
| CnigCSP5 | MK989607 | Y | 396 | 131 | 1–21 | chemosensory protein 9 | Oedaleus asiaticus | KX905065.1 | 366 | 4.57E-101 | 83.459 |
| CnigCSP6 | MK989608 | Y | 384 | 127 | 1–16 | chemosensory protein 9 | Oedaleus infernalis | MH568705.1 | 438 | 1.75E-122 | 86.99 |
| CnigCSP7 | MK989609 | 3′ | 333 | 110 | 1–29 | chemosensory protein 23 | Oedaleus infernalis | MH568719.1 | 243 | 1.74E-63 | 90.374 |
| CnigCSP8 | MK989610 | 3′ | 393 | 130 | NO | chemosensory protein 10 | Oedaleus infernalis | MH568706.1 | 355 | 2.38E-97 | 87.5 |
| CnigCSP9 | MK989611 | M | 693 | 230 | 1–18 | chemosensory protein 17 | Oedaleus infernalis | MH568713.1 | 300 | 3.01E-81 | 87.405 |
| CnigCSP10 | MK989612 | 3′ | 375 | 124 | 1–19 | chemosensory protein 1 | Oedaleus asiaticus | KX905057.1 | 457 | 2.76E-128 | 88.714 |
The mark of Y, 5′, 3′, and M means that the fragment of the unigene consists of complete open reading frame, 5′-end containing start codon, 3′-end containing stop codon, and the middle part without start and stop codon, respectively
In the transcriptomes of C. nigricornis, 71 candidate OR genes were identified, including 70 conventional ORs (CnigOR1–70) and one ORco (CnigORco). Of these, only 15 candidate OR genes had complete ORFs with lengths longer than 394 amino acids and had 4–7 TMDs (Table 3). Eight candidate IR genes were identified (CnigIR1–5, CnigIR8a, CnigIR25a and CnigIR76b), and six contained a full-length ORF with lengths longer than 319 amino acids (Table 4). Three candidate SNMPs were identified and named CnigSNMP1, CnigSNMP2 and CnigSNMP2a. Only CnigSNMP1 had complete ORFs encoding 532 amino acids (Table 5).
Table 3.
Summary of odorant receptors (ORs) identified in C. nigricornis
| Gene name | Accession number | Full length | ORF (bp) | Amino acid length (AA) | Tm domain | Homology match | Score | E-value | Identity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Species | Accession number | |||||||||
| CnigOR1 | MN004970 | 3′ | 522 | 173 | 1 | odorant receptor 115 | Locusta migratoria | KP843300.1 | 641 | 6.00E-180 | 89.13% |
| CnigOR2 | MN004971 | M | 315 | 104 | 2 | odorant receptor 44 | Locusta migratoria | KP843275.1 | 250 | 2.00E-62 | 82.41% |
| CnigOR3 | MN004972 | M | 558 | 185 | 3 | odorant receptor 17 | Locusta migratoria | KP843324.1 | 494 | 2.00E-135 | 86.37% |
| CnigOR4 | MN004973 | 3′ | 420 | 139 | 0 | odorant receptor 62 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964979.1 | 523 | 2.00E-144 | 90.07% |
| CnigOR5 | MN004974 | 3′ | 1122 | 373 | 5 | odorant receptor 116 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY965033.1 | 566 | 8.00E-157 | 90.47% |
| CnigOR6 | MN004975 | M | 747 | 248 | 2 | odorant receptor 125 | Locusta migratoria | KP843195.1 | 346 | 8.00E-91 | 77.36% |
| CnigOR7 | MN004976 | 5′ | 351 | 116 | 0 | odorant receptor 20 | Locusta migratoria | KP843332.1 | 342 | 5.00E-90 | 85.63% |
| CnigOR8 | MN004977 | 3′ | 591 | 193 | 2 | odorant receptor 74 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964991.1 | 566 | 4.00E-157 | 83.95% |
| CnigOR9 | MN004978 | 5′ | 1257 | 418 | 4 | odorant receptor 129 | Locusta migratoria | KP843262.1 | 1027 | 0 | 81.59% |
| CnigOR10 | MN004979 | 3′ | 1464 | 487 | 6 | odorant receptor 84 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY965001.1 | 496 | 1.00E-135 | 78.20% |
| CnigOR11 | MN004980 | 3′ | 873 | 290 | 2 | odorant receptor 22 | Locusta migratoria | KP843343.1 | 640 | 4.00E-179 | 80.23% |
| CnigOR12 | MN004981 | 3′ | 1077 | 358 | 0 | odorant receptor 94 | Locusta migratoria | KP843364.1 | 977 | 0 | 83.46% |
| CnigOR13 | MN004982 | Y | 1185 | 394 | 6 | odorant receptor 114 | Locusta migratoria | KP843317.1 | 555 | 2.00E-153 | 81.41% |
| CnigOR14 | MN004983 | 5′ | 1185 | 394 | 4 | odorant receptor 46 | Locusta migratoria | KP843249.1 | 1288 | 0 | 86.30% |
| CnigOR15 | MN004984 | 3′ | 567 | 188 | 2 | odorant receptor 8 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964925.1 | 582 | 4.00E-162 | 86.22% |
| CnigOR16 | MN004985 | 5′ | 1110 | 369 | 4 | odorant receptor 57 | Locusta migratoria | KP843340.1 | 1408 | 0 | 89.56% |
| CnigOR17 | MN004986 | 3′ | 717 | 238 | 1 | odorant receptor 68 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964985.1 | 758 | 0.00E+ 00 | 86.61% |
| CnigOR18 | MN004987 | 5′ | 450 | 149 | 2 | odorant receptor 70 | Locusta migratoria | KP843266.1 | 379 | 5.00E-101 | 82.04% |
| CnigOR19 | MN004988 | 3′ | 183 | 60 | 0 | olfactory receptor OR10 | Oedaleus asiaticus | MH196282.1 | 272 | 3.00E-69 | 95.83% |
| CnigOR20 | MN004989 | M | 1086 | 361 | 5 | odorant receptor 11 | Oedaleus asiaticus | MH196283.1 | 388 | 2.00E-103 | 89.10% |
| CnigOR21 | MN004990 | 3′ | 1050 | 349 | 6 | odorant receptor 92 | Locusta migratoria | KP843261.1 | 1282 | 0 | 88.72% |
| CnigOR22 | MN004991 | 3′ | 1104 | 367 | 4 | odorant receptor 112 | Locusta migratoria | KP843264.1 | 1109 | 0 | 85.13% |
| CnigOR23 | MN004992 | 5′ | 1182 | 394 | 3 | odorant receptor 59 | Locusta migratoria | KP843311.1 | 1208 | 0 | 88.62% |
| CnigOR24 | MN004993 | 3′ | 807 | 268 | 4 | odorant receptor 140 | Locusta migratoria | KP843287.1 | 872 | 0.00E+ 00 | 89.97% |
| CnigOR25 | MN004994 | Y | 1272 | 423 | 7 | odorant receptor 39 | Locusta migratoria | KP843237.1 | 1399 | 0 | 87.00% |
| CnigOR26 | MN004995 | M | 1287 | 428 | 6 | odorant receptor 98 | Locusta migratoria | KP843339.1 | 1301 | 0 | 87.59% |
| CnigOR27 | MN004996 | 3′ | 1296 | 431 | 4 | odorant receptor 63 | Locusta migratoria | KP843243.1 | 593 | 4.00E-165 | 84.40% |
| CnigOR28 | MN004997 | M | 1413 | 470 | 5 | odorant receptor 86 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY965003.1 | 372 | 2.00E-98 | 73.31% |
| CnigOR29 | MN004998 | 3′ | 1401 | 466 | 4 | odorant receptor 15 | Locusta migratoria | KP843322.1 | 595 | 1.00E-165 | 87.67% |
| CnigOR30 | MN004999 | Y | 1347 | 448 | 6 | odorant receptor 1 | Locusta migratoria | JQ766965.1 | 1742 | 0 | 89.35% |
| CnigOR31 | MN005000 | 3′ | 1287 | 428 | 4 | odorant receptor 3 | Locusta migratoria | KP843242.1 | 1568 | 0 | 89.17% |
| CnigOR32 | MN005001 | 3′ | 1296 | 431 | 6 | odorant receptor 35 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964952.1 | 1020 | 0 | 85.28% |
| CnigOR33 | MN005002 | 3′ | 1341 | 446 | 2 | odorant receptor 105 | Locusta migratoria | KY965022.1 | 198 | 4.00E-46 | 75.73% |
| CnigOR34 | MN005003 | 3′ | 909 | 302 | 3 | odorant receptor 85 | Locusta migratoria | KP843252.1 | 1044 | 0 | 87.31% |
| CnigOR35 | MN005004 | 3′ | 990 | 329 | 4 | odorant receptor 84 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY965001.1 | 773 | 0 | 87.50% |
| CnigOR36 | MN005005 | 5′ | 375 | 124 | 2 | odorant receptor 123 | Locusta migratoria | KP843260.1 | 294 | 2.00E-75 | 80.91% |
| CnigOR37 | MN005006 | 3′ | 1128 | 375 | 4 | odorant receptor 49 | Locusta migratoria | KP843251.1 | 1214 | 0 | 86.12% |
| CnigOR38 | MN005007 | 3′ | 711 | 236 | 3 | odorant receptor 33 | Locusta migratoria | KY964950.1 | 448 | 2.00E-121 | 78.06% |
| CnigOR39 | MN005008 | M | 1071 | 356 | 4 | odorant receptor 11 | Locusta migratoria | KP843352.1 | 787 | 0.00E+ 00 | 83.67% |
| CnigOR40 | MN005009 | M | 1185 | 394 | 5 | olfactory receptor OR41 | Oedaleus asiaticus | MH196313.1 | 518 | 3.00E-142 | 86.62% |
| CnigOR41 | MN005010 | 3′ | 192 | 63 | 0 | odorant receptor 21 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964938.1 | 237 | 1.00E-58 | 90.11% |
| CnigOR42 | MN005011 | Y | 1293 | 430 | 6 | odorant receptor 31 | Locusta migratoria | KP843247.1 | 1205 | 0 | 83.77% |
| CnigOR43 | MN005012 | 3′ | 1047 | 348 | 5 | odorant receptor 89 | Locusta migratoria | KP843305.1 | 1098 | 0 | 89.66% |
| CnigOR44 | MN005013 | Y | 1251 | 416 | 5 | odorant receptor 77 | Locusta migratoria | KP843362.1 | 1273 | 0 | 86.34% |
| CnigOR45 | MN005014 | 3′ | 1275 | 424 | 4 | odorant receptor 31 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964948.1 | 887 | 0 | 88.90% |
| CnigOR46 | MN005015 | Y | 1275 | 424 | 4 | odorant receptor 88 | Locusta migratoria | KP843346.1 | 479 | 1.00E-130 | 79.40% |
| CnigOR47 | MN005016 | 5′ | 1140 | 379 | 5 | odorant receptor 102 | Locusta migratoria | KP843271.1 | 1003 | 0 | 82.94% |
| CnigOR48 | MN005017 | 3′ | 1203 | 400 | 4 | olfactory receptor OR34 | Oedaleus asiaticus | MH196306.1 | 870 | 0.00E+ 00 | 89.97% |
| CnigOR49 | MN005018 | 3′ | 1389 | 462 | 1 | odorant receptor 96 | Locusta migratoria | KP843235.1 | 1155 | 0 | 83.61% |
| CnigOR50 | MN005019 | 3′ | 1125 | 374 | 5 | odorant receptor 103 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY965020.1 | 320 | 7.00E-83 | 80.14% |
| CnigOR51 | MN005020 | Y | 1248 | 415 | 7 | odorant receptor 36 | Locusta migratoria | KP843255.1 | 1086 | 0 | 85.62% |
| CnigOR52 | MN005021 | 3′ | 333 | 110 | 0 | odorant receptor 112 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY965029.1 | 300 | 3.00E-77 | 83.86% |
| CnigOR53 | MN005022 | Y | 1245 | 414 | 6 | odorant receptor 28 | Locusta migratoria | KP843306.1 | 1197 | 0 | 90.04% |
| CnigOR54 | MN005023 | M | 1296 | 431 | 5 | odorant receptor 23 | Locusta migratoria | KP843323.1 | 1120 | 0 | 85.07% |
| CnigOR55 | MN005024 | 3′ | 246 | 81 | 0 | odorant receptor 77 | Locusta migratoria | KP843362.1 | 134 | 2.00E-27 | 90.91% |
| CnigOR56 | MN005025 | M | 906 | 301 | 4 | odorant receptor 120 | Locusta migratoria | KP843236.1 | 754 | 0.00E+ 00 | 83.27% |
| CnigOR57 | MN005026 | 5′ | 1200 | 400 | 6 | odorant receptor 5 | Locusta migratoria | KF601291.1 | 257 | 6.00E-64 | 75.13% |
| CnigOR58 | MN005027 | 3′ | 1410 | 469 | 7 | odorant receptor 29 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964946.1 | 1589 | 0 | 88.53% |
| CnigOR59 | MN005028 | Y | 1374 | 457 | 7 | odorant receptor 1 | Locusta migratoria | KP843273.1 | 1515 | 0 | 86.70% |
| CnigOR60 | MN005029 | Y | 1329 | 442 | 4 | odorant receptor 105 | Locusta migratoria | KP843270.1 | 1022 | 0 | 80.62% |
| CnigOR61 | MN005030 | 3′ | 1389 | 462 | 5 | olfactory receptor OR35 | Oedaleus asiaticus | MH196307.1 | 599 | 1.00E-166 | 84.76% |
| CnigOR62 | MN005031 | Y | 1230 | 409 | 5 | odorant receptor 46 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964963.1 | 846 | 0 | 80.84% |
| CnigOR63 | MN005032 | Y | 1242 | 413 | 6 | odorant receptor 34 | Locusta migratoria | KP843363.1 | 1003 | 0 | 81.56% |
| CnigOR64 | MN005033 | Y | 1230 | 409 | 6 | odorant receptor 51 | Locusta migratoria | KP843350.1 | 1308 | 0 | 85.99% |
| CnigOR65 | MN005034 | 3′ | 1059 | 352 | 2 | odorant receptor 44 | Schistocerca gregaria | KY964961.1 | 1120 | 0 | 85.82% |
| CnigOR66 | MN005035 | 3′ | 1413 | 470 | 0 | odorant receptor 107 | Locusta migratoria | KP843267.1 | 1319 | 0 | 84.51% |
| CnigOR67 | MN005036 | 3′ | 1239 | 412 | 3 | odorant receptor 58 | Locusta migratoria | KP843325.1 | 1223 | 0 | 84.60% |
| CnigOR68 | MN005037 | 3′ | 405 | 134 | 0 | odorant receptor 44 | Locusta migratoria | KP843275.1 | 510 | 1.00E-140 | 89.38% |
| CnigOR69 | MN005038 | M | 732 | 243 | 4 | odorant receptor 17 | Locusta migratoria | KP843324.1 | 320 | 5.00E-83 | 76.85% |
| CnigOR70 | MN005039 | Y | 1347 | 448 | 4 | odorant receptor 105 | Locusta migratoria | KP843270.1 | 737 | 0 | 76.83% |
| CnigORco | MN005040 | Y | 1458 | 485 | 7 | olfactory receptor coreceptor | Ceracris kiangsu | KU043292.1 | 2560 | 0 | 98.35% |
The mark of Y, 5′, 3′, and M means that the fragment of the unigene consists of complete open reading frame, 5′-end containing start codon, 3′-end containing stop codon, and the middle part without start and stop codon, respectively
Table 4.
Summary of ionotropic receptors (IRs) identified in C. nigricornis
| Gene name | Accession number | Full length | ORF (bp) | Amino acid length (AA) | Tm domain | Homology match | Score | E-value | Identity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Species | Accession number | |||||||||
| CnigIR1 | MK990725 | 3′ | 879 | 292 | 2 | ionotropic receptor 6 | Locusta migratoria | KT279128.1 | 542 | 1.00E-149 | 79.56% |
| CnigIR2 | MK990726 | Y | 1533 | 510 | 3 | ionotropic receptor 26 | Locusta migratoria | KP843223.1 | 1435 | 0 | 92.99% |
| CnigIR3 | MK990727 | Y | 2322 | 773 | 4 | ionotropic receptor 21 | Locusta migratoria | KP843211.1 | 1256 | 0 | 91.18% |
| CnigIR4 | MK990729 | 3′ | 2034 | 677 | 1 | ionotropic receptor 29 | Locusta migratoria | KT279132.1 | 1690 | 0 | 91.89% |
| CnigIR5 | MK990730 | 3′ | 960 | 319 | 0 | ionotropic receptor 14 | Locusta migratoria | KT279126.1 | 324 | 5.00E-84 | 85.71% |
| CnigIR8a | MK990728 | Y | 2691 | 896 | 3 | ionotropic receptor 8a | Locusta migratoria | KR349063.1 | 3777 | 0 | 91.85% |
| CnigIR25a | MK990731 | Y | 2715 | 904 | 4 | ionotropic receptor IR25a | Oedaleus asiaticus | MH196264.1 | 4052 | 0 | 93.86% |
| CnigIR76b | MK990732 | Y | 1608 | 535 | 4 | ionotropic receptor 76b | Locusta migratoria | KP843210.1 | 2233 | 0 | 91.73% |
The mark of Y, 5′, 3′, and M means that the fragment of the unigene consists of complete open reading frame, 5′-end containing start codon, 3′-end containing stop codon, and the middle part without start and stop codon, respectively
Table 5.
Summary of sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs) identified in C. nigricornis
| Gene name | Accession number | Full length | ORF (bp) | Amino acid length (AA) | Tm domain | Homology match | Score | E-value | Identity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Species | Accession number | |||||||||
| CnigSNMP1 | MK976705 | Y | 1599 | 532 | 2 | sensory neuron membrane protein 1 | Schistocerca gregaria | AMS24657.1 | 631 | 0 | 70.93% |
| CnigSNMP2 | MK976706 | 5′ | 876 | 291 | 1 | sensory neuron membrane protein 2 | Schistocerca gregaria | AMS24658.1 | 433 | 2.00E-146 | 78.77% |
| CnigSNMP2a | MK976707 | 3′ | 663 | 220 | 1 | sensory neurone membrane protein SNMP2a | Oedaleus asiaticus | QAB43878.1 | 398 | 5.00E-135 | 90.00% |
The mark of Y, 5′, 3′, and M means that the fragment of the unigene consists of complete open reading frame, 5′-end containing start codon, 3′-end containing stop codon, and the middle part without start and stop codon, respectively
Homology relationship of olfactory-related genes
To reveal the homology relationships of all olfactory related genes of C. nigricornis with other insect gene sets, we conducted phylogenetic analyses based on the amino acid sequences of 121 OBPs from nine species (Additional file 2: Figure S5), 87 CSPs from seven species (Additional file 2: Figure S6), 293 ORs from three species (Additional file 2: Figure S7), 115 IRs from five species (Additional file 2: Figure S8), and 24 SNMPs from nine species (Additional file 2: Figure S9), respectively. All members of CSPs (Additional file 2: Figure S6), IRs (Additional file 2: Figure S8), and SNMPs (Additional file 2: Figure S9) show orthologous relationships with the counterparts from other orthopteran species. For OBPs, CnigOBP6 and CnigOBP8 are paralogous and may arouse by a recent gene duplication event; the remaining 18 CnigOBPs have orthologous relationships with the other orthopteran species (Additional file 2: Figure S5). For 71 CnigORs, 61 show orthologous relationships with orthopteran species, the other 10 CnigORs (CnigOR5/48, CnigOR17/18, CnigOR19/20, CnigOR35/36, CnigOR40/41) show 2:1 orthologous relationships with the orthopteran species, indicating in-paralogous or out-paralogous relationships among these CnigORs pairs.
Tissue-specific expression analyses by RNA-Seq
To fully understand the differential expression patterns of olfactory-related genes in different tissues, the Illumina reads of each RNA sample were mapped to the reference transcripts to determine the expression quantity. The average number of mapped reads was 75.26% (Additional file 1: Table S1). Fragments per kilobase per million mapped fragments (FPKM) values [49] were determined to measure the gene expression levels.
To detect olfactory-related differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of different tissues, we considered four combinations for comparison: antennae vs. head (A vs H), antennae vs. abdomen-thorax (A vs T), antennae vs. leg (A vs L) and antennae vs. wing (A vs W). A total of 21,484 transcripts were DEGs, and 6357 of them were assigned to GO terms. Among the 6357 DEGs, we found that cellular process, metabolic process and single-organism process represented a high percentage of the biological process category, catalytic activity and binding represented the majority of the molecular function category, cell and cell part represented the greatest proportion of the cellular component category (Fig. 1a). In the biological process category, significantly enriched GO terms were mainly associated with chemosensory perception, such as sensory perception of chemical stimulus, sensory perception of smell, detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of smell, detection of stimulus involved in sensory perception and sensory perception (Fig. 1b). This expression pattern suggests that chemosensory perception is differentially expressed in different tissues. To better understand these differences, we manually inspected the transcription of genes encoding binding proteins (OBPs and CSPs) and chemosensory membrane proteins (ORs, IRs and SNMPs) to find DEGs in different tissues. The hierarchical cluster analysis showed that all differentially expressed olfactory-related genes were clustered into three clusters (Fig. 1c). In Cluster I and Cluster III, a total of 105 genes had the highest expression in antennae, but the log2FPKM values of Cluster III were higher than those of Cluster I. In Cluster II, the expression detected in the head was higher than that detected in the antennae, legs, wings and abdomen-thorax.
Fig. 1.
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) analysis of C. nigricornis. a Gene ontology (GO) classifications of DEGs in C. nigricornis. b GO enrichment analysis in the top 25 DEGs of biological process category. c K-means clustering of 111 olfactory-related DEGs. A: antennae; H: head (antennae were cut off); L: leg; W: wing; T: abdomen-thorax. Log10 (FPKM+ 1) values were used, and FPKM values were the average values of each tissues, including female three biological repeats and male three biological repeats
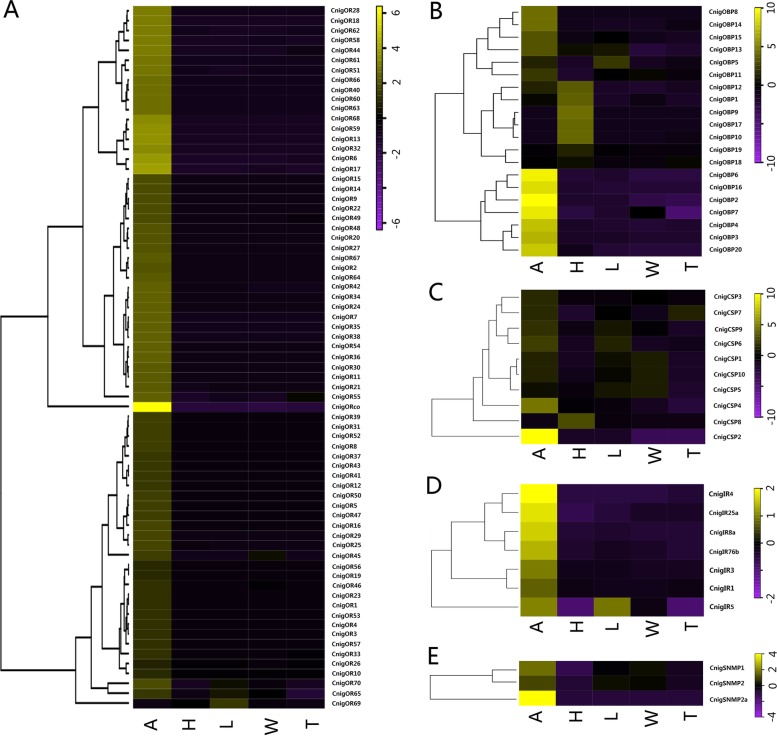
To clearly describe the DEGs of each olfactory-related gene, we performed cluster analysis on their DEGs and represented in heatmap (Fig. 2). Based on the expression levels in different tissues, most of the differentially expressed OBP genes were highly expressed in the antennae and head tissues. Among them, 12 candidate OBPs (CnigOBP2/3/4/6/7/8/11/13/14/15/16/20) showed antennae-specific expression, and seven candidate OBPs (CnigOBP1/9/10/12/17/18/19) showed head-specific expression (Fig. 2b). The expression analysis showed that except for CnigCSP5 and CnigCSP8, all of the differentially expressed CSP genes were highly expressed in the antennae. Among those genes highly expressed in the antennae, CnigCSP6 and CnigCSP9 were also highly expressed in the legs, CnigCSP1 and CnigCSP10 were also highly expressed in the wings, and CnigCSP7 was also highly expressed in the abdomen-thorax. CnigCSP5 was relatively highly expressed in the legs and wings, and CnigCSP8 was highly expressed in the head (Fig. 2c). Except for CnigOR69 that showed relatively high expression levels in the legs, all differentially expressed ORs showed antennal-specific or antennal-biased expression (Fig. 2a). The IRs showed a similar expression profile to the ORs, but more IRs than ORs were detected in the legs and wings (Fig. 2d). All SNMPs were highly expressed in the antennae (Fig. 2e).
Fig. 2.
Hierarchical clustering of differentially expressed olfactory-related genes with difference tissues in C. nigricornis. a odorant receptors (ORs); b odorant binding proteins (OBPs); c chemosensory proteins (CSPs); d ionotropic receptors (IRs); e sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs). A: antennae; H: head (antennae were cut off); L: leg; W: wing; T: abdomen-thorax. Log10 (FPKM+ 1) values were used, and FPKM values were the average values of each tissues including female three biological repeats and male three biological repeats
Sex- and tissue-specific expression analyses by qRT-PCR
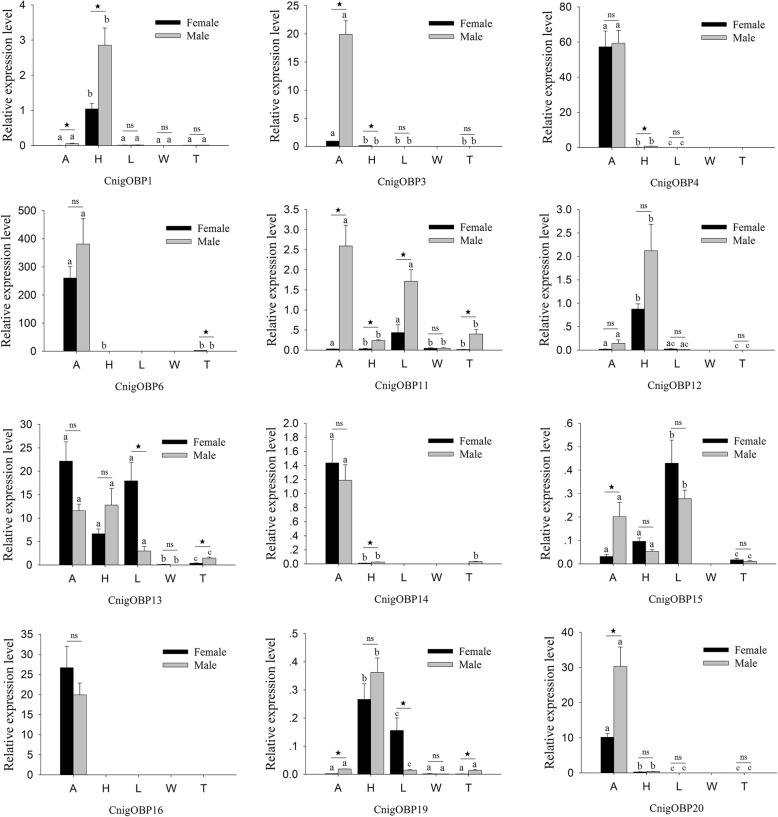
To explore the tissue distribution expression pattern of olfactory-related genes in female and male adults of C. nigricornis and to test the RNA-Seq results, we investigated the expression patterns of 12 OBPs, all CSPs and 12 ORs with qRT-PCR analyses. The results showed that the expression levels of the tested genes in different tissues were mostly consistent with the results of RNA-Seq. Based on the results of qRT-PCR assays, six OBP genes (CnigOBP3/4/6/14/16/20) had significantly increased expressed in the antennae, and CnigOBP3 and CnigOBP20 were predominantly expressed in the male antennae (P < 0.05) (Fig. 3). CnigOBP1, CnigOBP12 and CnigOBP19 were predominantly expressed in the head, and CnigOBP1 was significantly more highly expressed in the male head than in the female head among the three head-biased OBPs (Fig. 3). In addition, CnigOBP15 was highly expressed in the legs, CnigOBP11 was highly expressed in the antennae and legs, CnigOBP13 was highly expressed in three tissues (antennae, head and leg), and all 12 OBPs had no or little expression in the wings and abdomen-thorax (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of relative expression levels of odorant binding proteins (OBPs) from C. nigricornis. A: antennae; H: head (antennae were cut off); L: leg; W: wing; T: abdomen-thorax. The β-actin was used as the reference gene and CnigOBP3 in female antennae as a positive control. The error bars represent the standard error of three independent experiments. Different small letters above bars indicate significant differences among different tissues (P < 0.05). * indicates significant difference between both sexes in the same tissue (P < 0.05), and ns indicates no significant difference
The qRT-PCR results revealed that all 10 CSPs had significant differences in the expression levels among different tissues. Four CSP genes (CnigCSP1/2/3/4) were expressed more highly in the antennae than in other tissues (P < 0.05), and except for CnigCSP3, all antennae-biased CSPs were significantly more highly expressed in the male antennae than in the female antennae (Fig. 4). CnigCSP8 was predominantly expressed in the head, while CnigCSP5 was highly expressed in the legs. Meanwhile, there were significant differences in the expression levels of CnigCSP8 in the head and CnigCSP5 in the legs between males and females, and CnigCSP8 and CnigCSP5 were highly expressed in the female head and leg tissues, respectively (Fig. 4). The remaining four CSPs (CnigCSP6/7/9/10) were highly expressed in more than two tissues; among them, CnigCSP6, CnigCSP7 and CnigCSP9 were more highly expressed in the antennae and legs than in other tissues, and CnigCSP10 was more highly expressed in the antennae, head and legs than in the wings and abdomen-thorax (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of relative expression levels of chemosensory proteins (CSPs) from C. nigricornis. A: antennae; H: head (antennae were cut off); L: leg; W: wing; T: abdomen-thorax. The β-actin was used as the reference gene and CnigCSP1 in female antennae as a positive control. The error bars represent the standard error of three independent experiments. Different small letters above bars indicate significant differences among different tissues (P < 0.05). * indicates significant difference between both sexes in the same tissue (P < 0.05), and ns indicates no significant difference
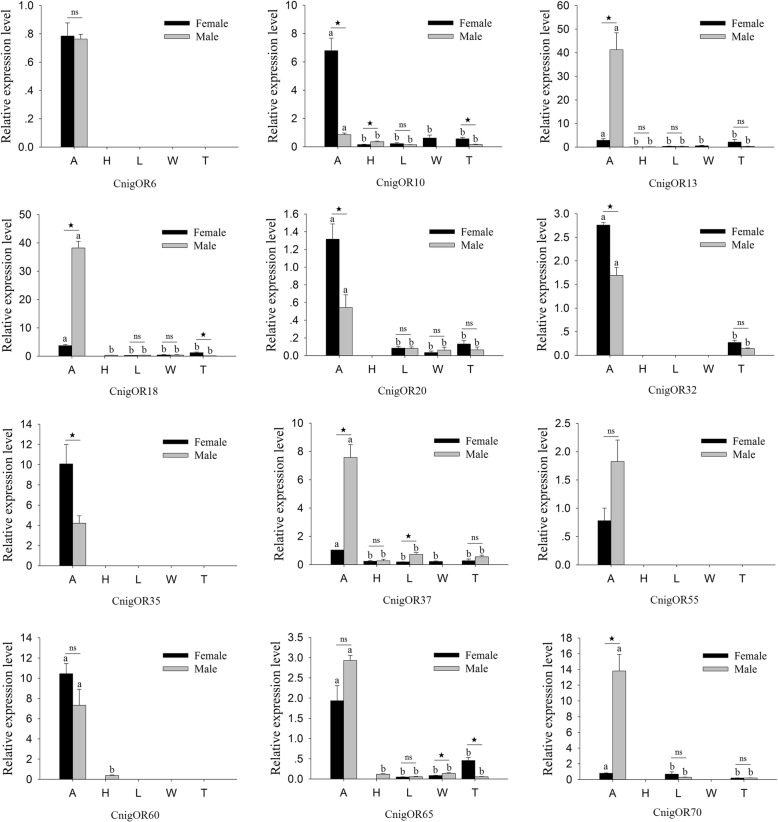
All randomly selected OR genes were strongly expressed in the antennae, whereas they were not or were more faintly expressed in other tissues (Fig. 5). Among the 12 ORs, four CnigOR genes (CnigOR13/18/R37/70) were more highly expressed in the male antennae than in the female antennae, four CnigOR genes (CnigOR10/20/32/35) were more highly expressed in the female antennae than in the male antennae (P < 0.05), and the remaining four CnigOR genes (CnigOR6/55/60/65) were not significantly different between the male and female antennae (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of relative expression levels of odorant receptors (ORs) from C. nigricornis. A: antennae; H: head (antennae were cut off); L: leg; W: wing; T: abdomen-thorax. The β-actin was used as the reference gene and CnigOR37 in female antennae as a positive control. The error bars represent the standard error of three independent experiments. Different small letters above bars indicate significant differences among different tissues (P < 0.05). * indicates significant difference between both sexes in the same tissue (P < 0.05), and ns indicates no significant difference
Discussion
Orthoptera insects have an exclusive evolutionary trend in their olfactory system, which is an excellent model for studying the olfactory evolution of insects [50]. However, few investigations have focused on the molecular basis of olfaction in these species. In this study, we sequenced and analyzed the transcriptomes of C. nigricornis from the antennae, head (antennae were cut off), legs, wings and abdomen-thorax, and the results of this study further enriched the molecular biological foundation of C. nigricornis. Furthermore, we also identified 112 candidate olfactory-related genes in the transcriptomes of C. nigricornis for the first time, including 20 OBPs, 10 CSPs, 71 ORs, eight IRs and three SNMPs. The numbers of candidate olfactory-related genes identified in the transcriptomes of C. nigricornis were similar to the numbers of candidate olfactory-related genes identified in the transcriptomes of O. asiaticus (15 OBPs, 60 ORs, 6 IRs and 3 SNMPs) [42, 51], but less than that identified in the genome of L. migratoria (22 OBPs, 142 ORs and 32 IRs) [35, 52]. One possible reason for this finding is that the olfactory-related genes in C. nigricornis and O. asiaticus were identified from transcriptome data, and these genes are usually expressed at low levels in transcriptome studies. One limiting factor in transcriptome sequencing is the inaccurate detection of genes with low transcriptional abundance, which may lead to the deletion of genes with relatively low expression levels [53]. However, the sequencing method or depth used in the genomic data of L. migratoria may have allowed the detection of genes with lower expression levels.
It has been demonstrated that OBPs increase the sensitivity of odor for insects and mediate the recognition and discrimination of odor compounds [54]. In this study, we identified 20 OBPs in C. nigricornis, differing from 22, 18, 15 and 14 OBPs identified in L. migratoria [52], O. infernalis [43], O. asiaticus [42] and S. gregaria [55], respectively. This may reflect that different insects evolved different physiological behaviors in the process of adapting to various environments, which might lead to divergent evolutionary trajectories of olfactory genes of the same ancestry, resulting in different functional genes among species [18]. Orthopteran insects possess a significantly smaller expansion of the OBP family than Dipteran insects, such as D. melanogaster [56] containing 51 OBPs and Aedes aegypti [57] containing 66 OBPs. However, this reduced number of OBPs seems to be balanced by the expansion of the CSP family, of which a large number of CSPs (70) were reported in the oriental locust L. migratoria [58]. This finding indicates the specific physiological and evolutionary level of the Orthopteran olfactory system.
Based on the RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR results, most OBPs identified in C. nigricornis were higher expressed in antennae than in other tissues, indicating that these OBPs might play roles in the recognition of sex pheromones and host volatile compounds, as in other insect species (Figs. 2b and 3) [59, 60]. Moreover, the expression profiles of most OBPs in the antennae showed male-biased expression, suggesting their possible crucial roles in detecting female pheromone and mating behavior (Fig. 3) [19]. However, we also found that several OBPs were more highly expressed in the head and legs, suggesting that these OBPs might participate in other physiological functions [43]. Among them, CnigOBP1, CnigOBP12 and CnigOBP19 were much more highly expressed in head tissues than in other tissues. The head tissues used in this study still contained other chemosensory organs, such as labium, maxillary palp, labial palp and proboscis, even though their antennae were cut off. Previous studies have suggested that the OBPs expressed in mouthparts and proboscis are associated with gustatory responses [61, 62]. This indicated that CnigOBP1, CnigOBP12 and CnigOBP19 might play important roles in taste functions.
CSPs have similar functions to OBPs in chemical communication in insects, as they bind small molecules, such as pheromones and odorants, and transport them to chemoreceptors [21]. However, CSPs usually exhibit much broader expression profiles than OBPs both in olfactory tissues and nonolfactory tissues and play multiple important roles in biological processes such as ecdysis, leg regeneration and embryo maturation [15, 25, 63]. An interesting example of the diverse roles of CSPs was observed in the locust L. migratoria, in which several CSPs showed increased expression in gregarious locusts, but these CSPs displayed contrasting expression trends when the locusts underwent the physiological transformation from the ‘gregarious’ phase to the ‘solitary’ phase, which indicated that CSPs are one factor triggering locust phase shift [23]. Our results show that CnigCSP1, CnigCSP2, CnigCSP3 and CnigCSP4 were antennae-enriched, and these four CSPs might be involved in the chemosensory process (Fig. 4). In addition, in nonolfactory tissues, the expression profiles of C. nigricornis CSPs were much broader than those of C. nigricornis OBPs (Figs. 3 and 4). CnigCSP6/7/9 showed higher expression in both antennae and legs, CnigCSP5 was mainly expressed in the legs, CnigCSP8 was predominantly expressed in the head and CnigCSP10 was highly expressed in the antennae, head and legs. We speculate that the broad and diverse expression patterns of C. nigricornis CSPs might have other crucial physiological functions, which need further functional verification.
ORs are usually expressed in the dendrites of antennal sensilla and act as biotransducers to convert chemical signals of odorant molecules into electrical signals [64]. To transmit odor-evoked signals, two types of ORs are required: one is a highly conserved ORco, and the other is a specific OR, which varies according to ORN type [65, 66]. In this study, we identified 70 specific ORs and a conserved ORco, and the RNA-Seq results showed that all ORs were highly expressed in the antennae, except CnigOR69, which were relatively highly expressed in nonolfactory leg tissues (Fig. 2a). The antennae-biased ORs may play an important role in odorant reception in antennae or be involved in the olfactory sensing process [67], and the nonolfactory tissues highly expressed ORs, which suggests that they may participate in other physiological processes in addition to olfaction [53]. Moreover, we also investigated the distribution of OR expression patterns in female and male tissues with qRT-PCR analyses. The expression profiles showed that all 12 randomly selected ORs were strongly expressed in the antennae, which was consistent with the results of RNA-Seq. Among the 12 ORs, four CnigOR genes (CnigOR13/18/R37/70) showed male-biased expression, suggesting that they may play a role in female pheromone detection and mating behavior, whereas four CnigOR genes (CnigOR10/20/32/35) displayed female-biased expression predicted to function in oviposition-related odorant detection [68, 69] (Fig. 5).
IRs, a new subfamily of ORs, are involved in not only olfaction but also gustation, hygrosensation and thermosensation, which are widely distributed throughout the body, including the labellum, leg, pharynx, and wing sensilla [70–74]. We identified eight IRs in C. nigricornis, of which CnigIR2 were not differentially expressed in different tissues, suggesting that this IR may have multiple functions. Except for CnigIR5, all differentially expressed IRs were strongly expressed in antennae (Fig. 2d). Recent studies have shown that antennae-enriched IRs play important roles in odor and thermosensation [75], the antennae-enriched IRs of C. nigricornis that were identified in our study may have similar roles.
We also identified three SNMPs, and the FPKM-value showed that all SNMPs were strongly expressed in antennae, indicating that they may be involved in the process of olfaction. However, CnigSNMP1 and CnigSNMP2 were also broadly expressed in nonolfactory tissues, including head, leg, wing and abdomen-thorax tissues (Fig. 2e). Similar patterns were also observed in other studies of D. melanogaster, A. aegypti, Spodoptera litura and Cnaphalocrocis medinalis [76–80]. The broad expression patterns of SNMP1 and SNMP2 imply that they may not only function in odorant perception, but also have different functions specific to the various tissues [78]. The exact role for CnigSNMP1 and CnigSNMP2 in olfactory and nonolfactory tissues remains inconclusive and requires further investigation.
Conclusions
The 112 candidate olfactory-related genes that we identified from C. nigricornis compose the comprehensive list of olfactory-related genes in this bamboo pest of C. nigricornis. Sex- and tissue-specific expression profiling revealed that most of the candidate olfactory-related genes were antennae-enriched, but some were nonantennae-enriched, and some were sex-biased, indicating their different roles in the olfactory system of C. nigricornis. Our results provide a foundation to facilitate functional studies of these olfactory-related genes in C. nigricornis at the molecular level.
Methods
Species and tissues collection
All adult male and adult female specimens of C. nigricornis were collected in Xi’an, China, in August 2018. Different tissues, including antennae, head (antennae were cut off), abdomen-thorax, legs and wings, were dissected from female and male specimens, respectively. Each type of tissue sample was collected from nine individuals as an independent biological replicate for transcriptome sequencing. To minimize biological variance, three independent biological replicates were performed for each tissue sample. All tissue samples were immediately placed into enzyme-free centrifuge tubes, which were immersed in liquid nitrogen and stored at − 80 °C until further use.
RNA extraction, library construction and Illumina sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from each frozen tissue using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) following the protocol recommended by the manufacturer. RNA integrity and purity were determined with an Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies, CA, USA) and a Nano Drop 2000 (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA). The cDNA library construction and Illumina sequencing were carried out by the Biomarker Technology Company, Beijing, China. First, qualified RNA from each tissue was mixed in equal amounts. Then, the cDNA library was prepared using the NEBNext Ultra™ RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (NEB, USA), and the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system was used to assess the library. Finally, the amplified mRNA library was sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq X Ten platform to generate 150 bp paired-end reads.
De novo assembly and functional annotation
Prior to assembly, low-quality reads and adaptor reads were removed from raw data through in-house Perl scripts to obtain clean reads. Then, the clean reads were de novo assembled using Trinity v2.4.0 [81] with default parameters except that ‘min_kmer_cov’ set to 2. Next, cd-hit-est v4.6.1 software [82] was used to remove duplicate and highly similar sequences to obtain nonredundant unigenes. Furthermore, the completeness of the nonredundant unigenes was assessed using BUSCO v3.0.2 software [48], and the insect lineage database (insecta_orthoDB9, created 13/02/2016) was used as a proxy for the minimum completeness assessment library.
BLAST v2.2.23 software [83] was used to search and annotate all assembled unigenes with the publicly available protein databases, including NR, Swiss-Prot, KEGG, KOG, COG and EggNOG, and an E-value cut-off of 1.0E-05. KOBAS2.0 was used to obtain KEGG Orthology results of unigenes in the KEGG annotation. Blast2GO [84] was used for GO annotation based on the protein annotation results of the NR database. For the GO classifications, the default parameters were used (E-value <1E-5, an annotation cut-off > 5 and a GO weight > 5). After the amino acid sequences of the unigenes were obtained, HMMER [85] software (E-value ≤1E-10) was used to BLAST search against the Pfam database to obtain the annotation information of unigenes.
Identification of olfactory-related genes
Olfactory-related genes from the transcriptomes of C. nigricornis were identified by the functional annotation results. To obtain more information, a tBLASTn program was also performed using available olfactory proteins from Orthoptera species as queries to identify candidate unigenes. All candidate olfactory genes were manually confirmed using the BLASTx program against the NR database at NCBI (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). The ORFs of candidate ORs, IRs, SNMPs, OBPs and CSPs were predicted using ORF Finder (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/). The N-terminal signal peptides and conserved domains of candidate OBPs and CSPs were predicted by the SignalP V 4.1 program (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/) [86] and SMART (simple modular architecture research tool, http://smart.embl.de/) [87], respectively. TMHMM Server Version 2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/) was used to predict the TMDs of candidate ORs, IRs and SNMPs.
Phylogenetic analysis
Phylogenetic analysis was performed based on the amino acid sequences of C. nigricornis olfactory-related genes using MEGA7.0 software [88]. The maximum likelihood method with Jones-Taylor-Thornton (JTT) model was used to create the phylogenetic trees. Branch support was assessed by bootstrapping with 1000 replicates. All the amino acid sequences used to construct the phylogenetic tree are shown in Additional file 3.
Differential expression analysis
Using the assembled transcriptome as reference sequences, the clean data from various samples of C. nigricornis were mapped back onto the reference sequences using Bowtie2 v2.1.0 software [89]. The unigene expression levels among various samples were estimated by RSEM [90] according to the readcount values of the unigenes for each sample, which were obtained from the mapping results. FPKM values can eliminate the effects of the sequencing depth and transcript length on readcounts. To make the unigene expression levels of various samples comparable, all the readcounts were transformed into FPKM values.
To detect the differential expression of candidate olfactory-related genes among different tissues from transcriptomes of C. nigricornis, we used the antennae as the experimental tissue, and four other tissues (head, abdomen-thorax, leg, and wing) were used as control samples. Therefore, a total of four combinations were compared, including antennae vs. head, antennae vs. abdomen-thorax, antennae vs. leg and antennae vs. wing. The differential expression analysis of each comparison combination was analyzed by the DESeq R package (1.10.1) [91]. The resulting P values were adjusted using Benjamini and Hochberg’s approach for controlling the false discovery rate (FDR). In general, the fold change (log2 ratio) and adjusted P value (FDR) were used as the key indexes for screening DEGs. In this study, |log2 (Fold Change)| > 2 and adjusted P value < 0.05 were used as the thresholds for identifying significant DEGs. The log2-transformed FPKM values of the DEGs were used for hierarchical clustering using the pheatmap R package. GO enrichment analysis of DEGs was implemented by the topGO R package-based Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
Expression profile analysis
To explore the tissue distribution expression pattern of olfactory-related genes in female and male adults and to verify the accuracy of transcriptome analysis, qRT-PCR analysis was performed to evaluate the expression profiles of putative olfactory-related genes in different tissues of male and female C. nigricornis adults. Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent, and cDNA was synthesized by Goldenstar™ RT6 cDNA Synthesis Mix (TsingKe, Beijing, China) following the protocol recommended by the manufacturer. A total of 12 OBPs, all CSPs and 12 ORs were randomly selected for qRT-PCR analysis. To correct sample-to-sample variation, ß-actin was selected as the reference gene. The specific primers used in the qRT-PCR analysis were designed online (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/) (Additional file 1: Table S7). qRT-PCR was performed on the CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, USA) using 2 x T5 Fast qPCR Mix (TsingKe, Beijing, China) with the following conditions: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 1 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 60 °C for 15 s. Finally a melting curve of the PCR products was analyzed to confirm the specificity of the primers. Nontemplate negative control reactions (replacing cDNA with H2O) were included in each experiment. Three biological replicates with three technical replicates were conducted for all experiments.
The results were analyzed using the BIO-RAD CFX Manager software. The relative quantification among all tissues was calculated by the comparative 2-△△CT method [92]. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s test were performed for the comparative analyses of each gene among different tissues, and Student’s t-test was used to analyze each gene in the same tissue from females and males. Both analyses were performed by SPSS Statistics 18.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. The summary of the Illumina sequencing data. Note: FA: female antennae; MA: male antennae; FH: female head (antennae were cut off); MH: male head (antennae were cut off); FL: female leg; ML: male leg; FW: female wing; MW: male wing; FT: female abdomen-thorax; MT: male abdomen-thorax. Representation of three biological repeats with Arabic numbers 1, 2 and 3. Table S2. Length distribution and quality metrics of C. nigricornis transcripts and unigenes. Table S3. BUSCO analyzed the assembly completeness of C. nigricornis. Table S4. The summary of functional annotation of C. nigricornis transcriptomes. Table S5. Conserved domains of odorant binding proteins (OBPs) in C. nigricornis. Table S6. Conserved domains of chemosensory proteins (CSPs) in C. nigricornis. Table S7. Primers used for qRT-PCR.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. Insect species distribution of C. nigricornis unigenes’ best-hit annotation term in NR database. Figure S2. Gene ontology (GO) classifications of C. nigricornis unigenes. Figure S3. Alignments of the C. nigricornis odorant binding proteins (OBPs). Boxes show the six conserved cysteine residues. Figure S4. Alignments of the C. nigricornis chemosensory proteins (CSPs). Boxes show the four conserved cysteine residues. Figure S5. Phylogenetic tree of odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. C. kiangsu (Ckia), L. migratoria (Lmig), O. asiaticus (Oasi), O. infernalis (Oinf), S. gregaria (Sgre), A. glycines (Agly), D. ponderosae (Dpon) and H. armigera (Harm). The OBPs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S6. Phylogenetic tree of chemosensory-binding proteins (CSPs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. Table S2. L. migratoria (Lmig), O. asiaticus (Oasi), O. infernalis (Oinf), A. gambiae (Agam), D. ponderosae (Dpon) and H. armigera (Harm). The CSPs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S7. Phylogenetic tree of odorant receptors (ORs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. Table S3. L. migratoria (Lmig) and A. lineolatus (Alin). The ORs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S8. Phylogenetic tree of ionotropic receptors (IRs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. L. migratoria (Lmig), O. asiaticus (Oasi), A. lineolatus (Alin) and D. melanogaster (Dmel). The IRs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S9. Phylogenetic tree of sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. A. lineolatus (Alin), A. aegypti (Aaeg), A. mellifera (Amel), B. mori (Bmor), D. melanogaster (Dmel), O. asiaticus (Oasi), S. gregaria (Sgre) and T. castaneum (Tcas). The SNMPs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font.
Additional file 3: Table S1. Amino acid sequences of 121 OBPs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S2. Amino acid sequences of 87 CSPs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S3. Amino acid sequences of 293 ORs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S4. Amino acid sequences of 115 IRs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S5. Amino acid sequences of 24 SNMPs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree.
Acknowledgements
We thank Xue Zhang for assisting us in collecting specimens and Yingchun Lu for assisting us in plotting data.
Abbreviations
- CSPs
Chemosensory binding proteins
- DEGs
Differentially expressed genes
- FPKM
Fragments per kilobase per million mapped fragments
- GO
Gene Ontology
- IR
Ionotropic receptor
- OBP
Odorant-binding protein
- OR
Odorant receptor
- ORF
Open reading frame
- qRT-PCR
Quantitative realtime polymerase chain reaction
- SNMP
Sensory neuron membrane protein
Authors’ contributions
YH and HY conceived and designed the experiments. HY conducted the experiments and wrote the paper. HHC, LNZ, CY analyzed the data. YH, HHC and HY discussed the results. YH identified insects. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31872217, 31372192) to Yuan Huang.
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that the data supporting the finding of this study are available in the article and its supplementary information files. The olfactory-related genes we identified from Ceracris nigricornis were all submitted to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) with the accession numbers were listed in Tables 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The Transcriptome Shotgun Assembly project has been deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession GHNZ00000000. The version described in this paper is the first version, GHNZ01000000. The raw data submitted to the NCBI with the accession numbers of SRR9089653, SRR9089654, SRR9089655, SRR9089656, SRR9089657, SRR9089658, SRR9089659, SRR9089660, SRR9089661, SRR9089662, SRR9089663, SRR9089664, SRR9089665, SRR9089666, SRR9089667, SRR9089668, SRR9089669, SRR9089670, SRR9089671, SRR9089672, SRR9089673, SRR9089674, SRR9089675, SRR9089676, SRR9089677, SRR9089678, SRR9089679, SRR9089680, SRR9089681, SRR9089682.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Hao Yuan, Email: yuanhao@snnu.edu.cn.
Huihui Chang, Email: chh127@snnu.edu.cn.
Lina Zhao, Email: 15529270320@163.com.
Chao Yang, Email: chaoy819@163.com.
Yuan Huang, Email: yuanh@snnu.edu.cn.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12864-019-6208-x.
References
- 1.Qiu Z, Liu F, Lu H, Yuan H, Zhang Q, Huang Y. De novo assembly and characterization of the transcriptome of grasshopper Shirakiacris shirakii. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):1110. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bian L, Sun X, Luo Z, Zhang Z, Chen Z. Design and selection of trap color for capture of the tea leafhopper, Empoasca vitis, by orthogonal optimization. Entomologia Experimentalis Et Applicata. 2014;151(3):247–258. doi: 10.1111/eea.12191. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cai X, Xu X, Bian L, Luo Z, Chen Z. Measurement of volatile plant compounds in field ambient air by thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(30):9105–9114. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-9076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jin S, Chen ZM, Backus EA, Sun XL, Xiao B. Characterization of EPG waveforms for the tea green leafhopper, Empoasca vitis Göthe (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae), on tea plants and their correlation with stylet activities. J Insect Physiol. 2012;58(9):1235–1244. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2012.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Song T, Wang K, Peng W, Wang J, Xiao R, Zeng F, Tang Y. Ecological effects of intercropping white clover on tea plantation in a subtropical hilly region. Acta Ecol Sin. 2006;26(11):3647–3655. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ji X, Wang M, Jiang L, Han B. Similarity and disparity of arthropod community compositions among ten tea-intercropping plantations with different species of fruits in the Dongtingshan Mountains, Taihu Lake. Chin J Appl Entomol. 2011;48(5):1471–1478. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ye H, Cui L, He X, Han B. Effect of intercropping tea with citrus, waxberry, or snake gourd on population density and spatial distribution of the tea green leafhopper and araneids. Acta Ecol Sinica. 2010;30:6019–6026. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vieira FG, Foreˆt S, He X, Rozas J, Field LM, Zhou J-J. Unique features of odorant-binding proteins of the parasitoid wasp Nasonia vitripennis revealed by genome annotation and comparative analyses. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deisig N, Kropf J, Vitecek S, Pevergne D, Rouyar A, Sandoz J, Lucas P, Gadenne C, Anton S, Barrozo R. Differential interactions of sex pheromone and plant odour in the olfactory pathway of a male moth. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Binyameen M, Hussain A, Yousefi F, Birgersson G, Schlyter F. Modulation of reproductive behaviors by non-host volatiles in the polyphagous Egyptian cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis. J Chem Ecol. 2013;39(10):1273–1283. doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Leal WS. Odorant reception in insects: roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu Rev Entomol. 2013;58:373–391. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-120811-153635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Justice R, Dimitratos S, Walter M, Woods D, Biessmann H. Sexual dimorphic expression of putative antennal carrier protein genes in the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol Biol. 2003;12(6):581–594. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2583.2003.00443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pelosi P, Iovinella I, Felicioli A, Dani FR. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: an overview across arthropods. Front Physiol. 2014;5:320. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vieira FG, Rozas J. Comparative genomics of the odorant-binding and chemosensory protein gene families across the Arthropoda: origin and evolutionary history of the chemosensory system. Genome Biol Evol. 2011;3:476–490. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evr033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pelosi P, Iovinella I, Zhu J, Wang G, Dani FR. Beyond chemoreception: diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol Rev. 2018;93(1):184–200. doi: 10.1111/brv.12339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Angeli S, Ceron F, Scaloni A, Monti M, Monteforti G, Minnocci A, Petacchi R, Pelosi P. Purification, structural characterization, cloning and immunocytochemical localization of chemoreception proteins from Schistocerca gregaria. Eur J Biochem. 1999;262(3):745–754. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zeng Y, Yang YT, Wu QJ, Wang SL, Xie W, Zhang YJ. Genome-wide analysis of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in the sweet potato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Insect Sci. 2019;26(4):620–634. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li X-M, Zhu X-Y, Wang Z-Q, Wang Y, He P, Chen G, Sun L, Deng D-G, Zhang Y-N. Candidate chemosensory genes identified in Colaphellus bowringi by antennal transcriptome analysis. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):1028. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2236-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brito NF, Moreira MF, Melo AC. A look inside odorant-binding proteins in insect chemoreception. J Insect Physiol. 2016;95:51–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2016.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wanner KW, Willis LG, Theilmann DA, Isman MB, Feng Q, Plettner E. Analysis of the insect os-d-like gene family. J Chem Ecol. 2004;30(5):889–911. doi: 10.1023/B:JOEC.0000028457.51147.d4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pelosi P, Calvello M, Ban L. Diversity of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in insects. Chem Senses. 2005;30(Suppl 1):i291–i292. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjh229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gong D-P, Zhang H-j, Zhao P, Lin Y, Xia Q-Y, Xiang Z-H. Identification and expression pattern of the chemosensory protein gene family in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2007;37(3):266–277. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.11.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Guo W, Wang X, Ma Z, Xue L, Han J, Yu D, Kang L. CSP and takeout genes modulate the switch between attraction and repulsion during behavioral phase change in the migratory locust. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(2):e1001291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang Y-N, Jin J-Y, Jin R, Xia Y-H, Zhou J-J, Deng J-Y, Dong S-L. Differential expression patterns in chemosensory and non-chemosensory tissues of putative chemosensory genes identified by transcriptome analysis of insect pest the purple stem borer Sesamia inferens (Walker) PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e69715. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cheng D, Lu Y, Zeng L, Liang G, He X. Si-CSP9 regulates the integument and moulting process of larvae in the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9245. doi: 10.1038/srep09245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Clyne PJ, Warr CG, Freeman MR, Lessing D, Kim J, Carlson JR. A novel family of divergent seven-transmembrane proteins: candidate odorant receptors in Drosophila. Neuron. 1999;22(2):327–338. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Benton R, Vannice KS, Gomez-Diaz C, Vosshall LB. Variant ionotropic glutamate receptors as chemosensory receptors in Drosophila. Cell. 2009;136(1):149–162. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Depan Cao YL, Wei J, Liao X, Walker WB, Li J, Wang G. Identification of candidate olfactory genes in Chilo suppressalis by antennal transcriptome analysis. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(8):846. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.9297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhao H, Du Y, Gao P, Wang S, Pan J, Jiang Y. Antennal transcriptome and differential expression analysis of five chemosensory gene families from the Asian honeybee Apis cerana cerana. PLoS One. 2016;11(10):e0165374. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gomez-Diaz C, Bargeton B, Abuin L, Bukar N, Reina JH, Bartoi T, Graf M, Ong H, Ulbrich MH, Masson J-F. A CD36 ectodomain mediates insect pheromone detection via a putative tunnelling mechanism. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11866. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Forstner M, Gohl T, Gondesen I, Raming K, Breer H, Krieger J. Differential expression of SNMP-1 and SNMP-2 proteins in pheromone-sensitive hairs of moths. Chem Senses. 2008;33(3):291–299. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjm087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rogers ME, Krieger J, Vogt RG. Antennal SNMPs (sensory neuron membrane proteins) of lepidoptera define a unique family of invertebrate CD36-like proteins. J Neurobiol. 2001;49(1):47–61. doi: 10.1002/neu.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Camacho JM, Ruiz-Ruano F, Martín-Blázquez R, López-León M, Cabrero J, Lorite P, Cabral-de-Mello D, Bakkali M. A step to the gigantic genome of the desert locust: chromosome sizes and repeated DNAs. Chromosoma. 2015;124(2):263–275. doi: 10.1007/s00412-014-0499-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dufresne F, Jeffery N. A guided tour of large genome size in animals: what we know and where we are heading. Chromosom Res. 2011;19(7):925–938. doi: 10.1007/s10577-011-9248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang X, Fang X, Yang P, Jiang X, Jiang F, Zhao D, Li B, Cui F, Wei J, Ma C. The locust genome provides insight into swarm formation and long-distance flight. Nat Commun. 2014;5:2957. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hittinger CT, Johnston M, Tossberg JT, Rokas A. Leveraging skewed transcript abundance by RNA-Seq to increase the genomic depth of the tree of life. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107(4):1476–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910449107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ban L, Scaloni A, D'ambrosio C, Zhang L, Yan Y, Pelosi P. Biochemical characterization and bacterial expression of an odorant-binding protein from Locusta migratoria. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003;60(2):390–400. doi: 10.1007/s000180300032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jin X, Brandazza A, Navarrini A, Ban L, Zhang S, Steinbrecht RA, Zhang L, Pelosi P. Expression and immunolocalisation of odorant-binding and chemosensory proteins in locusts. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62(10):1156–1166. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5014-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yu Y, Cui X, Jiang Q, Jin X, Guo Z, Zhao X, Bi Y, Zhang L. New isoforms of odorant-binding proteins and potential semiochemicals of locusts. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2007;65(1):39–49. doi: 10.1002/arch.20176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yu Y, Zhang S, Zhang L, Zhao X. Developmental expression of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in the embryos of Locusta migratoria. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2009;71(2):105–115. doi: 10.1002/arch.20303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li J, Zhang L, Wang X. An odorant-binding protein involved in perception of host plant odorants in locust Locusta migratoria. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2016;91(4):221–229. doi: 10.1002/arch.21319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang S, Pang B, Zhang L. Novel odorant-binding proteins and their expression patterns in grasshopper, Oedaleus asiaticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;460(2):274–280. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang Y, Tan Y, Zhou X-R, Pang B-P. A whole-body transcriptome analysis and expression profiling of odorant binding protein genes in Oedaleus infernalis. Comp Biochem Physiol D Genomics Proteomics. 2018;28:134–141. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2018.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li R, Jiang G-F, Dong S-Y. A head transcriptome provides insights into odorant binding proteins of the bamboo grasshopper. Genes Genomics. 2018;40(9):991–1000. doi: 10.1007/s13258-018-0706-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tomaselli S, Crescenzi O, Sanfelice D, Wechselberger R, Angeli S, Scaloni A, Boelens R, Tancredi T, Pelosi P, Picone D. Solution structure of a chemosensory protein from the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria. Biochemistry. 2006;45(35):10606–10613. doi: 10.1021/bi060998w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yang Y, Krieger J, Zhang L, Breer H. The olfactory co-receptor Orco from the migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) and the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria): identification and expression pattern. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):159. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.8.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Guo M, Krieger J, Große-Wilde E, Mißbach C, Zhang L, Breer H. Variant ionotropic receptors are expressed in olfactory sensory neurons of coeloconic sensilla on the antenna of the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria) Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(1):1. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM. BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(19):3210–3212. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mortazavi A, Williams BA, Mccue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 2008;5(7):621. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hansson BS, Stensmyr MC. Evolution of insect olfaction. Neuron. 2011;72(5):698–711. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhou Y-T, Li L, Zhou X-R, Tan Y, Pang B-P. Identification and expression profiling of candidate chemosensory membrane proteins in the band-winged grasshopper, Oedaleus asiaticus. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2019;30:33–44. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2019.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang Z, Yang P, Chen D, Jiang F, Li Y, Wang X, Kang L. Identification and functional analysis of olfactory receptor family reveal unusual characteristics of the olfactory system in the migratory locust. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72(22):4429–4443. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2009-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Li K, Wei H, Shu C, Zhang S, Cao Y, Luo C, Yin J. Identification and comparison of candidate odorant receptor genes in the olfactory and non-olfactory organs of Holotrichia oblita Faldermann by transcriptome analysis. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2017;24:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2017.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Laughlin JD, Ha TS, Jones DN, Smith DP. Activation of pheromone-sensitive neurons is mediated by conformational activation of pheromone-binding protein. Cell. 2008;133(7):1255–1265. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jiang X, Krieger J, Breer H, Pregitzer P. Distinct subfamilies of odorant binding proteins in locust (Orthoptera, Acrididae): molecular evolution, structural variation, and sensilla-specific expression. Front Physiol. 2017;8:734. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hekmat-Scafe DS, Scafe CR, McKinney AJ, Tanouye MA. Genome-wide analysis of the odorant-binding protein gene family in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 2002;12(9):1357–1369. doi: 10.1101/gr.239402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhou JJ, He XL, Pickett J, Field L. Identification of odorant-binding proteins of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti: genome annotation and comparative analyses. Insect Mol Biol. 2008;17(2):147–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2007.00789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhou X-H, Ban L-P, Iovinella I, Zhao L-J, Gao Q, Felicioli A, Sagona S, Pieraccini G, Pelosi P, Zhang L. Diversity, abundance, and sex-specific expression of chemosensory proteins in the reproductive organs of the locust Locusta migratoria manilensis. Biol Chem. 2013;394(1):43–54. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Swarup S, Williams TI, Anholt RR. Functional dissection of odorant binding protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Brain Behav. 2011;10(6):648–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2011.00704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Guo W, Ren D, Zhao L, Jiang F, Song J, Wang X, Kang L. Identification of odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) and functional analysis of phase-related OBPs in the migratory locust. Frontiers in physiology. 2018;9:984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 61.DelCampo ML, Palmer S, Caillaud M. Characterization of a new odorant binding protein gene in gustatory organs of Manduca sexta larvae (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae) Ann Entomol Soc Am. 2011;104(2):319–325. doi: 10.1603/AN10091. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Shanbhag S, Park S-K, Pikielny C, Steinbrecht R. Gustatory organs of Drosophila melanogaster: fine structure and expression of the putative odorant-binding protein PBPRP2. Cell Tissue Res. 2001;304(3):423–437. doi: 10.1007/s004410100388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Maleszka J, Foret S, Saint R, Maleszka R. RNAi-induced phenotypes suggest a novel role for a chemosensory protein CSP5 in the development of embryonic integument in the honeybee (Apis mellifera) Dev Genes Evol. 2007;217(3):189–196. doi: 10.1007/s00427-006-0127-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhang D-D, Löfstedt C. Moth pheromone receptors: gene sequences, function, and evolution. Front Ecol Evol. 2015;3:105. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2015.00105. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bengtsson JM, Trona F, Montagné N, Anfora G, Ignell R, Witzgall P, Jacquin-Joly E. Putative chemosensory receptors of the codling moth, Cydia pomonella, identified by antennal transcriptome analysis. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Jones PL, Pask GM, Rinker DC, Zwiebel LJ. Functional agonism of insect odorant receptor ion channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108(21):8821–8825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102425108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Leal WS, Choo Y-M, Xu P, da Silva CS, Ueira-Vieira C. Differential expression of olfactory genes in the southern house mosquito and insights into unique odorant receptor gene isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110(46):18704–18709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1316059110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Nakagawa T, Sakurai T, Nishioka T, Touhara K. Insect sex-pheromone signals mediated by specific combinations of olfactory receptors. Science. 2005;307(5715):1638–1642. doi: 10.1126/science.1106267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Grosjean Y, Rytz R, Farine J-P, Abuin L, Cortot J, Jefferis GS, Benton R. An olfactory receptor for food-derived odours promotes male courtship in Drosophila. Nature. 2011;478(7368):236. doi: 10.1038/nature10428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Depetris-Chauvin A, Galagovsky D, Grosjean Y. Chemicals and chemoreceptors: ecologically relevant signals driving behavior in Drosophila. Front Ecol Evol. 2015;3:41. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2015.00041. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ganguly A, Pang L, Duong V-K, Lee A, Schoniger H, Varady E, Dahanukar A. A molecular and cellular context-dependent role for Ir76b in detection of amino acid taste. Cell Rep. 2017;18(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Koh T-W, He Z, Gorur-Shandilya S, Menuz K, Larter NK, Stewart S, Carlson JR. The Drosophila IR20a clade of ionotropic receptors are candidate taste and pheromone receptors. Neuron. 2014;83(4):850–865. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.07.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Knecht ZA, Silbering AF, Cruz J, Yang L, Croset V, Benton R, Garrity PA. Ionotropic receptor-dependent moist and dry cells control hygrosensation in Drosophila. Elife. 2017;6:e26654. doi: 10.7554/eLife.26654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ni L, Klein M, Svec KV, Budelli G, Chang EC, Ferrer AJ, Benton R, Samuel AD, Garrity PA. The ionotropic receptors IR21a and IR25a mediate cool sensing in Drosophila. Elife. 2016;5:e13254. doi: 10.7554/eLife.13254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Rimal S, Lee Y. The multidimensional ionotropic receptors of Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Mol Biol. 2018;27(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/imb.12347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Benton R, Vannice KS, Vosshall LB. An essential role for a CD36-related receptor in pheromone detection in Drosophila. Nature. 2007;450(7167):289. doi: 10.1038/nature06328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Jin X, Ha TS, Smith DP. SNMP is a signaling component required for pheromone sensitivity in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105(31):10996–11001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803309105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Vogt RG, Miller NE, Litvack R, Fandino RA, Sparks J, Staples J, Friedman R, Dickens JC. The insect SNMP gene family. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;39(7):448–456. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Zhang J, Liu Y, Walker WB, Dong SL, Wang GR. Identification and localization of two sensory neuron membrane proteins from Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Insect Sci. 2015;22(3):399–408. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Liu S, Zhang YR, Zhou WW, Liang QM, Yuan X, Cheng J, Zhu ZR, Gong ZJ. Identification and characterization of two sensory neuron membrane proteins from Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2013;82(1):29–42. doi: 10.1002/arch.21069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng Q. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(7):644. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Li W, Godzik A. Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics. 2006;22(13):1658–1659. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25(17):3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(18):3674–3676. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Nastou KC, Tsaousis GN, Papandreou NC, Hamodrakas SJ. MBPpred: proteome-wide detection of membrane lipid-binding proteins using profile hidden Markov models. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-proteins and. Proteomics. 2016;1864(7):747–754. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Thomas Nordahl P. S?Ren B, Gunnar VH, Henrik N. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods. 2011;8(10):785–786. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Letunic I, Bork P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;46(D1):D493–D496. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33(7):1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009;10(3):R25. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Li B, Dewey CN. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12(1):323. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Anders S, Huber W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010;11(10):1–12. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. The summary of the Illumina sequencing data. Note: FA: female antennae; MA: male antennae; FH: female head (antennae were cut off); MH: male head (antennae were cut off); FL: female leg; ML: male leg; FW: female wing; MW: male wing; FT: female abdomen-thorax; MT: male abdomen-thorax. Representation of three biological repeats with Arabic numbers 1, 2 and 3. Table S2. Length distribution and quality metrics of C. nigricornis transcripts and unigenes. Table S3. BUSCO analyzed the assembly completeness of C. nigricornis. Table S4. The summary of functional annotation of C. nigricornis transcriptomes. Table S5. Conserved domains of odorant binding proteins (OBPs) in C. nigricornis. Table S6. Conserved domains of chemosensory proteins (CSPs) in C. nigricornis. Table S7. Primers used for qRT-PCR.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. Insect species distribution of C. nigricornis unigenes’ best-hit annotation term in NR database. Figure S2. Gene ontology (GO) classifications of C. nigricornis unigenes. Figure S3. Alignments of the C. nigricornis odorant binding proteins (OBPs). Boxes show the six conserved cysteine residues. Figure S4. Alignments of the C. nigricornis chemosensory proteins (CSPs). Boxes show the four conserved cysteine residues. Figure S5. Phylogenetic tree of odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. C. kiangsu (Ckia), L. migratoria (Lmig), O. asiaticus (Oasi), O. infernalis (Oinf), S. gregaria (Sgre), A. glycines (Agly), D. ponderosae (Dpon) and H. armigera (Harm). The OBPs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S6. Phylogenetic tree of chemosensory-binding proteins (CSPs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. Table S2. L. migratoria (Lmig), O. asiaticus (Oasi), O. infernalis (Oinf), A. gambiae (Agam), D. ponderosae (Dpon) and H. armigera (Harm). The CSPs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S7. Phylogenetic tree of odorant receptors (ORs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. Table S3. L. migratoria (Lmig) and A. lineolatus (Alin). The ORs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S8. Phylogenetic tree of ionotropic receptors (IRs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. L. migratoria (Lmig), O. asiaticus (Oasi), A. lineolatus (Alin) and D. melanogaster (Dmel). The IRs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font. Figure S9. Phylogenetic tree of sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs) from C. nigricornis and other insects. A. lineolatus (Alin), A. aegypti (Aaeg), A. mellifera (Amel), B. mori (Bmor), D. melanogaster (Dmel), O. asiaticus (Oasi), S. gregaria (Sgre) and T. castaneum (Tcas). The SNMPs of C. nigricornis are represented by red font.
Additional file 3: Table S1. Amino acid sequences of 121 OBPs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S2. Amino acid sequences of 87 CSPs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S3. Amino acid sequences of 293 ORs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S4. Amino acid sequences of 115 IRs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree. Table S5. Amino acid sequences of 24 SNMPs of Ceracris nigricornis and other insect species used to construct phylogenetic tree.
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that the data supporting the finding of this study are available in the article and its supplementary information files. The olfactory-related genes we identified from Ceracris nigricornis were all submitted to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) with the accession numbers were listed in Tables 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The Transcriptome Shotgun Assembly project has been deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession GHNZ00000000. The version described in this paper is the first version, GHNZ01000000. The raw data submitted to the NCBI with the accession numbers of SRR9089653, SRR9089654, SRR9089655, SRR9089656, SRR9089657, SRR9089658, SRR9089659, SRR9089660, SRR9089661, SRR9089662, SRR9089663, SRR9089664, SRR9089665, SRR9089666, SRR9089667, SRR9089668, SRR9089669, SRR9089670, SRR9089671, SRR9089672, SRR9089673, SRR9089674, SRR9089675, SRR9089676, SRR9089677, SRR9089678, SRR9089679, SRR9089680, SRR9089681, SRR9089682.