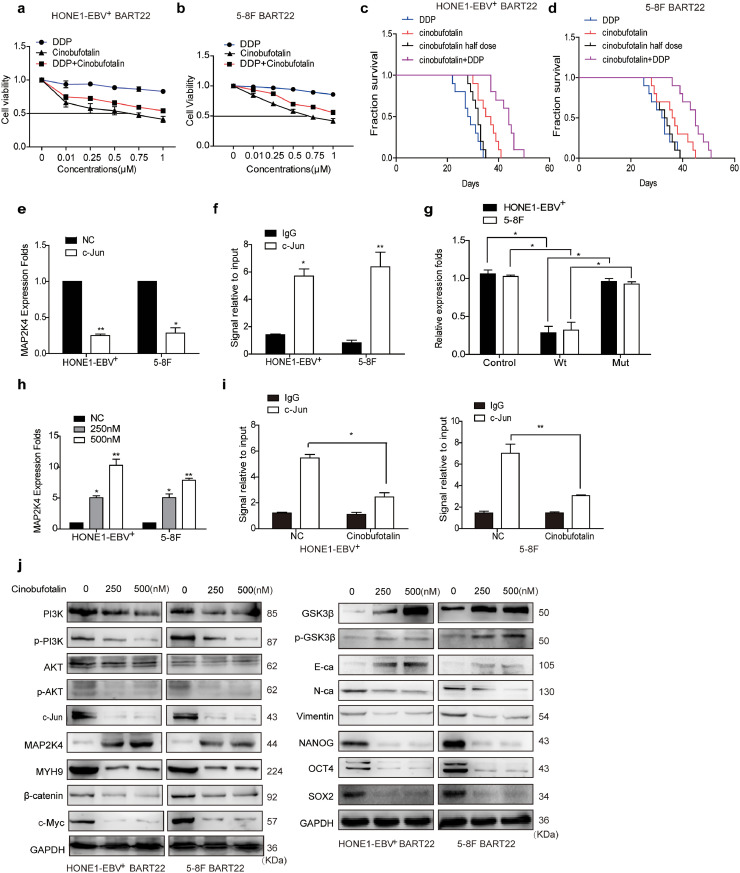
Fig. 6.
Cinobufotalin reversed EBV-miR-BART22-induced DDP resistanceby inducing the expression of MAP2K4.
(a)(b) Dose-response curves of HONE1-EBV+ and 5-8F treated with miR-BART22 48 h after treatment with DDP, cinobufotalin or DDP combined with cinobufotalin. Parametric generalized linear model with random effects. (c)(d) Animals were divided into four groups: DDP, Cinobufotalin, Cinobufotalin with half dose, and DDP combined with Cinobufotalin (each group: N = 10). Survival analysis was plotted. Log-rank test (P < .001). (e) QPCR analysis of MAP2K4 mRNA levels in HONE-EBV+ and 5-8F cells with c-Jun over-expressed or control (n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test). (f) ChIP analysis for c-Jun binding to the transcriptional regulatory region of MAP2K4 in HONE-EBV+ and 5-8F cells. (g) Luciferase reporter assays (n = 3 independent experiments, one-way ANOVA) were performed to confirm that c-Jun stimulated the activation of the MAP2K4 promoter. (h) QPCR analysis of MAP2K4 mRNA levels in HONE-EBV+ with cinobufotalin treated in 0.25, 0.5 μM or control (n = 3 independent experiments, Student's t-test). (i) ChIP analysis for c-Jun binding to the transcriptional regulatory region of MAP2K4 in HONE-EBV+ and 5-8F cells with cinobufotalin treatment. All data are presented as the mean ± SD. Experiments were repeated three times. (j) Western blot analysis of PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT, p-AKT, c-Jun, MAP2K4, MYH9, β-catenin, c-Myc, GSK3β, p-GSK3β, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin, Nanog, OCT4 and Sox2 expression in BART22-overexpressed NPC cells with cinobufotalin treatment in different dose.