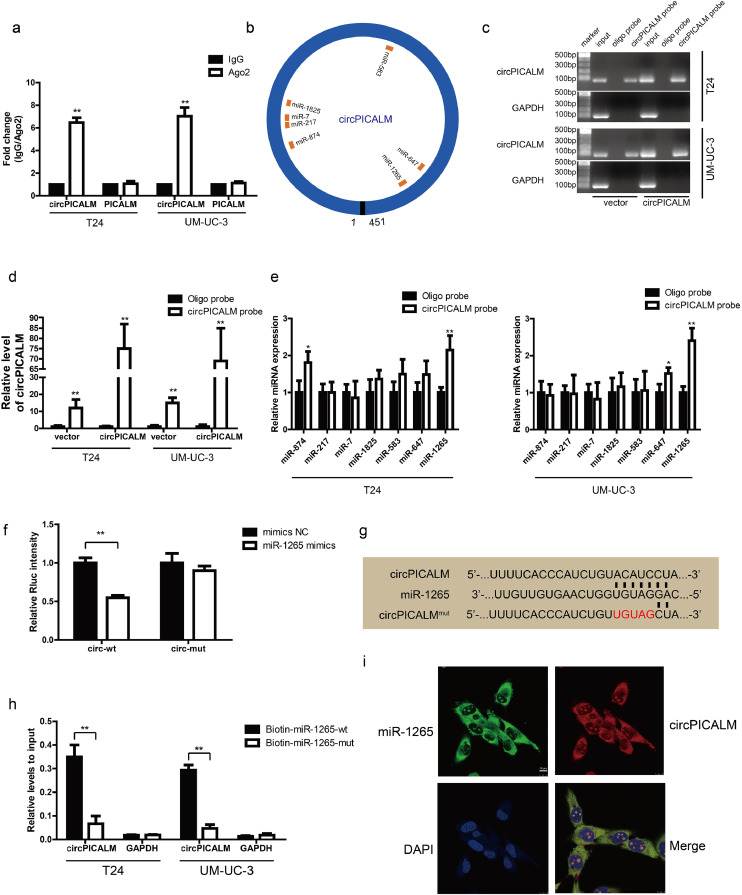
Fig. 4.
circPICALM binds to and sponges miR-1265.
a. RIP assay for circPICALM and PICALM mRNA fold changes in BC cells using anti-Ago2 or IgG antibodies. IgG was used as a negative control. b. Schematic illustration of the predicted binding sites between circPICALM and seven candidate miRNAs. c. and d. RNA pull-down assay with circPICALM or oligo probes, validated by gel electrophoresis and RT-PCR. e. Relative levels of seven candidate miRNAs in cell lysate pulled down by oligo or circPICALM probes were detected by RT-PCR. f. A dual-luciferase reporter assay in HEK-293 T cells to prove the interaction between circPICALM and miR-1265. Wild-type or mutant circPICALM sequences were cloned into psiCHECK-2 plasmids. Rluc intensity was normalized to firefly luciferase activity. g. Part of wild-type and mutant circPICALM sequences for the dual-luciferase reporter assay and the binding site for miR-1265. h. Biotin-labelled miR-1265 probe capture in circPICALM overexpression T24 and UM-UC-3 cells. The RNA abundance was measured by RT-PCR and normalized to input. i. Colocalization of miR-1265 and circPICALM in UM-UC-3 cells, demonstrated by FISH. Probe for miR-1265 was labelled by FAM and probe for circPICALM was labelled by cy3. Scale bar, 10 μm. (Data are presented as the mean ± SD, n = 3. Unpaired, two-tailed student's t-test, *P<0.05, **P<0.01).