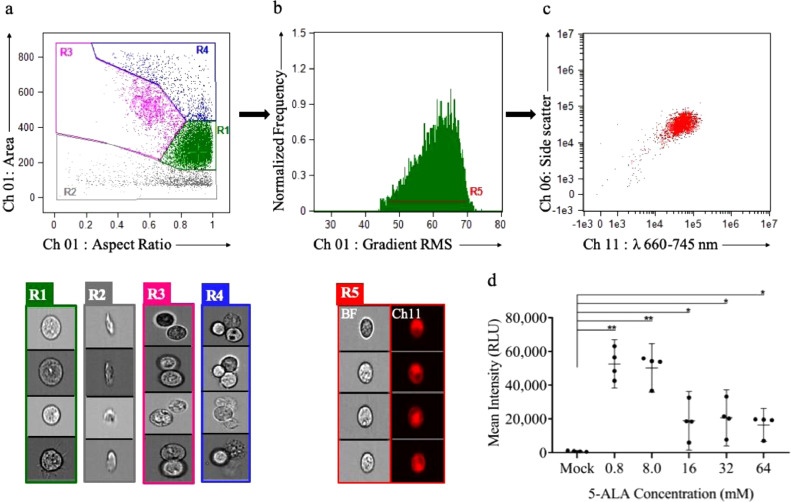
Fig. 2.
ISX analysis for glioma cells dosed with 5-ALA. Visual interrogation and gate setting to demonstrate PpIX fluorescence: (a) ISX scatter plot of Gli36 cells by aspect ratio (x-axis, shape and measure of circularity) vs. area (y-axis, size). Gate R1 (green): Single cells as detected by aspect ratio ∼1.0 and uniform area. Gate R2 (gray): Cell debris as detected by varying aspect ratio and low area. Gate R3 (pink): Doublet cells as detected by an aspect ratio ∼0.5 and high area. Gate R4(blue): Triplet cells as detected by an aspect ratio ∼1.0 and high area. Ch 01 brightfield images of cells (R1, green), cell debris (R2, gray), doublet cells (R3, pink), triplet cells (R4, blue). (b) The representative histogram of gradient RMS (Ch 01) vs. normalized frequency to identify cells in focus based on the sharpness of the image. Gate R5 (red): Gating of single cells in focus with PpIX fluorescence (Ch 11: λ 660–745 nm). R5-gated brightfield images (Ch 01) and corresponding fluorescence images (Ch 11) demonstrating PpIX fluorescence. (c) Scatter plot of fluorescence intensity (Ch 11) vs. side scatter (Ch 06) showing a homogeneous clustered population of focused, single cells demonstrating PpIX fluorescence (Ch11). (d) Dot-plot showing PpIX fluorescence (mean intensity in relative light units, RLU) of Gli36 cells at different 5-ALA doses showing maximal mean intensity at 0.8 mM. Data are mean 95% confidence interval (n = 4 biological replicates). *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)