Figure 7.
AnkG Allows for the Stable Accumulation of NF186 at the AIS by Inhibiting Its Endocytosis
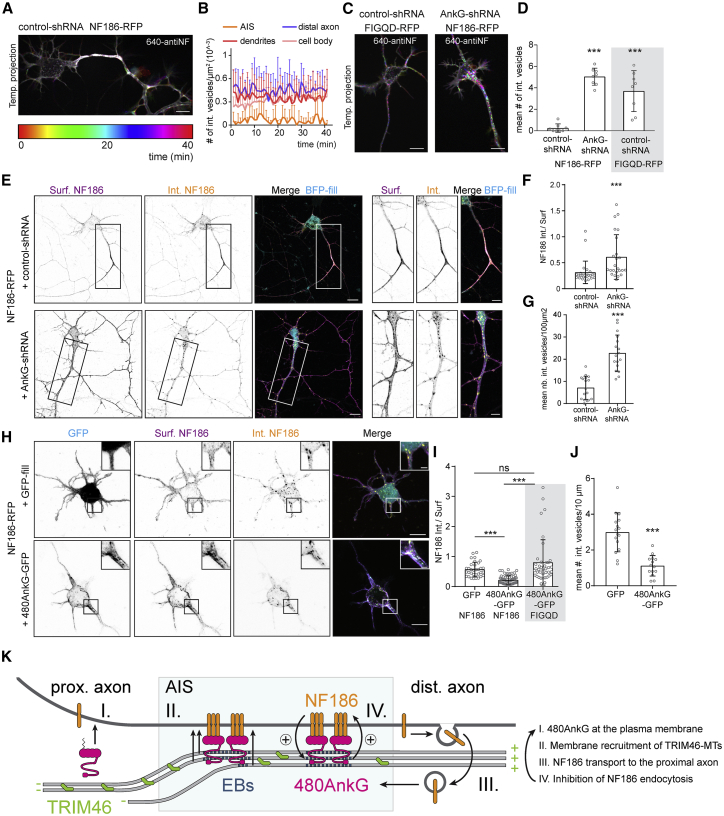
(A and B) Temporal-color coded maximum projection (A) from live imaging of a DIV4 neuron co-transfected at DIV0 with indicated constructs and incubated with a fluorescently tagged anti-NF antibody (640-antiNF). (B) Number of internalized NF vesicles in indicated compartments.
(C and D) Temporal-color coded maximum projections (C) from live imaging of DIV4 neurons co-transfected at DIV0 with indicated constructs incubated with 640-antiNF. (D) Mean number of 640-antiNF vesicles during the first 5 min post incubation in the proximal axons. One-way ANOVA, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001, n = 8 neurons, N = 2.
(E–G) DIV4 neurons (E) co-transfected at DIV0 with indicated constructs. (F) Fluorescence intensity ratio of internalized over surface NF186 in the proximal axon. (G) Mean number of internalized NF186 vesicles per 100 μm2 of axon. Mann-Whitney test, p = 1.7∗10–7 n = 17 axons.
(H–J) DIV1 neurons (H) transfected at DIV0 with indicated constructs. (I) Fluorescence intensity ratio of internalized over surface NF186 in the first 10 μm of proximal neurites. Kruskal-Wallis test, Dunn’s multiple comparison test. ns, p > 0.99, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001, n = 33 ROIs. (J) Number of internalized NF186 vesicles per 10 μm. Unpaired t test, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001, n = 14 neurons, N = 2.
(K) Model of the molecular pathways involved in AIS formation. See text for details.
In (A), (C), and (D), scale bars are 10 μm; in (E), scale bars are 10 and 2 μm in the zooms; and in (H), scale bars are 10 and 5 μm in the zooms. See also Figure S7.