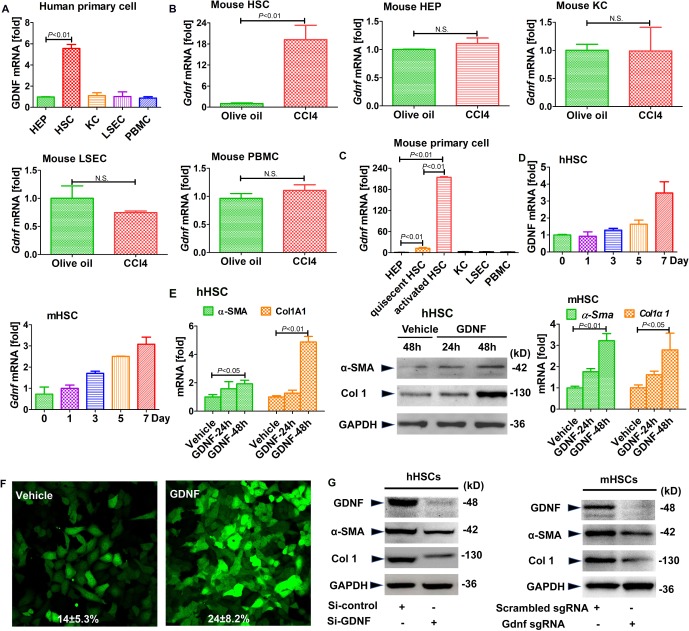
Figure 4.
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) induces hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation in human HSCs. Gdnf mRNA expression as determined by real-time PCR. (A) The different types of liver cells were extracted from human liver samples. (B) Gdnf mRNA expression in primary HSCs, hepatocyte (HEPs), KCs and liver sinusoidal endothelial cell (LSECs) isolated from olive oil or carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-treated mice aged 6 weeks. N.S., not significant. (C) Gdnf mRNA expression in 7-day-culture-activated mouse HSC compared with HEPs, KCs, LSECs and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) (n=3 per group). (D) Gdnf mRNA expression in cultured human and mouse HSCs at the indicated time points. (E) Real-time PCR and western blot analysis for α-SMA and Col1A1. Human and mouse primary HSCs were treated with GDNF (10 ng/mL) for the indicated time intervals. (F) Effect of GDNF on fully activated HSCs. GFP-Col-HSCs were plated and cultured in 6-well plates for 2 hours and then treated with GDNF (10 ng/mL) for an additional 48 hours; the cells were analysed by fluorescence microscopy (original magnification, x200, n=3) and positive cells were counted (%). (G) Western blot analysis for α-SMA and Col1A1. Primary human and mouse HSCs were plated and cultured in 6-well plates overnight, followed by si-GDNF or sgGdnf RNA (2 multiple of infection (MOI)) for 48 hours. Bars indicate the mean±SD of three independent experiments; n=3 per group; one-way analysis of variance with the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test was used in parts A, C and E, and the t-test with the non-parametric Mann-Whiney U test was used in part B.