Abstract
Objective:
Monoallelic de novo gain-of-function variants in the voltage gated sodium channel SCN8A are one of the recurrent causes of severe developmental and epileptic encephalopathy (DEE). In addition, a small number of de novo or inherited monoallelic loss-of-function variants have been found in patients with intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorder or movement disorders. Inherited monoallelic variants causing either gain- or loss-of-function, are also associated with less severe conditions such as benign familial infantile seizures or isolated movement disorders. In all three categories, the affected individuals are heterozygous for a SCN8A variant in combination with a wildtype allele. In the present study, we describe two unusual families with severely affected individuals who inherited biallelic variants of SCN8A.
Methods:
We identified two families with biallelic SCN8A variants by diagnostic gene panel sequencing. Functional analysis of the variants was performed using voltage clamp recordings from transfected ND7/23 cells.
Results:
We identified three probands from two unrelated families with DEE due to biallelic SCN8A variants. Each parent of an affected individual carried a single heterozygous SCN8A variant and exhibited mild cognitive impairment without seizures. In both families, functional analysis demonstrated segregation of one allele with complete loss-of-function, and one allele with altered biophysical properties consistent with partial loss-of-function.
Significance:
These studies demonstrate that SCN8A DEE may, in rare cases, result from inheritance of two variants both of which exhibit reduced channel activity. In these families heterozygosity for the dominant variants results in less severe disease than biallelic inheritance of two variant alleles. The clinical consequences of variants with partial and complete loss of SCN8A function are variable and likely to be influenced by genetic background.
INTRODUCTION
SCN8A, encoding the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.6, was first implicated in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy (DEE) in 2012 in a heterozygous individual with a de novo variant 1. The phenotypic spectrum observed in several hundred individuals now includes a range of epilepsies including benign familial infantile seizures (BFIS) with or without paroxysmal dyskinesia 2, less severe epilepsies with or without comorbid intellectual disability (ID) 3–6, and severe early-onset DEEs 1, 7, 8. Severe SCN8A DEE (MIM EIEE13) is characterized by intractable seizures with an average age at seizure onset of four months, cognitive deterioration, pyramidal/extra-pyramidal signs, progressive cerebral atrophy and visual impairment leading to cortical blindness 7–9. There are often prolonged focal seizures with prominent hypomotor and vegetative symptoms that may evolve to clonic or bilateral tonic-clonic manifestations. Epileptic myoclonus, spasm-like episodes, and recurrent convulsive status epilepticus are frequently observed 7–9. All affected individuals described to date are monoallelic (heterozygous) carriers of a gain-of-function or loss-of-function variant in combination with a wildtype allele.
Functional studies have demonstrated that SCN8A-related epilepsies are typically caused by monoallelic gain‐of‐function (GOF) alterations leading to neuronal hyperexcitability 1, 10–12. A small number of heterozygous loss‐of‐function (LOF) variants have been found in patients with ID, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or movement disorders who do not necessarily have epilepsy 10, 13–15. The less severe familial SCN8A-related disorders show an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, while the large majority of EIEE13 cases occur de novo 1–5, 7–9, 13–15. A similar pattern has been reported for SCN2A, in which GOF variants cause early onset seizures, and LOF variants tend to be associated with later onset seizures or with ID or ASD without epilepsy 16.
In the mouse, homozygosity for partial LOF alleles of Scn8a results in movement disorders including ataxia, tremor, and dystonia, while complete LOF results in juvenile lethality with loss of ambulation 17, 18. In the present paper, we describe the first two human families with biallelic variants in SCN8A. The index patients are born of heterozygous parents who exhibit mild cognitive deficits, while the probands suffer from DEE and severe ID. Functional analysis demonstrated a shared mechanism of inheritance of one complete LOF and one partial LOF allele by affected individuals in both families.
METHODS
DNA sequencing.
Both families underwent targeted gene panel sequencing as part of their formal diagnostic work-up at either the Institute of Human Genetics, University of Leipzig Hospital and Clinics (Family 1) or the Danish Epilepsy Centre (Family 2). The parents or legal guardians of all probands provided written informed consent, and the study were approved by the local ethical committees. Family 1: Targeted sequencing of a custom panel of 131 genes associated with epilepsy (TruSight Rapid Capture Kit) was performed. Genomic DNA was extracted from blood using standard methods, and the library was sequenced on a MiSeq v2 300 sequencer (Illumina). Family 2: Targeted sequencing of 78 epilepsy genes was performed. Genomic DNA was extracted from blood using standard methods, and SureSelect library building was followed by sequencing on the Ion PGM system (Ion PGM 200 Sequencing Kit), as previously described 19.
Variants with a mutant allele frequency <1% in the general population (gnomAD, Broad Institute, Cambridge, USA) were classified according to the ACMG guidelines 20. In-silico evaluation was performed using SIFT Blink (CraigVenter Institute, USA), Polyphen2 (Harvard, USA), CADD (University of Washington, USA), MutationTaster (Charité, Berlin), MPC (Harvard, USA) and the following splicing tools: SpliceSiteFinder-like, MaxEntScan, NNSPLICE, Human Splicing Finder. In addition, database synchronization by ClinVar (NCBI, USA) and Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD, Biobase, USA) was performed. Sanger sequencing was carried out to confirm all variants and to perform segregation analysis.
Electrophysiology.
Missense variants were introduced into the tetrodotoxin-resistant mouse cDNA Nav1.6R by site-directed mutagenesis with QuikChange II XL (Agilent Technologies) and analyzed as previously described 12. The 6-kb open reading frame of each construct was re-sequenced to eliminate clones containing extraneous mutations. Nav1.6 variants were expressed by transfection of neuron-derived ND7/23 cells (Sigma Aldrich) 12. Sodium currents were recorded 48 hours after transfection in the presence of 500 nM tetrodotoxin to block endogenous sodium currents, using the whole-cell configuration of the patch clamp recording technique 12.
RESULTS
Clinical features of affected children and parents from two families segregating biallelic SCN8A variants.
The clinical data of the three index patients are summarized in table 1.
Table 1.
Clinical features of affected individuals with inherited biallelic SCN8A variants.
| Family ID | Family 1 Patient A |
Family 1 Patient B |
Family 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | M | F | M |
| Current age | 4y | 2y | 27y |
| Family history | Both parents: mild cognitive deficits. Two maternal uncles and one maternal aunt have ID +/− epilepsy. One maternal half-brother has speech delay. | Both parents: mild cognitive deficits. Two maternal uncles and one maternal aunt have ID +/− epilepsy. One maternal half-brother has speech delay. | Both parents have mild cognitive deficits. |
| Development | Severe ID | Severe ID | Profound ID |
| Age of seizure onset | 3m | Few hours after birth | 7m |
| Seizure type at onset | Focal seizure | Convulsive status epilepticus | Tonic seizure and eye rolling |
| Seizure types | Clonic, focal or brief tonic seizures | Brief tonic and automotor seizures | Infantile febrile seizures, tonic seizures, absences |
| EEG features | 12m: Hypsarrhythmia 3y: moderate background slowing; mild non-specific EEG abnormalities | 8d: medium-weight generalized dischanges 4m: Hypsarrhythmia 17m: moderate background slowing; mild non-specific EEG abnormalities | 7y: Ictal regular generalized 3–4Hz paroxysms of 5–10 sec. 26y: 3–4 Hz spike-waves bilaterally in the posterior quadrants. |
| Movement disorder | No | No | Dyskinesia |
| Other neurological features | Hypotonia, strabismus divergens. 19m: audiotory neuropathy | Hypotonia 8m: Strabismus divergens | Hypotonia, spastic tetraplegia |
| Vision impairment | 6m: VEP/flash-VEP: binocular response pos. Hyperopia. | 11m: hyperopia | Myopia |
| Additional features | Bilateral hip dysplasia, constipation, hemangioma, swallowing difficulties, regurgitation, 28m: microcephaly (−3,4 SD) | Constipation, swallowing difficulties, apnea, dysphagia 5m: microcephaly (−5 SD)13m: PEG tube | Recurrent pneumonia, constipation. Phimosis, reflux, asthma, bilateral hip dysplasia, dysphagia, scoliosis, kyphosis |
| MRI | 4m and 26m: Pineal cyst, otherwise normal | 4m: Delayed myelination | 8y: Cerebral atrophy |
| Allele 1 | c.805G>A; p.(Gly269Arg) mat | c.805G>A; p.(Gly269Arg) mat | c.2464G>A; p.(Gly822Arg) pat |
| Allele 2 | c.4079C>A; p.(Thr1360Asn) pat | c.4079C>A; p.(Thr1360Asn) pat | c.4912C>T; p.(Arg1638Cys) mat |
Family 1:
The index patients were a sib pair (three-year-old male and a two-year-old female) born to unrelated parents (Figure 1A). Both parents had mild cognitive impairment/ borderline intellectual functioning. They both attended special school, obtained vocational training, and were able to live independent lives. Neuropsychological evaluations were not available. Additional affected family members included a maternal half-brother of the affected sibs and two of the mother’s half-brothers and one halfsister, all with mild ID and one with unclassified epilepsy. Unfortunately, none of the maternal relatives were available for genetic testing.
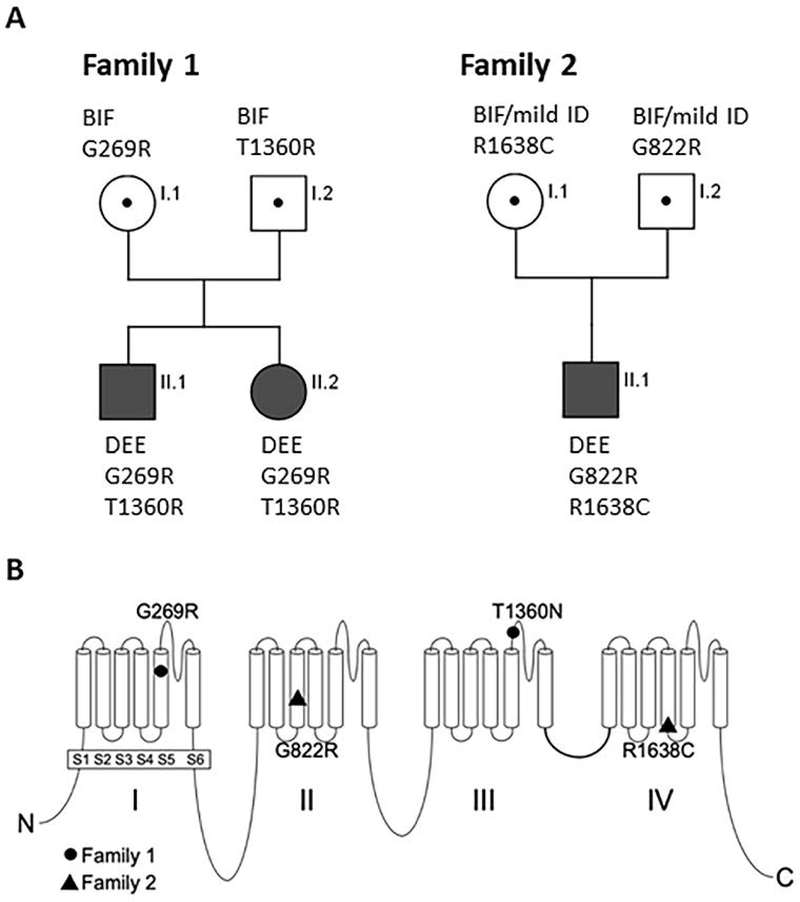
Figure 1:
Biallelic inheritance of DEE in two families, and the protein location of the novel variants. A) Individuals affected with DEE (epilepsy plus severe ID) are compound heterozygotes for inherited variants of SCN8A. Heterozygous parents exhibit mild cognitive deficits. Sanger sequencing of genomic DNA demonstrated inheritance of two mutant alleles by individuals affected with DEE (epilepsy with severe ID) and a single variant in heterozygous carriers with mild cognitive deficits. B) Location of four novel variants in the voltage-gated sodium channel SCN8A. Solid symbols, complete loss of function; open symbols, partial loss of function.
The male sib was born at term after an uncomplicated pregnancy and delivery (Apgar 10/10). Postnatally he needed treatment of hypoglycemia, and was tube fed for several days due to feeding difficulties. He presented with global developmental delay and onset of intractable daily focal seizures at three months of age. Treatment with levetiracetam (LEV) was initiated, which led to transient seizure reduction. However, during the course of the disease he developed clonic and daily brief tonic seizures (lasting a few seconds). His initial electroencephalogram (EEG) showed background slowing and multifocal epileptiform discharges, which progressed to hypsarrhythmia. Treatment with Sulthiame and Prednisolone was tried without any effect. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) performed at 4 months of age was normal, except for a small pineal cyst. At follow-up, he presented with muscular hypotonia, severe ID and microcephaly (−3,4 SD at 28m). Additional features included strabismus, hyperopia, and bilateral hip dysplasia (type IIa on the right and type Ib at the left side). At 19 month of age bilateral coxa valga were observed and confirmed by X-ray. Furthermore, he suffered from constipation and swallowing difficulties with regurgitation and vomiting after chunky food. At 19 months of age he was diagnosed with an auditory neuropathy with almost complete hearing loss. He could turn to both sides at 30 months of age, but was not able to sit, crawl, stand, walk or communicate. His epilepsy continued to be intractable, and currently he has one to two brief tonic seizures per week despite treatment with LEV, vigabatrin (VGB) and valproic acid (VPA). EEG at follow-up showed background slowing and mild non-specific abnormalities.
The female sib was born at term after a risk pregnancy due to maternal hypertension. Birth and postnatal adaptation were complicated by perinatal asphyxia and left cerebral hemorrhage. Apgar 1/1/2. Postnatally, she presented with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, and when only a few hours old she developed convulsive status epilepticus. She presented with daily dyscognitive seizures and brief focal motor seizures with a tonic component. She continued to have episodes of convulsive status epilepticus. EEG showed multifocal epileptiform discharges, which evolved to hypsarrhythmia at four month of age. At 10 months of age she suffered from daily brief tonic seizures. She was developmentally delayed from birth, and severe ID was present at follow-up. MRI at 4 months of age showed delayed myelination. At five months of age severe microcephaly was evident (−5 SD). At follow-up, she had adequate head control and was able to grab things, but was unable to turn or sit, and had poor eye contact. Additional features included hyperopia, strabismus, constipation, hypotonia, apneas and eating difficulties. Tube feeding was initiated at 13 months.
She experienced a transient response to phenobarbital, and her EEG improved during treatment with Prednisolon, 5 mg/kg/day, for two weeks, showing only background slowing and non-specific EEG abnormalities. VGB and sulthiame treatment resulted in no seizure improvement. Current treatment includes sulthiame and VPA and is accompanied by 10 to 15 absence seizures per day.
Family 2:
The proband was a 27-year-old male born to unrelated parents. Both parents had mild cognitive deficits. They were able to live independent lives with guidance and support. Both attended special school, received disability pensions and worked in a sheltered workshop. Neuropsychological evaluations were not available, and both parents were lost for follow-up. The patient was born at term after an uncomplicated pregnancy and delivery. He was readmitted to the hospital within the first week of life due to cyanosis, hypotonia and apathetic behavior. At six months of age delayed psychomotor development became evident (no eye contact, lack of head control, hypotonia), and at seven months of age he experienced his first seizure, characterized by eye rolling and stiffness of the whole body. His EEG was reported as slightly abnormal, but no antiepileptic treatment was initiated. A CT scan showed atrophy of the frontal lobes. At this approximate age he was removed from his parents and put in foster care. In the following years, he was diagnosed with severe ID, spastic tetraplegia, myopia and bilateral hip dysplasia. He never gained the ability to walk or communicate, and was admitted several times due to febrile seizures, asthmatic bronchitis, gastro-esophageal reflux, pneumonia and constipation. At the age of seven years, brief episodes with staring were noticed. Ictal EEG recordings showed regular diffuse 3–4 Hz epileptic discharges lasting for 5–10 sec. Oxcarbazepine was introduced but was administered irregularly for a few days by the foster mother, only during febrile episodes. At 8.5 years it was stopped. MRI performed at the age of eight years did not show abnormalities. When he was 9 years old, he was moved to a residential care institution where he now lives. Tonic-clonic seizures, occasional dystonic/dyskinetic episodes and eating difficulties were reported. At the age of 10 years, topiramate (TPM) and VPA were initiated, achieving seizure control for some years. He was also treated with risperidone for behavioral problems (agitation and screaming). At age 15 years, TPM was stopped. In the following years, the seizure frequency progressively increased and at twenty years of age, he was referred to the Danish Epilepsy Centre because of drug-resistant epilepsy with weekly tonic seizures and staring episodes. His interictal EEG showed subcontinuous theta-delta activity and high amplitude spike and slow waves, bilaterally in the posterior quadrants, as well as less prominent focal slowing and infrequent spike and slow waves in the fronto-temporal regions. The staring episodes were recorded on video-EEG and did not have an EEG correlate. LEV was added to VPA, with improvement of seizure duration and frequency from weekly to monthly. At latest examination, he was profoundly intellectually disabled, nonverbal, wheelchair bound and had spastic tetraplegia, dyskinesia, dysphagia, scoliosis, kyphosis and severe myopia.
Identification and inheritance of SCN8A mutations.
Family 1:
Gene panel testing revealed that the two affected sibs were compound heterozygotes for the SCN8A missense variants p.Gly269Arg (c.805G>A) located in the pore loop of Domain 1, and p.Thr1360Asn (c.4079C>A) in the pore loop of domain 3 (Figure 1B). Sanger sequencing demonstrated that both variants were inherited (Figure 1B).
Family 2:
Gene panel sequencing revealed that the index patient was compound heterozygous for the SCN8A missense variants p.Gly822Arg (c.2464G>A) located in the middle of transmembrane segment D2S3, and p.Arg1638Cys (c.4912C>T) at the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane segment D4S4. Sanger sequencing demonstrated that both variants were inherited (Figure 1B).
SCN8A is highly intolerant of variation in the general population, with a pLI of 1.00 and a missense z-score of 7.94 in the gnomAD database. There are only four protein truncations and 384 missense variants in the gnomAD database 21, compared to the prediction of 80 truncation and 1114 missense variants. The four variants detected in the present study are absent from the gnomAD database and are predicted to be deleterious by two or more prediction programs including CADD score, MPC score and PolyPhen.
Functional analysis of SCN8A variants.
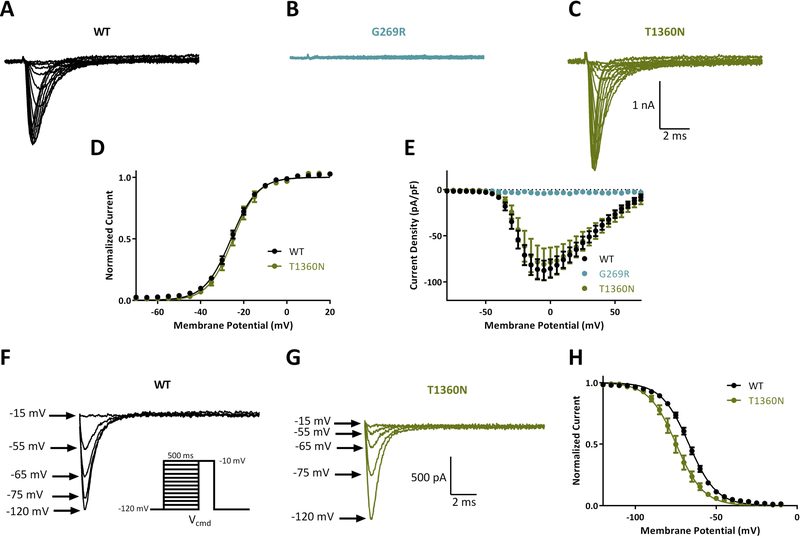
ND7/23 cells were transfected with Nav1.6 cDNA and sodium currents were recorded. Cells transfected with wildtype Nav1.6 generated current density of −90 ± 11 pA/pF (n = 37; Figure 2A). Transfection of variant G269R from Family 1 (allele 1) did not generate any detectable current (−6 ± 1.4 pA/pF; n = 5, Figure 2B) and was not significantly different (p>0.05) from non-transfected cells (−4 ± 0.8 pA/pF; n = 5). In contrast, the variant T1360N (Family 1, allele 2) generated current density similar in magnitude to the wildtype channel, −82 ± 17 pA/pF (n = 7; Figure 2C). The voltage-dependence of activation of T1360N channels did not differ from wildtype (Figure 2D–E; Table 2). However, analysis of voltage-dependent steady-state inactivation demonstrated a hyperpolarizing shift of −7.5 mV in the half maximal voltage of inactivation (V1/2) of T1360N compared to WT (**p<0.01; Figure 3F–H; Table 2). The predicted effect of this mutation is to reduce channel availability.
Figure 2:
Biophysical characterization of sodium channel variants in family 1. Representative traces of families of sodium channel currents recorded from ND7/23 cells expressing A. WT, B. G269R and C. T1360N. D. Averaged current-voltage (I-V) curves for WT (n = 37), G269R (n = 5) and T1360N (n = 7). E. Voltage dependence of channel activation. Example traces of steady state inactivation curves for WT (F) and T1360N (G). Inset shows voltage protocol for steady-state inactivation. H. Voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation for WT (n = 37) and T1360N (n = 7). Data represent means ± SEM. Smooth lines in E and H correspond to single Boltzmann equation fits to average data.
TABLE 2.
Activation and Inactivation Parameters of wildtype and variant Nav1.6 currents.
| Activation | Inactivation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1/2 (mV) | k | V1/2 (mV) | k | |
| WT (n=37) | −25.8 ± 0.8 | 5.37 ± 0.22 | −66.9 ± 0.9 | 7.75 ± 0.14 |
| Family 1, allele 2 T1360N (n=7) | −26.0 ± 1.6 | 5.29 ± 0.47 | −74.4 ± 1.6** | 7.79 ± 0.35 |
| Family 2, allele 2 R1628C (n=12) | −22.0 ± 0.8* | 6.65 ± 0.29** | −66.7 ± 2.0 | 10.4 ± 0.88*** |
p<0.05
p<0.01
p<0.001 compared to WT; unpaired t-test.
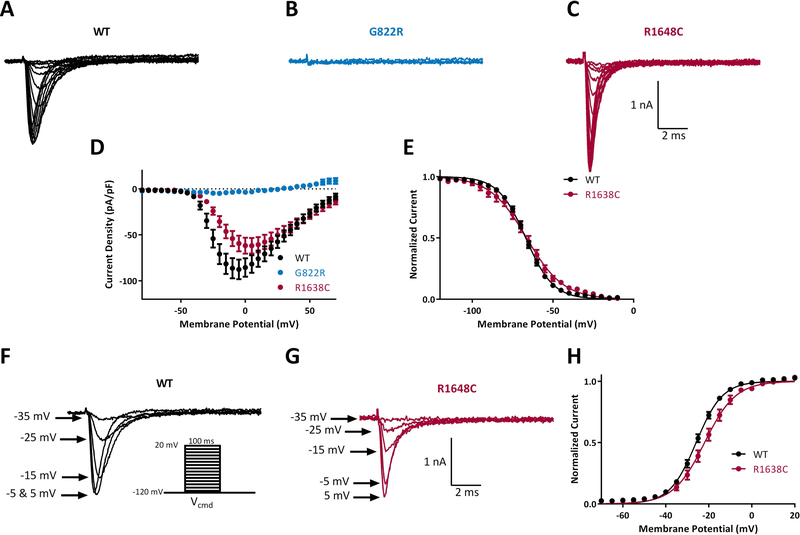
Figure 3.
Biophysical characterization of sodium channel variants in family 2. Representative traces of families of sodium channel currents recorded from ND7/23 cells expressing A. WT, B. G822R and C. R1648C. D. Averaged current-voltage (I-V) curves for WT (n = 37), G822R (n = 9) and R1638C (n = 12). E. Voltage dependence of steady state inactivation for WT (n = 37) and R1638C (n = 12). Example traces of sodium currents recorded for WT (F) and R1648C (G) showing a reduction in current amplitude in R1648C cells compared with WT at a given activation voltage. Inset shows activation voltage protocol. H. Voltage dependence of activation for WT (n = 37) and R1638C (n = 12). Data represent means ± SEM. Smooth lines in E and H correspond to single Boltzmann equation fits to average data.
Family 2 allele 1 (G822R) did not generate detectable sodium current (−7 ± 1 pA/pF; n = 12, Figure 3B, D). Family 2 allele 2 (R1638C) generated current density of −63 ± 8.7 pA/pF (n = 12) which did not differ from wildtype (p>0.05; Figure 3C, D). The V1/2 for activation of R1638C was shifted in a depolarizing direction by +3.8 mV in comparison with the WT channels (*p<0.05; Figure 3F–H; Table 2). This is predicted to reduce the number of channel opening at a given voltage. The V1/2 for steady-state inactivation between R1638C and WT channel did not differ (Figure 3E; Table 2). The depolarizing shift in voltage-dependent activation exhibited by R1638C is consistent with reduced neuronal activity.
DISCUSSION
We describe two pedigrees (Figure 1) in which probands with inherited biallelic variants of SCN8A are severely affected with DEE. The monoallelic (heterozygous) parents have only mild cognitive deficits. In each family, one parent had a more severe allele with complete loss-of-function and one parent had a partial LOF variant, with the probands inheriting one of each type of variant. These variants exhibit dominant expression in heterozygous carriers with mild phenotypes, and a much more severe phenotype in compound heterozygous carriers with two variant alleles. None of the four variants were previously described in patients, but all are predicted to be likely pathogenic and are absent from the control population in the gnomAD database 22. Functional tests demonstrated reduced or complete loss-of-function of the variant channels. In the only previous report of a patient with two variants of SCN8A, the missense variant (p.Ile1583Thr) was probably not deleterious, and the deletion was a somatic mosaic 23. In two families with biallelic variants of CACNA1A, the probands with biallelic variants suffered from DEE while the heterozygous parents and siblings had milder symptoms 24, 25, similar to our observations.
In addition to demonstrating a previously unreported inheritance pattern for SCN8A-related disorders, these families suggest an explanation for the observation that the frequency of SCN8A variants previously observed is lower than that for SCN1A 26, (Johannesen et al., personal communication). In contrast to SCN1A heterozygotes, who are often affected with Dravet syndrome, the SCN8A heterozygotes presented in this study were not sufficiently ill to be candidates for genetic testing. There are likely to be many more individuals with mild SCN8A-related phenotypes who will not be discovered until genetic testing becomes more widespread.
Electrophysiological analysis of the variants G269R and G822R identified complete absence of channel activity in transfected ND7/23 cells. G269R is located in segment 5 of domain I, and G822R is located in segment 3 of domain II, a region that is relatively lacking in variants causing dominant DEE 11. Both variants completely eliminate channel activity, indicating that the affected residues are essential for channel function. In contrast, the variants R1638C and T1360N retained channel activity with altered biophysical properties that are consistent with partial LOF. Depolarizing shifts of voltage-dependent activation in the R1638C mutation reduce the number of channels available to open at any membrane voltage and thereby reduce neuronal excitability. The hyperpolarized shift in channel inactivation in the T1360N channel reduce channel availability due to premature entry into inactivated channel states. The predicted result in affected compound heterozygotes is altered excitability of both excitatory and inhibitory neurons, modulating overall neuronal network function.
Both families segregate one allele with complete LOF and one allele with altered biophysical properties, both of which are predicted to result in reduced neuronal activity. In contrast, most of the de novo variants associated with DEE result in elevated neuronal activity 11. The most common biophysical effect of previously described SCN8A variants in DEE is impaired channel inactivation and elevated neuronal activity, e.g. the recurrent variant R1872W 12,27. Even in the presence of a wild type allele, variants with elevated channel activity produce a severe dominant phenotype. However, for the loss-of-function variants, the wildtype allele in heterozygous carriers provides compensating channel activity and heterozygous parents exhibit only mild cognitive deficits. In the individuals affected with DEE, who are compound heterozygotes for reduced function alleles, the total channel activity is predicted to be below 50% of normal resulting in the severe phenotype of SCN8A encephalopathy. However, it is not clear why reduced activity of Nav1.6 results in seizures. The biallelic LOF individuals in our families have phenotypes that are indistinguishable from monoallelic GOF variants, including early onset DEE with multiple seizure types (focal, clonic and tonic), severe ID with absent speech, axial hypotonia, central visual impairment, microcephaly and gastrointestinal symptoms, features that are all described in patients with elevated channel activity 7. It cannot be excluded that other rare genetic variants may contribute to the observed phenotypes.
A small number of heterozygous carriers of partial or complete LOF of SCN8A have been described previously, with variable consequences. Myoclonus in the absence of seizures was observed in one family with four affected family members 15. Mild to moderate ID or ASD in the absence of seizures was observed in four families 10,14. On the other hand, absence epilepsy was observed in a family with the heterozygous protein truncating variant p.Asn544fs*39 6 and focal epilepsy with mild ID was observed for the protein truncation variant p.Arg1820* 28. It is likely that variation in other genes in the genetic background contribute to this variation; the effects of modifier genes on seizure phenotypes have been well established in the mouse 18, 29. It is also possible that missense variants that appear to cause complete LOF in vitro may actually retain some activity in vivo that contributes to the relatively mild phenotype in the monoallelic (heterozygous) parents. Recent evidence suggests that the sodium channel alpha subunits may function as dimers 30. In this case, LOF alleles that produce full length protein could have a dominant negative effect in heterozygotes, resulting in less than 50% residual activity and a more severe phenotype than that of LOF alleles encoding truncated or unstable proteins.
SCN8A is widely expressed in both excitatory and inhibitory neurons of the CNS and PNS. LOF variants of Scn8a in the mouse result in severe movement disorders without seizures: loss of 90% of normal activity results in tremor, ataxia and dystonia 18 and loss of 100% of activity results in hind limb paralysis and juvenile lethality 17. Homozygosity for complete LOF alleles may also be incompatible with human life. Reduced activity of Nav1.6 in colonic mesenteric neurons may contribute to the GI disturbances in patients with SCN8A encephalopathy 31. Future studies of inhibitory neuron populations in SCN8A encephalopathy could be helpful to reconcile the existence of both gain-of-function and loss-of-function variants in patients with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy.
Key bullet points:
Biallelic inherited loss-of-function SCN8A variants were identified in probands with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy
Their heterozygous parents exhibited mild cognitive impairment without epilepsy
Functional analysis demonstrated segregation of one allele with complete loss-of-function and one with partial loss-of-function in both families
These dominant variants result in partial or complete loss of function of the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.6 and result in mild cognitive impairment in heterozygous carriers and severe DEE in individuals inheriting two mutant alleles.
Acknowledgements:
We thank the patients and their families for participating in this study. Funding to MHM and JLW was provided by NINDS R01 NS34509 and to MKP by NINDS RO1 NS103090. ERW was funded by a University of Virginia Robert R. Wagner Fellowship.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report. We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
REFERENCES
- 1.Veeramah KR, O’Brien JE, Meisler MH, Cheng X, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG, et al. De novo pathogenic SCN8A mutation identified by whole-genome sequencing of a family quartet affected by infantile epileptic encephalopathy and SUDEP Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:502–510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gardella E, Becker F, Moller RS, Schubert J, Lemke JR, Larsen LH, et al. Benign infantile seizures and paroxysmal dyskinesia caused by an SCN8A mutation Ann Neurol. 2016; 79:428–436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anand G, Collett-White F, Orsini A, Thomas S, Jayapal S, Trump N, et al. Autosomal dominant SCN8A mutation with an unusually mild phenotype Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2016;20:761–765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Han JY, Jang JH, Lee IG, Shin S, Park J. A Novel Inherited Mutation of SCN8A in a Korean Family with Benign Familial Infantile Epilepsy Using Diagnostic Exome Sequencing Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2017;47:747–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Butler KM, da Silva C, Shafir Y, Weisfeld-Adams JD, Alexander JJ, Hegde M, et al. De novo and inherited SCN8A epilepsy mutations detected by gene panel analysis Epilepsy Res. 2017;129:17–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Johannesen KM, Gardella E, Encinas AC, Lehesjoki AE, Linnankivi T, Petersen MB, et al. The spectrum of intermediate SCN8A-related epilepsy Epilepsia. 2019;60:830–844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gardella E, Marini C, Trivisano M, Fitzgerald MP, Alber M, Howell KB, et al. The phenotype of SCN8A developmental and epileptic encephalopathy Neurology. 2018;91:e1112-e1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Larsen J, Carvill GL, Gardella E, Kluger G, Schmiedel G, Barisic N, et al. The phenotypic spectrum of SCN8A encephalopathy Neurology. 2015;84:480–489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ohba C, Kato M, Takahashi S, Lerman-Sagie T, Lev D, Terashima H, et al. Early onset epileptic encephalopathy caused by de novo SCN8A mutations Epilepsia. 2014;55:994–1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu Y, Schubert J, Sonnenberg L, Helbig KL, Hoei-Hansen CE, Koko M, et al. Neuronal mechanisms of mutations in SCN8A causing epilepsy or intellectual disability Brain. 2019;142:376–390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Meisler MH, Helman G, Hammer MF, Fureman BE, Gaillard WD, Goldin AL, et al. SCN8A encephalopathy: Research progress and prospects Epilepsia. 2016;57:1027–1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wagnon JL, Barker BS, Hounshell JA, Haaxma CA, Shealy A, Moss T, et al. Pathogenic mechanism of recurrent mutations of SCN8A in epileptic encephalopathy Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2016;3:114–123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Trudeau MM, Dalton JC, Day JW, Ranum LP, Meisler MH. Heterozygosity for a protein truncation mutation of sodium channel SCN8A in a patient with cerebellar atrophy, ataxia, and mental retardation J Med Genet. 2006;43:527–530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wagnon JL, Barker BS, Ottolini M, Park Y, Volkheimer A, Valdez P, et al. Loss-of-function variants of SCN8A in intellectual disability without seizures Neurol Genet. 2017;3:e170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wagnon JL, Mencacci NE, Barker BS, Wengert ER, Bhatia KP, Balint B, et al. Partial loss-of-function of sodium channel SCN8A in familial isolated myoclonus Hum Mutat. 2018;39:965–969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wolff M, Johannesen KM, Hedrich UBS, Masnada S, Rubboli G, Gardella E, et al. Genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity suggest therapeutic implications in SCN2A-related disorders Brain. 2017;140:1316–1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.O’Brien JE, Meisler MH. Sodium channel SCN8A (Nav1.6): properties and de novo mutations in epileptic encephalopathy and intellectual disability Front Genet. 2013;4:213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kearney JA, Buchner DA, De Haan G, Adamska M, Levin SI, Furay AR, et al. Molecular and pathological effects of a modifier gene on deficiency of the sodium channel Scn8a (Na(v)1.6) Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:2765–2775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moller RS, Wuttke TV, Helbig I, Marini C, Johannesen KM, Brilstra EH, et al. Mutations in GABRB3: From febrile seizures to epileptic encephalopathies Neurology. 2017;88:483–492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology Genet Med. 2015;17:405–424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV, Samocha KE, Banks E, Fennell T, et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans Nature. 2016;536:285–291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Harkin LA, McMahon JM, Iona X, Dibbens L, Pelekanos JT, Zuberi SM, et al. The spectrum of SCN1A-related infantile epileptic encephalopathies Brain. 2007;130:843–852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Berghuis B, de Kovel CG, van Iterson L, Lamberts RJ, Sander JW, Lindhout D, et al. Complex SCN8A DNA-abnormalities in an individual with therapy resistant absence epilepsy Epilepsy Res. 2015;115:141–144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sintas C, Carreno O, Fernandez-Castillo N, Corominas R, Vila-Pueyo M, Toma C, et al. Mutation Spectrum in the CACNA1A Gene in 49 Patients with Episodic Ataxia Scientific reports. 2017;7:2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Reinson K, Oiglane-Shlik E, Talvik I, Vaher U, Ounapuu A, Ennok M, et al. Biallelic CACNA1A mutations cause early onset epileptic encephalopathy with progressive cerebral, cerebellar, and optic nerve atrophy American journal of medical genetics Part A. 2016;170:2173–2176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bayat A, Hjalgrim H, Moller RS. The incidence of SCN1A-related Dravet syndrome in Denmark is 1:22,000: a population-based study from 2004 to 2009 Epilepsia. 2015;56:e36–39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bunton-Stasyshyn RKA, Wagnon JL, Wengert ER, Barker BS, Faulkner A, Wagley PK, et al. Prominent role of forebrain excitatory neurons in SCN8A encephalopathy Brain. 2019;142:362–375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Moller RS, Larsen LH, Johannesen KM, Talvik I, Talvik T, Vaher U, et al. Gene Panel Testing in Epileptic Encephalopathies and Familial Epilepsies Mol Syndromol. 2016;7:210–219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Martin MS, Tang B, Papale LA, Yu FH, Catterall WA, Escayg A. The voltage-gated sodium channel Scn8a is a genetic modifier of severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:2892–2899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Clatot J, Hoshi M, Wan X, Liu H, Jain A, Shinlapawittayatorn K, et al. Voltage-gated sodium channels assemble and gate as dimers Nat Commun. 2017;8:2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bartoo AC, Sprunger LK, Schneider DA. Expression and distribution of TTX-sensitive sodium channel alpha subunits in the enteric nervous system J Comp Neurol. 2005;486:117–131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]