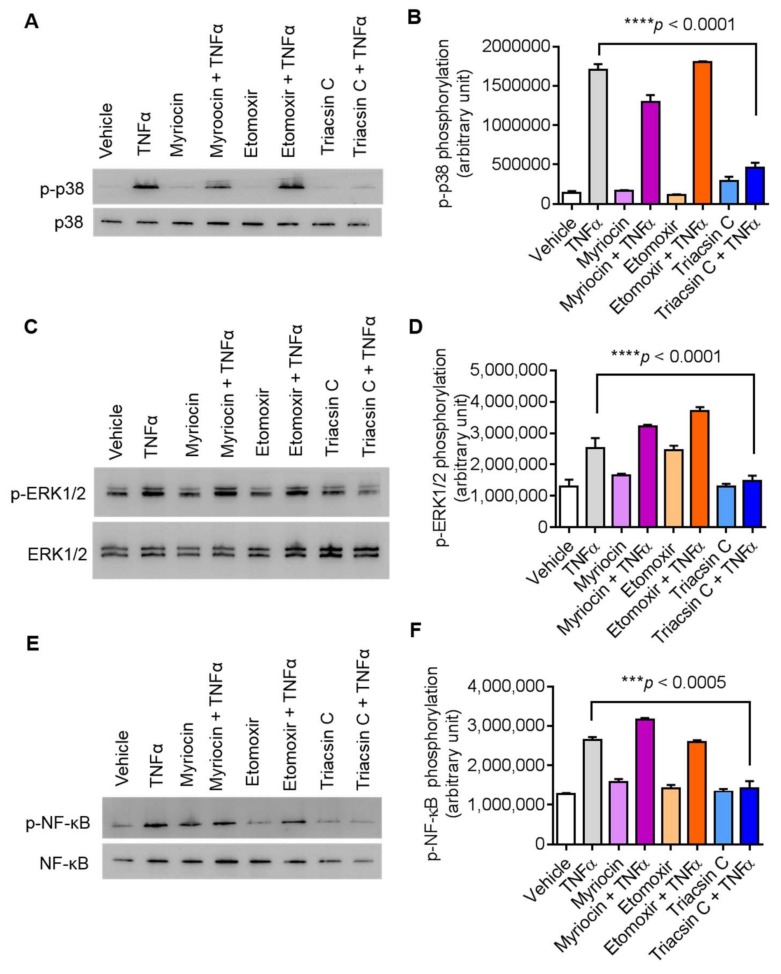
Figure 5.
Inhibition of ACSL1 affects TNFα-activated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in MDA-MB-231 cells. As shown in Figure 4A, TNFα treatment increases the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, and NF-κB in a time-dependent manner. MDA-MB-231 cells were pretreated with p38 inhibitor (SB203580, 10 μM), ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059, 10 μM), or NF-kB inhibitor (resveratrol, 1 μM) for 1 h and then treated with TNFα for 15 min. Cell lysates were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. Samples were run on denaturing gels. Immunoreactive bands were developed using an Amersham ECL Plus Western Blotting Detection System (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) and visualized by Molecular Imager® VersaDocTM MP Imaging Systems (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). (A) Phosphorylated proteins p38 MAPK, (C) ERK1/2, and (E) NF-κB are depicted in the upper panels and total respective proteins are shown in the lower panels. (B, D, F) Phosphorylation intensity of p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, and NF-κB was quantified using Image Lab software (version 6.0.1, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and are presented in arbitrary units. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). **** p < 0.001 versus TNFα without respective inhibitors.