Figure 3.
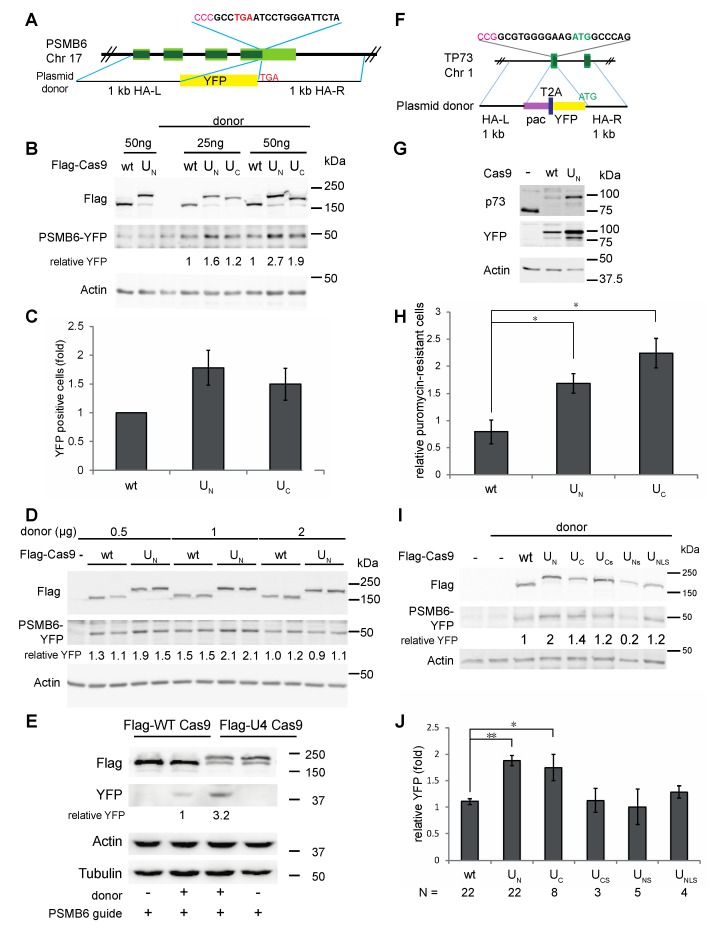
MRN recruitment by chimeric Cas9 improves insertion of large cassettes. (A). Schematic representation of targeted PSMB6 locus and donor plasmid. Stop codon is indicated in red. Guide sequence is in bold, with PAM sequence in pink (note that the guide is the minus strand). The region of the plasmid donor DNA with the 1 kb left and right homology arms (HA) and SYFP insert is shown. (B). Insertion of YFP tag at C-terminus of PSMB6 is more efficient with MRN-recruiting Cas9 constructs. HCT116 cells were transfected with the indicated amounts of Cas9/sgRNA encoding plasmids and with donor DNA. Amounts of total DNA in transfections were constant among samples, with empty plasmid (pBluescript) used to equalize amounts. Cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (C). FACS analysis of PSMB6-YFP edited cells. HEK293FT cells were transfected with Cas9/sgRNA encoding plasmids and donor DNA. Cells were passaged twice and analyzed by FACS, with 100,000 cells analyzed per point. Summary of three independent experiments is shown. (D). Titration of donor DNA in PSMB6-YFP editing. HEK293 cells were transfected with the Cas9/sgRNA-expressing plasmids and the donor DNA indicated. (E). Recombinant chimeric Cas9 yields more edited cells than wt Cas9. HEK293 cells were transfected with 2 µg of recombinant Flag-Cas9 or UC Flag-Cas9, 400 ng sgRNA, and 3.125 µg PSMB6-YFP donor plasmid, as indicated, using CRISPRMax reagent. Cells were harvested three days post-transfection, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Samples for this gel were not boiled to improve detection by the living colors antibody, which causes a slight change in migration of the 50 kDa PSMB6-YFP protein. (F). Schematic representation of targeted p73 locus and donor plasmid. Start codon is indicated in green. Guide sequence is in bold, with PAM sequence in pink (note that the guide is the minus strand). The region of the plasmid donor DNA with the 1 kb homology arms (HA) and SYFP insert is shown. (G). HEK293 cells were transfected with either wt or UN Cas9/sgRNA constructs and the donor plasmid, encoding the pac-2A-YFP cassette flanked by 1kb homology arms. Cells were selected with 0.5 µg/mL puromycin and were plated as single cells to isolate clones. SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis is shown for two of these clones compared to naive cells. (H). Insertion of pac-2A-YFP cassette at p73 locus is more efficient with MRN-recruiting Cas9 constructs. HEK293 cells were transfected in biological triplicates with Cas9/sgRNA plasmids and donor DNA. Two days post-transfection cells were replated, with serial dilutions, into duplicate 96-well plates with or without 0.5 µg/mL puromycin. The XTT assay was used to quantify the relative amounts of puromycin-resistant cells, with the values from the plate without puromycin used for normalization. N = 3, * p < 0.023. (I). Editing of PSMB6-YFP using truncated chimeric constructs. HEK293 cells were transfected with Cas9/sgRNA plasmids and donor DNA. Cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (J). Summary of editing of PSMB6-YFP by chimeric constructs. Quantification of multiple experiments using this system with the indicated wt and chimeric Cas9 constructs. In each experiment, the level of PSMB6-YFP signal obtained with one of the wt Cas9 samples was set to “1”, and the fold increase/decrease of the other samples was compared to this standard (** p < 10−7, * p < 0.04).