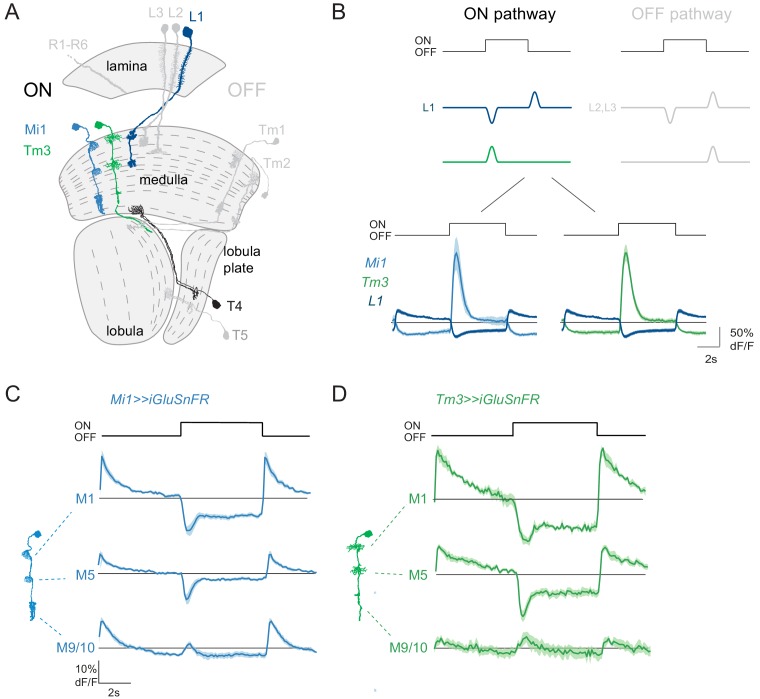
Figure 1. ON pathway medulla neurons that receive graded, glutamatergic input.
(A) Schematic of the fly visual system, highlighting major neurons of the ON (colored) and OFF (gray) pathways. Visual information travels from the photoreceptors (R1–R6) through the lamina, medulla and lobula complex (lobula + lobula plate). In the ON pathway, the L1 input and its two major postsynaptic targets Mi1 and Tm3 are highlighted, as well as their common target, the T4 ON-direction-selective cell. (B) Top: Schematic representation of the signal transformations that occur at the lamina-to-medulla neuron synapse. In the ON pathway, a sign inversion is required downstream of linear lamina neuron inputs. Bottom: In vivo calcium signals in response to 5 s full-field flashes. L1 calcium signals (dark blue, n = 6 [99]) are of the opposite sign to the calcium signal in its major postsynaptic partners Mi1 (light blue, n = 5 [89]) and Tm3 (green, n = 7 [84]). (C,D) In vivo iGluSnFR signals in response to 5 s long full-field flashes at the dendrites of Mi1 (C, n = 9[278] in layer M1, n = 9[250] in M5) and Tm3 (D, n = 6[137] in layer M1, n = 6[141] in M5), or at the output region of these neuron types in medulla layers M9/10 (n = 9[326] for Mi1 in C, n = 6[161] for Tm3 in D). All traces show mean ± SEM. Sample sizes are given as number of flies [number of cells].