Summary:
There are still children with cleft lip and/or palate (CLP) in low-resource areas who face social rejection. This stigma disadvantages children in education, employment, marriage, and community, and is exacerbated by barriers to care. Our study objective was to conduct a systematic review of the impact of social stigma of CLP for children in low-resource areas. We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses guidelines. A systematic search was conducted of 3 databases: Ovid Embase, Ovid Medline, and the African Journal Online from 2000 to October 5 2018. Common themes were identified using a grounded theory approach and quantitatively summarized. The Joanna Briggs Institute criteria were used to evaluate the risk-of-bias assessments. Four hundred seventy-seven articles were screened; 15 articles were included that focused on the impact of social stigma on CLP in low-resource areas. This was limited to English articles. The majority of studies originated in Nigeria or India. Themes were reported as follows: societal beliefs (n = 9; 60%), social impact (n = 7; 46%), marriage (n = 7; 46%), education (n = 6; 40%), employment (n = 5; 33%), and psychological distress (n = 3; 20%). Causes include the effect of “God’s will,” supernatural forces, evil spirits or ancestral spirits, exposure to an eclipse, black magic, or a contagion. Further, children with CLP may not be worth a full name or considered human and killed. Awareness of the impact of social stigma for children with CLP in low-resource areas generates support toward national education and awareness in low-resource areas.
INTRODUCTION
Cleft lip and/or palate (CLP) is the second most common congenital craniofacial anomaly, with 1 in 600 births worldwide.1 Low–middle-income countries have among the highest rates.1–3 Yet, there are cleft repairs in these countries that are still significantly delayed.4,5 Thus, children with CLP are especially vulnerable to the psychosocial consequences of CLP.5–11 Social stigma puts these children at additional disadvantages in education, employment, and marriage.5–11 Children with CLP are especially disadvantaged because of how CLP negatively hinders early education and social function.5–11 This carries forward into adulthood, making it difficult to seek higher-level education and employment.5,7,10 In low-resource areas, marriage has substantial economic benefits, and social benefits, which may be impeded by the social stigma of CLP.
Systematic reviews summarizing the psychosocial effects of cleft from high-income countries have previously been published12–15 and state that the majority of children and adults with CLP do not seem to experience major concerns in the social domain.12–15 Unfortunately, there is a stark contrast between high- and low-resource areas with barriers to treatment including cultural beliefs, geography, and financial support.4
No systematic review has summarized the impact of social stigma of CLP for pediatric patients in low-resource areas. Identifying the impact of social stigma on CLP for these patients can help prioritize resource allocation and provide further evidence toward incorporating quality-of-life measurements into outcome assessments for surgeons participating in international outreach and surgeons in low-resource areas.
Objective
This systematic review aims to summarize the impact of social stigma on CLP pediatric patients in low-resource areas. The research question is as follows: What are the common themes regarding the social impact of CLP in children living in low-resource areas compared with children without CLP?
METHODS
We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses guidelines (Fig. 1). A systematic search was registered in PROSPERO (ID: CRD42019112542). Four databases were searched: Embase, Medline, PubMed, and the African Journal Online from 2000 to October 5 2018. To maximize the number of search results, the African Journal Online was searched by the term “cleft” and search results were then manually sorted for relevance to the research question. The Medical Subject Heading terms and limits applied to the remaining 3 databases are outlined in Table 1. Inclusion criteria for the initial review were limited to articles focused on social stigma and CLP for a pediatric patient population. Pediatric age was defined as 18 years or less in accordance with the definition by the United Nations. Studies conducted only in countries designated as low- and- middle-income countries by the World Bank or reported as rural areas of higher-income countries were included in the study. Articles not in English, where we were unable to access the full text, and were not relevant to the current theme of social stigma and CLP were excluded. The primary review was conducted independently by 2 investigators (KYC, KS). The initial search resulted in 477 results, with 32 articles included in the full-text review. Following the secondary review, 15 articles were included in the study. A grounded theory approach was employed whereby the themes structuring the descriptive analysis were recorded throughout the article review process (KYC, KS, LW, TS). Articles were sorted into themes. Common themes that were discussed in these full-text articles were summarized to present a cohesive message. Quality appraisal was conducted using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) checklist.
Fig. 1.
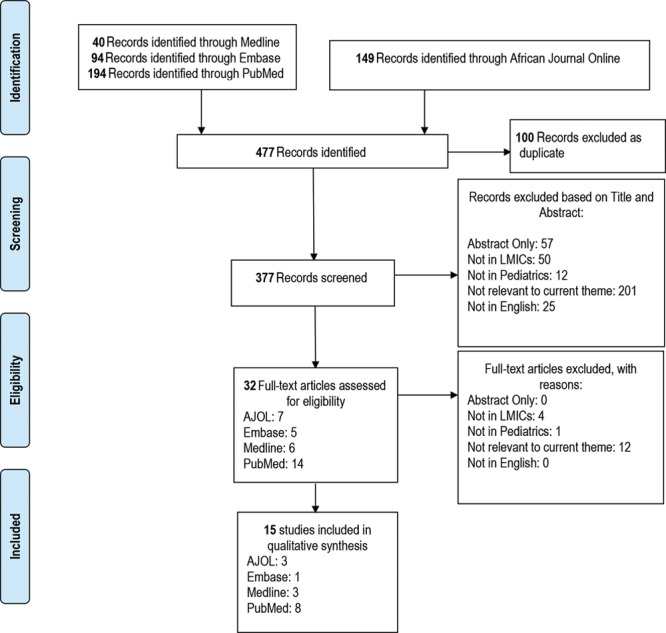
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses flow diagram for the screening process.
Table 1.
MeSH Search Terms for Medline, Embase and PubMed
| Where | Who | What | When |
| Medline | |||
| MeSH terms, combined with “OR”: Poverty Areas Poverty Developing Countries Social Welfare Rural Health Rural Population Hospitals, Rural Rural Health Services International Agencies Socioeconomic Factors |
Limits: “all infant (birth to 23 months)” “all child (0 to 18 years)” “newborn infant (birth to 1 month)” “infant (1 to 23 months)” “preschool child (2 to 5 years)” “child (6 to 12 years)” “adolescent (13 to 18 years)” |
MeSH Terms, combined with “OR”: Cleft lip Cleft palate |
Limits: 2000–2018/10/8 |
| Embase | |||
| MeSH terms, combined with “OR”: Socioeconomics International Cooperation Social Welfare Developing Country Poverty Rural Health Care Rural Population Rural Area Urban Rural Difference |
Limits: infant <to one year> child <unspecified age> preschool child <1 to 6 years> school child <7 to 12 years> adolescent <13 to 17 years>) |
MeSH terms Cleft lip Cleft lip palate Cleft face Cleft lip nose Unilateral cleft lip Cleft lip face palate Cleft palate |
Limits: 2000–2018/10/8 |
| PubMed | |||
| MeSH terms, combined with “OR”: Poverty Areas Poverty Developing Countries Social Welfare Rural Health Rural Population Hospitals, Rural Rural Health Services International Agencies Socioeconomic Factors |
Limits: Child: Birth to 18 years |
MeSH terms Cleft lip Cleft lip palate Cleft face Cleft lip nose Unilateral cleft lip Cleft lip face palate Cleft palate |
Limits: 2000/01/01–2018/10/08 |
All MeSH terms are exploded and focused.
MeSH, Medical Subject Heading.
RESULTS
There were 15 articles that focused on the impact of social stigma on CLP in low-resource areas (Table 2). Ages ranged from 0 to over 70 years. Of the 8 articles that reported sex, 75% (n = 6) reported a male dominance. Seven studies (47%) involved international collaboration with a high-income country. The majority of studies came from Nigeria (n = 4) and India (n = 4), with the majority of principal investigators from Nigeria (n = 4) and the United States (n = 4). Themes were reported as follows: societal beliefs (n = 9; 60%), social impact (n = 7; 46%), marriage (n = 7; 46%), education (n = 6; 40%), employment (n = 5; 33%), and psychological distress (n = 3; 20%) (Fig. 2).
Table 2.
Demographic Table Summarizing Themes Associated with Social Stigma of Included Articles
| Citation | Year | Title | CLP | Country of Study | Country of PI | Type of Study | Participant Age | Sex (M%, F%) | Themes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adigun and Adniran27 | 2004 | Unoperated adult cleft of the primary palate in Ilorin, Nigeria | CLP | Nigeria | Nigeria | Retrospective cohort | 15 to >25 y | M = 58%, F = 42%, n = 12 | Education |
| Agbenorku et al8 | 2007 | Endemicity of cleft lip/palate in a rural community in south-east Ghana | CLP | Ghana | Ghana | Cross-sectional | 10 to > 70 y | M = 77%, F = 23%, n = 13 | Marriage, education, employment, social impact, societal beliefs |
| Camille et al22 | 2014 | Advantages of early management of facial clefts in Africa | CLP | Côte d’Ivoire | Côte d’Ivoire | Retrospective cohort | 0–28 d | M = 61%, F = 39%, n = 70 | Social impact, societal beliefs |
| Chan et al9 | 2006 | Chinese attitudes toward cleft lip and palate: effects of personal contact | CLP | Hong Kong | Hong Kong | Qualitative | Mean age 13.9 y, 11–16 y | M = 55%, F = 45%, n = 40 | Marriage, employment, social impact, psychological distress, societal beliefs |
| El-Shazly et al16 | 2010 | Attitudes toward children with clefts in rural Muslim and Hindu societies | CLP | India, Egypt | USA | Qualitative | <18 y | Not reported, n = 100 | Marriage, education, employment, social impact, societal beliefs |
| Fadeyibi et al23 | 2012 | Psychosocial effects of cleft lip and palate on Nigerians: the Ikeja-Lagos experience | CLP | Nigeria | Nigeria | Qualitative | 0–6 y (45%), 6–12 y (19%), >12 y (36%) | M = 49%, F = 51%, n = 116 | Marriage, social impact, psychological distress |
| Fell et al5 | 2014 | The impact of a single surgical intervention for patients with a cleft lip living in rural Ethiopia | Isolated cleft lip | UK | Ethiopia | Qualitative | Mean age 14.2 y, 0 to >20 y | M = 62%, F = 38%, n = 356 | Marriage, education, employment, psychological distress |
| Kadambari21 | 2007 | A patient’s journey | CLP | Kenya | UK | Case study | 4 mo | M = 0%, F = 100%, n = 1 | Social impact |
| Mzezewa et al24 | 2014 | Neonatal cleft lip repair in babies with breastfeeding difficulties at Polokwane Mankweng Hospital Complex | Cleft lip | South Africa | South Africa | Prospective cohort | Median age 9 d, 3–28 d | M = 48%, F = 52%, n = 23 | Social impact |
| Naram et al18 | 2012 | Perceptions of family members of children with cleft lip and palate in Hyderabad, India, and its rural outskirts regarding craniofacial anomalies: a pilot study | CLP | India | USA | Qualitative | Mean age 28 mo | Not reported, n = 23 | Societal beliefs |
| Olasoji et al19 | 2007 | Cultural and religious components in Nigerian parents’ perceptions of the aetiology of cleft lip and palate: implications for treatment and rehabilitation | CLP | Nigeria | Nigeria | Qualitative | Not reported (not full population) |
Not reported | Societal beliefs |
| Owotade et al20 | 2012 | Awareness, knowledge and attitude on cleft lip and palate among antenatal clinic attendees of tertiary hospitals in Nigeria | CLP | Nigeria | Nigeria | Cross-sectional | Not reported (not full population) |
Not reported |
Societal beliefs |
| Parmar26 | 2007 | Hands-on training: working with a charity cleft team in Hyderabad | CLP | India | UK | Narrative | 3 mo to 13 y | Not reported | Marriage, employment |
| Reeve et al17 | 2004 | An international surgical exchange program for children with cleft lip/cleft palate in Manaus, Brazil: patient and family expectations of outcome | CLP | Brazil | USA | Qualitative | 6–20 y, majority <10 y | Not reported, n = 28 | Education, societal beliefs |
| Weatherley-White et al25 | 2004 | Perceptions, expectations, and reactions to cleft lip and palate surgery in native populations: a pilot study in rural India | CLP | India | USA | Qualitative | Not reported | M = 62%, F = 38%, n = 52 | Marriage, education, societal beliefs |
Fig. 2.
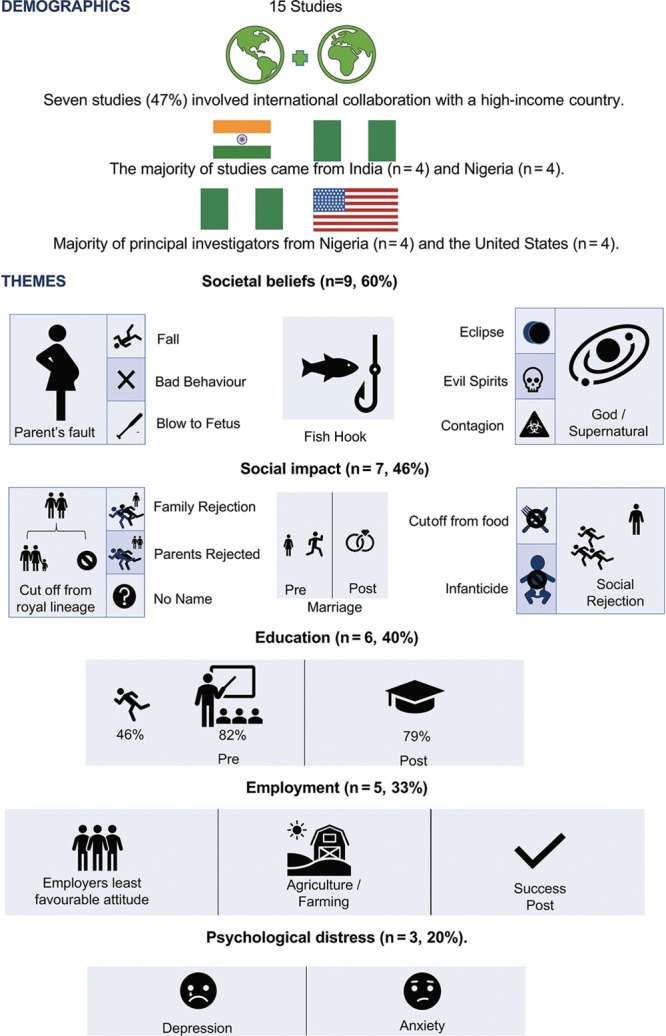
Infographic of the themes in the results.
Societal Beliefs
Etiology for cleft is seen to be punishment on the parent, blame on the parent, or personal conduct of the parent,16,17,23 including the parent slipping and falling,18 or force to the fetal face.10 One belief was that the father cut open the mouth of a fish to remove a fish hook whereas the mother was pregnant.17 Other causes include the effect of “God’s will,” supernatural forces, evil spirits or ancestral spirits,9.19 exposure to an eclipse,18 black magic,8 or a contagion.17 Further, children with CLP may not be seen as human.22 When asking the general community about cleft, very few knew that it affected the lip and face, much less its etiology.16
Social Impact
The social implications of CLP included social isolation or ostracism16 that range from rejection from family, being cutoff from a royal lineage or ascension to the throne,8 “being cutoff from society and food,”8,21 not being given a full name,23 or as a victim of infanticide.23 This may extend to the parents, in 1 instance the father being named as “the ghost child’s father.”8 The child may experience “lack of parental love and care from either or both parents,”23 and a child with CLP could be “terrifying for the mother.”24 There was 1 study that stated that parents, having the most intimate contact with persons with CLP, showed the most favorable attitude toward them.9
Marriage
Marriage appeared to be culture dependent, with mixed opinions as to whether CLP impeded the prospect of marriage. Fell et al. reported that in rural Ethiopia, the majority of patients who judged themselves for marriage had married preoperatively and “financial stability and status were more important than appearance” in marriage potential.5 In India, “there was a much greater emphasis on marriage (where) about 50% of parents were convinced that surgery would lead to better prospects of achieving a beneficial marriage,” especially for girls compared with boys (16:9).16,25
All studies stated that cleft surgery would increase marital prospects.5,8,9,16,23,25,26
Education
All studies discussed children with an inability to attend school. Children were either refused admission to school on the basis that it would frighten other children or refused to go to school because of taunting.5,8,21,27 Cleft repair provided hope, with many returning to school.5,8,17,27 In rural Ethiopia, the proportion almost doubled from 46% to 79%.5
Employment
Two studies described that patients were typically employed in agriculture and farming before and after surgery.5,8 One study reported that the employer group had the least favorable attitude toward people with CLP.9 The other 2 studies found that cleft surgery provided hope for a good career.21,27
Psychological Distress
Patients and their families felt unhappy with their lives, likely because of verbal insult.5,9,23 Patients had high levels of anxiety.9,23 Children were most often prevented from interacting with other people thus demonstrating a larger proportion of social dysfunction.23 Further, children and adolescents see parents as having negative feelings toward them with a lower degree of parental acceptance, which lead to a higher proportion of children with cleft feeling depressed compared with adults.23
Quality Assessment
The quality assessment was completed using the JBI checklist, a standardized checklist for cohort studies, qualitative research, and cross-sectional research (Figs. 3–5). The 3 cohort studies met <70% of JBI criteria. None of the studies explicitly stated if there were confounding factors, if groups or participants were free of the outcome at the start of the study, or explicitly used validated methods to assess outcomes. Outcomes were not explicitly stated, and thus it was difficult to identify whether follow-up was complete. Five of the 7 qualitative research studies met over 70% of JBI criteria. Although approval for research ethics was not explicitly stated, 6 of the 7 articles reported receiving consent before the research. The most common missing item was addressing the influence of the researcher on the research. One of the 2 cross-sectional studies met all criteria. The remaining study was a cohort study and case report. However, these standards are western standards and likely do not reflect the cultural context in many of these low-resource areas. Although the quality of the studies does vary, the themes reported are important to address for those involved with international outreach.
Fig. 3.
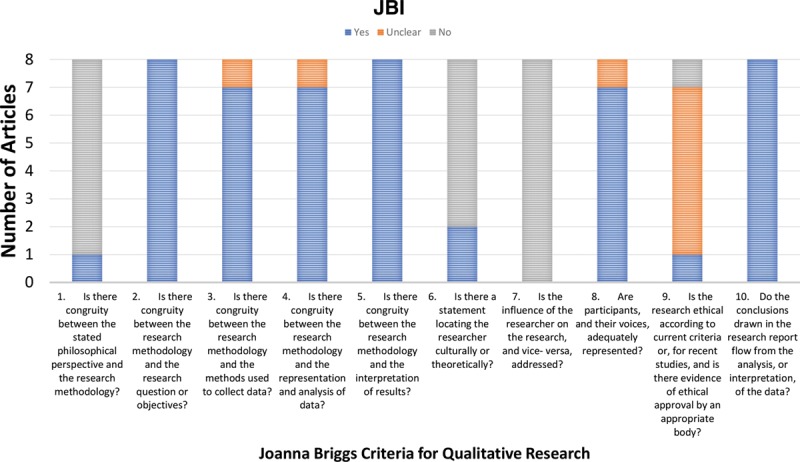
JBI criteria for qualitative research.
Fig. 5.
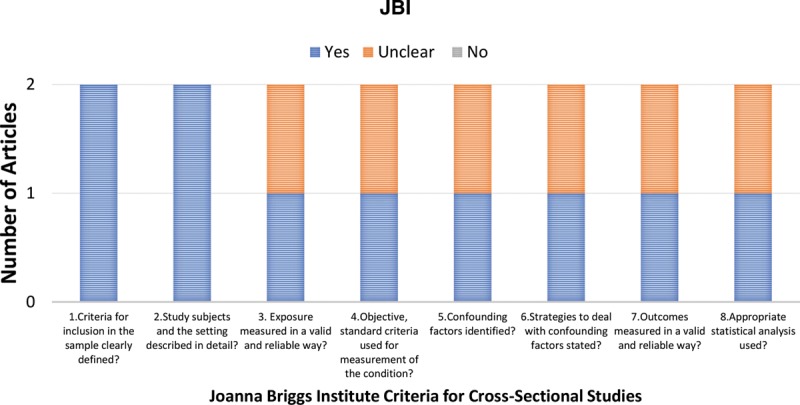
JBI criteria for cross-sectional studies.
Fig. 4.
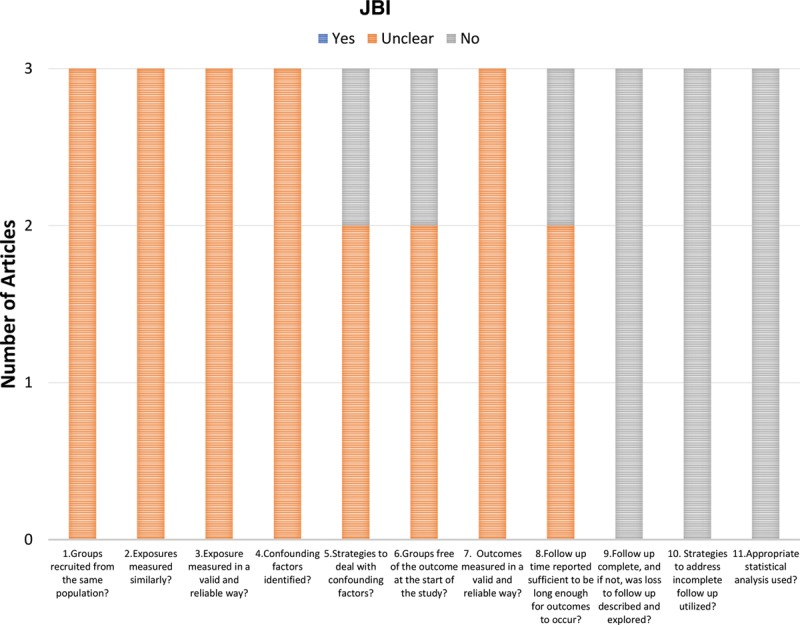
JBI criteria for cohort studies.
DISCUSSION
Social stigma is context dependent and is based on cultural perception of the cleft. Blame of the parent or the perception that the cleft is from a punishing supernatural force negatively influences the perception of the child with CLP. A child with CLP is subjected to bullying, rejection, and social isolation, even at times, from their family.5–11 This torment extends to school leading to a dropout from education and adds a further barrier to reaching their ideal employment.5–11 The inability to fully participate in the workforce translates into a substantial economic burden and lost productivity.6 Psychological distress naturally follows, with children being more affected than adults.5,9,23 Depending on the cultural context, the impact of cleft disease may or may not have an impact on marital status.
Cleft surgery provides hope to these children with a reenrolment back to school, hope for employment, social acceptance, and improved perception for marriage.5,8,17,27 Early surgical care is recommended.5,8,17,27 Cleft support and outreach should be through a diagonal approach.30 Building into the infrastructure of the community can help change the perception of the community.
This starkly contrasts against the culture in high-income countries, where the social domain is less of a concern. However, there are much more limited data and quality-of-life studies in low-resource areas. CLEFT-Q is a patient-reported outcome measure (PROMs) with domains in education, social and psychological function, that was created and validated in low-resource areas.28,29 We would recommend using this tool or other PROMs that have been validated in low-resource areas to assess the impact of cleft disease and treatment and gain a better understanding.
Finally, this further supports a need for government-led nation-wide policy in collaboration with nongovernment organizations to reduce stigma and increase public education surrounding CLP in low-resource areas.
Limitations
Because the rate of CLP is higher in low–middle-income countries in Asia and Latin America, social stigma is likely underreported in these countries. The extent of our literature search was limited to English articles. Using an online translation software of the title and abstract, none of these titles and abstracts discussed stigma and CLP. However, these full texts were not evaluated. In future studies, we will include the aid of French- and Spanish-speaking collaborators as these languages were needed. The predominance articles from Africa likely come from the use of African Journal Online. A future systematic review with other databases from different low- and middle-income countries would be valuable. Finally, the quality of literature could be improved with respect to the standards reported in the JBI checklist. Open discussion with colleagues in low-resource areas who are involved with research may help to generate awareness. Creation of culturally appropriate standards may also be of benefit for research in lower-resource areas.
CONCLUSIONS
Awareness of the impact of social stigma for children with CLP in low-resource areas demonstrates that there is a stark contrast between the psychosocial effects of CLP in high-income countries compared with low- and middle-income countries. To evaluate the benefit of cleft care on the psychosocial burden of CLP, this provides the use of PROMs developed in LMICs for collaborative NGOs and cleft care efforts. This also provides support for government-led nation-wide public education to raise awareness about CLP in low-resource areas.
Table 3.
JBI Qualitative Research Checklist
| Citation | Reeve et al17 | Chan et al9 | Weatherley-White et al25 | El-Shazly et al16 | Fadeyibi et al23 | Olasoji et al19 | Fell et al5 | Naram et al18 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Is there congruity between the stated philosophical perspective and the research methodology? | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | ||||||||
| 2. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the research question or objectives? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||||||
| 3. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the methods used to collect data? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | ||||||||
| 4. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the representation and analysis of data? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | ||||||||
| 5. Is there congruity between the research methodology and the interpretation of results? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||||||
| 6. Is there a statement locating the researcher culturally or theoretically? | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | ||||||||
| 7. Is the influence of the researcher on the research, and vice versa, addressed? | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | ||||||||
| 8. Are participants, and their voices, adequately represented? | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||||||
| 9. Is the research ethical according to current criteria or, for recent studies, and is there evidence of ethical approval by an appropriate body? | N | U | U | U | U | U | U | Y | ||||||||
| 10. Do the conclusions drawn in the research report flow from the analysis, or interpretation, of the data? | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||||||
Quality assessment using JBI checklist.
N, no; U, unclear; Y, yes.
Table 4.
JBI Cohort Research Checklist
| Citation | Camille et al22 | Adigun and Adniran27 | Mzezewa et al24 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Were the 2 groups similar and recruited from the same population? | U | U | U | |||
| 2. Were the exposures measured similarly to assign people to both exposed and unexposed groups? | U | U | U | |||
| 3. Was the exposure measured in a valid and reliable way? | U | U | U | |||
| 4. Were confounding factors identified? | U | U | U | |||
| 5. Were strategies to deal with confounding factors stated? | N | U | U | |||
| 6. Were the groups/participants free of the outcome at the start of the study (or at the moment of exposure)? | N | U | U | |||
| 7. Were the outcomes measured in a valid and reliable way? | U | U | U | |||
| 8. Was the follow-up time reported and sufficient to be long enough for outcomes to occur? | U | N | U | |||
| 9. Was follow-up complete, and if not, were the reasons to loss to follow up described and explored? | N | N | N | |||
| 10. Were strategies to address incomplete follow-up utilized? | N | N | N | |||
| 11. Was appropriate statistical analysis used? | N | N | N | |||
Quality assessment using JBI checklist.
N, no; U, unclear.
Table 5.
JBI Cross-sectional Study Checklist
| Criteria | Owotade et al20 | Agbenorku et al8 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Were the criteria for inclusion in the sample clearly defined? | Y | Y |
| 2. Were the study subjects and the setting described in detail? | Y | Y |
| 3. Was the exposure measured in a valid and reliable way? | Y | U |
| 4. Were objective, standard criteria used for measurement of the condition? | Y | U |
| 5. Were confounding factors identified? | Y | U |
| 6. Were strategies to deal with confounding factors stated? | Y | U |
| 7. Were the outcomes measured in a valid and reliable way? | Y | U |
| 8. Was appropriate statistical analysis used? | Y | U |
Quality assessment using JBI checklist.
N, no; U, unclear; Y, yes.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Christine B. Novak, PhD, for the revision of the manuscript before resubmission. The first two authors should be considered as co-first authors for this article.
Footnotes
Published online 28 October 2019.
Disclosure: The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
REFERENCES
- 1.Tanaka SA, Mahabir RC, Jupiter DC, et al. Updating the epidemiology of cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129:511e–518e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mossey PA, Little J, Munger RG, et al. Cleft lip and palate. Lancet. 2009;374:1773–1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Allori AC, Kelley T, Meara JG, et al. A standard set of outcome measures for the comprehensive appraisal of cleft care. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2017;54:540–554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yao CA, Swanson J, Chanson D, et al. Barriers to reconstructive surgery in low- and middle-income countries: a cross-sectional study of 453 cleft lip and cleft palate patients in Vietnam. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138:887e–895e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fell MJ, Hoyle T, Abebe ME, et al. The impact of a single surgical intervention for patients with a cleft lip living in rural Ethiopia. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67:1194–1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jones CM, Campbell CA, Magee WP, et al. The expanding role of education and research in international healthcare. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;76(suppl 3):S150–S154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Adeola DS, Ononiwu CNES. Cleft lip and palate in northern Nigerian children. Ann Afr Med. 2004;2:6–8. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Agbenorku P, Agbenorku M, Sefenu R, Matondo P, Osei D. Endemicity of cleft lip/palate in a rural community in South-East Ghana. J Sci Technol. 2007;27:45–50. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chan RK, McPherson B, Whitehill TL. Chinese attitudes toward cleft lip and palate: effects of personal contact. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2006;43:731–739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Daack-Hirsch S, Gamboa H. Filipino explanatory models of cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2010;47:122–133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Maine RG, Linden AF, Riviello R, et al. Prevalence of untreated surgical conditions in rural Rwanda: a population-based cross-sectional study in Burera District. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:e174013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Allori AC, Kelley T, Meara JG, et al. A standard set of outcome measures for the comprehensive appraisal of cleft care. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2017;54:540–554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Queiroz Herkrath AP, Herkrath FJ, Rebelo MA, et al. Measurement of health-related and oral health-related quality of life among individuals with nonsyndromic orofacial clefts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2015;52:157–172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hunt O, Burden D, Hepper P, et al. The psychosocial effects of cleft lip and palate: a systematic review. Eur J Orthod. 2005;27:274–285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Klassen AF, Tsangaris E, Forrest CR, et al. Quality of life of children treated for cleft lip and/or palate: a systematic review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65:547–557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.el-Shazly M, Bakry R, Tohamy A, et al. Attitudes toward children with clefts in rural Muslim and Hindu societies. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;64:780–783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Reeve M-E, Groce NE, Persing JA, Magge SN. An international surgical exchange program for children with cleft lip/cleft palate in Manaus, Brazil: patient and family expectations of outcome. J Craniofac Surg. 2004;15:170–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Naram A, Makhijani SN, Naram D, et al. Perceptions of family members of children with cleft lip and palate in Hyderabad, India, and its rural outskirts regarding craniofacial anomalies: a pilot study. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2013;50:e41–e46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Olasoji HO, Ugboko VI, Arotiba GT. Cultural and religious components in Nigerian parents’ perceptions of the aetiology of cleft lip and palate: implications for treatment and rehabilitation. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;45:302–305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Owotade FJ, Ogundipe OK, Ugboko VI, et al. Awareness, knowledge and attitude on cleft lip and palate among antenatal clinic attendees of tertiary hospitals in Nigeria. Niger J Clin Pract. 2014;17:6–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kadambari S. A patient’s journey. Med Teach. 2007;29:390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Camille A, Evelyne AK, Martial AE, et al. Advantages of early management of facial clefts in Africa. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;78:504–506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fadeyibi IO, Coker OA, Zacchariah MP, et al. Psychosocial effects of cleft lip and palate on Nigerians: the Ikeja-Lagos experience. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2012;46:13–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mzezewa S, Hamese K, Mashego TAB. Neonatal cleft lip repair in babies with breastfeeding difficulties at Polokwane Mankweng Hospital Complex. SAJCH South African J Child Heal. 2014;8:157–159. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Weatherley-White RC, Eiserman W, Beddoe M, et al. Perceptions, expectations, and reactions to cleft lip and palate surgery in native populations: a pilot study in rural India. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2005;42:560–564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Parmar J. Hands-on training: working with a charity cleft team in Hyderabad. Br Dent J. 2007;202:291–293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Adigun IA, Adeniran JO. Unoperated adult cleft of the primary palate in Ilorin, Nigeria. Sahel Med J. 2004;7:18–20. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tsangaris E, Wong Riff KWY, Goodacre T, et al. Establishing content validity of the CLEFT-Q: a new patient-reported outcome instrument for cleft lip/palate. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017;5:e1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wong Riff KW, Tsangaris E, Goodacre T, et al. International multiphase mixed methods study protocol to develop a cross-cultural patient-reported outcome instrument for children and young adults with cleft lip and/or palate (CLEFT-Q). BMJ Open. 2017;7:e015467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chung KY. Plastic and reconstructive surgery in global health: let’s reconstruct global surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017;5:e1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Google Translate. https://translate.google.com/?langpair=en%7Ces. Accessed July 01, 2019.


