Abstract
Objective The aim of this study was to design and evaluate a smartphone-based application for improving self-management in patients with asthma and evaluate its effects on their knowledge.
Methods In this applied research, based on the Clinical Practice Guideline and a systematic review, a questionnaire was designed to determine the application information content and functionality requirements by 15 pediatric and adult asthma and allergy specialist. Then the application was designed and developed using Adobe Air software on the Android operating system. Usability evaluation of the mobile application was performed using the standard questionnaire for user interaction satisfaction (QUIS), which completed by 30 patients with asthma, 8 information technology (IT) specialists, and 2 asthma and allergy specialists. Self-management knowledge of 30 asthma patients was measured using a researcher-made questionnaire before and after using the application.
Results The number of specialists in the both Delphi rounds was 15 and the mean work experiences were 17.6 years. The most important elements for asthma self-management were avoiding exposure to allergen and triggers (96%), drug treatment (94.6%), and how to use the therapeutic tools (92.4%), and the most important functionalities were alerting the patients when they did not control asthma (92%), setting reminders for timely drug use (85.4%) and therapeutic tools (82.6%), recording prescription drugs (82.6%), and peak flow meter values (82%). Usability evaluation showed that 30 patients with asthma, 8 IT specialists, and 2 physicians evaluated the application at a “good” level. The mean score of the patients' knowledge before intervention was 2.43 ± 0.95 which after intervention was significantly increased to 4.3 ± 0.56 ( p < 0.001).
Conclusion Considering the desirable outcomes of application evaluation and a positive impact of this educational intervention on asthma patients' knowledge, it is possible to use mobile-based self-management programs to help these patients to manage illness and gain knowledge and self-management skills.
Keywords: smartphone, application, usability, knowledge, asthma
Background and Significance
Asthma is a common, chronic, noncommunicable disorder of the respiratory tract, affecting more than 334 million people of all ages in all parts of the world. 1 It is predicted that the number of patients suffering from asthma will increase by 100 million more by 2025. 2 Asthma is a growing cause of morbidity and mortality in the world and imposes a significant burden on patients, families, and health care systems by reducing productivity. 3 During 2008 to 2013, asthma was responsible for $3 billion days off work and school, $29 billion due to asthma-related mortality, and $50.3 billion in medical costs. 4
Despite the availability of effective treatment options, many patients with asthma cannot control their symptoms so that almost 50% of them have symptoms more than once a week. 5 6 Therefore, improving patient participation, self-management, and adherence to therapeutic guidelines may help improve asthma symptoms. 7 Asthma self-management as part of regular and planned care can lead to an improvement in patient outcomes such as increased knowledge, self-esteem and quality of life, as well as a reduction in hospitalization, emergency visits and days off work or school. 8
Despite the evidence showing the benefits of asthma self-management programs, patients use them rarely 9 10 and the implementation of traditional self-management programs involve a written action plan in clinical practice is low, with only one in five patients. 11 Therefore, there is a need for innovative methods of self-management. Today, there is a more tendency to use mobile health, especially mobile applications, as a tool to provide appropriate and relevant services for asthma. 12 Mobile health (mHealth) applications are regarded as a multifunctional medium to communicate information, share experiences, and collect patients' data which are highly customizable, low cost, and readily available. These applications have the potential to overcome some of the limitations of traditional asthma management programs. 13
Several studies have been conducted to design and evaluate a mobile-based application for patients with asthma, some of which shown a positive impact, including studies showing that these interventions improve the quality of life, symptoms, and adherence to treatment. 14 15 16 17 18 19 At the same time, studies also revealed that the use of a smartphone-based application did not have a significant effect on asthma control, quality of life, and the number of health care visits and costs. 20 21 22
The results of several studies that evaluated the content of smartphone-based applications showed that the content of existing asthma mobile applications did not have appropriate and comprehensive quality information. 23 24 25 A recent study by Househ and colleagues showed that most of the asthma applications focused on self-monitoring and self-assessment, and the quality of health information was low among all of them. They emphasized that, despite the potential of applications for patients with asthma, a major effort is required to develop evidence-based asthma applications to protect patients' privacy and confidence. 24 To our knowledge, many applications were designed for asthma self-management; however, most of them have not been based on the clinical guidelines and have not been developed with the participation of clinical experts. 26 Therefore, it was suggested that the medical experts to be involved in mobile asthma application projects and the applications should be empirically evidence-based. 27
Objectives
With regard to the importance of training in daily asthma management, and the role of mobile applications in improving self-management, 28 29 30 and also the lack of reliable information in these applications, 23 24 25 designing an evidence-based application to promote self-management seems to be necessary. Therefore, the aim of this study was to design a mobile application based on the guideline, evaluate its usability by performing user evaluation, and examine its effects on their knowledge.
Methods
This applied developmental study was conducted at a central outpatient clinic of Asthma and Allergy affiliated to Kashan University of Medical Sciences in Iran and included five steps ( Fig. 1 ).
Fig. 1.
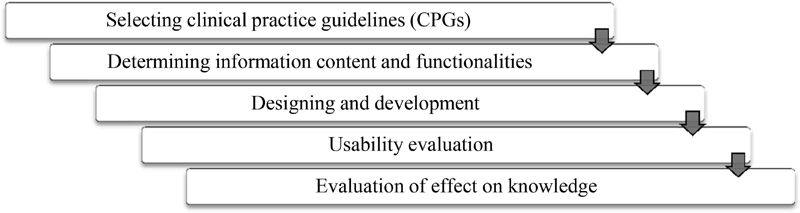
Research steps.
Selecting Clinical Practice Guidelines
At this stage, to determine the elements for self-management of asthma, we searched the databases for clinical guidelines and medical literatures with the keywords “Asthma Self-management,” “Asthma,” and “Asthma Treatment” (The search databases are shown in Supplementary Appendix A , available in the online version). Inclusion criteria for clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) were: the full text dealing with the self-management of asthma and available in English or Persian and released in the past 10 years. If more than one version existed, the latest one was included. Then a panel was established with five asthma and allergy specialists to select the most appropriate guideline.
Determining Information Content and Functionalities
In brief, a checklist was constructed to determine the information content and functionalities of the asthma self-management application based on the selected guideline from the previous stage and a systematic review conducted by the authors in this field. 28 The content validity of the checklist confirmed separately by specialists in the field of health information management (two people), nurse (eight people), and asthma and allergy specialists (five people). The minimum acceptable Content Validity Ratio (CVR) value for 15 participants was 0.42 based on the Lawshe's table and 0.79 for the Content Validity Index (CVI). The reliability of the checklist was measured on questionnaire field out by 20 patients with asthma using the internal consistency method and Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software (Cronbach's α = 0.892). The final checklist included five sections: information content (12 questions), information record (six questions), graphical representation of data (two questions), reminder and alert (seven questions), and communication with physician (four questions). A two-round Delphi's process was performed.
First Delphi Round
In this round, the checklist sent to 15 asthma and allergy specialists (which were faculty members and had at least 3 years of work experience) by e-mail to determine the necessity of application information contents and functionalities. Experts at this stage were not similar to the experts in content validity. The data collection finished after completing and returning the checklist by 15 participants. The answers were scored from 1 to 5 (very low = 1, low = 2, average = 3, high = 4, and very high = 5). The minimum score for acceptance of each item was 3.75. Items with a score of less than 2.5 were eliminated. The descriptive statistics (frequency, relative frequency, and mean) were calculated to analyze the findings of the Delphi phases, and the items were prioritized and analyzed based on the mean.
Second Delphi Round
All answers of the first Delphi round which reached a score between 2.5 and 3.75 were included in a checklist for the second Delphi round. The checklist was again distributed to the same group of participants to judge them.
Designing and Development
At first, the application information content and functionalities were designed based on the feedback received from the experts. The user interface graphic was designed on the Android platform using the Adobe Air software. The ActionScript 3, Java (in some classes and component) and PHP (in communication functionality) languages were used for programming. SQLite was used to design application database. Moreover, the designing program functionalities (information recording and reminders) were performed using the Query in this software. The application was developed with the help of health information management specialists, a medical informatics specialist, and a software engineer.
Usability Evaluation
In this step, the application was installed on the Android-based smartphone of 30 patients with asthma (with age > 18 years and at least primary education), eight IT professionals (with at least a bachelor's degree with 2 years of work experience), and two asthma and allergy specialists. After learning how to use the application to users, they were asked to use it for a month. After 1 month, user comments about the application gathered using the standard Questionnaire for User Interaction Satisfaction (QUIS). 31 This 10-point Likert's scale questionnaire (0–9) had five main parts (23 questions), included overall reaction to the software (six questions), screen design and layout (four questions), terminology and systems information (four questions), learning (four questions), and system capabilities (five questions). The English language version of the questionnaire was translated into Persian (Iranian language). Its face validity confirmed by five experts in health information management and medical informatics. The reliability of the questionnaire was 0.94 based on the previous study. 32 The mean and standard deviation (SD) were calculated for analyzing the findings of application usability evaluation. The scores were classified into three levels as follows: weak (0–3), average (3–6), and good (6–9). Comments from different groups compared using Kruskal–Wallis and Mann–Whitney U -tests in SPSS software.
Evaluation of Effect on Knowledge
A researcher-made questionnaire consisting of two parts was designed to examine the self-management knowledge of patients with asthma, before and after using the application. The first section included patients' demographic characteristics (six questions) and the second part included 19 questions about self-management activities. After obtaining informed consent verbally, the questionnaires were distributed among 30 patients (with age > 18 years, an android-based mobile phone, and at least primary education). The responses were scored in five Likert's scales from very low to very high. The pretest questionnaire was completed and the application was installed on patients' smartphones. A brief description of how to use the application was given to users and a daily Short Message Service (SMS) reminder was sent to encourage patients to use the app. To evaluate the effect of the application on knowledge, the participants completed the posttest questionnaire, which was similar to the pretest questionnaire, after 1 month. The mean and standard deviation of scores in both the pre- and poststeps were calculated by SPSS software. In the next step, the nonparametric Wilcoxon's test was employed to evaluate the effects of the application.
Results
Selecting Clinical Practice Guidelines
Following the search for literatures, four CPGs for asthma self-management 33 34 35 36 were selected ( Table 1 ). Consulting with an expert group of five asthma and allergies specialists and considering the inclusion criteria, the most appropriate guideline (National Asthma Guide: Guidelines for Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment 36 ) was selected. In fact, it was chosen because of the native and comprehensive nature of this guideline.
Table 1. Cinical practice guidelines selected for the asthma self-management.
| Clinical practice guidelines | Year of publication | Place of publication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| British Thoracic Society Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. British guideline on the management of asthma: SIGN 153 | 2016 | England | 33 |
| National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report 3 (EPR-3): Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma | 2007 | America | 34 |
| Pocket Guide for Asthma Management and Prevention | 2017 | America | 35 |
| National Asthma Guide: Guidelines for Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment (Ministry of Health and Medical Education) | 2016 | Iran | 36 |
Determining Information Content and Functionalities
First and Second Delphi's Rounds
The number of participating women and men in the both Delphi rounds was 11 and 4, respectively. The lowest, highest, and mean work experiences were 6, 25, and 17.6 years, respectively. The results of the information content of asthma self-management in the first Delphi round are presented in Table 2 . Of the 12 elements in the first Delphi round, 11 elements were accepted. Only one element “self-assessing the asthma symptoms control” was reviewed in the second Delphi round which was approved after consultation with participants.
Table 2. Experts' views on application information content.
| Row | Information Content | Elements | Mean | Judge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basic facts about the nature of the condition | Clinical signs of disease | 4.33 | Accept |
| 2 | Definition of asthma | 3.93 | Accept | |
| 3 | The nature of treatment: relievers and preventers | Drug treatment | 4.73 | Accept |
| 4 | Nondrug treatments | 4.07 | Accept | |
| 5 | Allergen and trigger avoidance | Recognizing and avoiding exposure to allergen and triggers | 4.8 | Accept |
| 6 | How to use treatment | How to use the Therapeutic tools | 4.62 | Accept |
| 7 | How to use the peak flow meter and interpret its results | 3.33 | Accept | |
| 8 | Self-monitoring and assessment skills | Assessment of asthma control and risk factors | 4.47 | Accept |
| 9 | Follow up, care and monitoring of patients based on disease control | 4.4 | Accept | |
| 10 | Use of tools to self-assess asthma symptoms (ACT) | 3.13 | Revise | |
| 11 | Recognizing and responding appropriately to acute exacerbations | Definition of asthma attack | 4.27 | Accept |
| 12 | Asthma attacks severity criteria | 4 | Accept |
Abbreviation: ACT, asthma control test.
The physicians' views on the necessity of the application functionalities in the first Delphi round are shown in Table 3 . The results showed that the functionalities of “data charts,” “communicating with the physician by text messaging and phone calls,” and “sharing asthma charts with the physician” were removed in the first Delphi round. The “set reminder for peak flow meter,” “asthma control self-assessment,” and “communication with physicians through social networks” functionalities were reviewed again in the second Delphi round and then approved after consultation with participants.
Table 3. Experts' views on application functionalities.
| Row | Groups | Functionalities | Mean | Judge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Information record | Drugs used | 4.13 | Accept |
| 2 | Peak flow meter values | 4.1 | Accept | |
| 3 | Symptoms | 3.93 | Accept | |
| 4 | Asthma attacks | 3.87 | Accept | |
| 5 | Triggers | 3.86 | Accept | |
| 6 | Patient's weight to calculate a dose | 2.26 | Reject | |
| 7 | Reminder/alert | Alert for uncontrolled asthma | 4.6 | Accept |
| 8 | Timely reminders to take medication | 4.27 | Accept | |
| 9 | Reminder for respiratory assistance devices use | 4.13 | Accept | |
| 10 | Reminder for appointments | 3.87 | Accept | |
| 11 | Reminder for flu vaccination | 3.8 | Accept | |
| 12 | Peak flow meter test reminder | 2.8 | Revise | |
| 13 | Reminder for asthma self-assessment | 2.67 | Revise | |
| 14 | Graphical representation of data | Respiratory test charts | 2.4 | Reject |
| 15 | Current patient status | 2.33 | Reject | |
| 16 | Communication with physician | Communicate with doctor via social networks | 2.8 | Revise |
| 17 | Share the patient's status charts with doctor | 2.4 | Reject | |
| 18 | Communicate with doctor via SMS | 2.33 | Reject | |
| 19 | Communicate with doctor via phone call | 1.53 | Reject |
Abbreviation: SMS, short message service.
Designing and Development
Based on the feedback received from the experts in the Delphi phase, the application functionalities were implemented on the Android operating system. Supplementary Appendix B (available in the online version) shows examples of application layouts. The application contains an extensive collection of evidence-based educational materials which are available in written format and quizzes.
Usability Evaluation
The number of women and men participating in the usability evaluation was 15 each. Sixty percent of patients were with asthma duration of 4 years or less. Half of the patients (50%) had “mild persistent” asthma. Twenty-seven patients (90%) had a lower education than a bachelor, and 10% had higher education. The mean age of patients was 32.9 ± 12.95 years. Among the eight IT professionals, five were males and three were females. The mean age and working experience were 34.38 ± 6.9 and 9.25 ± 5.84 years, respectively. Six of them had higher education levels. The specialists who participated in the evaluation were both female with mean age and work experience of 49 ± 0 and 14 ± 2.22 years, respectively. The data analysis results of the application usability are presented in Table 4 . Mean usability evaluation scores were in the range of 6 to 9, which considered at a “good” level. There was no statistically significant difference between the three groups in all domains.
Table 4. Usability evaluation of the app by patients, IT specialists and physicians.
| Row | Assessment areas | Patients | IT specialists | Physicians | p -Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |||
| 1 | Overall reaction to the software | 7.88 ± 0.98 | 7.66 ± 0.57 | 8.58 ± 0.58 | 0.344 |
| 2 | Screen design and layout | 8.25 ± 0.85 | 7.87 ± 0.59 | 8.62 ± 0.53 | 0.119 |
| 3 | Terminology and systems information | 8.04 ± 0.85 | 8.09 ± 0.61 | 8.5 ± 0.7 | 0.696 |
| 4 | Learning | 8.1 ± 0.88 | 8.37 ± 0.51 | 8.25 ± 0.7 | 0.869 |
| 5 | System capabilities | 8.06 ± 0.99 | 7.8 ± 0.72 | 8 ± 0 | 0.471 |
| Total | 8.05 ± 0.78 | 7.92 ± 0.51 | 8.39 ± 0.49 | 0.644 | |
Abbreviations: IT, information technology; SD, standard deviation.
Note: All questions were scored in a range of 0 to 9.
Evaluation of Effect on Knowledge
The mean and standard deviation of asthma patients' self-management knowledge scores before and after intervention are shown in Table 5 . Based on the results of the study, the total mean of pre-intervention knowledge scores was 2.43 ± 0.95 and post-intervention was 4.3 ± 0.56, which was statistically significant.
Table 5. Evaluation of effect on knowledge of asthma patients before and after intervention.
| Row | Domains | Before | After | p -Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | ||||
| 1 | Basic facts about the nature of the condition | 2.53 ± 1.12 | 4.2 ± 0.65 | <0.001 |
| 2 | Recognizing and responding appropriately to acute exacerbations | 2.21 ± 1.14 | 4.08 ± 0.7 | <0.001 |
| 3 | The nature of treatment: relievers and | 2.71 ± 1.05 | 4.08 ± 0.63 | <0.001 |
| 4 | Allergen and trigger avoidance | 2.95 ± 1.35 | 4.46 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| 5 | How to use treatment | 1.95 ± 1.03 | 4.09 ± 0.69 | <0.001 |
| 6 | Self-monitoring and assessment skills | 1.63 ± 1.03 | 4.26 ± 0.78 | <0.001 |
| Total | 2.43 ± 0.95 | 4.18 ± 0.56 | <0.001 | |
Abbreviation: SD, standard deviation.
Discussion
In this study, an asthma self-management application was designed and developed with the functionalities of providing educational information, recording data, setting a reminder, and communicating with the physician. The usability evaluation showed that the application was “good” from the evaluators' point of view and the findings indicated a positive impact of the application on patients' knowledge of self-management activities. Similarly, several studies have been conducted on the design and development of asthma self-management applications. 14 15 16 17 20 21 22 37 38 Of these, four studies assessed an application. 14 15 21 38 Only one of these studies examined the application's impact on the self-management knowledge, in which patients reported ease of use, clarity, and timeliness of the application and improvements in self-management knowledge than before the intervention. 21
In the present study, elements of asthma self-management application were classified into six categories. Physicians considered “avoiding exposure to allergen and triggers,” “drug treatment” and “how to use the therapeutic tools” as the most important elements in asthma self-management. These findings were similar to those of other studies on asthma patients. 23 39 40 41 42 Unlike the present study, in two studies, “how to use the respiratory assistance devices and peak flow meter” were considered to be of minor importance from the patients' point of view. 43 44 The reason for this difference is probably due to the difference in target groups in two previous studies with our study. Given that inhalation therapy and inhalation techniques are the basis of asthma treatment and the lack of proper use of these devices may lead to poor asthma control and increase costs 45 ; therefore, it is better this information content considered in asthma self-management education from the viewpoint of physicians.
According to the findings, functionalities of asthma self-management application were classified into the following four categories: data recording, graphically displaying data, providing of reminders and alerts, and communicating with a physician. The most important functionalities from the asthma and allergy experts' viewpoint were “alerting to patient when asthma was not controlled,” setting a reminder for timely drug use, and recording medication and peak flow meter values. Other studies also showed similar results. 16 46 In a study by Geryk et al (2016), the parents of children with asthma reported “recording data, physician communication, and sharing data via e-mail” and physicians reported “reminder for physician appointment” as the most important functionalities of the applications. 47 But because of the difference in targeting groups, asynchronous communication via e-mail and lack of sufficient time for physicians to connect to the internet, 48 49 this functionality was different in our study than in previous studies. Therefore, in this study, e-mail is not a good medium for interactions between patients and physicians in the viewpoints of experts. Regarding the features of the application, graphically displaying data were removed. Although this feature was removed because the specialist rated low, however, it might be rated high by the patients. As in the study of Rudin et al, 38 this feature was included in the application functionalities and patients with asthma generally agreed to the need to easily review their most recent 1 to 2 months of symptom scores.
The findings from the usability evaluation revealed that the application was “good” from the point of view of asthma patients, IT specialists, and doctors. These findings were similar to results of other studies. 50 51 52 In all of these studies, applications were at the “good” level from the user's perspective. In most of these studies, application usability evaluation was conducted solely from the perspective of a group of users. Since usability evaluation is an important process in the design and implementation of applications and identifies the weaknesses and strengths, 53 it is suggested that future studies employ the opinions of different users, 54 including patients, nurses, and physicians to identify system problems.
The results showed that the mean self-management knowledge score of asthma patients increased after the intervention than before the intervention. This significant difference was indicative of the effect of educational intervention in improving knowledge of patients about self-management activities. Other similar studies confirmed this finding. 55 56 57 Knowledge is one of the essential components for behavior change and is achieved through training in various subjects. 58 Training asthma patients also increases self-management knowledge and, subsequently, improves quality of life. 59 Considering the positive effects of educational applications on the knowledge level of asthma patients, it is recommended that health practitioners and health policy-makers use this tool as an effective method along with other educational methods and make the necessary plans to develop it.
Strengths and Limitations
There are several strengths and limitations of this study. The strengths included the use of a native and comprehensive guideline for asthma self-management, and experts' views in designing the application. However, this study also has limitations. We did not involve patients in the application development. Instead, they were involved in application usability testing. Therefore, it is suggested that future studies consider both physicians and patients in designing the apps. The pre- and postintervention methods, used to assess the effect of the application on the asthma patients' knowledge, did not have a simultaneous control group. Therefore, it is recommended that studies to be designed and implemented that have a control group that is similar to the intervention group in terms of demographic characteristics and other effective factors. Another limitation is related to the 1-month follow-up period and a small number of samples in assessing the asthma patients' knowledge that should be considered in future studies. The usability evaluation was based solely on the QUIS questionnaire. This questionnaire is a useful tool for gaining an overall impression of the usability of an interactive system. Nevertheless, it is not detailed enough to provide specific information about possible usability problems with a system. This should be complemented with some other kind of usability evaluation. Finally, we did not assess patient engagement and use of the application for recording information, setting a reminder, communicating with the physician, which should be taken into consideration in future studies.
Implications for Future Research
Considering the use of a valid guideline to provide educational content to asthma patients in this study and lack of reliable information in available asthma applications, the involvement of health care providers and health monitoring organizations in controlling the mHealth application quality seems to be necessary. 60 It is also recommended to design a system for evaluating the application content validity in the country. The development of a multicomponent smartphone application aimed at improving self-management through a medication reminder and other features, such as education, and a medication log, is warranted. 61 In order for physician to recommend this application to patients, effectiveness evaluations for improving health and economic outcomes are necessary. 62 63
Conclusion
The result of this study was an Android-based self-management application for patients with asthma which designed based on the nationalized localized guideline. Considering the desirable results of the application usability evaluation by participations (patients, physicians, and IT specialists) and the positive effects of this educational intervention on the asthma patients' knowledge, it is recommended to use these tools as a training method to manage the disease and acquire an awareness of the self-management skills. Future studies need to examine the effectiveness of application on self-management activities, clinical, and economic outcomes.
Clinical Relevance Statement
Due to the benefits of mobile health applications in self-management and patients' lack of awareness of them, only clinical professionals can encourage patients to use these applications.
Multiple Choice Questions
-
According to the findings of this study, which of the following communication tools are “not suitable” for interaction between patient and physician?
SMS.
E-mail.
Social networks.
Phone call.
Correct Answer: The correct answer is option b, because of the asynchronous communication and lack of sufficient time for physicians to connect to the internet, e-mail is not a good medium for interactions between patients and physicians.
-
According to the findings, which of the following functionalities of an asthma application are more important “in the first place?”
Alerting to patients.
Graphically displaying data.
Communicating with physician.
Recording data.
Correct Answer: The correct answer is option a, the most important functionalities from the asthma and allergy experts' viewpoint were “alerting to patient when asthma was not controlled,” setting a reminder for timely drug use, and recording medication and peak flow meter values.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the experts who participated in the Delphi phase. We would also like to extend our appreciation to the patients and IT specialists who participated in the usability evaluation phase.
Funding Statement
Funding This study was supported by a grant from Kashan University of Medical Sciences Research Council (Number: 9606).
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Protection of Human and Animal Subjects
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Kashan University of Medical Sciences (Number: IR.KAUMS.REC.1396.6).
Supplementary Material
References
- 1.Global Asthma Network.The global asthma report 2014Available at:http://www.globalasthmareport.org/2014/about/executive.php. Accessed September 23, 2019
- 2.Bousquet J, Bousquet P J, Godard P, Daures J P. The public health implications of asthma. Bull World Health Organ. 2005;83(07):548–554. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bateman E D, Hurd S S, Barnes P J et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(01):143–178. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00138707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nurmagambetov T, Kuwahara R, Garbe P. The economic burden of asthma in the United States, 2008–2013. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018;15(03):348–356. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201703-259OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McDaniel M K, Waldfogel J. Racial and ethnic differences in the management of childhood asthma in the United States. J Asthma. 2012;49(08):785–791. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2012.702840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Adler R N, McBride J. Tools and strategies for improving asthma management. Fam Pract Manag. 2010;17(01):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Eakin M N, Rand C S. Improving patient adherence with asthma self-management practices: what works? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012;109(02):90–92. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2012.06.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.British Thoracic Society Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network.British Guideline on the Management of Asthma Thorax 20086304iv1–iv121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hoskins G, McCowan C, Donnan P T, Friend J A, Osman L M; Asthma UK Scotland; Scottish Executive Health Department.Results of a national asthma campaign survey of primary care in Scotland Int J Qual Health Care 20051703209–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ring N, Malcolm C, Wyke S et al. Promoting the use of personal asthma action plans: a systematic review. Prim Care Respir J. 2007;16(05):271–283. doi: 10.3132/pcrj.2007.00049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Honkoop P J, Simpson A, Bonini M et al. MyAirCoach: the use of home-monitoring and mHealth systems to predict deterioration in asthma control and the occurrence of asthma exacerbations; study protocol of an observational study. BMJ Open. 2017;7(01):e013935. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Morrison D, Wyke S, Agur K et al. Digital asthma self-management interventions: a systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2014;16(02):e51. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Marcano Belisario J S, Huckvale K, Greenfield G, Car J, Gunn L H. Smartphone and tablet self management apps for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(11):CD010013. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010013.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Burbank A J, Lewis S D, Hewes M et al. Mobile-based asthma action plans for adolescents. J Asthma. 2015;52(06):583–586. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2014.995307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cingi C, Yorgancioglu A, Cingi C C et al. The “physician on call patient engagement trial” (POPET): measuring the impact of a mobile patient engagement application on health outcomes and quality of life in allergic rhinitis and asthma patients. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015;5(06):487–497. doi: 10.1002/alr.21468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cook K A, Modena B D, Simon R A. Improvement in asthma control using a minimally burdensome and proactive smartphone application. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016;4(04):730–7370. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu W-T, Huang C D, Wang C H, Lee K Y, Lin S M, Kuo H P. A mobile telephone-based interactive self-care system improves asthma control. Eur Respir J. 2011;37(02):310–317. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00000810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rhee H, Allen J, Mammen J, Swift M. Mobile phone-based asthma self-management aid for adolescents (mASMAA): a feasibility study. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:63–72. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S53504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Badawy S M, Barrera L, Sinno M G, Kaviany S, O'Dwyer L C, Kuhns L M. Text messaging and mobile phone apps as interventions to improve adherence in adolescents with chronic health conditions: a systematic review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2017;5(05):e66. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.7798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ryan D, Price D, Musgrave S D et al. Clinical and cost effectiveness of mobile phone supported self monitoring of asthma: multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2012;344:e1756. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Licskai C, Sands T W, Ferrone M. Development and pilot testing of a mobile health solution for asthma self-management: asthma action plan smartphone application pilot study. Can Respir J. 2013;20(04):301–306. doi: 10.1155/2013/906710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zairina E, Abramson M J, McDonald C F et al. Telehealth to improve asthma control in pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial. Respirology. 2016;21(05):867–874. doi: 10.1111/resp.12773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huckvale K, Morrison C, Ouyang J, Ghaghda A, Car J. The evolution of mobile apps for asthma: an updated systematic assessment of content and tools. BMC Med. 2015;13(01):58. doi: 10.1186/s12916-015-0303-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Househ M, Hossain N, Jamal A et al. A cross-sectional content analysis of Android applications for asthma. Health Informatics J. 2017;23(02):83–95. doi: 10.1177/1460458215627289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huckvale K, Car M, Morrison C, Car J. Apps for asthma self-management: a systematic assessment of content and tools. BMC Med. 2012;10(01):144. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tinschert P, Jakob R, Barata F, Kramer J N, Kowatsch T. The potential of mobile apps for improving asthma self-management: a review of publicly available and well-adopted asthma apps. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2017;5(08):e113. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.7177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lienhard K R, Legner C.Principles in the design of mobile medical apps: guidance for those who care. in 13th International Conference on Wirtschaftsinformatik (WI 2017), February 12–15, 2017St. Gallen, Switzerland. 1066–1080
- 28.Farzandipour M, Nabovati E, Sharif R, Arani M H, Anvari S. Patient self-management of asthma using mobile health applications: a systematic review of the functionalities and effects. Appl Clin Inform. 2017;8(04):1068–1081. doi: 10.4338/ACI-2017-07-R-0116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Berry D L, Blonquist T M, Nayak M M, Grenon N, Momani T G, McCleary N J. Self-care support for patients with gastrointestinal cancer: iCancerHealth. Appl Clin Inform. 2018;9(04):833–840. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1675810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Badawy S M, Thompson A A, Kuhns L M. Medication adherence and technology-based interventions for adolescents with chronic health conditions: a few key considerations. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2017;5(12):e202. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.8310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chin J P, Diehl V A, Norman K L.Development of an instrument measuring user satisfaction of the human-computer interfaceACM Digital Library.1988 10.1145/57167.57203 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Alexandru C-A.Usability testing and improvement of telemedicine websites, in School of Informatics2010, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh:257. Available at:http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/publications/thesis/online/IM100870.pdf. Accessed November 13, 2019
- 33.James D R, Lyttle M D. British guideline on the management of asthma: SIGN clinical guideline 141, 2014. Arch Dis Childhood Educ Pract. 2016;101:319–322. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2015-310145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.National Asthma Education and Prevention Program.Expert panel report 3 (EPR3): guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007120(5, Suppl):S94–S138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Global Initiative for Asthma.Pocket guide for asthma management and prevention: a pocket guide for health professionalsAvailable at:https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/GINA-2019-main-Pocket-Guide-wms.pdf. Accessed September 23, 2019
- 36.Ministry of Health and Medical Education, Department of Noncommunicable Disease Management, National Committee of Chronic Respiratory Diseases: National Asthma Guideline: Prevention, Diagnosis and Management Protocol, vol. 1. Tehran, Iran: Mehre Touba Publications; 2016
- 37.Haze K A, Lynaugh J.Building patient relationships: a smartphone application supporting communication between teenagers with asthma and the RN care coordinator Comput Inform Nurs 20133106266–271., quiz 272–273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rudin R S, Fanta C H, Predmore Z et al. Core components for a clinically integrated mHealth app for asthma symptom monitoring. Appl Clin Inform. 2017;8(04):1031–1043. doi: 10.4338/ACI-2017-06-RA-0096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sapir T, Moreo K F, Greene L S et al. Assessing patient and provider perceptions of factors associated with patient engagement in asthma care. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(05):659–666. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201608-602OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Croft D R, Peterson M W. An evaluation of the quality and contents of asthma education on the World Wide Web. Chest. 2002;121(04):1301–1307. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.4.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nagappa A et al. Evaluation of web sites for quality and contents of asthma patient education. J Young Pharm. 2009;1(03):278. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Park H-W, Min K U, Kim Y Y, Cho S H. Assessing the quality and contents of asthma-related information on the Korean internet as an educational material for patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19(03):364–368. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Basyouni M H et al. Online health information needs for patients with asthma in Saudi Arabia. J Consum Health Internet. 2015;19(01):13–24. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Loerbroks A, Sheikh A, Leucht V, Apfelbacher C J, Icks A, Angerer P. Determinants of patients' needs in asthma treatment: a cross-sectional study. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2016;26:16044. doi: 10.1038/npjpcrm.2016.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lavorini F, Usmani O S. Correct inhalation technique is critical in achieving good asthma control. Prim Care Respir J. 2013;22(04):385–386. doi: 10.4104/pcrj.2013.00097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Peters D, Davis S, Calvo R A, Sawyer S M, Smith L, Foster J M. Young people's preferences for an asthma self-management app highlight psychological needs: a participatory study. J Med Internet Res. 2017;19(04):e113. doi: 10.2196/jmir.6994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Geryk L L, Roberts C A, Sage A J, Coyne-Beasley T, Sleath B L, Carpenter D M. Parent and clinician preferences for an asthma app to promote adolescent self-management: a formative study. JMIR Res Protoc. 2016;5(04):e229. doi: 10.2196/resprot.5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Antoun J. Electronic mail communication between physicians and patients: a review of challenges and opportunities. Fam Pract. 2016;33(02):121–126. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmv101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Patt M R, Houston T K, Jenckes M W, Sands D Z, Ford D E. Doctors who are using e-mail with their patients: a qualitative exploration. J Med Internet Res. 2003;5(02):e9. doi: 10.2196/jmir.5.2.e9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ghazisaeedi M et al. Designing a mobile-based self-care application for patients with heart failure. J Health Biomed Informat. 2016;3(03):195–204. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Langarizadeh M, Behzadian H, Samimi M. Development of personal health record application for gestational diabetes, based on smart phone. J Urmia Nurs Midwifery Fac. 2016;14(08):714–727. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ayatollahi H, Hasannezhad M, Fard H S, Haghighi M K. Type 1 diabetes self-management: developing a web-based telemedicine application. Health Inf Manag. 2016;45(01):16–26. doi: 10.1177/1833358316639456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hamborg K C, Vehse B, Bludau H B. Questionnaire based usability evaluation of hospital information systems. Electronic J Inform Syst Eval. 2004;7(01):21–30. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Joshi A, Wilhelm S, Aguirre T, Trout K, Amadi C. An interactive, bilingual touch screen program to promote breastfeeding among Hispanic rural women: usability study. JMIR Res Protoc. 2013;2(02):e47. doi: 10.2196/resprot.2872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jan R-L, Wang J Y, Huang M C, Tseng S M, Su H J, Liu L F. An internet-based interactive telemonitoring system for improving childhood asthma outcomes in Taiwan. Telemed J E Health. 2007;13(03):257–268. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2006.0053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Krishna S, Francisco B D, Balas E A, König P, Graff G R, Madsen R W; Randomized trial.Internet-enabled interactive multimedia asthma education program: a randomized trial Pediatrics 200311103503–510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wyatt T H, Hauenstein E J. Pilot testing Okay With Asthma: an online asthma intervention for school-age children. J Sch Nurs. 2008;24(03):145–150. doi: 10.1177/1059840522334455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mehdipour A et al. Evaluation of knowledge, attitudes and performance of the parents of preschool and primary school children referred to health centers of Qom city about the importance of preserving primary teeth and its related factors, Iran. Qom Univ Med Sci J. 2016;10(06):94–105. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Qiu B, Huang L, Li Y.Health education for asthmatic patients and caregivers from nursing perspective 2017. Turku University of Applied Sciences; available at:https://www.theseus.fi/handle/10024/138328
- 60.Buijink A W, Visser B J, Marshall L. Medical apps for smartphones: lack of evidence undermines quality and safety. Evid Based Med. 2013;18(03):90–92. doi: 10.1136/eb-2012-100885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Badawy S M, Thompson A A, Liem R I. Technology access and smartphone app preferences for medication adherence in adolescents and young adults with sickle cell disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016;63(05):848–852. doi: 10.1002/pbc.25905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Badawy S M, Kuhns L M. Economic evaluation of text-messaging and smartphone-based interventions to improve medication adherence in adolescents with chronic health conditions: a systematic review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2016;4(04):e121. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.6425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Iribarren S J, Cato K, Falzon L, Stone P W. What is the economic evidence for mHealth? A systematic review of economic evaluations of mHealth solutions. PLoS One. 2017;12(02):e0170581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


