Abstract
Background
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) metabolomic investigations are a powerful tool for studying neurometabolic diseases. We aimed to assess the effect of CSF contamination with blood on the concentrations of selected biomarkers.
Methods
CSF samples were spiked in duplicate with increasing volumes of whole blood under two conditions: (A) pooled CSF spiked with fresh whole blood and frozen to cause red blood cell (RBC) lysis; (B) pooled CSF spiked with fresh blood and centrifuged (the supernatant with no RBCs was frozen until the moment of analysis). CSF concentrations of amino acids, biogenic amines, pterins, and vitamins were analysed by HPLC coupled with tandem mass spectrometry, electrochemical and fluorescence detection.
Results
Aspartate, glutamate, taurine, ornithine, glycine, citrulline, pyridoxal 5´-phosphate, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, and thiamine showed higher values when RBCs were lysed when compared with those of CSF with no RBC, while arginine, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic and homovanillic acids showed lower values. When RBCs were removed from CSF, only some amino acids, thiamine and pyridoxal 5´-phosphate showed moderately higher values when compared with the non-spiked CSF sample.
Conclusions
CSF-targeted metabolomic analysis is feasible even when substantial RBC contamination of CSF has occurred since CSF centrifugation to remove RBC prior to freezing eliminated most of the interferences observed.
Keywords: Cerebrospinal fluid, Amino acids, Biogenic amines, Pterins, Vitamins, Blood contamination
Background
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a biological fluid that is mainly produced by the choroid plexus, which constitutes the interface between blood vessels and CSF [1, 2]. The composition of CSF is also controlled by the blood–brain barrier, which separates blood from the brain parenchyma [3]. Both structures deliver substrates for brain cell metabolism and remove the corresponding waste [1, 4, 5]. In general, the blood–brain barrier greatly restricts the influx of most molecules, including amino acids and other compounds [6]. Amino acids, with few exceptions (e.g., glutamine), show lower values in CSF when compared with those of plasma [7, 8]. For other metabolites, biosynthetic pathways are compartmentalized in the brain, and similar concentrations may be observed in CSF and blood since no transport from blood to CSF is expected; this is the case for biogenic amines and pterins [9, 10]. In contrast, some vitamins have to be transported into the brain through central nervous system barriers by specific transporters, and differences between vitamin concentrations in CSF and blood samples are noticeable [11, 12]. While folate is one of the few molecules more concentrated in CSF when compared to plasma, other vitamins such as thiamine and pyridoxine display lower values in CSF when compared to those of blood [12, 13].
CSF metabolomic investigations have been demonstrated to be a powerful tool for studying specific neurometabolic pathways and related diseases and for exploring metabolic transport from the blood into the brain [14]. Several neurogenetic conditions are caused by specific disturbances in these processes (Table 1). In recent decades, targeted metabolomic approaches have been used for the study of these neurogenetic conditions [14]. Owing to the important differences in the metabolite concentrations between blood and CSF, contamination of CSF with blood may cause dramatic effects in the measured concentrations of most of the above-mentioned metabolites [15–18]. CSF is collected by lumbar puncture, which is an invasive method. Since blood/plasma contamination can be frequently observed by different causes (traumatic lumbar punctures, impaired blood–brain barrier permeability or intraventricular bleeding) [19–21], a misinterpretation of metabolic profiles is a problem that should be minimized to avoid repeated lumbar puncture procedures and diagnostic errors.
Table 1.
CSF biomarkers and their semiological value for different diseases (left columns)
| Biomarkers | Diseases and expected value: high or low (↑/↓) |
A). Blood/CSF ratio mean value of CSF pools 1 and 2 (standard error of the mean) | B). Plasma/CSF ratio mean value of CSF pools 1 and 2 (standard error of the mean) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin | 28 (3.9) | 29 (3.2) | |
| Amino acids | |||
| Taurine | – | 4.9 (0.2) | 2.9 (0.5) |
| Aspartate | – | 15 (8.2) | 1.3 (0.07) |
| Threonine | – | 1.9 (0.1) | 1.7 (0.2) |
| Serine | Serine deficiency (↓) | 1.6 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) |
| Glutamate | – | 7.3 (1.7) | 1.6 (0.1) |
| Glutamine | Hyperamoniemias (↑) | 1.05 (0.03) | 1.1 (0.1) |
| Glycine | Hyperglycinemias (↑) | 3.2 (0.06) | 2.2 (0.1) |
| Alanine | Mitochondrial Dis. (↑) | 2.5 (0.3) | 2.5 (0.4) |
| Citrulline | – | 2.6 (0.2) | 2.1 (0.3) |
| Valine | BCAA defects (↑/↓) | 2.5 (0.3) | 2.6 (0.5) |
| Methionine | – | 2.4 (0.3) | 2.5 (0.4) |
| Isoleucine | BCCA defects (↑/↓) | 2.3 (0.2) | 2.3 (0.3) |
| Leucine | BCCA defects (↑/↓) | 2.3 (0.3) | 2.2 (0.4) |
| Tyrosine | – | 2.05 (0.2) | 1.8 (0.2) |
| Phenylalanine | – | 1.4 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.2) |
| Ornithine | – | 4.6 (0.6) | 1.9 (0.02) |
| Lysine | – | 2.2 (0.3) | 2.2 (0.3) |
| Hystidine | – | 1.9 (0.01) | 1.8 (0.1) |
| Arginine | – | 0.55 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.1) |
| 5-HIAA | Serotonin related (↓) | 0.6 (0.04) | 0.93 (0.04) |
| HVA | Dopamine (↑/↓) | 0.78 (0.01) | 0.9 (0.01) |
| Biopterin | Pterin defects (↑/↓) | 1.0 (0.1) | 0.9 (0.1) |
| Neopterin |
Pterin defects (↑/↓) Immune events (↑) |
1.1 (0.1) | 1.1 (0.1) |
| Thiamine | Transport defects (↓) | 3.0 (0.05) | 2.2 (0.05) |
| 5-MTHF | Transport/metabolism defects (↓) | 1.75 (0.1) | 1.0 (0.1) |
| PLP | Transport/metabolism defects (↓) | 3.7 (0.3) | 2.5 (0.3) |
Blood/CSF ratios for the two experimental conditions: A) Red blood cells (RBC) lysed in CSF and B) RBC removed from CSF. CSF samples were spiked with 20% of whole blood. A total of 20 CSF aliquots coming from 50 CSF samples were analysed (see details in Additional file 2: Figure S1)
When CSF blood contamination occurs, the most critical metabolites for data interpretation can be glycine (the ratio blood/CSF glycine values is very high) and vitamins such as pyridoxine, thiamine and folate: In genetic diseases leading to brain pyridoxine, folate, and thiamine deficiencies, the blood concentrations of these vitamins can be normal, while CSF values may be near undetectable. Thus, blood contamination could mask the CSF vitamin deficiency. The monoamines HVA and 5-HIAA are sensitive to haemoglobin oxidation
BCAA Branched chain amino acids
With this background, we aimed to assess the effect of CSF contamination with blood on the concentrations of selected molecules which are biomarkers for the study of different neurometabolic conditions.
Methods
Samples
CSF samples were collected from patients where lumbar puncture was done to rule out meningoencephalitis, and stored at − 80 °C, following a previously reported protocol [22]. The remnants of 50 CSF anonymized samples with no red blood cell (RBC) contamination (assessed by light microscopy as less than 5 RBC per field) were thawed, pooled (25 samples for pool 1 and the other 25 for pool 2), reaching a final volume of 10 mL for each pool. The pooled samples were divided into 1 mL aliquots, which were spiked with different volumes of whole blood (at that moment, a fresh blood sample was withdrawn from a healthy volunteer). Non-spiked CSF samples and four spiking conditions were prepared in duplicate in the 2 CSF pools. The CSF pools were spiked with increasing volumes of whole blood: 2.5%, 5%, 10%, and 20%, in 2 different conditions: (A) CSF samples spiked with fresh whole blood and then frozen at − 80 °C to cause RBC lysis. (B). CSF samples spiked with fresh blood, then centrifuged at 1500×g 10 min at 4 °C, with the clear supernatant frozen at − 80 °C. Details of the protocol are stated in Additional file 1: Table S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S1. The total sample preparation time spent was 45 min (all samples were frozen at the same time). With these conditions we could assess the effect of whole blood interference (RBC can increase metabolite concentrations in CSF and can cause oxidative/catabolic effects on some of the metabolites studied (condition A) when compared with plasma contamination (condition B), where an increase in metabolites which are more concentrated in plasma than CSF is expected).
Initially, to identify a cut-off value at which blood contamination can cause substantial interference in the measurement of the above-mentioned metabolites, CSF was spiked with whole blood volume range from 1 to 0.02%. No relevant effects were detected in most metabolite concentrations studied under these conditions (data not shown).
Methods
The concentration of albumin in CSF, used as a surrogate biomarker of CSF RBC contamination or impaired blood–brain and blood-CSF barriers, was analysed using an Abbot automated analyser (Architect c8000) by spectrophotometric procedures. Other biomarkers of blood contamination such as haemoglobin concentration were analysed by an automated procedure (Advia 2120, Siemens Diagnostics). CSF amino acids were analysed by UHPLC coupled to tandem mass spectrometry detection in a Xevo QT Waters system, as previously reported [23]. Biogenic amines (5-hydroxyindoleacetic (5-HIAA) and homovanillic (HVA) acids) and pterins (biopterin and neopterin) were analysed as biomarkers of serotonin and dopamine deficiencies (and in the case of neopterin, also as a biomarker of neuroinflammatory conditions) by HPLC with electrochemical and fluorescence detection as previously reported [22]. The vitamins thiamine, thiamine-diphosphate (TDP), 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) and pyridoxal 5´-phosphate (PLP) were analysed by HPLC with fluorescence detection as reported [14, 22, 24]. Typical chromatograms of these procedures are presented in Additional file 3: Figure S2.
Data analysis
The precision of the different techniques was initially calculated using the coefficient of variation (CV = standard deviation/average × 100%) from 20 replicates and was below 10% for all of the metabolites studied, as previously reported [22–24]. Thus, we considered that the effect of blood contamination on CSF samples was not significant when it was lower than 10% when compared with the value obtained in the non-spiked CSF samples. CSF parameters studied here are accredited by the ENAC (ISO 15,189 norm) and certified by AENOR agencies (ISO 9001 norm). CSF amino acids, pterins, and biogenic amines are subjected to external quality control schemes from ERNDIM (data of the results available on request).
Ethical issues
CSF anonymized samples from remnants were collected in our Hospital following our diagnostic protocols, and the study was conducted only once such investigations were concluded. In every case, informed consent was obtained from each patient before performing the lumbar puncture and CSF collection. The Ethical committee of Sant Joan de Déu Hospital approved the study. All samples from the patients were obtained following the 2013 revised Helsinki Declaration of 1964.
Results
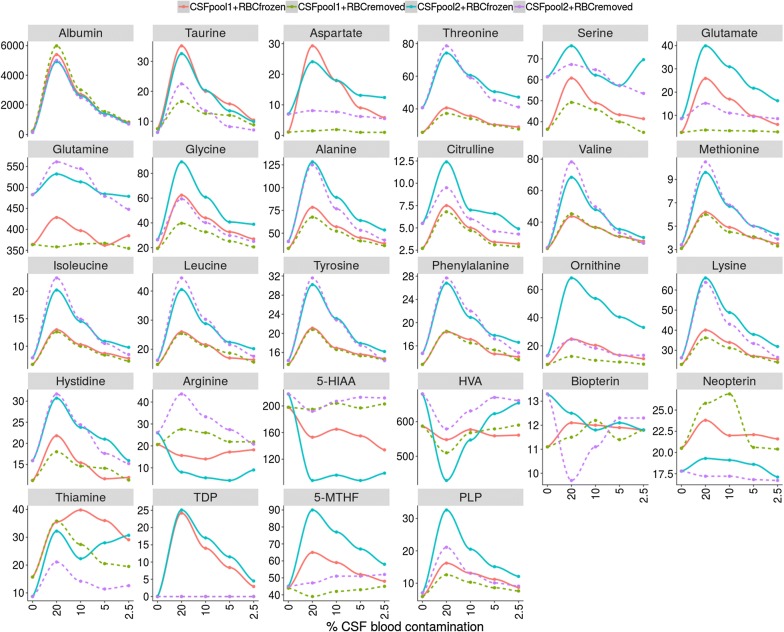
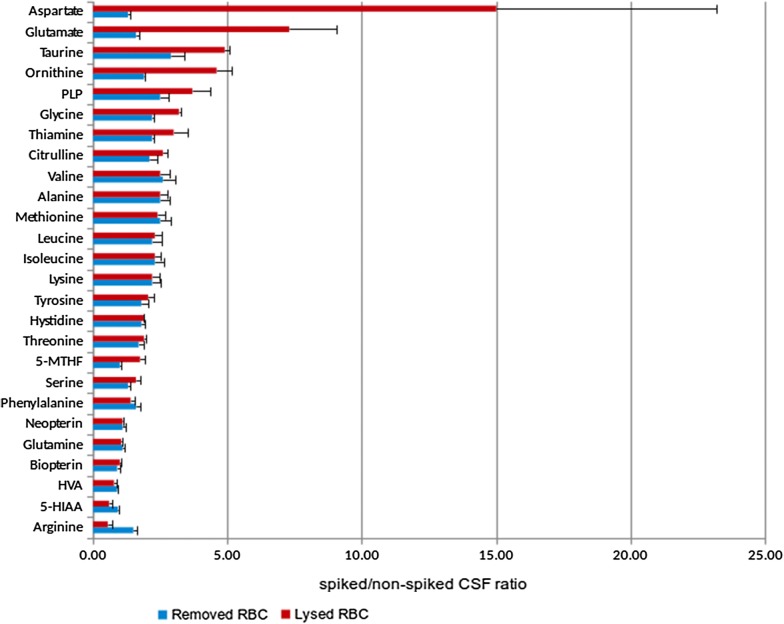
The absolute values of the different metabolites studied are depicted in Fig. 1. In Table 1, a list of the metabolites analysed is presented together with the related neurological diseases, the interpretation of a change in the metabolite concentrations and the mean differences in the expected concentration between blood and CSF when CSF was contaminated with 20% of blood under the 2 different experimental conditions designed: condition A: lysed RBC; condition B: removed RBC. Figure 2 is a horizontal bar representation of the differences stated in Table 1. Aspartate, glutamate, taurine, ornithine, glycine, and citrulline had higher values when RBC were lysed when compared with RBC removed from CSF before freezing. PLP, 5-MTHF, and thiamine also showed this tendency. Arginine, 5-HIAA, and HVA had lower values when RBC were lysed in the CSF samples, while the rest of metabolites studied were consistent between the two different conditions.
Fig. 1.
Graphical representation of the concentrations of the different biomarkers analysed in non-spiked CSF samples, and in CSF samples spiked with 20%, 10%, 5% and 2.5% of whole blood, respectively. Albumin is expressed in g/L, amino acids in µmol/L and biogenic amines, pterins and vitamins in nmol/L
Fig. 2.
Horizontal bar representation of the differences between spiked/non-spiked CSF ratio of all metabolites in the two experimental conditions. a Red bar: red blood cells (RBC) lysed before CSF freezing. b Blue bar: RBC removed from CSF by centrifugation before freezing. CSF samples were spiked with 20% of whole blood
In Table 2 and Fig. 1 data from the different spiking conditions (represented as the percentage of variation and absolute values when compared with non-spiked CSF samples, respectively) are shown. The 2.5% spiking condition A (lysed RBC) still had percentages of variation moderately higher than 10% for most metabolites. However, in the spiking condition B (RBC removed from CSF), only some amino acids, thiamine and PLP had variations higher than 10% when compared with the non-spiked CSF sample values. As expected, albumin was still highly elevated under all conditions. TDP, an intracellular form of thiamine, was only increased under the spiking condition A, but undetectable when RBC were removed from CSF by centrifugation. While most metabolites displayed changes in concentrations when RBCs were added to CSF, arginine, 5-HIAA and HVA had decreased values. Pterins and glutamine concentrations did not vary under the different spiking conditions.
Table 2.
Percentage of variation of the different biomarkers measured according to the different volumes of blood spiked into the CSF (expressed as percentage) when compared with the non-spiked CSF samples
| Biomarkers (% blood contamination) |
A) RBC lysed | B) RBC removed | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 10% | 5% | 2.5% | 20% | 10% | 5% | 2.5% | |
| Albumin | 2724 | 1372 | 667 | 323 | 2877 | 1379 | 669 | 318 |
| Taurine | 393 | 194 | 112 | 48 | 189 | 91 | 45 | 14 |
| Aspartate | 1404 | 842 | 401 | 252 | 42 | 25 | < 10 | < 10 |
| Threonine | 70 | 43 | 21 | 14 | 69 | 38 | 14 | < 10 |
| Serine | 45 | 18 | 13 | < 10 | 22 | 15 | < 10 | < 10 |
| Glutamate | 611 | 394 | 205 | 107 | 57 | 27 | 16 | < 10 |
| Glutamine | 14 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 |
| Glycine | 229 | 114 | 61 | 43 | 114 | 60 | 21 | < 10 |
| Alanine | 174 | 95 | 46 | 23 | 154 | 72 | 30 | 11 |
| Citrulline | 151 | 56 | 22 | < 10 | 112 | 42 | 20 | < 10 |
| Valine | 138 | 79 | 40 | 23 | 161 | 83 | 36 | 13 |
| Methionine | 141 | 78 | 38 | 20 | 151 | 73 | 39 | 11 |
| Isoleucine | 125 | 68 | 34 | 19 | 136 | 69 | 29 | < 10 |
| Leucine | 113 | 62 | 27 | 17 | 123 | 65 | 30 | < 10 |
| Tyrosine | 84 | 43 | 20 | 11 | 87 | 41 | 19 | < 10 |
| Phenylalanine | 63 | 38 | 18 | 11 | 66 | 39 | 18 | < 10 |
| Ornithine | 346 | 256 | 154 | 107 | 86 | 41 | 14 | < 10 |
| Lysine | 113 | 66 | 31 | 16 | 100 | 50 | 22 | < 10 |
| Hystidine | 93 | 44 | 18 | < 10 | 80 | 42 | 18 | < 10 |
| Arginine | − 47 | − 56 | − 51 | − 39 | 51 | 27 | < 10 | < 10 |
| 5-HIAA | − 42 | − 37 | − 41 | − 44 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 |
| HVA | − 22 | − 11 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 |
| Biopterin | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 |
| Neopterin | 12 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 |
| Thiamine | 198 | 154 | 175 | 169 | 135 | 68 | 37 | 27 |
| 5-MTHF | 74 | 52 | 33 | 19 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 | < 10 |
| PLP | 270 | 157 | 102 | 60 | 157 | 80 | 45 | 29 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 3.02 | 1.55 | 0.76 | 0.37 | ||||
| TDP (nmol/L) | 25 | 14 | 11 | 4.5 | ||||
Data are expressed as the mean value of the 2 CSF pools from the 2 conditions: A) spiked CSF frozen containing lysed-RBC cells (left columns), and B) spiked CSF with RBC removed by centrifugation prior freezing (right columns). A percentage of variation below 10% (comparing spiked CSF samples to the non-spiked CSF samples) was considered as the cut-off value for a proper interpretation of the results, considering the coefficient of variation for every biomarker measured when procedures were standardized. Haemoglobin and TDP values are expressed in g/dL and nmol/L, respectively since their values in condition B were not detectable. A total of 20 CSF aliquots coming from 50 CSF samples were analysed (Additional file 2: Figure S1)
Results of the surrogate biomarkers of CSF blood contamination (albumin and haemoglobin) are stated in Additional file 1: Table S1 and Additional file 2: Figure S1.
Discussion
CSF metabolomic analysis is a good analytical tool for the study of the neurometabolic conditions stated here [14]. Furthermore, in such diseases, the quantification of these metabolites in blood/urine is not reliable, because they usually display normal or even paradoxical results [25]. This is especially true when the metabolic pathways studied are highly active in the brain, or the genetic blood–brain barrier transport diseases related to vitamins and other metabolites.
CSF RBC contamination is frequent and has been recognized as a substantial confounding factor for proper interpretation of CSF analysis data describing concentrations of amino acids and other molecules [26, 27]. However, literature regarding blood contamination effects on biogenic amines, pterins and vitamins is scarce [28]. The main causes of CSF blood contamination are traumatic lumbar punctures or spontaneous intrathecal bleeding, which can occur in several situations, especially in newborns. Moreover, impaired blood–brain barrier permeability can occur under different conditions, such as in asphyxia and epilepsy [19–21]. Thus, having an estimation of when a misinterpretation of the metabolic profile can occur due to RBC/plasma contamination is important, considering that lumbar puncture is an invasive intervention, that it is difficult to perform, and that the final volume collected is sometimes low in paediatric patients.
Albumin, a protein synthesized in the liver, is a good surrogate biomarker for compromised permeability of the blood–brain barrier and also for blood contamination. However, since its concentration in the blood largely exceeds that of the CSF (by approximately 100-fold), its concentration may remain elevated even in the case of low RBC/plasma contamination (in our hands around 1% of blood contamination; data not shown). Haemoglobin measures are an alternative surrogate marker when RBC lysis has occurred, and in our hands, values around 0.35 g/dL of haemoglobin may be a signal for cautious interpretation of the data presented here (Table 2), since it corresponds to a CSF blood contamination approximately from 2.5%, which is the limit where some metabolites may display artefactual results after haemolysis.
With regards to amino acids, several reports have indicated differences between blood and CSF compartments [8], but to our knowledge precise definitions of the limits under which RBC contamination can cause a misinterpretation of the metabolic profiles were not established. While lysed RBCs affected the concentrations of most amino acids at 2.5% of blood contamination, centrifugation of the spiked CSF samples to remove RBC resolved the problem in most cases. In any case, the amino acids that had higher values were aspartate, glutamate, threonine, ornithine, glycine and citrulline. The explanation for this is that some of these amino acids display higher concentration in RBC when compared with plasma (aspartate, glutamate and threonine) [8]. Amongst the other amino acids, glycine has the highest plasma/CSF ratio [29]. Regarding ornithine, arginase activity is high in RBC, and this would explain our observation that arginine values were lower when RBC lysis occurred while ornithine values increased, as it is the product of the reaction catalysed by arginase [8]. Once again, centrifugation of the samples prevented all of these contamination biases. Some of the results in Table 2 were striking, however. No precise correlations with the expected values were observed for some amino acids considering the different percentages of blood contamination. A possible explanation is that some amino acids are present in CSF at very low concentrations physiologically (close to the quantification limits) and for other amino acids, the matrix effect, common in UPLC-MS/MS technology, could contribute to such differences [22].
Biogenic amines and pterins are synthesized peripherally in some tissues but also in the brain, and no substantial transport has been documented between blood and brain (only OAT3 transporters efflux both 5-HIAA and HVA from CSF to blood [2]). Since their concentrations in blood are similar to those of CSF [9, 10], no significant changes were observed after CSF blood contamination. Interestingly, both 5-HIAA and HVA had lower values when RBC lysis was caused. Autoxidation of these molecules by haemoglobin/free radicals is a potential mechanism explaining this observation [30], and thus, one should be cautious when interpreting data when CSF has not been centrifuged prior freezing, since low 5-HIAA and HVA values are surrogate biomarkers of serotonin and dopamine deficiencies and may be an indication of therapeutic intervention [31]. In any case, centrifugation and RBC removal prior to freezing corrected the results when compared with non-spiked CSF.
Vitamins displayed unpredictable results, except for folate. Folate forms (especially 5-MTHF) are highly concentrated in RBC when compared with plasma and this would explain the positive interference observed when RBC lysis occurred, but not after RBC removal. Only thiamine and PLP had increased values when comparing spiked CSF samples at 2.5% with non-spiked samples under both experimental conditions, although it was less remarkable when RBC removal was performed. These effects were minimized when the CSF blood contamination was 1% (data not shown). Regarding thiamine, active conversion of free thiamine, TMP and TDP occur inside cells (RBCs have a high activity of either thiamine phosphokinase, which phosphorylates thiamine to form TDP, or thiamine phosphatases, which convert TDP to TMP and thiamine) [32]. This would explain the plateau results observed when RBC lysis occurred, results that were minimized when RBCs were removed. In any case, thiamine values are higher in blood than in CSF, and thus, the results should be cautiously interpreted when RBC contamination occurs [12]. TDP, a strictly intracellular thiamine vitamer [32], would be a good surrogate biomarker of RBC lysis in CSF samples since undetectable amounts of TDP were observed when RBCs were removed from CSF. With PLP, the observations were similar, and although less significant, even when RBCs were removed from CSF, PLP displayed higher concentrations in the spiked CSF samples. As with thiamine, a complex intracellular metabolic pathway accounts for the synthesis of the different pyridoxine-related vitamers [13]. Moreover, some of these vitamins can be degraded by nucleophiles and oxygen-derived free-radicals, as CSF has low concentrations of other molecules that can react with these compounds [13]. Thus, results should be analysed cautiously concerning to these two vitamins, since either in thiamine or pyridoxine related disorders, which cause severe neurological phenotypes, diagnostic hallmarks are low CSF thiamine and PLP values [12, 13, 33].
Conclusions
CSF-targeted metabolomic analysis is feasible even when remarkable RBC CSF contamination occurs since CSF centrifugation to remove RBC prior to freezing prevents most of the biases observed. However, data should be cautiously interpreted, especially for some metabolites. CSF albumin, haemoglobin, and TDP can be used as surrogate biomarkers of the potential confounding effect of CSF plasma/RBC contamination.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. Percentage of blood contamination, albumin and haemoglobin levels from CSF spiked with increasing amounts of blood.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. CSF blood spiking protocol. A total of 20 CSF aliquots were analysed. In the picture, the colours of the 5 CSF sample are presented. Even in the 2.5% spiking condition, the red colour was intense. The median CSF blood contamination observed in our laboratory typically ranged from 0.01 to 0.035 g/dL of a haemoglobine, which is lower than the 0.35 g/dL observed in the 2.5% blood contamination condition.
Additional file 3: Figure S2. Typical chromatograms of the different metabolites analysed in non-spiked CSF samples: (1) Amino acids. (2) Biogenic amines. (3) Pterins. (4) 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. (5) Pyridoxal 5´-phosphate. (6) Thiamine.
Acknowledgements
The Department of Clinical Biochemistry is part of the CIBERER-ISCIII and ‘Centre Daniel Bravo de Diagnòstic I Recerca en Malalties Minoritàries’. “We are indebted to the “Biobanc de l’Hospital Infantil Sant Joan de Déu per a la Investigació” integrated into the Spanish Biobank Network of ISCIII for the sample and data procurement.”
Abbreviations
- CSF
cerebrospinal fluid
- RBC
red blood cells
- UHPLC
ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography
- 5-HIAA
5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid
- HVA
homovanillic acid
- HPLC
high-performance liquid chromatography
- TDP
thiamine-diphosphate
- 5-MTHF
5-methyltetrahydrofolate
- PLP
pyridoxal 5´-phosphate
- BCAA
branched-chain amino acids
Authors’ contributions
MB contributed to conception and design, acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, drafted the initial manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted. MC, CS, MCS, LMS, JM, GF, AGC and AO contributed to analysis and acquisition of data, reviewed and revised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. MML and RA contributed to conception and design, analysis and interpretation of data, reviewed and supervised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. Every one of the authors has participated sufficiently in the study, meeting the appropriate authorship criteria, and each has seen, reviewed and approved this version of the manuscript and takes full responsibility for it. We all agree to its submission for publication. Nobody who qualifies for authorship has been omitted from the list of authors. All the authors have complete access to the study data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII-FIS PI15/01082 and PI18/00111), the FEDER Funding Program from the European Union and CIBERER-ISCIII.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from each patient before performing the lumbar puncture and CSF collection or genetic study. The Ethical committee of Sant Joan de Déu Hospital approved the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12987-019-0154-5.
References
- 1.Hladky SB, Barrand MA. Fluid and ion transfer across the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers; a comparative account of mechanisms and roles. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2016;13:19. doi: 10.1186/s12987-016-0040-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Spector R. Nature and consequences of mammalian brain and CSF efflux transporters: four decades of progress. J Neurochem. 2010;112:13–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Redzic Z. Molecular biology of the blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: similarities and differences. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2011;8:3. doi: 10.1186/2045-8118-8-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nedergaard M. Garbage truck of the brain. Science. 2013;340:1529–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.1240514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Akaishi T, Onishi E, Abe M, Toyama H, Ishizawa K, Kumagai M, et al. The human central nervous system discharges carbon dioxide and lactic acid into the cerebrospinal fluid. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2019;16:8. doi: 10.1186/s12987-019-0128-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mann GE, Yudilevich DL, Sobrevia L. Regulation of amino acid and glucose transporters in endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:183–252. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00022.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kornhuber ME, Kornhuber J, Kornhuber AW, Hartmann GM. Positive correlation between contamination by blood and amino acid levels in cerebrospinal fluid of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1986;69:212–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90606-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Duran M. Amino acids. In: Blau N, Duran M, Gibson KM, editors. Laboratory guide to the methods in biochemical genetics. Berlin: Springer; 2008. pp. 53–90. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Coppus AW, Fekkes D, Verhoeven WM, Tuinier S, Egger JI, van Duijn CM. Plasma amino acids and neopterin in healthy persons with Down’s syndrome. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2007;114:1041–1045. doi: 10.1007/s00702-007-0656-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mori S, Takanaga H, Ohtsuki S, Deguchi T, Kang YS, Hosoya K, et al. Rat organic anion transporter 3 (rOAT3) is responsible for brain-to-blood efflux of homovanillic acid at the abluminal membrane of brain capillary endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:432–440. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000050062.57184.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Steinfeld R, Grapp M, Kraetzner R, Dreha-Kulaczewski S, Helms G, Dechent P, et al. Folate receptor alpha defect causes cerebral folate transport deficiency: a treatable neurodegenerative disorder associated with disturbed myelin metabolism. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;85:354–363. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ortigoza-Escobar JD, Molero-Luis M, Arias A, Oyarzabal A, Darín N, Serrano M, et al. Free-thiamine is a potential biomarker of thiamine transporter-2 deficiency: a treatable cause of Leigh syndrome. Brain. 2016;139:31–38. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Footitt EJ, Heales SJ, Mills PB, Allen GF, Oppenheim M, Clayton PT. Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate in cerebrospinal fluid; factors affecting concentration. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011;34:529–538. doi: 10.1007/s10545-011-9279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ormazabal A, Molero-Luis M, Garcia-Cazorla A, Artuch R. Biomarkers for the study of catecholamine and serotonin genetic diseases. In: Garg U, Smith LD, editors. Biomarkers in inborn errors of metabolism. Cambridge: Clinical aspects and laboratory determination; 2017. pp. 301–329. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Akiyama T, Kobayashi K, Higashikage A, Sato J, Yoshinaga H. CSF/plasma ratios of amino acids: reference data and transports in children. Brain Dev. 2014;36:3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2012.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.MacNeill AL, Andre BG, Zingale Y, Packer RA, McGrath S. The effects of iatrogenic blood contamination on total nucleated cell counts and protein concentrations in canine cerebrospinal fluid. Vet Clin Pathol. 2018;47:464–470. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Srinivasan L, Shah SS, Abbasi S, Padula MA, Harris MC. Traumatic lumbar punctures in infants hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2013;32:1150–1152. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e31829862b7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.McFarlin KE, Kruesi MJ, Nadi NS. RBC contamination and amino acid concentration in the CSF of children. Psychiatry Res. 1990;32:99–101. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(90)90141-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tan R, Traylor M, Rutten-Jacobs L, Markus H. New insights into mechanisms of small vessel disease stroke from genetics. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017;131:515–531. doi: 10.1042/CS20160825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Krueger M, Mages B, Hobusch C, Michalski D. Endothelial edema precedes blood-brain barrier breakdown in early time points after experimental focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:17. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0671-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Klebe D, McBride D, Krafft PR, Flores JJ, Tang J, Zhang JH. Posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus development after germinal matrix hemorrhage: established mechanisms and proposed pathways. J Neurosci Res. 2019 doi: 10.1002/jnr.24394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Batllori M, Molero-Luis M, Ormazabal A, Casado M, Sierra C, García-Cazorla A, et al. Analysis of human cerebrospinal fluid monoamines and their cofactors by HPLC. Nat Protoc. 2017;12:2359–2375. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2017.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Casado M, Sierra C, Batllori M, Artuch R, Ormazabal A. A targeted metabolomic procedure for amino acid analysis in different biological specimens by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Metabolomics. 2018;14:76. doi: 10.1007/s11306-018-1374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ormazabal A, García-Cazorla A, Pérez-Dueñas B, Gonzalez V, Fernández-Alvarez E, Pineda M, et al. Determination of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in cerebrospinal fluid of paediatric patients: reference values for a paediatric population. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;371:159–162. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2006.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wassenberg T, Willemsen MA, Geurtz PB, Lammens M, Verrijp K, Wilmer M, et al. Urinary dopamine in aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: the unsolved paradox. Mol Genet Metab. 2010;101:349–356. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Aasebø E, Opsahl JA, Bjørlykke Y, Myhr KM, Kroksveen AC, Berven FS. Effects of blood contamination and the rostro-caudal gradient on the human cerebrospinal fluid proteome. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e90429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Krishnamurthy V, Nabil N, Reddy SM, Doreswamy SM. Dilemma in diagnosis of pyogenic meningitis in cerebrospinal fluid contaminated with blood: does leucocyte esterase test help? J Cytol. 2019;36:44–47. doi: 10.4103/JOC.JOC_75_18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Verbeek MM, Blom AM, Wevers RA, Lagerwerf AJ, van de Geer J, Willemsen MA. Technical and biochemical factors affecting cerebrospinal fluid 5-MTHF, biopterin and neopterin concentrations. Mol Genet Metab. 2008;95:127–132. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Swanson MA, Coughlin CR, Jr, Van Hove JL. Corrigendum: Swanson MA, Coughlin CR Jr, Scharer GH, et al: Biochemical and molecular predictors for prognosis in nonketotic hyperglycinemia. Ann Neurol 2015;78:606–618. Ann Neurol. 2016;79:505. doi: 10.1002/ana.24600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kato Y, Oki K, Suga N, Ono S, Ishisaka A, Miura Y, et al. A novel quinone derived from 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid reacts with protein: possible participation of oxidation of serotonin and its metabolite in the development of atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;101:500–510. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ng J, Papandreou A, Heales SJ, Kurian MA. Monoamine neurotransmitter disorders–clinical advances and future perspectives. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11:567–584. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Collie JTB, Greaves RF, Jones OAH, Lam Q, Eastwood GM, Bellomo R. Vitamin B1 in critically ill patients: needs and challenges. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017;55:1652–1668. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2017-0054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zeng WQ, Al-Yamani E, Acierno JS, Jr, Slaugenhaupt S, Gillis T, MacDonald ME, Ozand PT, Gusella JF. Biotin-responsive basal ganglia disease maps to 2q36.3 and is due to mutations in SLC19A3. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;77:16–26. doi: 10.1086/431216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. Percentage of blood contamination, albumin and haemoglobin levels from CSF spiked with increasing amounts of blood.
Additional file 2: Figure S1. CSF blood spiking protocol. A total of 20 CSF aliquots were analysed. In the picture, the colours of the 5 CSF sample are presented. Even in the 2.5% spiking condition, the red colour was intense. The median CSF blood contamination observed in our laboratory typically ranged from 0.01 to 0.035 g/dL of a haemoglobine, which is lower than the 0.35 g/dL observed in the 2.5% blood contamination condition.
Additional file 3: Figure S2. Typical chromatograms of the different metabolites analysed in non-spiked CSF samples: (1) Amino acids. (2) Biogenic amines. (3) Pterins. (4) 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. (5) Pyridoxal 5´-phosphate. (6) Thiamine.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.