Abstract
Objectives
Mathematical models are increasingly important in planning for the upcoming chronic hepatitis C (CHC) elimination efforts. Such models require reliable natural history inputs to make accurate predictions on health and economic outcomes. Yet, hepatitis C virus disease progression is known to vary widely in the literature and published inputs are currently outdated. The objectives of this study were to obtain updated estimates of fibrosis progression rates (FPR) in treatment-naïve patients with CHC and to explore sources of heterogeneity.
Design
A systematic review was conducted using Ovid-MEDLINE, Ovid-EMBASE and PubMed databases (January 1990 to January 2018) to identify observational studies of hepatic fibrosis in treatment-naïve patients with CHC.
Outcomes
Stage-constant FPRs were estimated for each study given the reported fibrosis scores and duration of infection. Stage-specific FPRs (ie, F0→F1; F1→F2; F2→F3; F3→F4) were estimated using Markov maximum likelihood estimation. Estimates were pooled using random-effects meta-analysis and heterogeneity was evaluated by stratification and random-effects meta-regression.
Results
The review identified 111 studies involving 131 groups of patients (n=42 693). The pooled stage-constant FPR was 0.094 (95% CI 0.088 to 0.100); stage-specific FPRs were F0→F1: 0.107 (95% CI 0.097 to 0.118); F1→F2: 0.082 (95% CI 0.074 to 0.091); F2→F3: 0.117 (95% CI 0.107 to 0.129); F3→F4: 0.116 (95% CI 0.104 to 0.131). Stratified analysis revealed substantial variation in progression by study population. Meta-regression indicated associations between progression and infection age, duration, source, viral genotype and study population. Findings indicate that FPRs display substantial heterogeneity across study populations and pooled values from more homogenous subpopulations should be considered when estimating prognosis.
Conclusions
This large meta-analysis presents updated prognostic estimates for CHC derived from newer studies using better diagnostic methods and improves estimates for important patient populations in terms of clinical policy (eg, injection drug users, non-clinical populations, liver clinic patients) and should be a valuable resource for patients, clinicians and clinical policymakers.
Keywords: hepatic fibrosis, cirrhosis, hepatitis C, viral hepatitis
Strengths and limitations of this study.
Our updated meta-analysis is now the largest review of hepatitis C virus prognosis including English and non-English language observational studies.
We use Markov maximum likelihood estimation method, which does not rely on the assumption of a linear disease progression to obtain detailed stage-specific estimates of fibrosis progression.
Further, we restrict our meta-analysis to newer studies using better diagnostic methods compared with earlier reviews; and we present more precise prognostic estimates for important chronic hepatitis C subpopulations in terms of clinical policy (ie, injection drug users, blood transfusion cohorts, liver clinic patients and non-clinical populations).
However, findings indicate that fibrosis progression rates display substantial heterogeneity across study populations and pooled values from more homogenous subpopulations should be considered when estimating prognosis.
Introduction
An estimated ~1% of the world’s population is infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV).1 2 Chronic HCV (CHC) eventually leads to fibrosis, cirrhosis, advanced liver disease and death.1 3 4 The level of CHC-related hepatic fibrosis is typically detected through histology using the meta-analysis of histological data in viral hepatitis (METAVIR) (scoring system with scores ranging from F0 indicating no fibrosis to F4 indicating cirrhosis. Published estimates of CHC prognosis have shown large variability in the rate of fibrosis progression across these stages.5–8
Fortunately, HCV treatment has been revolutionised by highly effective therapies making elimination a plausible objective. Recently, the WHO launched a global strategy to this end, targeting a 90% reduction in new infections, a 65% reduction in liver-related death, a diagnosis rate of 90% and a treatment rate of 80% by 2030. This will necessitate radical expansions in prevention, screening and linkage to care.9
However, a key challenge to the development of national elimination strategies has been the lack of reliable estimates of local disease burden, HCV prevalence and the prevalence of the undiagnosed population.9 Currently, the only way to estimate such unknown parameters involves mathematical modelling. For this reason, WHO has been assisting countries through expert consultation and modelling initiatives.9 Mathematical models are also increasingly important for estimating the health and economic consequences of scaling up screening and treatment programmes. However, these models require reliable natural history inputs to make accurate predictions.10 11 Yet, HCV disease progression is known to vary widely in the literature and published natural history inputs are currently outdated.5–8
In general, the variability in HCV disease progression has been attributed to differences in the study population (eg, liver clinic, blood donors, injection drug users (IDU)); differences due to study setting (ie, clinical vs non-clinical); differences among study subjects with respect to clinical risk factors for disease progression;12–14 as well as to variation in the methods used for calculating fibrosis progression rates (FPR).15
The established clinical risk factors for rapid progression of hepatic fibrosis include older age, male gender, excessive alcohol use, high body mass index and hepatitis B virus (HBV) or HIV coinfection.12–14 However, more recent studies have indicated race/ethnicity and viral genotype as possible risk factors as well.16–20 Studies have also suggested that patients identified in clinical settings display a more rapid progression compared with those identified in non-clinical settings, for example, by screening programmes.5
In terms of methodological variability, studies generally estimate progression using two methods: a direct method involving serial biopsies, and an indirect method involving a single biopsy and the estimated duration of infection.15 Multiple biopsies are less common and often involve patients who need to be monitored closely for rapid progression; while the more common indirect method assumes a constant progression rate from the time of infection despite evidence indicating variability between stages.5 21 22
To account for stage-specific variation in progression, Yi et al22 have proposed the Markov maximum likelihood estimation (MMLE) method, which can estimate accurate stage-specific FPRs from observational studies where only a single biopsy and the estimated duration of infection are available. This has improved the external validity and accuracy of stage-specific progression estimates by allowing much larger numbers of single biopsy studies to inform HCV prognosis.22
A previous systematic review from our group has estimated FPRs using this method.5 This study has been widely used in pharmacoeconomic evaluations. However, since its publication, a decade ago, new prognostic studies have become available, highlighting additional sources of variability (ie, viral genotype, race/ethnicity) that merit further investigation.16–19 23 24
Given the availability of new research and the importance of natural history estimates particularly for informing forthcoming elimination policies, the objectives of this study were: (1) to refine progression estimates through an updated systematic review of observational studies examining hepatic fibrosis in treatment-naïve HCV-infected individuals and (2) to further explore additional sources of heterogeneity.
Materials and methods
Data sources
A systematic literature search was conducted using Ovid-MEDLINE, Ovid-EMBASE and PubMed databases without language restriction by an experienced medical librarian (JB) (original: January 1990 to August 2007; update: January 2007 to January 2018). Additionally, the search was supplemented by citation searches and by reviewing references of relevant studies. Search strings for each database are provided in online supplementary materials.
bmjopen-2018-027491supp001.pdf (1.8MB, pdf)
Study selection
Records were imported to EndNote V.X7.7.1 (Thomson Reuters, New York City, NY, USA). After duplicate removal, potentially relevant studies were screened against eligibility criteria by two independent reviewers. Disagreements were resolved through discussion.
Studies were included if they satisfied the following criteria: (1) CHC defined as the presence of anti-HCV antibody detected by second or third-generation ELISA and at least one of the following: HCV RNA detected by PCR, recombinant immunoblot assay, elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or liver biopsy; (2) full-length peer-reviewed original observational study; and (3) no HCV treatment prior to biopsy. Studies involving fewer than 20 cases, postliver transplant patients and those where FPRs could not be calculated were excluded. Multiple reports from the same study were identified by comparing author, year and sample size. The report with the most complete information was preferred, if equivalent, then the most recent publication was included.
Data extraction
Study, host, viral and liver disease-related information was extracted in duplicate by two independent reviewers using piloted forms. For non-English studies, native speakers were contacted for help with full-text review and data extraction processes. A complete list of abstracted data items and all abstracted data are provided in the online supplementary material. Studies that reported results in subgroups, which may influence disease progression, were extracted separately.
Age at HCV acquisition, for studies that did not report this information, was imputed by taking the difference between age at assessment and the estimated duration of infection. For some studies that report composite fibrosis stages (eg, F0/F1), data were distributed 50:50 across F0 and F1. Stage distribution was not performed when more than two stages were reported collectively (eg, F0/F1/F2). Definitions used by reviewers and criteria used to convert histological and non-invasive scores to the METAVIR system are provided in online supplementary tables S1 and S2, respectively.
Study quality
Because the included studies vary widely by study design, population and setting, and since the study outcomes (ie, FPRs) were generated using the MMLE method (given the duration of infection and the fibrosis scores reported in each study), rather than being directly extracted from the included studies, instead of applying a generic quality appraisal tool, we addressed issues that may bias outcome measurement and the accuracy of FPR estimation more directly. To improve the accuracy of case ascertainment, the updated meta-analysis was restricted to newer studies where all participants had confirmatory RNA testing for CHC. Further, studies were stratified by two independent reviewers by the mode of infection, which can influence the estimation of the duration of infection, as well as by study design, setting and population to address issues around representativeness/generalisability of findings. The categories were based on the criteria described in online supplementary table S2. Finally, other clinical factors such as excess alcohol use and HIV or HBV coinfection among study subjects, which may impact outcomes, were adjusted for using meta-regression analyses.
Estimation of FPRs
Two methods were used to estimate the annual FPRs for each included study: (1) the stage-constant FPR (scFPR) was estimated by dividing the total number of transitions in METAVIR units by the person-years of HCV infection; (2) the stage-specific FPRs (ie, F0→1, F1→2, F2→3 and F3→F4) were estimated using the MMLE method.22
Data synthesis
Identified groups were stratified by methodological and clinical subgroups. Estimates were pooled by random-effects meta-analyses. Time to cirrhosis was determined using the pooled stage-specific progression rates (αs)5 22:
Finally, the pooled FPRs and their 95% CIs were used to estimate the mean cumulative probability of cirrhosis up to 40 years after HCV exposure for clinically important subpopulations.
Heterogeneity
For all estimates, publication bias, small study effects and heterogeneity were assessed by visual inspection of funnel plots of the natural log of FPRs against inverse variance. A statistical test for funnel plot asymmetry was not performed due to presence of significant heterogeneity (online supplementary figure S1).25 26 Heterogeneity was quantified using the I2 statistic, with values of 25% and 75% indicating low and high heterogeneity.27 Previously identified sources of heterogeneity (eg, study related, methodological, clinical and viral) were explored through stratification and random-effects meta-regression analyses using a linear mixed model-maximum likelihood method weighted by a multiplicative variance adjustment factor.5 12–14 18 Missing values were imputed using the mean values. The natural log of FPRs was used as the dependent variable.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SAS (SAS version 9.4) and PROC MIXED and PROC MIXED ML procedures were used for all meta-analyses and meta-regression analyses. The plots were generated using RStudio V.1.1.383 (RStudio, Boston, MA, USA). A two-sided significance level of 0.05 was used to indicate significance for hypothesis tests.
Results
Study selection
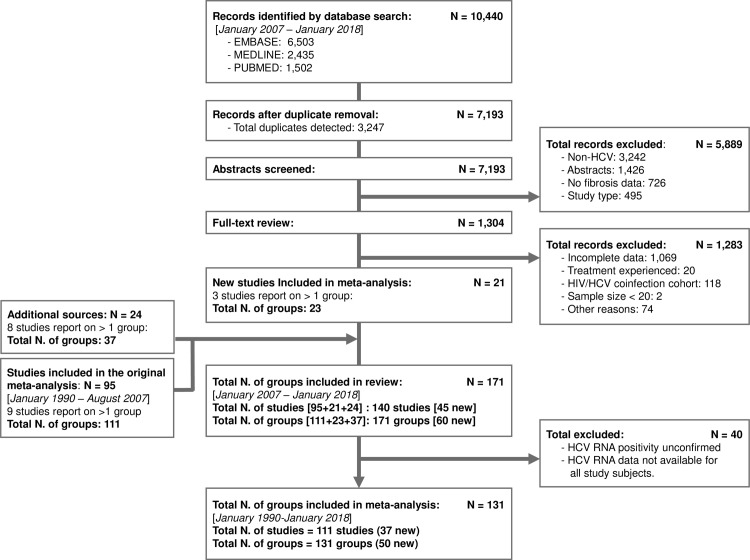
The current study is an update of a previous review covering the period from January 1990 to August 2007.5 The updated literature search (January 2007 to January 2018) identified a total of 10 440 records (figure 1). Following duplicate removal, 7193 abstracts were screened, and 1304 records were included for full-text review. Overall, the update identified 45 new studies reporting on 60 new patient groups (24 689 HCV-infected subjects) resulting in total of 140 studies and 171 groups of patients (57 810 subjects) in combination with the earlier review. Group-level summary of study and participant characteristics is provided in online supplementary tables S3 and S4, respectively.
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram showing the study selection progress. The literature search recovered a total of 5718 citations. Following duplicate removal and supplementary citation searches, the review process identified a total of 45 new studies reporting on 60 groups of HCV-infected patients. Together with the 95 studies reporting on 111 groups identified by the original review, the current update identified a total of 140 studies of 171 HCV-infected groups of patients. Meta-analysis was restricted to 111 studies reporting on 131 study groups where chronic hepatitis C (CHC) was confirmed by HCV RNA testing in all subjects. HCV, hepatitis C virus.
However, the updated meta-analysis was restricted to newer studies where all participants had HCV RNA testing. After elimination of 40 study groups where RNA status was either missing or unclear, the updated meta-analysis included 111 studies reporting on 131 groups of patients (42 693 subjects and 723 058 person-years of follow-up time). The study characteristics of the 40 study groups excluded from the meta-analysis are described in online supplementary table S5.
Study characteristics
The study characteristics of the 131 groups included in the meta-analysis are summarised in table 1. A majority, 84% (n=110), of the included groups were assessed in a clinical setting (vs non-clinical). Compared with the original review, the update identified relatively more patients evaluated in a non-clinical setting (12% (n=3068) of original vs 31% (n=5392) of new subjects). In terms of study design, a majority, 68% (n=88), used a cross-sectional/retrospective versus a retrospective-prospective study design. Majority of study groups (124 out of 131) assessed hepatic fibrosis using only histology; only seven performed a non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis (six used liver stiffness measurements (LSM) and one used a combination of invasive and non-invasive methods).
Table 1.
Summary of subgroups included in the meta-analysis
| Updated review (1990–2018) |
Original review (1990–2007) |
New groups (2007–2018) |
||||
| n | SS | n | SS | n | SS | |
| All groups | 131 | 42 693 | 81 | 25 492 | 50 | 17 201 |
| Study setting | ||||||
| Clinical | 110 | 34 233 | 70 | 22 424 | 40 | 11 809 |
| Non-clinical | 21 | 8460 | 11 | 3068 | 10 | 5392 |
| Study design | ||||||
| Cross-sectional/retrospective | 88 | 29 088 | 72 | 22 921 | 16 | 6167 |
| Retrospective-prospective | 43 | 13 605 | 9 | 2571 | 34 | 11 034 |
| Study population | ||||||
| Females | 5 | 1420 | 4 | 1400 | 1 | 20 |
| Blood donors | 3 | 408 | 2 | 223 | 1 | 185 |
| Paediatric patients | 2 | 223 | 0 | . | 2 | 223 |
| Post-transfusion | 2 | 509 | 1 | 469 | 1 | 40 |
| Liver clinic | 91 | 32 524 | 61 | 21 338 | 30 | 11 186 |
| Injection drug users | 10 | 5132 | 4 | 670 | 6 | 4462 |
| Community | 4 | 1451 | 3 | 1044 | 1 | 407 |
| Dialysis patients | 6 | 408 | 3 | 191 | 3 | 217 |
| Renal transplant | 4 | 179 | 3 | 157 | 1 | 22 |
| Infectious diseases | 4 | 439 | 0 | . | 4 | 439 |
| Publication year | ||||||
| <2000 | 4 | 629 | 4 | 629 | 0 | 0 |
| 2000 to <2005 | 56 | 16 460 | 54 | 16 309 | 2 | 151 |
| 2005 to <2010 | 37 | 12 041 | 23 | 8554 | 14 | 3487 |
| ≥2010 | 34 | 13 563 | 0 | . | 34 | 13 563 |
| Age at assessment | ||||||
| <40 | 23 | 5540 | 13 | 2166 | 10 | 3374 |
| ≥40 | 108 | 37 153 | 68 | 23 326 | 40 | 13 827 |
| Estimated age at infection (years) | ||||||
| <20 | 11 | 2318 | 4 | 662 | 7 | 1656 |
| 30 to <40 | 95 | 35 926 | 64 | 21 576 | 31 | 14 350 |
| 20 to <30 | 19 | 3864 | 13 | 3254 | 6 | 610 |
| ≥40 | 6 | 585 | 0 | . | 6 | 585 |
| Estimated duration of infection (years) | ||||||
| <10 | 8 | 834 | 2 | 212 | 6 | 622 |
| 10 to <20 | 71 | 21 949 | 50 | 13 800 | 21 | 8149 |
| ≥20 | 52 | 19 910 | 29 | 11 480 | 23 | 8430 |
| HCV genotype | ||||||
| Genotype 1 | 10 | 3000 | 5 | 1854 | 5 | 1146 |
| Genotype 2 | 1 | 90 | 0 | . | 1 | 90 |
| Genotype 3 | 3 | 1426 | 0 | . | 3 | 1426 |
| Genotype 4 | 1 | 117 | 0 | . | 1 | 117 |
The meta-analysis was restricted to 131 study groups (81 from the original review and 50 new groups) where CHC was confirmed by HCV RNA testing in all subjects.
CHC, chronic hepatitis C; HCV, hepatitis C virus; n, number of groups included in the meta-analysis; SS, total sample size in each group.
Regarding the patient populations, liver clinic patients were the most frequently studied group (69%). In total, there were 91 groups of liver clinic patients; 10 of IDUs; 6 of dialysis patients; 5 of females, 4 community, renal transplant recipients and infectious disease patients; 3 of blood donor groups; and 2 of paediatric and post-transfusion groups (table 1). Furthermore, the update identified a total of 10 evaluations of genotype 1, three of genotype 3 and one each of genotype 2 and 4 infected groups.
Clinical characteristics of study subjects
The clinical characteristics of subjects are summarised in online supplementary table S6. The majority of the subjects were male (62%) and white (69%). The mean age at assessment of liver fibrosis was 44 years, the mean age at infection was 26 years and the mean duration of infection was 18 years. The average prevalence of excess alcohol use was 20%. IDU accounted for 43% and blood transfusion for 26% of infections. Cirrhosis was present in 12%. The majority of the subjects (76%) had an elevated ALT. The mean ALT of all subjects was 88 IU/L. In terms of viral genotype, the average prevalence of genotype 1 was 56%, genotype 3 was 18%. On average, 2% of subjects were coinfected with HIV and 0.4% with HBV.
Overall FPRs
The pooled scFPR was 0.094 (95% CI 0.088 to 0.100) METAVIR units per year (table 2). The stage-specific FPR estimates were generally lower for transitioning between F0→F1 (0.107; 95% CI 0.097 to 0.118) and F1→F2 (0.082; 95% CI 0.074 to 0.091); relative to F2→F3 (0.117; 95% CI 0.107 to 0.129) and F3→F4 (0.116; 95% CI 0.104 to 0.131). Overall, the estimated time to cirrhosis was 39 years. The I2 statistic indicated a high level of heterogeneity which was relatively more pronounced at earlier stages. The pooled FPRs stratified by study update are provided in online supplementary table S7. Forest plots of the pooled stage-specific FPRs are provided in online supplementary figures S29–S5.
Table 2.
Random-effects meta-analysis of hepatic fibrosis progression rates stratified by CHC subgroups
| n | F0 → F1 | I2 | F1 → F2 | I2 | F2 → F3 | I2 | F3 → F4 | I2 | scFPR | I2 | TTC (years) | ||||||
| Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | ||||||||
| All groups | 131 | 0.107 | 0.097 to 0.118 | 98% | 0.082 | 0.074 to 0.091 | 97% | 0.117 | 0.107 to 0.129 | 94% | 0.116 | 0.104 to 0.131 |
89% | 0.094 | 0.088 to 0.100 | 85% | 39 |
| Study setting | |||||||||||||||||
| Clinical | 110 | 0.114 | 0.103 to 0.126 | 98% | 0.086 | 0.077 to 0.096 | 98% | 0.118 | 0.106 to 0.132 | 93% | 0.119 | 0.105 to 0.133 |
89% | 0.097 | 0.091 to 0.103 | 82% | 37 |
| Non-clinical | 21 | 0.077 | 0.058 to 0.104 | 98% | 0.065 | 0.053 to 0.081 | 96% | 0.111 | 0.088 to 0.139 | 91% | 0.101 | 0.068 to 0.150 | 94% | 0.076 | 0.036 to 0.150 | 90% | 47 |
| Study design | |||||||||||||||||
| Cross-sectional/retrospective | 88 | 0.114 | 0.101 to 0.129 | 98% | 0.082 | 0.072 to 0.094 | 98% | 0.119 | 0.107 to 0.133 | 93% | 0.120 | 0.105 to 0.136 |
87% | 0.097 | 0.090 to 0.104 | 84% | 38 |
| Retrospective-prospective | 43 | 0.093 | 0.079 to 0.110 | 98% | 0.082 | 0.071 to 0.094 | 96% | 0.114 | 0.094 to | 95% | 0.110 | 0.087 to 0.140 |
92% | 0.088 | 0.078 to 0.098 | 85% | 41 |
| Study population† | |||||||||||||||||
| Females | 5 | 0.048 | 0.026 to 0.088 | 97% | 0.051 | 0.043 to 0.061 | 27%* | 0.071 | 0.049 to | 47%* | 0.051 | 0.025 to 0.106 | 46%* | 0.053 | 0.036 to 0.078 | 53%* | 74 |
| Blood donors | 3 | 0.067 | 0.017 to 0.264 | 96% | 0.051 | 0.020 to 0.128 | 82% | 0.094 | 0.018 to 0.487 | 83% | 0.057 | 0.009 to 0.340 | 55%* | 0.065 | 0.028 to 0.152 | 42%* | 63 |
| Paediatric patients | 2 | 0.201 | 0.074 to 0.550 | 0%* | 0.087 | 0.015 to 0.506 | 56%* | 0.096 | 0.107 to 0.125 | 87% | 0.055 | 0.028 to 0.585 | 0%* | 0.133 | 0.009 to 0.984 | 0%* | 45 |
| Post-transfusion | 2 | 0.065 | 0.034 to 0.125 | 0%* | 0.079 | 0.002 to 2.593 | 80% | 0.114 | 0.038 to 0.341 |
0%* | 0.134 | 0.033 to 0.545 | 0%* | 0.081 | 0.028 to 0.230 | 0%* | 44 |
| Liver clinic | 91 | 0.106 | 0.095 to 0.118 | 98% | 0.082 | 0.072 to 0.092 | 98% | 0.111 | 0.100 to 0.123 |
94% | 0.112 | 0.100 to 0.127 | 88% | 0.092 | 0.087 to 0.099 | 65%* | 40 |
| Injection drug users | 10 | 0.109 | 0.071 to 0.168 | 99% | 0.071 | 0.052 to 0.096 | 96% | 0.121 | 0.086 to 0.170 | 92% | 0.194 | 0.135 to 0.278 | 84% | 0.094 | 0.072 to 0.123 | 88% | 37 |
| Community | 4 | 0.134 | 0.082 to 0.218 | 94% | 0.088 | 0.047 to 0.164 | 96% | 0.111 | 0.074 to 0.167 | 83% | 0.133 | 0.065 to 0.271 | 88% | 0.104 | 0.086 to 0.125 | 22%* | 35 |
| Dialysis patients | 6 | 0.121 | 0.060 to 0.244 | 95% | 0.074 | 0.047 to 0.116 | 69%* | 0.250 | 0.114 to 0.547 | 71%* | 0.114 | 0.069 to 0.189 | 0%* | 0.100 | 0.068 to 0.148 | 20%* | 35 |
| Renal transplant | 4 | 0.225 | 0.094 to 0.540 | 89% | 0.173 | 0.070 to 0.426 | 84% | 0.190 | 0.074 to 0.490 | 64%* | 0.117 | 0.041 to 0.331 | 0%* | 0.190 | 0.076 to 0.475 | 60%* | 24 |
| Infectious diseases | 4 | 0.144 | 0.084 to 0.247 | 89% | 0.211 | 0.145 to 0.307 | 48%* | 0.273 | 0.096 to 0.774 | 89% | 0.256 | 0.047 to 1.379 | 92% | 0.171 | 0.097 to 0.302 | 68%* | 19 |
| Publication year | |||||||||||||||||
| <2000 | 4 | 0.068 | 0.030 to 0.154 | 96% | 0.049 | 0.024 to 0.103 | 84% | 0.124 | 0.058 to 0.264 | 48%* | 0.172 | 0.058 to 0.513 | 48%* | 0.068 | 0.033 to 0.143 | 61%* | 49 |
| 2000 to <2005 | 56 | 0.119 | 0.101 to 0.140 | 98% | 0.076 | 0.064 to 0.091 | 98% | 0.116 | 0.101 to 0.132 | 91% | 0.122 | 0.106 to 0.140 | 79% | 0.095 | 0.087 to 0.105 | 83% | 38 |
| 2005 to <2010 | 37 | 0.096 | 0.081 to 0.113 | 98% | 0.085 | 0.074 to 0.097 | 94% | 0.100 | 0.085 to 0.117 | 92% | 0.092 | 0.074 to 0.114 | 89% | 0.087 | 0.078 to 0.097 | 82% | 43 |
| ≥2010 | 34 | 0.106 | 0.088 to 0.129 | 98% | 0.096 | 0.080 to 0.116 | 97% | 0.143 | 0.113 to 0.181 | 96% | 0.137 | 0.102 to 0.184 | 95% | 0.102 | 0.090 to 0.116 | 86% | 34 |
| Age at assessment | |||||||||||||||||
| <40 | 23 | 0.128 | 0.096 to 0.172 | 98% | 0.088 | 0.069 to 0.112 | 96% | 0.142 | 0.114 to 0.177 | 86% | 0.141 | 0.105 to 0.189 | 80% | 0.113 | 0.095 to 0.134 | 78% | 33 |
| ≥40 | 108 | 0.103 | 0.093 to 0.114 | 98% | 0.081 | 0.072 to 0.091 | 98% | 0.113 | 0.102 to 0.125 | 94% | 0.113 | 0.099 to 0.127 | 90% | 0.091 | 0.085 to 0.097 |
84% | 40 |
| Estimated age at infection (years) | |||||||||||||||||
| <20 | 11 | 0.097 | 0.060 to 0.155 | 98% | 0.061 | 0.044 to 0.085 | 94% | 0.118 | 0.082 to 0.170 | 84% | 0.108 | 0.065 to 0.179 | 77% | 0.083 | 0.063 to 0.110 |
75%* | 45 |
| 20 to <30 | 95 | 0.100 | 0.090 to 0.112 | 98% | 0.075 | 0.068 to 0.084 | 98% | 0.104 | 0.095 to 0.115 | 93% | 0.109 | 0.096 to 0.124 | 90% | 0.088 | 0.083 to 0.094 | 83% | 42 |
| 30 to <40 | 19 | 0.128 | 0.100 to 0.164 | 97% | 0.127 | 0.099 to 0.163 | 95% | 0.177 | 0.136 to 0.229 | 91% | 0.146 | 0.115 to 0.185 | 75%* | 0.124 | 0.104 to 0.146 | 79% | 28 |
| ≥40 | 6 | 0.200 | 0.143 to 0.278 | 82% | 0.147 | 0.090 to 0.239 | 83% | 0.234 | 0.094 to 0.584 | 91% | 0.246 | 0.098 to 0.619 | 78% | 0.160 | 0.108 to 0.237 | 52%* | 20 |
| Estimated duration of infection (years) | |||||||||||||||||
| <10 | 8 | 0.218 | 0.162 to 0.295 | 90% | 0.175 | 0.118 to 0.261 | 87% | 0.290 | 0.136 to 0.619 | 89% | 0.314 | 0.157 to 0.629 | 62%* | 0.209 | 0.168 to 0.258 | 0%* | 17 |
| 10 to <20 | 71 | 0.128 | 0.113 to 0.145 | 98% | 0.081 | 0.070 to 0.094 | 98% | 0.130 | 0.116 to 0.145 | 89% | 0.133 | 0.117 to 0.152 | 82% | 0.106 | 0.099 to 0.114 | 75%* | 35 |
| ≥20 | 52 | 0.075 | 0.067 to 0.084 | 97% | 0.075 | 0.067 to 0.084 | 95% | 0.092 | 0.080 to 0.104 | 89% | 0.090 | 0.076 to 0.106 | 91% | 0.076 | 0.071 to 0.081 | 70%* | 49 |
| HCV genotype | |||||||||||||||||
| Genotype 1 | 10 | 0.072 | 0.049 to 0.108 | 98% | 0.074 | 0.052 to 0.107 | 96% | 0.072 | 0.061 to 0.083 | 58%* | 0.056 | 0.029 to 0.107 | 92% | 0.072 | 0.055 to 0.093 | 83% | 59 |
| Genotype non-1 | 6 | 0.096 | 0.065 to 0.142 | 93% | 0.091 | 0.070 to 0.117 | 76% | 0.102 | 0.069 to 0.149 | 79% | 0.175 | 0.112 to 0.274 | 63%* | 0.096 | 0.072 to 0.128 | 65%* | 37 |
| Genotype 3 | 3 | 0.134 | 0.084 to 0.213 | 77% | 0.103 | 0.084 to 0.126 | 2%* | 0.112 | 0.049 to 0.253 | 83% | 0.247 | 0.165 to 0.370 | 0%* | 0.119 | 0.080 to 0.175 | 36%* | 30 |
| Genotype non-3 | 15 | 0.079 | 0.060 to 0.103 | 98% | 0.079 | 0.062 to 0.102 | 95% | 0.076 | 0.067 to 0.087 | 66%* | 0.073 | 0.043 to 0.122 | 93% | 0.077 | 0.065 to 0.092 | 78% | 52 |
Annual fibrosis progression rates based on random-effects meta-analyses. The meta-analysis was restricted to 131 study groups where CHC was confirmed by HCV RNA testing in all subjects.
The estimates are not adjusted for covariates and maybe confounded; genotype non-1 and genotype non-3 groups are composed of 65% genotype 3 and 82% genotype 1, respectively; the size of CIs of each subgroup depends on the number of studies, study size and the extent of heterogeneity across the studies included in the subgroup.
*Study subgroups with low to moderate heterogeneity.
†Study populations are ordered by progression from slow to fast based on TTC.
CHC, chronic hepatitis C; HCV, hepatitis C virus; I2, the proportion of variability in progression rates due to heterogeneity versus sampling error; n, number of groups included in the meta-analysis; scFPR, stage-constant annual fibrosis progression rate (assuming linear progression from stage F0 to F4); TTC, time to cirrhosis (based on unadjusted stage-specific FPRs).
Stratification by study setting and design
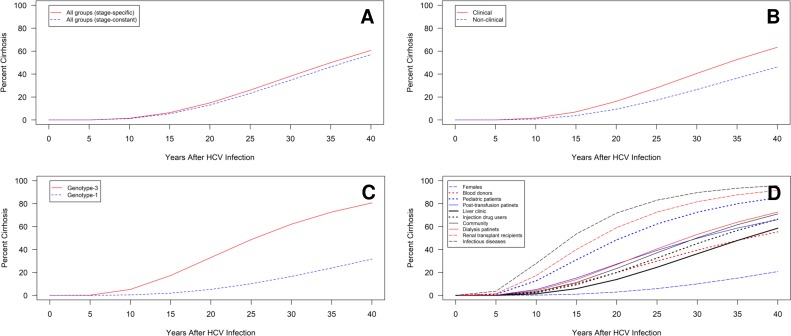
Time-to-cirrhosis estimates indicated a faster progression to cirrhosis in groups initially identified in a clinical versus non-clinical setting (37 years vs 47 years) (table 2). In terms of study design, there was only a small difference in progression among cross-sectional/retrospective versus retrospective-prospective design (38 years vs 41 years), which was lost following adjustment for covariates (online supplementary table S8). The cumulative probability of cirrhosis by study setting is presented in figure 2.
Figure 2.
Cumulative probability of cirrhosis for various patient populations. The cumulative probability of cirrhosis over years of HCV infection for (A) all study groups by estimation method; and groups stratified by (B) study setting; (C) viral genotype; and (D) study population using stage-specific progression rate estimates. Cumulative probabilities are projected using unadjusted estimates and may be confounded. A high degree of heterogeneity is present within the liver clinic, injection drug use and community populations, as well as for genotype 1-infected groups and for studies stratified by study setting. HCV, hepatitis C virus.
Stratification by study population
Time-to-cirrhosis estimates indicated a relatively slower progression to cirrhosis for the female (74 years), blood donor (63 years), paediatric (45 years) and post-transfusion cohorts (44 years) and a faster progression for infectious disease (19 years), renal transplant (24 years), dialysis (35 years), community (35 years) and IDU (37 years) populations relative to liver clinic populations (40 years) (table 2).
In general, simple stratification by study population was able to explain heterogeneity in estimates primarily for the later stages of disease. However, a high level of heterogeneity persisted for liver clinic, IDU and community groups. The unadjusted cumulative probability of cirrhosis for different study populations is displayed in figure 2.
Based on time-to-cirrhosis estimates derived from covariate-adjusted FPRs, female (52 years), blood donor (55 years) and post-transfusion (44 years) groups maintained a relatively slower progression, while paediatric groups (36 years) displayed a slightly faster progression relative to liver clinic populations (38 years) (online supplementary table S8). Infectious disease (34 years) and community (33 years) groups maintained a relatively faster progression following adjustments, while the covariate-adjusted progression was somewhat comparatively slower for dialysis patients (47 years), renal transplant (39 years) and IDUs (40 years).
Stratification by publication year
Based on unadjusted time-to-cirrhosis estimates, earlier studies (< year 2000) indicated a slower progression to cirrhosis (49 years) versus studies published after 2000 (table 2). This was also apparent following covariate adjustment (online supplementary table S8).
Stratification by age and duration of infection
In terms of age, groups with a younger mean age at assessment (<40 years) displayed a faster progression to cirrhosis (33 years) versus an older age (≥40) (40 years) (table 2), while groups with an older age at infection (≥30 years) displayed a more rapid progression (20–28 years) relative to a younger age (<30 years) (42–45 years). Fibrosis also progressed faster (17 years) in groups with a shorter duration of infection (<10 years).
Stratification by viral genotype
Regarding viral genotype, groups infected with viral genotype 1 displayed a much slower progression to cirrhosis versus genotype 3 (59 years vs 30 years) (table 2). Slower progression for genotype 1 versus genotype 3 groups remained following covariate adjustments (43 years vs 34 years) (online supplementary table S8). In the stratified analysis, genotype 3 groups exhibited considerably less heterogeneity versus genotype 1. The unadjusted cumulative probability of cirrhosis for genotypes 1 and 3 is displayed in figure 2.
Univariate analysis
In the univariate analyses, most clinical covariates displayed an association with at least one progression estimate except for HIV coinfection, male sex, white and Asian race (online supplementary table S9). For more advanced stages of disease, genotype 1 was associated with a slower progression to advanced fibrosis (F2→F3; relative risk (RR)=0.53) and to cirrhosis (F3→F4; RR=0.39); while genotype 3 was associated with faster progression to cirrhosis (RR=2.62). Additionally, injection drug-related infections displayed faster progression (RR=1.65) and black race slower progression (RR=0.47) to cirrhosis.
Regarding study-related factors, studies conducted in a non-clinical setting (vs clinical) indicated a slower progression in the earlier stages of disease (RR=0.68–0.75). In terms of study population, relative to liver clinic patients, IDUs (RR=1.72) and infectious disease groups (RR=2.26) displayed a faster progression and females (RR=0.46) displayed a slower progression to cirrhosis. For earlier stages, dialysis, renal transplant and infectious disease populations all exhibited a faster progression (RR=2.12–2.54) and females again displayed a slower progression (RR=0.45). Many covariates (eg, infectious diseases, females, genotype 3) were also associated with the overall progression (scFPR).
Multivariable analysis
After adjusting for multiple covariates (table 3), the duration of infection remained independently associated with slower progression for all FPRs (RR=0.94–0.97). Age at infection was also independently associated with faster progression between F1→F2 (RR=1.03) and with overall progression (scFPR; RR=1.01). Similarly, blood transfusion-related infection displayed faster progression from F0→F1 (RR=2.37) and in overall progression (scFPR; RR=1.63). Regarding viral genotype, following adjustment for covariates, genotype 1 was significantly associated with a slower progression between F2→F3 (RR=0.58) and faster progression from F0→F1 (RR=1.61). No significant association was observed for viral genotype 3 or for ethnicity. In terms of study-related factors, only dialysis populations maintained a significant association after covariate adjustment, exhibiting a slower progression versus liver clinic patients, at early stages (F1→F2; RR=0.58). Based on the adjusted R2, covariates explained ~38%–56% of the heterogeneity in the stage-specific FPR estimates and 87% in the stage-constant estimate.
Table 3.
Random-effects meta-regression of covariates associated with hepatic fibrosis progression rates
| Covariates | F0→F1* | F1→F2* | F2→F3* | F3→F4* | scFPR* | |||||||||||||||
| β | SE | P value | RR | β | SE | P value | RR | β | SE | P value | RR | β | SE | P value | RR | β | SE | P value | RR | |
| Intercept | −2.564 | 0.555 | <0.0001 | _ | −3.482 | 0.675 | <0.0001 | _ | −1.031 | 0.608 | 0.093 | _ | −1.400 | 0.766 | 0.071 | _ | −2.438 | 0.312 | <0.0001 | _ |
| Study design | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-sectional/retrospective (Ref) | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 |
| Retrospective -prospective |
−0.088 | 0.093 | 0.347 | 0.92 | 0.041 | 0.113 | 0.717 | 1.04 | −0.001 | 0.100 | 0.991 | 1.00 | 0.036 | 0.126 | 0.773 | 1.04 | 0.011 | 0.050 | 0.834 | 1.01 |
| Study population | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Liver clinic (Ref) | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 |
| Females | −0.149 | 0.334 | 0.656 | 0.86 | 0.318 | 0.400 | 0.428 | 1.37 | −0.073 | 0.349 | 0.834 | 0.93 | −0.616 | 0.442 | 0.166 | 0.54 | −0.046 | 0.170 | 0.790 | 0.96 |
| Blood donors | −0.040 | 0.256 | 0.875 | 0.96 | −0.318 | 0.314 | 0.313 | 0.73 | −0.276 | 0.289 | 0.342 | 0.76 | −0.707 | 0.395 | 0.076 | 0.49 | −0.175 | 0.166 | 0.296 | 0.84 |
| Paediatric patients | 0.361 | 0.475 | 0.449 | 1.43 | 0.831 | 0.567 | 0.145 | 2.30 | −0.054 | 0.521 | 0.918 | 0.95 | −0.199 | 0.750 | 0.791 | 0.82 | 0.479 | 0.307 | 0.121 | 1.61 |
| Post-transfusion | −0.343 | 0.407 | 0.402 | 0.71 | −0.206 | 0.493 | 0.676 | 0.81 | −0.143 | 0.466 | 0.760 | 0.87 | −0.853 | 0.651 | 0.192 | 0.43 | −0.093 | 0.282 | 0.742 | 0.91 |
| Injection drug users | 0.278 | 0.221 | 0.211 | 1.32 | −0.310 | 0.268 | 0.251 | 0.73 | 0.120 | 0.243 | 0.621 | 1.13 | 0.499 | 0.293 | 0.091 | 1.65 | 0.070 | 0.115 | 0.543 | 1.07 |
| Community | 0.226 | 0.209 | 0.283 | 1.25 | 0.167 | 0.248 | 0.503 | 1.18 | 0.016 | 0.204 | 0.938 | 1.02 | 0.192 | 0.241 | 0.428 | 1.21 | 0.125 | 0.087 | 0.154 | 1.13 |
| Dialysis patients | −0.121 | 0.203 | 0.551 | 0.89 | −0.550 | 0.248 | 0.028 | 0.58 | 0.299 | 0.250 | 0.233 | 1.35 | −0.103 | 0.307 | 0.738 | 0.90 | −0.235 | 0.153 | 0.127 | 0.79 |
| Renal transplant recipients | −0.012 | 0.236 | 0.961 | 0.99 | 0.262 | 0.285 | 0.359 | 1.30 | 0.064 | 0.274 | 0.815 | 1.07 | −0.372 | 0.412 | 0.368 | 0.69 | 0.164 | 0.191 | 0.390 | 1.18 |
| Infectious diseases | −0.261 | 0.241 | 0.282 | 0.77 | 0.304 | 0.294 | 0.304 | 1.35 | 0.264 | 0.257 | 0.305 | 1.30 | 0.211 | 0.314 | 0.502 | 1.24 | −0.013 | 0.139 | 0.924 | 0.99 |
| Publication year |
||||||||||||||||||||
| <2000 (Ref) | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 | _ | _ | _ | 1.00 |
| 2000 to <2005 | 0.406 | 0.241 | 0.094 | 1.50 | 0.116 | 0.299 | 0.698 | 1.12 | −0.010 | 0.295 | 0.973 | 0.99 | −0.543 | 0.369 | 0.143 | 0.58 | 0.227 | 0.164 | 0.169 | 1.25 |
| 2005 to <2010 | 0.492 | 0.242 | 0.044 | 1.64 | 0.352 | 0.300 | 0.242 | 1.42 | −0.009 | 0.297 | 0.975 | 0.99 | −0.583 | 0.372 | 0.120 | 0.56 | 0.310 | 0.165 | 0.062 | 1.36 |
| ≥2010 | 0.404 | 0.246 | 0.103 | 1.50 | 0.356 | 0.306 | 0.246 | 1.43 | 0.227 | 0.301 | 0.451 | 1.26 | −0.500 | 0.377 | 0.187 | 0.61 | 0.369 | 0.166 | 0.028 | 1.45 |
| Gender—male† | 0.592 | 0.437 | 0.178 | 1.81 | 0.704 | 0.520 | 0.179 | 2.02 | −0.103 | 0.454 | 0.822 | 0.90 | −0.157 | 0.564 | 0.781 | 0.85 | 0.289 | 0.217 | 0.186 | 1.34 |
| Age at HCV infection (years) | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.698 | 1.00 | 0.033 | 0.013 | 0.012 | 1.03 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.292 | 1.01 | 0.020 | 0.014 | 0.169 | 1.02 | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 1.01 |
| Duration of infection (years) | −0.063 | 0.010 | <0.0001 | 0.94 | −0.028 | 0.012 | 0.022 | 0.97 | −0.048 | 0.010 | <0.0001 | 0.95 | −0.043 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.96 | −0.049 | 0.005 | <0.0001 | 0.95 |
| Injection drug use† | 0.194 | 0.248 | 0.435 | 1.21 | −0.114 | 0.298 | 0.701 | 0.89 | −0.117 | 0.262 | 0.656 | 0.89 | 0.301 | 0.328 | 0.361 | 1.35 | 0.090 | 0.132 | 0.497 | 1.09 |
| Blood transfusion† | 0.862 | 0.298 | 0.005 | 2.37 | 0.260 | 0.355 | 0.466 | 1.30 | 0.219 | 0.302 | 0.469 | 1.25 | 0.464 | 0.369 | 0.211 | 1.59 | 0.486 | 0.145 | 0.001 | 1.63 |
| Excess alcohol use† | −0.312 | 0.263 | 0.238 | 0.73 | 0.591 | 0.314 | 0.062 | 1.81 | 0.177 | 0.273 | 0.517 | 1.19 | 0.245 | 0.329 | 0.458 | 1.28 | 0.201 | 0.131 | 0.126 | 1.22 |
| HIV positive† | 0.075 | 0.839 | 0.929 | 1.08 | 0.532 | 1.009 | 0.599 | 1.70 | −0.506 | 0.907 | 0.578 | 0.60 | 0.191 | 1.105 | 0.863 | 1.21 | −0.312 | 0.429 | 0.469 | 0.73 |
| Genotype 1† | 0.473 | 0.221 | 0.034 | 1.61 | −0.380 | 0.264 | 0.153 | 0.68 | −0.539 | 0.224 | 0.018 | 0.58 | −0.313 | 0.274 | 0.256 | 0.73 | −0.051 | 0.108 | 0.637 | 0.95 |
| Genotype 3† | 0.226 | 0.277 | 0.416 | 1.25 | 0.036 | 0.331 | 0.914 | 1.04 | −0.273 | 0.285 | 0.341 | 0.76 | 0.194 | 0.347 | 0.577 | 1.21 | 0.093 | 0.133 | 0.487 | 1.10 |
| White† | 0.160 | 0.197 | 0.420 | 1.17 | −0.047 | 0.238 | 0.845 | 0.95 | −0.325 | 0.208 | 0.120 | 0.72 | 0.032 | 0.256 | 0.900 | 1.03 | −0.045 | 0.102 | 0.660 | 0.96 |
| Black† | −0.302 | 0.273 | 0.272 | 0.74 | 0.332 | 0.330 | 0.317 | 1.39 | −0.011 | 0.287 | 0.970 | 0.99 | −0.609 | 0.356 | 0.089 | 0.54 | −0.005 | 0.139 | 0.971 | 0.99 |
| Asian† | 0.086 | 0.354 | 0.808 | 1.09 | 0.268 | 0.431 | 0.534 | 1.31 | 0.003 | 0.404 | 0.994 | 1.00 | 0.933 | 0.534 | 0.083 | 2.54 | 0.061 | 0.242 | 0.800 | 1.06 |
| I2 res | 96% | 96% | 86% | 77% | 39% | |||||||||||||||
| Adjusted R2 | 56% | 38% | 54% | 53% | 87% | |||||||||||||||
Linear mixed model-maximum likelihood method.
Values in bold indicate statistical significance.
*Log progression rates.
†Proportion.
β, coefficient;HCV, hepatitis C virus; I2 res, the proportion of residual variability due to heterogeneity; adjusted R2, the proportion of heterogeneity explained by covariates in the model; Ref, reference category;scFPR, stage-constant annual fibrosis progression rates (assuming linear progression from F0 to F4).
Discussion
Our large systematic review of HCV natural history presents updated and refined estimates of CHC-related hepatic fibrosis progression in treatment-naïve patients. Overall, the updated estimates were generally consistent with previous studies and indicated an average time to cirrhosis of ~39 years.5 14 28 However, the current study found a slightly slower progression compared with our previous analysis, especially at the earliest stage of fibrosis.5 This is possibly because the updated review included more studies where patients were identified through screening efforts in non-clinical settings, and thus involved less symptomatic patients when compared with the original study.
In general, the current update improves upon our previous analysis by focusing on more recent studies where CHC was confirmed by better diagnostic methods and by incorporating substantially more subjects identified in a non-clinical setting (8460 vs 3068) and more IDU populations (5132 vs 670) thereby providing more precise estimates of progression for these important subpopulations. Further, we identified study population as an important source of heterogeneity indicating that population-specific estimates should be considered when estimating prognosis. With respect to the IDU population, based on the 10 groups identified, we found a faster average time to cirrhosis for this population (37 years), when compared with our earlier estimate (40 years), and to a previous review, which used similar methods (46 years).29 Following covariate adjustments, the progression was slightly slower (40 years); this could be due to the inclusion of more genotype 3-infected individuals in the present study.
In our updated analysis we also further explored the effects of viral genotype and race/ethnicity on prognosis. Univariate analyses identified genotype 3 as a predictor of faster progression and genotype 1 a predictor of slower progression from advanced fibrosis to cirrhosis. Similarly, a previous meta-analysis of scFPR also found a faster progression for genotype 3 versus genotype non-3 groups.18 Due to the small number of studies a meta-regression could not be used to explore confounders in that study. In our large meta-regression, genotype 1 displayed a faster progression at the earliest stages but a slower progression at more advanced stages of fibrosis. Similarly, univariate analysis also indicated a slower progression from significant fibrosis to cirrhosis for black race and female populations in agreement with previous studies20 23 24; although these relationships were lost upon covariate adjustment.
To help describe the differences in disease progression across the different groups, our updated analysis used the covariate-adjusted stage-specific FPRs to estimate the average expected time to cirrhosis for each group. After adjustment for confounders, we found that time to cirrhosis was 43 years for genotype 1 versus 34 years for genotype 3 groups. In general, adjusted progressions were slower for the blood donors (55 years), females (52 years) and black patients (46 years) and generally faster for IDUs (40 years), infectious disease units and community patients (~34 years) and Asian populations (29 years).
Our study is limited in several ways. We excluded reports where the data on infection duration were not available. Thus, the results may not be generalisable to individuals with an unknown source of infection. Moreover, estimates based on self-report, such as the duration of infection, alcohol and drug use, may suffer from recall bias. Studies in IDUs suggest that there may exist a median lag of ~3 years between the first year of drug use and HCV infection.17 30 Therefore, the accuracy of the estimates of infection duration may vary by the mode of infection,31 resulting in a possible underestimation of FPRs for IDUs. Additionally, alcohol use tends to be inconsistently reported. Finally, aggregated analyses may suffer from ecological fallacy.32 It is also important to note that although newer non-invasive methods are replacing biopsy, non-invasive prognosis currently remains limited making biopsy-based stage-specific estimates the most suitable method for representing the natural history of HCV at the current time.33
Finally, our analyses identified substantial heterogeneity, especially among earlier versus later stages of fibrosis. This is not surprising as published estimates are known to vary extensively. While we have explained some of this variation, it is possible that some heterogeneity is also related to sampling variability associated with biopsies, though non-invasive estimates also demonstrate considerable variability.33 Other sources of variation may include obesity, steatosis, insulin resistance or genetic factors that can moderate fibrogenesis, which remain largely unreported in the literature.34–38 Furthermore, I2 statistic, which measures the extent of variation due to heterogeneity versus sampling error, may be inflated when study sizes are large or sampling error is low as in our case.39
Our study also has significant strengths: (1) it is the largest meta-analysis of HCV prognosis including English and non-English language studies; (2) it uses the MMLE method to obtain detailed stage-specific estimates of HCV prognosis in treatment-naïve patients, a method that does not rely on the assumption of linear disease progression; (3) compared with our original study, the current update improves the precision of prognostic estimates for important patient groups in terms of clinical policy (ie, asymptomatic patients identified in non-clinical settings through screening efforts, IDUs, blood transfusion populations, liver clinic patients); (4) our update was also restricted to more recent studies where CHC is identified using better diagnostic tests; (5) further, the large numbers of included studies have allowed for us to explain ~38%–87% of the apparent heterogeneity in progression; and finally, (6) we present natural history data that can be easily applied to mathematical models for estimating HCV prevalence, disease burden, resource utilisation, budget impact and cost-effectiveness, all of which will be necessary for planning appropriate elimination programmes in the near future. Furthermore, given the level of heterogeneity identified across studies, our updated analysis suggests that pooled progression estimates from more homogenous subpopulations should be considered when estimating prognosis in policy models.
In conclusion, the accurate estimation of HCV disease progression remains important in the era of HCV elimination particularly due to existing policy question around elimination strategies, which necessitate a variety of modelling-based methods to help inform policy.40 41 The current study is now the largest and most detailed review of HCV prognosis, which presents more precise prognostic estimates for important subpopulations in terms of clinical policy and should be a valuable resource for clinicians, patients and particularly clinical policymakers.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
AE has received a doctoral fellowship from the Canadian Network on Hepatitis C (CanHepC).
Footnotes
Contributors: AE conducted the study, collected, analysed and drafted the manuscript. MK and HHT contributed to the study design, as well as the analysis and interpretation of the results and the drafting of the manuscript. JF, JW and PG contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the results and the drafting of the manuscript. TH and JW contributed to data collection and JB is a medical librarian who helped develop and conduct the systematic literature search.
Funding: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: JF has received research support from AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, Janssen and Merck, Abbot and Regulus, and consulting fees from AbbVie, Gilead Sciences, Janssen and Merck.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement: All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.
References
- 1. Wasley A, Alter MJ. Epidemiology of hepatitis C: geographic differences and temporal trends. Semin Liver Dis 2000;20:0001–16. 10.1055/s-2000-9506 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Blach S, Zeuzem S, Manns M, et al. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;2:161–76. 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30181-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Alter MJ. Epidemiology of hepatitis C. Hepatology 1997;26:62S–5. 10.1002/hep.510260711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Charlton M. Hepatitis C infection in liver transplantation. Am J Transplant 2001;1:197–203. 10.1034/j.1600-6143.2001.001003197.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Thein H-H, Yi Q, Dore GJ, et al. Estimation of stage-specific fibrosis progression rates in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Hepatology 2008;48:418–31. 10.1002/hep.22375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Poynard T, Ratziu V, Charlotte F, et al. Rates and risk factors of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 2001;34:730–9. 10.1016/S0168-8278(00)00097-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. McCaughan GW, George J. Fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gut 2004;53:318–21. 10.1136/gut.2003.026393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Wiese M, Fischer J, Löbermann M, et al. Evaluation of liver disease progression in the German hepatitis C virus (1b)-contaminated anti-D cohort at 35 years after infection. Hepatology 2014;59:49–57. 10.1002/hep.26644 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Papatheodoridis GV, Hatzakis A, Cholongitas E, et al. Hepatitis C: the beginning of the end-key elements for successful European and national strategies to eliminate HCV in Europe. J Viral Hepat 2018;25:6–17. 10.1111/jvh.12875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Sweeting MJ, De Angelis D, Brant LJ, et al. The burden of hepatitis C in England. J Viral Hepat 2007;14:570–6. 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2007.00851.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Trubnikov M, Yan P, Archibald C. Estimated prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in Canada, 2011. Can Commun Dis Rep 2014;40:429–36. 10.14745/ccdr.v40i19a02 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Poynard T, Bedossa P, Opolon P. Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. the OBSVIRC, METAVIR, CLINIVIR, and DOSVIRC groups. Lancet 1997;349:825–32. 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)07642-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Marcellin P, Asselah T, Boyer N. Fibrosis and disease progression in hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002;36:S47–56. 10.1053/jhep.2002.36993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Freeman A, et al. Estimating progression to cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2001;34:809–16. 10.1053/jhep.2001.27831 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Poynard T, Ratziu V, Benmanov Y, et al. Fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: detection and significance. Semin Liver Dis 2000;20:0047–56. 10.1055/s-2000-9258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Goossens N, Negro F. Is genotype 3 of the hepatitis C virus the new villain? Hepatology 2014;59:2403–12. 10.1002/hep.26905 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Rüeger S, Bochud P-Y, Dufour J-F, et al. Impact of common risk factors of fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2015;64:1605–15. 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-306997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Probst A, Dang T, Bochud M, et al. Role of hepatitis C virus genotype 3 in liver fibrosis progression--a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat 2011;18:745–59. 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01481.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Bochud P-Y, Cai T, Overbeck K, et al. Genotype 3 is associated with accelerated fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 2009;51:655–66. 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.05.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Crosse K, Umeadi OG, Anania FA, et al. Racial differences in liver inflammation and fibrosis related to chronic hepatitis C. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2:463–8. 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00162-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Datz C, Cramp M, Haas T, et al. The natural course of hepatitis C virus infection 18 years after an epidemic outbreak of non-A, non-B hepatitis in a plasmapheresis centre. Gut 1999;44:563–7. 10.1136/gut.44.4.563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Yi Q, Wang PP, Krahn M. Improving the accuracy of long-term prognostic estimates in hepatitis C virus infection. J Viral Hepat 2004;11:166–74. 10.1046/j.1365-2893.2003.00484.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Terrault NA, Im K, Boylan R, et al. Fibrosis progression in African Americans and Caucasian Americans with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;6:1403–11. 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Wiley TE, Brown J, Chan J. Hepatitis C infection in African Americans: its natural history and histological progression. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97:700–6. 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05555.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ioannidis JPA, Trikalinos TA. The appropriateness of asymmetry tests for publication bias in meta-analyses: a large survey. CMAJ 2007;176:1091–6. 10.1503/cmaj.060410 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003;327:557–60. 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Sweeting MJ, De Angelis D, Neal KR, et al. Estimated progression rates in three United Kingdom hepatitis C cohorts differed according to method of recruitment. J Clin Epidemiol 2006;59:144–52. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.06.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Smith DJ, Combellick J, Jordan AE, et al. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) disease progression in people who inject drugs (PWID): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Drug Policy 2015;26:911–21. 10.1016/j.drugpo.2015.07.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Hagan H, Thiede H, Des Jarlais DC. Hepatitis C virus infection among injection drug users. Epidemiology 2004;15:543–9. 10.1097/01.ede.0000135170.54913.9d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Bruden DL, McMahon BJ, Hennessy TW, et al. Estimating the date of hepatitis C virus infection from patient interviews and antibody tests on stored sera. Am J Gastroenterol 2004;99:1517–22. 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30826.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Thompson SG, Higgins JPT. How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Stat Med 2002;21:1559–73. 10.1002/sim.1187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Erman A, Sathya A, Nam A, et al. Estimating chronic hepatitis C prognosis using transient elastography‐based liver stiffness: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Viral Hepat 2018;25:502–13. 10.1111/jvh.12846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Patin E, Kutalik Z, Guergnon J, et al. Genome-Wide association study identifies variants associated with progression of liver fibrosis from HCV infection. Gastroenterology 2012;143:1244–52. 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.07.097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Paris AJ, Snapir Z, Christopherson CD, et al. A polymorphism that delays fibrosis in hepatitis C promotes alternative splicing of AZIN1, reducing fibrogenesis. Hepatology 2011;54:2198–207. 10.1002/hep.24608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Lo Iacono O, Venezia G, Petta S, et al. The impact of insulin resistance, serum adipocytokines and visceral obesity on steatosis and fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25:1181–91. 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03309.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Fartoux L, et al. Insulin resistance is a cause of steatosis and fibrosis progression in chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2005;54:1003–8. 10.1136/gut.2004.050302 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Hui JM, Sud A, Farrell GC, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with chronic hepatitis C and virus infection fibrosis progression. Gastroenterology 2003;125:1695–704. 10.1053/j.gastro.2003.08.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Rücker G, Schwarzer G, Carpenter JR, et al. Undue reliance on I 2 in assessing heterogeneity may mislead. BMC Med Res Methodol 2008;8 10.1186/1471-2288-8-79 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Wong WWL, Erman A, Feld JJ, et al. Model-Based projection of health and economic effects of screening for hepatitis C in Canada. CMAJ Open 2017;5:E662–72. 10.9778/cmajo.20170048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Erman A, Wong WWL, Feld JJ, et al. The health impact of delaying direct-acting antiviral treatment for chronic hepatitis C: a decision-analytic approach. Liver Int 2019. doi: 10.1111/liv.14247. [Epub ahead of print: 11 Sep 2019]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2018-027491supp001.pdf (1.8MB, pdf)