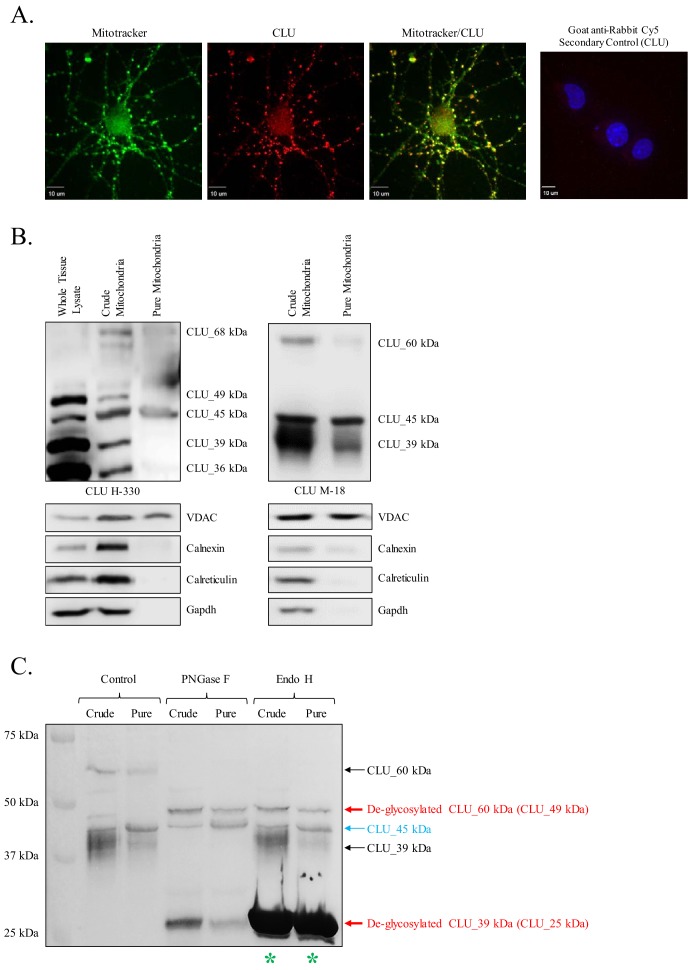
Figure 3. Identification of a mitochondrial CLU protein isoform.
(A) DIV 9 Mitotracker-stained (green) primary neurons were probed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU H-330 (red) and visualized using 40X confocal microscopy. (B) Pure cortical mitochondria were isolated as indicated. Equal concentrations of whole tissue lysate, crude mitochondria, and pure mitochondria were analyzed via SDS-PAGE and probed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU H-330 (left panel) and anti-CLU M-18 (right panel) (n = 3 independent isolations). Biochemical characterization of isolated fractions was performed using a panel of organelle-specific antibodies: voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) (mitochondria), calnexin and calreticulin (ER), and Gapdh (cytosol). (C) Crude and pure mitochondria were isolated and subjected to endoglycosidase treatment using PNGase F and Endo H. Deglycosylated mitochondrial lysates were then analyzed for CLU immunoreactivity using anti-CLU M-18. Red font: deglycosylated protein isoforms; blue font: isoforms that were unaffected by glycosidase treatment; green asterisk: excess Endo H enzyme.