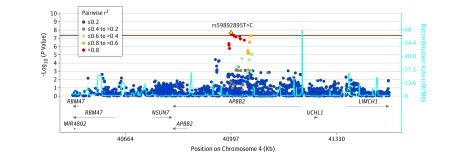
Figure 2. Association at the Amyloid-β A4 Precursor Protein-Binding Family B Member 2 (APBB2) Locus on Chromosome 4.
The association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and primary open-angle glaucoma were plotted by genomic position on chromosome 4 and degree of statistical significance. The horizontal line shows the threshold for genome-wide significance, P = 5 × 10−8. The dots indicate the extent of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between each tested SNP with rs59892895 (based on pairwise r2 values calculated from the discovery analysis). LD refers to the association between alleles of SNPs located close to one another on the same chromosome; SNPs in strong LD can serve as proxies for one another. Estimated recombination rates were plotted in light blue to reflect the LD structure in individuals with African ancestry. The estimated recombination rate shows the average frequency in which recombination occurs at a particular location. The extent of LD drops with increasing recombination rate. The horizontal lines accompanied by arrows in the lower panel of the plot reflect the genes mapping to the given genomic locations. The arrows indicate the direction of transcription of the genes. The horizontal lines labeled APBB2 and RBM47 reflect 2 different gene transcripts of different lengths for both genes.