Abstract
In the US Carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) is primarily attributed to the presence of the genes blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3, which are transmitted via plasmids. Carbapenem-resistant Kp (CR-Kp) infections are associated with hospital outbreaks. They are difficult to treat, and associated with high mortality rates prompting studies of how resistance is obtained. In this study, we determined the presence of CRISPR-Cas in 304 clinical Kp strains. The CRISPR-Cas system has been found to prevent the spread of plasmids and bacteriophages, and therefore limits the horizontal gene transfer mediated by these mobile genetic elements. Here, we hypothesized that only those Kp strains that lack CRISPR-Cas can acquire CR plasmids, while those strains that have CRISPR-Cas are protected from gaining these plasmids and thus maintain sensitivity to antimicrobials. Our results show that CRISPR-Cas is absent in most clinical Kp strains including the clinically important ST258 clone. ST258 strains that continue to be sensitive to carbapenems also lack CRISPR-Cas. Interestingly, CRISPR-Cas positive strains, all non-ST258, exhibit lower resistance rates to antimicrobials than CRISPR-Cas negative strains. Importantly, we demonstrate that the presence of CRISPR-Cas appears to inhibit the acquisition of blaKPC plasmids in 7 Kp strains. Furthermore, we show that strains that are unable to acquire blaKPC plasmids contain CRISPR spacer sequences highly identical to those found in previously published multidrug-resistance-containing plasmids. Lastly, to our knowledge this is the first paper demonstrating that resistance to blaKPC plasmid invasion in a CRISPR-containing Kp strain can be reversed by deleting the CRISPR-cas cassette.
Introduction
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) is a gram-negative bacterium that predominately causes nosocomial infections including sepsis, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia. With increasing spread they now also cause community-acquired infectons. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CR-Kp) has increased in prevalence in the United States from 1.6% in 2001 to 10.4% in 2011 [1]. Treating CR-Kp is challenging. The combination of increased vulnerability of hospitalized patients with serious comorbidities, and inadequate treatment options explain overall 30-day mortality rates that are as high as 39–50% in bacteremic CR-Kp infected patients [2–7]. In the United States, resistance to carbapenem antibiotics in Kp strains is predominantly conferred by the two antibiotic resistance genes, blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3, which encode class A carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamases, the Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPC) are transfered through plasmids. In these KPC ß-lactamases convey resistance also against clavulanic acid, monobactams, and cephalosporins [8, 9]. The majority of clinical isolates of CR-Kp in the US belong to the multi-locus sequence type (MLST)-defined clone ST258 [4]. This clone emerged in the US in the 2000s and is now prevalent worldwide [3, 10]. Finally, numerous hospital outbreaks have been associated with the ST258 clone and its related variants making its investigation clinically imperative [11, 12].
While the presence of either blaKPC-2 or blaKPC-3 is likely not the only factor contributing to the success of ST258, their acquisition provides the bacteria with a significant advantage against antibiotic therapeutics. It is noteworthy that not all ST258 strains exhibit resistance to carbapenem. As transmission of blaKPC genes is facilitated by plasmids, we analyzed the presence and function of CRISPR-Cas in carbapenem-sensitive (CS)-Kp and CR-Kp hospital strains. The CRISPR-Cas system is composed of cas genes followed by groupings of brief direct repeats and variable spacer regions that match infective agents of bacteria and archea, such as bacteriophages and plasmids [13–16]. This system has been found to prevent the spread of plasmids and bacteriophages [17–19], and therefore limit the horizontal gene transfer by these mobile genetic elements. For example, it was recently determined that hospital acquired, multidrug resistant strains of Enterococcus faecium lack CRISPR while community-acquired, drug sensitive strains of E. faecium contained CRISPR [20]. Additional studies demonstrated a significant association between antibiotic resistance in E. faecium strains and the absence of a CRISPR-Cas system, and correlation between decreased CRISPR-Cas and reduced defense against plasmid acquisition [21, 22]. CRISPR-Cas has therefore been compared in its function to an acquired immune system in bacteria.
We explored presence of the CRISPR-Cas systems in clinical Kp strains including those of the ST258 clonal background. Previous analysis on Kp genomes have identified presence of CRISPR-Cas, though its role in this species is yet to be defined [23, 24]. Until this study, little was known about the prevalence of CS-Kp strains and the predisposition of Klebsiella strains to become resistant to carbapenem antibiotics. While investigation of the overall prevalence of CRISPR-Cas in Kp has begun, the presence of CRISPR-Cas in CR versus CS-Kp and in the clinically important ST258 clone has not yet been studied. This project aimed to further elucidate the function of CRISPR-Cas in Kp immunity and examine the ST258 clonal background that has spread globally and has been highly associated with recent hospital outbreaks.
Materials and methods
Clinical isolates
Specimen collection was done under the approved IRB#648612 from Stony Brook University. No informed consent was obtained as samples were laboratory leftovers and deidentified. 304 hospital Kp isolates derived from bodily fluids from 265 patients were randomly collected from the microbiology laboratory at Stony Brook University Hospital (SBUH) between 2015–2016 (over a 14-month period) (S1 Table). The SBUH Microbiology laboratory regardless of the site of isolation kept isolates and our laboratory collect them. 83.3% were isolated from urine samples; 9.8% from respiratory samples, 4.6% from wounds and 2.2% from blood. This unbiased approach was chosen to permit identification of carbapenem sensitive ST258 strains. Sensitivity to all antibiotics was determined by the SBUH microbiology laboratory as part of standard diagnostic work up and obtained by us by review of medical records.
Sequence typing of ST258 clone
Screening of ST258 clonal background was performed by PCR and sequencing of the gapA and tonB genes (S1 Fig). PCR was performed on colony DNA, analyzed by gel electrophoresis, and PCR products were purified using the Qiagen PCR purification kit. Purified PCR products were sent for Sanger sequencing to Genewiz™. If gapA and tonB results were gapA3 and tonB79, ST258 clonal background was confirmed by regular MLST typing of the rest of the gene array [25].
CRISPR-Cas detection
Primers designed to detect cas1, cse1 and cas3 genes by PCR are listed in Table 1. Primers were designed using sequences provided by the webtool CRISPRFinder, which contained 111 CRISPR positive K. pneumoniae genomes and were representative of different CRISPR-Cas cas genes consistently seen in Kp CRISPR-Cas systems [16]. PCR was performed on colony DNA and results were analyzed by gel electrophoresis.
Table 1. Primers used in this study.
| Gene/CRISPR-Cas system type | Primer | Sequence | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| cas1 | FOR Cas1 K2 | GCTGTTTGTCAAAGTTACCCGCGAACTC | For Cas1 gene |
| cas1 | REV Cas1 K2 | GGTTTTGATCGCCTCATGAGTCACAGTTG | For Cas1 gene |
| cse1 | FOR Cse1 K2 | CAGTTTAACCGATATTTTCAGCCAGCCGG | For Cse1 gene |
| cse1 | REV Cse1 K2 | CATCAGTTAATTGCTGCTGTTGCTGACTTTCG | For Cse1 gene |
| cas3 | FOR Cas3 K2 | GGGTTTCGCTACAAAATCAACATGCCATCG | For Cas3 gene |
| cas3 | REV Cas3 K2 | CACGAGTTTTTTACGCTCATCAAACCAGAGC | For Cas3 gene |
| I-E CRISPR1 | F-trp 1 |
CAGTTCCTGCAACCTGGCCT | For intact CRISPR1-Cas systems |
| I-E CRISPR1 | R-Cas2 2 |
CTGGCAGCAGGTGATACAGC | |
| I-E CRISPR1 | F-iap 3 |
CTGGCATAACGCCACCGG | For incomplete CRISPR1-Cas systems |
| I-E CRISPR1 | R-cysH 4 |
GAGACCCGGTTCTTCGGGC | |
| I-E* CRISPR2 | FU-Cas3 5 |
GTAGCGAAACCCTGATCAAGCG | For intact CRISPR-Cas systems IE*-CRISPR2 |
| I-E* CRISPR2 | R-L2 6 |
GCGCTACGTTCTGGGGATG | |
| I-E* CRISPR2 | R-L2 6 |
GCGCTACGTTCTGGGGATG | For incomplete CRISPR-Cas systems IE*-CRISPR2 |
| I E* CRISPR2 | F-HP2 7 |
CGTCGCAAAACTCGACCAGA | |
| I-E* CRISPR3 | F-HP1 8 |
GACGCTGGTGCGATTCTTGAG | For intact CRISPR-Cas systems IE*-CRISPR3 |
| I-E* CRISPR3 | RU-Cas2 9 |
CGCAGTATTCCTCAACCGCCT | |
| For CRISPR deletion | Down-70 | GCCGCGATGGCATGTTGATTTTGTAGCGAAACCCTGATCAAGCGCCTCATCATATGAATATCCTCCTTAG | For I-E* CRISPR2 deletion |
| For CRISPR deletion | Up-70 | CGCGCTACGTTCTGGGGATGACAAAAGCGTTTTACCCCCGGCTGCGGGCCGTGCAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC | For I-E* CRISPR2 deletion |
Transformation assays
blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 plasmids were extracted by classic alkaline lysis extraction from previously reported CR strains M#34 and M#36 [4]. pPROBEKT plasmid (KmR, pVS1/p15a vector, with GFP-reporter gene) was used as a control for transformation [26]. 40 CS-Kp strains, 20 with and 20 without CRISPR-Cas, were randomly chosen for these studies and belong to different ST types as indicated by the combination of gapA and tonB alleles. CS-Kp strains were rendered electrocompetent and 100 ng of each of the plasmids was used in each of the transformation assays.
Spacer analysis
Based on previously published CRISPR-Cas architectures, primers were designed to amplify the CRISPR region in the two different CRISPR-Cas systems, type I-E and type I-E*, differentiated by flanking 3’ and 5’ genes (Fig 1) [22]. Primers used are listed in Table 1.
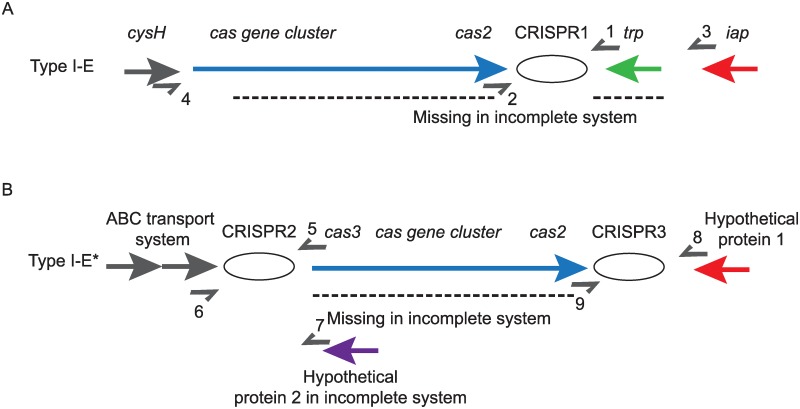
Fig 1. Primer locations with respect to CRISPR-Cas architecture.
Names and localization of genes are depicted. Dotted lines represent DNA regions that may be deleted in certain strains. Primers are shown as half-arrows and numbers correspond to specific primers detailed in Table 1. CRISPR array regions are depicted with an ellipse. A) Type I-E CRISPR-Cas system architecture. A complete type I-E, CRISPR1 array will be amplified with primers 1 and 2; an incomplete type I-E CRISPR1 system will be amplified with primers 3 and 4. B) Type I-E* CRISPR-Cas system architecture. A complete type I-E*, CRISPR2 will be amplified with primers 5 and 6 and an incomplete type I-E*, CRISPR2 system will be amplified with primers 6 and 7. A complete type I-E* CRISPR3 system will be amplified with primers 8 and 9.
Genewiz™ was used to sequence PCR products. PCR sequences were analyzed with the CRISPRfinder tool to identify direct repeats and spacer sequences. Spacer sequences were then BLASTed using the NCBI non-redundant nucleotide database than includes all deposited genomes, plasmids or phages. BLAST search identified sequence homologies to previously reported DNA sequences.
CRISPR deletion isogenic strains
To produce isogenic strains lacking CRISPR spacer regions, a Red/ET recombination system was used following manufacturer’s protocol (Quick and Easy Escherichia coli gene deletion kit; Gene Bridges, Heidelberg, Germany), but with modifications. Briefly, a linear DNA fragment with a chloranphenicol resistance and 70bp arms homologous to DNA upstream and downstream of I-E* CRISPR2 was amplified by PCR from the plasmid pCLF3 [27] with the primers listed in Table 1. The linear fragment was used to replace I-E* CRISPR2 regions in the 7 CRISPR-positive strains analyzed using the pRed/ET Tetracycline resistant plasmid. Positive transformants were confirmed by PCR using I-E* CRISPR2 specific primers.
Results
ST258 is significantly more carbapenem-resistant than other Kp clonal backgrounds
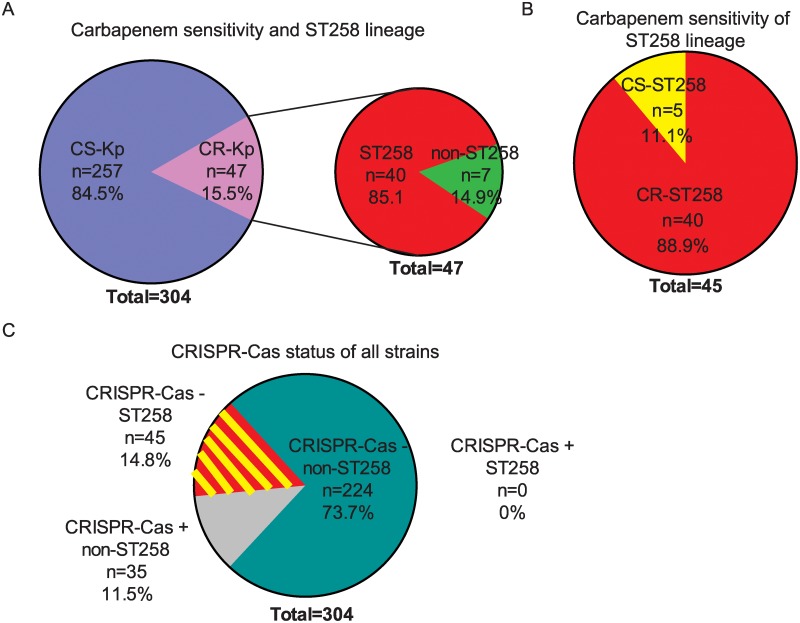
A PCR-based approach was designed that would allow identification of ST258 strains including those with maintained sensitivity to carbapenem antibiotics. We randomly collected 304 Kp strains (resistance unknown at collection time) that were identified by the microbiology laboratory of Stony Brook University Hospital (SBUH). PCR sequence typing for 2 genes (gapA, tonB) was performed to identify strains that strains belong to the ST258 clonal background. Those strains bearing gapA3 and tonB79 alleles were further typed by standard MLST (see Materials and methods section and S1 Fig). This approach identified a total of 45 ST258 strains (14.8%), 40 CR (89.2%) and 5 CS (11.1%) (Fig 2A). The ST258 clonal background accounted for 85.1% of all CR samples identified (Fig 2B). 257 Kp strains were identified as CS (84.5%), 5 of which were ST258. As expected Kp strains of the ST258 clonal background were significantly more likely to be CR compared with Kp strains of the non-ST258 clonal backgrounds (p < 0.0001, two-sided T test).
Fig 2. Characterization of clinical isolates.
A) Of all Kp strains (n = 304), 15.5% were carbapenem-resistant (CR) (pink). Of those CR-Kp, 85.1% were ST258 strains (red), and 14.9% of CR strains were non-ST258 strains (green). B) Of 45 ST258 strains, 88.9% were CR (red) and 11.1% were carbapenem-sensitive (CS) (yellow). C) Analysis of the CRISPR-Cas content of all Kp strains (n = 304) identified only 11.5% CRISPR-Cas positive strains (grey), none of which were of the ST258 lineage. 88.5% of all Kp strains did not have CRISPR-Cas (green + red/yellow stripes), including all ST258 strains (both CR and CS, red/yellow stripes).
All Kp strains with CRISPR-Cas were sensitive to carbapenems and had higher pan-sensitivity to other antibiotics
Next, cas genes were amplified by PCR to identify strains containing CRISPR-Cas systems (Materials and methods, Table 1). CRISPR-Cas was significantly less likely to be in strains of the ST258 clonal background (0/45) compared with strains of all other clonal backgrounds (35/259) (p = 0.0088, two-sided T test). MLST typing showed that CRISPR-Cas positive strains belonged to different clonal backgrounds including ST35 (n = 8), ST14 (n = 4), ST15 (n = 2), ST111 (n = 4), ST234 (n = 4), ST134 (n = 2), ST3887 (n = 2), ST116 (n = 1), ST151 (n = 1), ST431 (n = 1), ST1916 (n = 1), ST2861 (n = 1), ST3030 (n = 1). CRISPR-Cas was significantly more common in CS-Kp strains compared with CR-Kp strains (p = 0.0072, two-sided T test). Antibiograms of the 35 CRISPR-Cas positive CS-Kp strains (11.5%) (Fig 2C) were compared with antibiograms of a random sample of non-ST258 CS-Kp that lacked CRISPR-Cas (n = 47) as well as to all CS-Kp of ST258 clonal background (n = 5) (Table 2). As expected, all 35 CRISPR-Cas positive Kp strains were sensitive to carbapenems and resistant to ampicillin (resistance is chromosomally encoded). Additionally, CRISPR-Cas positive strains, all non-ST258, exhibited retained sensitivity to most of the other antibiotics (30/33, 91%) when compared with non-ST258, CRISPR-Cas negative strains (31/47, 66%) (p-value = 0.015). Finally, it is notable that a majority of ST258 CS-Kp strains (4/5, 80%) exhibited resistance against multiple antibiotics, including amikacin, aztreonam, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin and tobramycin. Indeed, only one of the CS-ST258 strains, SBU#53, was pan-sensitive to antibiotics, with the exception of the chromosomally encoded ampicillin resistance.
Table 2. Antibiogram analysis of CS-Kp strains.
Numbers and percentages represent non-susceptibilities for that specific antibiotic.
| CS, CRISPR-Cas positive (n = 33), n (%) | non-ST258 CS, CRISPR-Cas negative (n = 47), n (%) | ST258 CS, CRISPR-Cas negative (n = 5), n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amikacin | 0 (0) | 3 (6.4) | 4 (80) |
| Ampicillin/Sulbactam | 3 (9.1) | 11 (23.4) | 3 (60) |
| Aztreonam | 1 (3.0) | 8 (17.0) | 4 (80) |
| Cefepime | 0 (0) | 7 (14.9) | 2 (40) |
| Ceftazidime | 1 (3.0) | 7 (14.9) | 4 (80) |
| Ceftriaxone | 0 (0) | 9 (19.1) | 4 (80) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0 (0) | 4 (8.5) | 4 (80) |
| Gentamicin | 0 (0) | 4 (8.5) | 1 (20) |
| Levofloxacin | 0 (0) | 4 (8.5) | 4 (80) |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 1 (3.0) | 4 (8.5) | 1 (20) |
| Tigecycline | 0 (0) | 1 (2.1) | 0 (0) |
| Tobramycin | 0 (0) | 5 (10.6) | 4 (80) |
| Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole | 2 (6.1) | 9 (19.1) | 3 (60) |
CRISPR-Cas inhibits transformation of blaKPC plasmids in CS-Kp
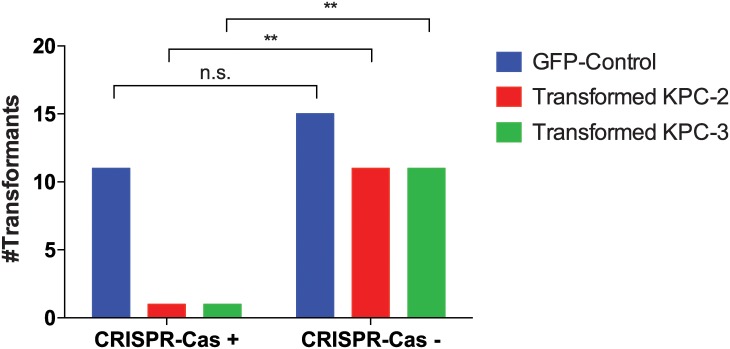
Next, transformation studies were performed to explore whether the presence of CRISPR-Cas protects against the acquisition of blaKPC plasmids in CS-Kp strains. These experiments showed successful transformation with a control plasmid in 11 of 20 CS-Kp strains with CRISPR-Cas (Fig 3). However, of these 11 strains, only 2 (18%) could be transformed with either the blaKPC-2 (SBU#63) or the blaKPC-3 (SBU#20) plasmid (but not both) (Fig 3). In contrast, 15 of 20 CS-Kp isolates that lacked CRISPR-Cas sequences were successfully transformed with the control plasmid and 11 of those (73%) were successfully transformed with both blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3. Hence, these data indicate higher transformation success of blaKPC plasmids in strains lacking CRISPR-Cas compared with strains containing CRISPR-Cas (Fisher’s exact test, p-value = 0.0017 for both plasmids). No significant difference in control plasmid transformation was observed between groups. We also attempted to transform all CS ST258 strains (n = 5) with a control plasmid and blaKPC. Since kanamycin resistance was required for the selection of transformed bacteria with this control plasmid, only 2 of 5 isolates could be studied in this experiment (SBU#53 and SBU#181) as the rest were kanamycin resistant. Both strains were able to be transformed with blaKPC-2, but not with blaKPC-3.
Fig 3. Plasmid transformation assays.
Transformation of blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 plasmids was significantly less successful in CRISPR-Cas positive strains compared with CRISPR-Cas negative strains.
CRISPR spacer sequences in strains protected from plasmid acquisition match other multidrug-resistant plasmids
The CRISPR spacer sequences in strains that could not be transformed with blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 plasmids were further analyzed. Specifically, we explored whether spacer sequences in the CRISPR array of these strains contained genomic sequences homologous to known multi-drug resistant plasmids. CRISPR in these strains was amplified and then sequenced via a PCR primer set generated from a previously published CRISPR-Cas database of 55 Kp strains (18). These PCR primers amplify all described Kp-CRISPR-Cas architectures [24] (Fig 1).
PCR was performed on 7 of the CRISPR-Cas positive strains (SBU #28, 31, 61, 63, 70, 83, and 142), all of which were resistant to transformation with blaKPC plasmids. In each of these strains, sequence data identified the CRISPR-Cas system as I-E* CRISPR type [24] (Fig 1). Strains SBU #28, 70, and 142 had I-E* CRISPR2 and I-E* CRISPR3, whereas strains SBU #31, 61, 63 and 83 contained only I-E* CRISPR2. The I-E* CRISPR2 and I-E* CRISPR3 direct repeat sequences were found to be identical to the previously reported consensus sequences [24]. Each CRISPR-Cas positive strain contained between 3 and 11 spacer sequences. Spacer sequences exhibited an 87–100% match to exogenous DNA from either known plasmids or phages [28]. Notably, at least one spacer sequence in each of the clinical isolates analyzed either partially or fully matched plasmids (89–100% identity) that were reported to confer resistance to one of the following: metals, non-carbapenem antibiotics, carbapenem antibiotics via blaKPC genes plasmids, or carbapenem antibiotics via blaNDM genes (Table 3).
Table 3. A list of CRISPR sequence identities in each strain analyzed.
| Strain | CRISPR spacer # | Identity % | Plasmid | Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBU#28 | 2 | 94 | pKPN-498 | Heavy metals |
| SBU#31 | 1 | 100 | pNJST258N1 | Heavy metals |
| SBU#61 | 2 | 94 | pKPN-498 | Heavy metals |
| SBU#63 | 2 | 89 | pKPC-224e | blaKPC-3 |
| SBU#63 | 2 | 89 | pKQPS142a | Heavy metals |
| SBU#70 | 5 | 94 | pKPN-498 | Heavy metals |
| SBU#70 | 6 | 91 | pKN-LS6 | Heavy metals |
| SBU#83 | 1 | 96 | pKPC-c9fd, pKPC-4b66 | blaKPC-2 |
| SBU#142 | 2 | 100 | pKPC-224e | blaKPC-3 |
| SBU#142 | 3 | 100 | pCREC-TJ2-NDM | blaNDM |
| SBU#142 | 6 | 100 | pKPC2_095132 | blaKPC-2 |
With deletion of CRISPR spacer sequences, transformation was enabled in Kp strain #61
Attempts were made to delete the I-E* CRISPR2 spacer sequences in the 7 above described CRISPR-Cas positive strains (using homologous recombination, as this CRISPR2 was present in both I-E and I-E* strains). Inherent resistance of some strains to the pRedET plasmid permitted successful deletion of the I-E* CRISPR2 spacer in only strains SBU#28, SBU#61, and SBU#70. Once the I-E* CRISPR2 spacer was deleted, only SBU#61 was successfully transformed with blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 plasmids. Notably, SBU#61 only carries I-E* CRISPR2, whereas SBU#28 and SBU#70 also carry I-E* CRISPR3.
Discussion
This study determined the prevalence of CS-Kp in ST258 colonized patients in one major hospital in New York State. CR-Kp was responsible for 15.5% of Kp infections in our patient population, which is slightly below that reported in three NYC hospitals between 2006–2014 (17.3%) [29]. ST258 was responsible for 85.1% of the CR-Kp in our patient population, which is higher than previously reported [4, 7]. Additionally, this study determined the prevalence of CRISPR-Cas in CR-Kp and CS-Kp for both ST258 and all other strains tested. CRISPR-Cas was only identified in CS-Kp strains that were not of the ST258 clonal background, which has been reported by others [30–32]. Overall the proportion of strains with CRISPR-Cas systems in our isolate population was only 11.5%, consistent with data of other analyzed Kp genomes, but much lower than data derived from Escherichia coli isolates [33]. This difference could be related to the species itself or to technical differences in our studies, as our approach detected only the presence of Cas proteins (full CRISPR-Cas systems). As the CRISPR-Cas system appears not to be highly prevalent in Kp species, it remains to be determined how the absence or presence of the system could be contributing to the evolution of Kp strains.
Our data describe CS strains that belong to the ST258 clonal background that lacked CRISPR-Cas systems an. Of these strains 80% strains exhibit other drug resistance. Future in depth characterization of the sole pan-sensitive CS ST258 strain identified in this study, and others if identified, might help explain why some strains do not acquire antibiotic resistance. Ultimately, it would be interesting to know what, if any, fitness advantage there is for pan-sensitive strains.
Most of the Kp strains containing CRISPR-Cas were pan-sensitive whereas resistance to multiple antibiotics was observed in the strains lacking CRISPR. In line with this, our transformation studies demonstrated successful transformation of the blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 plasmids into a significantly larger proportion of Kp strains lacking CRISPR-Cas. Although some strains could not be transformed with the control plasmid, successful control plasmid transformation was comparable among strains with and without CRISPR-Cas systems. The impedance of transformation may have been due to transformation competency preparation restriction-modification systems inherent to the strains or incompatibility (Inc) groups if the strains harbored other plasmids.
Notably, transformation of the blaKPC-2 plasmid was successful in only 1 CS-Kp strain containing CRISPR-Cas (SBU#63), as was transformation of the blaKPC-3 plasmid (SBU#20). Interestingly, the former strain had a CRISPR-Cas spacer sequence that matched a published blaKPC-3 plasmid. The ability to be transformed with one plasmid but not the other could be related to the CRISPR-associated spacer sequences that match either blaKPC-2 or blaKPC-3 plasmids, but not both, as is the case in SBU#63. Sequence analysis of spacers in 7 CRISPR-Cas positive strains indicated that they contained sequences that were more than 90% identical to sequences found in multidrug-resistance plasmids carrying either carbapenemase genes or resistance genes against heavy metals. CRISPR-Cas and its associated spacer sequences could therefore help explain why some Kp strains are less susceptible to the acquisition of antibiotic-resistance plasmids.
Furthermore, after successful deletion of the I-E* CRISPR2 region in strain SBU#61, which previously could not be transformed with any blaKPC plasmids, transformation of this strain with blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 plasmid was successful. This supports the notion that CRISPR sequences initially shielded this strain from acquiring carbapenem resistance by preventing integration of the blaKPC-2 and/or blaKPC-3 plasmid. At this point it remains unclear why transformation with blaKPC-2 and or blaKPC-3 was not successful in other tested strains SBU#28 or SBU#70, even though the CRISPR cassette was also deleted. It is important to note, however, these strains contained CRISPR3 spacers, and our deletion strategy only targeted the CRISPR2 locus. This CRISPR3 sequences may still target sequences in the plasmids, preventing the transformation.
One major limitation of our data is that we do not have the complete sequences of the blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 plasmids of our Kp strains, and, in addition, we did not do transformation studies using other plasmids identified to have high identity to the spacer regions. As a result, we cannot conclusively demonstrate that CRISPR-Cas spacers convey immunity due to similarity of the CRISPR spacers to plasmid sequences. Lack of transformation success could also be due to the presence of other plasmids that share the same incompatibility system with the blaKPC plasmids, although 6 of the 7-sequenced CRISPR-Cas positive were pan-sensitive to all antibiotics pointing against that line of thought. Finally, these results, while based on limited data from 7 CRISPR-Cas positive strains, do differ from a previous analysis of CRISPR-Cas in E. coli isolates where the proportion of spacers matching plasmid genomes was found to be low (20%), and there was no association between CRISPR-Cas and antibiotic resistance [34].
PCRs done to amplify CRISPRs sequences assigned all of our strains to the I-E* CRISPR type, a subtype of the Kp I-E CRISPR type [24]. It would be interesting to investigate whether phenotypic or geographic differences exist between strains harboring different CRISPR types.
A limitation of this study is that this study only analyzed clinical isolates from SBUH and results may therefore not reflect the transmission or characteristics of Kp strains and plasmids present in other geographical areas. Future studies are needed to investigate why some ST258 strains remain sensitive to carbapenems and whether these strains compensate by having other fitness advantages or virulence genes. It is possible that the ST258 clone evolved rapidly in the past in a selective pressure environment (i.e. the clinical setting) without the CRISPR-Cas system as a barrier against acquisition of exogenous DNA. Although whole genome sequence studies suggested that ST258 spread via local expansion rather than by repeated uptake of multiple antibiotic-resistance plasmids, acquisition of novel virulence genes has been described in ST258. This acquisition remains a concern for other Kp clones as well because it may contribute to the evolution of hypervirulent, multidrug-resistant strains [35, 36]. While further studies need to be done, decreased prevalence of the CRISPR-Cas system in the ST258 clonal background may be a major contributor to its clonal success, acquisition of antibiotic resistance plasmids and virulence genes, hospital outbreaks, and global spread.
Supporting information
(EPS)
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the laboratory of Dr. Leandro Cerchietti for their assistance in allowing us to carry out some of the laboratory experiments detailed in this paper.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by: 1. Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Award Number: R21 AI114259, Recipient: Bettina C. Fries; 2. Alpha Omega Foundation, Award Number: Carolyn L. Kuckein Student Research Fellowship, Recipient: Natalie A. Mackow; and 3. Infectious Diseases Society of America, Award Number: Medical Scholars Program, Recipient: Natalie A. Mackow. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Centers for Disease C, Prevention. Vital signs: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013;62(9):165–70. . [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hauck C, Cober E, Richter SS, Perez F, Salata RA, Kalayjian RC, et al. Spectrum of excess mortality due to carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(6):513–9. 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.01.023 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen L, Mathema B, Chavda KD, DeLeo FR, Bonomo RA, Kreiswirth BN. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: molecular and genetic decoding. Trends Microbiol. 2014;22(12):686–96. 10.1016/j.tim.2014.09.003 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Diago-Navarro E, Chen L, Passet V, Burack S, Ulacia-Hernando A, Kodiyanplakkal RP, et al. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae exhibit variability in capsular polysaccharide and capsule associated virulence traits. J Infect Dis. 2014;210(5):803–13. Epub 2014/03/19. 10.1093/infdis/jiu157 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hirsch EB, Tam VH. Detection and treatment options for Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases (KPCs): an emerging cause of multidrug-resistant infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65(6):1119–25. 10.1093/jac/dkq108 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Neuner EA, Yeh JY, Hall GS, Sekeres J, Endimiani A, Bonomo RA, et al. Treatment and outcomes in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011;69(4):357–62. Epub 2011/03/15. 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2010.10.013 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Satlin MJ, Chen L, Patel G, Gomez-Simmonds A, Weston G, Kim AC, et al. Multicenter Clinical and Molecular Epidemiological Analysis of Bacteremia Due to Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) in the CRE Epicenter of the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(4). 10.1128/AAC.02349-16 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen L, Chavda KD, DeLeo FR, Bryant KA, Jacobs MR, Bonomo RA, et al. Genome Sequence of a Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 258 Isolate with Prophage-Encoded K. pneumoniae Carbapenemase. Genome Announc. 2015;3(3). 10.1128/genomeA.00659-15 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Munoz-Price LS, Poirel L, Bonomo RA, Schwaber MJ, Daikos GL, Cormican M, et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(9):785–96. Epub 2013/08/24. 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70190-7 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yigit H, Queenan AM, Anderson GJ, Domenech-Sanchez A, Biddle JW, Steward CD, et al. Novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase, KPC-1, from a carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45(4):1151–61. 10.1128/AAC.45.4.1151-1161.2001 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bowers JR, Kitchel B, Driebe EM, MacCannell DR, Roe C, Lemmer D, et al. Genomic Analysis of the Emergence and Rapid Global Dissemination of the Clonal Group 258 Klebsiella pneumoniae Pandemic. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0133727 10.1371/journal.pone.0133727 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Marsh JW, Krauland MG, Nelson JS, Schlackman JL, Brooks AM, Pasculle AW, et al. Genomic Epidemiology of an Endoscope-Associated Outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC)-Producing K. pneumoniae. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144310 10.1371/journal.pone.0144310 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mojica FJ, Diez-Villasenor C, Garcia-Martinez J, Soria E. Intervening sequences of regularly spaced prokaryotic repeats derive from foreign genetic elements. J Mol Evol. 2005;60(2):174–82. 10.1007/s00239-004-0046-3 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bolotin A, Quinquis B, Sorokin A, Ehrlich SD. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindrome repeats (CRISPRs) have spacers of extrachromosomal origin. Microbiology. 2005;151(Pt 8):2551–61. 10.1099/mic.0.28048-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pourcel C, Salvignol G, Vergnaud G. CRISPR elements in Yersinia pestis acquire new repeats by preferential uptake of bacteriophage DNA, and provide additional tools for evolutionary studies. Microbiology. 2005;151(Pt 3):653–63. 10.1099/mic.0.27437-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Grissa I, Vergnaud G, Pourcel C. CRISPRFinder: a web tool to identify clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Web Server issue):W52–7. 10.1093/nar/gkm360 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hargreaves KR, Flores CO, Lawley TD, Clokie MR. Abundant and diverse clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat spacers in Clostridium difficile strains and prophages target multiple phage types within this pathogen. MBio. 2014;5(5):e01045–13. 10.1128/mBio.01045-13 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Barrangou R, Marraffini LA. CRISPR-Cas systems: Prokaryotes upgrade to adaptive immunity. Mol Cell. 2014;54(2):234–44. 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.011 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marraffini LA, Sontheimer EJ. CRISPR interference limits horizontal gene transfer in staphylococci by targeting DNA. Science. 2008;322(5909):1843–5. 10.1126/science.1165771 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Palmer KL, Gilmore MS. Multidrug-resistant enterococci lack CRISPR-cas. MBio. 2010;1(4). 10.1128/mBio.00227-10 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Burley KM, Sedgley CM. CRISPR-Cas, a prokaryotic adaptive immune system, in endodontic, oral, and multidrug-resistant hospital-acquired Enterococcus faecalis. J Endod. 2012;38(11):1511–5. 10.1016/j.joen.2012.07.004 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Price VJ, Huo W, Sharifi A, Palmer KL. CRISPR-Cas and Restriction-Modification Act Additively against Conjugative Antibiotic Resistance Plasmid Transfer in Enterococcus faecalis. mSphere. 2016;1(3). 10.1128/mSphere.00064-16 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ostria-Hernandez ML, Sanchez-Vallejo CJ, Ibarra JA, Castro-Escarpulli G. Survey of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and their associated Cas proteins (CRISPR/Cas) systems in multiple sequenced strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. BMC Res Notes. 2015;8:332 10.1186/s13104-015-1285-7 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shen J, Lv L, Wang X, Xiu Z, Chen G. Comparative analysis of CRISPR-Cas systems in Klebsiella genomes. J Basic Microbiol. 2017;57(4):325–36. 10.1002/jobm.201600589 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Diancourt L, Passet V, Verhoef J, Grimont PA, Brisse S. Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43(8):4178–82. 10.1128/JCM.43.8.4178-4182.2005 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Diago-Navarro E, Calatayud-Baselga I, Sun D, Khairallah C, Mann I, Ulacia-Hernando A, et al. Antibody-Based Immunotherapy To Treat and Prevent Infection with Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017;24(1). 10.1128/CVI.00456-16 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Porwollik S, Santiviago CA, Cheng P, Long F, Desai P, Fredlund J, et al. Defined single-gene and multi-gene deletion mutant collections in Salmonella enterica sv Typhimurium. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e99820 10.1371/journal.pone.0099820 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Coordinators NR. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue):D8–D20. 10.1093/nar/gks1189 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Park SO, Liu J, Furuya EY, Larson EL. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Three New York City Hospitals Trended Downwards From 2006 to 2014. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3(4):ofw222 10.1093/ofid/ofw222 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li HY, Kao CY, Lin WH, Zheng PX, Yan JJ, Wang MC, et al. Characterization of CRISPR-Cas Systems in Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Uncovers Its Potential Association With Antibiotic Susceptibility. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1595 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01595 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wyres KL, Wick RR, Judd LM, Froumine R, Tokolyi A, Gorrie CL, et al. Distinct evolutionary dynamics of horizontal gene transfer in drug resistant and virulent clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS Genet. 2019;15(4):e1008114 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008114 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Huang W, Wang G, Sebra R, Zhuge J, Yin C, Aguero-Rosenfeld ME, et al. Emergence and Evolution of Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with both blaKPC and blaCTX-M Integrated in the Chromosome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(7). 10.1128/AAC.00076-17 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Aydin S, Personne Y, Newire E, Laverick R, Russell O, Roberts AP, et al. Presence of Type I-F CRISPR/Cas systems is associated with antimicrobial susceptibility in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(8):2213–8. 10.1093/jac/dkx137 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Touchon M, Charpentier S, Pognard D, Picard B, Arlet G, Rocha EP, et al. Antibiotic resistance plasmids spread among natural isolates of Escherichia coli in spite of CRISPR elements. Microbiology. 2012;158(12):2997–3004. 10.1099/mic.0.060814-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Deleo FR, Chen L, Porcella SF, Martens CA, Kobayashi SD, Porter AR, et al. Molecular dissection of the evolution of carbapenem-resistant multilocus sequence type 258 Klebsiella pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(13):4988–93. Epub 2014/03/19. 10.1073/pnas.1321364111 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Holt KE, Wertheim H, Zadoks RN, Baker S, Whitehouse CA, Dance D, et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(27):E3574–81. 10.1073/pnas.1501049112 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(EPS)
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.