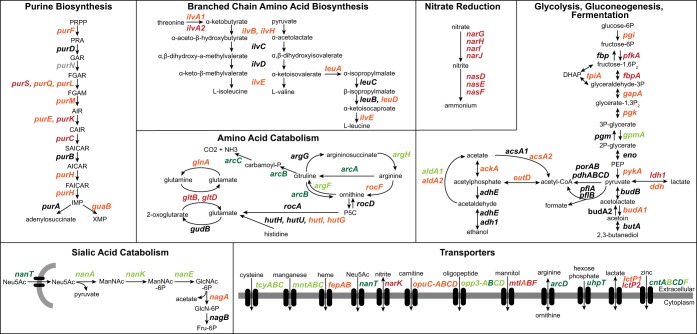
FIG 2.
Metabolic pathways that are differentially expressed in human sputum compared to in vitro growth. A subset of notable metabolic pathways that showed differential expression (DESeq2, adjusted P value of <0.05, >2-fold change) in human sputum compared to exponential growth in chemically defined medium with glucose as a primary carbon source and/or compared to all in vitro conditions. Genes labeled in dark green indicate increased expression in CF sputum in both comparisons, light green indicates increased expression under one condition, orange indicates decreased expression under one condition, and red indicates decreased expression in sputum versus both in vitro comparisons. Pathways for purine biosynthesis and arginine biosynthesis were adapted from previous studies (58–60). Abbreviations for chemical compounds are in parentheses: N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc), N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcNAc-6P), glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcN-6P), fructose-6-phosphate (Fru-6P), phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP), 5′-phosphoribosylamine (PRA), glycine amide ribonucleotide (GAR), 5′-phosphoribosyl-N-formylglycineamide (FGAR), 5′-phophoribosylformylglycinamidine (FGAM), 5′-aminoimidazole ribotide (AIR), 5′-phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide (SAICAR), 5′-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), 5′-formamidoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribotide (FAICAR), 5′phosphoribosyl-4-carboxy-5-aminoimidazole (CAIR).