Significance
Ketone bodies, mainly β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate, are important alternative energy sources in a state of energy deficit or metabolic crisis. The consumption of ketogenic diets, such as low-carbohydrate and medium-chain triglyceride diets, and time-restricted feeding lead to ketogenesis, which influences longevity and health. β-Hydroxybutyrate also acts as a signaling molecule via GPR109A and GPR41; however, to date, the specific G protein-coupled receptors responsible for acetoacetate and its physiological functions remain unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that acetoacetate acts as an endogenous agonist of GPR43 by ligand screening in a heterologous expression system, and that it, rather than short-chain fatty acids, maintains energy homeostasis via GPR43-mediated lipid metabolism under ketogenic conditions.
Keywords: ketone body, fasting, low carbohydrate, gut microbiota, FFAR2
Abstract
Ketone bodies, including β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate, are important alternative energy sources during energy shortage. β-Hydroxybutyrate also acts as a signaling molecule via specific G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs); however, the specific associated GPCRs and physiological functions of acetoacetate remain unknown. Here we identified acetoacetate as an endogenous agonist for short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) receptor GPR43 by ligand screening in a heterologous expression system. Under ketogenic conditions, such as starvation and low-carbohydrate diets, plasma acetoacetate levels increased markedly, whereas plasma and cecal SCFA levels decreased dramatically, along with an altered gut microbiota composition. In addition, Gpr43-deficient mice showed reduced weight loss and suppressed plasma lipoprotein lipase activity during fasting and eucaloric ketogenic diet feeding. Moreover, Gpr43-deficient mice exhibited minimal weight decrease after intermittent fasting. These observations provide insight into the role of ketone bodies in energy metabolism under shifts in nutrition and may contribute to the development of preventive medicine via diet and foods.
Under ketogenic conditions, such as fasting and diabetes, ketone bodies produced in the liver from fatty acids serve as the main source of energy (1–3). In particular, the brain uses ketone bodies as an alternative energy source, because it cannot use fatty acids when blood glucose is insufficient. In addition, consumption of ketogenic diets, such as low-carbohydrate and medium-chain triglyceride diets, and time-restricted feeding lead to ketogenesis, which influences longevity and health (4). However, the key ketone body that affects metabolism has not been identified, and the detailed molecular mechanism remains unclear.
β-Hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate, the 2 predominant ketone bodies, are energy-rich compounds that transport energy from the liver to other tissues (5). β-Hydroxybutyrate is formed by the reduction of acetoacetate in the mitochondria. Ketogenesis occurs either when blood glucose levels are low and other cellular carbohydrate stores, such as glycogen, have been exhausted or in the presence of insufficient insulin, such as in type I diabetes (6). Ketone body production involves enzymatic degradation of fatty acids via β-oxidation to form acetyl-CoA in the hepatic mitochondria, which results in the release of energy stored in fatty acids (5).
In addition to their role as energy sources, ketone bodies participate in various cellular processes as signaling molecules. Recent studies show that the G protein-coupled receptors GPR109A/HCAR2 and GPR41/FFAR3 are activated by the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate (2, 7, 8). GPR109A, a niacin receptor, has been identified as the receptor of the anti-dyslipidemic drug nicotinic acid (9). GPR109A activation inhibits lipolytic and atherogenic activities, induces vasodilation, and is responsible for niacin-induced flushing (10, 11).
Under ketogenic conditions, GPR109A exhibits anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects (8). In contrast, GPR41 has been identified as a receptor for short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate (12). As a gut microbiota-related energy sensor, GPR41 regulates energy homeostasis in enteroendocrine cells, adipose tissue, and the peripheral nervous system (2, 13, 14), and under ketogenic conditions suppresses energy expenditure via the sympathetic nervous system (2).
GPR43/FFAR2 is another SCFA receptor that couples with either Gq or Gi/o family G proteins. Stimulation of GPR43 by SCFAs leads to inhibition of cAMP production, activation of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) cascade, and elevation of [Ca2+]i levels (15, 16). Although GPR43 is expressed mainly in metabolism-related tissues, such as adipose tissue, it is also involved in modulating host metabolic processes via the gut microbiota (17–19).
In this study, we identified the ketone body acetoacetate as a GPR43 ligand through ligand screening in a heterologous expression system. We subsequently investigated the roles of GPR43 in lipid metabolism and energy regulation under ketogenic conditions. Our results provide insight into the role of GPR43 as a sensor of dietary energy sources and ketone bodies as signaling molecules in metabolic processes.
Results
The Ketone Body Acetoacetate Is an Endogenous Ligand of GPR43.
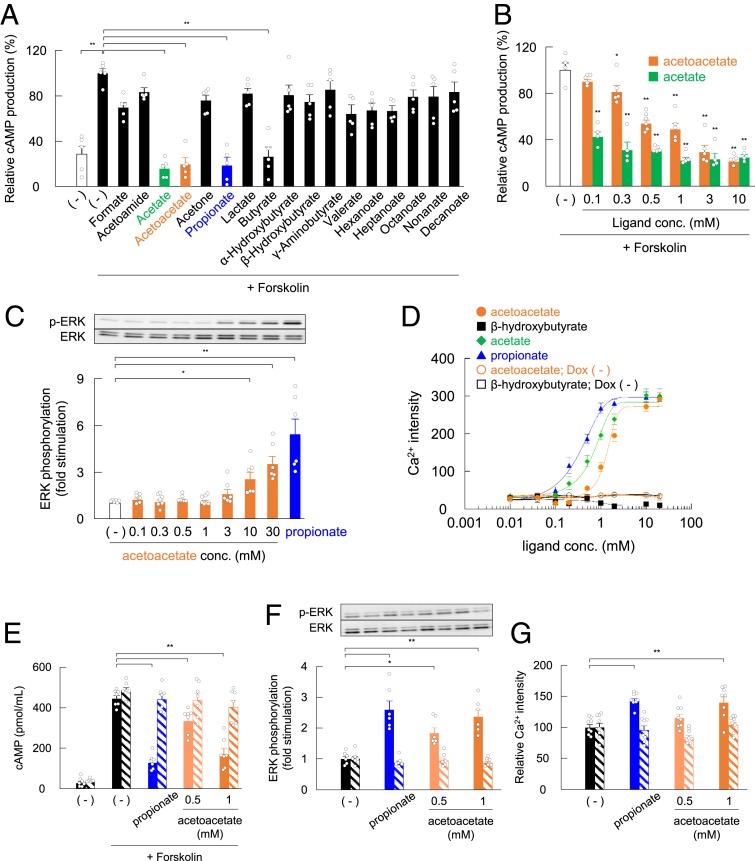
We first examined the agonistic effects of various monocarboxylates on GPR43 in the heterologous expression system. Acetoacetate, but not β-hydroxybutyrate, decreased intracellular cAMP concentration in HEK293 cells expressing mouse GPR43, similar to acetate and propionate, which are potent GPR43 agonists (Fig. 1A). Moreover, acetoacetate significantly suppressed cAMP levels induced by forskolin in a dose-dependent manner (∼0.3 mM) in GPR43-overexpressing HEK293 cells, with an EC50 of 0.76 mM (Fig. 1B), whereas these effects were not observed in doxycycline-uninduced control [Dox (−)], non–GPR43-expressing HEK293 cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S1 A and B). GPR43 is a Gq and Gi/o dual-coupled receptor (15) that activates the ERK cascade and elevates [Ca2+]i level while inhibiting the production of cAMP. We found that acetoacetate promoted ERK1/2 phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner in GPR43-overexpressing HEK293 cells (Fig. 1C), whereas these effects were not observed in Dox (−) control HEK293 cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S1C). Moreover, acetoacetate, but not β-hydroxybutyrate, increased [Ca2+]i levels in GPR43-overexpressing HEK293 cells, with an EC50 of 1.42 mM, whereas these effects were not observed in Dox (−) control HEK293 cells (Fig. 1D).
Fig. 1.
Acetoacetate is a ligand for GPR43. (A and B) cAMP levels in response to monocarboxylic acids (5 mM each) treatment (A) or acetoacetate and acetate in a dose-dependent manner (B) in Flp-in GPR43 T-REx HEK293 cells. After 24 h in culture, cells were treated with doxycycline (10 μg/mL) and cultured for another 24 h. Cells precultured with 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) for 30 min were treated in the presence of each ligand for 10 min. The intracellular cAMP levels were determined using a cAMP assay kit, and data are presented as relative to the forskolin-induced cAMP levels (n = 4 to 6). (C) Effects of acetoacetate on ERK1/2 phosphorylation in Flp-in GPR43 T-REx HEK293 cells. After 24 h in culture with doxycycline (10 μg/mL), cells were cultured for another 24 h in serum-free DMEM. The cells were treated with various concentrations (0.1 to 30 mM) of acetoacetate or 1 mM propionate for 10 min (n = 6 or 7). (D) Mobilization of [Ca2+]i induced by acetate, propionate, acetoacetate, and β-hydroxybutyrate was monitored in Flp-in GPR43 T-REx HEK293 cells; data are presented as Ca2+ intensity. Open symbols represent values from cells without doxycycline treatment; closed symbols, values from cells with doxycycline treatment. (E) cAMP levels in response to acetoacetate in mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF)-derived adipocytes. Adipocytes precultured with IBMX for 30 min were treated in the presence of 500 μM or 1 mM acetoacetate or 1 mM propionate for 10 min (n = 8). (F) Effects of acetoacetate on ERK1/2 phosphorylation in MEF-derived adipocytes. The adipocytes were treated with 500 μM or 1 mM acetoacetate or 1 mM propionate for 10 min (n = 8). (G) [Ca2+]i induced by acetoacetate in MEF-derived adipocytes; data indicate the peak of Ca2+ intensity (n = 8). Hatched bars represent adipocytes from Gpr43−/− mice (E–G). **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, compared with (−), Dunnett’s test. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
GPR43 is abundantly expressed in adipocytes (18); therefore, we investigated whether acetoacetate can activate endogenous GPR43 in adipocytes. Acetoacetate (500 and 1,000 μM), as well as propionate, significantly inhibited the production of cAMP but activated the ERK cascade and elevated [Ca2+]i levels in wild-type mouse adipocytes, whereas no effect was observed in Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 1 E–G). Collectively, these results suggest that acetoacetate is a potential potent endogenous agonist of GPR43, like acetate and propionate.
GPR43 Deficiency Inhibits Fasting-Induced Lipid Utilization.
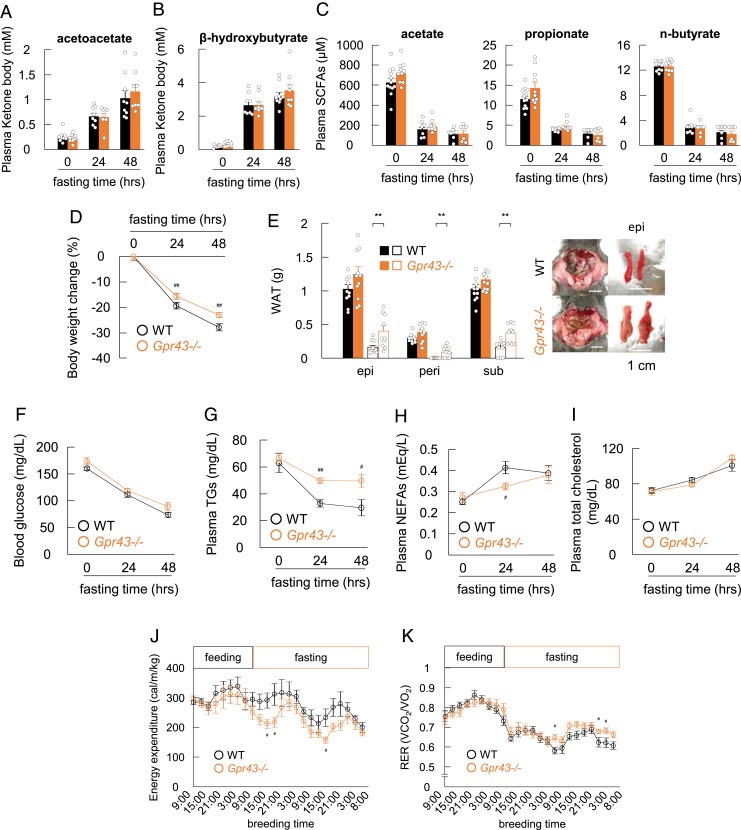
We next examined the effects of acetoacetate on lipid metabolism via GPR43 under ketogenic conditions induced by fasting. After 48 h of starvation, plasma concentrations of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, particularly acetoacetate (∼1 mM), which can strongly activate GPR43, were markedly increased in both the wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 2 A and B). In addition, acetoacetate levels in several tissues were elevated during fasting (SI Appendix, Fig. S2A). In contrast, plasma SCFA (acetate, propionate, and n-butyrate) concentrations were dramatically decreased in both wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 2C), indicating that acetoacetate, rather than SCFAs, acts as a ligand for GPR43 during fasting.
Fig. 2.
GPR43 deficiency prevents body weight loss in the fasting condition. (A–C) Wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice were fasted and assessed for plasma acetoacetate (A), β-hydroxybutyrate (B), and SCFA (C) levels at 0, 24, and 48 h (n = 7 to 12). (D and E) Body weight changes were monitored for 48 h in the fasting condition. Relative body weight change (D), fat mass (E, Left) and representative macroscopic appearance (E, Right) were measured (n = 10 to 12). (Scale bar: 1 cm.) Open squares represent values for fasting mice for 48 h; closed squares, values for nonfasting mice. (F–I) Blood glucose (F), plasma TG (G), NEFA (H), and total cholesterol (I) levels were measured after 0, 24, and 48 h of fasting (n = 8 to 12). (J and K) Energy expenditure (J) and respiratory exchange ratio (RER; K) of fasted-mice in time course changes (n = 7). **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. ##P < 0.01; #P < 0.05 compared with wild-type mice, Student’s t test. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
In 7-wk-old wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice matched by average weight (SI Appendix, Fig. S2 B and C), the decrease in body weight was significantly lower in the Gpr43−/− mice compared with the wild-type mice during fasting (Fig. 2D). After 48 h of starvation, the adipose tissue weight was significantly higher in the Gpr43−/− mice compared with the wild-type mice (Fig. 2E), whereas lean body mass was comparable in the 2 groups (SI Appendix, Fig. S2D). Furthermore, during fasting, plasma levels of glucose and triglycerides (TGs) were significantly reduced in the wild-type mice (Fig. 2 F and G), whereas nonesterified fatty acid (NEFA) and cholesterol levels were increased (Fig. 2 H and I). However, plasma TG levels in the Gpr43−/− mice remained unchanged relative to those in the wild-type mice during fasting (Fig. 2G), and plasma NEFA levels were lower in the Gpr43−/− mice during fasting (Fig. 2H). Energy expenditure was similar in the Gpr43−/− mice and wild-type mice during feeding but was significantly lower in the Gpr43−/− mice during fasting (Fig. 2J). The respiratory exchange ratio was significantly lower in the wild-type mice compared with the Gpr43−/− mice under fasting conditions (Fig. 2K). These results suggest that during fasting, Gpr43−/− mice cannot promote energy expenditure by utilizing free fatty acids (FFAs).
Acetoacetate Regulates Plasma Lipoprotein Lipase Activity via Adipose GPR43.
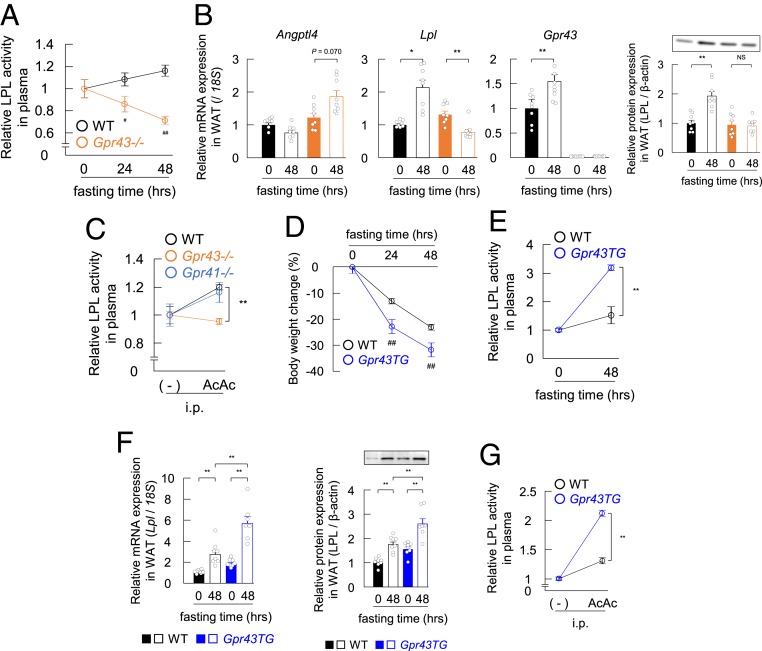
We previously reported that GPR43 regulates lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity (18). These results suggested that the TG-to-FFA conversion in the plasma of Gpr43−/− mice did not occur during fasting. Therefore, we investigated LPL activity in the plasma of Gpr43−/− mice during fasting. Under fasting conditions, although decreases in plasma insulin and increases in plasma appetite-related gastric hormone ghrelin were similar in the Gpr43−/− mice and wild-type mice after 48 h of starvation (SI Appendix, Fig. S3 A and B), LPL activity was markedly decreased in the plasma of the Gpr43−/− mice during fasting (Fig. 3A). These results indicate that GPR43 is stimulated possibly by acetoacetate under fasting conditions, thereby accelerating lipolysis by activating plasma LPL activity.
Fig. 3.
Adipose GPR43 influences plasma LPL activity. (A) Plasma LPL activity was measured after 0, 24, and 48 h of fasting (n = 8 to 12). LPL activity is expressed as relative to the LPL levels in nonfasting mice. (B) Effects of fasting on the expression of Angptl4, Lpl, and Gpr43 genes and LPL protein in WAT of wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice (n = 8). (C) Plasma LPL activity was measured in wild-type, Gpr43−/−, and Gpr41−/− mice at 20 min after treatment with acetoacetate (500 mg/kg i.p.; n = 8). LPL activity is expressed as relative to the LPL levels of nontreated mice. (D) Mice with adipose tissue-specific GPR43 overexpression (adipose Gpr43TG mice) were fasted for 0, 24, and 48 h, and body weight changes were monitored (n = 8). (E) Plasma LPL activity was measured after 0 and 48 h of fasting (n = 7 or 8). LPL activity was expressed as relative to the LPL levels of nonfasting mice. (F) Effects of fasting on the Lpl gene (Left) and LPL protein (Right) expression in WAT of wild-type and adipose Gpr43TG mice (n = 7 or 8). (G) Plasma LPL activity was measured in wild-type and adipose Gpr43TG mice at 20 min after treatment with acetoacetate (500 mg/kg i.p.; n = 8). LPL activity was expressed as relative to the LPL levels of nontreated mice. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, Tukey-Kramer test. ##P < 0.01 compared with wild-type mice, Student’s t test. AcAc, acetoacetate, NS, not significant. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
In addition, Gpr43 mRNA was abundantly expressed in adipose tissues but not in muscle tissue and liver (18). Therefore, we examined direct changes in Lpl mRNA levels in several LPL-related tissues under fasting conditions. As expected, Lpl mRNA and protein levels in the white adipose tissue (WAT) were increased in the wild-type mice but decreased in the Gpr43−/− mice during fasting (Fig. 3B), although these effects were not observed in non–Gpr43-expressing tissues, such as muscle (SI Appendix, Fig. S3C). However, hepatic Lpl mRNA and protein levels were also increased in the wild-type mice but unchanged in the Gpr43−/− mice (SI Appendix, Fig. S3D).
Interestingly, the Gpr43 mRNA level was markedly increased in the liver at 48 h after starvation (SI Appendix, Fig. S3D), whereas opposite trends were observed in the expression of angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4), an LPL activity-suppressing factor, in the WAT and liver of both the Gpr43−/− and wild-type mice (Fig. 3B, and SI Appendix, Fig. S3D). In these tissues, mRNA levels of Gpr41, another SCFA receptor, were comparable in the 2 groups of mice (SI Appendix, Fig. S3E). These results suggest that under fasting conditions, adipose and liver GPR43 might influence systemic LPL activation.
We next investigated whether acetoacetate directly decreases plasma TG levels via GPR43-mediated LPL activation. Intraperitoneal administration of acetoacetate significantly increased plasma LPL activity in both the Gpr43−/− and wild-type mice, whereas acetoacetate influenced LPL activity to a lesser extent in the Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 3C). In addition, the effect of lithium acetoacetate was not exerted by lithium α-hydroxybutyrate (SI Appendix, Fig. S3F). Moreover, a 250 mg/kg dose of acetoacetate, which is close to physiological concentrations under fasting conditions (SI Appendix, Fig. S3G), and the i.p. administration of acetoacetate significantly increased plasma LPL activity in the wild-type mice but abolished this activity in the Gpr43−/− mice (SI Appendix, Fig. S3H).
To clarify whether the systemic action of plasma LPL activity depends on adipose GPR43, we performed experiments in adipose-specific Gpr43-overexpressing mice (adipose Gpr43TG mice) (18). The decrease in body weight was markedly higher in the adipose Gpr43TG mice compared with the wild-type mice during fasting (Fig. 3D), and plasma LPL activity was significantly elevated in the adipose Gpr43TG mice was (Fig. 3E). Among the 3 tissues, only WAT showed significantly increased Lpl mRNA and protein levels in the adipose Gpr43TG mice compared with the wild-type mice (Fig. 3F and SI Appendix, Fig. S4 A and B).
We then administered acetoacetate to adipose Gpr43TG mice to identify the contribution of WAT to plasma LPL activity. The results show that increases in plasma LPL activities via acetoacetate administration were markedly higher in the adipose Gpr43TG mice compared with the wild-type mice (Fig. 3G). These results demonstrate that acetoacetate regulates lipid metabolism by controlling the activation of LPL via adipose GPR43.
Intestinal SCFA-GPR43 Signaling Is Suppressed by Fasting.
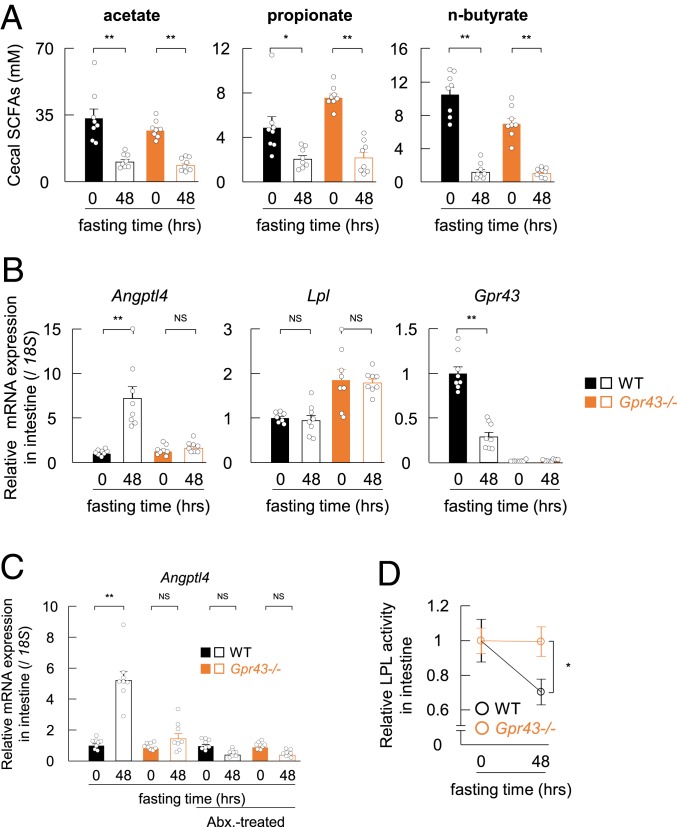
Concomitantly, we investigated the influence of SCFA-GPR43 signaling on the intestinal environment under ketogenic conditions based on SCFAs being potent GPR43 ligands and highly abundant in the intestinal tract (19). In addition to plasma SCFA concentrations, cecal SCFA concentrations were dramatically decreased after 48 h of starvation (Fig. 4A). Because SCFAs are mainly derived from gut microbial fermentation (19), we then examined cecal gut microbiota composition under fasting conditions. The total bacterial abundance decreased significantly in both the wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice after 48 h of fasting (SI Appendix, Fig. S5A).
Fig. 4.
Gut microbial metabolites and GPR43 regulate the intestinal Angptl4-LPL axis in fasted mice. (A) Mice were fasted and assessed for cecal SCFA levels at 0 and 48 h (n = 8). (B) mRNA expression of Angptl4, Lpl, and Gpr43 in the small intestines of wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice (n = 8). (C) Wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice were treated with antibiotics in drinking water for 1 wk, followed by fasting for 48 h. Shown is the mRNA expression of Angptl4 in small intestines of wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice with or without antibiotic treatment (n = 8). (D) Intestinal LPL activity was measured in fasted-mice (n = 8). LPL activity is expressed as relative to the LPL levels of nonfasting mice. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, Tukey–Kramer test. Abx, antibiotics, NS, not significant. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing, we confirmed that fasting significantly altered the relative abundance of the major phyla that constitute the gut microbiota (SI Appendix, Fig. S5B). Specifically, during fasting, the abundances of Firmicutes and Actinobacteria were markedly decreased, whereas the abundance of Bacteroidetes was slightly elevated in both the wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice. Interestingly, fasting induced dramatic expansion of Verrucomicrobia, and we confirmed that fasting similarly altered gut microbiota composition in both the wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice, as indicated by principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on taxonomic datasets (SI Appendix, Fig. S5C). These results indicate that changes in gut microbiota composition due to a lack of fermentation substrates under fasting conditions dramatically decreased intestinal SCFA concentration.
In addition to the decreases in intestinal SCFA concentration, Gpr43 mRNA levels decreased dramatically in the small intestine after 48 h of fasting (Fig. 4B). This was followed by a marked increase in Angptl4 mRNA levels in the small intestines of the wild-type mice but not of the Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 4B), whereas colonic expression of Angptl4 was similar in the 2 groups of mice (SI Appendix, Fig. S5D). Moreover, levels of the gut hormones GLP-1 and PYY were similar in the wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice after 48 h of starvation (SI Appendix, Fig. S5 E and F). In addition, elimination of gut microbiota by antibiotic treatment dramatically decreased SCFA levels in the cecum (SI Appendix, Fig. S5 G and H), although antibiotic treatment did not increase Angptl4 mRNA levels in the wild-type mice after 48 h of starvation (Fig. 4C). Furthermore, LPL activity was decreased in the small intestine during fasting in the wild-type mice but was unchanged in the Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 4D). These findings demonstrate that decreased levels of SCFAs and GPR43 induce Angptl4 expression in the intestine under fasting conditions, during which LPL activity and intestinal metabolic activity are suppressed.
Acetoacetate Regulates Lipid Metabolism via GPR43 under Eucaloric Ketogenic Diet Conditions.
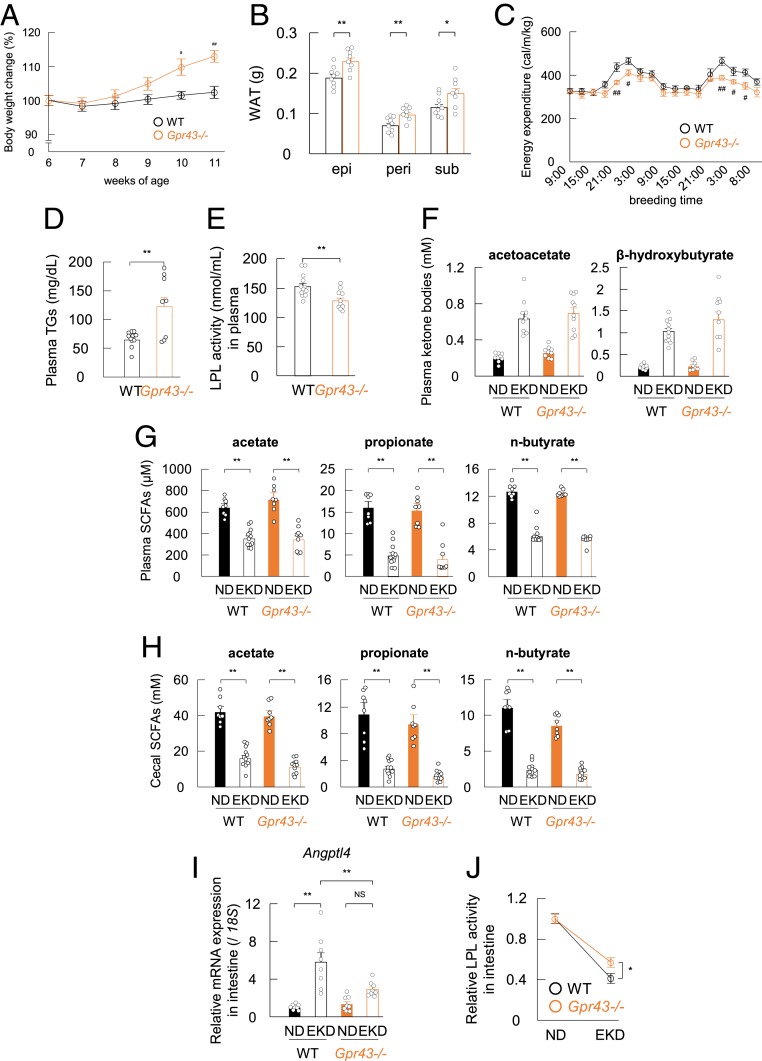
We then investigated the metabolic effects of acetoacetate-GPR43 activation under ketogenic conditions other than fasting. A ketogenic diet is associated with markedly increased levels of ketone bodies (20). A eucaloric ketogenic diet (EKD) composed predominantly of fat with very small amounts of carbohydrates (SI Appendix, Table S1) can provide adequate caloric support while minimizing spikes in blood glucose and is used clinically (21–23). Although the body weight of EKD-fed wild-type mice remained constant, that of Gpr43−/− mice increased significantly (Fig. 5A), and the weight of adipose tissues was also significantly higher in the Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 5B), although the energy expenditure under an EKD was significantly lower in these mice (Fig. 5C). In addition, although levels of plasma insulin and glucose were similar in the 2 groups (SI Appendix, Fig. S6 A and B), plasma TG levels were significantly higher (Fig. 5D), and LPL activity was significantly lower in the Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 5E). Nevertheless, the EKD showed similar effects on the plasma levels of ketone bodies in the 2 groups (Fig. 5F).
Fig. 5.
Acetoacetate regulates lipid metabolism via GPR43 during EKD feeding. Wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice were fed an EKD for 6 wk. (A–F) Body weight change (A), fat mass (B), energy expenditure (C), plasma TG levels (D), plasma LPL activity (E), and plasma acetoacetate (F, Left) and β-hydroxybutyrate (F, Right) levels were determined after EKD feeding (n = 8 to 12). (G and H) At 6 wk after feeding, SCFA levels were measured in plasma (G) and cecum (H) (n = 8 to 12). (I) mRNA expression of Angptl4 in the small intestines of wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice (n = 8). (J) Intestinal LPL activity was measured in EKD-fed mice (n = 10 to 12). LPL activity is expressed as relative to the LPL levels of normal diet (ND)-fed mice. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. ##P < 0.01; #P < 0.05 compared with wild-type mice, Student’s t test. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Plasma and cecal SCFA concentrations were also dramatically decreased under an EKD (Fig. 5 G and H). Because an EKD changes gut microbial diversity (24), we further examined the cecal microbiota composition under an EKD. Using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing, we confirmed that the EKD substantially altered the relative abundance of the major phyla constituting the gut microbiota (SI Appendix, Fig. S6C). Specifically, with an EKD, the abundance of Proteobacteria markedly increased, whereas that of Bacteroidetes decreased in both the wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice. In addition, we confirmed that the EKD altered the gut microbiota composition in both wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice, as indicated by PCoA based on taxonomic datasets (SI Appendix, Fig. S6D). Therefore, changes in gut microbiota composition induced by the low-carbohydrate and high-fat EKD dramatically decreased intestinal SCFA concentration. Furthermore, the increase in Angptl4 mRNA levels and decrease in LPL activity in the small intestine were greater in the wild-type mice compared with the Gpr43−/− mice under an EKD (Fig. 5 I and J). These results suggest that the EKD and fasting conditions led to changes in systemic lipid metabolism.
GPR43 Regulates Lipid Metabolism under Intermittent Fasting.
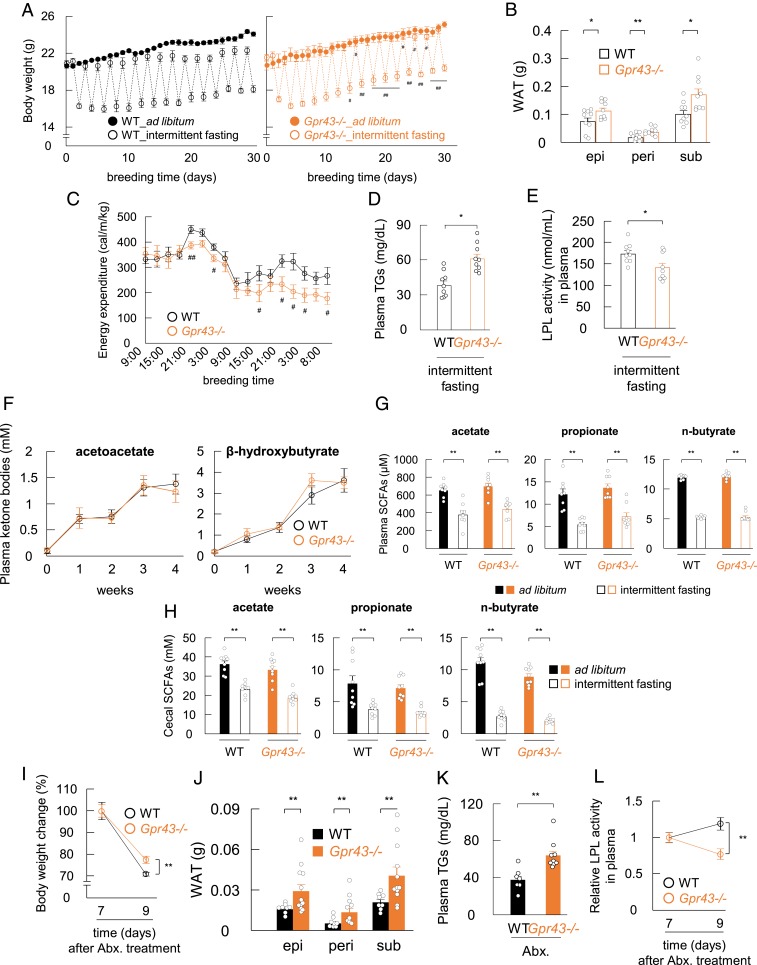
We next examined acetoacetate-GPR43 energy metabolism under intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting is an effective and natural strategy for weight management (25, 26), but the underlying mechanism is poorly understood. Previous studies have indicated that ketone bodies might contribute to the efficacy of intermittent fasting for weight loss (25, 26). Interestingly, reduced body weight was not observed in the Gpr43−/− mice during intermittent fasting (Fig. 6A), and the adipose tissue weight was significantly higher in the Gpr43−/− mice compared with the wild-type mice (Fig. 6B). Moreover, energy expenditure was significantly lower in the Gpr43−/− mice compared with the wild-type mice (Fig. 6C). Although decreases in plasma insulin were similar in the 2 groups (SI Appendix, Fig. S7A), plasma TG levels were significantly higher (Fig. 6D) and LPL activity was significantly lower in the Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 6E). Furthermore, plasma ketone body, SCFA, and cecal SCFA levels were similar in the 2 groups under intermittent fasting conditions (Fig. 6 F–H).
Fig. 6.
LPL activity is regulated by GPR43 signaling under ketogenic conditions. (A) Body weight change was measured during the intermittent fasting (n = 9). (B–E) Fat mass (B), energy expenditure (C), plasma TG levels (D), and LPL activity (E) were analyzed under refed conditions after intermittent fasting (n = 8 or 9). (F–H) Plasma acetoacetate (F, Left), plasma β-hydroxybutyrate (F, Right), and SCFAs in plasma (G) and cecum (H) were measured under refed conditions after intermittent fasting (n = 8 or 9). (I–L) Wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice were treated with antibiotics in drinking water for 1 wk and then fasted for 48 h. Body weight change (I) and fat mass (J) were measured in antibiotic-treated and fasted mice (n = 8 to 12), and plasma TG levels (K) and LPL activity (L) were analyzed (n = 7 to 9). LPL activity is expressed as relative to the LPL levels of antibiotic-treated and nonfasted mice. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. ##P < 0.01; #P < 0.05 compared with intermittent fasting of wild-type mice, Student’s t test. Abx, antibiotics. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Finally, we examined the effect of antibiotic treatment on metabolic parameters under fasting conditions, because GPR43 is also activated by SCFAs produced by gut microbial fermentation of dietary fiber (1). Although the plasma acetate levels were markedly decreased by antibiotic treatment during fasting (SI Appendix, Fig. S7B), the body weight reduction was significantly lower in the Gpr43−/− mice compared with the wild-type mice (Fig. 6I), and adipose tissue weight was significantly higher in the Gpr43−/− mice (Fig. 6J). Although decreases in plasma insulin concentration were similar in the 2 groups (SI Appendix, Fig. S7C), plasma TG levels were significantly higher (Fig. 6K) and LPL activity was significantly lower (Fig. 6L) in the Gpr43−/− mice under fasting conditions with antibiotic treatment, although the between-group differences were less significant relative to those observed under conventional conditions (Figs. 2G and 3A). Furthermore, plasma ketone body levels were significantly increased under fasting conditions with antibiotic treatment (SI Appendix, Fig. S7D). Collectively, these results indicate that acetoacetate, rather than SCFAs, modulates metabolism via GPR43 under ketogenic conditions.
Discussion
The ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate acts as a signaling molecule via GPR109A and GPR41 in addition to functioning as an energy source (2, 7, 8). However, the specific receptors and function of acetoacetate, another ketone body, remain unclear. The findings in this study suggest that acetoacetate functions as an endogenous agonist for GPR43 with affinity similar to that of acetate and propionate under ketogenic conditions, such as fasting and a low-carbohydrate diet. Acetoacetate-GPR43 signaling promoted lipid utilization in the plasma via lipolysis by plasma LPL activation, because adipose LPL production was increased under ketogenic conditions (SI Appendix, Fig. S8).
Our results show that during fasting, the total plasma ketone body concentration was markedly increased (from 0.3 to 4 mM) and total plasma SCFA concentration was considerably decreased (from 0.5 to 0.1 mM). This indicates that the primary ligand for GPR43 switches from SCFAs to ketone bodies in the plasma under fasting conditions. Furthermore, the total cecal SCFA concentration also decreased markedly (from 50 mM to 10 mM) due to changes in gut microbiota composition and a lack of fermentation substrates during fasting. However, compared with acetoacetate, SCFAs (10 mM) remained the primary ligands for GPR43 in the intestinal tract even under fasting condition. Therefore, intestinal LPL activity might be inhibited by suppression of SCFA-GPR43 signaling. Fasting is thus characterized by an independent biphasic change (i.e., ketone body-dependent GPR43 regulation in the whole body and SCFA-dependent GPR43 regulation in the intestinal tract), which promotes LPL activity in the body and suppresses intestinal LPL activity. These effects might increase the efficiency of systemic energy utilization by lipolysis and decrease intestinal energy utilization by inhibiting intestinal lipolysis during fasting.
We observed that acetoacetate-induced GPR43 activation regulates systemic LPL activity in the plasma and also might be involved in peripheral LPL activity and Angptl4 expression. GPR43 is also expressed in various tissues, including the gastrointestinal tract (27, 28) and is involved in modulating host energy homeostasis (29). Although in the present study, plasma GLP-1, PYY, and ghrelin concentrations were comparable in the wild-type and Gpr43−/− mice under fasting conditions, acetate-GPR43 signaling via other tissues and LPL-independent mechanisms might be involved in energy metabolism under ketogenic conditions. Further studies are needed to clarify the relationship between intestinal Angptl4 level and GPR43.
Ketone bodies play important roles in such brain functions as neuroprotection and energy metabolism (6). In addition, GPR109A and GPR41 act as ketone body receptors activated by β-hydroxybutyrate. GPR109A exhibits neuroprotective effects via anti-inflammatory responses in a stroke model and Parkinson’s disease models via β-hydroxybutyrate or a ketogenic diet (8, 30), and GPR109A levels increase in the brain under a ketogenic diet and in Parkinson’s disease (31, 32). Moreover, GPR41 activates sympathetic neurons via β-hydroxybutyrate or under fasting conditions (2) and promotes metabolic benefits through gut-brain neural circuits via gut microbial SCFAs (33). Although GPR43 is expressed at low levels in the brain, it is related to the maturation of microglia (1, 34), and a previous study reported that gut microbial SCFAs regulate neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease (35).
Interestingly, we found that Gpr43 mRNA levels in the brain decreased significantly under 3 ketogenic conditions and especially in response to a ketogenic diet (SI Appendix, Fig. S9). This finding might indicate that acetoacetate-GPR43 signaling is also related to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease and stroke, in addition to metabolic disorders, and that increased understanding of the associated mechanism might provide insight into therapeutic strategies for these disorders.
We have demonstrated that the ketone body acetoacetate, rather than SCFAs, maintains energy homeostasis by regulating metabolic parameters through GPR43-mediated lipid metabolism under ketogenic conditions. These findings might represent a central mechanism underlying the effects of ketone bodies as nutritional signaling molecules on systemic homeostasis. In addition, our results suggest that the efficacy of intermittent fasting and a ketogenic diet for body weight control depends on acetoacetate-GPR43 activation. Therefore, our results might contribute to the development of preventive and predictive medicine via diet and foods.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture, animal studies, immunoblotting, ketone body measurement, SCFA measurement, biochemical analyses, RNA isolation and real-time qRT-PCR, adipocyte culture, gut microbiota composition in cecum, and the statistical analysis for this study are described in detail in SI Appendix, Materials and Methods. The composition of diets for animal study and the sequences of primers for qRT-PCR are provided in SI Appendix, Tables S1 and S2.
Data Availability.
All other data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its Supplementary Information files or are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Mai Arita and Shizuka Kasuga for the in vitro assay, members of the Nisshin Oillio Collaboratory for valuable discussions, and Dr. Masafumi Fujimoto for advice on the kinetic-binding assay. This work was supported in part by research grants from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (KAKENHI Grants JP15H05344, JP16H01355, and JP18K19731, to I.K. and JP18K17920, to J.M.), the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (Grant JP17gm1010007, to I.K.), the Lotte Foundation (to I.K.), the Institute for Fermentation Osaka (to I.K.), the Food Science Institute Foundation (to I.K.), the Smoking Research Foundation (to I.K.), and the Uehara Memorial Foundation (to I.K.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
Data deposition: 16S rRNA sequence data have been deposited into the DNA Data Bank of Japan under accession nos. DRA007272 (fasting) and DRA007271 (eucaloric ketogenic diet).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1912573116/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Kimura I., Ichimura A., Ohue-Kitano R., Igarashi M., Free fatty acid receptors in health and disease. Physiol. Rev., 10.1152/physrev.00041.2018 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kimura I., et al. , Short-chain fatty acids and ketones directly regulate sympathetic nervous system via G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 8030–8035 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wolever T. M., Brighenti F., Royall D., Jenkins A. L., Jenkins D. J., Effect of rectal infusion of short-chain fatty acids in human subjects. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 84, 1027–1033 (1989). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roberts M. N., et al. , A ketogenic diet extends longevity and healthspan in adult mice. Cell Metab. 26, 539–546.e5 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rui L., Energy metabolism in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 4, 177–197 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Puchalska P., Crawford P. A., Multi-dimensional roles of ketone bodies in fuel metabolism, signaling, and therapeutics. Cell Metab. 25, 262–284 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Offermanns S., Hydroxy-carboxylic acid receptor actions in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 28, 227–236 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rahman M., et al. , The β-hydroxybutyrate receptor HCA2 activates a neuroprotective subset of macrophages. Nat. Commun. 5, 3944 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gille A., Bodor E. T., Ahmed K., Offermanns S., Nicotinic acid: Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 48, 79–106 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Benyó Z., et al. , GPR109A (PUMA-G/HM74A) mediates nicotinic acid-induced flushing. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 3634–3640 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Offermanns S., The nicotinic acid receptor GPR109A (HM74A or PUMA-G) as a new therapeutic target. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 27, 384–390 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brown A. J., et al. , The Orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11312–11319 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Samuel B. S., et al. , Effects of the gut microbiota on host adiposity are modulated by the short-chain fatty-acid binding G protein-coupled receptor, Gpr41. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 16767–16772 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xiong Y., et al. , Short-chain fatty acids stimulate leptin production in adipocytes through the G protein-coupled receptor GPR41. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 1045–1050 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Le Poul E., et al. , Functional characterization of human receptors for short-chain fatty acids and their role in polymorphonuclear cell activation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 25481–25489 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stoddart L. A., Smith N. J., Jenkins L., Brown A. J., Milligan G., Conserved polar residues in transmembrane domains V, VI, and VII of free fatty acid receptor 2 and free fatty acid receptor 3 are required for the binding and function of short-chain fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 32913–32924 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Canfora E. E., Jocken J. W., Blaak E. E., Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11, 577–591 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kimura I., et al. , The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat. Commun. 4, 1829 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sonnenburg J. L., Bäckhed F., Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 535, 56–64 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nandivada P., et al. , Eucaloric ketogenic diet reduces hypoglycemia and inflammation in mice with endotoxemia. Lipids 51, 703–714 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Martin-McGill K. J., Jackson C. F., Bresnahan R., Levy R. G., Cooper P. N., Ketogenic diets for drug-resistant epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 11, CD001903 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.McSwiney F. T., Doyle L., Low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets in male endurance athletes demonstrate different micronutrient contents and changes in corpuscular haemoglobin over 12 weeks. Sports (Basel) 7, E201 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McSwiney F. T., et al. , Keto-adaptation enhances exercise performance and body composition responses to training in endurance athletes. Metabolism 81, 25–34 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Olson C. A., et al. , The gut microbiota mediates the anti-seizure effects of the ketogenic diet. Cell 173, 1728–1741.e13 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kim K. H., et al. , Intermittent fasting promotes adipose thermogenesis and metabolic homeostasis via VEGF-mediated alternative activation of macrophage. Cell Res. 27, 1309–1326 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li G., et al. , Intermittent fasting promotes white adipose browning and decreases obesity by shaping the gut microbiota. Cell Metab. 26, 672–685.e4 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maslowski K. M., et al. , Regulation of inflammatory responses by gut microbiota and chemoattractant receptor GPR43. Nature 461, 1282–1286 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tolhurst G., et al. , Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 61, 364–371 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gancheva S., Jelenik T., Álvarez-Hernández E., Roden M., Interorgan metabolic crosstalk in human insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 98, 1371–1415 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fu S. P., et al. , Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms. J. Neuroinflammation 12, 9 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hasan-Olive M. M., et al. , A ketogenic diet improves mitochondrial biogenesis and bioenergetics via the PGC1α-SIRT3-UCP2 axis. Neurochem. Res. 44, 22–37 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wakade C., Chong R., Bradley E., Thomas B., Morgan J., Upregulation of GPR109A in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 9, e109818 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.De Vadder F., et al. , Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 156, 84–96 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Erny D., et al. , Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 965–977 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sampson T. R., et al. , Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167, 1469–1480.e12 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All other data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its Supplementary Information files or are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.