Abstract
Background:
An outbreak of the rare and highly pathogenic Nipah virus infection occurred in Kozhikode, Kerala, India, during May 2018.
Methodology:
Outbreak control activities included laboratory case confirmation and isolation. Contact surveillance was initiated and close contacts were home quarantined for the maximum incubation period of the disease. Field visits and verbal autopsy of the deaths were done to elicit the details of exposure.
Results:
Of the 18 confirmed cases, 16 succumbed (case fatality rate, 88.8%). The mean incubation period was 9 days. The transmission was person to person wherein the primary case served as a point source for 15 other cases including 2 health-care workers. The mean age of the affected cases was 41 years with male preponderance. More than 2600 contacts were under surveillance. The outbreak was contained within 3 weeks and declared closed by July the same year.
Conclusion:
Early detection of the outbreak and prompt isolation of cases along with strengthening of infection control practices and barrier nursing helped in containing the outbreak.
Keywords: Acute encephalitis, henipavirus, Kozhikode, Nipah virus outbreaks
INTRODUCTION
Nipah virus infection (NiV) is an emerging highly pathogenic zoonotic disease, outbreaks of which have been reported from South East Asian countries. The virus belongs to the genus Henipavirus and subfamily Paramyxoviridae.[1] The natural reservoirs of the virus are fruit bats of the genus Pteropus, and the virus has been isolated from bat urine and partially eaten fruits in Malaysia.[2] Human infection begins with fever and brain inflammation leading to disorientation or coma.[3] Some patients present with acute respiratory distress syndrome and mortality ranges from 40% to 70%.[1] Laboratory confirmation is done by serum neutralization, ELISA, or reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests. NiV is classified as a Biosafety level 4 agent, and most countries in South East Asia lack diagnostic facilities. Intensive supportive care forms the mainstay of treatment and ribavirin may provide symptomatic relief.[4] As a specific vaccine is unavailable, robust surveillance system for early case detection and prompt control measures is the only way to prevent human transmission.
Outbreaks of NiV have been reported from Malaysia, Singapore, Bangladesh, and India. Direct contact with infected pigs was the mode of transmission in the first outbreak in Malaysia (1999). The outbreaks in Bangladesh and India were linked to consumption of fresh date palm sap contaminated by fruit bats.[5,6] The first evidence of human-to-human transmission was seen in Siliguri, West Bengal, India (2001) where hospital visitors and health workers contracted the infection after exposure to patients, indicating transmission in health-care setting.[5] Human-to-human spread was also documented in Bangladesh (2004).[7,8,9]
The outbreak which occurred in the Southern state of Kerala, India, in May 2018, was the third NiV outbreak in India, the first two being in Siliguri and Nadia, West Bengal (2007). Eighteen confirmed cases were reported from the districts of Kozhikode and Malappuram with high mortality and person-to-person transmission. Here, we describe the epidemiology of this outbreak which posed a unique challenge to the health system.
METHODOLOGY
Our hospital is a tertiary care public center in Kozhikode, North Kerala, catering to five districts with enormous case load. Twelve confirmed cases, the primary case, and four probable cases were admitted in this institution (Hospital A) also designated as the dedicated isolation facility for the treatment of NiV cases. Our team was actively involved in outbreak response, surveillance, and data management and was part of the Nipah task force at institutional and district level. Triaging as per case definition [Table 1] and reporting of cases was a daily activity. Contact surveillance for early detection and case isolation was initiated in liaison with the district team.
Table 1.
Case definition of Nipah virus infection*
| Case | Definition |
|---|---|
| Suspected NiV infection | Person from an area/locality affected by NiV outbreak who has Acute fever with new onset of altered mental status or seizure and/or Acute fever with severe headache and/or Acute fever with cough or shortness of breath |
| Probable NiV infection | Suspected case - patients/s who resided in the same village where suspected/confirmed case of NiV infection were living during the outbreak period and who died before complete diagnostic specimens could be collected Suspected case who came in direct contact with confirmed case in a hospital setting during the outbreak period and who died before complete diagnostic specimens could be collected |
| Confirmed NiV infection | Suspected case who has laboratory confirmation of NiV infection either by NiV RNA identified by PCR from respiratory secretions, blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid Isolation of NiV from respiratory secretions , blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid |
*Adapted from NCDC interim guidelines 2018. NiV: Nipah virus, PCR: Polymerase chain reaction, NCDC: National Centre for Disease Control
Case confirmation
Confirmation of NiV infection was by detecting viral RNA by RT-PCR in samples of blood, urine, and throat swabs at Manipal Center for Virus Research (MCVR). Case management was by the medical teams with intensive supportive therapy.
Contact surveillance
Case-based contact tracing and daily surveillance was done by telecommunication, and they were home quarantined for 21 days.
Field visits to the homes of the cases and verbal autopsy were conducted. Interactions with the community, health centers, and animal husbandry helped identify the possible source of infection.
To search for missed cases, auditing of similar deaths at our institution from 3 months before the outbreak was done.
National health agencies (National Centre for Disease Control, National Institute of Virology [NIV], and National Institute of Epidemiology) provided technical support for outbreak containment. Barrier nursing and infection control practices were strengthened, training on use of personal protective equipment fast tracked and protocol for the management of dead bodies complied with.
Surveillance activities continued for twice the maximum incubation period (42 days) after the last case.
RESULTS
In all 147 suspects as per Case definition [Table 1] were admitted in Hospital A from May 5 to May 31, 2018. Of the 18 confirmed cases, 12 were managed in our institution. Initial confirmation of NiV outbreak was done at the NIV, Pune. Of the 18 confirmed cases, 16 succumbed to their illness, and the case fatality rate (CFR) was 88.8%. The last case expired on May 31, 3 weeks after the outbreak began, but surveillance continued and the outbreak was officially declared closed in mid-July 2018.
Case linkages: Index case
The first case noticed by the system and confirmed as a Nipah case (virologically and by postmortem) was a 27-year-old male (Case 1) managed at a private facility from May 17, for fever, altered sensorium, and respiratory distress and expired on May 18.
Primary case
The index case was linked to the primary case – a 26-year-old male (Case 0) who was his sibling. Case 0 had been referred to Hospital A on May 5, from a peripheral government facility (Hospital B) where he was on treatment for 3 days with similar symptoms. He expired on the same day and was reported in routine surveillance as a case of encephalitis.
Cases in the first set
Further 15 cases in the first generation of the outbreak were linked to Case 0 [Figure 1]. All were admitted in various hospitals between 17th and 29th May. Three clusters of infection could be identified based on the exposure linkages identified by the team: one family cluster, where the family members were exposed to the primary case during caregiving and two hospital clusters – one at Hospital B where the primary case had been admitted for 1 day and one at Hospital A [Figure 1]. All these cases were exposed to the primary case during his stay at the concerned hospitals.
Figure 1.
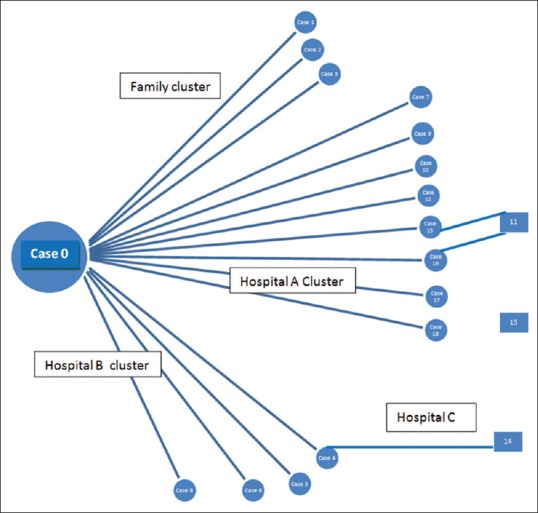
Transmission of Nipah virus infection (confirmed cases) 2018
Family cluster – The index case (Case 1) was linked to 2 more cases. Case 2, a 53-year-old female, related to Case 0 and was a hospital visitor at Hospital B when Case 0 was admitted there. Case 3, a 59-year-old male, was also a family contact and caregiver for Case 0 when he was admitted in hospital. These three cases constitute the family cluster. This clustering of cases from a single family in the affected village within a short span of 12 days resulted in the treating physicians at the private facility to have a high index of suspicion of a serious communicable disease outbreak. NiV infection was confirmed by virologic study at MCVR
Hospital A cluster – Eight NiV cases were exposed to the primary case at Hospital A on May 5. Two were patients (Case 17 and 18), one was a health-care worker (Case 7), and the rest were hospital visitors (Cases 9, 10, 12, 15, and 16). Case 7 and Case 18 survived
Hospital B cluster – Four cases were exposed to the primary case at Hospital B where he was treated before referral to Hospital A. One was a health-care worker (Case 5) and the rest were hospital visitors/caregivers to patients in the Hospital B (Cases 4, 6, and 8).
Cases in the second set
Three confirmed cases were noted in the second generation. Two were exposed from Hospital A (Case 11 and 13) whereas Case 14 was exposed at Hospital C when Case 4 was admitted there before being hospitalized at Hospital B.
Epidemiology
The Kozhikode outbreak was identified as a person-to-person propagated outbreak. Hospital transmission was noted at three hospitals and two health-care workers were affected. The second generation had only three cases. Of the 18 confirmed cases of NiV infection, 14 were from Kozhikode district and 4 were from the neighboring district of Malappuram but exposed from Hospital A (at Kozhikode). The mean age of cases was 41 years (±15.9) (range, 19–75 years) with male predominance (61.1%). The outbreak peaked from 12th to 18th May 2018 [Figure 2] with a mean incubation period of 9.3 days (±1.9) (range, 6–14 days). Only two survived (CFR: 88.8%). Clinical features in most cases included signs of acute encephalitis, fever, headache, altered sensorium, seizures, and vomiting. A proportion of the cases also had severe respiratory symptoms whereas a few cases reported with diarrhea. Average duration of hospital stay for the deceased was 3.4 days (range, 1–9 days) and for the two survivors was 23 days.
Figure 2.
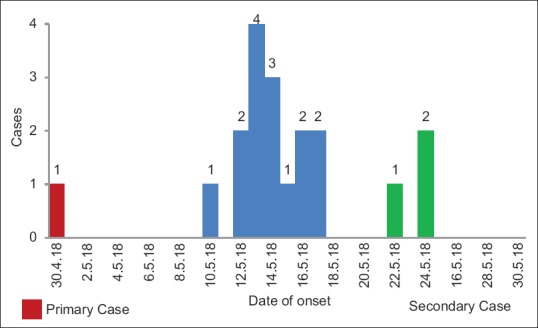
Epidemic curve of Nipah virus outbreak (confirmed cases)
Missed cases
Assuming the possibility of undiagnosed NiV cases, detailed audit of similar deaths 3 months before the outbreak was done at Hospital A. Of the total deaths line-listed, 15 had symptoms of fever, altered sensorium, and respiratory distress. Four deaths were clinically presumed probable of NiV infection as per case definition and could have had exposure to the primary case at Hospital A. As all these cases expired before confirmation of the outbreak, laboratory confirmation for NiV was not done. However, their contacts were put under surveillance as enhanced vigilance.
Source of infection and transmission
Fruit bats are known reservoirs of NiV infection. While the exact mode of transmission from bats to the primary case is unclear, further exploration revealed that exposure may have occurred either in the process of cleaning of a bat infested unused well or during visits to the nearby forest. Fruit bats were mapped in the area and specimen studies for virus confirmed from captured bats by animal husbandry and National agencies. However, further transmission of NiV infection from the primary case was human to human [Table 2]. No other animal hosts was evident and no new local transmission was noted from the village of the primary case or in other villages.
Table 2.
Details of source of infection of Nipah cases
| Case | Age | Sex | Date of onset of symptom | Contact/exposure history |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 0 (Primary Case, Probable Case) | 26 | Male | April 30, 2018 | Probable source of infection could be from the forest during trekking or eating fruits bitten by bats or from bats from unused well Treated at Hospital B on 3rd and 4th of May and refereed to Hospital A on 5th of May |
| Confirmed Cases | ||||
| Case 1 - index case | 27 | Male | May 13, 2018 | Family caregiver and sibling of Case 0 in hospital Household contact |
| Case 2 | 53 | Female | May 14, 2018 | Aunt of Case 0 who visited him at Hospital B and hugged and kissed him |
| Case 3 | 59 | Male | May 13, 2018 | Family contact (father) of Case 0 Caregiver at Hospital B and A |
| Case 4 | 49 | Male | May 12, 2018 | Inpatient at Hospital B where Case 0 was admitted |
| Case 5 | 32 | Female | May 15, 2018 | Health-care staff on duty at Hospital B when Case 0 was admitted |
| Case 6 | 48 | Female | May 16, 2018 | Hospital visitor at Hospital B when Case 0 was admitted |
| Case 7 | 19 | Female | May 13, 2018 | Health-care worker on duty at Hospital A when Case 0 was in emergency room of Hospital A |
| Case 8 | 45 | Male | May 13, 2018 | Admitted at Hospital B when Case 0 was admitted |
| Case 9 | 52 | Male | May 10, 2018 | Hospital visitor at Hospital A on 5th May - Contact with Case 0 on same day at diagnostic area |
| Case 10 | 27 | Male | May 14, 2018 | Hospital visitor at Hospital A on 5th May - Contact with Case 0 on same day at diagnostic area |
| Case 11 | 75 | Female | May 22, 2018 | Patient at Hospital A - Contact with Case 15 and 16 admitted in same area at Hospital A |
| Case 12 | 55 | Male | May 16, 2018 | Hospital visitor at Hospital A on 5th May. Contact with Case 0 at emergency room |
| Case 13 | 28 | Male | May 24, 2018 | Hospital visitor at Hospital A emergency room on May 14, 2018 - Possible contact with a missed case |
| Case 14 | 25 | Male | May 24, 2018 | Patient at Hospital C - Contact with Case 4 admitted in same ward |
| Case 15 | 32 | Female | May 14, 2018 | Hospital caregiver at Hospital A. Contact with Case 0 at radiology diagnostic area on 5th May |
| Case 16 | 23 | Female | May 12, 2018 | Hospital caregiver at Hospital A. Contact with Case 0 at radiology diagnostic area on 5th May |
| Case 17 | 48 | Male | May 17, 2018 | Hospital visitor at Hospital A on 5th May. Contact with Case 0 at emergency roo |
| Case 18 | 27 | Male | May 18, 2018 | Patient at Hospital A - Contact with case 0 on 5th May at diagnostic area |
Contact surveillance
Contact surveillance for confirmed and probable cases was carried out. More than 2600 contacts were followed up for 21 days each and put under home quarantine. Symptomatics were transported in dedicated ambulances to Hospital A where they were triaged as suspected/probable cases as per case definition and the samples were sent for the confirmation of diagnosis. Surveillance continued for 42 days till mid-July 2018.
DISCUSSION
A rare outbreak of NiV encephalitis occurred in Kozhikode district of Kerala during May 2018 with 18 confirmed cases and a primary case. The mode of transmission was person to person, similar to the outbreaks at Bangladesh and Siliguri. The NiV of this outbreak showed 97% similarity to Bangladesh lineage (NiV-BD).[10] Lower number of cases occurred when compared to the Siliguri (66 cases) and Bangladesh outbreak (44 cases),[11] but more cases when compared to other sporadic outbreaks in Bangladesh (3–16 cases) and Nadia (5 cases).[11] The seasonality also conforms to the fruit-bearing season of January–May in South India as seen in the Siliguri and Bangladesh outbreaks[6] corresponding to the breeding season of the Pteropus bats.[12]
The high CFR (88.8%) is slightly more than the outbreaks in Siliguri (68%)[5] and Bangladesh (77%).[12] Lower mortality in Malaysian outbreak (40%) has been attributed to the different strain of NiV.[3]
Epidemiological linkages showed person-to-person transmission and a single patient (Case 0) served as a point source for 15 confirmed cases. All the cases were infected from health-care settings in the late stages of illness. Even the family contacts may have been infected during the stay of Case 0 at Hospital B. Human propagation of the virus was first observed in Siliguri where hospital cases served as the source of infection for 33 health-care workers/visitors[5] and also documented in Bangladesh.[7,8,9]
Bats were mapped in the local area and 19% of the Pteropus giganteus specimens collected were reported as positive for NiV,[13] but other animal host were not identified. Drinking of raw date palm sap is not a custom in these parts of Kerala, but the primary case may have had bat exposure from the well or from the nearby forest. As there are no pig farms in the affected area, pig as an intermediate host is unlikely in this outbreak. Phylogenetic analysis at NIV, Pune, showed high similarity (99.7%–100%) between NiV sequences in P. giganteus and human NiV samples from Kerala.[14]
All cases in the current outbreak were adults with the youngest age being 19 years and males were more affected. The outbreak at Siliguri was also characterized by infection in those above 15 years[5] with a male: female ratio of 1.4:1.[5] Infection among children have been observed in Naogaon, Rajbari, and Meherpur in Bangladesh (range, 2–60 years).[15,16] Children were not affected in the Kozhikode outbreak possibly because contact of children with cases during the infectious phase might have been low. Transmission of the disease from the cases occurred during their stay in the hospital, indicating that transmission mainly occurs during the late stage of the disease when symptoms of encephalitis and respiratory distress are severe and droplet and contact secretions are highly infectious as has been observed in Siliguri.[17]
The average incubation period of this outbreak was 9 days similar to outbreaks in Bangladesh (9 days)[12] and Malayasia (10 days).[18]
Only two health-care workers were affected, one survived and both were exposed when the outbreak was still unrecognized unlike the Siliguri outbreak where the number of health-care workers affected were more.[5] Further cases were arrested as isolation of cases, and barrier nursing was intensified within 2 days of identification of the virus and the outbreak contained.
CONCLUSION
Person-to-person transmission is the key epidemiological feature of the outbreak which occurred in Kerala. Transmission occurred mainly in health-care settings and the mortality rate was high. The outbreak was contained by case isolation, early initiation of barrier nursing, infection control practices, contact surveillance, and home quarantine.
Recommendations
The range of the Pteropus bats extends from South East Asia to India.[19] Continued surveillance in these areas with diagnostic support is vital for early detection of NiV infection. Adherence to infection control practices is essential for curtailing nosocomial spread. Caregiver education on droplet and contact precautions can help in reducing transmission in the early stage of the outbreak. The WHO's current list of blueprint priority diseases includes eight dangerous pathogens including Nipah[20] and accelerated research and development is vital to improve preparedness and response against such public health emergencies.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge all members of the District Nipah task force. We are indebted to the Institutional Nipah group as well as the residents/staff of Community Medicine Department of GMC, Kozhikode.
REFERENCES
- 1.Fact Sheet Nipah Virus Infection. World Health Organisation, South East Asia Region. [Last accessed on 2018 May 25]. Available from: http://www.searo.who.int/entity/emerging_diseases/links/CDS_Nipah_ .
- 2.Chua KB, Koh CL, Hooi PS, Wee KF, Khong JH, Chua BH, et al. Isolation of nipah virus from Malaysian Island flying-foxes. Microbes Infect. 2002;4:145–51. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01522-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Goh KJ, Tan CT, Chew NK, Tan PS, Kamarulzaman A, Sarji SA, et al. Clinical features of nipah virus encephalitis among pig farmers in Malaysia. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1229–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200004273421701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chong HT, Kamarulzaman A, Tan CT, Goh KJ, Thayaparan T, Kunjapan SR, et al. Treatment of acute nipah encephalitis with ribavirin. Ann Neurol. 2001;49:810–3. doi: 10.1002/ana.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chadha MS, Comer JA, Lowe L, Rota PA, Rollin PE, Bellini WJ, et al. Nipah virus-associated encephalitis outbreak, Siliguri, India. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:235–40. doi: 10.3201/eid1202.051247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Luby SP, Rahman M, Hossain MJ, Blum LS, Husain MM, Gurley E, et al. Foodborne transmission of nipah virus, Bangladesh. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1888–94. doi: 10.3201/eid1212.060732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gurley ES, Montgomery JM, Hossain MJ, Bell M, Azad AK, Islam MR, et al. Person-to-person transmission of nipah virus in a Bangladeshi community. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1031–7. doi: 10.3201/eid1307.061128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Homaira N1, Rahman M, Hossain MJ, Epstein JH, Sultana R, Khan MS et al. Nipah virus outbreak with person-to-person transmission in a district of Bangladesh, 2007. Epidemiol Infect. 2007;1:1–7. doi: 10.1017/S0950268810000695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sazzad HM, Hossain MJ, Gurley ES, Ameen KM, Parveen S, Islam MS, et al. International Conference on Emerging Infectious Disease. Atlanta, USA: CDC; 2010. Nipah Outbreak and Health Care Worker Transmission in Bangladesh. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Arunkumar G, Abdulmajeed J, Aswathyraj S, Santhosha D, Shakir M, et al. International Conference on Emerging Infectious Diseases. Atlanta, USA: CDC; 2018. Outbreak of Nipah Virus in Kerala, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kulkarni DD, Tosh C, Venkatesh G, Senthil Kumar D. Nipah virus infection: Current scenario. Indian J Virol. 2013;24:398–408. doi: 10.1007/s13337-013-0171-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.National Guideline for Management, Prevention and Control of Nipah Virus Infection Including Encephalitis. Directorate General of Health Services Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. 1st ed. Dhaka: World Health Organisation Country Office Bangladesh; 2011. Dec, [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mourya D, Yadav P, Sudeep A, Gokhale M, Gangakhedkar R, Bhargava B. International Conference on Emerging Infectious Diseases. Atlanta, USA: CDC; 2018. Pteropus Bats Positivity for Nipah Virus from Kozhikode, Kerala, India: Possible Link of Infection to Human. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mourya DT. Animal Reservoirs for Nipah Virus. ICMR International Consultation on Research to Combat Nipah Virus Disease, 6-8 August New Delhi, India. [Last accessed on 2018 Dec 15]. Available from: http://www.searo.who.int/entity/research-policy/meetings/combat-nipah virus .
- 15.Hossain MJ, Gurley ES, Montgomery JM, Bell M, Carroll DS, Hsu VP, et al. Clinical presentation of nipah virus infection in Bangladesh. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:977–84. doi: 10.1086/529147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Luby SP, Gurley ES, Hossain MJ. Transmission of human infection with nipah virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:1743–8. doi: 10.1086/647951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hughes JM, Wilson ME, Luby SP, Gurley ES, Hossain J. Transmission of human infection with Nipah Virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:1743–8. doi: 10.1086/647951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chong HT, Kunjapan SR, Thayaparan T, Tong J, Petharunam V, Jusoh MR, et al. Nipah encephalitis outbreak in Malaysia, clinical features in patients from Seremban. Can J Neurol Sci. 2002;29:83–7. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100001785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nowak RM. Walker's Bats of the World. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 20.World Health Organization. Research and Development - List of Priority Diseases. [Last accessed on 2019 May 5]. Available from: http://www.who.int/blueprint/priority-diseases/en/


