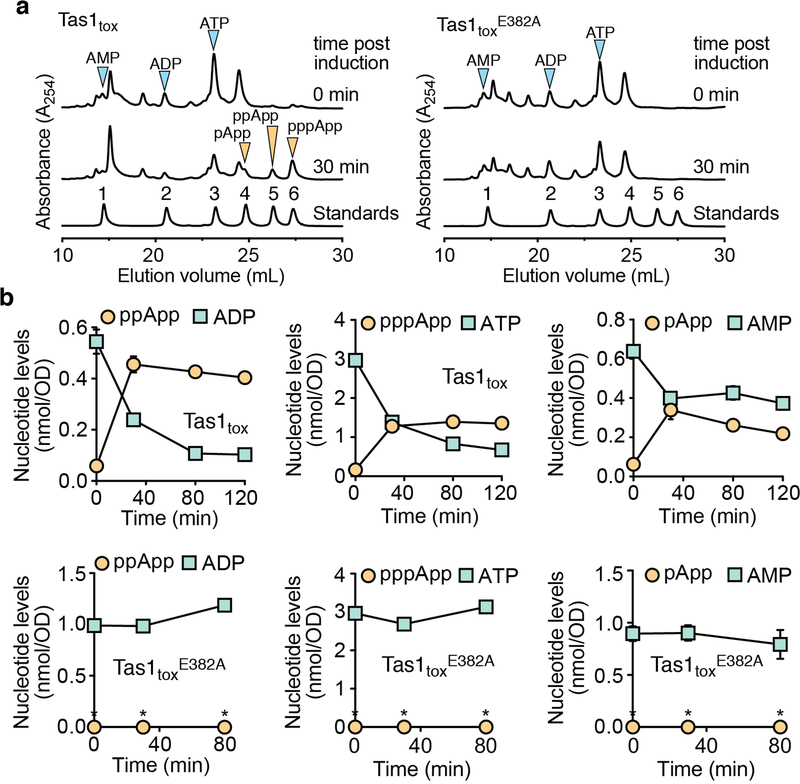
Extended Data Figure 8 |. Tas1tox overexpression in E. coli leads to (p)(p)pApp accumulation and a reduction in cellular 5′ adenosine nucleotides.
a) Anion exchange-chromatography traces of metabolites extracted from E. coli cells overexpressing Tas1tox (left) or Tas1toxE382A (right) at the indicated time points. A trace generated from a mixture of standards containing an equimolar amount of AMP (1), ADP (2), ATP (3), pApp (4), ppApp (5) and pppApp (6) using the same gradient is shown for comparison. Peaks of adenosine 5′-nucleotides and (p)(p)pApp are indicated by blue and orange arrowheads, respectively. Traces are representative of three biological replicates. b) Quantification of adenosine 5′-nucleotide and (p)(p)pApp levels in the E. coli strains from (a) as a function of time post induction. Data are mean ± SD for metabolites extracted from three separate cultures. Metabolites below the detection limit are indicated with an asterisk.