Abstract
Fanconi anemia is a rare recessive disease characterized by multiple congenital abnormalities, progressive bone marrow failure, and a predisposition to malignancies. It results from mutations in one of the 22 known FANC genes. The number of Japanese Fanconi anemia patients with a defined genetic diagnosis was relatively limited. In this study, we reveal the genetic subtyping and the characteristics of mutated FANC genes in Japan and clarify the genotype-phenotype correlations. We studied 117 Japanese patients and successfully subtyped 97% of the cases. FANCA and FANCG pathogenic variants accounted for the disease in 58% and 25% of Fanconi anemia patients, respectively. We identified one FANCA and two FANCG hot spot mutations, which are found at low percentages (0.04-0.1%) in the whole-genome reference panel of 3,554 Japanese individuals (Tohoku Medical Megabank). FANCB was the third most common complementation group and only one FANCC case was identified in our series. Based on the data from the Tohoku Medical Megabank, we estimate that approximately 2.6% of Japanese are carriers of disease-causing FANC gene variants, excluding missense mutations. This is the largest series of subtyped Japanese Fanconi anemia patients to date and the results will be useful for future clinical management.
Introduction
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare recessive disease characterized by multiple congenital abnormalities, progressive bone marrow failure, and predisposition to malignancies. It results from mutations in one of the 22 known FANC genes.1 These genes are summarized in Online Supplementary Table S1. The proteins encoded by these genes participate in a DNA interstrand cross-link repair pathway that deals with DNA damage due to endogenous aldehydes, which are particularly deleterious to hematopoietic stem cells.2 However, more recent studies have shown that biallelic mutations in FANCM cause infertility and early onset cancer but not a typical FA phenotype, and some of the FA genes are actually ‘FA-like’ since the patients with mutations in these genes do not display hematologic defects (Online Supplementary Table S1). Molecular subtyping is critical for the accurate diagnosis and clinical management of the FA patients. However, finding causative mutations for a FA patient is not an easy task.3,4
In this study, we successfully subtyped 113 of the 117 Japanese FA patients and identified 215 mutant alleles through a comprehensive strategy starting from a simple genome polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-direct sequencing approach, then progressing to next generation sequencing. The co-ordinated strategies included whole-exome sequencing (WES) and targeted exome sequencing (targeted-seq). In some cases in which we could not reach a conclusive diagnosis, additional methods, such as array-comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) or RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) analysis, were extremely useful in detecting deletions or splicing abnormalities, respectively. Similar to other ethnic groups, we found that the FA-A and FA-G groups are the most prevalent in Japan. The FANCC mutation is rare and, a little surprisingly, FA-B is the third most prevalent subtype in Japan. The patients with the rare complementation groups, such as FA-D1, E, F, I, N, P, and T, were detected in less than 5% of the cases. We noted striking genotype-phenotype correlation in Japanese FA-B, D1, I, and N cases. In addition, we report the allele frequency of FA-associated deleterious genetic variations in the general Japanese population using the 3.5KJPNv2 database from the Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization (ToMMo).
Methods
Patients and samples
We studied 117 Japanese FA patients from 104 families in total. They overlap with previously reported cases (Online Supplementary Table S2)5-10 and an additional 13 new FA patients were recruited. The diagnosis of FA was confirmed on the basis of chromosomal breakage tests and clinical features. Informed consent was obtained from the family for all subjects involved in this study, and the study was approved by the Research Ethics Committees of all participating hospitals and universities, including Tokai University, Kyoto University, and Nagoya University. Genomic DNA or total RNA was isolated from peripheral blood or cultured fibroblasts using Puregene (Qiagen) or RNAeasy (Qiagen) kit, respectively. cDNA was synthesized with a PrimeScript RT reagent kit (Takara).
Mutation screening for FANCA and FANCG, and ALDH2 genotyping
Mutation analyses by PCR of FANCA or FANCG genes, Multiplex Ligation-mediated Probe Amplification (MLPA) tests for FANCA (Falco Biosystems), and ALDH2 genotyping were performed as previously described.11,12
Targeted-sequencing and whole-exome sequencing
Ten and 67 patients were examined by targeted-seq and WES, respectively, as previously described.8 In targeted-seq, 184 genes, including 15 FA genes (FANCA, B, C, D1, D2, E, F, G, I, J, L, M, N, O and P), were covered. All the mutation variants identified by targeted-seq or WES were verified by PCR and Sanger sequencing.
Array-comparative genomic hybridization analysis
For 10 patients, aCGH was performed as previously described.6 The probes covered 19 FA genes (FANCA, B, C, D1, D2, E, F, G, I, J, L, M, N, O, P, Q, S, T, U) as well as FA-related genes, including NBS1, three RAD51 paralogs (XRCC3, RAD51B, and RAD51D), FAAP20, FAAP24, and FAAP100.
RNA-sequencing
We performed RNA-seq for three patients (Cases 62, 98, and 104). Libraries for RNA-seq were prepared using the TruSeq RNA Sample Prep Kit (Illumina) at Macrogen, and sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform with a standard 126-bp paired-end read protocol. Exon skipping events were identified using Genomon-fusion13 in which patient-specific spliced junctions were identified compared with those identified in a control sample.
Whole-genome sequencing
We performed WGS of DNA samples from one patient (Case 64) and his parents. The TruSeq DNA PCR-Free Library Preparation Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for library preparation. The prepared libraries were subjected to next-generation sequencing using a HiSeq X platform. We detected mutation variants as previously described.8
Estimating allele frequencies of the Fanconi anemia-associated deleterious genetic variations in the general Japanese population
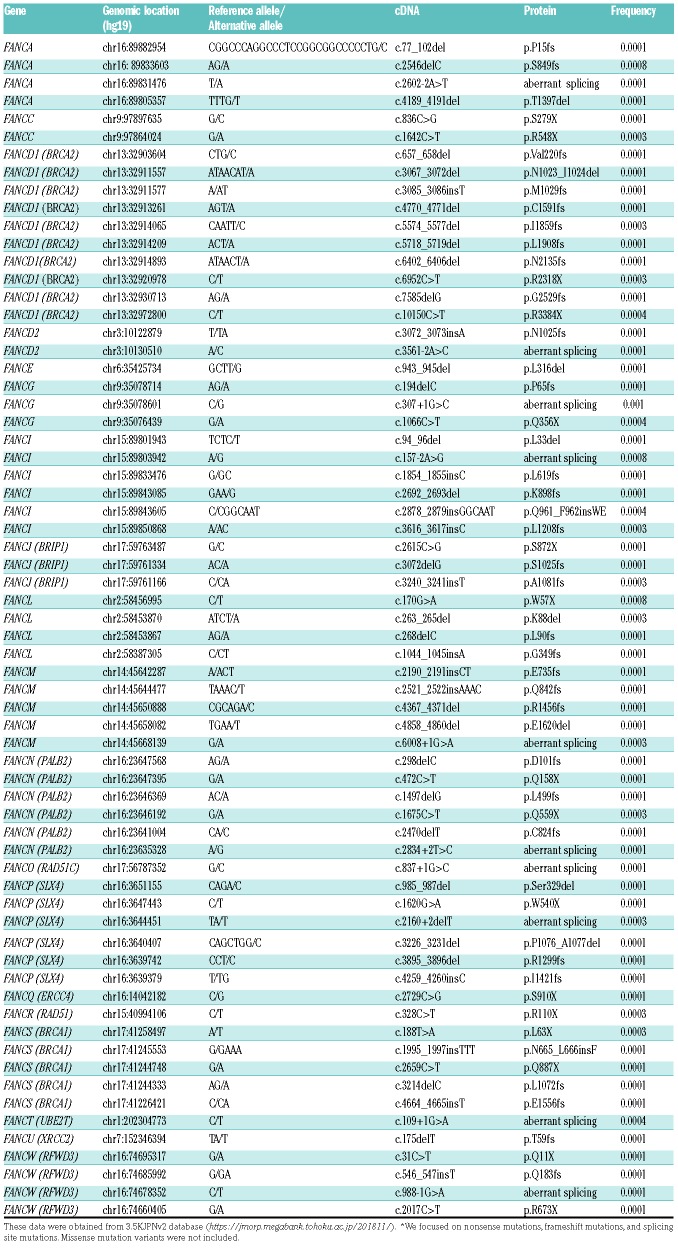
We analyzed the 3.5KJPNv2 database, which was created with data generated by WGS of 3,554 individuals of the resident cohort of the ToMMo Project. The ToMMo project was established to develop a biobank that combines medical and genome information in the Tohoku area.14 As of 5th November 2018, the allele frequencies, including indel variations, were released in the publicly accessible 3.5KJPNv2 database (https://jmorp.mega-bank.tohoku.ac.jp/201811/). Our analysis focused on nonsense mutations, frameshift mutations (indels) and splicing donor or acceptor site mutations with less than 1% allele frequencies.
Results
Genetic subtyping of 117 Japanese Fanconi anemia patients through a comprehensive mutation screening
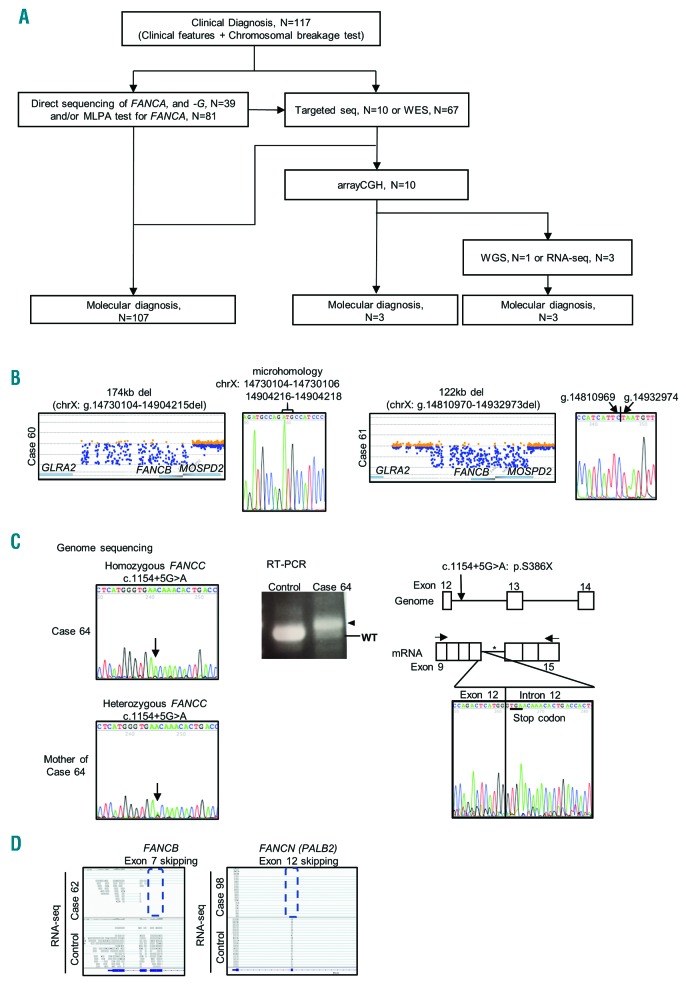
We started mutation analysis of FA patients by direct sequencing of FANCA and FANCG, and MLPA analysis for FANCA in 2009. WES and targeted-seq analyses were initiated in 2012, and molecular diagnosis was successfully achieved in 107 (91.5%) of the 117 patients (Figure 1A). We also examined the ALDH2 genotype which has been reported to affect FA phenotypes (see Discussion section) (Online Supplementary Table S2).5,10 Unfortunately, mutations were found in only one allele in seven (six FA-A and one FA-G) of the 107 patients. Since the mutations in these patients were clearly pathogenic and rare, we assumed this was diagnostic, and did not perform further analysis.
Figure 1.
A comprehensive analysis successfully subtyped most of the Japanese Fanconi anemia (FA) patients. (A) Schematic presentation of the diagnostic strategy for the 117 FA patients. (B) The array-comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) data displayed complete loss of the FANCB gene in Case 60 and Case 61. Sanger sequencing data identified the precise junctions in the two cases. (C) The whole-genome sequencing (WGS) analysis detected homozygous FANCC mutations in intron 12, resulting in a splicing defect. The Sanger sequencing data (left) identified the homozygous mutations in the patient (Case 64) and the heterozygous mutation in the patient’s mother. The real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis showed a larger product (arrowhead) than the wild-type product, and sequencing analysis of the RT-PCR product (right) revealed the 120bp intron retention (*) after exon 12, resulting in a stop codon. (D) The RNA sequence reads of exon 7 in FANCB and exon 12 in FANCN were absent for Case 62 and Case 98, respectively. Corresponding whole-exome sequencing (WES) read alignments for Case 62 and Case 98 were diagnostic for the FANCB or FANCN mutations, as shown in Online Supplementary Figure S2A and B. N: number.
For the remaining ten unclassified cases, we screened large deletions in FA and related genes using our custom-designed aCGH in 2014. It revealed large deletions in two FA-B cases and one FA-T case (Figure 1B). The FANCB deletions spanned the entire genic area of FANCB (complete loss), and the defects extended into neighboring genes MOSPD2 and/or GLRA2. Reanalysis of the WES data suggested putative junctions, where were amplified and sequenced. While the junction in Case 60 had a 3 bp overlapping microhomology, implying microhomology-mediated end joining as the mechanism (see Online Supplementary Figure S1 for further details), there was no such homologous sequence in the break point in Case 61, suggesting that the re-ligation was mediated by non-homologous end joining (Figure 1B).15 Two cases of entire FANCB deletion have been described in the literature16,17 without elucidation of the junctional sequence. All of these FANCB large deletions seem to be distinct, but uniformly accompany severe phenotypic malformations (see below). The FA-T case with a large deletion was previously described.6
After aCGH, seven FA cases remained unclassified. We performed WGS for Case 64, in which the parents’ genome was available, and RNA-seq analysis was carried out for three cases (Cases 62, 98, and 104), in which the patients’ fibroblast cell lines were available. Interestingly, these analyses identified three cases with aberrant splice site mutations. WGS revealed that Case 64 harbored a homozygous mutation (c.1154+5G>A) in intron 12 of the FANCC gene. Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) confirmed that the mutation caused a splicing abnormality, resulting in retention of 120bp of intron 12 and a subsequent in-frame nonsense codon (Figure 1C). In Case 62, RNA-seq analysis revealed skipping of FANCB exon 7 (Figure 1D). This was likely to be caused by a mutation in the first nucleotide of exon 7, which did not alter the encoded amino acid (p.Leu499Leu). This mutation was considered non-pathogenic when the WES results were originally evaluated. However, it has been increasingly recognized that similar synonymous mutations affect splicing and cause genetic disorders and cancer.18,19 RNA-seq and WES also revealed that Case 98 had a homozygous mutation (c.3350+5G>A) in intron 12 of PALB2/FANCN gene, resulting in skipping of exon 12 (Figure 1D).
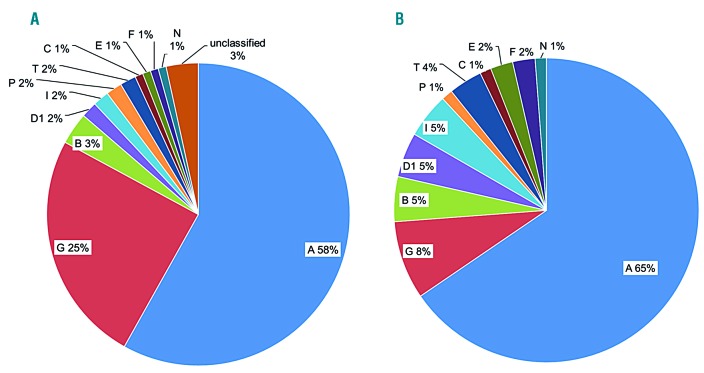
Collectively, 113 (97%) of 117 Japanese FA patients were subtyped, and a total of 215 mutant alleles were identified (Online Supplementary Table S2 and Figure 2A and B). FA-A and FA-G accounted for 58% and 25% of FA patients, respectively (Figure 2A). Interestingly, FANCB was the third most common complementation group in our series (approx. 3%). In notable contrast to a previous report from the Rockefeller University Fanconi Anemia Mutation Database,20 FA-C represented an extremely rare complementation group in Japan (Online Supplementary Table S1). In keeping with this, there was not a single record with an IVS4+4 mutation in the 3.5KJPN or the East Asian population represented in the Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC) database. In Europeans, the allele frequency of the mutation was relatively high (0.04%) in the ExAC database, which reflects a high frequency of the IVS4+4A>T mutation in Ashkenazi-Jewish FA-C cases.21
Figure 2.
Frequency distribution of total (A) versus unique (B) Fanconi anemia (FA) gene mutations in the 117 Japanese FA patients. The frequency of the total FA gene mutation was based on subtyping of 117 FA cases, while frequency of unique FA gene mutations was derived from 84 genetic variants detected in the 117 FA patients.
Characteristics of Japanese FANCA pathogenic variants
In 68 FA-A patients (from 59 unrelated families), 130 mutant alleles were identified that consisted of 55 different FANCA variants (listed in Online Supplementary Table S3 and Online Supplementary Figure S3A). The mutant alleles included nine missense mutations, eight nonsense mutations, 16 small insertions/deletions (indels), 12 large deletions, one large duplication, and nine splicing mutations. All of the nine missense mutations were rated as “damaging” by both SIFT and PolyPhen-2 prediction programs, including two novel variants (c.2723_2725TCT>GCC, p.LS908_909RP; c.3965T>G, p.V1322G). Three of the eight nonsense mutations, six of the 16 small indels, and four of the nine splicing mutations were novel (Online Supplementary Table S3). We consider that these 13 novel mutations are all pathogenic. The large duplication and all of the large deletions except one (c.3765+827_3814del) were detected by the MLPA assay. We did not identify the precise breakpoints of these FANCA deletions; therefore, it was unclear whether they were novel or not.
Similar to the previous reports from Western countries,20,22,23 the mutational spectrum in Japanese FA patients was broad (Figure 2B). However, some mutations were recurrently detected. The FANCA c.2546delC mutation was the most frequent (41 of 130 alleles; 31.5%), and other mutations such as c.978_c.979delGA, c.2602-2A>T, and c.2602-1G>A were detected in at least three unrelated families. c.1303C>T, c.2170A>C, c.2840C>G, c.3720_3724del, c.4168-2A>G were each detected in two unrelated families. The 45 remaining mutation variants were unique and were detected in single patients. FANCA c.2546delC existed at 0.08% frequency among 3,554 individuals from 3.5KJPNv2 in the ToMMo (Table 1), but not in the ExAC database (0%). This mutation was also commonly identified in Korean FA-A patients,24 and therefore seems to be a hotspot in the East Asian population.
Table 1.
Allele frequency of FA-associated deleterious variants* in Japanese population.
Characteristics of Japanese FANCG pathogenic variants
In 29 FA-G patients (from 27 unrelated families), 57 mutant alleles were identified, and seven different FANCG variants were detected (Online Supplementary Table S4 and Online Supplementary Figure S3B). There were fewer unique mutation variants in FA-G compared with FA-A (Figure 2B). Three of the seven FANCG variants were novel. Of the three novel variants, two (c.907_908del and c.1386delC) were clearly pathogenic, whereas one mutation in intron 12 (c.1637-15G>A) was of uncertain significance. As previously reported, c.307+1G>C and 1066C>T accounted for most of the FANCG mutant alleles (49 of 57; 86%) in the Japanese FA-G patients.25,26 Thirteen of the 29 FA-G patients were homozygous for c.307+1G>C, and eight were compound heterozygous with one c.307+G>C allele. Five of the eight remaining FA-G patients had homozygous c.1066C>T mutations. Four cases were compound heterozygous for the c.307+G>C and c.1066C>T mutations. In the 3.5KJPNv2 data, FANCG c.307+1G>C and c.1066C>T mutation variants were present with frequencies of 0.1% and 0.04%, respectively (Table 1). These mutations were similarly detected in Korean FA-G patients24 but hardly ever observed in the other ethnic populations according to the ExAC database.
VACTERL-H phenotype caused by FANCB, FANCI, and other Fanconi anemia gene variants
We identified FANCB mutations in four affected males. The FANCB gene maps to the X-chromosome. Two of the four FA-B patients had a complete loss of the FANCB gene, as detected by aCGH (Figure 1B). In the remaining two patients, one harbored a nonsense mutation (c.516G>A/p.W172X) and one had a synonymous mutation (c.1497G>T/p.L499L) resulting in exon 7 skipping (Figure 1D and Online Supplementary Figure S4A). All four mutations were unique. The two FA-B cases with complete loss of FANCB displayed severe somatic abnormalities, consistent with VACTERL-H association (Table 2). The VACTERL-H association is defined as having three or more of the following defects: vertebral anomalies, anal atresia, cardiac anomalies, tracheal-esophageal fistula, esophageal atresia, renal structural abnormalities, limb anomalies, and hydrocephalus.27 This set of anomalies has been reported in rare cases of FA, and is particularly associated with FA-B, I, J, N, or O cases.28 The most frequent combination patterns in these patients with VACTERL-H association were cardiac-renal-limb anomalies (CRL), anal-renal-limb anomalies (ARL), and vertebral-renal-limb anomalies (VRL), which accounted for more than half of the patients. Cases 60 and 61 had five and seven features of the VACTERL-H anomalies, respectively.
Table 2.
Clinical phenotype of 10 Japanese Fanconi anemia patients with VACTERL-H association.
Compared with these two FA-B cases, Case 62 with C-terminally truncated FANCB protein showed a less severe phenotype and experienced later onset of bone marrow failure (Online Supplementary Figure S4A). A recent biochemical study revealed that FANCB together with FAAP100 and FANCL are the central subcomplex components of the FA core complex, which is essential for ID2 complex monoubiquitination, a key activation event in the FA pathway. The FANCB:FAAP100 subunits form a scaffold that drives dimer formation of FANCL,29 which is the E3 ligase component in the FA core complex. The truncated FANCB protein in Case 62 might, to some extent, maintain the ability to interact with FAAP100 or FANCL protein.30 We were unable to obtain clinical information from another FA-B patient (Case 63).
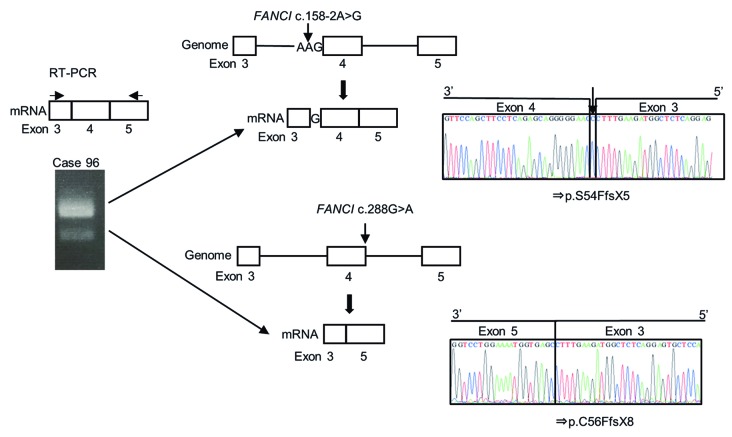
Two FA-I cases were identified, and both had compound heterozygous mutations (Online Supplementary Figure S4B). Case 96, with N-terminal premature termination codons, had the five features of the VACTERL-H anomalies and died within two months after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) (Tables 2 and 3). On the other hand, Case 97, with C-terminal mutations, had only two features of the VACTERL-H and survived for more than 17 years after HSCT. In Case 96, a c.158-2A>G mutation in intron 3 and a c.288G>A mutation in the last codon of exon 4 caused splicing defects that resulted in a single nucleotide (guanine) insertion after exon 3 and skipping of exon 4, respectively (Figure 3). For Case 97, cells were not available and we could not verify the actual splicing defect caused by the c.3006+3A>G mutation. The patient’s mother had only the c.3346_3347 insT mutation, while the father’s genome was unavailable. The mutation at the +3 splice donor position was indicative of a potential splice defect31 and we therefore considered that c.3006+3A>G would be a pathogenic mutation. This mutation was very rare and not reported as an SNV in the 3.5KJNv2 and ExAC database.
Table 3.
Hematologic findings and outcome of 10 Japanese Fanconi anemia patients with VACTERL-H association.
Figure 3.
The two FANCI variants in Case 96 caused two types of splicing defects. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis was carried out using a forward flanking primer on exon 3 and a reverse flanking primer on exon 5 as indicated. Two types of products were obtained, and the sequencing analyses revealed a single nucleotide insertion (top) and exon 4 skipping (bottom).
We also revisited available clinical data from 103 additional FA patients, and identified seven more cases with VACTERL-H (Tables 2 and 3). These include three FA-A, one FA-C case, two FA-G cases, and one FA-P case. All these seven cases met with VACTERL-H criteria with only three features. Four of the seven cases showed the CRL defect combination pattern. Compared with these cases, FA-B and FA-I cases with VACTERL-H association appeared to have higher number of malformations (from 5 to 7). We were unable to obtain detailed clinical information from the remaining nine patients. Thus, altogether there were ten VACTERL-H cases out of 108 cases with clinical data in our series, which seems slightly high compared to the previous report by Alter and Rosenberg (108 cases out of 2,245).28
Early-onset malignancies associated with the FANCD1 (BRCA2) or FANCN (PALB2) complementation group
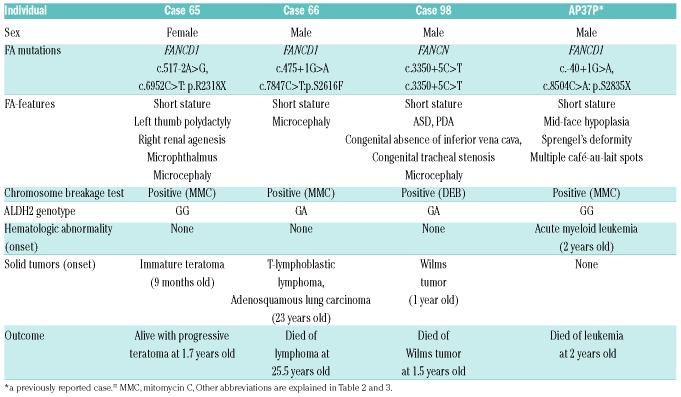
We identified two FA-D1 patients and one FA-N patient in our series. To the best of our knowledge, no FA-N cases and only one FA-D1 case (AP37P in Table 4) have been previously reported from Japan.32,33 The two FA-D1 cases in our study had compound heterozygous mutations, of which one was an N-terminal splice site mutation and the other was a nonsense or missense mutation (Online Supplementary Figure S4C). Both of the two FANCD1 (BRCA2) splice site mutations (c.475+1G>A, c.517-2A>G) were regarded as deleterious. The one missense mutation (FANCD1 c.7847C>T/p.S2616F) was rated as “damaging” by both SIFT and PolyPhen-2 prediction programs. It is notable that this missense mutation falls into the region termed “FA cluster” (amino acid position 2336-2729) where all of the five FA-D1-associated BRCA2 missense mutations are found.34 One FA-N patient had a homozygous splice mutation (c.3350+5C>T), resulting in skipping of exon 12 and C-terminal truncation (Figure 1D and Online Supplementary Figure S4D). This truncation may affect PALB2 interaction with RNF168 or BRCA2 which is mediated by the PALB2 C-terminal WD40 domain.35,36
Table 4.
Clinical features of Japanese Fanconi anemia (FA)-D1 and FA-N cases.
The three FA-D1 patients (including the previous Japanese case), as well as the one FA-N patient, all developed early-onset malignancies; this is in line with previous reports from Western countries (Table 4).34,37,38 Although it is important to note that the first clinical manifestation in such cases could be onset of malignancy without prior clinical problems, Cases 65 and 98 had severe physical anomalies as well. Their malformations did not fully meet VACTERL-H criteria (Table 2). Alter et al. had previously reported that FA-D1 and FA-N patients were characterized by frequent VACTERL-H association and early-onset tumors, such as Wilms tumor, or acute myeloid leukemia (AML), with a cumulative incidence of malignancy as high as 97% by the age of 5.2 years.34 Thus, Case 66 was highly unusual as a FA-D1 patient. He developed T-lymphoblastic lymphoma at 23 years of age, with a relatively short stature, and severe microcephaly (Online Supplementary Appendix). He received standard chemotherapy for the lymphoma, which caused prolonged pancytopenia. Then a mitomycin C-induced chromosome breakage test was performed, and he was diagnosed as FA. We list Case 66 as FA-D1, since he had biallelic, likely deleterious, BRCA2 variants but no other FA gene mutations. This case may expand the clinical spectrum of FA-D1. Alternatively, for the moment, the possibility that hidden FA gene variants caused his FA phenotype cannot be excluded.
Allele frequency of pathogenic variations in 22 Fanconi anemia genes in the Japanese population
To estimate the frequency of pathogenic FA gene variations in the Japanese population, we analyzed WGS data for 22 FA genes from the 3.5KJPNv2 database. We identified 66 deleterious genetic variations (nonsense, frameshifts, and splicing site mutations) in 19 FA genes (Table 1). In addition to the three common FANCA [c.2546elC (0.08%)] and FANCG mutations [c.307+1G>C (0.1%); c.1066C>T (0.04%)], carriers with FANCA c.2602-2A>T, FANCD1 c.6952C>T, FANCG c.194delC, or FANCI c.157-2A>G mutations were detected at low percentages (0.01-0.08%), and these variants were identified as causative mutations in Japanese FA patients. Allele frequencies of FANCL c.170G>A (p.W57X) variants were relatively high (0.08%); however, no patients with these variants were identified in our FA collection.
Monoallelic mutations in some FA genes, such as BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, PALB2 and RAD51C, cause adult-onset cancer predisposition39-41 and we identified 25 deleterious variants in these genes (5 in BRCA1, 10 in BRCA2, 3 in BRIP1, 6 in PALB2, and 1 in RAD51C). BRCA1 c.188T>A (p.L63X) and BRCA2 c.6952C>T (p.R2318X) are well-known mutations in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) in Japan.42 The BRCA2 c.10150C>T (p.R3384X) was more prevalent than p.R2318X, but it has been classified as non-pathogenic because of its location near the 3′-end.43 The PALB2 c.2834+2T>C was recently identified in a Japanese female with bilateral breast cancer.44
From these analyses of allele frequency of FA-associated deleterious variants in 3,554 individuals, we estimated that approximately 2.6% of the Japanese could be considered to be carriers of pathogenic variations in FA genes.
Discussion
In this study, we report the largest series of subtyped Japanese FA patients to date by updating our previously reported cases with an additional 13 new cases (Online Supplementary Table S2). We employed various methods, including PCR-direct sequencing and next generation sequencing. WES and targeted exome sequencing were extremely useful in identifying mutations, as reported previously.8 However, approximately half of the cases were undiagnosed even after these procedures.8 When combined with the data generated by FANCA-MLPA, the diagnosis rate was much enhanced, since FANCA deletion was frequent, and WES/target-seq is not necessarily effective in identifying deletions. We also noted that mutations affecting splicing, such as intronic or synonymous variants, were difficult to detect by WES or targeted-seq. The former weak point was complemented by the use of aCGH, while RNA-seq was useful in detecting splicing abnormalities. We think the identification of two synonymous mutations affecting splicing is of great significance, since this type of mutations could have been easily overlooked. Thus, our approach ultimately achieved molecular diagnosis in most of the cases, and many private and novel mutations were identified in 11 of the 22 known FA genes.
Given the present results, we suggest that a molecular work-up of Japanese FA patients should start with screening for the three most-common mutations (FANCA c.2546delC, FANCG c.307+1G>C, and FANCG c.1066C>T) along with an MLPA assay for FANCA. As a next step, targeted-seq or WES analysis should be considered. For the remaining unclassified cases, aCGH, WGS, and RNA-seq analysis may be useful to identify large indels or splicing defects. Through these combined and comprehensive efforts, correct genetic diagnosis may be obtained in more than 90% of the Japanese FA patients.
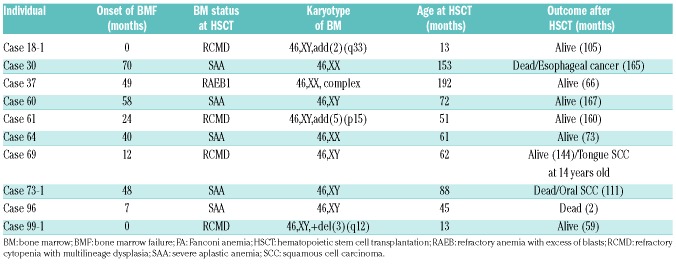
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) converts acetaldehyde to acetate, and potentially catalyzes other aldehydes as well. In East Asian countries, including Japan, a significant fraction (approx. 50%) of the population carries ALDH2 variant ALDH2*504Lys which is encoded by the so-called A allele, and affects alcohol tolerance and some aspects of human health.45 We have previously described a subset of severe FA cases that were homozygous for the ALDH2*504Lys variant (the AA genotype), and who experienced bone marrow failure and/or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) immediately after birth.5,7 We also found several FA-B and FA-I cases that were accompanied by severe physical abnormalities, termed VACTERL-H. Two (Cases 18-1, 99-1) of the six previously reported FA cases carrying a homozygous ALDH2 AA genotype also displayed these severe malformations7 (Table 2), but, interestingly, their siblings (Cases 18-2, 99-2) with ALDH2 GG genotype displayed relatively minor physical abnormalities (Online Supplementary Table S2). We note here that the FA-B or FA-I patients with VACTERL-H anomalies were carriers of the ALDH2 GG or the GA genotype. The impact of endogenous aldehyde catabolism on bone marrow stem cells is very clear, and this effect also extends to the role of the FA proteins in preventing severe malformations. It has been suggested that the extent of physical abnormalities and severity of hematologic defects tend to be correlated.46 In any event, FA-B and FA-I groups often exhibit severe malformations, as described previously47,48 and confirmed here in Japanese cases. Since many of our cases were referred to us in order to carry out HSCT, our data could be biased toward a proportion of patients with more severe malformations and may not reflect all individuals carrying FA gene variants. The relatively high incidence of VACTERL-H anomalies in our series could reflect this46 and/or this may be due to the impact of the ALDH2 genotype.
An important issue is how prevalent the FA-causing variants in the Japanese population are. We estimate that at least approximately 2.6% of the Japanese population might carry pathogenic variants in FA genes, using the 3.5KJPNv2 database. In Japan, approximately ten individuals with FA are born per one million births each year according to the report from the Japanese Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.49 FA-G accounted for 25% of Japanese FA patients according to our study and approximately two FA-G patients are estimated to be born each year in Japan. Our estimated allele frequency for FANCG (0.16%) from the 3.5KJPNv2 database is a reasonable one given the birth rate of the FA-G patients. Rogers et al. reported that at least one FA disease-causing variant among 16 FA genes (nonsense, splice altering, frame shifts, and a subset of missense variants that are judged to be highly deleterious) was identified in 4.3% of individuals from the ESP and 1KGP studies.50 This estimate was substantially higher than ours, but our numbers may increase if we include deleterious missense mutation data in the future.
In conclusion, the molecular diagnostic strategy and data described in this study provide a basis for future molecular work-ups and clinical management for Japanese FA patients. In four cases, we failed to achieve a definitive subtyping; this could be due to technical problems or due to novel FA genes awaiting discovery. These remain as “unclassified”, and could be of particular interest in further attempts to elucidate FA etiology.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank patients and families for participating in the study, Dr. James Hejna (Kyoto University) for critical reading of the manuscript, and Akiko Watanabe and Fan Peng for technical and secretarial help.
Footnotes
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP15H01738 [to MT], grants from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare [to SK and to EI], and grants from Uehara Memorial Foundation [to MT], and Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders [to MT].
Check the online version for the most updated information on this article, online supplements, and information on authorship & disclosures: www.haematologica.org/content/104/10/1962
References
- 1.Nalepa G, Clapp DW. Fanconi anaemia and cancer: an intricate relationship. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(3):168-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garaycoechea JI, Crossan GP, Langevin F, et al. Alcohol and endogenous aldehydes damage chromosomes and mutate stem cells. Nature. 2018;553(7687):171-177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chandrasekharappa SC, Lach FP, Kimble DC, et al. Massively parallel sequencing, aCGH, and RNA-Seq technologies provide a comprehensive molecular diagnosis of Fanconi anemia. Blood. 2013;121(22):e138-148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.De Rocco D, Bottega R, Cappelli E, et al. Molecular analysis of Fanconi anemia: the experience of the Bone Marrow Failure Study Group of the Italian Association of Pediatric Onco-Hematology. Haematologica. 2014;99(6):1022-1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hira A, Yabe H, Yoshida K, et al. Variant ALDH2 is associated with accelerated progression of bone marrow failure in Japanese Fanconi anemia patients. Blood. 2013;122(18):3206-3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hira A, Yoshida K, Sato K, et al. Mutations in the Gene Encoding the E2 Conjugating Enzyme UBE2T Cause Fanconi Anemia. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;96(6):1001-1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yabe M, Yabe H, Morimoto T, et al. The phenotype and clinical course of Japanese Fanconi Anaemia infants is influenced by patient, but not maternal ALDH2 genotype. Br J Haematol. 2016;175(3):457-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Muramatsu H, Okuno Y, Yoshida K, et al. Clinical utility of next-generation sequencing for inherited bone marrow failure syndromes. Genet Med. 2017;19(7):796-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sekinaka Y, Mitsuiki N, Imai K, et al. Common Variable Immunodeficiency Caused by FANC Mutations. J Clin Immunol. 2017;37(5):434-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yabe M, Koike T, Ohtsubo K, et al. Associations of complementation group, ALDH2 genotype, and clonal abnormalities with hematological outcome in Japanese patients with Fanconi anemia. Ann Hematol. 2019;98(2):271-280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tachibana A, Kato T, Ejima Y, et al. The FANCA gene in Japanese Fanconi anemia: reports of eight novel mutations and analysis of sequence variability. Hum Mutat. 1999;13(3):237-244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Matsuo K, Wakai K, Hirose K, Ito H, Saito T, Tajima K. Alcohol dehydrogenase 2 His47Arg polymorphism influences drinking habit independently of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 Glu487Lys polymorphism: analysis of 2,299 Japanese subjects. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15(5): 1009-1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shiraishi Y, Fujimoto A, Furuta M, et al. Integrated analysis of whole genome and transcriptome sequencing reveals diverse transcriptomic aberrations driven by somatic genomic changes in liver cancers. Creighton C, editor. PLoS One. 2014; 9(12):e114263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yasuda J, Kinoshita K, Katsuoka F, et al. Genome analyses for the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project toward establishment of personalized healthcare. J Biochem. 2019; 165(2):139-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ceccaldi R, Rondinelli B, D’Andrea AD. Repair Pathway Choices and Consequences at the Double-Strand Break. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(1):52-64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Umaña LA, Magoulas P, Bi W, Bacino CA. A male newborn with VACTERL association and Fanconi anemia with a FANCB deletion detected by array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH). Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A(12):3071-3074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Flynn EK, Kamat A, Lach FP, et al. Comprehensive analysis of pathogenic deletion variants in Fanconi anemia genes. Hum Mutat. 2014;35(11):1342-1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chamary JV, Parmley JL, Hurst LD. Hearing silence: non-neutral evolution at synonymous sites in mammals. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(2):98-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Supek F, Miñana B, Valcárcel J, Gabaldón T, Lehner B. Synonymous Mutations Frequently Act as Driver Mutations in Human Cancers. Cell. 2014;156(6):1324–1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Neveling K, Endt D, Hoehn H, Schindler D. Genotype-phenotype correlations in Fanconi anemia. Mutat Res. 2009;668(1-2):73-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Whitney MA, Saito H, Jakobs PM, Gibson RA, Moses RE, Grompe M. A common mutation in the FACC gene causes Fanconi anaemia in Ashkenazi Jews. Nat Genet. 1993;4(2):202-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kimble DC, Lach FP, Gregg SQ, et al. A comprehensive approach to identification of pathogenic FANCA variants in Fanconi anemia patients and their families. Hum Mutat. 2018;39(2):237-254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Castellà M, Pujol R, Callen E, et al. Origin, functional role, and clinical impact of Fanconi anemia FANCA mutations. Blood. 2011;117(14):3759-3769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Park J, Chung N-G, Chae H, et al. FANCA and FANCG are the major Fanconi anemia genes in the Korean population. Clin Genet. 2013;84(3):271-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yamada T, Tachibana A, Shimizu T, Mugishima H, Okubo M, Sasaki MS. Novel mutations of the FANCG gene causing alternative splicing in Japanese Fanconi anemia. J Hum Genet. 2000;45(3):159-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yagasaki H, Oda T, Adachi D, et al. Two common founder mutations of the fanconi anemia group G gene FANCG/XRCC9 in the Japanese population. Hum Mutat. 2003;21(5):555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Solomon BD, Pineda-Alvarez DE, Raam MS, et al. Analysis of component findings in 79 patients diagnosed with VACTERL association. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A(9): 2236-2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Alter BP, Rosenberg PS. VACTERL-H Association and Fanconi Anemia. Mol Syndromol. 2013;4(1-2):87–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.van Twest S, Murphy VJ, Hodson C, et al. Mechanism of Ubiquitination and Deubiquitination in the Fanconi Anemia Pathway. Mol Cell. 2017;65(2):247-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.McCauley J, Masand N, McGowan R, et al. X-linked VACTERL with hydrocephalus syndrome: further delineation of the phenotype caused by FANCB mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A(10):2370-2380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Krawczak M, Thomas NST, Hundrieser B, et al. Single base-pair substitutions in exon-intron junctions of human genes: nature, distribution, and consequences for mRNA splicing. Hum Mutat. 2007;28(2):150-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ikeda H, Matsushita M, Waisfisz Q, et al. Genetic reversion in an acute myelogenous leukemia cell line from a Fanconi anemia patient with biallelic mutations in BRCA2. Cancer Res. 2003;63(10):2688-2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bakker JL, Thirthagiri E, van Mil SE, et al. A novel splice site mutation in the noncoding region of BRCA2: implications for Fanconi anemia and familial breast cancer diagnostics. Hum Mutat. 2014;35(4):442-446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Alter BP, Rosenberg PS, Brody LC. Clinical and molecular features associated with biallelic mutations in FANCD1/BRCA2. J Med Genet. 2007;44(1):1-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Xia B, Sheng Q, Nakanishi K, et al. Control of BRCA2 cellular and clinical functions by a nuclear partner, PALB2. Mol Cell. 2006; 22(6):719-729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Luijsterburg MS, Typas D, Caron M-C, et al. A PALB2-interacting domain in RNF168 couples homologous recombination to DNA break-induced chromatin ubiquitylation. Elife. 2017;6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Reid S, Schindler D, Hanenberg H, et al. Biallelic mutations in PALB2 cause Fanconi anemia subtype FA-N and predispose to childhood cancer. Nat Genet. 2007;39(2): 162-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wagner JE, Tolar J, Levran O, et al. Germline mutations in BRCA2: shared genetic susceptibility to breast cancer, early onset leukemia, and Fanconi anemia. Blood. 2004;103(8):3226-3229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Prakash R, Zhang Y, Feng W, Jasin M. Homologous Recombination and Human Health: The Roles of BRCA1, BRCA2, and Associated Proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(4):a016600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Katsuki Y, Takata M. Defects in homologous recombination repair behind the human diseases: FA and HBOC. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016;23(10):T19-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Paulo P, Maia S, Pinto C, et al. Targeted next generation sequencing identifies functionally deleterious germline mutations in novel genes in early-onset/familial prostate cancer. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(4):e1007355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hirotsu Y, Nakagomi H, Sakamoto I, Amemiya K, Mochizuki H, Omata M. Detection of BRCA1 and BRCA2 germline mutations in Japanese population using next-generation sequencing. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2015;3(2):121-129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Borg A, Haile RW, Malone KE, et al. Characterization of BRCA1 and BRCA2 deleterious mutations and variants of unknown clinical significance in unilateral and bilateral breast cancer: the WECARE study. Hum Mutat. 2010;31(3):E1200-1240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nakagomi H, Hirotsu Y, Okimoto K, et al. PALB2 mutation in a woman with bilateral breast cancer: A case report. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017;6(4):556-560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gross ER, Zambelli VO, Small BA, Ferreira JCB, Chen C-H, Mochly-Rosen D. A personalized medicine approach for Asian Americans with the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2*2 variant. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:107-127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rosenberg PS, Huang Y, Alter BP. Individualized risks of first adverse events in patients with Fanconi anemia. Blood. 2004;104(2):350-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Holden ST, Cox JJ, Kesterton I, Thomas NS, Carr C, Woods CG. Fanconi anaemia complementation group B presenting as X linked VACTERL with hydrocephalus syndrome. J Med Genet. 2006;43(9):750-754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Savage SA, Ballew BJ, Giri N, et al. Novel FANCI mutations in Fanconi anemia with VACTERL association. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170A(2):386-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yabe M, Yabe H. [Diagnosis and management of inherited bone marrow failure syndrome]. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2015;56(10):1914-1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rogers KJ, Fu W, Akey JM, Monnat RJ. Global and disease-associated genetic variation in the human Fanconi anemia gene family. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(25):6815-6825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]